Determination of Pressure Drop and Flow Velocity in Old Rough Pipes †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
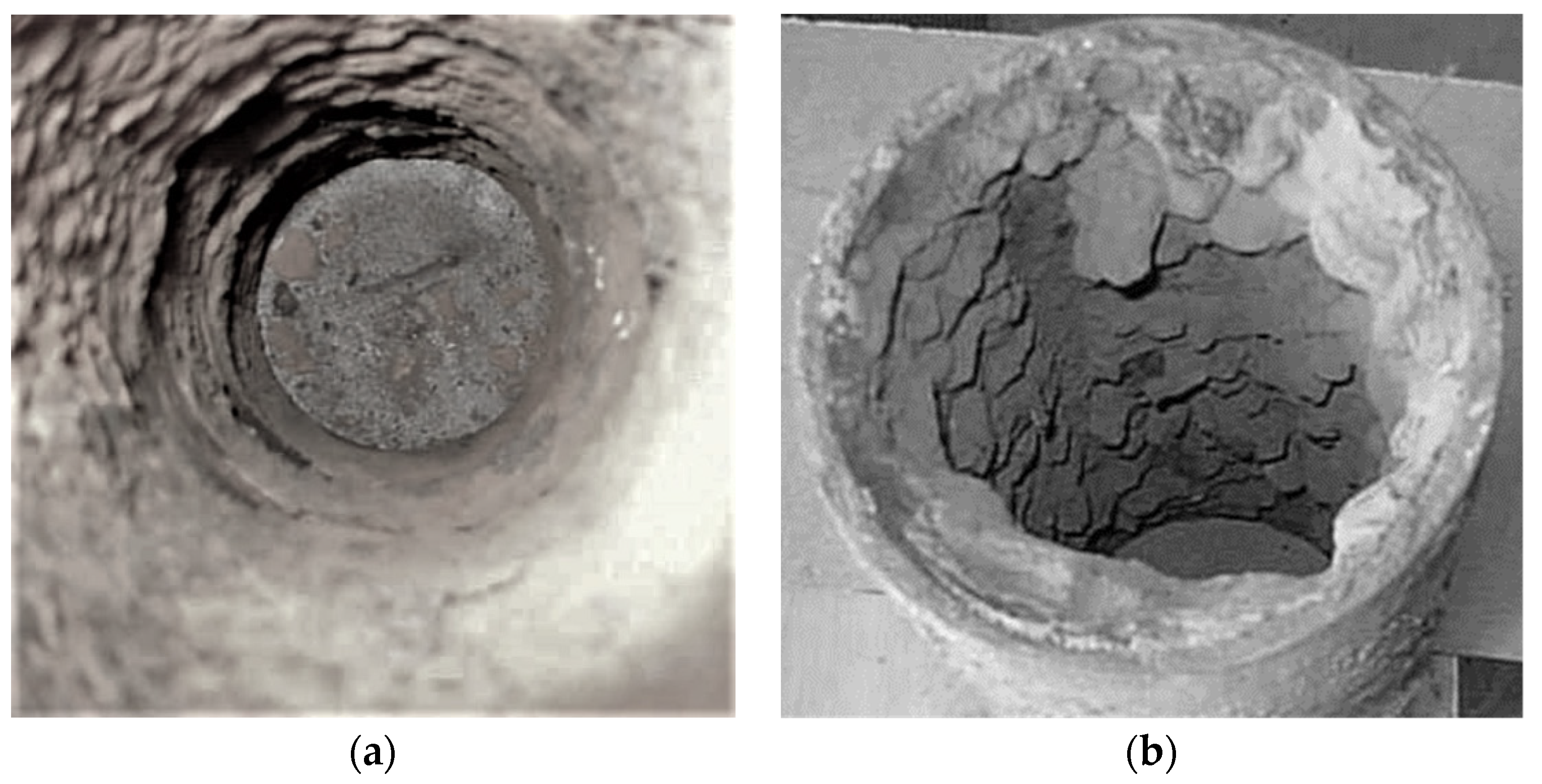
Description of the Pipe Model
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- In case of pipes with non-homogenous diameter the flow velocity is larger than in pipes with nominal diameter, leading to errors in water quality modelling and risk assessment in WDS.
