Computational Fluid Dynamics Heat Transfer Analysis of Double Pipe Heat Exchanger and Flow Characteristics Using Nanofluid TiO2 with Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modelling
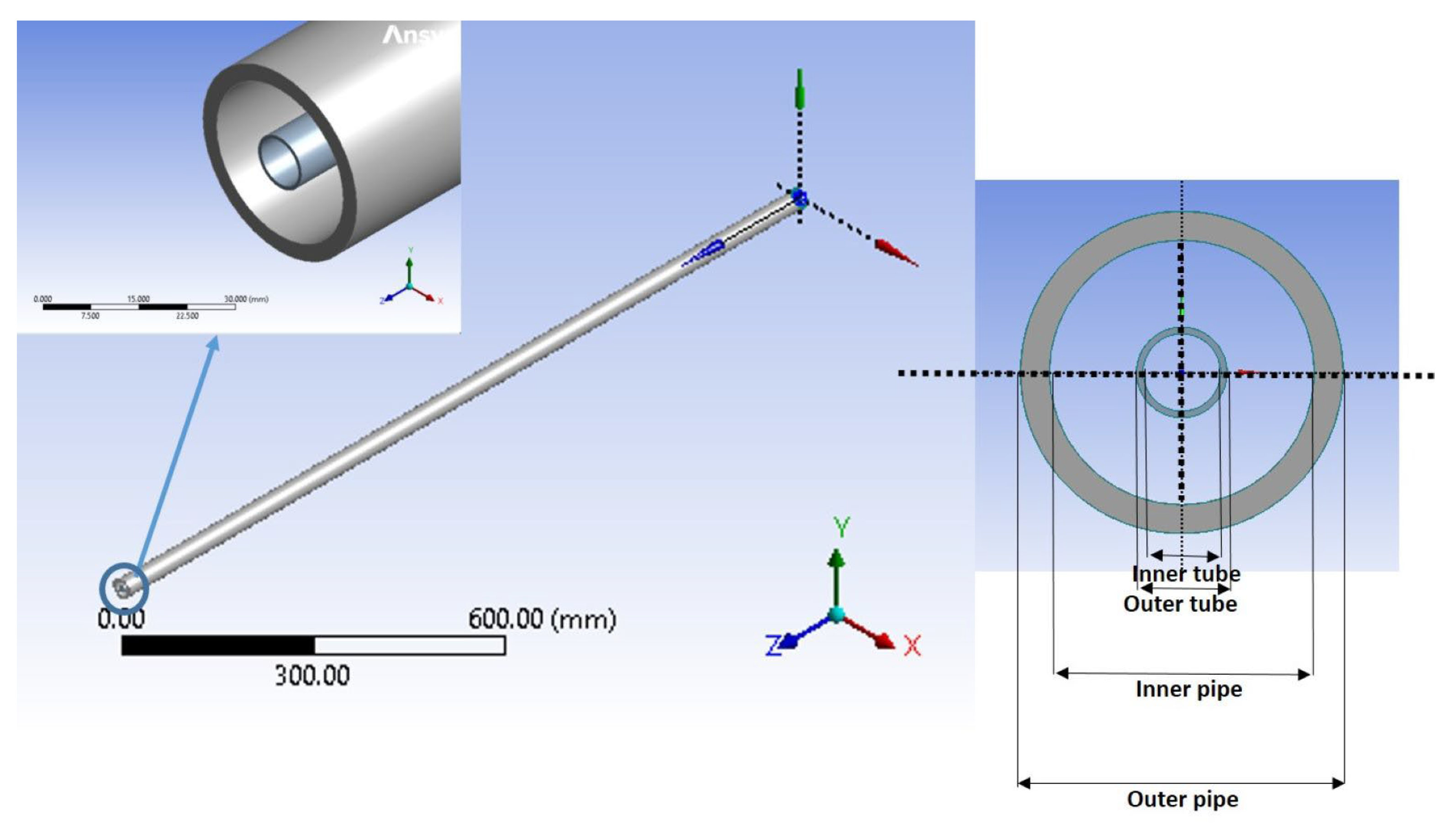
2.1. Geometry
2.2. Mesh Development
2.3. Numerical Method
- The flow is steady and incompressible.
