Closed-Loop Temperature and Force Control of Additive Friction Stir Deposition
Abstract
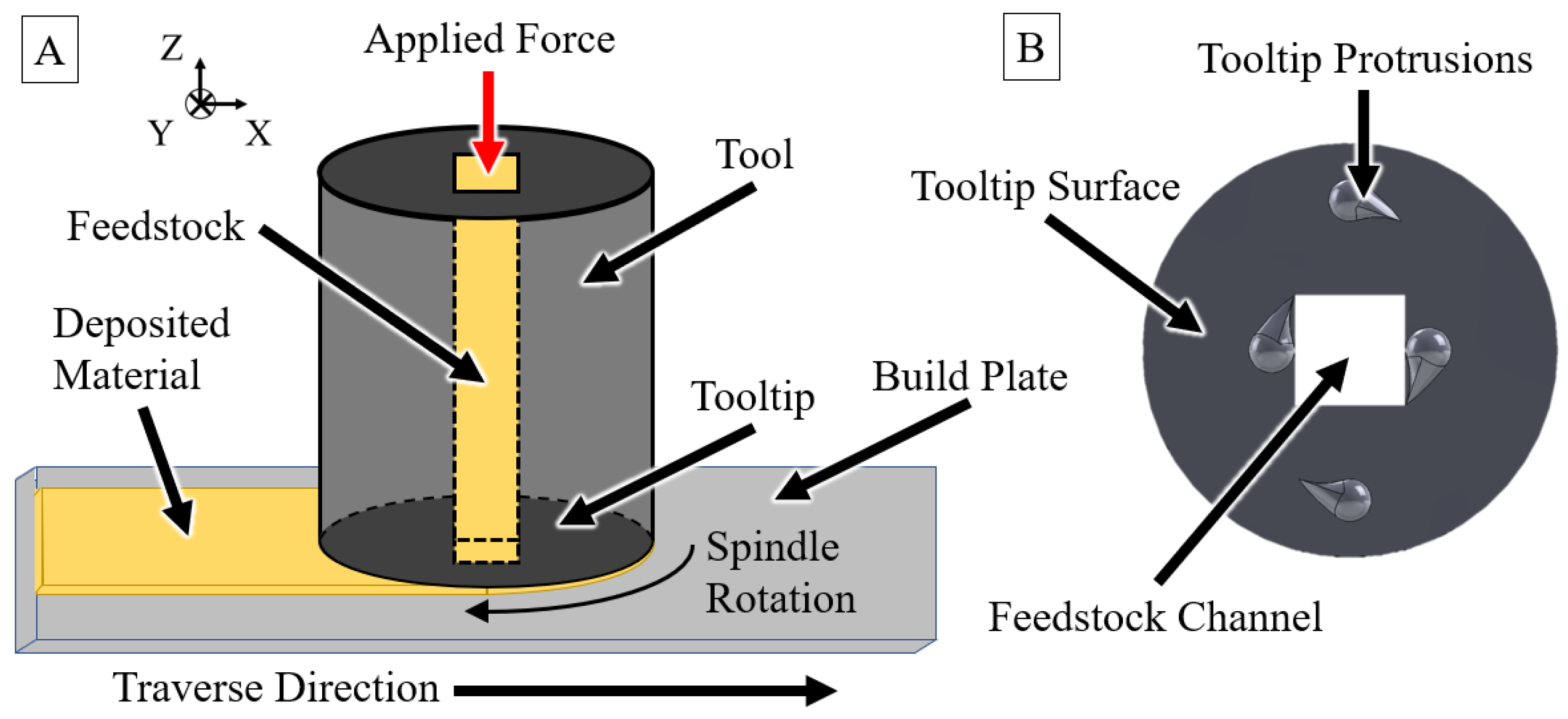
:1. Introduction
2. Process Description
3. Preexisting Setup
3.1. Preexisting Hardware
3.2. Preexisting Control Design
4. Modified Setup
4.1. Modified Hardware
4.2. Modified Control Design
4.2.1. Temperature Control
4.2.2. Force Control
5. Experimental Procedure and Results
5.1. Controller Implementation
5.2. Experimental Design
5.3. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, W.M.; Nicholas, E.D.; Needham, J.C.; Murch, M.G.; Temple-Smith, P.; Dawes, C.J. Friction Stir Welding. GB Patent No. 9125978.8, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, S.; Mishra, R. Building without melting: A short review of friction-based additive manufacturing techniques. Int. J. Addit. Subtractive Mater. Manuf. 2017, 1, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Haridas, R.S.; Agrawal, P. Friction stir-based additive manufacturing. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2022, 27, 141–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Kumar, N.; Dixit, A.R. Friction stir additive manufacturing—An innovative tool to enhance mechanical and microstructural properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 263, 114832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, S.; Sidhar, H.; Mishra, R. Friction Stir Additive Manufacturing: Route to High Structural Performance. JOM 2015, 67, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Z.; Jones, M.E.; Brady, G.W.; Griffiths, R.J.; Garcia, D.; Rauch, H.A.; Cox, C.D.; Hardwick, N. Non-beam-based metal additive manufacturing enabled by additive friction stir deposition. Scr. Mater. 2018, 153, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, A.; Hake, T.; Zaeh, M.F. An Analytical Approach of Modelling Friction Stir Welding. Procedia CIRP 2014, 18, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colligan, K.J.; Mishra, R.S. A conceptual model for the process variables related to heat generation in friction stir welding of aluminum. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbacher, A.; Smith, C.B.; Duffie, N.A.; Ferrier, N.J.; Pfefferkorn, F.E.; Zinn, M.R. Combined Temperature and Force Control for Robotic Friction Stir Welding. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2014, 136, 021007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, R.; Roy, G.G.; Lienert, T.J.; Debroy, T. Three-dimensional heat and material flow during friction stir welding of mild steel. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, K.; Lyne, S.G.; Kiss, L. Optimization of Friction Stir Welding Tool Advance Speed via Monte-Carlo Simulation of the Friction Stir Welding Process. Materials 2014, 7, 3435–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Tan, Z.J.; Li, J.Y.; Zu, Y.; Liu, W.; Sha, J. Experimental and numerical studies of re-stirring and re-heating effects on mechanical properties in friction stir additive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 104, 767–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.N.; Young, B. Material properties of normal and high strength aluminium alloys at elevated temperatures. Thin-Walled Struct. 2019, 137, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhshi, F.; Gerlich, A. Potentials and strategies of solid-state additive friction-stir manufacturing technology: A critical review. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 36, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.C.; Rutherford, B.A.; Avery, D.Z.; Phillips, B.J.; Rao, H.; Rekha, M.Y.; Brewer, L.N.; Allison, P.G.; Jordon, J.B. The effect of solutionizing and artificial aging on the microstructure and mechanical properties in solid-state additive manufacturing of precipitation hardened Al–Mg–Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 819, 141351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.J.; Williamson, C.J.; Kinser, R.P.; Jordon, J.B.; Doherty, K.J.; Allison, P.G. Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization of Additive Friction Stir-Deposition of Aluminum Alloy 5083 Effect of Lubrication on Material Anisotropy. Materials 2021, 14, 6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Z.; Mishra, R.S. Additive friction stir deposition: A deformation processing route to metal additive manufacturing. Mater. Res. Lett. 2021, 9, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.J.; Avery, D.Z.; Liu, T.; Rodriguez, O.L.; Mason, C.J.T.; Jordon, J.B.; Brewer, L.N.; Allison, P.G. Microstructure-deformation relationship of additive friction stir-deposition Al–Mg–Si. Materialia 2019, 7, 100387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, D.Z.; Phillips, B.J.; Mason, C.J.T.; Palermo, M.; Williams, M.B.; Cleek, C.; Rodriguez, O.L.; Allison, P.G.; Jordon, J.B. Influence of Grain Refinement and Microstructure on Fatigue Behavior for Solid-State Additively Manufactured Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 2778–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson-Wedge, K.; Stubblefield, G.; Zhu, N.; Long, B.; Daniewicz, S.R.; Allison, P.G.; Sowards, J.; Rodriguez, O.; Amaro, R. Characterization of the evolution of 2219-T87 aluminum as a function of the friction stir welding process. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 142, 105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, M.E.J.; Griffiths, R.J.; Garcia, D.; Sietins, J.M.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, H.Z. Morphological and microstructural investigation of the non-planar interface formed in solid-state metal additive manufacturing by additive friction stir deposition. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson-Wedge, K.; Avery, D.Z.; Daniewicz, S.R.; Sowards, J.W.; Allison, P.G.; Jordon, J.B.; Amaro, R.L. Characterization of the fatigue behavior of additive friction stir-deposition AA2219. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 142, 105951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.J.T.; Rodriguez, R.I.; Avery, D.Z.; Phillips, B.J.; Bernarding, B.P.; Williams, M.B.; Cobbs, S.D.; Jordon, J.B.; Allison, P.G. Process-structure-property relations for as-deposited solid-state additively manufactured high-strength aluminum alloy. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 40, 101879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, O.G.; Allison, P.G.; Brewer, L.N.; Rodriguez, O.L.; Jordon, J.B.; Liu, T.; Whittington, W.R.; Martens, R.L.; McClelland, Z.; Mason, C.J.T.; et al. Influence of texture and grain refinement on the mechanical behavior of AA2219 fabricated by high shear solid state material deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 724, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, B.A.; Avery, D.Z.; Phillips, B.J.; Rao, H.M.; Doherty, K.J.; Allison, P.G.; Brewer, L.N.; Jordon, J.B. Effect of thermomechanical processing on fatigue behavior in solid-state additive manufacturing of Al-Mg-Si alloy. Metals 2020, 10, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.; Perry, M.; Sietins, J.; Zhu, Y.; Hardwick, N.; Cox, C.; Rauch, H.; Yu, H. A Perspective on Solid-State Additive Manufacturing of Aluminum Matrix Composites Using MELD. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 28, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.W.; Williams, M.B.; Rao, H.M.; Kinser, R.P.; Allison, P.G.; Jordon, J.B. Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of a Solid-State Additive Manufactured Magnesium Alloy. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2021, 144, 061013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.B.; Robinson, T.W.; Williamson, C.J.; Kinser, R.P.; Ashmore, N.A.; Allison, P.G.; Jordon, J.B. Elucidating the Effect of Additive Friction Stir Deposition on the Resulting Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Magnesium Alloy WE43. Metals 2021, 11, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priedeman, J.L.; Phillips, B.J.; Lopez, J.J.; Tucker Roper, B.E.; Hornbuckle, B.C.; Darling, K.A.; Jordon, J.B.; Allison, P.G.; Thompson, G.B. Microstructure Development in Additive Friction Stir-Deposited Cu. Metals 2020, 10, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.J.; Garcia, D.; Song, J.; Vasudevan, V.K.; Steiner, M.A.; Cai, W.; Yu, H.Z. Solid-state additive manufacturing of aluminum and copper using additive friction stir deposition: Process-microstructure linkages. Materialia 2021, 15, 100967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, O.; Allison, P.G.; Jordon, J.B.; Rodriguez, O.; Brewer, L.; Mcclelland, Z.; Whittington, W.; Francis, D.; Su, J.; Martens, R.; et al. Microstructures and mechanical behavior of Inconel 625 fabricated by solid-state additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 694, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, D.Z.; Rivera, O.G.; Mason, C.J.T.; Phillips, B.J.; Jordon, J.B.; Su, J.; Hardwick, N.; Allison, P.G. Fatigue Behavior of Solid-State Additive Manufactured Inconel 625. JOM 2018, 70, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Haridas, R.S.; Yadav, S.; Thapliyal, S.; Gaddam, S.; Verma, R.; Mishra, R.S. Processing-structure-property correlation in additive friction stir deposited Ti-6Al-4V alloy from recycled metal chips. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 47, 102–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubblefield, G.; Fraser, K.; Phillips, B.; Jordon, J.B.; Allison, P.G. A Meshfree Computational Framework for the Numerical Simulation of the Solid-state Additive Manufacturing Process, Additive Friction Stir-deposition (AFS-D). Mater. Des. 2021, 202, 109514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubblefield, G.G.; Fraser, K.A.; Van Iderstine, D.; Mujahid, S.; Rhee, H.; Jordon, J.B.; Allison, P.G. Elucidating the Influence of Temperature and Strain Rate on the Mechanics of AFS-D Through a Combined Experimental and Computational Approach. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 305, 117593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbacher, A.; Duffie, N.; Ferrier, N.; Pfefferkorn, F.; Zinn, M. Toward Automation of Friction Stir Welding Through Temperature Measurement and Closed-Loop Control. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2011, 133, 051008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, K.; Sorensen, C. Advances in Temperature Control for FSP; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, A.; Munro, T.R.; Hovanski, Y. Evaluating Temperature Control in Friction Stir Welding for Industrial Applications. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, A.; Gamper, J.; Krutzlinger, M.; Zens, A.; Zaeh, M. Adaptive model-based temperature control in friction stir welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.J.; Mason, C.J.T.; Beck, S.C.; Avery, D.Z.; Doherty, K.J.; Allison, P.G.; Jordon, J.B. Effect of Parallel Deposition Path and Interface Material Flow on Resulting Microstructure and Tensile Behavior of Al-Mg-Si Alloy Fabricated by Additive Friction Stir Deposition. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 295, 117169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, D.Z.; Cleek, C.E.; Phillips, B.J.; Rekha, M.Y.; Kinser, R.P.; Rao, H.M.; Brewer, L.N.; Allison, P.G.; Jordon, J.B. Evaluation of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy Repaired via Additive Friction Stir Deposition. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2022, 144, 031003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.J.T.; Avery, D.Z.; Phillips, B.J.; Jordon, J.B.; Allison, P.G. Strain Rate Dependent Plasticity Model for Precipitate Hardened Aerospace Aluminum Alloy Produced with Solid-State Additive Manufacturing. J. Dyn. Behav. Mater. 2021, 8, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Avery, D.Z.; Rutherford, B.A.; Phillips, B.J.; Allison, P.G.; Jordon, J.B.; Brewer, L.N. The Effect of Anodization on the Mechanical Properties of AA6061 Produced by Additive Friction Stir-Deposition. Metals 2021, 11, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.; Hartley, W.D.; Rauch, H.; Griffiths, R.; Wang, R.; Kong, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, H. In Situ Investigation into Temperature Evolution and Heat Generation during Additive Friction Stir Deposition: A Comparative Study of Cu and Al-Mg-Si. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 34, 101386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbacher, A.; Duffie, N.; Ferrier, N.; Pfefferkorn, F.; Zinn, M. Effects of tool–workpiece interface temperature on weld quality and quality improvements through temperature control in friction stir welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 71, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meld Manufacturing. B8 Operator Manual; Meld Manufacturing: Christiansburg, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, H.K. Nonlinear Systems, 3rd ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Parida, B.; Vishwakarma, S.; Pal, S. Design and development of fixture and force measuring system for friction stir welding process using strain gauges. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Pal, S.; Bag, S. Design and development of force and torque measurement setup for real time monitoring of friction stir welding process. Measurement 2017, 103, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstic, M. Delay Compensation for Nonlinear, Adaptive, and PDE Systems; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]













| Protocol | (°C) | (N) | Max Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | - - | 102.3 ± 130.8 | 396.8 N |
| B | - - | 151.2 ± 257.1 | 350.1 N |
| C | - - | 138.3 ± 175.3 | 565.8 N |
| D | 6.0 ± 6.8 | - - | 8.1 °C |
| E | 8.2 ± 4.5 | - - | 11.3 °C |
| F | 6.5 ± 3.8 | - - | 10.5 °C |
| G | 5.4 ± 6.5 | 140.1 ± 213.5 | 13.2 °C, 376.9 N |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merritt, G.R.; Williams, M.B.; Allison, P.G.; Jordon, J.B.; Rushing, T.W.; Cousin, C.A. Closed-Loop Temperature and Force Control of Additive Friction Stir Deposition. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2022, 6, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp6050092
Merritt GR, Williams MB, Allison PG, Jordon JB, Rushing TW, Cousin CA. Closed-Loop Temperature and Force Control of Additive Friction Stir Deposition. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2022; 6(5):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp6050092
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerritt, Glen R., Malcolm B. Williams, Paul G. Allison, James B. Jordon, Timothy W. Rushing, and Christian A. Cousin. 2022. "Closed-Loop Temperature and Force Control of Additive Friction Stir Deposition" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 6, no. 5: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp6050092
APA StyleMerritt, G. R., Williams, M. B., Allison, P. G., Jordon, J. B., Rushing, T. W., & Cousin, C. A. (2022). Closed-Loop Temperature and Force Control of Additive Friction Stir Deposition. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 6(5), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp6050092








