Technical and Policy Analysis: Time Series of Land Subsidence for the Evaluation of the Jakarta Groundwater-Free Zone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Land Subsidence Mapping Materials
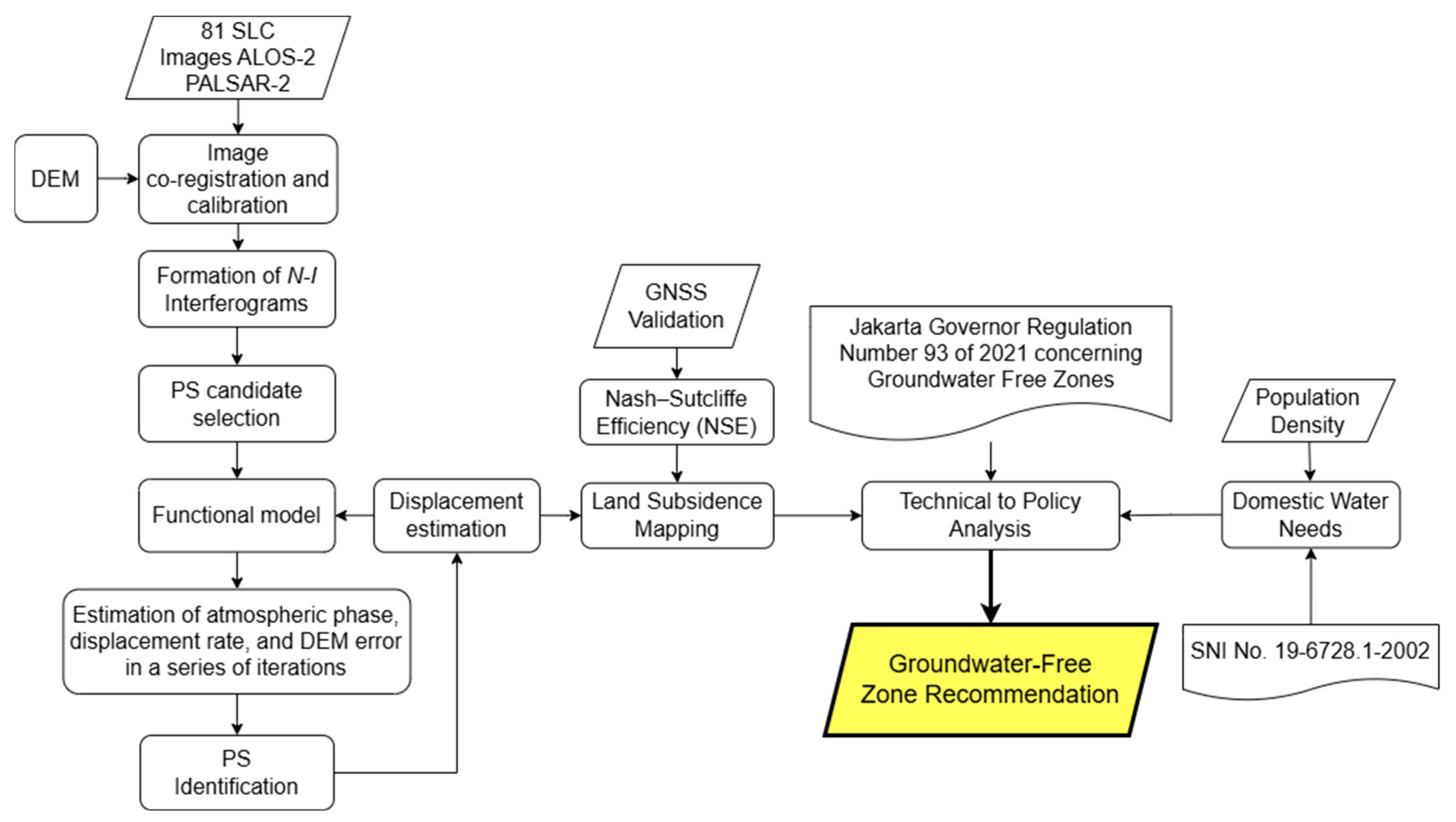
2.3. Data Processing with PS-InSAR Technique
2.3.1. Data Preparation
2.3.2. Interferometric Phase
2.3.3. Atmospheric Phase Screen Calculation
2.4. GNSS Validation
2.5. Time Series of Domestic Water Needs Mapping and Analysis
2.6. Analysis of the Groundwater-Free Zone Regulation
3. Results
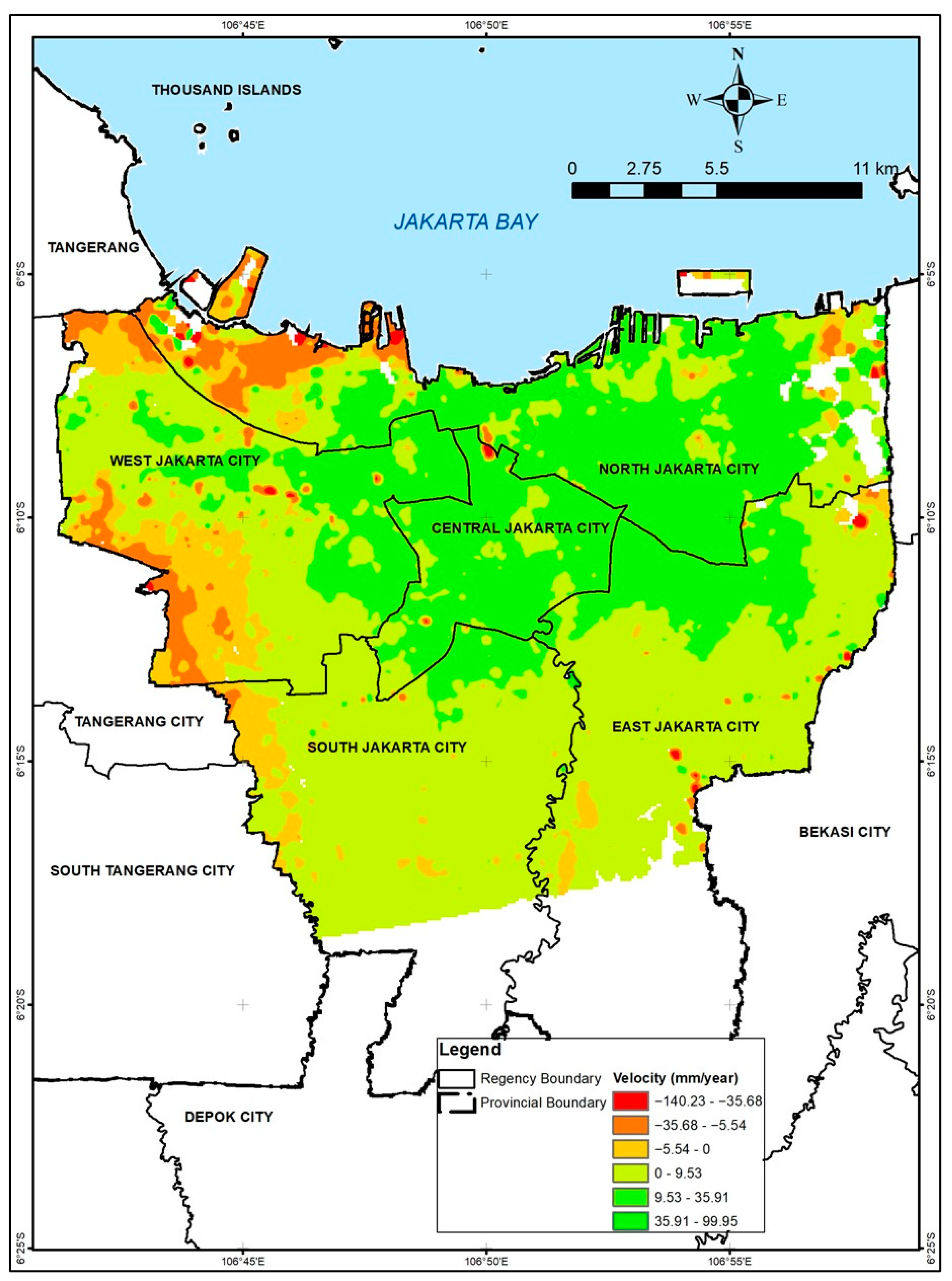
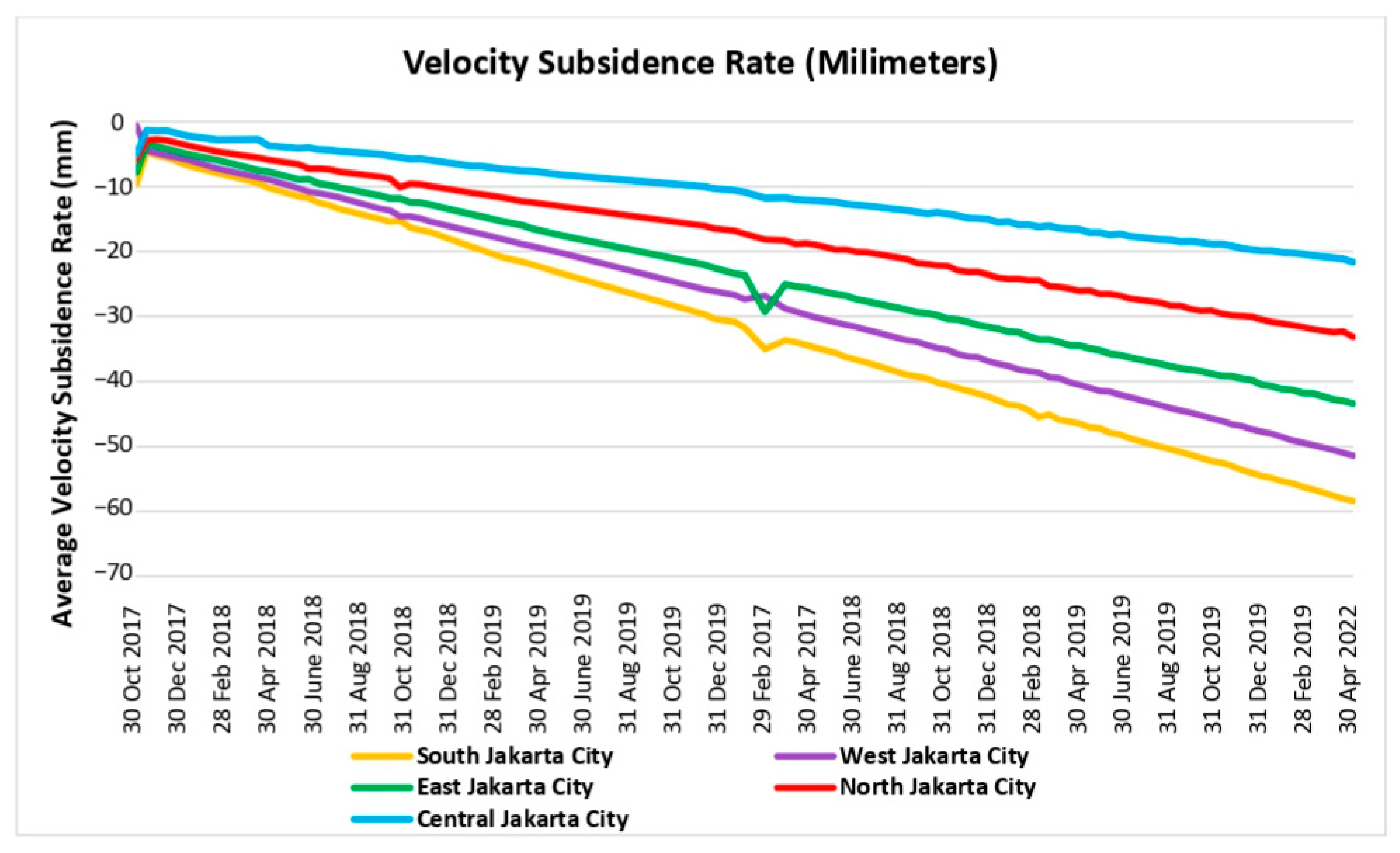
3.1. Land Subsidence Analysis
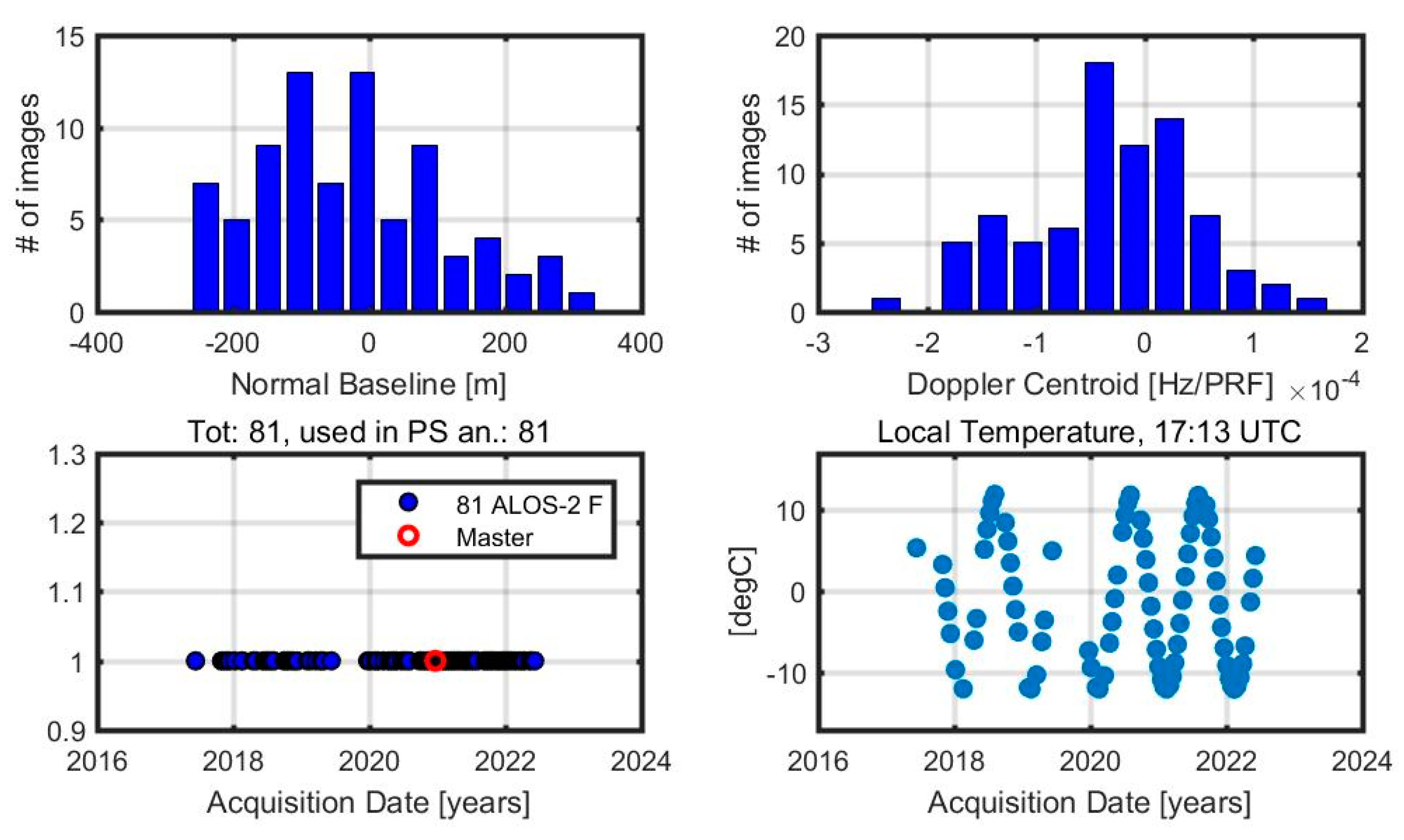
3.1.1. Atmospheric Phase Screen (APS) Calculation
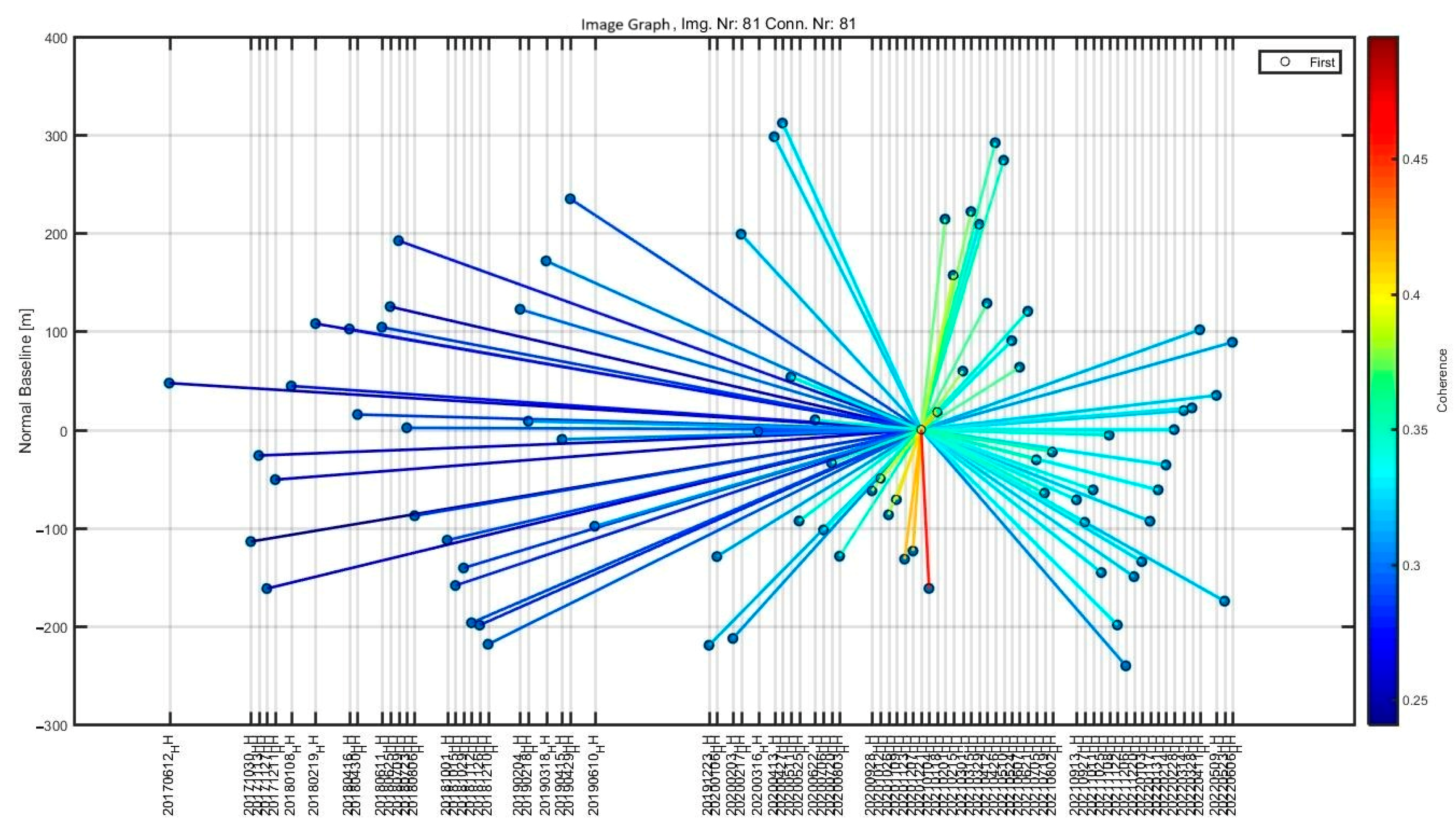
3.1.2. The Second Selection of PS Points
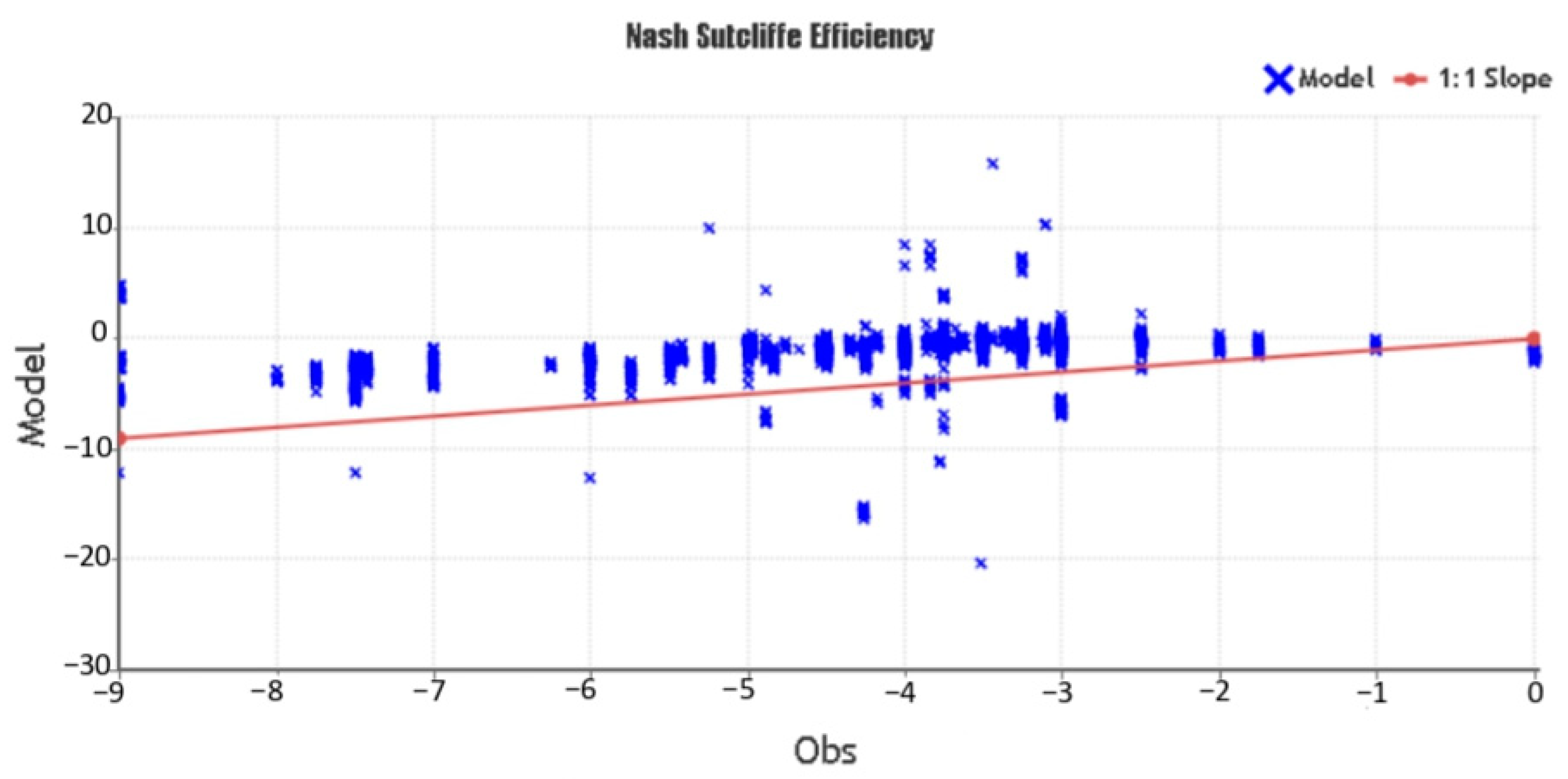
3.1.3. GNSS Validation
3.1.4. Land Subsidence Mapping
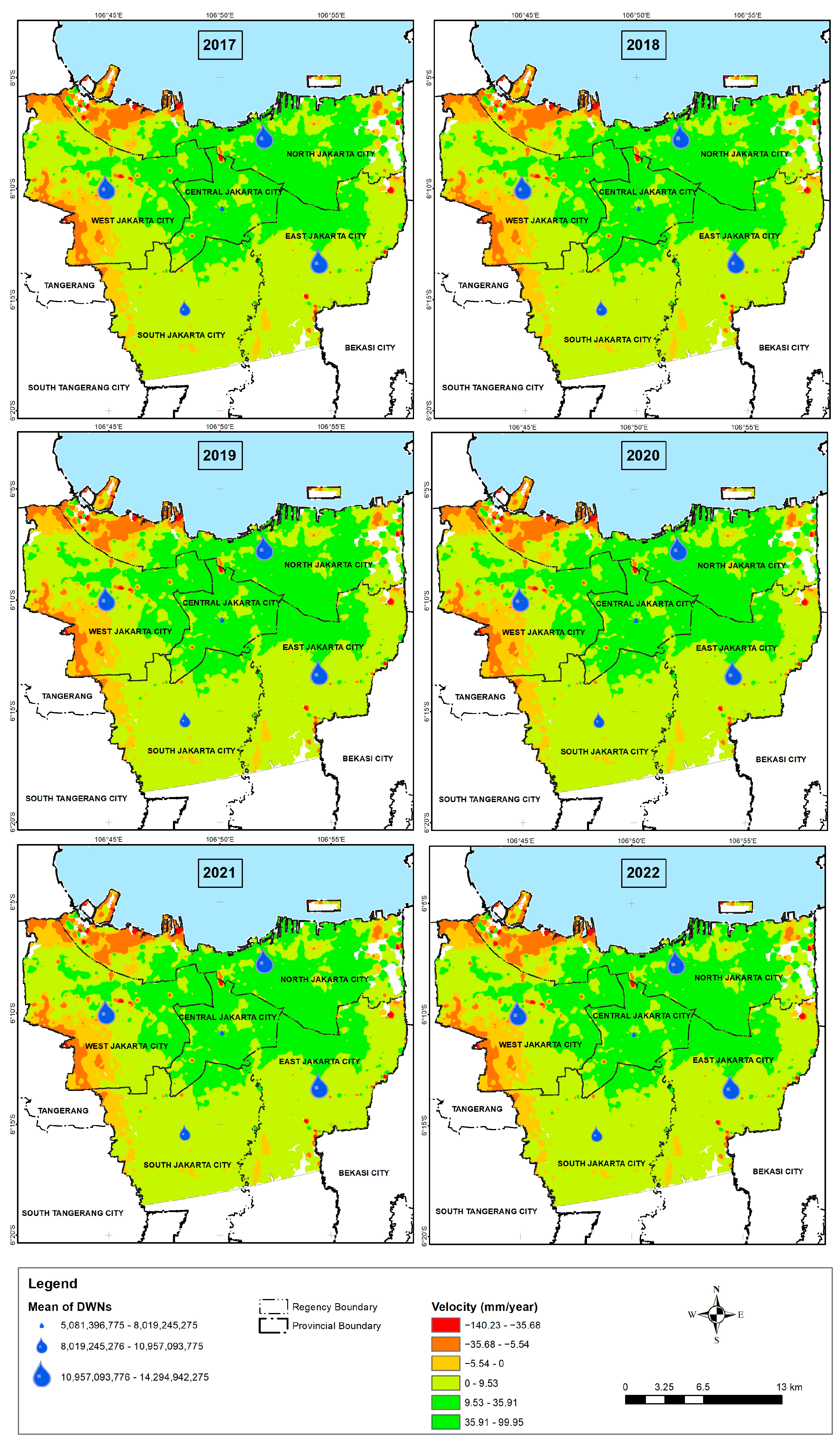
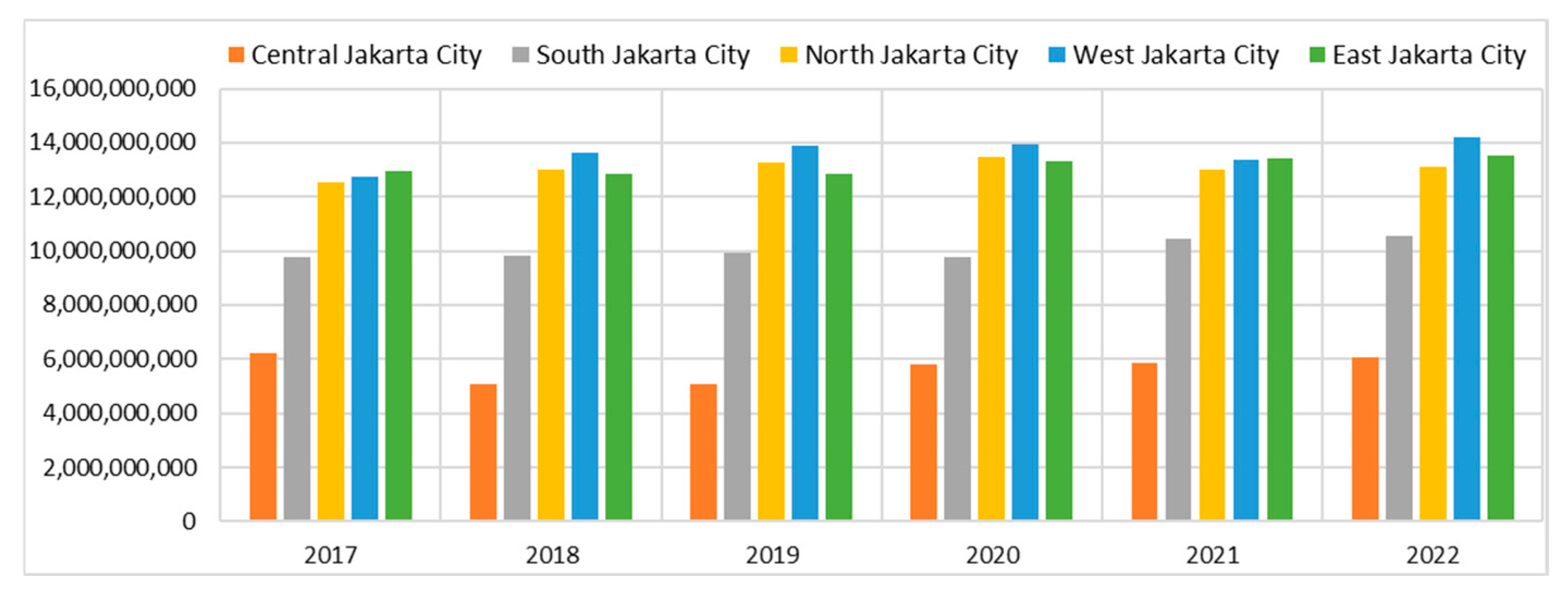
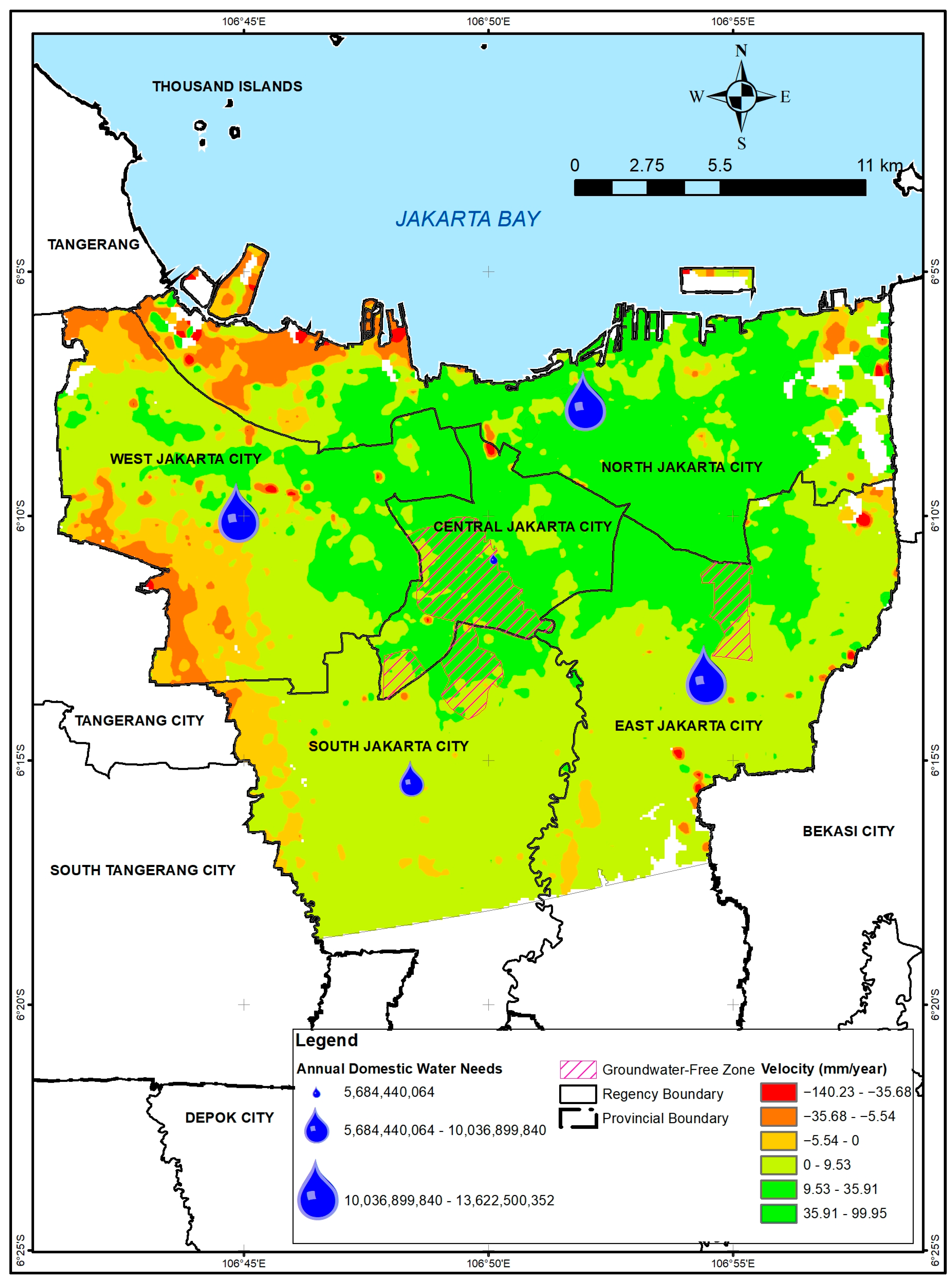
3.2. Domestic Water Needs
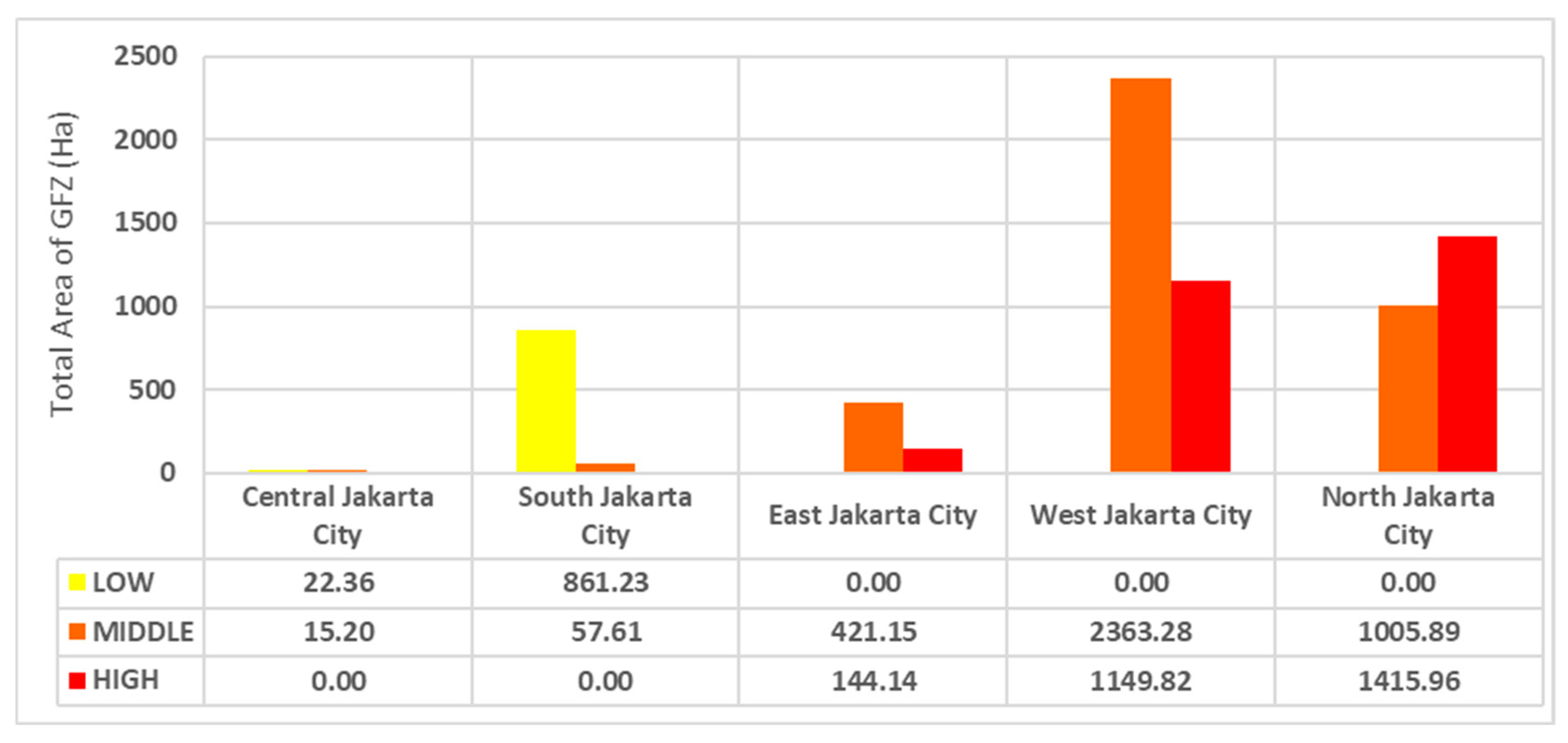
3.3. Analysis of the Groundwater-Free Zone Regulation
3.4. Recommendation for New Groundwater-Free Zones in Jakarta
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- West Jakarta;
- North Jakarta;
- South Jakarta;
- East Jakarta;
- Central Jakarta.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barragán, J.M.; Andrés, M. Analysis and trends of the world’s coastal cities and agglomerations. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 114, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komar, P.D.; McDougal, W.G. Coastal Erosion and Engineering Structures: The Oregon Experience. J. Coast. Res. 1988, 81, 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, S.K.; Ahirwal, J. Ecological Restoration of Coal Mine Degraded Lands: Topsoil Management, Pedogenesis, Carbon Sequestration, and Mine Pit Limnology. In Phytomanagement of Polluted Sites: Market Opportunities in Sustainable Phytoremediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 83–111. [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, L.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Honsel, L.E. Population development as a driver of coastal risk: Current trends and future pathways. Cambridge Prism. Coast. Futur. 2023, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surjan, A.; Parvin, G.A.; Atta-ur-Rahman; Shaw, R. Expanding Coastal Cities: An Increasing Risk. In Urban Disasters and Resilience in Asia; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, R.; Scrimgeour,, R.; Friedrich,, L.; Fletcher,, S.; Griffin, H. The Contributions of Marine and Coastal Area-Based Management Approaches to Sustainable Development Goals and Targets; UN Environment: Nairobi, Kenya, 2018; pp. 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sterzel, T.; Lüdeke, M.K.B.; Walther, C.; Kok, M.T.; Sietz, D.; Lucas, L. Typology of coastal urban vulnerability under rapid urbanization. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0220936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentaschi, L.; Vousdoukas, M.I.; Pekel, J.; Voukouvalas, E.; Feyen, L. Global long-term observations of coastal erosion and accretion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panthi, J.