Abstract
Numerous studies have observed and analyzed the dynamics of language change from a diffusion perspective. As a complex and changeable system, the process of language change is characterized by a long memory that conforms to ultraslow diffusion. However, it is not perfectly suited for modeling with the traditional diffusion model. The Caputo nonlocal structural derivative is a further development of the classic Caputo fractional derivative. Its kernel function, characterized as an arbitrary function, proves highly effective in dealing with ultraslow diffusion. In this study, we utilized an extended logarithmic function to formulate a Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model for qualitatively analyzing the evolution process of language. The mean square displacement that grows logarithmically was derived through the Tauberian theorem and the Fourier–Laplace transform. Its effectiveness and credibility were verified by the appearance of already popular words on Japanese blogs. Compared to the random diffusion model, the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model proves to be more precise in simulating the process of language change. The microscopic mechanism of ultraslow diffusion was explored using the continuous time random walk model, which involves a logarithmic function with a long tail. Both models incorporate memory effects, which can provide useful guidance for modeling diffusion behavior in other social phenomena.
1. Introduction
Language is an intricate and continuously evolving system, profoundly influenced by social, cultural, and technological advances [1,2]. Within this complex environment, vocabulary emerges as the most dynamic and responsive constituent [3]. Empirical studies have consistently demonstrated that language change is a time-dependent phenomenon, and that its statistical characteristics can be analyzed from a diffusion-based perspective [4,5,6,7,8]. In this context, Ebeling found the relationships formed over a long period of time between letters and sentences within texts by utilizing the random walk model [6]. Similarly, an analysis of the correlations at long range in an embedded sentence series based on ‘The Story of the Stone’ revealed that these series are generated by fractional Brownian motion, reconciling them with anomalous diffusion [7]. Moreover, the statistical properties of word use in samples of English, as well as text from French, Chinese, and Japanese have been found to exhibit a pronounced ultraslow diffusion phenomenon [8]. The investigation of language dynamics necessitates a holistic approach that integrates empirical experimentation, theoretical modeling, and rigorous data comparison [9]. While the existence of ultraslow diffusion has been firmly established, investigations into deterministic mathematical models remain relatively limited in language change.
The intricate and multifaceted properties of language change require a comprehensive knowledge of its underlying dynamical mechanism. Anomalous diffusion occurs in many physical phenomena, and is typically identified when the mean square displacement (MSD) follows a power law relationship with respect to time (sub-diffusion when the time exponent is less than one, and super-diffusion when it is greater than one) [10,11,12]. Ultraslow diffusion is a diffusion process that is slower than sub-diffusion [13,14,15,16]; it has been observed in a variety of systems including disordered media [13], soft materials [14], and phospholipid monolayers [15]. In statistical mechanics, ultraslow diffusion reveals the dynamical properties of particles on long time scales. The MSD of ultraslow diffusion is given as follows [16]:
Here, , and its value depends on the evolution rate for the ultraslow diffusion of solute. Equation (1) displays a statistical process that is slower than the power law, and in some cases, even slower than the logarithmic function. When , this process is considered as the classic Sinai diffusion model, which can depict the heat transport in disordered topological quantum wire [16,17]. When , Equation (1) decays to the Harris law for characterizing the time evolution of aging processes in materials science [18]. When , this process is the characteristic way to identify ultraslow diffusion in the migration of polymers in cells [13].
Mathematical and physical modeling approaches are commonly applied to investigate the mechanisms governing diffusion behavior. Numerous theoretical investigations rooted in fractional theory and its extensions have been introduced to explain ultraslow diffusion [19,20]. Examples include the distributed order fractional Fokker–Planck equation [19] and the nonlocal Fokker–Planck equations [20]. Models like the comb models, the structural derivative diffusion models, and the distributed order fractional derivative models have been utilized to capture the logarithmically increasing behavior of MSD over time [13,21,22,23]. Microscopic models, such as the random walk model [11] and fractional Brownian motion [12], can be used to explain the evolution law and statistical characteristics of particles. The random walk is a statistical framework for simulating the characteristics of particle migration with time and its spatial distribution [24]. Its extension, the continuous time random walk (CTRW) model, is employed for studying ultraslow diffusion processes [25]. In ref. [26], the ultraslow diffusion model was developed, incorporating a random waiting time with a probability decay following a logarithmic rate. Havlin et al. [27] presented a CTRW model using the logarithmic function as the asymptotic waiting time distribution, which recently was extended by Liang et al. [28], substituting the inverse Mittag–Leffler (ML) function for the logarithmic function. Particularly, Chechkin studied the relation between distributed order fractional Fokker–Planck equations and the CTRW model [19]. These contributions have enriched our understanding of ultraslow diffusion phenomena, and the associated mathematical frameworks.
