Fractal Characterization of the Pore-Throat Structure in Tight Sandstone Based on Low-Temperature Nitrogen Gas Adsorption and High-Pressure Mercury Injection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials, Experiments, and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experiments
2.2.1. Casting Thin Section (CTS) Imaging
2.2.2. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM) Imaging
2.2.3. HPMI
2.2.4. LT−N2−GA
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Fractal Dimension Based on HPMI
2.3.2. Fractal Dimensions Based on N2−GA
- Calculation of pore-specific surface area using the BET equation
- 2.
- BJH method for pore size analysis
- 3.
- Calculation of fractal dimensions using the FHH fractal model
3. Results
3.1. Microscopic Characteristics of Pores and Throats
3.2. Pore-Throat Distribution Characteristics Based on HPMI
3.2.1. Basic Features
3.2.2. Pore-Throat Fractal Dimensions (D)
3.3. Pore Distribution Characteristics Based on LT−N2−GA
3.3.1. Basic Characteristics
3.3.2. Pore-Throat Fractal Dimensions (D)
4. Analysis and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Tight Sandstone Pores Based on HPMI
4.1.1. Reservoir Pore-Throat Structure Characteristics
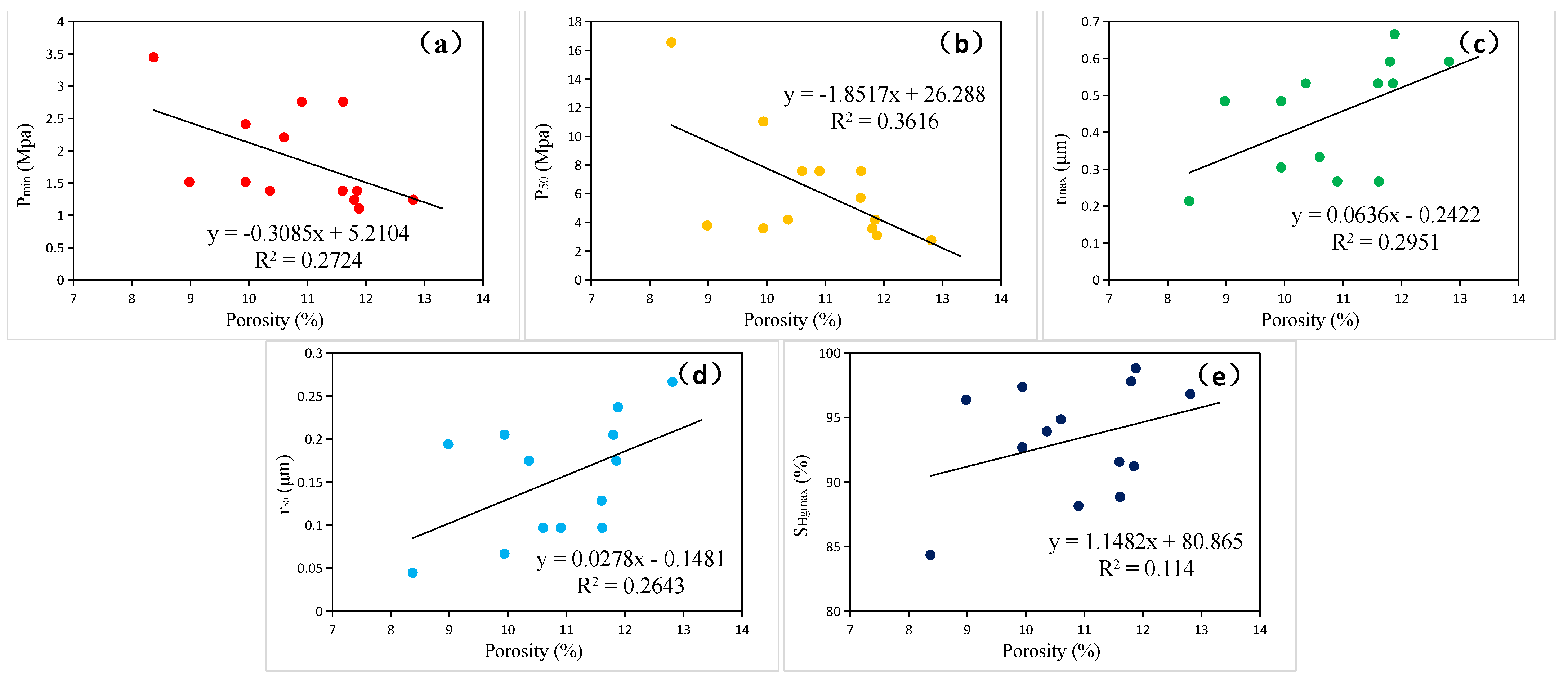
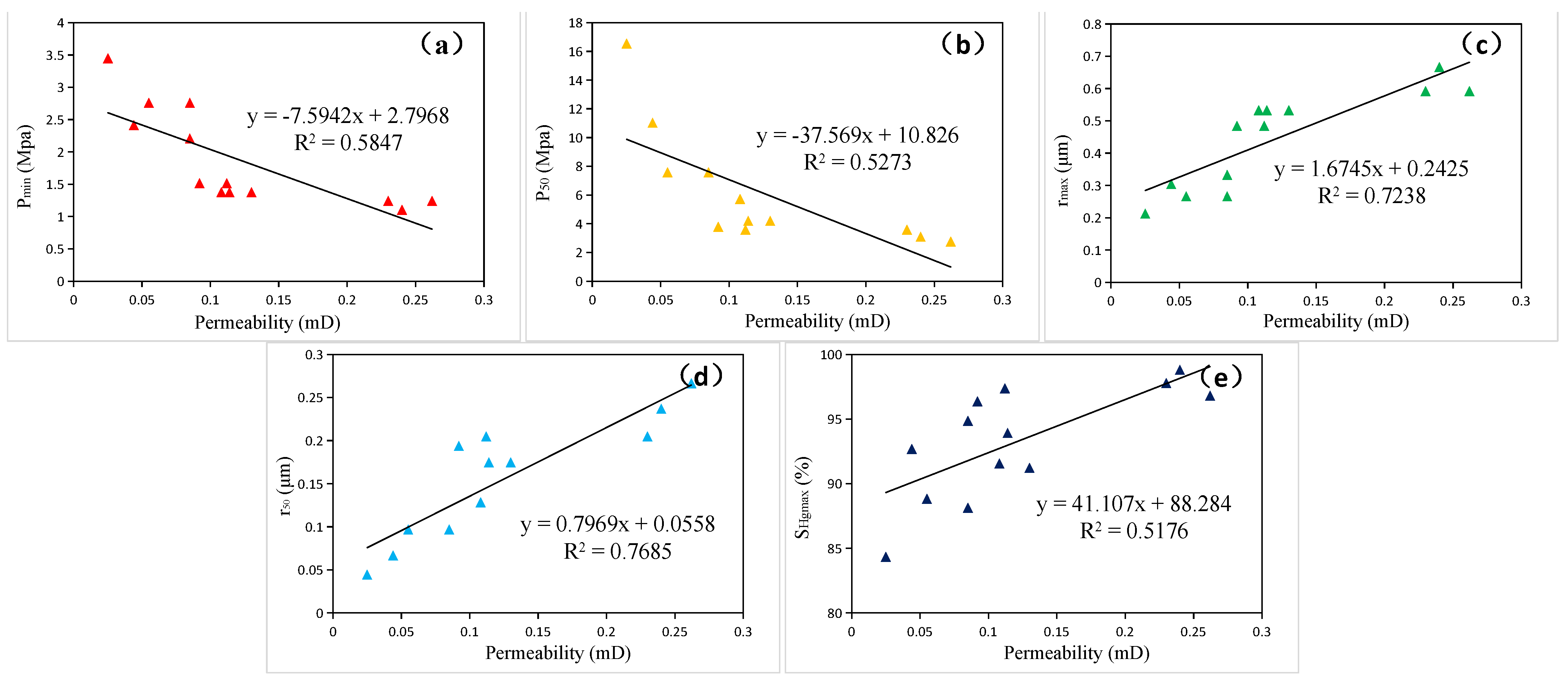
4.1.2. Relationship between D and Physical Properties
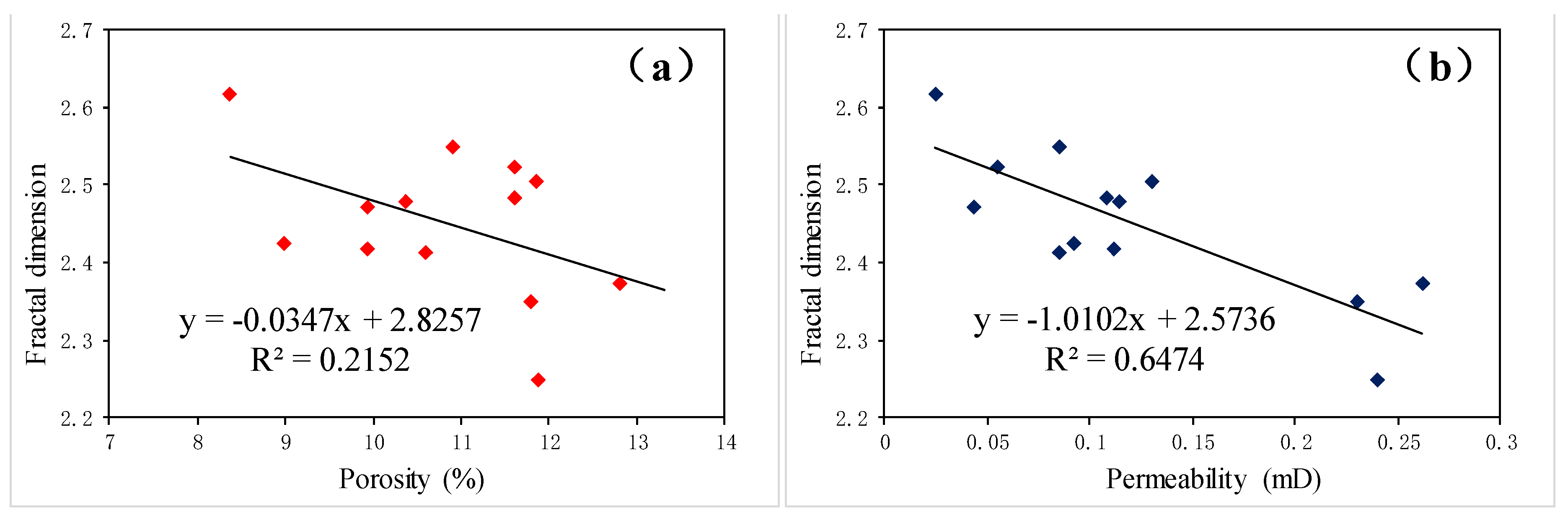
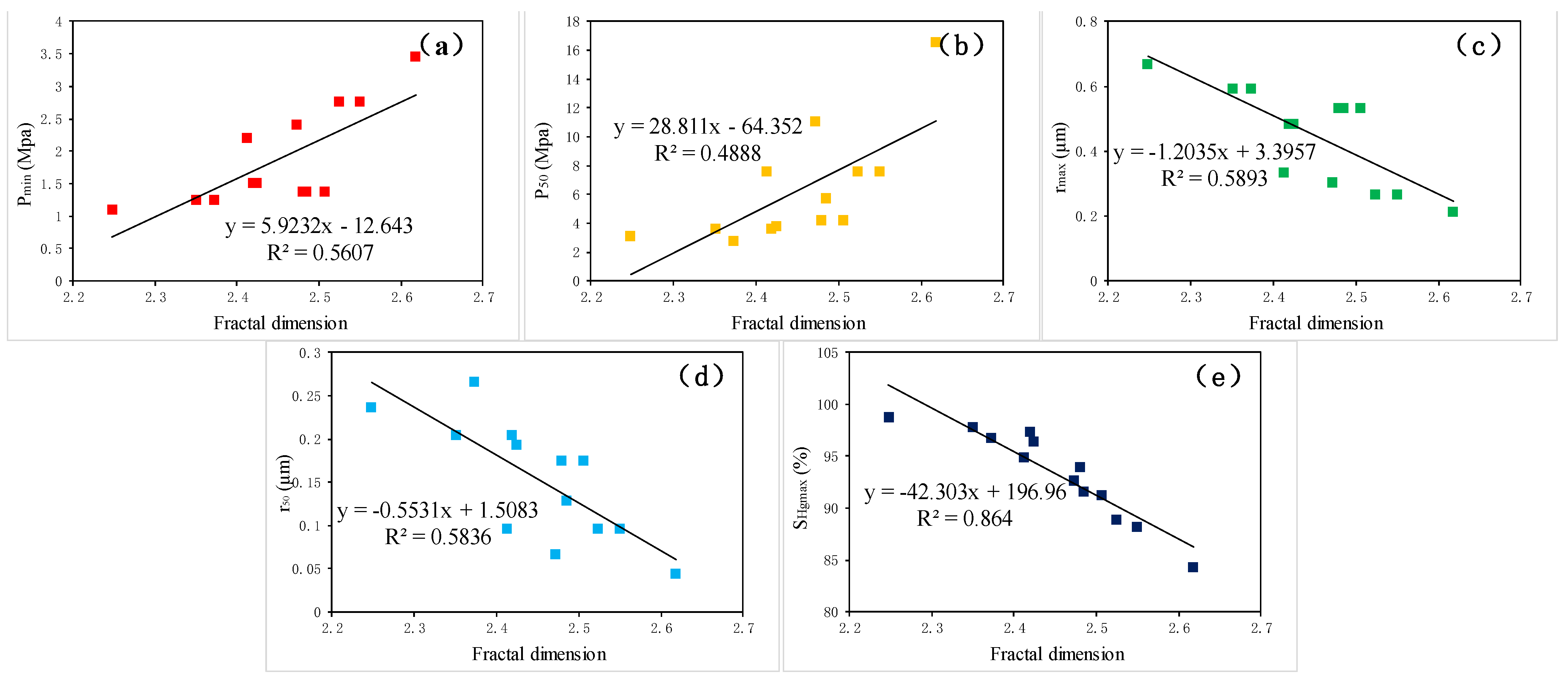
4.1.3. Relationship between D and Pore-Throat Structure Parameters
4.2. Analysis of Tight Sandstone Pores Based on LT−N2−GA
4.2.1. Relationships between Porosity and Permeability and Pore-Throat
Structure Parameters
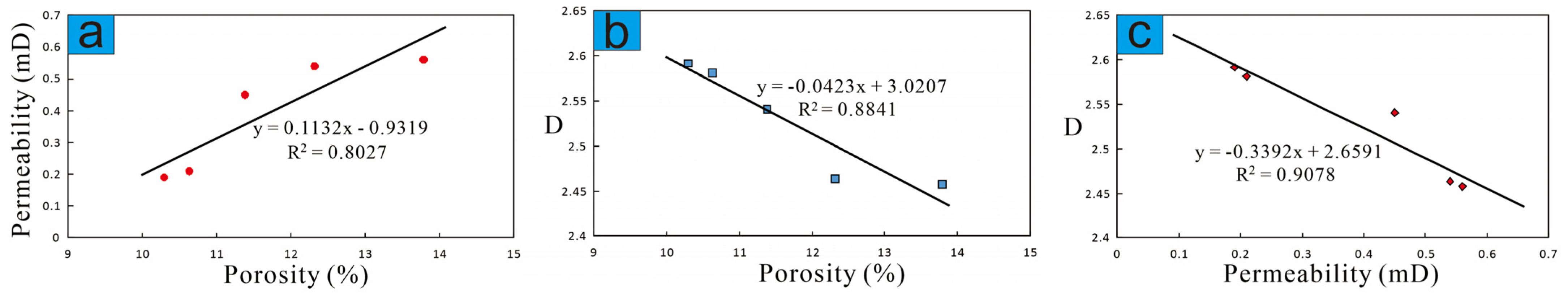
4.2.2. Relationship between D, Porosity, and Permeability
4.2.3. Relationship between D and Pore-Throat Structure Parameters
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The pore types in the tight sandstone reservoirs of Chang 6 to Chang 8 members in the Longdong area include residual intergranular pores, dissolution pores, intercrystalline pores, and microfractures. The throat types primarily include sheet-shaped throats, curved-sheet-shaped throats, and tubular throats.
- (2)
- In the studied area, there is a relatively small proportion of pores with a radius larger than 735 nm in reservoirs. For pores with a radius smaller than 735 nm, the fractal dimensions serve as an effective metric to characterize the complexity of pore-throat structures (all the R2 values are above 0.9). Integrated analysis of the HPMI and LT−N2−GA tests reveals that for smaller pores, utilizing fractal dimensions is more effective in characterizing pore-throat structures.
- (3)
- D shows a relatively poor negative correlation with porosity but a strong negative correlation with permeability. It exhibits a significant positive correlation with Pmin and P50, a favorable negative correlation with rmax and r50, and a very strong negative correlation with SHgmax.
- (4)
- The fractal dimensions (D) exhibit a strong negative correlation with porosity, permeability, and BJH average pore diameter; a strong positive correlation with BET specific surface area; and a relatively weak positive correlation with BJH total pore volume. The pore-throat structure of the tight sandstone reservoir in the target area is complex, and the heterogeneity is significant.
