Investigation of Structure and Dynamics in Disordered Materials Using Containerless Techniques with In-Situ Quantum Beam and Thermophysical Property Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Levitation Techniques
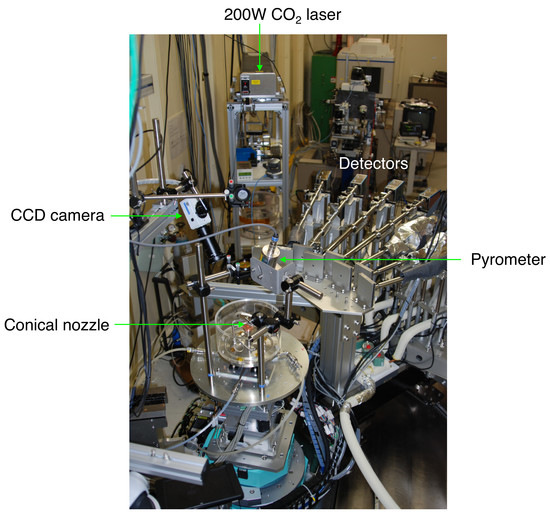
3. Conical Nozzle Levitation
- (i)
- Although X-ray diffraction data suffers from a Q-dependent decrease in coherent scattering cross section, high-energy X-rays provide high-Q data with small scattering angles, which suppress the energy- and 2θ-dependent correction terms.
- (ii)
- High-energy X-rays expand the capability of transmission geometry due to high penetration power. We can probe the bulk structure of a 2–3 millimeter diameter liquid droplet.
- (iii)
- High-flux X-rays are suitable for time-resolved diffraction experiments when combined with an area detector [4].
3.1. Atomistic and Electronic Structures of a Non-Glass Forming Liquid
3.2. Atomistic and Electronic Structures of CaO–Al2O3 Glasses
4. Electrostatic Levitation
4.1. Thermophysical Property Measurement
4.1.1. Density
4.1.2. Surface Tension and Viscosity
4.1.3. Measurement of Molten Refractory Materials
4.2. An Electrostatic Levitation Furnace in the International Space Station (ISS-ELF)
4.2.1. Necessity of Microgravity
4.2.2. International Space Station Electrostatic Levitation Furnace (ISS-ELF)
5. Acoustic Levitation
5.1. Thermophysical Properties
5.2. Solvent Evaporation
5.3. X-ray Diffraction
5.4. Neutron Diffraction/Scattering
5.5. Other Techniques
6. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angell, C.A. Formation of glasses from liquids and biopolymers. Science 1995, 267, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muck, O. German Patent No. 42204, 30 October 1923.
- Hennet, L.; Holland Moritz, D.; Weber, R.; Meyer, A. High-Temperature Levitated Materials. In Neutron Scattering—Applications in Biology, Chemistry, and Materials Science; Fernandez-Alonso, F., Price, D.L., Eds.; Experimental Methods in the Physical Sciences; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; Volume 49, pp. 583–636. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, J.K.R.; Tamalonis, A.; Benmore, C.J.; Alderman, O.L.G.; Sendelbach, S.; Hebden, A.; Williamson, M.A. Aerodynamic levitator for in situ X-ray structure measurements on high temperature and molten nuclear fuel materials. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 073902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, L.B.; Barnes, A.C.; Salmon, P.S.; Hennet, L.; Fischer, H.E.; Benmore, C.J.; Kohara, S.; Weber, J.K.R.; Bytchkov, A.; Wilding, M.C.; et al. Joint diffraction and modeling approach to the structure of liquid alumina. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 024201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skinner, L.B.; Benmore, C.J.; Weber, J.K.R.; Du, J.; Neuefeind, J.; Tumber, S.K.; Parise, J.B. Low cation coordination in oxide melts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 157801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohara, S.; Akola, J.; Patrikeev, L.; Ropo, M.; Ohara, K.; Itou, M.; Fujiwara, A.; Yahiro, J.; Okada, J.T.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Atomic and electronic structures of an extremely fragile liquid. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5892–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skinner, L.B.; Benmore, C.J.; Weber, J.K.R.; Williamson, M.A.; Tamalonis, A.; Hebden, A.; Wiencek, T.; Alderman, O.L.G.; Guthrie, M.; Leibowitz, L.; Parise, J.B. Molten uranium dioxide structure and dynamics. Science 2014, 346, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, P.S.; Martin, R.A.; Mason, P.E.; Cuello, G.J. Topological versus chemical ordering in network glasses at intermediate and extended length scales. Nature 2005, 435, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, A.; Richet, P.; Catlow, C.R.A.; Price, G.D. Molecular dynamics simulations of vitreous silica structures. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 345–346, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.B.; Thornton, D.E. Structural aspects of the electrical resistivity of binary alloys. Phys. Rev. B 1971, 4, 3004–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, T.E.; Ziman, J.M. A theory of the electrical properties of liquid metals. Philos. Mag. 1965, 11, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Q.; Benmore, C.J.; Weber, J.K.R. Structure of liquid SiO2: A measurement by high-energy X-ray diffraction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 4, 057802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachariasen, W.H. The atomic arrangement in glass. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1932, 54, 3841–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohara, S.; Akola, J.; Morita, H.; Suzuya, K.; Weber, J.K.R.; Wilding, M.C.; Benmore, C.J. Relationship between topological order and glass forming ability in densely packed enstatite and forsterite composition glasses. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14780–14785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akola, J.; Kohara, S.; Ohara, K.; Fujiwara, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Masuno, A.; Usuki, T.; Kubo, T.; Nakahira, A.; Nitta, K.; et al. Network topology for the formation of solvated electrons in binary CaO–Al2O3 composition glasses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10129–10134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Q.; Benmore, C.J.; Sen, S.; Sharma, R.; Yargar, J. Intermediate range order in vitreous silica from a partial structure factor analysis. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 144204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.C. Longer range order in single component network glasses? Phys. Chem. Glasses 2008, 49, 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Price, D.L.; Ellison, A.J.G.; Saboungi, M.