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Nolte, A.; Boving, T.B. Science of the Total Environment Saltwater intrusion into coastal aquifers in the contiguous United States—A systematic review of investigation approaches and monitoring networks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamlington, B.D.; Bellas-Manley, A.; Willis, J.K.; Fournier, S.; Vinogradova, N.; Nerem, R.S.; Piecuch, C.G.; Thompson, P.R.; Kopp, R. The rate of global sea level rise doubled during the past three decades. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trihatmoko, E. Dinamika Wilayah Kepesisiran Jawa Tengah Bagian Utara Dengan Pendekatan Geomorfologi. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Trihatmoko, E.; Nurlinda, N.; Darussalam, A.; Purwitaningsih, S.; Sartohadi, J.; Banowati, E.; Naibaho, B.B.; Husna, V.N.; Juhadi, J.; Aji, A. Preserving coastal ecosystem through micro-zonation analysis of Karimunjawa, Indonesia. Env. Monit Assess 2023, 196, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongsokarto, M.; Trihatmoko, E.; Nurlinda; Widodo, J.; Sanjoto, T.B.; Marfai, A.M.; Aji, A.; Annaufal, M.H.; Yulianasari, D.; Syarifatunnada, H. Sequencing seabed morphology through bathymetric profiling on Brebes coastal area. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1357, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Lincke, D.; Hinkel, J.; Brown, S.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Meyssignac, B.; Hanson, S.E.; Merkens, J.-L.; Fang, J. A global analysis of subsidence, relative sea-level change and coastal flood exposure. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Wibowo, I.R.R. On correlation between urban development, land subsidence and flooding phenomena in Jakarta. IAHS-AISH Proc. Rep. 2015, 370, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljammaz, A.; Sultan, M.; Izadi, M.; Abotalib, A.Z.; Elhebiry, M.S.; Emil, M.K.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Saleh, M.; Becker, R. Land Subsidence Induced by Rapid Urbanization in Arid Environments: A Remote Sensing-Based Investigation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Jain, K.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Gupta, V.; Varade, D.; Singh, H.; Narayan, A.B.; Budillon, A. Analyzing urbanization induced groundwater stress and land deformation using time-series Sentinel-1 datasets applying PSInSAR approach. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 844, 157103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, V.K.; Doubre, C.; Weber, C.; Gourmelen, N.; Masson, F. Recent land subsidence caused by the rapid urban development in the Hanoi region (Vietnam) using ALOS InSAR data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Whittaker, B.; Reddish, D. Mining subsidence and displacement prediction using influence function methods for steep seams. Min. Sci. Technol. 1989, 8, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi; Bachrun, R.; Ornam, K. Typology of Slum Management in Coastal Settlement as a Reference of Neighborhood Planning in Konawe. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 846, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, G. Spatially Varying Relationships between Land Subsidence and Urbanization: A Case Study in Wuhan, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Amelung, F.; Abidin, H.; Hong, S.