This study aims to analyze the ultraslow diffusion mechanism of changes in the Japanese language on Japanese social media using the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative. The Caputo nonlocal structural derivative can be treated as a further development of the classic Caputo fractional derivative. Its kernel function is an arbitrary function, rather than a power law function, which greatly expands its application space in practical engineering [29,30,31]. In physical systems, the convolution operator encodes with historical memory, which has been used to study the creep phenomenon in concrete [30] and superfast diffusion in solar cells [31]. Physically, the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative acts as a memory operator, which is consistent with the time history dependence observed in language change.
In this paper, we propose the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative ultraslow diffusion model with a logarithmic function to analyze the significant influence of time on language change. Similar to the Caputo fractional derivative diffusion model, the essential methodology employed in solving the fundamental solution and the MSD of the proposed model lies in Fourier–Laplace transforms [11]. Specifically, the Laplace transform of the logarithmic function was acquired through the Tauberian theorem [21]. To explain the feasibility of the proposed model in fitting the ultraslow diffusion of already popular words on Japanese blogs, we merge theory with experiments in Section 3. Thorough sensitivity analysis by varying parameters, the applicability and relevance for the proposed model in capturing the intricacies of linguistic dynamics is enhanced. In addition, we also attempt to reveal the internal laws of language change using the CTRW model with the long-tailed distribution of waiting time, an approach which helps to gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental mechanisms underlying ultraslow diffusion in language.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 presents the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative, and establishes the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative ultraslow diffusion model. In Section 3, the proposed model is utilized to simulate the experimental data, and employs CTRW theory to analyze the microscopic mechanism. A brief discussion is shown in Section 4. Section 5 provides the conclusions of this study.
2. Theory
2.1. The Caputo Nonlocal Structural Derivative
The integer derivative depicts the local characteristics of the dynamic process at a certain space-time point, while the fractional derivative can capture the dynamic processes with memory and global characteristics. The fractional derivatives are primarily characterized by two widely employed definitions: the Riemann–Liouville fractional derivative and the Caputo fractional derivative [11].
Due to the singularity of the definition, the Riemann–Liouville fractional derivative is difficult to apply to engineering practice and physical mechanics modeling, and is mainly employed for theoretical derivation. In scientific and engineering applications, the Caputo fractional derivative is more efficient and applicable. The classical Caputo fractional derivative of the continuous function over time is as follows [11]:
Here, . For more complex systems with extremely irregular structures, the power law metric has some limitations in describing the mechanism effectively. Based on Equation (2), the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative is the following:
Here, represents the time Caputo nonlocal structure derivative operator; is a continuous function in ; and is the time structural function. The selection of the structural functions is the most difficult and important step in modeling. The existing method is derived from a structural function based on the experience and the actual problem being solved. Certainly, the singularity of the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative corresponding to the kernel function is also the focus that should be considered. If , Equation (3) decays to the Caputo fractional derivative in Equation (2) with [32,33]. Similar to the fractional derivative, the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative performs the derivative operation first, and then the integral operation, so that . This definition establishes the foundation for describing and analyzing specific features of scientific and engineering applications. For convenience, we introduce the Laplace transform and Fourier transform [21]:
Accordingly, and represent the inverse Laplace transform and Fourier transform, respectively. The Laplace transform of Equation (5) is as follows:
where means the Laplace transform of , , and is the Laplace transform of . In fact, the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative follows the Euclidean distance measure, and the convolution operator involves long-range temporal correlations that can be used to analyze the characteristics of dynamic processes using different kernel functions.