-L.; Hu, R.-Z.; Egami, T.; Howells, W.S. Short-, intermediate- and extended-range order in rubidium germanate glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 55, 11249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Cooper, A.R. Topologically disordered networks of rigid polytopes. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1990, 123, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGreevy, R.L.; Pusztai, L. Reverse Monte Carlo simulation: a new technique for the determination of disordered structures. Mol. Simul. 1988, 1, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Shimoyama, T.; Hosono, H. Solvated electrons in high-temperature melts and glasses of the room-temperature stable electride [Ca24Al28O64]4+·4e-. Science 2016, 333, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimbach, I.; Rhiem, F.; Beule, F.; Knodt, D.; Heinen, J.; Jones, R.O. pyMolDyn: Identification, structure and properties of cavities/vacancies in condensed matter and molecules. J. Comput. Chem. 2017, 38, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohara, S.; Ohno, H.; Takata, M.; Usuki, T.; Morita, H.; Suzuya, K.; Akola, J.; Pusztai, L. Lead silicate glasses: Binary network-former glasses with large amounts of free volume. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 134209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, W.-K.; Chang, S.K.; Barber, D.; Man, K.F.; Gutt, G.; Rulison, A.; Spjut, R.E. An electrostatic levitator for high-temperature containerless materials processing in 1-g. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1993, 64, 2961–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Okada, J.T.; Paradis, P.-F.; Watanabe, Y. Thermophysical property measurements of high temperature melts using an electrostatic levitation method. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 11RD03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-K.; Thiessen, D.B.; Rhim, W.-K. A noncontact measurement technique for the density and thermal expansion coefficient of solid and liquid metals. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1996, 67, 3175–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, W.-K.; Ohsaka, K.; Paradis, P.-F.; Spjut, R.E. Noncontact technique for measuring surface tension and viscosity of molten materials using high temperature electrostatic levitation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1999, 70, 2796–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord Rayleigh, J.S.W. On the capillary phenomena of jets. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1879, 29, 71–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, H. Hydrodynamics, 6th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1932; pp. 473–639. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, T.; Paradis, P.-F.; Okada, J.; Kumar, M.V.; Watanabe, Y. Viscosity of molten Mo, Ta, Os, Re and W measured by electrostatic levitation. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013, 65, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, P.-F.; Ishikawa, T.; Yoda, S. Hybrid electrostatic-aerodynamic levitation furnace for the high temperature processing of oxide materials on the ground. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2001, 72, 2811–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Yu, J.; Paradis, P.-F. Non-contact surface tension and viscosity measurements of molten oxides with a pressurized hybrid electrostatic-aerodynamic levitator. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 053901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, P.-F.; Yu, J.; Ishikawa, T.; Aoyama, T.; Yoda, S.; Weber, J.K.R. Contactless density measurement of superheated and undercooled liquid Y3Al5O12. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 249, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, P.-F.; Yu, J.; Ishikawa, T.; Aoyama, T.; Yoda, S. Contactless density measurement of liquid and high temperature solid BiFeO3 and BaTiO3. Appl. Phys. A 2004, 79, 1965–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, P.-F.; Yu, J.; Aoyama, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Yoda, S. Contactless density measurement of liquid Nd-doped 50%CaO-50%Al2O3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 86, 2234–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaru, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Okada, J.T.; Nakamura, Y.; Ohkuma, H.; Yukizono, S.; Sakai, Y.; Takada, T. Overview of the electrostatic levitation furnace (ELF) for the International Space Station (ISS). Int. J. Microgravity Sci. Appl. 2015, 32, 32104. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull, D. Undercoolability and Exposure of Metastable Structures. In Undercooled Alloy Phases, Proceedings of the Hume-Rothery Memorial Symposium, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–6 March 1986; Collings, E.W., Koch, C.C., TMS, Eds.; Metallurgical Society, Inc.: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1986; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, S.; Felten, J.J.; Rix, J.E.; Weber, J.K.R.; Nordine, P.C.; Beno, M.A.; Ansell, S.; Price, D.L. Levitation apparatus for structural studies of high temperature liquids using synchrotron radiation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1997, 68, 3512–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landron, C.; Launay, X.; Rifflet, J.C.; Echegut, P.; Auger, Y.; Ruffier, M.; Coutures, J.-P.; Lemonier, M.; Gailhanou, M.; Bessiere, M.; et al. Development of a levitation cell for synchrotron radiation experiments at very high temperature. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 1997, 124, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, J.J.; Weber, R.; Kim, J.; Liaw, P.K.; Choo, H. Aerodynamic levitation processing of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 445–446, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, E.H. Levitation in Physics. Science 1989, 243, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro, M.D.L.; Capote, F.P. (Eds.) Analytical Applications of Ultrasound; Techniques and Instrumentation in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 26, pp. 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Bucks, K.; Müller, H. Über einige Beobachtungen an schwingenden Piezoquarzen und ihrem Schallfeld. Z. Phys. 1933, 84, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, C.S.; Day, D.E. Description of the containerless melting of glass in low gravity. In Proceedings of the 15th National Technical Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 4–6 October 1983; Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering: Azusa, CA, USA, 1983; pp. 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Holt, R.G.; Apfel, R.E. Investigations of liquid surface rheology of surfactant solutions by droplet shape oscillations: Theory. Phys. Fluids 1995, 7, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmatz, M.; Collas, P. Acoustic radiation potential on a sphere in plane, cylindrical and spherical standing wave fields. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 77, 928–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whymark, R.R. Acoustic field positioning for containerless processing. Ultrasonics 1975, 13, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, C.A.; Whymark, R.R.; Danley, T.J.; Merkley, D.R. Materials processing in the reduced gravity environment of space. MRS Symp. Proc. 1982, 9, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, E.H. Compact acoustic levitation device for studies in fluid dynamics and material science in the laboratory and microgravity. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1985, 56, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lierke, E.G.; Grossenbach, R.; Flogel, K.; Clancy, P. Acoustic Positioning for Space Processing of materials science samples in mirror furnaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Atlanta, GA, USA, 31 October–2 November 1983; McAvoy, B.R., Ed.; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Volume 2, pp. 1129–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Hatano, H.; Kanai, Y.; Ikegami, Y.; Fujii, T.; Saito, K. Ultrasonic levitation and positioning of samples. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 21 (Suppl. 3), 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyers, R.W. Computer-aided experiments in containerless processing of materials. In Solidification of Containerless Undercooled Melts; Herlach, D.M., Matson, D.M., Eds.; Wiley-VHC Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Suryanarayana, P.V.R.; Bayazitoglu, Y. Surface tension and viscosity from damped free oscillations of viscous droplets. Int. J. Thermophys. 1991, 12, 137151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.K.R.; Rey, C.A.; Neuefeind, J.; Benmore, C.J. Acoustic levitator for structure measurements on low temperature liquid droplets. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2009, 80, 083904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmore, C.J.; Weber, J.K.R. Amorphization of molecular liquids of pharmaceutical drugs by acoustic levitation. Phys. Rev. X 2011, 1, 011004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmore, C.J.; Weber, J.K.R.; Tailor, A.N.; Cherry, B.R.; Yarger, J.L.; Mou, Q.; Weber, W.; Neuefeind, J.; Byrn, S.R. Structural characterization and aging of glassy pharmaceuticals made using acoustic levitation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.K.R.; Benmore, C.J.; Suthar, K.J.; Tamalonis, A.J.; Alderman, O.L.G.; Sendelbach, S.; Kondev, V.; Yarger, J.; Rey, C.A.; Byrn, S.R. Using containerless methods to develop amorphous pharmaceuticals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1861, 3686–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristiglio, V.; Grillo, I.; Fomina, M.; Wien, F.; Shalaev, E.; Novikov, A.; Brassamin, S.; Réfrégiers, M.; Pérez, J.; Hennet, L. Combination of acoustic levitation with small angle scattering techniques and synchrotron radiation circular dichroism. Application to the study of protein solutions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1861, 3693–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






















© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kohara, S.; Ohara, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Tamaru, H.; Weber, R. Investigation of Structure and Dynamics in Disordered Materials Using Containerless Techniques with In-Situ Quantum Beam and Thermophysical Property Measurements. Quantum Beam Sci. 2018, 2, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs2010005
Kohara S, Ohara K, Ishikawa T, Tamaru H, Weber R. Investigation of Structure and Dynamics in Disordered Materials Using Containerless Techniques with In-Situ Quantum Beam and Thermophysical Property Measurements. Quantum Beam Science. 2018; 2(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs2010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleKohara, Shinji, Koji Ohara, Takehiko Ishikawa, Haruka Tamaru, and Richard Weber. 2018. "Investigation of Structure and Dynamics in Disordered Materials Using Containerless Techniques with In-Situ Quantum Beam and Thermophysical Property Measurements" Quantum Beam Science 2, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs2010005
APA StyleKohara, S., Ohara, K., Ishikawa, T., Tamaru, H., & Weber, R. (2018). Investigation of Structure and Dynamics in Disordered Materials Using Containerless Techniques with In-Situ Quantum Beam and Thermophysical Property Measurements. Quantum Beam Science, 2(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs2010005