- The pipe wall roughness in old pipes is not constant at different Re numbers when using nominal diameters. This should be taken into account in WDS models to decrease the modelling errors.
- Sedimentation settling may reduce the pipe nominal diameter up to 50%, which will lead to large roughness values in WDS model calibration. Therefore the flow conditions and pipe installation age should be taken into account in the model preparation phase. Actual pipe diameters should be estimated and used in the WDS model calibration because this leads to more realistic roughness values and average flow velocities. This is very important in case of water quality modelling and risk assessment.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lansey, K.E.; El-Shorbagy, W.; Ahmed, I.; Araujo, J.; Haan, C.T. Calibration assessment and data collection for water distribution networks. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 127, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.T.; Spall, R.E.; Barfuss, S.L. Application of three RANS turbulence models to aged water transmission pipes. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 137, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiljev, A.; Koppel, T. Estimation of real-time demands on the basis of pressure measurements by different optimization methods. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2015, 80, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annus, I.; Vassiljev, A. Different approaches for calibration of an operational water distribution system containing old pipes. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxall, J.B.; Saul, A.J.; Skipworth, P.J. Modeling for hydraulic capacity. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2004, 96, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijiapurapu, S.; Cui, J. Performance of turbulence models for flows through rough pipes. Appl. Math. Model. 