- (5)
- There is a strong positive correlation between porosity and permeability. As porosity, permeability, and pore connectivity develop, the reservoir’s storage performance and oil and gas recovery efficiency improve.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katz, B.; Lin, F. Lacustrine Basin Unconventional Resource Plays: Key Differences. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 56, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qin, C.; Feng, Q.; Javadpour, F.; Rui, Z. A Framework for Predicting the Production Performance of Unconventional Resources Using Deep Learning. Appl. Energy 2021, 295, 117016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatt, R. Important Geological Properties of Unconventional Resource Shales. Open Geosci. 2011, 3, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Jia, C.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Jiang, F.; Hu, T.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y. Buoyance-Driven Hydrocarbon Accumulation Depth and Its Implication for Unconventional Resource Prediction. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashayeri, C.; Jha, B. Evaluation of Transfer Learning in Data-Driven Methods in the Assessment of Unconventional Resources. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 207, 109178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.J.; Almond, S.; Ward, R.S.; Jackson, R.B.; Adams, C.; Worrall, F.; Herringshaw, L.G.; Gluyas, J.G.; Whitehead, M.A. Oil and Gas Wells and Their Integrity: Implications for Shale and Unconventional Resource Exploitation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 56, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Guo, Q.; Yu, J.; Zheng, M.; Chen, N.; Yi, Q. China’s Conventional and Unconventional Natural Gas Resources: Potential and Exploration Targets. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2018, 3, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Padmanabhan, E.; Prusty, B.K. Review of Gas Adsorption in Shales for Enhanced Methane Recovery and CO2 Storage. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 175, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafnan, S.; Awotunde, A.; Glatz, G.; Adjei, S.; Alrumaih, I.; Gowida, A. Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm in Unconventional Resources: Applicability and Limitations. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 207, 109172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Pang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; He, Z.; Qin, Z.; Fan, X. A Review on Pore Structure Characterization in Tight Sandstones. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 177, 436–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhu, R.; Liu, K.; Su, L.; Bai, B.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X.; Wang, J. Tight Gas Sandstone Reservoirs in China: Characteristics and Recognition Criteria. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 88–89, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Li, H.A. Pore Structure Characterization, Permeability Evaluation and Enhanced Gas Recovery Techniques of Tight Gas Sandstones. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 28, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.-Y.; Zhang, J.-J.; Xiang, W.; Fang, Y.-P.; Xue, Y.-J.; Cao, J.-X.; Tian, R.-F. Effect of Microscopic Pore Structures on Ultrasonic Velocity in Tight Sandstone with Different Fluid Saturation. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 2683–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W. Comparative Analysis of the Pore Structure of Fusain in Lignite and High-Volatile Bituminous Coal. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 90, 103955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongzan, W.; Guanhua, N.; Xinyue, Z.; Yicheng, Z.; Gang, W.; Zhenyang, W.; Qiming, H. Fine Characterization of Pore Structure of Acidified Anthracite Based on Liquid Intrusion Method and Micro-CT. Energy 2023, 263, 125639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Yang, Z.; Gao, T.; Li, H.; Lin, W. Characteristics of Micro- and Nano-Pores in Shale Oil Reservoirs. