Effects of In-Situ Stress on Damage and Fractal during Cutting Blasting Excavation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Basis
2.1. Static Stress Field
2.2. Stress Field under Blasting Load
2.3. Superimposed Stress Field of Blasting Load and In-Situ Stress
3. Numerical Simulation
3.1. Material Parameters
3.2. Material Parameter Verification
3.3. Computation Module
4. Analyzed and Discussed
4.1. The Influence of In-Situ Stress on the Stress Field around the Empty Hole
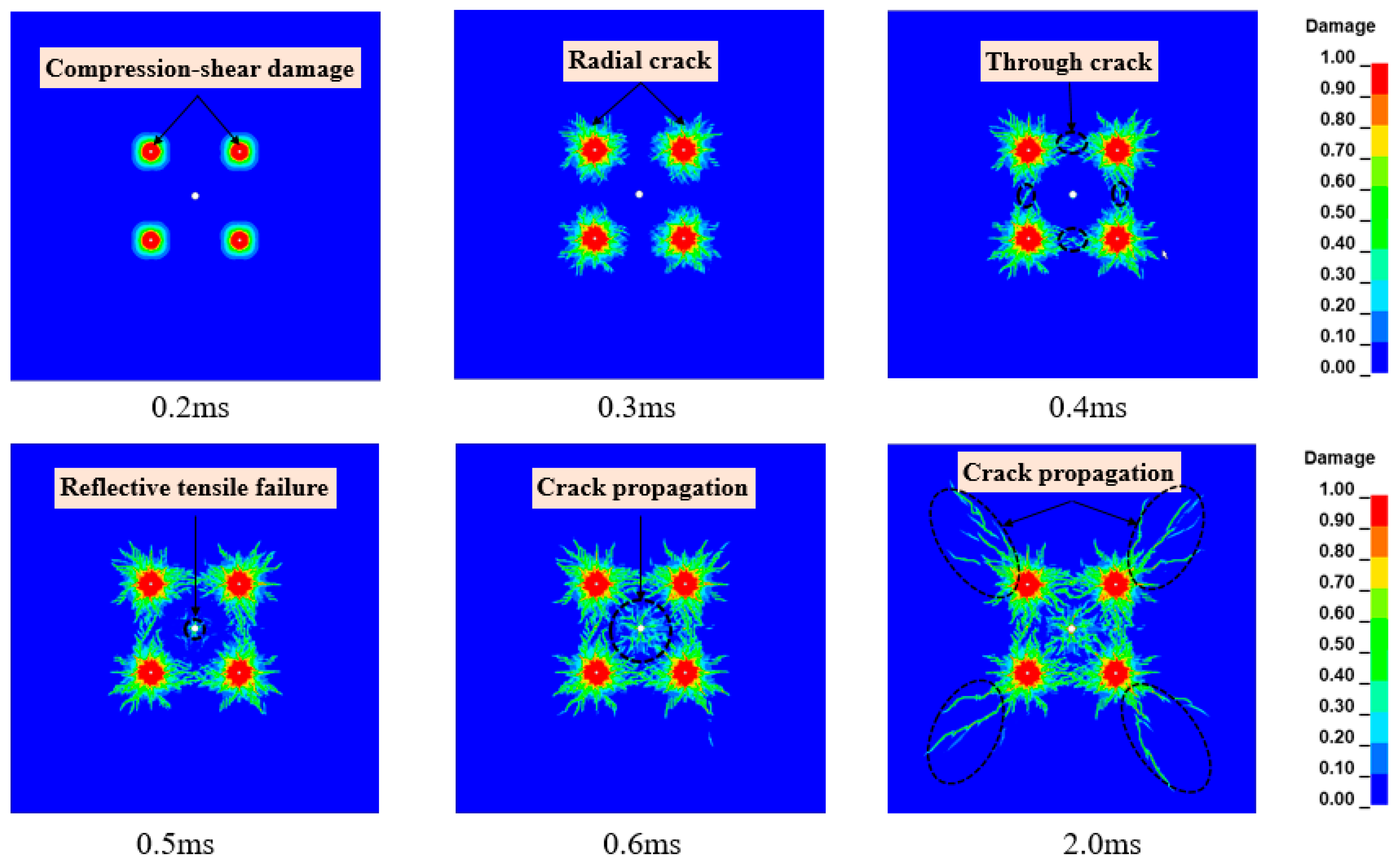
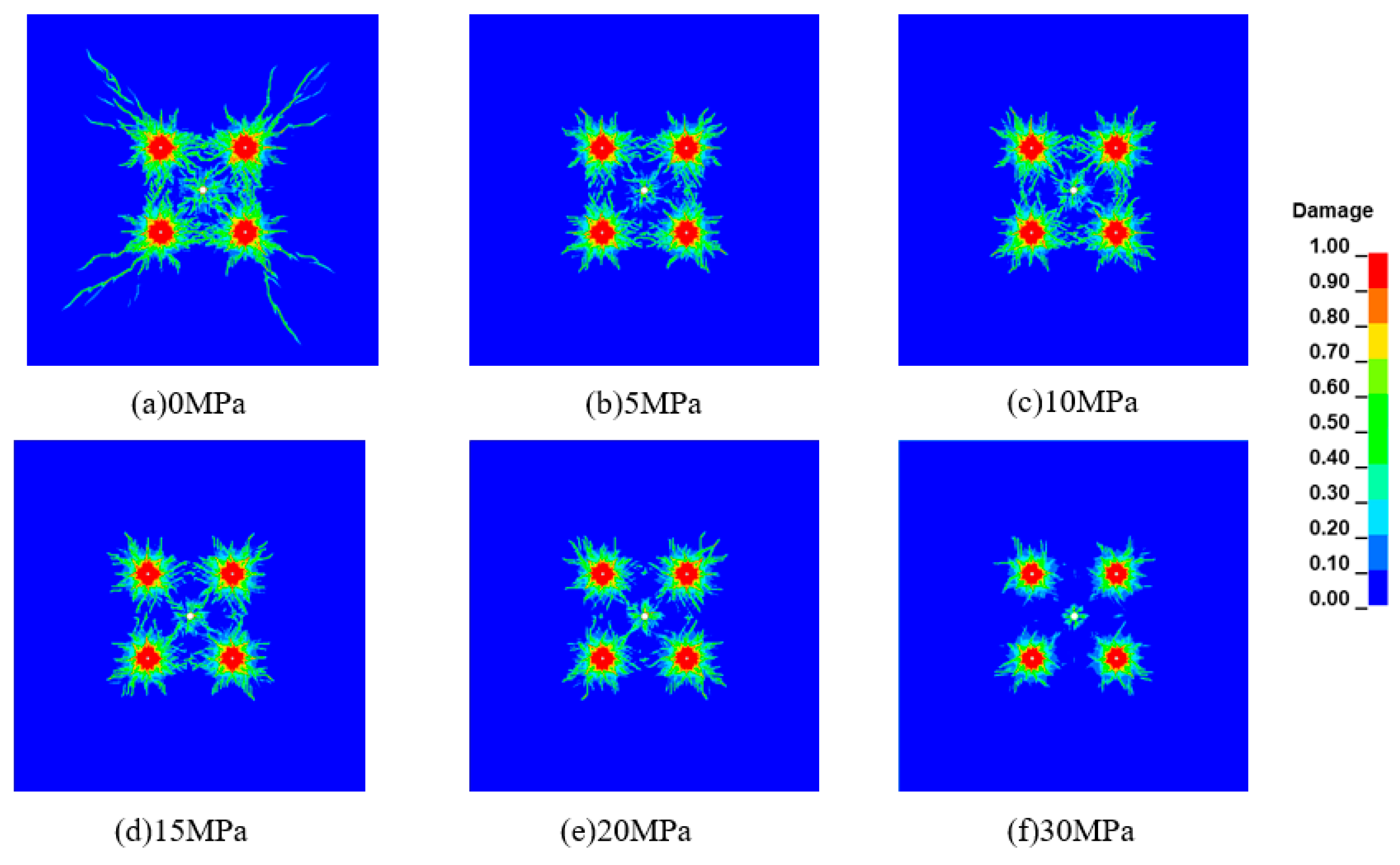
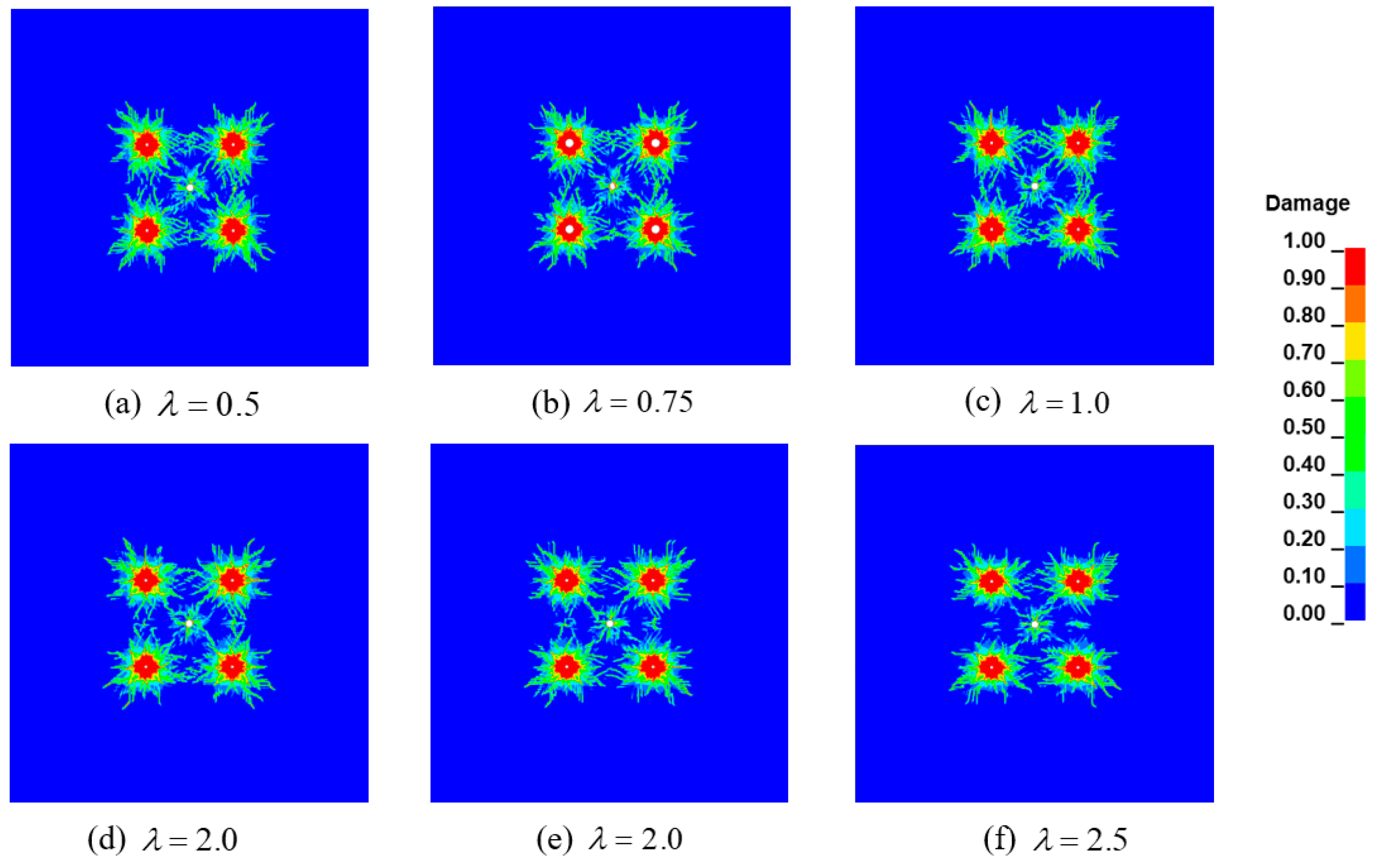
4.2. Damage Characteristics of Rock Mass under Different In-Situ Stress Conditions
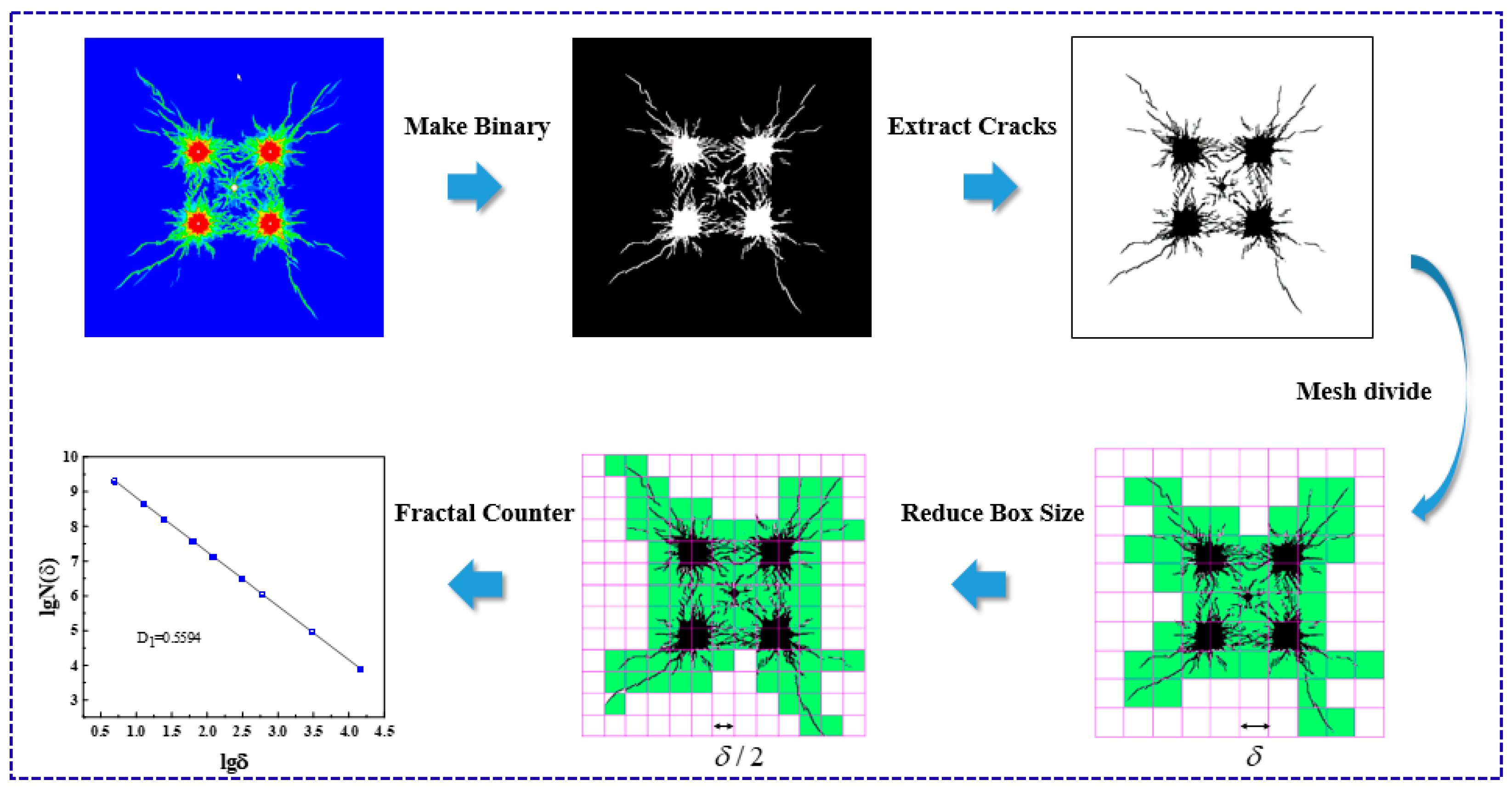
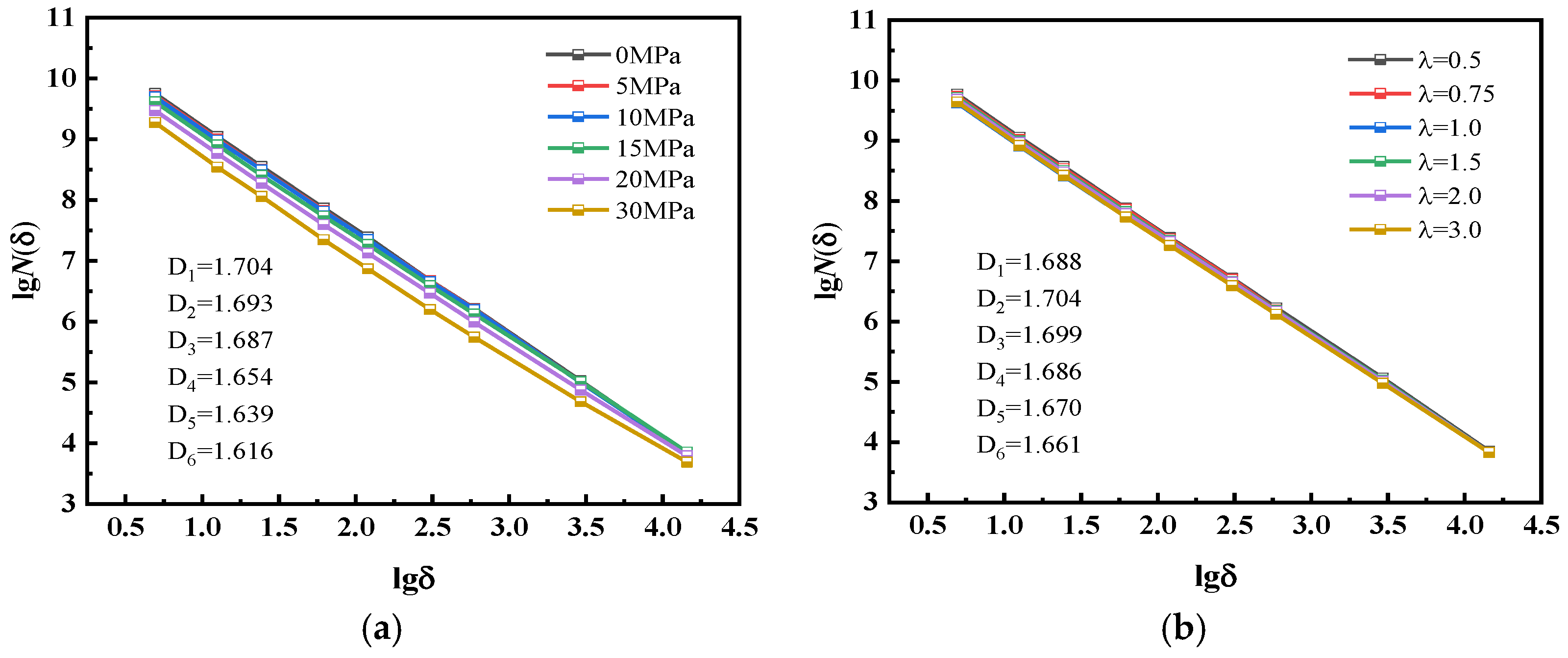
5. Damage Analysis of Rock Mass Based on Fractal Dimension
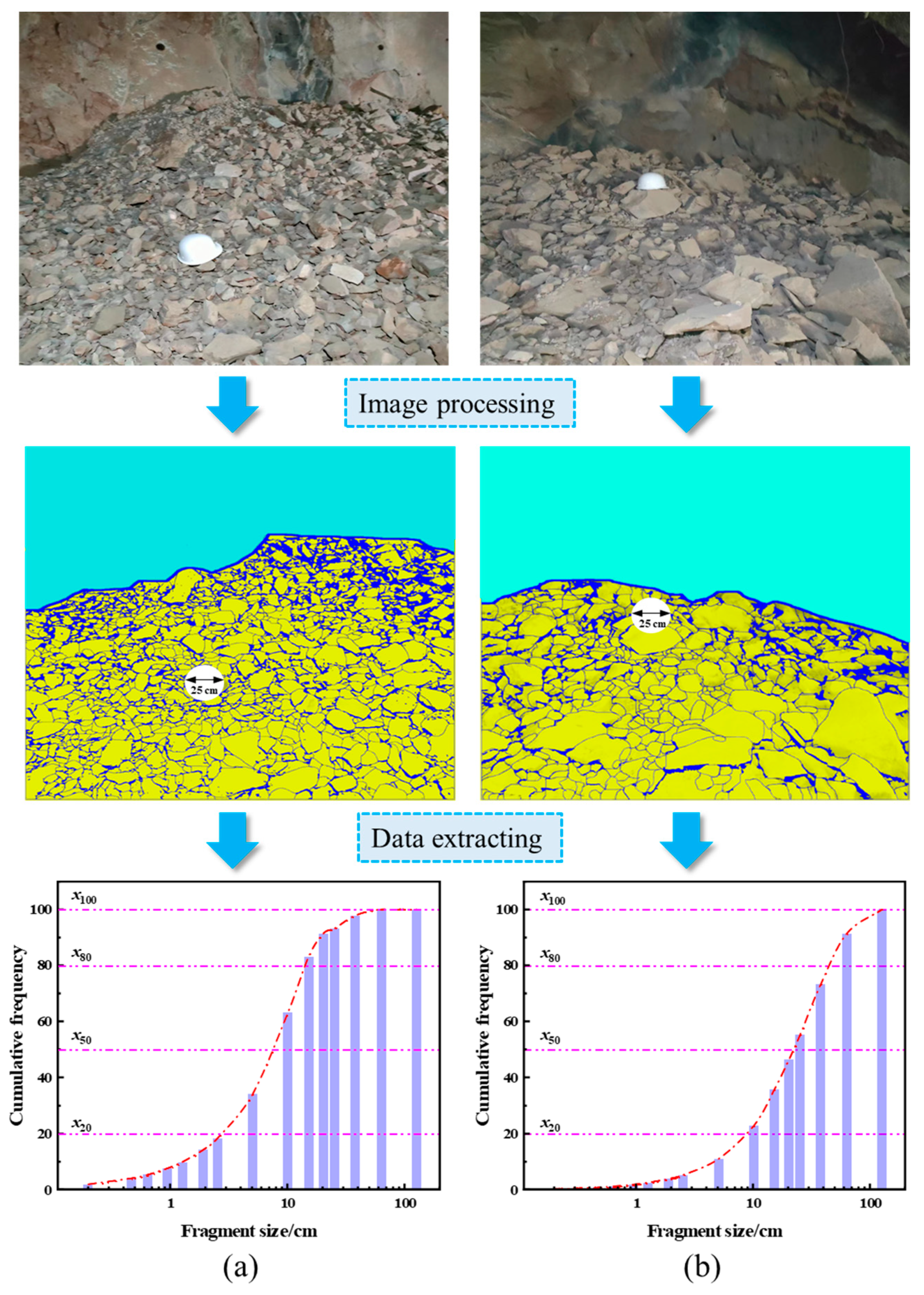
6. Engineering Case Analysis
6.1. Engineering Situations
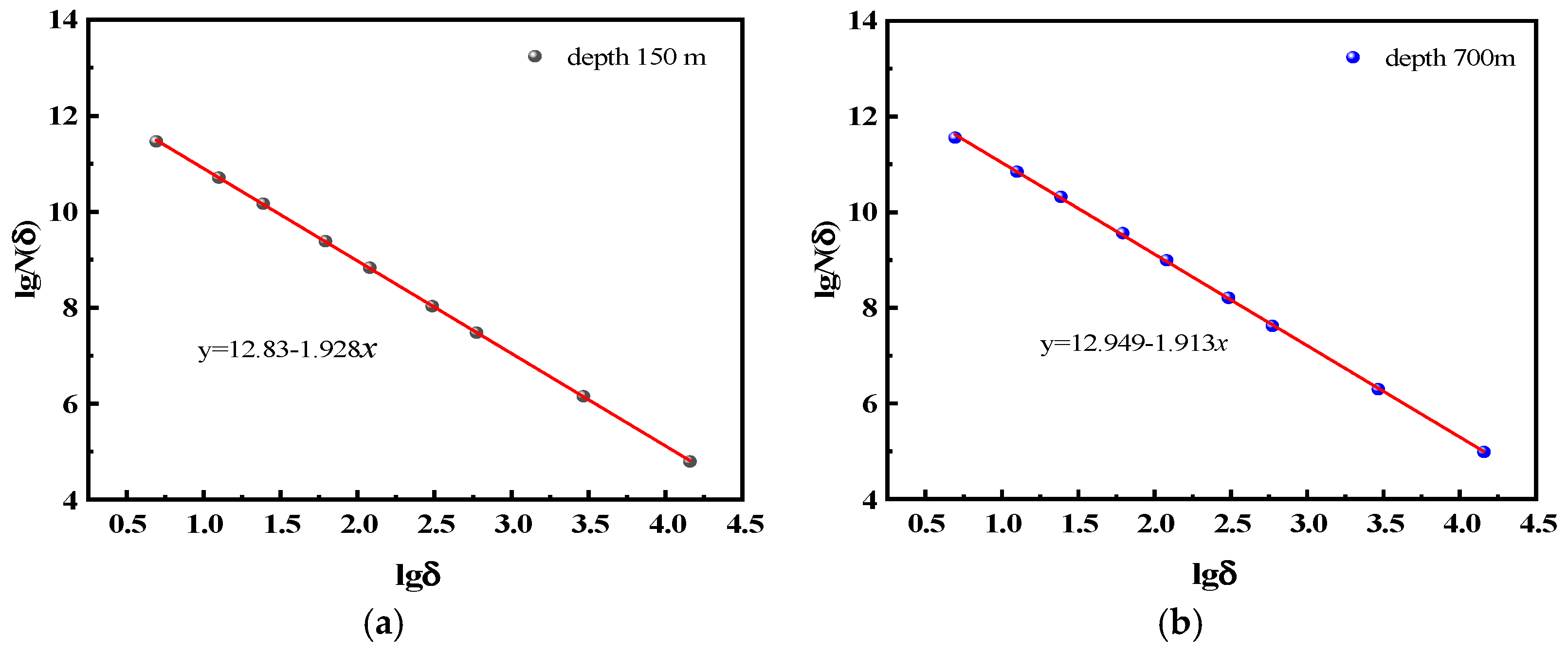
6.2. Comparative Analysis of Blast Blocks for Different Depths of Buried Rock
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the initial stage, the damage area is basically the same. This stage is the formation stage of the cutting hole fracture zone, and the in-situ stress has little effect. The second stage is the propagation of cracks in the cutting area, which is greatly affected by the in-situ stress at this stage;
- (2)
- Damage to the rock mass is primarily influenced by the magnitude of tensile stress, which serves as an indicator of damage in the hollowing zone. As in-situ stress or the lateral pressure coefficient increases, the inter-hole tensile stress weakens more significantly, leading to greater inhibition of damage in the hollowing zone. Excessive in-situ stress or lateral pressure coefficient will prevent cracks between cavities from penetrating;
- (3)