-H. Sinking cities in Indonesia: ALOS PALSAR detects rapid subsidence due to groundwater and gas extraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tomás, R.; Li, Z.; Motagh, M.; Li, T.; Hu, L.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Gong, X. Imaging Land Subsidence Induced by Groundwater Extraction in Beijing (China) Using Satellite Radar Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levers, C.; Romero-Muñoz, A.; Baumann, M.; De Marzo, T.; Fernández, P.D.; Gasparri, N.I.; Gavier-Pizarro, G.I.; Waroux, Y.l.P.d.; Piquer-Rodríguez, M.; Semper-Pascual, A.; et al. Agricultural expansion and the ecological marginalization of forest-dependent people. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2100436118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z. Application of InSAR technology in monitoring land subsidence in the North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 786. [Google Scholar]
- Chaussard, E.; Bürgmann, R.; Shirzaei, M.; Fielding, E.J.; Baker, B. Predictability of hydraulic head changes and characterization of aquifer-system and fault properties from InSAR-derived ground deformation. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 6572–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Hudnut, K.W.; Ingebritsen, S.E.; Phillips, S.P.; Peltzer, G.; Rogez, F.; Rosen, P.A. Detection of aquifer system compaction and land subsidence using interferometric synthetic aperture radar, Antelope Valley, Mojave Desert, California. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, D.; Cao, J.; Qin, J.; Cao, Y.; He, Y. Study on the Relationship between Groundwater and Land Subsidence in Bangladesh Combining GRACE and InSAR. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkens, G.; Bucx, T.; Dam, R.; de Lange, G.; Lambert, J. Sinking coastal cities. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 372, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minderhoud, P.; Coumou, L.; Erban, L.; Middelkoop, H.; Stouthamer, E.; Addink, E. The relation between land use and subsidence in the Vietnamese Mekong delta. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 634, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, N.; Borrelli, M.; Rossi, M.; Crescenzo, G. Historical and recent subsidence processes in the Piana del Sele coastal plain, southern Italy: Insights from D-InSAR data and field observations. Remote Sens. 2012, 13, 3409. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Wang, R.; Feng, L. Levelling data analysis for land subsidence monitoring in Shanghai, China. Measurement 2019, 140, 342–352. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yao, L.; Chen, Y. An integrated GNSS-InSAR method for large-scale surface deformation monitoring: A case study in the North China Plain. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 379. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, W. A hybrid GNSS and InSAR time series analysis method for monitoring land subsidence. Remote Sens. 2014, 12, 3543. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Li, X.; Hu, J. Monitoring land subsidence with InSAR and its application in urban areas: A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2649. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Gong, H. SBAS-InSAR monitoring of land subsidence in vegetated areas: A case study in the Beijing Plain, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 5174–5194. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Gong, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, R. InSAR monitoring of land subsidence and its driving factors in the central Yangtze River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125546. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Ding, X.; Wu, Q. D-InSAR monitoring of land subsidence in Shanghai: A case study from 2016 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3912. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H. The application of D-InSAR technology in land subsidence monitoring. Geod. Geodyn. 2017, 8, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, G.; Gong, H. Multi-temporal InSAR analysis for monitoring land subsidence in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 845. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X. Multi-temporal InSAR analysis of land subsidence in Wuhan, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 253. [Google Scholar]
- Parizzi, A.; Brcic, R.; De Zan, F. InSAR Performance for Large-Scale Deformation Measurement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 8510–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Hu, J.; Ding, X. PS-InSAR based subsidence monitoring and influencing factors analysis in coastal areas: A case study in Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1583. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Arroyo-Domínguez, N.; Martel, R.; Calderhead, A.I.; Normand, J.C.L.; Gárfias, J.; Rivera, A. Land subsidence in major cities of Central Mexico: Interpreting InSAR-derived land subsidence mapping with hydrogeological data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 47, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, E.J.; Blom, R.G.; Goldstein, R.M. Rapid subsidence over oil fields measured by SAR interferometry. Geo-physical Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 3215–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Hoffmann, J. The application of satellite differential SAR interferometry-derived ground displace-ments in hydrogeology. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, X. InSAR-based monitoring of urban subsidence in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Sensors. 2021, 21, 3726. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, A.; Sultan, M.; Becker, R.; Alsefry, S.; Alharbi, T.; Gebremichael, E.; Alharbi, H.; Abdelmohsen, K. Use of Geophysical and Remote Sensing Data for Assessment of Aquifer Depletion and Related Land Deformation. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 39, 543–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Sun, Z. PS-InSAR monitoring of land subsidence in the Pearl River Delta, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1809. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, J.