Dynamic Analysis of a Delayed Fractional Infectious Disease Model with Saturated Incidence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
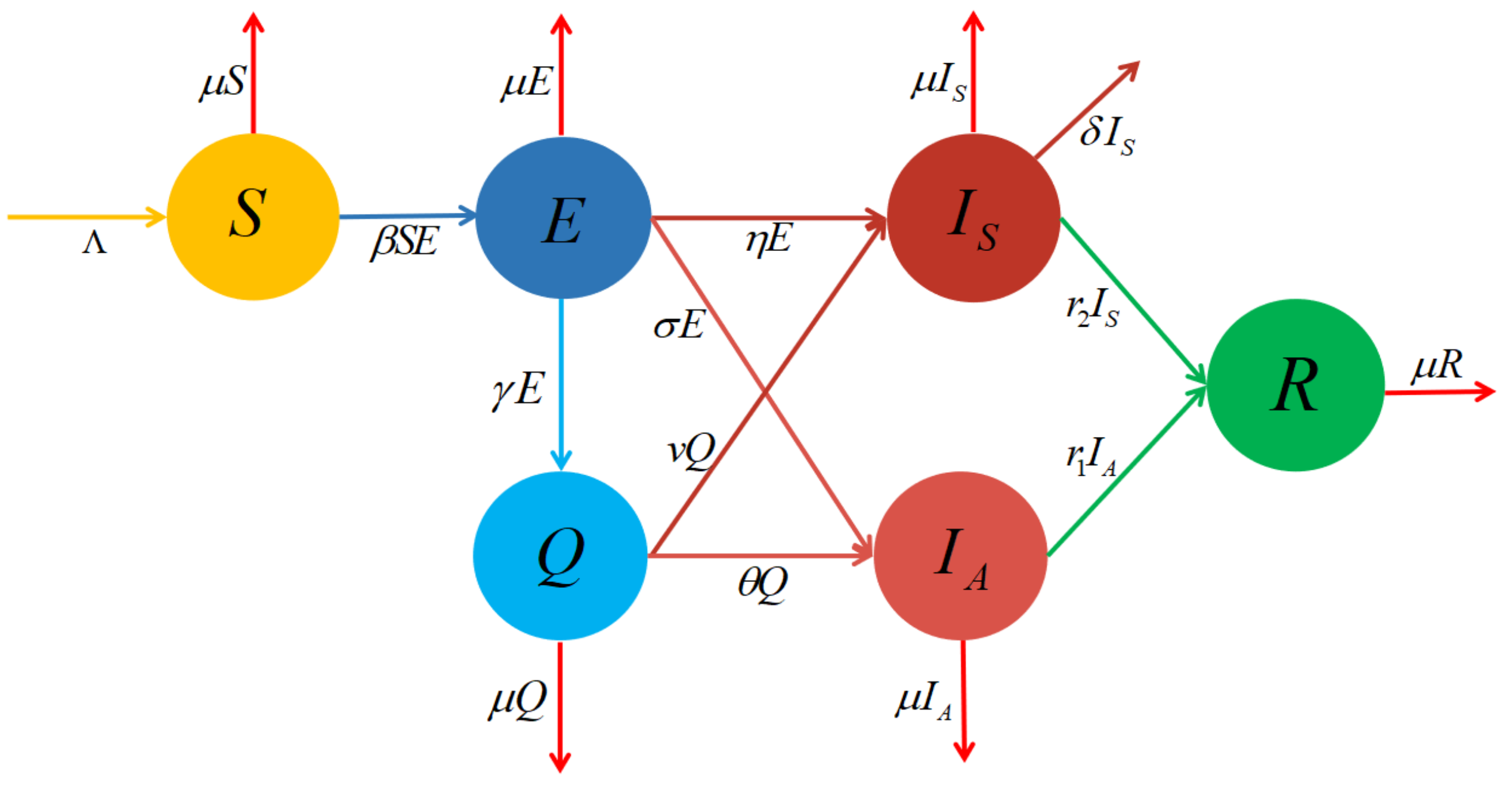
3. Model Description
4. Basic Properties
4.1. Invariant Region and Boundedness
4.2. Solution Nonnegativity
4.3. Disease-Free Equilibrium (DFE)
4.4. Existence of Endemic Equilibrium Point
5. Stability Analysis
5.1. Local Stability of DFE
5.2. Local Stability Analysis of the Endemic Equilibrium
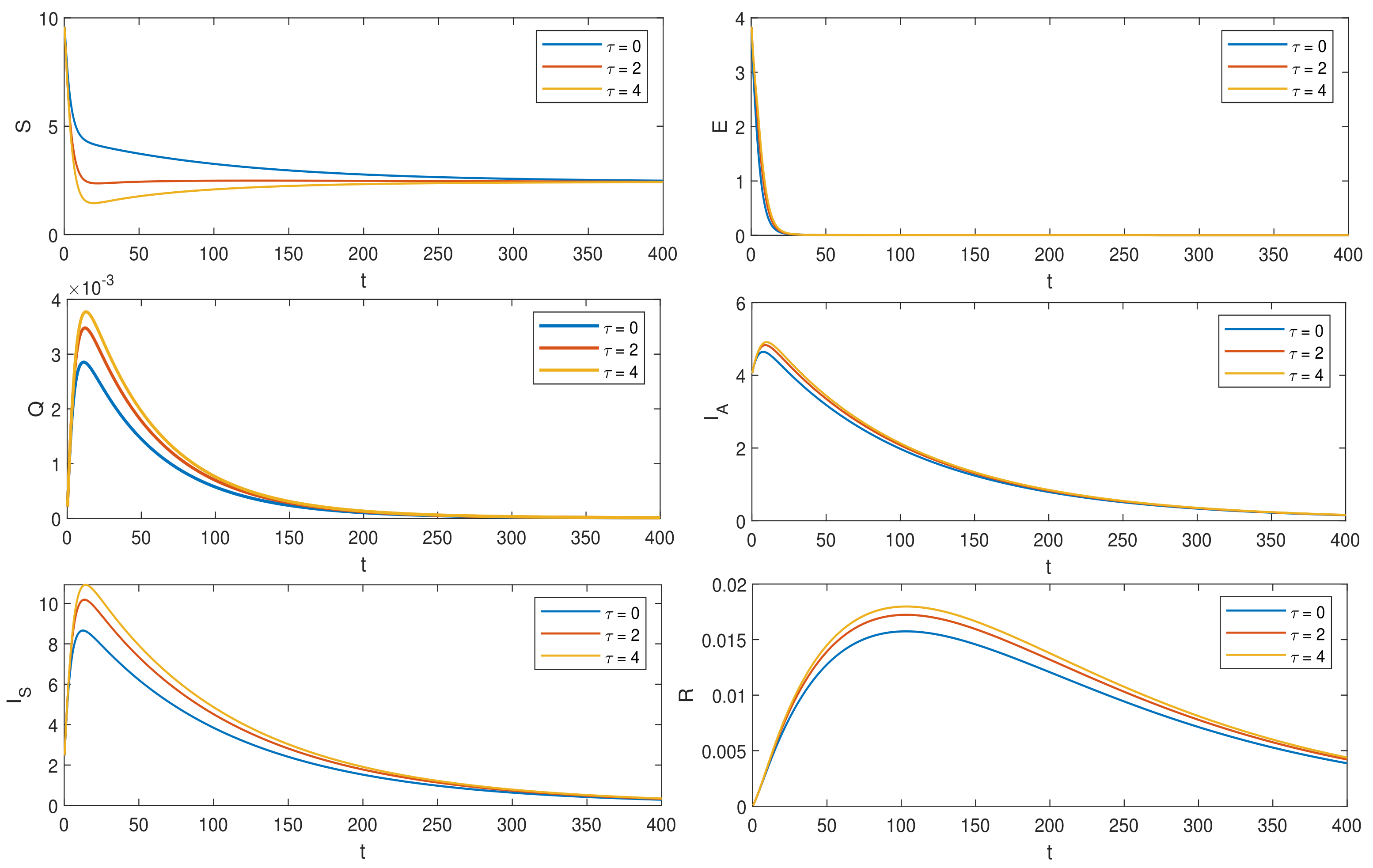
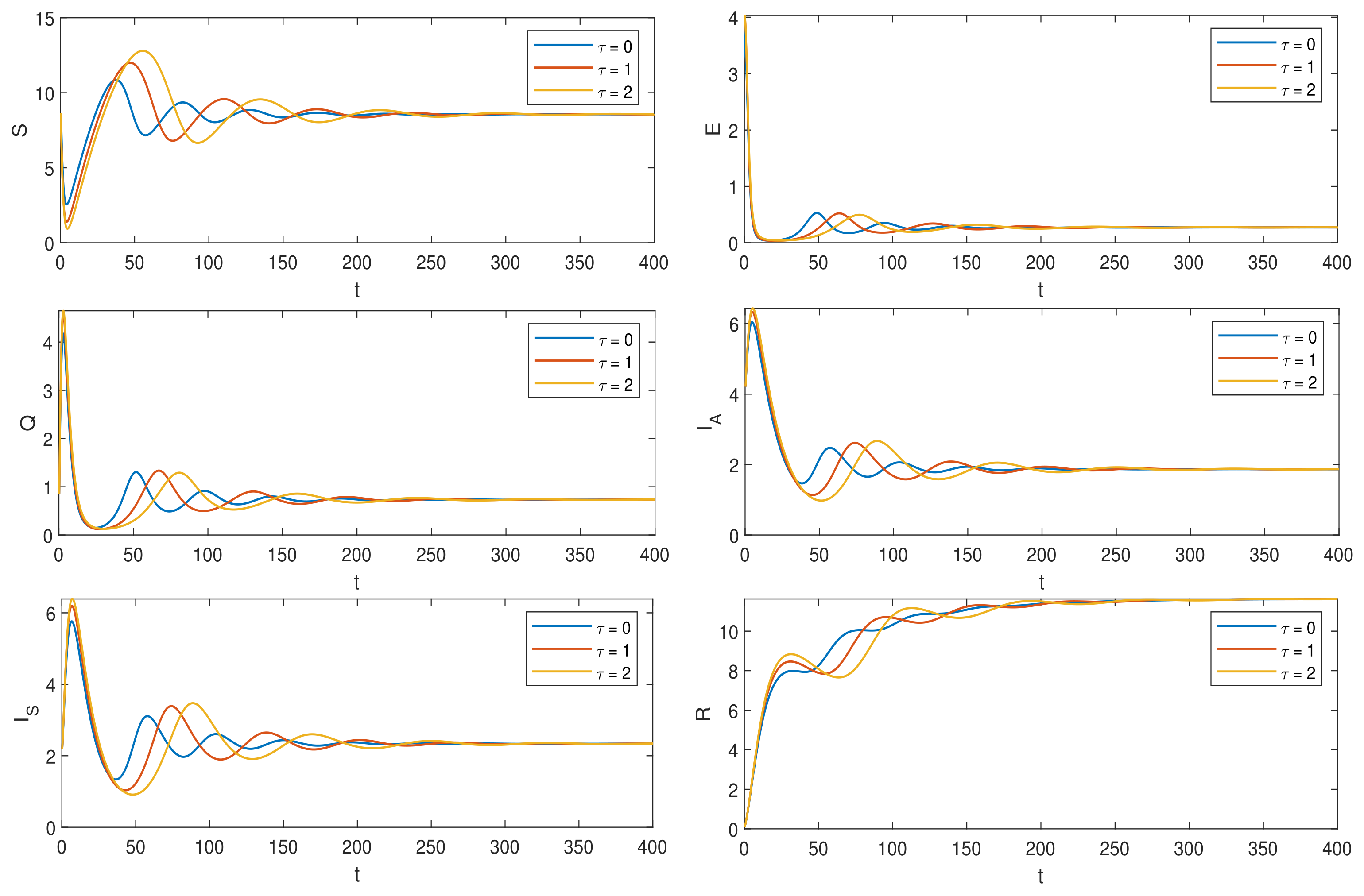
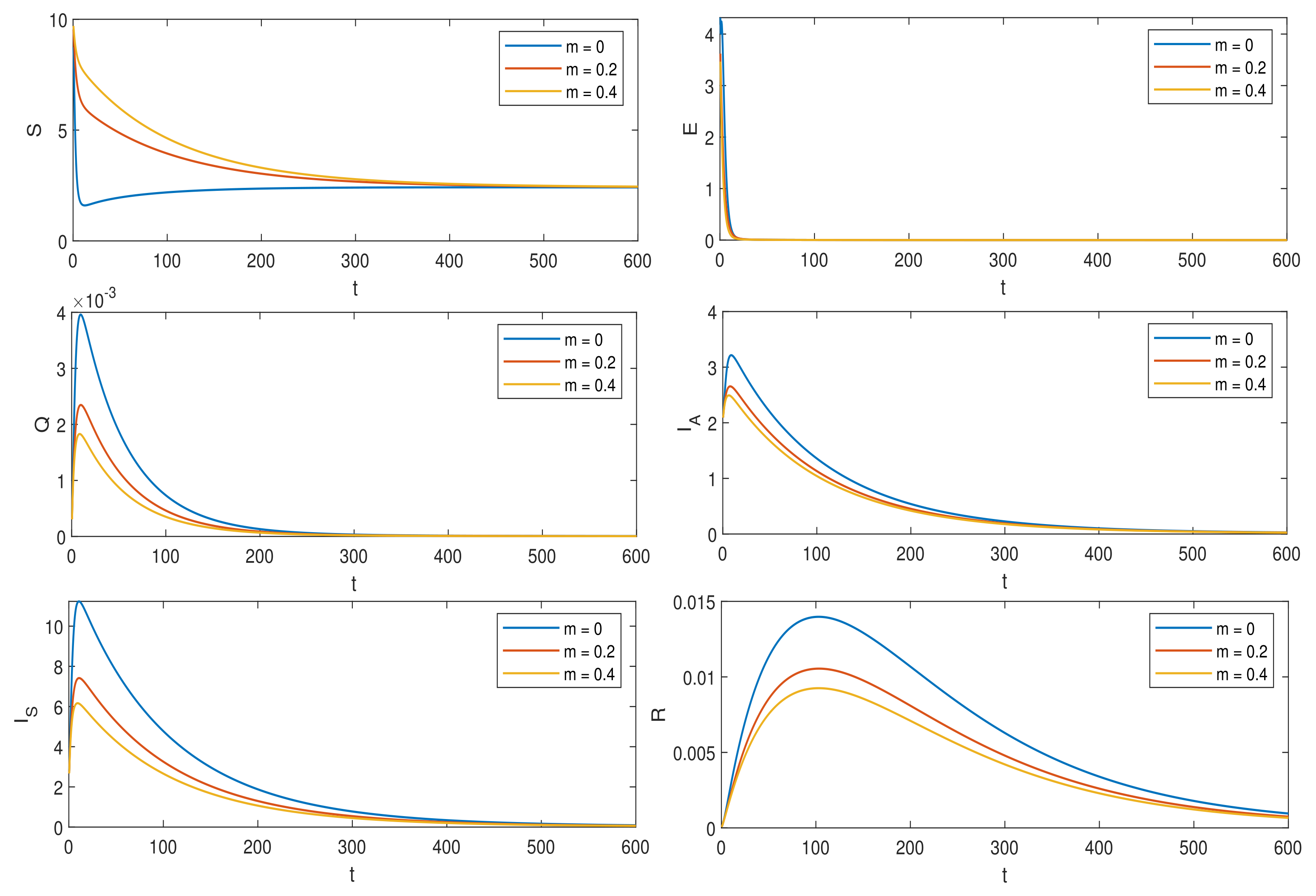
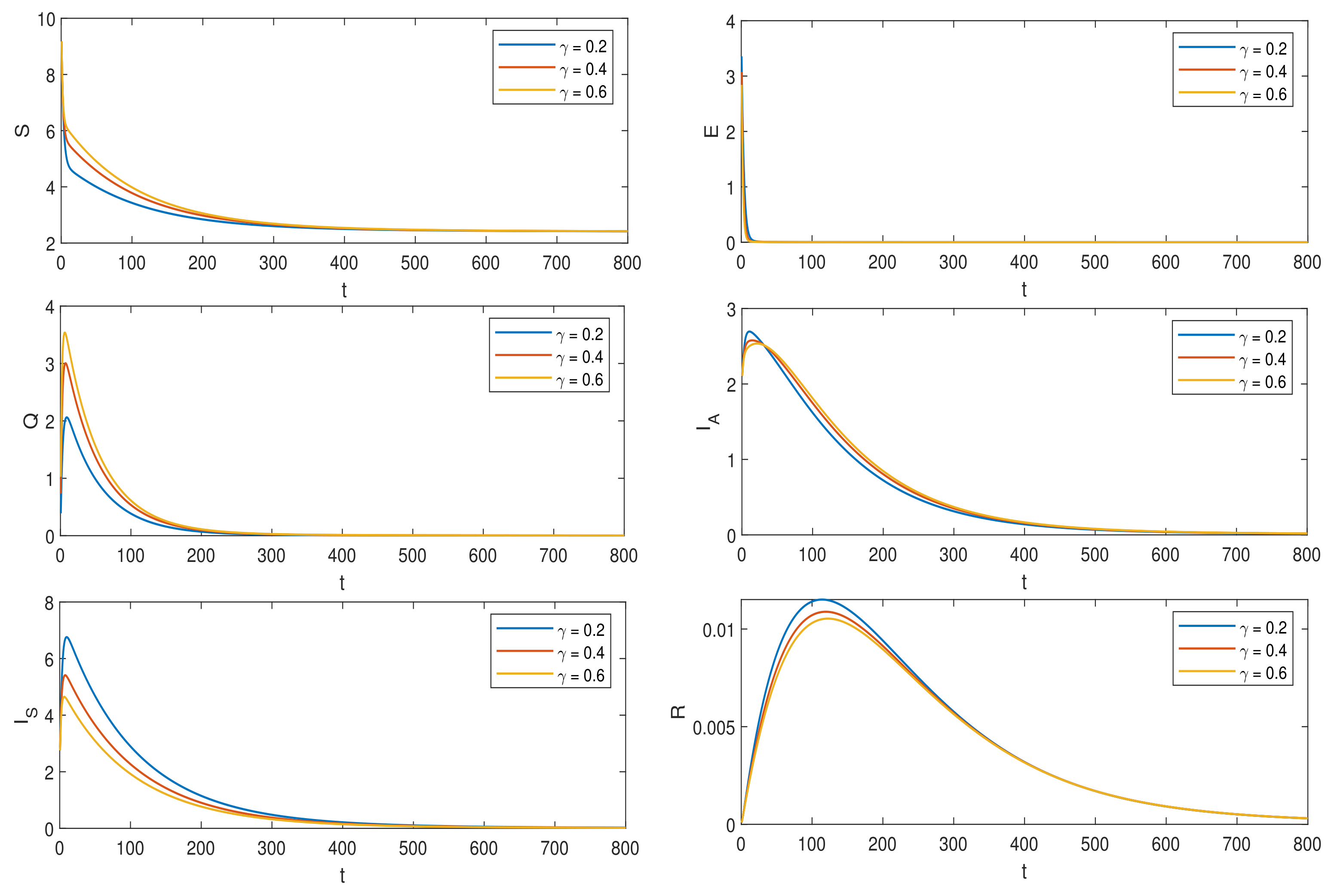
6. Numerical Simulations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SIR | susceptible infectious recovered |
| SEIR | susceptible exposed infectious recovered |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| HRSV | human respiratory syncytial virus |
| SIRC | susceptible infectious recovered cleaared |
| DFE | disease-free equilibrium |
References
- Unkel, S.; Farrington, C.P.; Garthwaite, P.H.; Robertson, C.; Andrews, N. Statistical methods for the prospective detection of infectious disease outbreaks: A review. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A (Stat. Soc.) 2012, 175, 49–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasution, H.; Jusuf, H.; Ramadhani, E.; Husein, I. Model of Spread of Infectious Disease. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 685–689. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørnstad, O.N.; Finkenstädt, B.F.; Grenfell, B.T. Dynamics of measles epidemics: Estimating scaling of transmission rates using a time series SIR model. Ecol. Monogr. 2002, 72, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Jiang, D.; Shi, N. Global stability of two-group SIR model with random perturbation. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2009, 360, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bentout, S.; Chen, Y.; Djilali, S. Global dynamics of an SEIR model with two age structures and a nonlinear incidence. Acta Appl. Math. 2021, 171, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, S.; Camacho, A.; Kucharski, A.J.; Eggo, R.M.; Edmunds, W.J. Real-time forecasting of infectious disease dynamics with a stochastic semi-mechanistic model. Epidemics 2018, 22, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, K.; Heesterbeek, J.A.P. Daniel Bernoulli’s epidemiological model revisited. Math. Biosci. 2002, 180, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehrhardt, M.; Gašper, J.; Kilianová, S. SIR-based mathematical modeling of infectious diseases with vaccination and waning immunity. J. Comput. Sci. 2019, 37, 101027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Graef, J.R.; Wang, L.; Karsai, J. Global dynamics of a SEIR model with varying total population size. Math. Biosci. 1999, 160, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korobeinikov, A. Global properties of SIR and SEIR epidemic models with multiple parallel infectious stages. Bull. Math. Biol. 2009, 71, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, L.; Rodo, X. A modified SEIR model to predict the COVID-19 outbreak in Spain and Italy: Simulating control scenarios and multi-scale epidemics. Results Phys. 2021, 21, 103746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossikhin, Y.A.; Shitikova, M.V. Applications of fractional calculus to dynamic problems of linear and nonlinear hereditary mechanics of solids. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1997, 50, 15–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povstenko, Y.Z. Thermoelasticity that uses fractional heat conduction equation. J. Math. Sci. 2009, 162, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillie, R.T.; Bollerslev, T.; Mikkelsen, H.O. Fractionally integrated generalized autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity. J. Econom. 1996, 74, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Ganji, R.M.; Nkomo, N.S.; Lv, Y.P. A numerical study of fractional order population dynamics model. Results Phys. 2021, 27, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeborn, T.J.; Critcher, S. Cole-impedance model representations of right-side segmental arm, leg, and full-body bioimpedances of healthy adults: Comparison of fractional-order. Fractal Fract. 2021, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, R.; Mahariq, I.; Shah, K.; Awais, M.; Elsayed, F. Numerical solution of the second order linear and nonlinear integro-differential equations using Haar wavelet method. Arab. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2021, 28, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.A.; Zu, J.; Owolabi, K.M. Modeling the mechanics of viral kinetics under immune control during primary infection of HIV-1 with treatment in fractional order. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 545, 123816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Huang, S.; Zheng, S.; Wang, H.O. Stability Analysis and Bifurcation Control for a Fractional Order SIR Epidemic Model with Delay. In Proceedings of the 2020 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Shenyang, China, 27–29 July 2020; pp. 724–729. [Google Scholar]
- Jajarmi, A.; Yusuf, A.; Baleanu, D.; Inc, M. A new fractional HRSV model and its optimal control: A non-singular operator approach. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 547, 123860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoan, L.V.C.; Akinlar, M.A.; Inc, M.; Gómez-Aguilar, J.F.; Chu, Y.M.; Almohsen, B. A new fractional-order compartmental disease model. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Song, M.; Takeuchi, Y. Global stability of an SIR epidemicmodel with time delay. Appl. Math. Lett. 2004, 17, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rihan, F.A.; Alsakaji, H.J.; Rajivganthi, C. Stochastic SIRC epidemic model with time-delay for COVID-19. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddar, A. Stability analysis in a delayed SIR epidemic model with a saturated incidence rate. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control. 2010, 15, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, L. Stability analysis of an SEIQV epidemic model with saturated incidence rate. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2012, 13, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, P.; Lehtinen, S.; Angst, D.C.; Low, N.; Bonhoeffer, S. Quantifying the impact of quarantine duration on COVID-19 transmission. eLife 2021, 10, e63704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, S.; Simonetta, V.; Remarque, E.; Ruello, A.; Bombardieri, E.; Bollati, V.; Trombetta, C. Characterization of antibody response in asymptomatic and symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xia, J. Stability and bifurcation control of a delayed fractional-order eco-epidemiological model with incommensurate orders. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 8278–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matignon, D. Stability results for fractional differential equations with applications to control processing. Comput. Eng. Syst. Appl. 1996, 2, 963–968. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, C.; Jiang, Y.L.; Teng, Z. Dynamical analysis of a fractional-order predator-prey model incorporating a prey refuge. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 54, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Modu, G.U.; Yusuf, A.; Kumam, P.; Yusuf, I. A mathematical model of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) containing asymptomatic and symptomatic classes. Results Phys. 2021, 21, 103776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | m | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.02537 | 0.0106 | 0.0805 | 0.12 | 0.0668 | 2.0138 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 0.018 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.8 |
| Parameters | ||||||
| 1 | 0.4478 | 0.0101 | 3.2084 | 1.6728 | 5.7341 | 1.6728 |
| 2 | 0.2 | 0.08 | 0.2 | 0.018 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, P.; Wang, Z. Dynamic Analysis of a Delayed Fractional Infectious Disease Model with Saturated Incidence. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6030138
Ding P, Wang Z. Dynamic Analysis of a Delayed Fractional Infectious Disease Model with Saturated Incidence. Fractal and Fractional. 2022; 6(3):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6030138
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Peng, and Zhen Wang. 2022. "Dynamic Analysis of a Delayed Fractional Infectious Disease Model with Saturated Incidence" Fractal and Fractional 6, no. 3: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6030138
APA StyleDing, P., & Wang, Z. (2022). Dynamic Analysis of a Delayed Fractional Infectious Disease Model with Saturated Incidence. Fractal and Fractional, 6(3), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6030138