- Under hydrostatic in-situ stress, with the increase in in-situ stress, the damage area and fractal dimension of blasting cracks gradually decrease. Under non-hydrostatic in-situ stress, when the principal stress difference is small, the in-situ stress has a promoting effect on the damage area and fractal dimension of surrounding rock, and the rock mass crushing effect is better. When the principal stress difference is large, the in-situ stress has an inhibitory effect on the damage area and fractal dimension of surrounding rock, which is not conducive to blasting rock breaking;
- (4)
- Both numerical simulations and field experiments indicate that in-situ stress impedes crack propagation. As in-situ stress rises, the fractal dimension progressively diminishes, suggesting that blasting results in the formation of larger blocks, consequently decreasing the extent of rock fragmentation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, M.C.; Ren, S.L.; Tao, Z.G. Disaster prevention and control methods for deep buried tunnels. J. Eng. Geol. 2022, 30, 1777–1797. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.P.; Jia, C.; Sun, Z.Z.; Liu, H.L.; Cheng, S. Research status and development trend of major engineering disaster prevention and control technology in deep underin-situ. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2021, 52, 2539–2556. [Google Scholar]
- Hen, L.; Zhou, Z.L.; Gao, S. Research status and prospects of blasting excavation of tunnel under high stress condition. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2023, 54, 849–865. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, G.Y.; Deng, J.; Ren, S.J.; Wang, C.P.; Song, Z.Y.; Wang, J.R.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.Q. Research on temperature measurement model of loose coal considering humidity using acoustic wave method. Fuel 2024, 373, 132317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, G. Study on cyclic blasting failure characteristics and cumulative damage evolution law of tunnel rock mass under initial in-situ stress. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 150, 107310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, R.; Xu, P.; Song, Y. Experimental study on the effect of initial compression stress field on blast-induced crack behaviors. J. China Coal Soc. 2013, 38, 404–410. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Yang, J.; Yu, Q. Laboratory study on the dynamic response of rock under blast loading with active confining pressure. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2018, 102, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Tian, S.; Zhang, S.; Zong, L.; Xu, S. Expanding law of cracks formed by slotted cartridge blast under unidirectional confining pressure. J. Vib. Shock 2019, 38, 186–195. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E.T.; Hoek, E. Trends in relationships between measured in-situ stresses and depth. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1978, 15, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhu, W.C.; Wei, C.H.; Wei, J. Numerical simulation on two-hole blasting under different in-situ stress conditions. Rock Soil Mech. 2013, 34, 466–471. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Yang, R.; Yang, L. Experimental results of blast-induced cracking fractal characteristics and propagation behavior in deep rock mass. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 142, 104772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.W.; An, X.M. Numerical simulation of blasting-induced rock fractures. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2008, 45, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, J.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Rock-like brittle material fragmentation under coupled static stress and spherical charge explosion. Eng. Geol. 2017, 220, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.P.; Johansson, D.; Greberg, J. Effects of in-situ stresses on the fracturing of rock by blasting. Comput. Geotech. 