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Liu, K.; Zhou, C.; Ke, Y. Time-series evolution patterns of land subsidence in the eastern Beijing Plain, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Dzurisin, D.; Wicks, C.; Diefenbach, A. Radar interferometry for monitoring volcanoes. Science 2018, 362, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnardi, M.; Amelung, F. Multi-temporal InSAR processing for volcano deformation monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111962. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y. Monitoring peatland subsidence and water table variations using InSAR: A case study in the western Jilin Province, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1376. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, B.; Ding, X. Monitoring peatland subsidence in the Sanjiang Plain, China using multi-temporal InSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 227, 220–231. [Google Scholar]
- Widodo, J.; Sulaiman, A.; Awaluddin, A.; Riyadi, A.; Nasucha, M.; Perissin, D.; Sumantyo, J.T.S. Application of SAR Interferometry Using ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 Data as Precise Method to Identify Degraded Peatland Areas Related to Forest Fire. Geosciences 2019, 9, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widodo, J.; Izumi, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Kausarian, H.; Perissin, D.; Sumantyo, J.T.S. Detection of peat fire risk area based on impedance model and DInSAR approaches using ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 data. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 22395–22407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heleno, S.I.N.; Oliveira, L.G.S.; Henriques, M.J.; Falcão, A.P.; Lima, J.N.P.; Cooksley, G.; Ferretti, A.; Fonseca, A.M.; Lobo-Ferreira, J.P.; Fonseca, J.F.B.D. Persistent Scatterers Interferometry detects and measures ground subsidence in Lisbon. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2152–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widodo, J.; Trihatmoko, E.; Khomarudin, M.R.; Ardha, M.; Nugroho, U.C.; Setyaningrum, N. Dynamic Geo-Visualization of Urban Land Subsidence and Land Cover Data Using PS-InSAR and Google Earth Engine (GEE) for Spatial Planning Assessment. Urban Sci. 2024, 8, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Ramirez, R.E.; Tapete, D. Accuracy of Sentinel-1 PSI and SBAS InSAR Displacement Velocities against GNSS and Geodetic Leveling Monitoring Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, X.; Qi, Y.; Huang, P.; Sun, W.; Xu, W.; Tan, W.; Li, X.; Liu, X. Integration of DInSAR-PS-Stacking and SBAS-PS-InSAR Methods to Monitor Mining-Related Surface Subsidence. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri-Gavkosh, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Sohani, Y.; Ebrahimian, H.; Morovat, F.; Ashrafi, S. Land subsidence: A global challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzampoglou, P.; Ilia, I.; Karalis, K.; Tsangaratos, P.; Zhao, X.; Chen, W. Selected Worldwide Cases of Land Subsidence Due to Groundwater Withdrawal. Water 2023, 15, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Fukuda, Y.; Pohan, Y.E.; Deguchi, T. Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its relation with urban development. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 1753–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batubara, B.; Kooy, M.; Zwarteveen, M. Politicising land subsidence in Jakarta: How land subsidence is the outcome of uneven sociospatial and socionatural processes of capitalist urbanization. Geoforum 2023, 139, 103689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdohardono, D.; Sudarsono, B. Land subsidence monitoring system in Jakarta, Indonesia. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Japan-Indonesia IDNDR Project: Volcanology, Tectonics, Flood and Sediment Hazards, Jakarta, Indonesia, 21–23 September 1998; pp. 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ardha, M.; Suhadha, A.G.; Julzarika, A.; Yulianto, F.; Yudhatama, D.; Darwista, R.Z. Utilization of Sentinel-1 satellite imagery data to support land subsidence analysis in DKI Jakarta, Indonesia. J. Degrad. Min. Lands Manag. 2021, 8, 2587–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benattou, M.M.; Balz, T.; Liao, M. Measuring surface subsidence in Wuhan, China with Sentinel-1 data using PSInSAR. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, F.; Gharechelou, S.; Golian, S.; Johnson, B.A. Aquifer and land subsidence interaction assessment using Sen-tinel-1 data and DInSAR technique. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhadha, A.G.; Prayoga, O.; Harintaka, H. Precise coseismic displacement related to the 2022 Pasaman earthquake using multi-geometry of Sentinel-1 InSAR. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2941, 030008. [Google Scholar]
- Widodo, J.; Herlambang, A.; Sulaiman, A.; Razi, P.; Perissin, D.; Kuze, H.; Sumantyo, J.T. Land sub-sidence rate analysis of Jakarta Metropolitan Region based on D-InSAR processing of Sentinel data C-Band frequency. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1185, 12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L. Long-term Landsat monitoring of mining subsidence based on spatiotemporal variations in soil moisture: A case study of Shanxi Province, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.M.; Ge, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, X. Estimating horizontal and vertical movements due to underground mining using ALOS PALSAR. Eng. Geol. 2012, 143–144, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.M.; Ge, L.; Li, X. Assessments of land subsidence in the Gippsland Basin of Australia using ALOS PALSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 159, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayuaji, L.; Sumantyo, J.T.S.; Kuze, H. ALOS PALSAR D-InSAR for land subsidence mapping in Jakarta, Indonesia. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, D.H.T.; Trung, L.; Toan, T.L. Mapping ground subsidence phenomena in Ho Chi Minh City through the radar interferometry technique using ALOS PALSAR data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8543–8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, N.; Kaiser, M.; Koch, M.; Gaber, A. Assessing the accuracy of ALOS/PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-1 radar images in estimating the land subsidence of coastal areas: A case study in Alexandria City. Egypt. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Ng, A.H.M.; Li, X.; Abidin, H.Z. Land subsidence characteristics of Bandung Basin as revealed by ENVISAT ASAR and ALOS PALSAR interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, A.M.; Sato, T.; Tomiyama, N.; Isezaki, N.; Yamanokuchi, T. Ground subsidence in Semarang-Indonesia in-vestigated by ALOS–PALSAR satellite SAR interferometry. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2010, 40, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Liao, M.; Shi, X. Detection of coal-mining-induced subsidence and mapping of the resulting de-formation using time series of ALOS-PALSAR data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, R.F.; Rostika, M.D.; Abadi, A.W.; Rakhmatika, M. A Review Disaster Mitigation of Jakarta Land Subsidence Areas. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 325, 01002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasibuan, H.S.; Tambunan, R.P.; Rukmana, D.; Permana, C.T.; Elizandri, B.N.; Putra, G.A.Y.; Wahidah, A.N.; Ristya, Y. Policymaking and the spatial characteristics of land subsidence in North Jakarta. City Environ. Interact. 2023, 18, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Djaja, R.; Darmawan, D.; Hadi, S.; Akbar, A.; Rajiyowiryono, H.; Sudibyo, Y.; Meilano, I.; Kasuma, M.A.; Kahar, J.; et al. Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its geodetic monitoring system. Nat. Hazards 2001, 23, 365–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Djaja, R.D.; Gamal, M. Land subsidence characteristics of Jakarta between 1997 and 2005, as estimated using GPS surveys. GPS Solut. 2007, 12, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badan Pusat Statistik. Jumlah Penduduk Menurut Kabupaten/Kota di Provinsi DKI Jakarta (Jiwa) 2013–2023). 2024. Available online: https://jakarta.bps.go.id/id/statistics-table/2/MTI3MCMy/jumlah-penduduk-menurut-kabupaten-kota-di-provinsi-dki-jakarta-html (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Perissin, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T. The SARPROZ InSAR tool for urban subsidence/manmade structure stability monitoring in China. In Proceedings of the ISRSE, Sidney, Australia, 10–15 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aye, P.P.; Koontanakulvong, S.; Tran, L.T. Estimation of Groundwater Flow Budget in the Upper Central Plain, Thailand from Regional Groundwater Model. Internet J. Soc. Soc. Manag. Syst. 2017, 11, 90–100. [Google Scholar]
- Badan Standardisasi Nasional (BSN). Penyusunan Neraca Sumber Daya–Bagian 1: Sumber Daya Air Spasial; BSN: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2002; pp. 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dimyati, M.; Trihatmoko, E.; Marfai, M.A. 10 years erosion-sedimentation monitoring: System based automatic interpretation in coastal area of brebes regency, central Java province, Indonesia. Geogr. Tech. 2021, 16, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimbatan-Fadgyas, R. Indigenous Toponyms in Landslide Hazard Mapping for Land Use and Infrastructure Planning. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hisyam, F.; Sabila, W.I. Kajian Toponimi Kampung di Sepanjang Sungai Brantas, Kota Malang. J. Dialog Penanggulangan Bencana 2020, 11, 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Afroosheh, F.; Riyazinejad, M.; Shahrashoub, M.; Toosi, G.; Saffari, M. A Field Study of The Environmental Effects of Marginalization in the 19th District of Tehran Using Rapid Impact Assessment Matrix (RIAM). Environ. Energy Econ. Res. 2018, 2, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousis, M. Ecological Marginalization in Rural Areas: Actors, Impacts, Responses. Sociol. Ruralis 1998, 38, 86–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, F.; Teixeira, A.; Sousa, I.; Leivas, J.; Takemura, C.; Garçon, E. Large-scale water balance modeling using remote sensing and weather data: Application in an agricultural growing region of the coastal northeast Brazil. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 32, 101072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y.S.; Rao, B.V. Groundwater depletion and groundwater balance studies of Kandivalasa River Sub Basin, Vizianagaram District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 6, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W.M.; Reilly, T.E.; Franke, O.L. Sustainability of Ground-Water Resources, U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1186. U.S. Geol. Surv. Circ. 1999, 1186, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Wu, J.; Ye, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wei, Z.; Li, Q.; Yu, J. Regional land subsidence simulation in Su-Xi-Chang area and Shanghai City, China. Eng. Geol. 2008, 100, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajehali, M.; Safavi, H.R.; Pour, S.I. Evaluation of management scenarios for land subsidence reduction and groundwater rehabilitation in Damane-Daran plain, Iran. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 100995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M.; Gorelick, S. The effects of pulsed pumping on land subsidence in the Santa Clara Valley, California. J. Hydrol. 1996, 174, 375–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Very good | 0.75 < NSE < 1.00 |
| Good | 0.65 < NSE < 0.75 |
| Satisfactory | 0.50 < NSE < 0.65 |
| Unsatisfactory | NSE < 0.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Widodo, J.; Trihatmoko, E.; Setyaningrum, N.; Izumi, Y.; Handika, R.; Ardha, M.; Arief, R.; Sobue, S.; Nurlinda, N.; Pranantya, P.A.; et al. Technical and Policy Analysis: Time Series of Land Subsidence for the Evaluation of the Jakarta Groundwater-Free Zone. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9030067
Widodo J, Trihatmoko E, Setyaningrum N, Izumi Y, Handika R, Ardha M, Arief R, Sobue S, Nurlinda N, Pranantya PA, et al. Technical and Policy Analysis: Time Series of Land Subsidence for the Evaluation of the Jakarta Groundwater-Free Zone. Urban Science. 2025; 9(3):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9030067
Chicago/Turabian StyleWidodo, Joko, Edy Trihatmoko, Nugraheni Setyaningrum, Yuta Izumi, Rendi Handika, Mohammad Ardha, Rahmat Arief, Shinichi Sobue, Nurlinda Nurlinda, Pulung Arya Pranantya, and et al. 2025. "Technical and Policy Analysis: Time Series of Land Subsidence for the Evaluation of the Jakarta Groundwater-Free Zone" Urban Science 9, no. 3: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9030067
APA StyleWidodo, J., Trihatmoko, E., Setyaningrum, N., Izumi, Y., Handika, R., Ardha, M., Arief, R., Sobue, S., Nurlinda, N., Pranantya, P. A., Wiranu, J. R., & Khomarudin, M. R. (2025). Technical and Policy Analysis: Time Series of Land Subsidence for the Evaluation of the Jakarta Groundwater-Free Zone. Urban Science, 9(3), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9030067