2.2. The Caputo Nonlocal Structural Derivative Ultraslow Diffusion Model
Based on the definition of the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative in Equation (3), the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion equation is directly indicated as follows:
If approaches the power law function, Equation (7) will turn into a fractional diffusion equation [32]. The structural function with different forms is a memory kernel that yields substantially different results. According to the MSD of ultraslow diffusion, the time structural function for language change is assumed to be the reciprocal of a logarithmic function at long times:
Then, substituting Equation (8) into Equation (7), the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative model of ultraslow diffusion in language change is as follows:
Here, is the generalized diffusion coefficient; its dimensions are essentially related to the structural function ; is the last date of observation; and is the counts of the observed words within the data set. means the probability density function (PDF) of the observed words appearing times at date , and (the Dirac delta function). By taking the Laplace transform of Equation (9) we obtain the following:
When , is a slowly varying function, and its Laplace transform can be calculated via the Tauberian theorem [21] as follows:
See Appendix A for the Tauberian theorem. Inserting Equation (11) into Equation (10) leads to the following expression:
Using the Fourier transform, Equation (12) becomes the following:
And after simplifying the model, Equation (13) can be expressed as follows:
Applying the inverse Fourier transform, Equation (14) yields the following:
Then, can be solved via the inverse Laplace transform. Moreover, the MSD can be determined as was shown in ref. [27] to be the following:
Alternatively, ultraslow diffusion could be characterized by the single exponent with the structural function , . Similarly, the Laplace transform of satisfies the following:
thus, the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative ultraslow diffusion model governed through this function as it occurs in language change is the following:
And Equation (12) is replaced by the following:
By inference, the analytical results occur as the following:
As a generalization of the logarithmic function, the inverse ML function has been employed in the local structural derivative ultraslow diffusion model. Subsequently, the corresponding MSD is derived as follows [28]:
In order to more intuitively display the differences between different mean square displacements of ultraslow diffusion, Figure 1 illustrates the MSDs in Equations (16), (22), and (23) with . For brevity, all of the results are stated with dimensionless units. It can be seen in Figure 1 that the MSDs exhibit a significantly slower behavior compared to classical ultraslow diffusion as time increases. All curves indicate that the growth rate in MSD gradually shortens with decreasing . Note that the inverse ML function has no complete analytical expression, so its calculation is more complicated. In this case, the simplest and most effective technique should be adopted for the simulation of anomalous dynamics.
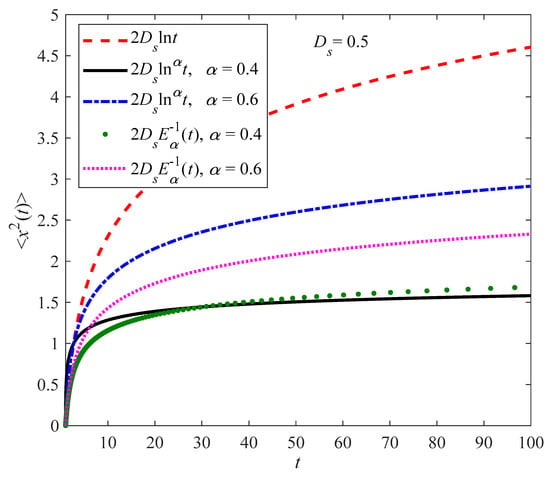
Figure 1.
MSDs of the structural derivative ultraslow diffusion model with different structural functions.
3. Applications and the CTRW Model of Language Change
According to the basic assumption of language change, we theoretically derived the differential equation for ultraslow diffusion through the relationship between macroscopic physical quantities. In this section, we merge theory with experiments to verify the accuracy of the proposed macroscopic constitutive mechanics model of ultraslow diffusion by simulating the appearance of already popular words in the language database from Japanese social media [34]. Moreover, the CTRW model is employed to analyze the statistical characteristics of language change from the perspective of microscopic statistical mechanics.
3.1. Applications and Results
In the pursuit of revealing the microscopic mechanism of mechanical behavior, statistical mechanics models are frequently used in the study of anomalous dynamics. Several investigations have been carried out to delve into the complex dynamic behavior of language change [3,4]. In order to elucidate the temporal evolution of frequently employed adjectives in social media data, Watanabe investigated about three billion Japanese blog articles over six years, and explained the process of a word appearance by the random diffusion model [34]. The keywords database is composed of 1771 basic adjectives samples, meticulously extracted from articles of the aforementioned Japanese blog, and is divided into three categories to avoid being affected by special events. The results confirmed that the MSD of a word appearance grows logarithmically. Utilizing the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model, we estimated the ultraslow diffusion of word appearance, and compared the results with the random diffusion model to verify the validity and credibility.
Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 illustrate the experimental data for these three categories of already popular words on Japanese blogs and the MSD predicted by the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model in Equation (22) () and by the random diffusion model (), respectively. In those figures, the circles represent the MSD of words in ref. [34]; the red lines denote the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model in Equation (22); and the blue lines indicate the random diffusion model. Figure 2 illustrates the fitting results of the MSD for the first category words that appear too frequently at time on average. The words are sampled from the Poisson distribution whose Poisson parameter is higher than 20. Although the MSD grows logarithmically as increases, the fitting curve of our model with simulates the experimental data precisely whether in the initial or final stage. Figure 3 shows the fitting results of the MSD for the words without significant seasonality on Japanese blogs. Note also that there is perfect agreement between the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model and the data; even the parameters and are similar to those of the first category in Figure 2, while the random diffusion model mismatches the data under the same diffusion coefficient. In contrast to the former two categories in Figure 2 and Figure 3, Figure 4 shows the fitting results of the MSD for words excluding significant seasonality and outliers caused by special news events on Japanese blogs. From this figure, the diffusion coefficient of the random diffusion model is almost identical to the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model, and the power index is close to 1. Meanwhile, the dynamic process approaches classical ultraslow diffusion as . Essentially, constantly developing languages mostly meet the basic dynamic law, which involves classical ultraslow diffusion. Without considering the effect of the seasonal and special news events words, the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model and the random diffusion model can achieve good accuracy. Although Equation (22) has an additional parameter, it can better illustrate the complex changes in language systems. Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 show the fitting parameters and error results for different models. The fitting results indicate that the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model outperforms the random diffusion model, as shown by the lower maximum absolute errors and mean square errors.
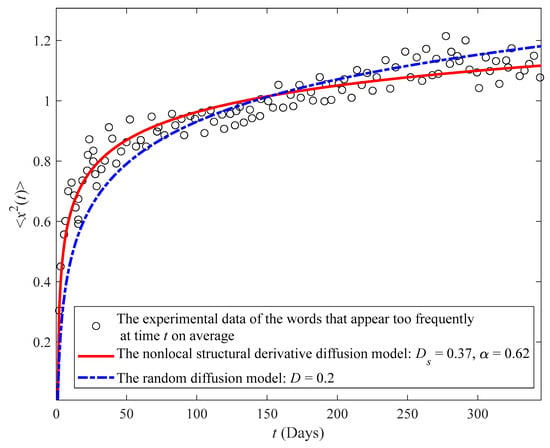
Figure 2.
MSDs of words that appear too frequently at time , on average, fitted by the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model () and by the random diffusion model (). The experimental data are from ref. [34].
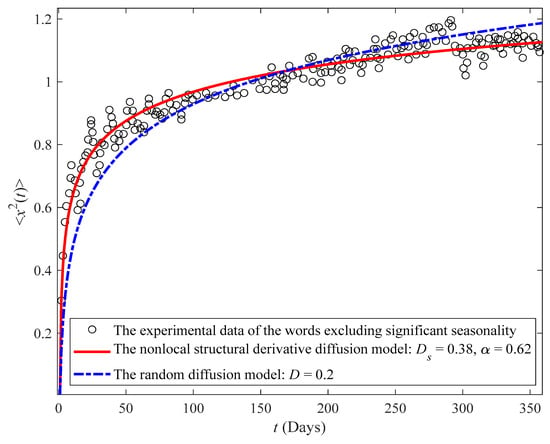
Figure 3.
MSDs of words excluding significant seasonality on Japanese blogs fitted by the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model () and by the random diffusion model (). The experimental data are from ref. [34].
