A Heterogeneous Duopoly Game under an Isoelastic Demand and Diseconomies of Scale
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model
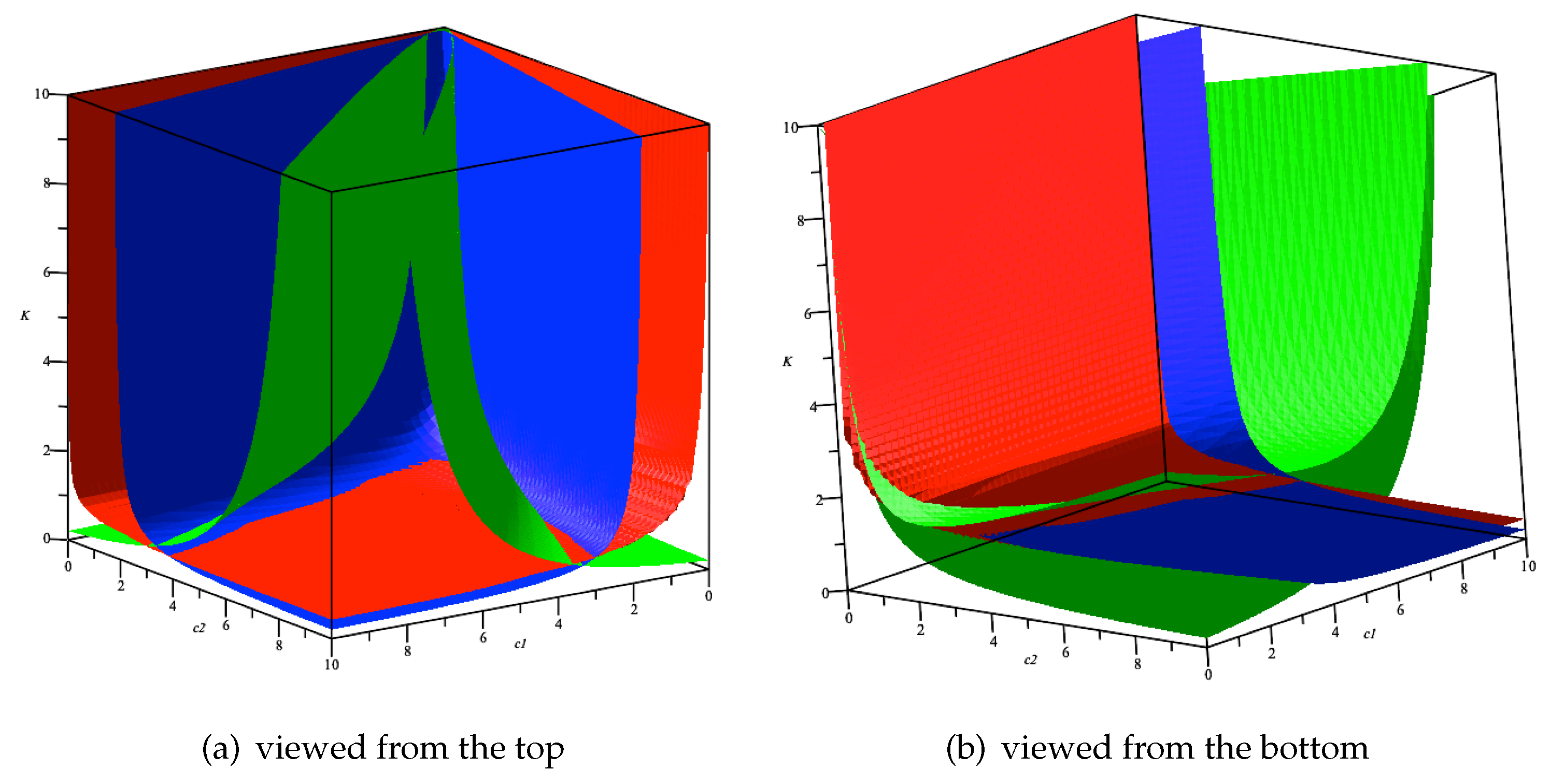
3. Local Stability
- ,
- ,
- .
- Both locally stable;
- Both locally unstable;
- One locally stable and the other locally unstable.