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2021, 11, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Jiang, S.; Thul, D.; Lu, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, B. Impacts of Clay on Pore Structure, Storage and Percolation of Tight Sandstones from the Songliao Basin, China: Implications for Genetic Classification of Tight Sandstone Reservoirs. Fuel 2018, 211, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.; Ran, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Cui, Y. Impact of Diagenesis on the Reservoir Quality of Tight Oil Sandstones: The Case of Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation Chang 7 Oil Layers in Ordos Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 145, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Cao, J.; Li, M.; Pang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, X.; Dai, Q.; Yang, L.; et al. Review of Diagenetic Facies in Tight Sandstones: Diagenesis, Diagenetic Minerals, and Prediction via Well Logs. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 185, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, G. Nanoscale Pore Morphology and Distribution of Lacustrine Shale Reservoirs: Examples from the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin. J. Energy Chem. 2015, 24, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhan, H.; Li, C.; You, Y.; Yang, C.; Jiang, H. Pore Structure Characterization of Chang-7 Tight Sandstone Using MICP Combined with N2GA Techniques and Its Geological Control Factors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Song, D.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, M.; Wang, L. Quantitative Analysis of Coal Nanopore Characteristics Using Atomic Force Microscopy. Powder Technol. 2019, 346, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, J.; Ao, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Sun, X. Pore Changes of Slickwater-Containing Shale under Supercritical CO2 Treatment. Fuel 2022, 312, 122775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Rezaee, R. Fractal Analysis of the Pore Structure for Clay Bound Water and Potential Gas Storage in Shales Based on NMR and N2 Gas Adsorption. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 177, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellerhals, R.; Shaw, J.; Arora, V.K. On Grain Size from Thin Sections. J. Geol. 1975, 83, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloreda-Jurado, P.J.; Hernández-Saz, J.; Chicardi, E.; Paúl, A.; Sepúlveda, R. Pore Morphology Evolution and Atom Distribution of Doped Fe2O3 Foams Developed by Freeze-Casting after Redox Cycling. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, P.; Chammana, P.; Oungpakornkaew, P.; Rungsritanapaisan, P.; Amornprapa, W.; Charoenphonphanich, C.; Sriprapha, K. Impact of Soot Nanoparticle Size and Quantity on Four-Ball Steel Wear Characteristics Using EDS, XRD and Electron Microscopy Image Analysis. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollamby, M.J. Practical Applications of Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 10566–10579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avdeev, M.V.; Tropin, T.V.; Aksenov, V.L.; Rosta, L.; Garamus, V.M.; Rozhkova, N.N. Pore Structures in Shungites as Revealed by Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. Carbon 2006, 44, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, S.; Bahadur, J.; Elsworth, D.; Melnichenko, Y.; He, L.; Wang, Y. Estimation and Modeling of Coal Pore Accessibility Using Small Angle Neutron Scattering. Fuel 2015, 161, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yuan, Q.; Huang, D.; Peng, H. Characterization, Factors, and Fractal Dimension of Pore Structure of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 3395–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Sun, X.-M.; Wang, Y.-R.; Li, H. Relationship between Fractal Characteristics of Pore-Structure and Thermal Properties of FA-Based AAM under Different Curing Conditions. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Cao, S.; Yilmaz, E. Quantitative Analysis of Pore Characteristics of Nanocellulose Reinforced Cementitious Tailings Fills Using 3D Reconstruction of CT Images. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 1428–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Z.; Qian, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, Q.; Xing, Y.; Zhao, Y. Improved Corrosion Resistance of ZrO2/MgO Coating for Magnesium Alloys by Manipulating the Pore Structure. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 2403–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Song, W.; Fu, J. Pore Structure, Mechanical Behavior and Damage Evolution of Cemented Paste Backfill. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rao, F.; Song, S.; Ma, Q. Deterioration in the Microstructure of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers in Marine Environment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 2747–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, S.; Xiao, D.; Li, B. Pore Structure Characteristics of Tight Sandstones in the Northern Songliao Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 88, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Chen, F.; Meng, Y. A Comparison of Experimental Methods for Describing Shale Pore Features—A Case Study in the Bohai Bay Basin of Eastern China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 152, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, L.; Dang, W.; Luo, T.; Sun, W.; Jiang, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhang, S.; Ji, W.; Shao, S.; et al. Discussion on the Rising Segment of the Mercury Extrusion Curve in the High Pressure Mercury Intrusion Experiment on Shales. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 102, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B. How Long Is the Coast of Britain? Statistical Self-Similarity and Fractional Dimension. Science 1967, 156, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, K.; Wang, C.; Cao, R.; Lin, H.; Fang, L. Experimental Investigation of the Pore Fractal Characteristics and Damage Degradation Mechanism of Sandstone after Cyclic Freeze-thaw Treatments. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 4843–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Ning, L.; Zhao, H.; Bi, J. Pore and Fracture Development in Coal under Stress Conditions Based on Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Fractal Theory. Fuel 2022, 309, 122112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hong, G.; Oh, S.; Choi, S. Application of Various Fractal Models in Characterizing the Morphology of Pore Structures of Hydrating Cement Pastes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 3818–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G. Fractal Analysis of Tight Gas Sandstones Using High-Pressure Mercury Intrusion Techniques. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 24, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Bo, J.; Fengli, L.; Jiegang, L. Structure and Fractal Characteristic of Micro- and Meso-Pores in Low, Middle-Rank Tectonic Deformed Coals by CO2 and N2 Adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 253, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Ouyang, S.; Luo, B.; Zhao, D.; Sun, W.; Awan, R.S.; Lu, Z.; Li, G.; Zang, Q. Investigation of Pore-Throat Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Tight Sandstones Using HPMI, CRMI, and NMR Methods: A Case Study of the Lower Shihezi Formation in the Sulige Area, Ordos Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 210, 110053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B.; Passoja, D.E.; Paullay, A.J. Fractal Character of Fracture Surfaces of Metals. Nature 1984, 308, 721–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.H.; Corey, A.T. Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media; Hydrology Paper; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1964; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Geological Applications of Capillary Pressure: A Review1|AAPG Bulletin|GeoScienceWorld. Available online: https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/aapgbull/article/76/6/840/38801/Geological-Applications-of-Capillary-Pressure-A (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Dollimore, D.; Spooner, P.; Turner, A. The Bet Method of Analysis of Gas Adsorption Data and Its Relevance to the Calculation of Surface Areas. Surf. Technol. 1976, 4, 121–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, M. Chapter Fourteen—Surface Area: Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET). In Progress in Filtration and Separation; Tarleton, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 585–608. ISBN 978-0-12-384746-1. [Google Scholar]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Sayari, A. Adsorption Study of Surface and Structural Properties of MCM-41 Materials of Different Pore Sizes. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Nie, B. Fractal Characteristics of Coal Samples Utilizing Image Analysis and Gas Adsorption. Fuel 2016, 182, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengyang, W.; Shixiong, H.; Wenjing, S.; Wei, C. Fractal Dimension of Coal Particles and Their CH4 Adsorption. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ren, D.; Du, K.; Qi, Y.; Ye, F. Impacts of Mineral Composition and Pore Structure on Spontaneous Imbibition in Tight Sandstone. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 201, 108397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zheng, M.; Bi, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, X. Pore Throat Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Tight Oil Sandstone: A Case Study in the Ordos Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 149, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, D.H. Manual of Symbols and Terminology for Physicochemical Quantities and Units, Appendix II: Definitions, Terminology and Symbols in Colloid and Surface Chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1972, 31, 577–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherm Models: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati-Ashtiani, M. Characterization of Nano-Porous Bentonite (Montmorillonite) Particles Using FTIR and BET-BJH Analyses. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2011, 28, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, M.L.; Esparza, J.M.; Campero, A.; Cordero, S.; Kornhauser, I.; Rojas, F. On Comparing BJH and NLDFT Pore-Size Distributions Determined from N2 Sorption on SBA-15 Substrata. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardestani, R.; Patience, G.S.; Kaliaguine, S. Experimental Methods in Chemical Engineering: Specific Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution Measurements—BET, BJH, and DFT. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruifei, W.; Pingping, S.; Ziqi, S.; Hua, Y. Characteristics of Micro-Pore Throat in Ultra-Low Permeability Sandstone Reservoir. Acta Pet. Sin. 2009, 30, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, G.; Ni, G.; Wang, L. Comparative Analysis of Pore Structure Parameters of Coal by Using Low Pressure Argon and Nitrogen Adsorption. Fuel 2022, 309, 122120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Huang, Y. A Review of the Pore Structure of Pervious Concrete: Analyzing Method, Characterization Parameters and the Effect on Performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 129971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, P.; Han, H.; Hu, L.; Guo, C.; Gao, Y.; Xie, Y. The Calculations of Pore Structure Parameters from Gas Adsorption Experiments of Shales: Which Models Are Better? J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 94, 104060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Yao, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Y. Influence of Pore Structure Parameters on Flow Characteristics Based on a Digital Rock and the Pore Network Model. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 31, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Peng, P. The Effect of Sample Particle Size on the Determination of Pore Structure Parameters in Shales. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 163, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, A.; Jamshidi, S. Specific Surface and Porosity Relationship for Sandstones for Prediction of Permeability. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2014, 71, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odler, I.; Köster, H. Investigation on the Structure of Fully Hydrated Portland Cement and Tricalcium Silicate Pastes. III. Specific Surface Area and Permeability. Cem. Concr. Res. 1991, 21, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhmann, A.J.; Tutolo, B.M.; Bagley, B.C.; Mildner, D.F.R.; Seyfried, W.E., Jr.; Saar, M.O. Permeability, Porosity, and Mineral Surface Area Changes in Basalt Cores Induced by Reactive Transport of CO2-Rich Brine. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 1908–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibiryakov, B.; Leite, L.W.B.; Sibiriakov, E. Porosity, Specific Surface Area and Permeability in Porous Media. J. Appl. Geophys. 2021, 186, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Fan, T.; Karubandika, G.M.; Meng, M. Pore Characteristics of the Carbonate Shoal from Fractal Perspective. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 174, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Cheng, Q.; Zuo, R.; Wang, X. Mapping Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Lineaments Extracted from Remote Sensing Image Using Fractal and Multifractal Models. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 28, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-Y.; Yang, K.; Zai, Y. Multifractal Characteristics of Shale and Tight Sandstone Pore Structures with Nitrogen Adsorption and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Pet. Sci. 2020, 17, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

