Optimization of the Emulsion Electrospinning for Increased Activity of Biopharmaceuticals †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Emulsion Preparation for Electrospinning Process
2.2.2. Electrospinning Process
2.2.3. Fiber Characterization—Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.2.4. Protein Release Characterization
2.2.5. Activity of the Encapsulated Proteins
3. Results
3.1. Influence of the Protein Stabilizers in the Water Phase
3.2. Influence of the PVA in the Water Phase
3.3. Influence of the Electrospinning Parameters on the Activity of the Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Yu, D.G.; Li, J.J.; Williams, G.R.; Zhao, M. Electrospun amorphous solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drugs: A review. J. Control. Release 2018, 292, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarin, A.L. Coaxial electrospinning and emulsion electrospinning of core-shell fibers. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzgo, M.; Mickova, A.; Rampichova, M.; Doupnik, M. Blend electrospinning, coaxial electrospinning, and emulsion electrospinning techniques. In Core-Shell Nanostructures for Drug Delivery and Theranostics, 1st ed.; Focarete, M., Tamprieri, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 325–347. ISBN 978-0-08-102198-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sy, J.C.; Klemm, A.S.; Shastri, V.P. Emulsion as a Means of Controlling Electrospinning of Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, P.; Szabó, E.; Domokos, A.; Hirsch, E.; Galata, D.; Farkas, B.; Démuth, B.; Andersen, S.K.; Vigh, T.; Verreck, G.; et al. Scale-up of electrospinning technology: Applications in the pharmaceutical industry. Wiley Interdiscip. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, T.; Arinzeh, T.L. Examining the formulation of emulsion electrospinning for improving the release of bioactive proteins from electrospun fibers: Formulation of Emulsion Electrospinning. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2014, 102, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Ye, Z.; Ren, H.; Chen, N.; Zeng, Q.; Wu, X.; Lu, T. Bioactivity assessment of PLLA/PCL/HAP electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Life Sci. 2016, 148, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Place, L.W.; Sekyi, M.; Taussig, J.; Kipper, M.J. Two-Phase Electrospinning to Incorporate Polyelectrolyte Complexes and Growth Factors into Electrospun Chitosan Nanofibers. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Mesa, C. Polymer–surfactant and protein–surfactant interactions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 286, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, T.; Matos, J.; Collins, G.; Arinzeh, T.L. Evaluating protein incorporation and release in electrospun composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2015, 103, 3117–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Qian, Y.; Li, L.; Pan, L.; Njunge, L.W.; Dong, L.; Yang, L. Evaluation of emulsion electrospun polycaprolactone/hyaluronan/epidermal growth factor nanofibrous scaffolds for wound healing. J. Biomater. Appl. 2016, 30, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribst, A.A.L.; Cota, J.; Murakami, M.T.; Cristianini, M. Effects of High Pressure Homogenization on the Activity, Stability, Kinetics and Three-Dimensional Conformation of a Glucose Oxidase Produced by Aspergillus niger. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, S.; Wagner, G.; Urban, K.; Ulrich, J. High-Pressure Homogenization as a Process for Emulsion Formation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2004, 27, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juttulapa, M.; Piriyaprasarth, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Sriamornsak, P. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on stability of emulsions containing zein and pectin. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; He, S.; Cheng, L.; Chen, F.; Zhou, S.; Weng, J. Biodegradable ultrafine fibers with core-sheath structures for protein delivery and its optimization. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Sun, Y.; Yang, F.; van den Beucken, J.J.J.P.; Fan, M.; Chen, Z.; Jansen, J.A. Bioactive Electrospun Scaffolds Delivering Growth Factors and Genes for Tissue Engineering Applications. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Yu, D.; Zhu, L.; Branford-White, C.; White, K.; Chatterton, N.P. Electrospun diclofenac sodium loaded Eudragit® L 100-55 nanofibers for colon-targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 408, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
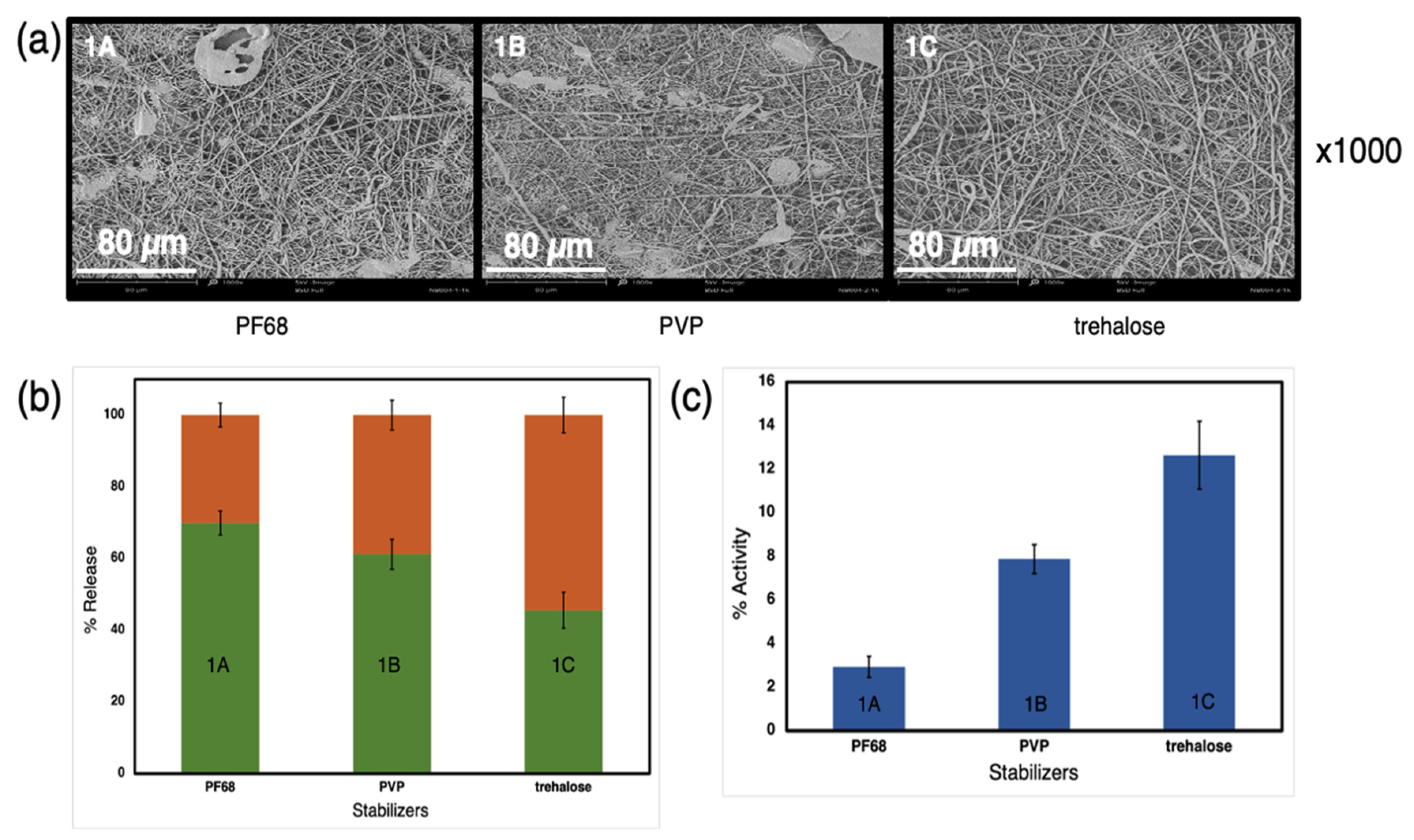
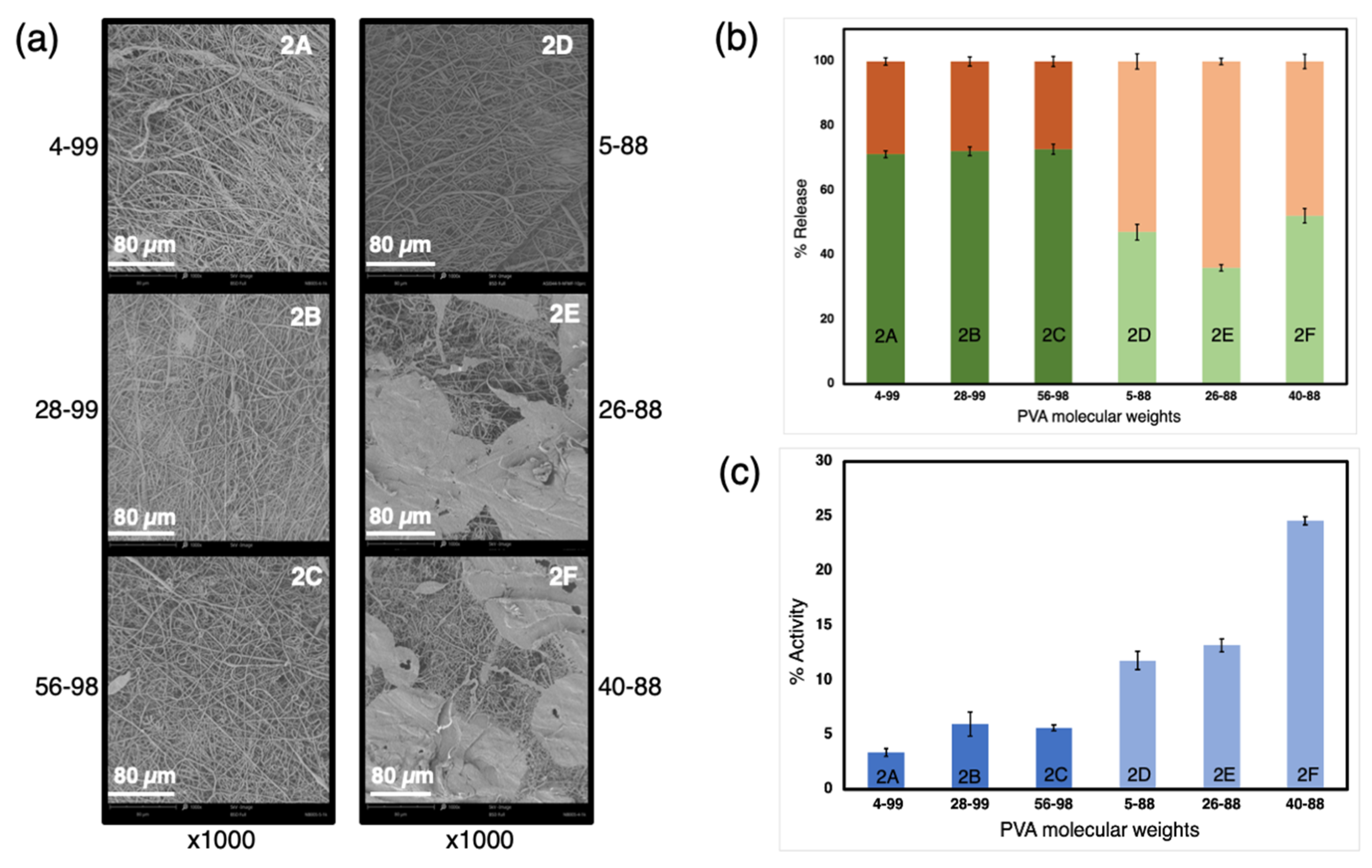
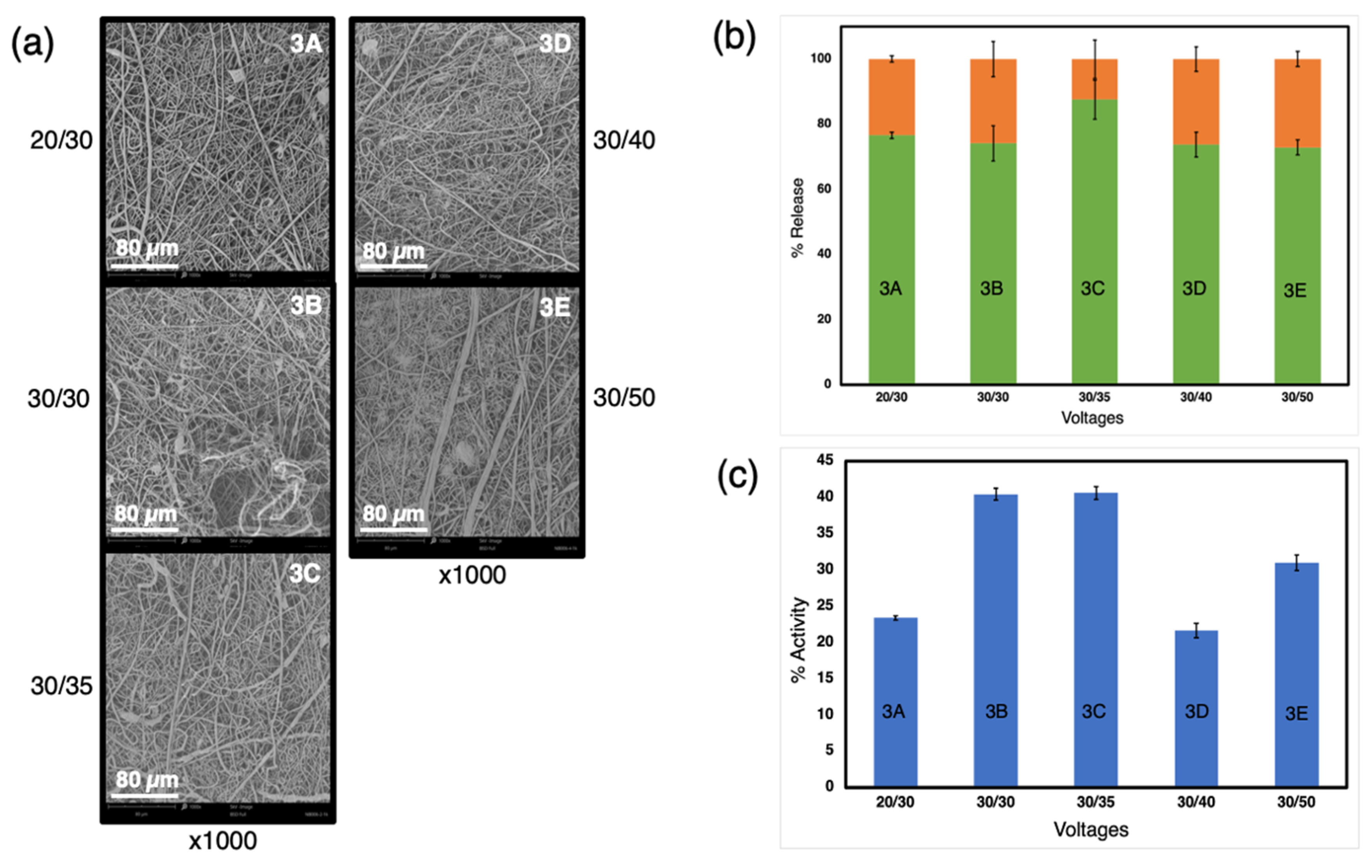
| Exp. | Sample | Composition of Water Phase | Voltage (−/+) kV | Emulsion Mixing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1A | 3% 5–88 kDa polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) + 6% PF68 + 0.2% Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) + distilled water (DW) | 30/40 | by homoge-nizer |