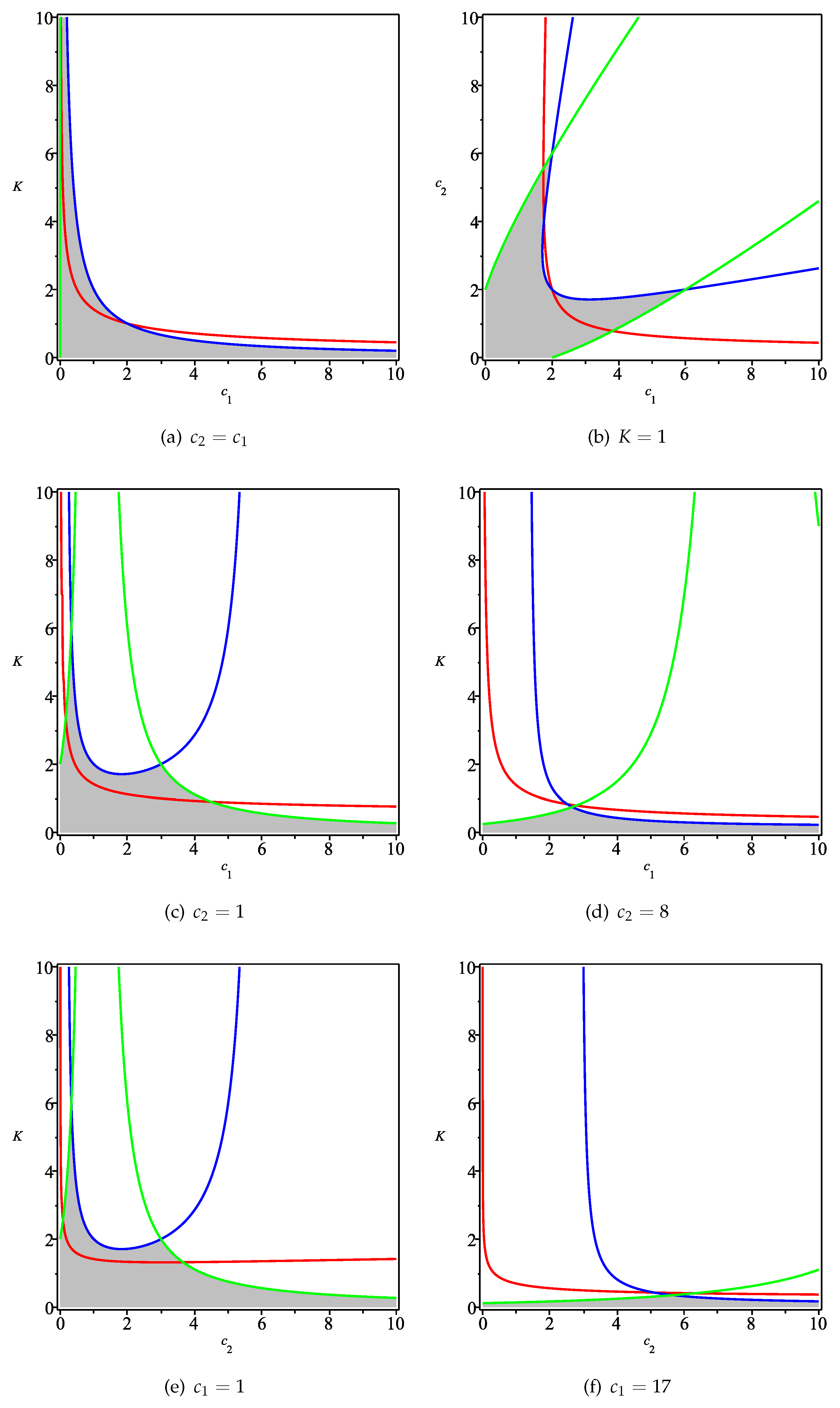
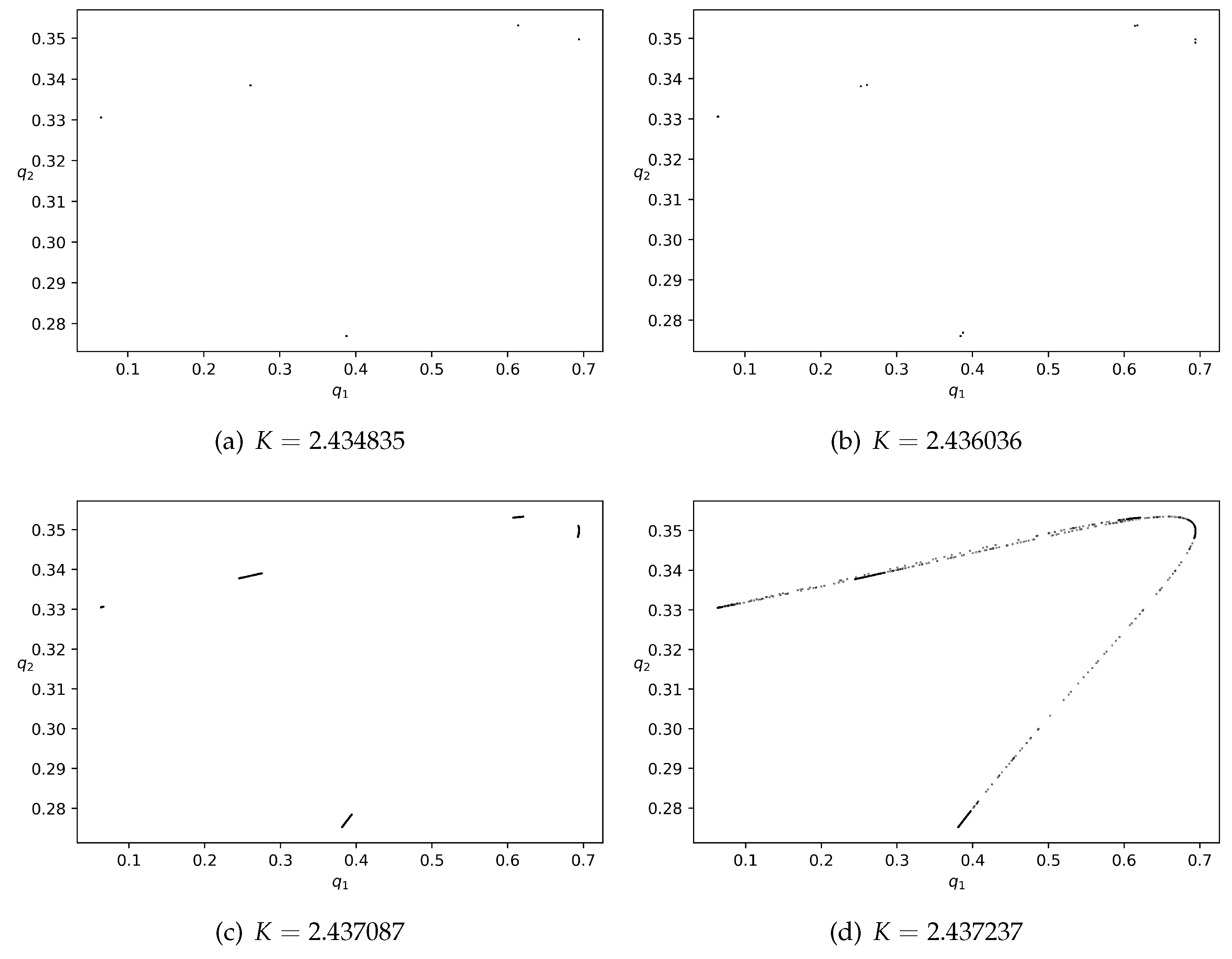
4. Numerical Simulations
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cournot, A.A. Recherches sur les Principes Mathématiques de la Théorie des Richesses; L. Hachette: Paris, France, 1838. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, F.M. The stability of the Cournot oligopoly solution: The effects of speeds of adjustment and increasing marginal costs. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1961, 28, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubiel-Teleszynski, T. Nonlinear dynamics in a heterogeneous duopoly game with adjusting players and diseconomies of scale. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2011, 16, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puu, T. Chaos in duopoly pricing. Chaos Solitons Fractals 1991, 1, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischi, G.I.; Naimzada, A.; Sbragia, L. Oligopoly games with local monopolistic approximation. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2007, 62, 371–388. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, E.; Agiza, H.; Hassan, S. On modifications of Puu’s dynamical duopoly. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2000, 11, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.; Naimzada, A.; Tramontana, F. Nonlinear dynamics and global analysis of a heterogeneous Cournot duopoly with a local monopolistic approach versus a gradient rule with endogenous reactivity. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015, 23, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Askar, S.S.; Alnowibet, K. Nonlinear oligopolistic game with isoelastic demand function: Rationality and local monopolistic approximation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2016, 84, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsadany, A.A. Dynamics of a Cournot duopoly game with bounded rationality based on relative profit maximization. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 294, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopel, M. Simple and complex adjustment dynamics in Cournot duopoly models. Chaos Solitons Fractals 1996, 7, 2031–2048. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Liang, H.; Shi, L.; He, Q. Complex dynamics of Kopel model with nonsymmetric response between oligopolists. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 156, 111860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimzada, A.; Tramontana, F. Controlling chaos through local knowledge. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 42, 2439–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tramontana, F. Heterogeneous duopoly with isoelastic demand function. Econ. Model. 2010, 27, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischi, G.I.; Kopel, M.; Szidarovszky, F. Expectation-stock dynamics in multi-agent fisheries. Ann. Oper. Res. 2005, 137, 299–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, D. Computing equilibria of semi-algebraic economies using triangular decomposition and real solution classification. J. Math. Econ. 2014, 54, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McManus, M.; Quandt, R.E. Comments on the stability of the Cournot oligipoly model. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1961, 28, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agiza, H.N.; Elsadany, A.A. Chaotic dynamics in nonlinear duopoly game with heterogeneous players. Appl. Math. Comput. 2004, 149, 843–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.T. Basic principles of mechanical theorem proving in elementary geometries. J. Autom. Reason. 1986, 2, 221–252. [Google Scholar]
- Kalkbrener, M. A generalized Euclidean algorithm for computing triangular representations of algebraic varieties. J. Symb. Comput. 1993, 15, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aubry, P.; Moreno Maza, M. Triangular sets for solving polynomial systems: A comparative implementation of four methods. J. Symb. Comput. 1999, 28, 125–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. Computing triangular systems and regular systems. J. Symb. Comput. 2000, 30, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mou, C.; Wang, D. Decomposing polynomial sets into simple sets over finite fields: The zero-dimensional case. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 60, 2983–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jury, E.; Stark, L.; Krishnan, V. Inners and stability of dynamic systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1976, 10, 724–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.E.; Hong, H. Partial cylindrical algebraic decomposition for quantifier elimination. J. Symb. Comput. 1991, 12, 299–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Sample Point of | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| true | true | true | |