2010, 34, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijiapurapu, S.; Cui, J. Simulation of turbulent flow in a ribbed pipe using large eddy simulation. Numer. Heat Transf. A Appl. 2007, 51, 1137–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stel, H.; Morales, R.E.M.; Franco, A.T.; Junqueira, S.L.M.; Erthal, R.H.; Gonc¸alves, M.A.L. Numerical and experimental analysis of turbulent flow in corrugated pipes. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 2010, 132, 071203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stel, H.; Franco, A.T.; Junqueira, S.L.M.; Erthal, R.H.; Mendes, R.; Gonc¸alves, M.A.L.; Morales, R.E.M. Turbulent flow in d-type corrugated pipes: Flow pattern and friction factor. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 2012, 134, 121202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calomino, F.; Tafarojnoruz, A.; De Marchis, M.; Gaudio, R.; Napoli, E. Experimental and numerical study in the flow field and friction factor in a pressurized corrugated pipe. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kändler, N. Optimal Algorithm for Rehabilitation of a Water Distribution Network. Master’s Thesis, Tallinn University of Technology, Tallinn, Estonia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, D.C. Turbulence Modeling for CFD; DCW Industries Inc.: La Canada, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Annus, I.; Kaur, K.; Vassiljev, A.; Laanearu, J.; Šanin, M. Flow dynamics in a pipe with a sudden change in diameter. In Proceedings of the 14th International CCWI Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 7–9 November 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Vreeburg, J.H.G.; Blokker, E.J.M.; Horst, P.; van Dijk, J.C. Velocity-based self-cleaning residential drinking water distribution systems. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2009, 9, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreeburg, J.H.G.; Boxall, J.B. Discolouration in potable water distribution systems: A review. Water Res. 2007, 41, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

