Estimation of PM10 Distribution using Landsat5 and Landsat8 Remote Sensing †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
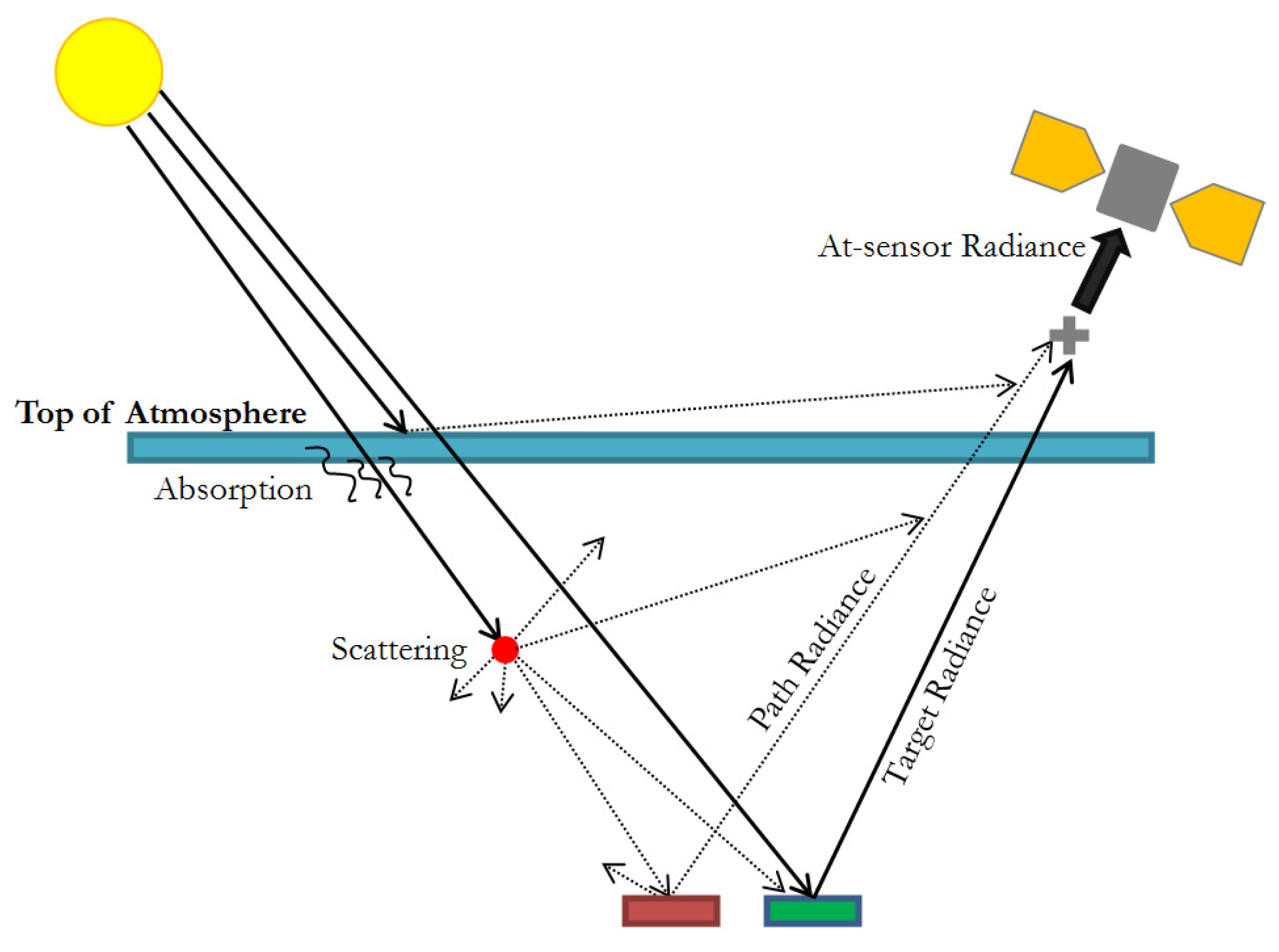
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Adquisition
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
References
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakiya, R.S.; Singh, S.K.; Shah, U. GIS application for spatial and temporal analysis of the air pollutants in urban area. Int. J. Adv. Remote Sens. GIS 2015, 4, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Ait Quality Guidelines. Global Update 2005 Ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Ambient (Outdoor) Air Quality and Health: Fact Sheet. 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs313/en/ (accessed on 31 May 2018).