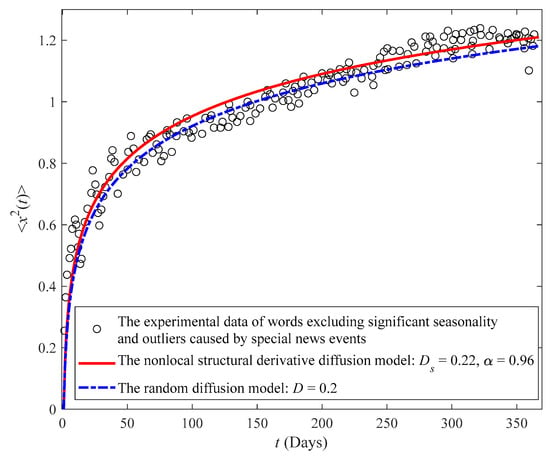
Figure 4.
MSDs of words excluding significant seasonality and outliers caused by special news events on Japanese blogs fitted by the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model () and by the random diffusion model (). The experimental data are from ref. [34].

Table 1.
The fitting results of different models for words that appear too frequently at time on average on Japanese blogs (the diffusion coefficient is dimensionless).

Table 2.
The fitting results of different models for words excluding significant seasonality on Japanese blogs (the diffusion coefficient is dimensionless).

Table 3.
The fitting results of different models for words excluding significant seasonality and outliers caused by special news events on Japanese blogs (the diffusion coefficient is dimensionless).
The above three sample experimental data clarify the elementary process of a word appearance over a period of one year. Ultraslow diffusion involves long-term behavior. To explore the statistical attributes underlying linguistic evolution on long time scales, ref. [8] conducted a comprehensive examination of three nationwide media language databases in Japanese, including newspaper articles for 10 years, blog articles for 5 years, and page views of Wikipedia for 2 years. By tracking the number of occurrences for already popular words, the development trajectory of already popular words in three language databases was discovered to obey the law of ultraslow diffusion. The words are sampled from the Poisson distribution whose Poisson parameter is higher than 30. To correspond with the previous data, we focused on researching the dynamical statistical properties for word appearance on blog articles over 5 years using the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative ultraslow diffusion model. Figure 5 shows the simulation results of the MSD capturing variations in word counts associated with the growth of the specified keyword over a period of days. The corresponding parameters and the fitting errors of different models are listed in Table 4. The results confirm that the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative model can provide a qualitative description of language change approximately over a long time limit.
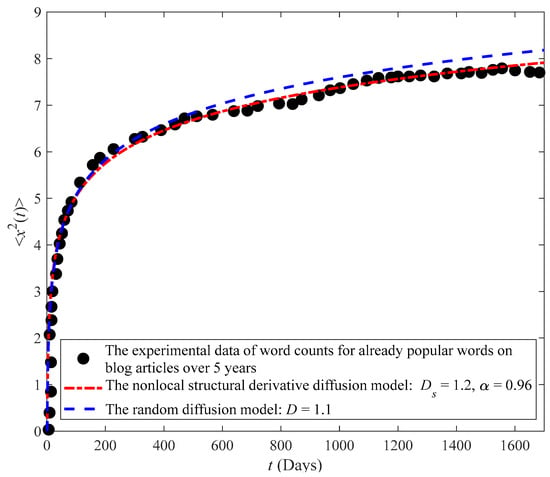
Figure 5.
Fitting results of the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative model in Equation (22) and the random diffusion model with the MSDs for already popular words in blog articles. The experimental data are from ref. [8].

Table 4.
The fitting results of different models for words appearing in blog articles over 5 years.
3.2. The CTRW Model of Language Change
Prior research has shown that CTRW theory is an intuitive and effective statistical mechanics approach, and the CTRW model with the long-tailed distribution of waiting time has been proposed to explain ultraslow diffusion [25]. Language change is an ultraslow dynamic process with irregularity and randomness, and words can be seen as constantly moving particles. Therefore, the process of language change is suitable for interpretation using CTRW theory. Based on the characteristics of MSD in ultraslow diffusion, the waiting time PDF of the observed words appearing can be assumed to be the following logarithmic function [27]:
Then, its Laplace transform can be can be derived as follows:
See Appendix B for details of the derivation process. Here, is a characteristic time that can be set to 1. If an appearing length PDF is a Gaussian distribution, its Fourier transform is the following:
Combining Equations (25) and (26), the Montroll–Weiss function yields the following:
and by performing the inverse Fourier–Laplace transform on the above equation, is obtained as follows:
From Equation (28), the MSD is calculated as follows:
which is related to the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative model in Equation (22). Figure 6 displays plots of the PDF versus waiting time with , the exponential and the power law distributions. From these curves, one can see that the long-time tail of the logarithmic function is more sustained than that of the exponential and power law distributions. When the parameter increases, the logarithmic function moves closer to the power law distribution.