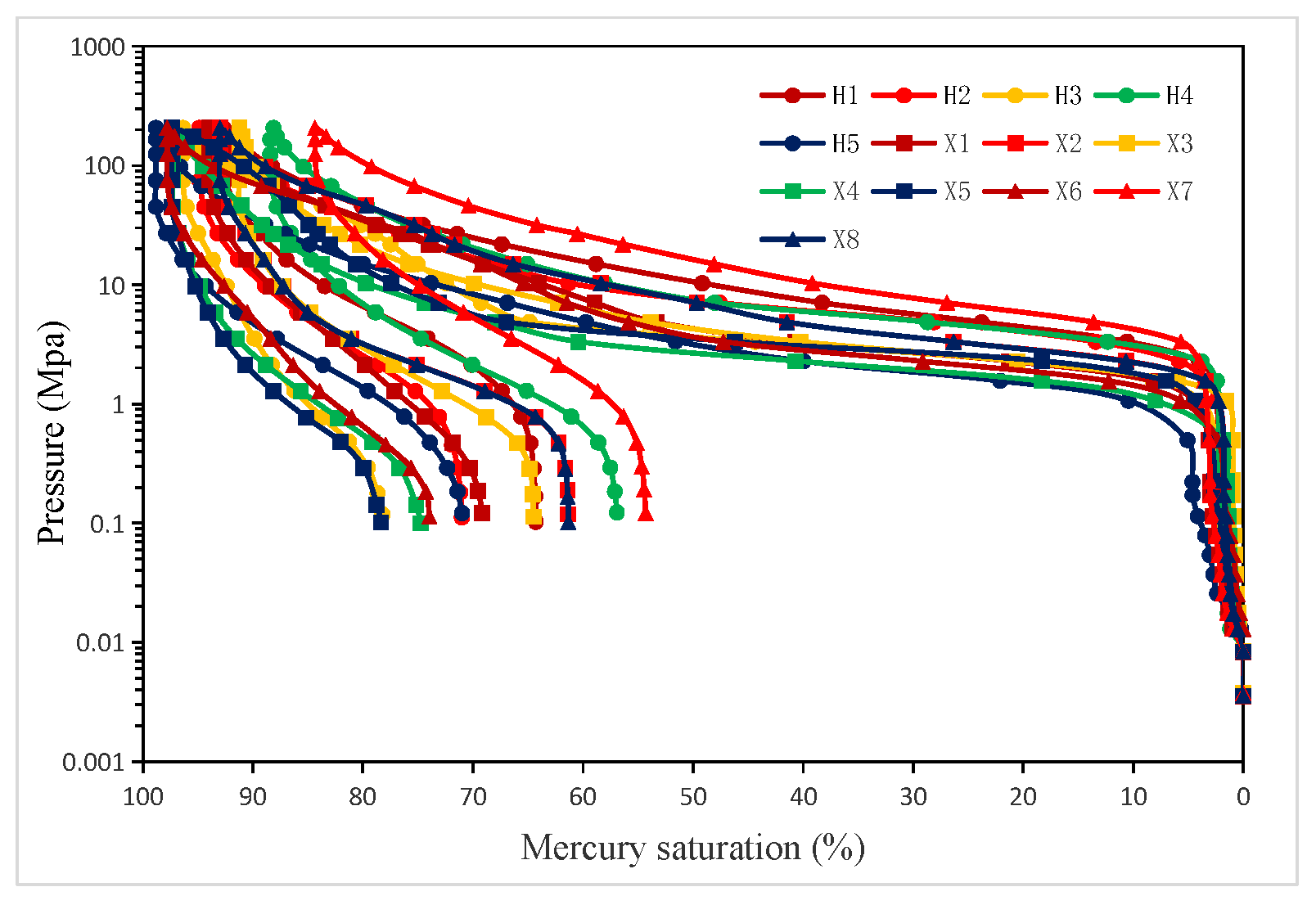


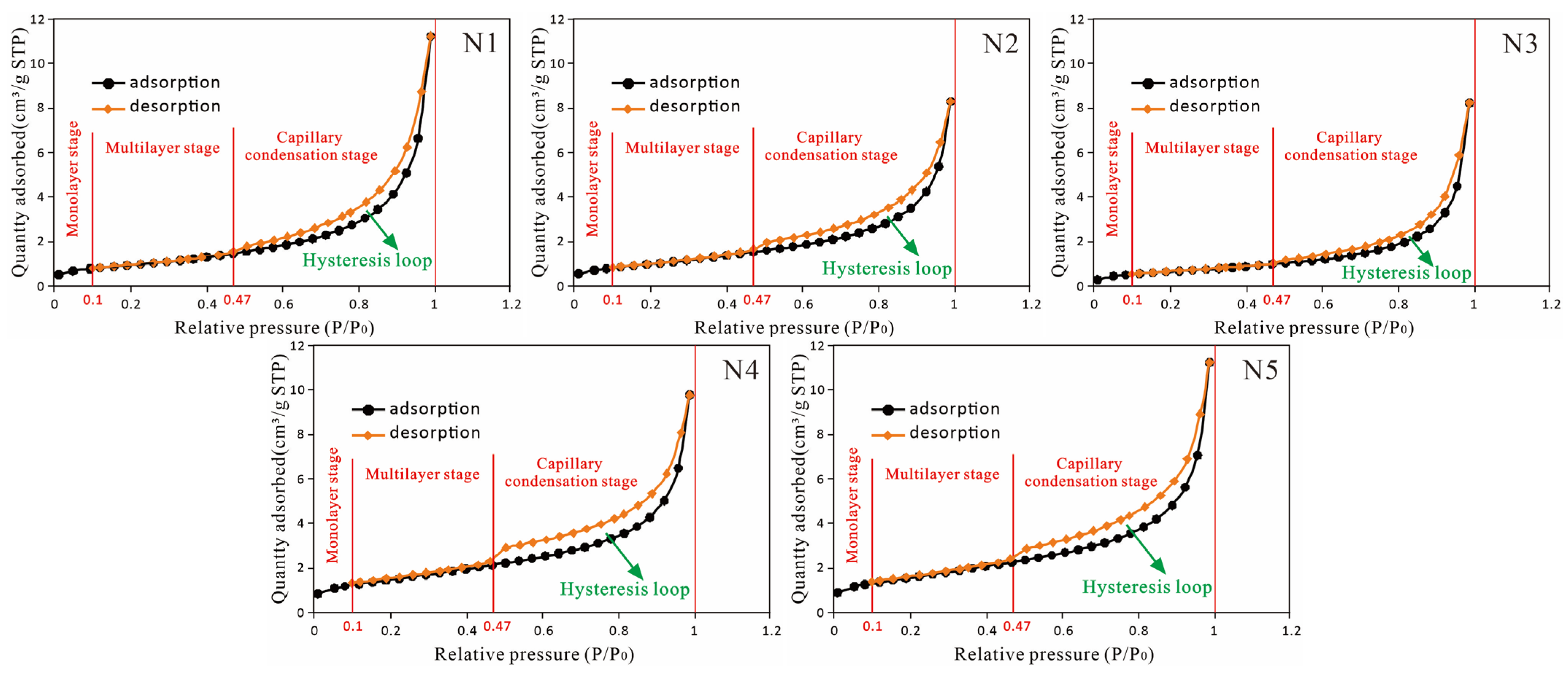
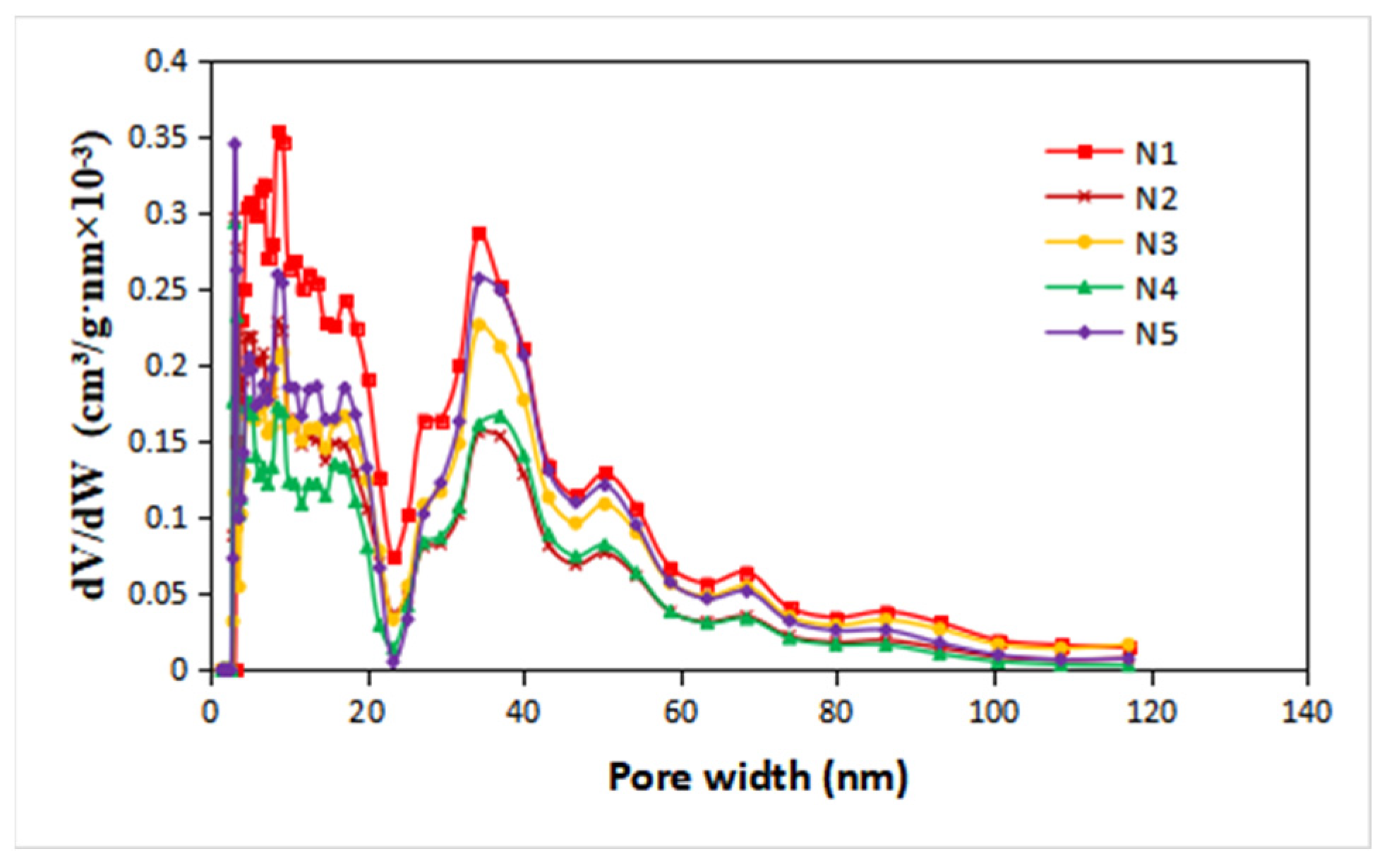
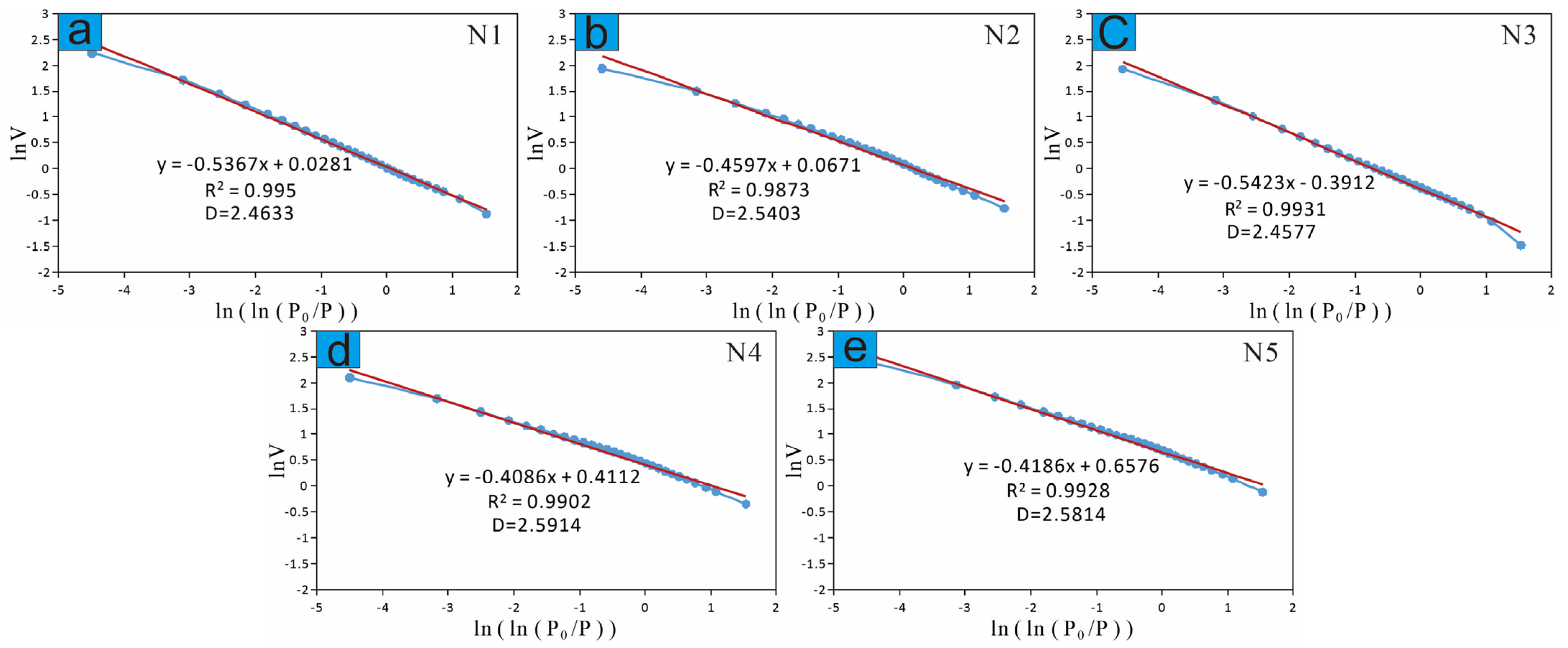



| Sample | Depth | Member | Φ (%) | K (mD) | Pmin (Mpa) | P50 (MPa) | rmax (μm) | r50 (μm) | SHgmax (%) | D | Small Pores | Large Pores | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R12 | D1 | R22 | D2 | |||||||||||
| H1 | 2199.51 | Ch 6 | 9.94 | 0.044 | 2.41 | 11.03 | 0.30 | 0.067 | 92.69 | 2.47 | 0.969 | 2.46 | 0.875 | 2.9957 |
| H2 | 2127.4 | Ch 6 | 10.60 | 0.085 | 2.21 | 7.59 | 0.33 | 0.097 | 94.85 | 2.41 | 0.977 | 2.40 | 0.939 | 2.9969 |
| H3 | 2068.3 | Ch 6 | 8.98 | 0.092 | 1.52 | 3.79 | 0.48 | 0.194 | 96.37 | 2.42 | 0.964 | 2.41 | 0.894 | 2.9949 |
| H4 | 2098.4 | Ch 6 | 10.90 | 0.085 | 2.76 | 7.59 | 0.27 | 0.097 | 88.14 | 2.55 | 0.984 | 2.54 | 0.867 | 2.9970 |
| H5 | 2241.6 | Ch 6 | 11.88 | 0.24 | 1.10 | 3.10 | 0.67 | 0.237 | 98.81 | 2.25 | 0.970 | 2.21 | 0.928 | 2.9867 |
| X1 | 1549.5 | Ch 7 | 10.36 | 0.114 | 1.38 | 4.21 | 0.53 | 0.175 | 93.92 | 2.48 | 0.988 | 2.46 | 0.951 | 2.9937 |
| X2 | 1835.4 | Ch 6 | 11.60 | 0.108 | 1.38 | 5.72 | 0.53 | 0.128 | 91.57 | 2.48 | 0.989 | 2.48 | 0.654 | 2.9961 |
| X3 | 1842 | Ch 6 | 11.85 | 0.13 | 1.38 | 4.21 | 0.53 | 0.175 | 91.23 | 2.51 | 0.985 | 2.50 | 0.893 | 2.9983 |
| X4 | 2028.8 | Ch 7 | 12.81 | 0.262 | 1.24 | 2.76 | 0.59 | 0.266 | 96.81 | 2.37 | 0.995 | 2.36 | 0.911 | 2.9970 |
| X5 | 2117.9 | Ch 8 | 9.94 | 0.112 | 1.52 | 3.59 | 0.48 | 0.205 | 97.37 | 2.42 | 0.958 | 2.40 | 0.975 | 2.9932 |
| X6 | 1763.2 | Ch 7 | 11.80 | 0.23 | 1.24 | 3.59 | 0.59 | 0.205 | 97.79 | 2.35 | 0.921 | 2.34 | 0.993 | 2.9936 |
| X7 | 2011.2 | Ch 6 | 8.37 | 0.025 | 3.45 | 16.55 | 0.21 | 0.044 | 84.35 | 2.62 | 0.966 | 2.61 | 0.920 | 2.9939 |
| X8 | 1782.36 | Ch 7 | 11.61 | 0.055 | 2.76 | 7.59 | 0.27 | 0.097 | 88.84 | 2.52 | 0.966 | 2.52 | 0.849 | 2.9969 |
| Sample | Depth (m) | Member | Φ (%) | K (mD) | BET Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | BJH Average Pore Diameter (nm) | BJH Total Pore Volume (cm³/g) | Fractal Dimensions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | R2 | ||||||||
| N1 | 1817.52 | Ch 7 | 12.32 | 0.54 | 2.846 | 17.665 | 0.0145 | 2.4633 | 0.995 |
| N2 | 2241.60 | Ch 6 | 11.38 | 0.45 | 3.846 | 12.801 | 0.0108 | 2.5403 | 0.9873 |
| N3 | 2099.63 | Ch 6 | 13.79 | 0.56 | 4.846 | 19.577 | 0.0106 | 2.4577 | 0.9931 |
| N4 | 1782.36 | Ch 7 | 10.29 | 0.19 | 5.846 | 11.603 | 0.0128 | 2.5914 | 0.9902 |
| N5 | 2082.00 | Ch 6 | 10.63 | 0.21 | 6.846 | 12.558 | 0.0176 | 2.5814 | 0.9928 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, T.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, H.; Shang, Y.; Cui, G. Fractal Characterization of the Pore-Throat Structure in Tight Sandstone Based on Low-Temperature Nitrogen Gas Adsorption and High-Pressure Mercury Injection. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8060356
He T, Zhou Y, Chen Z, Zhang Z, Xie H, Shang Y, Cui G. Fractal Characterization of the Pore-Throat Structure in Tight Sandstone Based on Low-Temperature Nitrogen Gas Adsorption and High-Pressure Mercury Injection. Fractal and Fractional. 2024; 8(6):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8060356
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Taping, Yaoqi Zhou, Zhaobing Chen, Zhenwei Zhang, Huanyu Xie, Yuehan Shang, and Gaixia Cui. 2024. "Fractal Characterization of the Pore-Throat Structure in Tight Sandstone Based on Low-Temperature Nitrogen Gas Adsorption and High-Pressure Mercury Injection" Fractal and Fractional 8, no. 6: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8060356
APA StyleHe, T., Zhou, Y., Chen, Z., Zhang, Z., Xie, H., Shang, Y., & Cui, G. (2024). Fractal Characterization of the Pore-Throat Structure in Tight Sandstone Based on Low-Temperature Nitrogen Gas Adsorption and High-Pressure Mercury Injection. Fractal and Fractional, 8(6), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8060356