| true | false | true | |
| true | false | false | |
| true | true | true | |
| true | false | true | |
| true | false | false | |
| true | true | true | |
| true | false | true | |
| true | false | false | |
| false | false | false | |
| true | true | true | |
| true | false | true | |
| false | false | true | |
| false | false | false | |
| true | true | true | |
| false | true | true | |
| false | false | true | |
| false | false | false | |
| true | true | true | |
| false | true | true | |
| false | true | false | |
| false | false | false | |
| true | true | true | |
| false | true | true | |
| false | true | false | |
| false | false | false | |
| true | true | true | |
| false | true | true | |
| false | false | true | |
| false | false | false | |
| true | true | true | |
| true | false | true | |
| false | false | true | |
| false | false | false | |
| true | true | true | |
| true | false | true | |
| true | false | false | |
| false | false | false | |
| true | true | true | |
| true | false | true | |
| true | false | false | |
| true | true | true | |
| true | false | true | |
| true | false | false |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Su, L. A Heterogeneous Duopoly Game under an Isoelastic Demand and Diseconomies of Scale. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6080459
Li X, Su L. A Heterogeneous Duopoly Game under an Isoelastic Demand and Diseconomies of Scale. Fractal and Fractional. 2022; 6(8):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6080459
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaoliang, and Li Su. 2022. "A Heterogeneous Duopoly Game under an Isoelastic Demand and Diseconomies of Scale" Fractal and Fractional 6, no. 8: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6080459
APA StyleLi, X., & Su, L. (2022). A Heterogeneous Duopoly Game under an Isoelastic Demand and Diseconomies of Scale. Fractal and Fractional, 6(8), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6080459