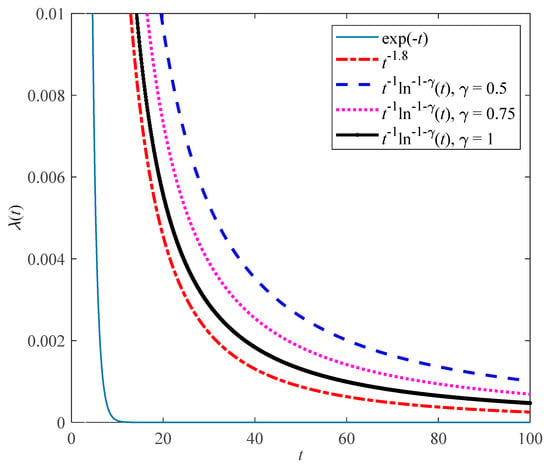
Figure 6.
The PDF of waiting time with , and the exponential and power law distributions.
Figure 7 shows the motion path particle trajectory of the CTRW model with . Note that with a decrease in , the waiting time between two adjacent jumps gradually increases, while the tail gradually strengthens, and the diffusion rate of particles becomes slower. As the value of increases, the time interval between consecutive jumps decreases, leading to a diminished prominence of the tail. Building upon this theory, it is possible to interpret the long-range dependence as a scale transformation, which is represented by time in the context of language change. Statistically, the relationship between ultraslow diffusion and time scale is strong. In contrast to Brownian motion, the ultraslow behavior of language change exhibits long-range dependence, which can be explained through the waiting time probability density function. Thus, the CTRW model is instrumental in providing insights into the dynamics of language change.
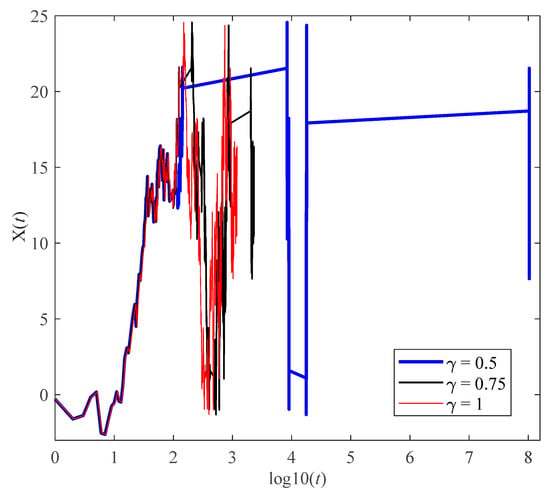
Figure 7.
The motion path particle trajectory of the CTRW model with .
4. Discussion
This study investigates the elementary dynamics of language change using the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative ultraslow diffusion model, and employs the fading memory concept of CTRW theory to analyze its microscopic mechanism. The analytical solutions including the corresponding PDF and the MSD are derived. Although the language diffusion process is classified as ultraslow diffusion, the traditional logarithmic model is inadequate for accurately reflecting this phenomenon. In practice, simulating dynamic processes that occur in complex systems is challenging due to various factors. The Caputo nonlocal structural derivative model of ultraslow diffusion provides a valuable tool for describing long-range correlations, while the waiting time distribution in CTRW theory can reveal the underlying dynamics. These features may offer valuable guidance for modeling diffusion behavior in other social phenomena. It is important to emphasize that language diffusion in linguistics is a complex dynamical phenomenon, and the current study addresses only a part of the whole system. So while the empirical and theoretical findings on language change have already been revealed, this study proposes a novel theoretical insight for a more precise and comprehensive description of language evolution.