- The thermo-physical properties of the fluid are temperature independent.
- The flow is turbulent.
2.4. Boundary Conditions
- Inner tube inlet–imposed mass flow rate (mass flow rate inlet);
- Inner tube outlet–imposed pressure (pressure outlet);
- Outer pipe inlet–imposed mass flow rate (mass flow rate inlet);
- Outer pipe outlet–imposed pressure (pressure outlet);
- Tube centreline–axis of symmetry (axis);
- Double pipe heat exchanger walls (wall).
3. Data Reduction Equations
3.1. Thermal and Physical Properties of Nanofluids
3.2. Heat Transfer Coefficient, Heat Transfer Rate and Nusselt Number
4. Results and Discussion
- The nanofluid Reynolds number varies from 4000 to 18,000.
- The temperature of the nanofluid is 298.15 K.
- The hot water flow rate is 3.0 LPM.
- The hot water temperature is 308.15 K, 313.15 K and 323.15 K.
4.1. Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient
4.2. Nondimensional Study of the Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| heat transfer surface area | |
| specific heat, | |
| nanoparticle diameter, | |
| tube pipe diameter, | |
| heat transfer coefficient, | |
| thermal conductivity, | |
| length of the test tube, | |
| mass flow rate, | |
| Nusselt number | |
| pressure drop, | |
| Peclet number | |
| Prandtl number | |
| heat transfer rate, | |
| Reynolds number | |
| temperature, | |
| mean velocity, | |
| hot water flow rate, litres per minute | |
| Subscript | |
| average | |
| base fluid | |
| Fluid | |
| hot fluid | |
| inlet | |
| outlet | |
| particles | |
| nanofluid | |
| water | |
| tube wall | |
| Greek symbols | |
| volume fraction | |
| density, | |
| thermal diffusivity, | |
| viscosity, | |
References
- Omidi, M.; Farhadi, M.; Jafari, M. A comprehensive review on double pipe heat exchangers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 110, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Kavitha, R.; Algani, Y.M.A.; Kulkarni, K.; Gupta, M.K. Heat transfer enhancement in a double pipe heat exchanger with copper oxide nanofluid: An experimental study. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 56, 3446–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godson, L.; Raja, B.; Lal, D.M.; Wongwises, S. Enhancement of heat transfer using nanofluids—An overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.F.; Danışmaz, M.; Majel, B.M. Thermal performance investigation of double pipe heat exchanger embedded with extended surfaces using nanofluid technique as enhancement. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 43, 102774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, S.; Li, S.; Eastman, J.A. Measuring Thermal Conductivity of Fluids Containing Oxide Nanoparticles. 1999. Available online: http://heattransfer.asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/ (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Yu, L.; Liu, D.; Botz, F. Laminar convective heat transfer of alumina-polyalphaolefin nanofluids containing spherical and non-spherical nanoparticles. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2012, 37, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, M.M.; Miqdad, M.; Mahbubul, I.M.; Saidur, R.; Kamalisarvestani, M.; Sohel, M.R.; Hepbasli, A.; Rahim, N.A.; Amalina, M.A. Effect of nanoparticle shape on the heat transfer and thermodynamic performance of a shell and tube heat exchanger. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 44, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-Z.; Xia, Y.; Ku, X.-K. Flow and heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids containing rod-like particles in a turbulent pipe flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 93, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, B.C.; Cho, Y.I. Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles. Exp. Heat Transf. 1998, 11, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayou, S.; Ting, T.W.; Vigolo, B. Comparison of heat transfer performance of water-based graphene nanoplatelet- and multi-walled carbon nanotube-nanofluids in a concentric tube heat exchanger. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 125, 108976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Behery, S.M.; Badawy, G.H.; El-Askary, W.A.; Mahfouz, F.M. Effects of Nanofluids on the Thermal Performance of Double Pipe Heat Exchanger. ERJ Eng. Res. J. 2022, 45, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-Z.; Xia, Y.; Ku, X.-K. Pressure drop and heat transfer of nanofluid in turbulent pipe flow considering particle coagulation and breakage. J. Heat Transf. 