- Emili, E.; Popp, C.; Petitta, M.; Riffler, M.; Zebisch, M. PM10 remote sensing from geostationary SEVIRI and polar-orbiting MODIS sensors over the complex terrain of the European Alpine region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2485–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Retrieval of high-resolution atmospheric particulate matter concentrations from satellite-based aerosol optical thickness over the Pearl River Delta Area, China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7914–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; MatJafri, M.Z.; Abdullah, K.; Saleh, N.M. PM10 retrieval in urban area from space. In Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery XIII; Shen, S.S., Lewis, P.E., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Orlando, FL, USA, 2007; p. 65651Z. [Google Scholar]
- ESPA Ordering Interface. Available online: https://espa.cr.usgs.gov (accessed on 8 May 2017).
- Yoram, J.K. Aerosol optical thickness and atmospheric path radiance. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 2677–2692. [Google Scholar]
- Landsat USGS. Differences between Landsat 4–7 and Landsat 8 Surface Reflectance Algorithms. 2018. Available online: https://landsat.usgs.gov/landsat-surface-reflectance-data-products (accessed on 31 May 2018).
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immitzer, M.; Vuolo, F.; Atzberger, C. First Experience with Sentinel-2 Data for Crop and Tree Species Classifications in Central Europe. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random Forests for land cover classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by Random Forest. R. News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computin; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 31 May 2018).

| LANDSAT-5 TM | LANDSAT-8 OLI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Band (Description) | Wavelength (Micrometers) | Resolution (Meters) | Band (Description) | Wavelength (Micrometers) | Resolution (Meters) |
| 1 (Blue) | 0.45–0.52 | 30 | 2 (Blue) | 0.45-0.51 | 30 |
| 2 (Green | 0.52–0.60 | 30 | 3 (Green | 0.53-0.59 | 30 |
| 3 (Red) | 0.53–0.60 | 30 | 4 (Red) | 0.64-0.67 | 30 |
| 4 (Near infrared) | 0.76–0.90 | 30 | 5 (Near infrared) | 0.85-1.88 | 30 |
| 5 (SWIR1 1) | 1.55–1.75 | 30 | 6 (SWIR 1 1) | 1.57-1.65 | 30 |
| 7 (SWIR1 2) | 2.08–2.35 | 30 | 7 (SWIR 1 2) | 2.11-2.29 | 30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Pacheco, V.M.; López-Sánchez, C.A.; Álvarez-Álvarez, E.; López, M.J.S.; García-Expósito, L.; Yudego, E.A.; Carús-Candás, J.L. Estimation of PM10 Distribution using Landsat5 and Landsat8 Remote Sensing. Proceedings 2018, 2, 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2231430
Fernández-Pacheco VM, López-Sánchez CA, Álvarez-Álvarez E, López MJS, García-Expósito L, Yudego EA, Carús-Candás JL. Estimation of PM10 Distribution using Landsat5 and Landsat8 Remote Sensing. Proceedings. 2018; 2(23):1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2231430
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Pacheco, V. M., C. A. López-Sánchez, E. Álvarez-Álvarez, M. J. Suárez López, L. García-Expósito, E. Antuña Yudego, and J. L. Carús-Candás. 2018. "Estimation of PM10 Distribution using Landsat5 and Landsat8 Remote Sensing" Proceedings 2, no. 23: 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2231430
APA StyleFernández-Pacheco, V. M., López-Sánchez, C. A., Álvarez-Álvarez, E., López, M. J. S., García-Expósito, L., Yudego, E. A., & Carús-Candás, J. L. (2018). Estimation of PM10 Distribution using Landsat5 and Landsat8 Remote Sensing. Proceedings, 2(23), 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2231430