| 1B | 3% 5–88 kDa PVA + 6% PVP + 0.2% HRP + DW | |||
| 1C | 3% 5–88 kDa PVA + 6% trehalose + 0.2% HRP + DW | |||
| 2 | 2A | 3% 4–99 PVA + 6% trehalose + 0.2% HRP + DW | 30/40 | by homoge-nizer |
| 2B | 3% 28–99 PVA + 6% trehalose + 0.2% HRP + DW | |||
| 2C | 3% 56–98 PVA + 6% trehalose + 0.2% HRP + DW | |||
| 2D | 3% 5–88 PVA + 6% trehalose + 0.2% HRP + DW | |||
| 2E | 3% 26–88 PVA + 6% trehalose + 0.2% HRP + DW | |||
| 2F | 3% 40–88 PVA + 6% trehalose + 0.2% HRP + DW | |||
| 3 | 3A | 3% 56–98 kDa PVA + 6% trehalose + 0.2% HRP + DW | 20/30 | by hand |
| 3B | 30/30 | |||
| 3C | 30/35 | |||
| 3D | 30/40 | |||
| 3E | 30/50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burlaga, N.; Bartolewska, M.; Buzgo, M.; Simaite, A. Optimization of the Emulsion Electrospinning for Increased Activity of Biopharmaceuticals. Proceedings 2021, 78, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08673
Burlaga N, Bartolewska M, Buzgo M, Simaite A. Optimization of the Emulsion Electrospinning for Increased Activity of Biopharmaceuticals. Proceedings. 2021; 78(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08673
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurlaga, Natalia, Magdalena Bartolewska, Matej Buzgo, and Aiva Simaite. 2021. "Optimization of the Emulsion Electrospinning for Increased Activity of Biopharmaceuticals" Proceedings 78, no. 1: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08673
APA StyleBurlaga, N., Bartolewska, M., Buzgo, M., & Simaite, A. (2021). Optimization of the Emulsion Electrospinning for Increased Activity of Biopharmaceuticals. Proceedings, 78(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08673