2018, 104, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Yan, P.; Lu, W.B. Effects of In-situ Stress on Blasting Damage during Deep Tunnel Excavation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 11447–11458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.P.; Song, K.W.; Luo, Y. Study on the influence of high in-situ stress on cut blasting and blasting stress wave. Blasting 2019, 36, 13–18+53. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.Q.; Yan, P.; Wang, G.H. Effect of in-situ stress level on frequency spectrum of blasting vibration in a deep-buried tunnel. Explos. Shock. Waves. 2019, 39, 118–129. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.X.; Liang, X.T.; Yang, R.S. Study on stress evolution and damage fracture of cut blasting in high in-situ stress roadway. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 52, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.X.; Lu, W.B.; Zhang, Q.B.; Jiang, Q.H. Damage evolution mechanisms of rock in deep tunnels induced by cut blasting. Tunn. Underin-Situ Space Technol. 2016, 58, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Ding, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Y. Crack propagation behavior in slit charge blasting under high static stress conditions. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2019, 119, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, X.T. Numerical simulation research on rock breaking mechanism offour-hole cut blasting under in-situ stress. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 41, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.X.; Lu, W.B.; Zhang, Q.B.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhao, J. Analysis of damage mechanisms and optimization of cut blasting design under high in-situ stresses. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 66, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jin, Q.K.; Gao, W.X.; Huang, F. Some problems in the research of rockdamage model by blasting. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 1999, 18, 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.D.; Liu, K.W.; Sha, Y.Y.; Yang, J.C.; Hong, Z.X. Experimental and numerical investigation on rock fracturing in tunnel contour blasting under initial stress. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2024, 185, 104844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Y.; Ding, C.X. Fracture mechanism due to blast-imposed loading under high static stress conditions. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2018, 107, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Gong, F.Q. Research progress and prospect of deep mining rock mechanics based on coupled static-dynamic loading testin. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 846–866. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch, E.G. Die Theorie der Elastizit und die Bedrfnisse der Festigkeitslehre. Zeit Vereines Dtsch. 1898, 2, 797–807. [Google Scholar]
- Miklowitz, J. The Theory of Elastic Waves and Waveguides; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, C.P.; Johansson, D.; Nyberg, U.; Beyglou, A. Stress wave interaction between two adjacent blast holes. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2016, 49, 1803–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.D.; Liu, Z.G.; Yi, C.P.; Gao, K.; Xuan, G. Quantitative assessment of the effect of in-situ stresses on blast-induced damage to rock. Comput. Struct. 2023, 287, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Su, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, X. Analyzing the Energy and Damage Constitutive of Cemented Backfill with Different Water Content under Dynamic Load. Materials 2023, 16, 5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.H.; He, T.; Liu, Y.W.; Chen, X.; Liu, L. Study on Dynamic Splitting Properties of S-PP Hybrid Fiber Concrete after High Temperatures. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Zhu, Z.M.; Wang, M.; Ying, P.; Wang, F.; Wan, D.; Li, X.; Gao, W. A plastic damage constitutive model for rock-like material focusing on the hydrostatic pressure induced damage and the interaction of tensile and shear damages under impact and blast loads. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 150, 104921. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Y.B.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Gao, W.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Yan, T. Study on explosion impact pressure and damage distribution law of rock powder segmented charge. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 163, 108517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J.G. Effect of confining pressure on damage accumulation of rock under repeated blast loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2021, 156, 103961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cai, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, J.; Xu, Z. Study on high temperature dynamic characteristics and mesoscopic simulation of HFRC under dynamic and static combined loading. Structures 2024, 60, 105824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Gao, W.X.; Guo, L.J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S. Influences of the number of non-consecutive joints on the dynamic mechanical properties and failure characteristics of a rock-like material. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 146, 107101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Li, X.L.; Wang, J.G.; Hu, Q.; Tao, Z.; Hu, T. Insights into natural tuff as a building material: Effects of natural joints on fracture fractal characteristics and energy evolution of rocks under impact load. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 163, 108584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.D.; Lu, W.B.; Leng, Z.D.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhou, H.X.; Zhang, S.C. Analysis of wave-type and seismic component induced by rock blasting considering source characteristics. Rock Soil Mech. 2021, 42, 2830–2844. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, C.P.; Sjöberg, J.; Johansson, D. Numerical modelling for blast-induced fragmentation in sublevel caving mines. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 68, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banadaki, M.M.D. Stress-Wave Induced Fracture in Rock Due to Explosive Action. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.X.; Yang, R.S.; Lei, Z. Fractal damage and crack propagation in decoupled charge blasting. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 141, 106503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.L.; Yang, R.S.; Ding, C.X. Multi-scale research on blasting damage of rock based on fractal theory. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2024, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B. Fractals; Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.L.; Yang, R.S.; Ding, Z.W. Blasting damage control of slit charge structure. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2023, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.P.; Gao, F.; Zhou, H.W.; Zuo, J. Fractal Fracture and Fragmentation in Rocks. J. Disaster Prev. Mitig. Eng. 2003, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.Q.; Li, Y.; Xiao, C.L. Fractal damage and crack propagation of PMMA in multiple slit charge blasting. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

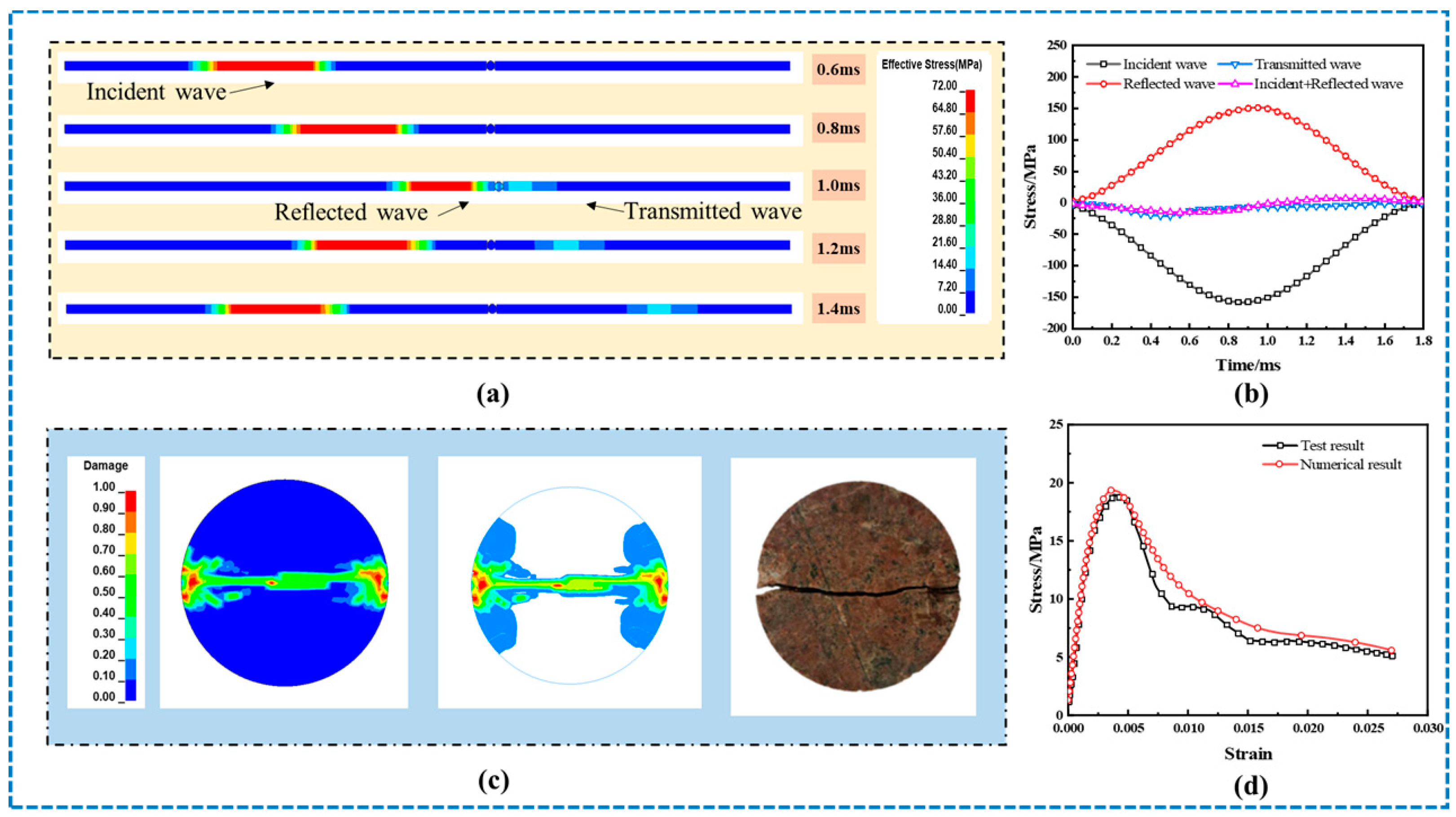
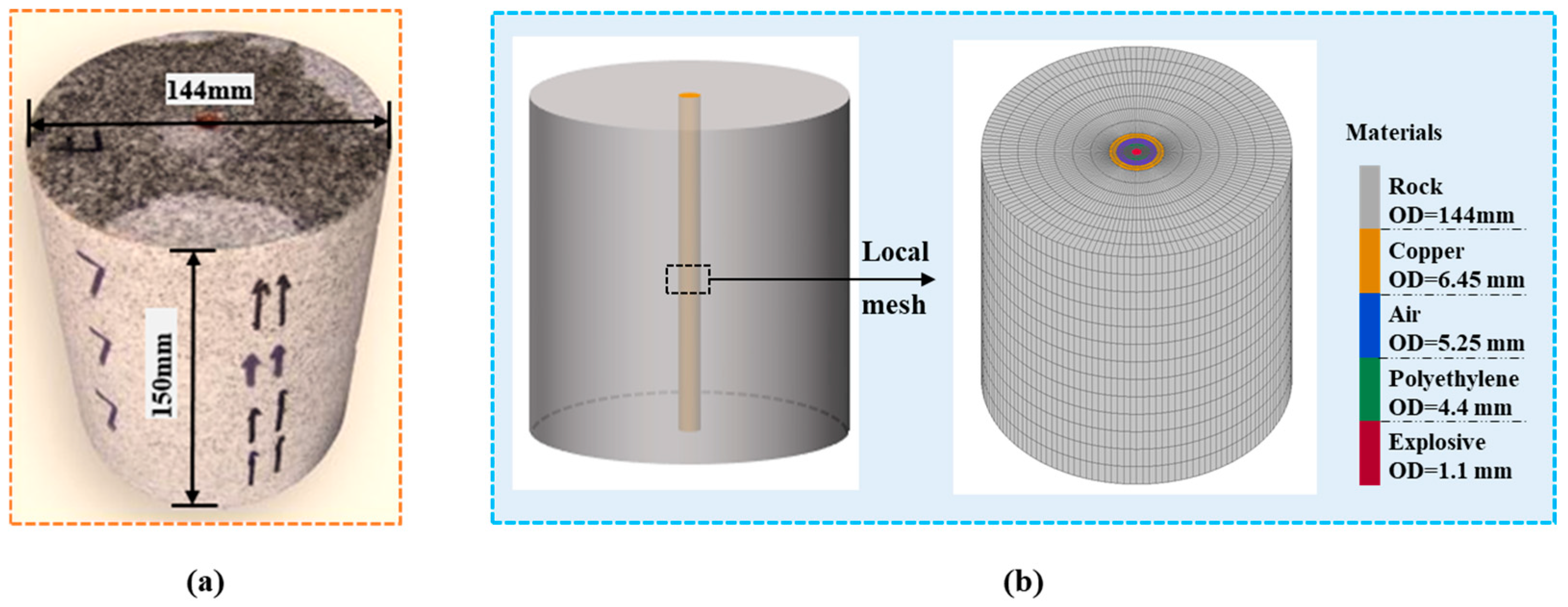
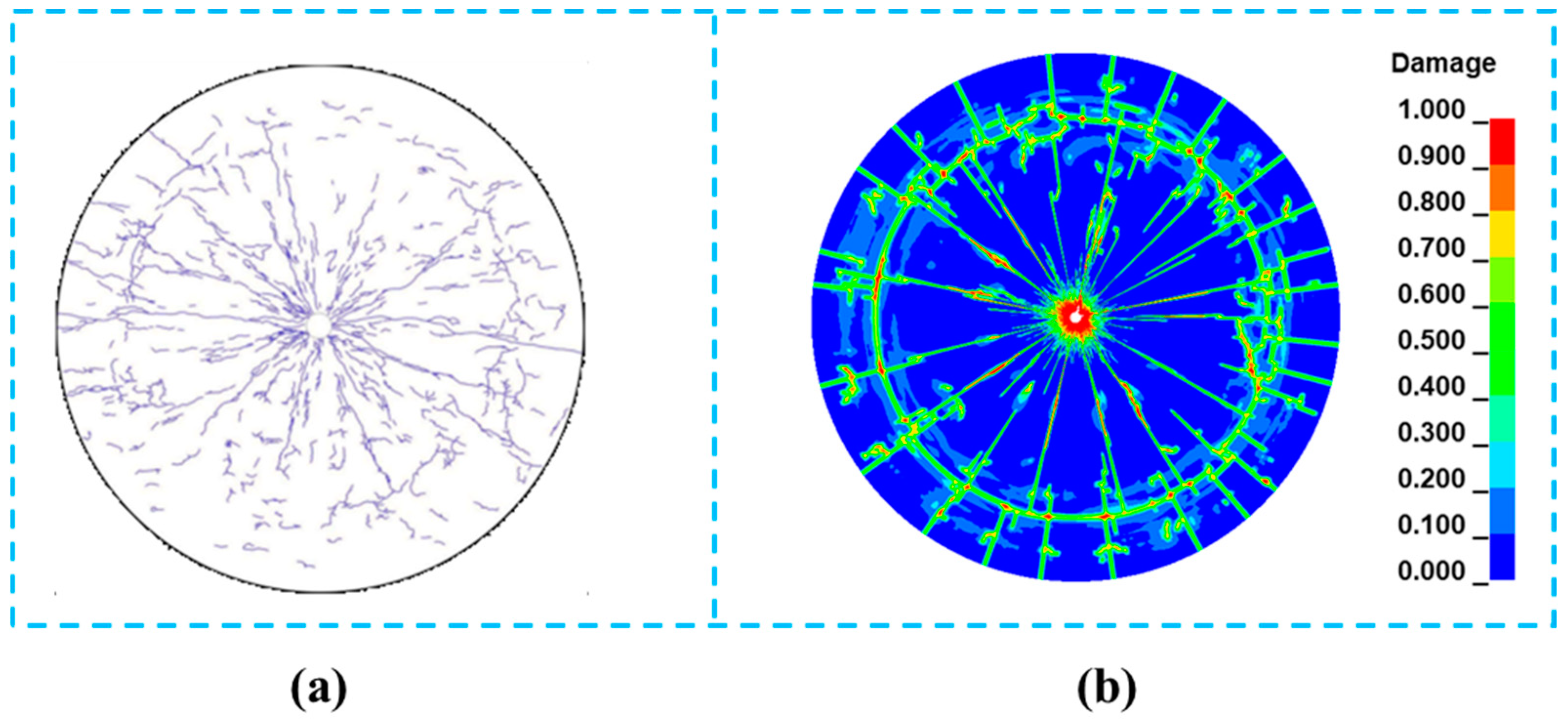

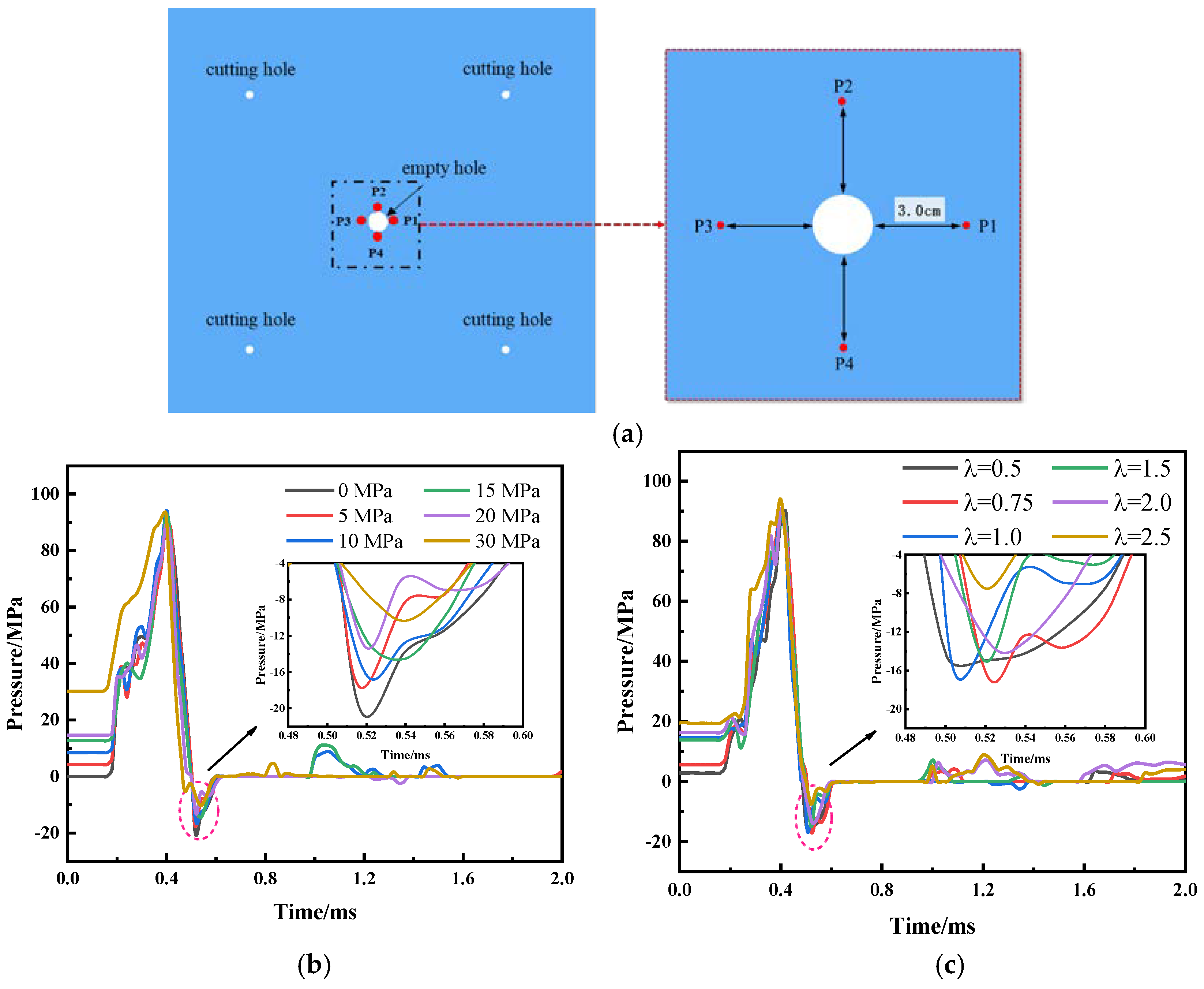



| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.62 kg·m−3 | Elastic modulus | 21.8 GPa | Shear strength | 13.4 MPa | Tensile strength | 12.3 MPa |
| Uniaxial Compressive Strength | 112 MPa | Poisson ratio | 0.26 | Initial porosity | 1.10% | Longitudinal wave velocity | 4600 m·s−1 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2620 kg·m−3 | 8.65 GPa | 1.60 | 1.22 | ||||
| 1.22 | 0.04 | 0.61 | 0.112 GPa | ||||
| 0.11 | 0.12 | 3 × 1025 s−1 | 0.20 | ||||
| 0.5 | 1.0 | 3 × 1025 s−1 | 0.10 | ||||
| 55.44 GPa | 6.0 GPa | 0.07 GPa | 67.64 GPa | ||||
| 0.68 | 0.53 | 55.44 GPa | 32.44 GPa | ||||
| 0 GPa | 3 × 10−5 s−1 | 3 × 10−6 s−1 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /kg·m−3 | 1000 | A/GPa | 220 | B/GPa | 0.2 | 0.35 | |
| R1 | 4.5 | R2 | 1.1 | E0/GPa | 8.56 | D/s−1 | 4000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Gao, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J. Effects of In-Situ Stress on Damage and Fractal during Cutting Blasting Excavation. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8080450
Wu Y, Zhang X, Li Z, Gao W, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Zhou J. Effects of In-Situ Stress on Damage and Fractal during Cutting Blasting Excavation. Fractal and Fractional. 2024; 8(8):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8080450
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yongbo, Xiaojun Zhang, Zhuo Li, Wenxue Gao, Zehui Xu, Yifeng Zhang, and Jiguo Zhou. 2024. "Effects of In-Situ Stress on Damage and Fractal during Cutting Blasting Excavation" Fractal and Fractional 8, no. 8: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8080450
APA StyleWu, Y., Zhang, X., Li, Z., Gao, W., Xu, Z., Zhang, Y., & Zhou, J. (2024). Effects of In-Situ Stress on Damage and Fractal during Cutting Blasting Excavation. Fractal and Fractional, 8(8), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8080450