2014, 136, 111701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS FLUENT. Theory Guide; ANSYS, Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Duangthongsuk, W.; Wongwises, S. Heat transfer enhancement and pressure drop characteristics of TiO2–water nanofluid in a double-tube counter flow heat exchanger. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldossary, S.; Sakout, A.; El Hassan, M. CFD simulations of heat transfer enhancement using Al2O3–air nanofluid flows in the annulus region between two long concentric cylinders. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalatpour, M.; Solano, J.P. Thermal-hydraulic characteristics and exergy performance in tube-on-sheet flat plate solar collectors: Effects of nanofluids and mixed convection. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 118, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.V.; Sarma, P.K.; Azmi, W.H.; Mamat, R.; Kadirgama, K. Correlations to predict friction and forced convection heat transfer coefficients of water based nanofluids for turbulent flow in a tube. Int. J. Microscale Nanoscale Therm. Fluid Transp. Phenom. 2012, 3, 283–307. [Google Scholar]
- Hassaan, A.M. Evaluation for the performance of heat transfer process in a double pipe heat exchanger using nanofluids. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2022, 236, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Li, Q. Investigation on convective heat transfer and flow features of nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2003, 125, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Lin, J.; Yang, H. Particle Distribution and Heat Transfer of SiO2/Water Nanofluid in the Turbulent Tube Flow. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhulaifi, A.S. A Simplified Approach for the Determination of Penetrant Residual Velocity for Penetration Processes. Designs 2022, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, W.H.; Sharma, K.V.; Sarma, P.K.; Mamat, R.; Anuar, S.; Rao, V.D. Experimental determination of turbulent forced convection heat transfer and friction factor with SiO2 nanofluid. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2013, 51, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, J.R.; Manova, S.; Angeline, A.A.; Asirvatham, L.G.; Gautam, S. Numerical Study on the Heat Transfer Characteristics of Cu-Water and TiO2-Water Nanofluid in a Circular Horizontal Tube. Energies 2023, 16, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Grid | Mesh Nodes | Mesh Elements | Twall (Wall Temperature) | h (Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 42,330 | 41,910 | 299.28326 | 11,032.24565 |
| 2 | 53,680 | 53,200 | 299.30795 | 10,624.9118 |
| 3 | 75,330 | 74,740 | 299.32455 | 10,347.64332 |
| 4 | 96,005 | 95,340 | 299.34390 | 10,052.82923 |
| 5 | 106,555 | 105,840 | 299.34387 | 10,052.16872 |
| Thermophysical Properties | Density kg/m3 | Thermal Conductivity W/m·K | Specific Heat J/kg·K | Dynamic Viscosity Pa·s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 998.816 | 0.606226774 | 4180.02945 | 0.000890439 |
| TiO2 (21 nm) | 4250 | 8.953 | 686.2 | NA |
| Volume Fraction φ | Density kg/m3 | Specific Heat J/kg.K | Dynamic Viscosity Pa.s | Thermal Conductivity W/m.K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 vol.% | 1005.31885 | 4150.48902 | 0.000900264 | 0.623608995 |
| 0.4 vol.% | 1011.821217 | 4121.328268 | 0.000920779 | 0.625314903 |
| 0.6 vol.% | 1018.323584 | 4092.53992 | 0.00094172 | 0.627022068 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhulaifi, A.S. Computational Fluid Dynamics Heat Transfer Analysis of Double Pipe Heat Exchanger and Flow Characteristics Using Nanofluid TiO2 with Water. Designs 2024, 8, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8030039
Alhulaifi AS. Computational Fluid Dynamics Heat Transfer Analysis of Double Pipe Heat Exchanger and Flow Characteristics Using Nanofluid TiO2 with Water. Designs. 2024; 8(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8030039
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhulaifi, Abdulaziz S. 2024. "Computational Fluid Dynamics Heat Transfer Analysis of Double Pipe Heat Exchanger and Flow Characteristics Using Nanofluid TiO2 with Water" Designs 8, no. 3: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8030039
APA StyleAlhulaifi, A. S. (2024). Computational Fluid Dynamics Heat Transfer Analysis of Double Pipe Heat Exchanger and Flow Characteristics Using Nanofluid TiO2 with Water. Designs, 8(3), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8030039