When exploring the characteristics of ultraslow diffusion, the MSD has always been a convenient and effective statistical measure. This study examines the trend and change behaviors of language using both mechanical constitutive and statistical mechanical models. The Caputo nonlocal structural derivative model provides a macroscopic view that is consistent with CTRW theory, and both methods yield the same result. The classic fractional derivative diffusion model originates from the CTRW model [11]. However, the correlation between the CTRW model and the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model need a comprehensive examination. Meanwhile, the CTRW model considers the microscopic motions of words, and the utilization of the waiting time probability density function provides a means to elucidate the dynamic characteristics observed in word time series. Nevertheless, the significance of the structural function of the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative model is somewhat ambiguous in our framework. It may reflect a scale change of time or a time-dependent parameter that reflects the language structure. Furthermore, the quantitative relation between the parameter of the structural function and the parameter of the waiting time PDF cannot be fully determined. Therefore, the subsequent focus of this research should be on relating the structural function to the language medium and developing efficient numerical algorithms to simulate these processes. Additionally, we need to investigate other characteristics of word selection and use in language to better understand the impact of the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative and CTRW theory on dynamic processes.
By combining theory with experiment, this study delved into the dynamic process of language change. The validity of the proposed models was tested using various applications. It is important to note that the aim of our modeling was not only to describe the measured results in practical experiments quantitatively, but to demonstrate the underlying reasons for the existence of such phenomena through qualitative analysis. Thus, before using the proposed models, we needed to first investigate the basic characteristics of language change. In this study, several sets of experimental data for language were analyzed to verify the ultraslow diffusion models. However, a single property cannot fully match the physical phenomena and mathematical models. To gain a more comprehensive understanding of the mechanism of ultraslow diffusion, more actual data are needed for examination. Moreover, the applicable range of the models must also be determined.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we presented a qualitative analysis for the ultraslow diffusion of language change through the macroscopic mechanical constitutive model and microscopic statistical models. Our findings led to the following conclusions:
- By employing a logarithmic function family, the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model provides a new model for the ultraslow diffusion of language change. Its MSD is inversely proportional to the structural function.
- The MSD of the continuous time random walk model is equivalent to the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model, which provides a new way to find the statistical moments of language change.
- Compared to the random diffusion model, the Caputo nonlocal structural derivative diffusion model is more effective in characterizing ultraslow diffusion of language change, as demonstrated by improved fitting curves and errors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.X. and Y.L.; methodology, W.X. and Y.L.; software, H.L. and S.Z.; validation, W.X., Y.L. and H.L.; formal analysis, W.X. and H.L.; investigation, W.X., H.L. and S.Z.; resources, W.X.; data curation, W.X., H.L. and S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, W.X. and Y.L.; writing—review and editing, W.X., Y.L., H.L. and S.Z.; visualization, W.X., Y.L. and H.L.; supervision, W.X. and Y.L.; project administration, W.X. and Y.L.; funding acquisition, W.X. and Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research described in this paper was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 12202225), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2021QA042).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Tauberian Theorem
In the Tauberian theorem [21], for the function , when its Laplace transform has the following asymptotic form:
Then, satisfies the following:
and vice versa. Here, should be a slowly varying function at infinity, which satisfies ; is a positive constant.
For example, if , by the l’Hospital’s rule, so the is a slowly varying function at infinity.
Appendix B. Laplace Transform of the Long-Tailed Pausing Time Densities
If is a slowly varying function, and is defined as a long-tailed pausing time density:
the Laplace transform of the Equation (A3) is the following:
Now, rewrite and analyze the properties of [27], as follows:
then, differentiate and match with respect to :
Note that Equation (A6) is just the Laplace transform of . Then, using the following Abelian theorem:
thus, is derived from the integral.