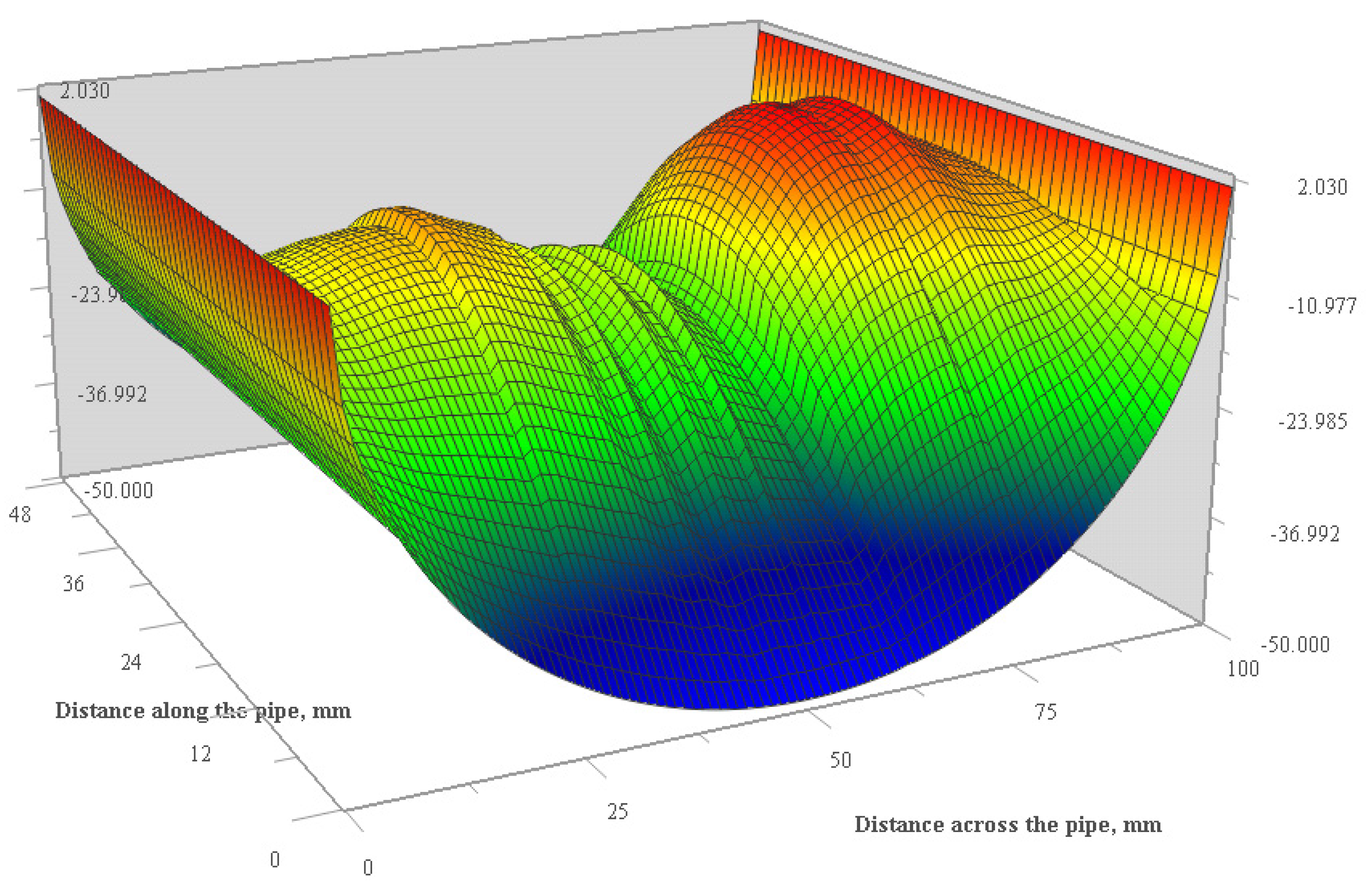

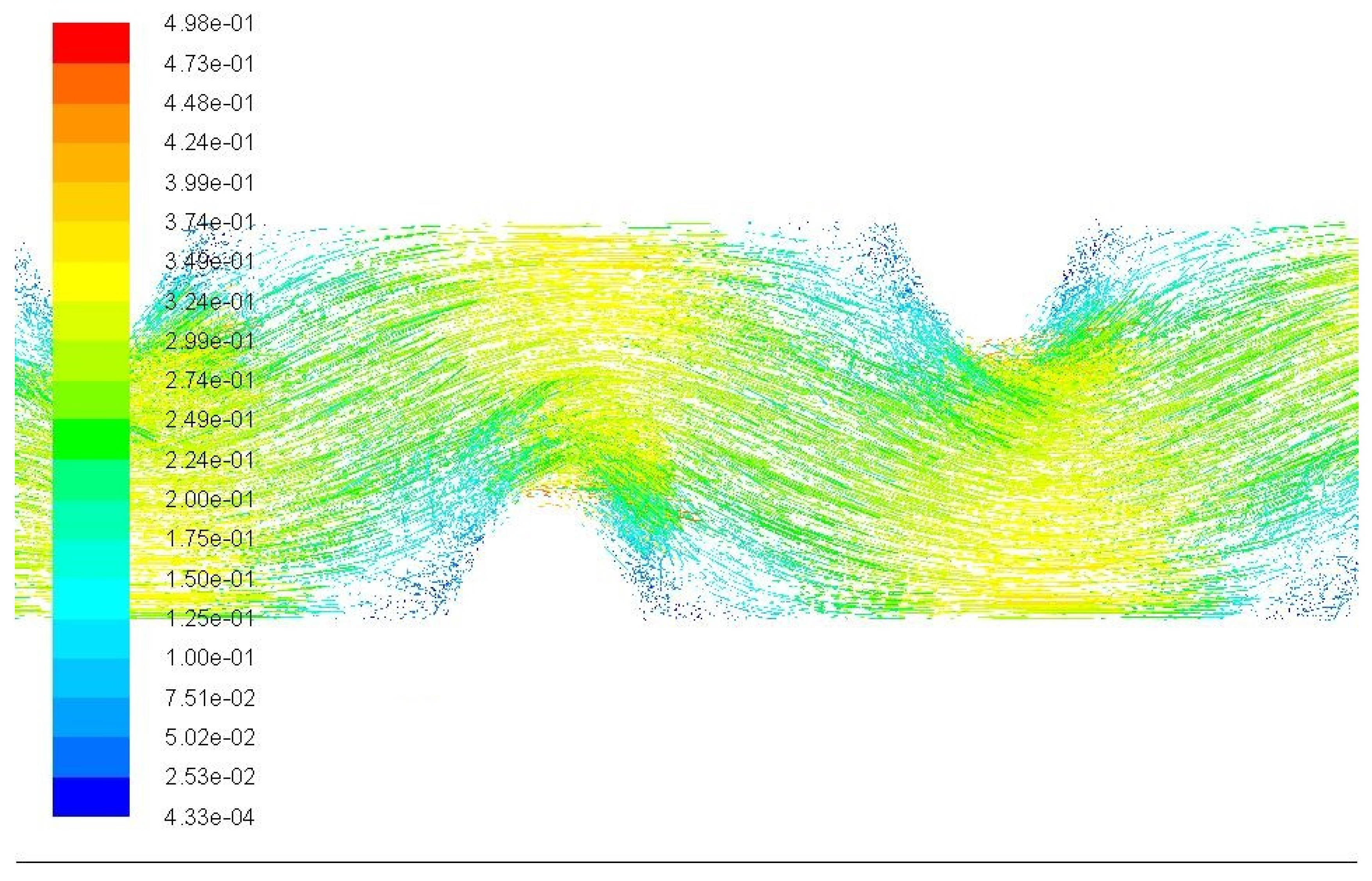
| Pressure Drop, Pa | QCFD, L/s | Umean, CFD, m/s | Roughness in CDF Model, mm | Roughness Estimated by EPANET2, mm | Umean at Nominal Diameter, m/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2500 | 10.50 | 1.48 | 1.00 | 2.66 | 1.34 |
| 2000 | 9.46 | 1.33 | 1.00 | 2.56 | 1.20 |
| 1500 | 8.27 | 1.17 | 1.00 | 2.43 | 1.05 |
| 1100 | 7.15 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 2.3 | 0.91 |
| 900 | 6.51 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 2.22 | 0.83 |
| 700 | 5.80 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 2.09 | 0.74 |
| 500 | 4.96 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 1.96 | 0.63 |
| 300 | 3.89 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 1.81 | 0.49 |
| 200 | 3.19 | 0.45 | 1.00 | 1.74 | 0.41 |
| 100 | 2.26 | 0.32 | 1.00 | 1.66 | 0.29 |
| 50 | 1.60 | 0.23 | 1.00 | 1.59 | 0.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaur, K.; Annus, I.; Vassiljev, A.; Kändler, N. Determination of Pressure Drop and Flow Velocity in Old Rough Pipes. Proceedings 2018, 2, 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110590
Kaur K, Annus I, Vassiljev A, Kändler N. Determination of Pressure Drop and Flow Velocity in Old Rough Pipes. Proceedings. 2018; 2(11):590. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110590
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaur, Katrin, Ivar Annus, Anatoli Vassiljev, and Nils Kändler. 2018. "Determination of Pressure Drop and Flow Velocity in Old Rough Pipes" Proceedings 2, no. 11: 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110590
APA StyleKaur, K., Annus, I., Vassiljev, A., & Kändler, N. (2018). Determination of Pressure Drop and Flow Velocity in Old Rough Pipes. Proceedings, 2(11), 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110590