References
- Epps, P.; Law, D.; Pat-El, N. Historical Linguistics and Endangered Languages: Exploring Diversity in Language Change; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, J. Dynamic preferences and self-actuation of changes in language dynamic. Lang. Dyn. Chang. 2019, 9, 61–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burridge, J.; Blaxter, T. Inferring the drivers of language change using spatial models. J. Phys. Complex. 2021, 2, 035018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevalainen, T.; Raumolin-Brunberg, H.; Mannila, H. The diffusion of language change in real time: Progressive and conservative individuals and the time depth of change. Lang. Var. Chang. 2011, 23, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenstein, J.; O’Connor, B.; Smith, N.A.; Xing, E.P. Diffusion of lexical change in social media. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebeling, W.; Neiman, A. Long-range correlations between letters and sentences in texts. Phys. A 2012, 215, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Gu, C.; Yang, H.; Gao, Z. Long-range correlations in sentence series from A Story of the Stone. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H. Empirical observations of ultraslow diffusion driven by the fractional dynamics in languages. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 012308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, E.; Michel, J.B.; Jackson, J.; Tang, T.; Nowak, M.A. Quantifying the evolutionary dynamics of language. Nature 2007, 449, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Benson, D.A.; Meerschaert, M.; LaBolle, E.; Scheffler, H. Random walk approximation of fractional-order multiscaling anomalous diffusion. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 026706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, R.; Klafter, J. The random walk’s guide to anomalous diffusion: A fractional dynamics approach. Phys. Rep. 2000, 339, 1–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, R.; Jeon, J.H.; Cherstvy, A.G.; Barkai, E. Anomalous diffusion models and their properties: Non-stationarity, non-ergodicity, and ageing at the centenary of single particle tracking. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 24128–24164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Z.; Magin, R. A survey of models of ultraslow diffusion in heterogeneous materials. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2019, 71, 040802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, L.P.; Lomholt, M.A.; Lizana, L.; Fogelmark, K.; Metzler, R.; Ambjörnsson, T. Severe slowing-down and universality of the dynamics in disordered interacting many-body systems: Ageing and ultraslow diffusion. New J. Phys. 2014, 16, 113050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Schönhoff, M.; Möhwald, H. Lipids coupled to polyelectrolyte multilayers: Ultraslow diffusion and the dynamics of electrostatic interactions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 9135–9142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, H.E.; Havlin, S. Generalisation of the Sinai anomalous diffusion law. J. Phys. A-Math. Theor. 1999, 20, L615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinai, Y.G. The limit behavior of a one-dimensional random walk in a random medium. Teor. Vero. Prim. 1983, 27, 256–268. [Google Scholar]
- Lomholt, M.A.; Lizana, L.; Metzler, R.; Ambjörnsson, T. Microscopic origin of the logarithmic time evolution of aging processes in complex systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 208301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chechkin, A.V.; Klafter, J.; Sokolov, I.M. Fractional Fokker-Planck equation for ultraslow kinetics. Europhys. Lett. 2003, 63, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemppainen, J.T.; Zacher, R. Long-time behaviour of non-local in time Fokker-Planck equations via the entropy method. Math. Mod. Meth. Appl. Sci. 2019, 29, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandev, T.; Iomin, A.; Kantz, H.; Metzler, R.; Chechkin, A. Comb model with slow and ultraslow diffusion. Math. Modell. Nat. Phenom. 2016, 11, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, W. A non-local structural derivative model for characterization of ultraslow diffusion in dense colloids. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2018, 56, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochubei, A.N. Distributed order calculus and equations of ultraslow diffusion. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2008, 340, 252–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenflo, R.; Mainardi, F.; Moretti, D.; Pagnini, G.; Paradisi, P. Discrete random walk models for space-time fractional diffusion. Chem. Phys. 2002, 284, 521–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisov, S.; Bystrik, Y.; Kantz, H. Limiting distributions of continuous-time random walks with superheavy-tailed waiting times. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 022117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerschaert, M.M.; Scheffler, H.P. Stochastic model for ultraslow diffusion. Stoch. Proc. Appl. 2006, 116, 1215–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlin, S.; Weiss, G.H. A new class of long-tailed pausing time densities for the CTRW. J. Stat. Phys. 1990, 58, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, W. Continuous time random walk model with asymptotical probability density of waiting times via inverse Mittag-Leffler function. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2018, 57, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liang, Y. New methodologies in fractional and fractal derivatives modeling. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2017, 102, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Chen, W.; Xu, W.; Liang, Y. Non-local structural derivative Maxwell model for characterizing ultra-slow rheology in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liang, Y. A non-local structural derivative model based on the Caputo fractional derivative for superfast diffusion in heterogeneous media. Fractals 2020, 28, 2050122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations; Academic Press: San Diego, Chile, 1999; pp. 14–50. [Google Scholar]
- Giona, M.; Cerbelli, S.; Roman, H.E. Fractional diffusion equation and relaxation in complex viscoelastic materials. Phys. A 1992, 191, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H. Ultraslow diffusion in language: Dynamics of appearance of already popular adjectives on Japanese blogs. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.07066v3. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).