Tuning of Dielectric Properties of Polymers by Composite Formation: The Effect of Inorganic Fillers Addition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Scientific Approach to Design Polymer Composites
3. Experimental Techniques for the Synthesis of Composites
3.1. Sol Gel Method
3.2. Solution Casting Technique
3.3. Radiation Technique
4. Factors Affecting Dielectric Properties of Polymer Composites
4.1. Dispersion Mechanism in Composites
4.2. Filler Size and Shape
4.3. Porosity
4.4. Loading of Fillers
5. Dielectric Properties and Relaxation Behavior of PMMA and PMMA Based Composite Films
5.1. Alumina (Al2O3) Nanoparticles
5.2. Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Nanoparticles
5.3. Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles
5.4. Tin Oxide (SnO2) Nanoparticles
5.5. Silica (SiO2) Nanoparticles
5.6. Lithium Triflate (LiCF3SO3) as Ionic Salt and Mont Morillonite (MMT) Clay
5.7. Lithium Chlorate Ionic Salt and MMT-Clay
5.8. Sr2TiMnO6 (STMO)/CaCu3Ti4O12 (CCTO) Ceramics
6. Some Reported Experimental Results (Case Studies)
7. Future Development and Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arbatti, M.; Shan, X.; Cheng, Z.-Y. Ceramic–Polymer Composites with High Dielectric Constant. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1369–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popielarz, R.; Chiang, C.K.; Nozaki, R.; Obrzut, J. Dielectric properties of polymer/ferroelectric ceramic composites from 100 Hz to 10 GHz. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, S.M. Dielectric Polymers in Functional Polymers. Polymers and Polymeric Composites: A Reference Series, 2nd ed.; Mazumder, M.J., Sheardown, H., Al Ahmed, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-92067-2. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Jiang, P.; Tanaka, T. A review of dielectric polymer composites with high thermal conductivity. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2011, 27, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bataineh, Q.M.; Ahmad, A.; Alsaad, A.M.; Ahmad, D. Optical characterization of PMMA/metal oxide nanoparticles thin films: Bandgap engineering using a novel derived model. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, S.; Liew, C.-W.; Ramesh, K. Evaluation and investigation on the effect of ionic liquid onto PMMA-PVC gel polymer blend electrolytes. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 2132–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, K.G. Advance Materials. Wiley Online Libr. 1998, 10, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, U.; Hu¨sing, N. Synthesis of Inorganic Materials, 2nd ed.; Wiley VCH: Weinheim, German, 2005; ISBN 978-3-527-31037-1. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, U. Polymers Reinforced by Covalently Bonded Inorganic Clusters. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3487–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Work, W.J.; Horie, K.; Hess, M.; Stepto, R.F.T. Definitions of terms related to polymer blends, composites, and multiphase polymeric materials. Pure Appl. Chem. 2004, 76, 1985–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeba, F.; Gupta, A.K.; Kulshrestha, V.; Bafna, M.; Jain, A. Investigations on dielectric properties of PVDF/PMMA blends. Mater. Today Proc. Sci. Direct 2022, 66, 3547–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobhna, C.; Sengwa, R.J. Effect of different inorganic nanoparticles on the structural, dielectric and ion transportation properties of polymers blend based nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes. Electrochem. Acta 2017, 247, 924–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suporva, M.; Martynkova, G.S.; Barabaszova, K. Effect of Nano fillers Dispersion in Polymer Matrices: A Review. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2011, 3, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghule, B.; Laad, M. Polymer composites with improved dielectric properties: A review. Ukr. J. Phys. 2021, 66, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Di-Benedetto, S.A.; Tewari, P.; Lanagan, M.T.; Ratner, M.A.; Marks, T.J. Nanoparticle, size, shape, and interfacial effects on leakage current density, permittivity, and breakdown strength of metal oxide-polyolefin nanocomposites: Experiment and theory. Chem. Mater 2010, 22, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, M.T.; Jantunen, H. Polymer-Ceramic Composites of 0-3 Connectivity for Circuits in Electronics: A Review. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2010, 7, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafna, M.; Sain, N.; Khandelwal, A.; Deeba, F.; Gupta, A.K. Study of refractive index and dispersion behavior of KMnO4 doped poly-methyl-methacrylate(PMMA)composites. Mater. Today Proc. Sci. Direct. 2022, 66, 3481–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, D.; Parker, J.; Wright, P. Complexes of alkali metal ions with poly (ethylene oxide). Polymer 1973, 14, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Liew, C.W.; Morris, E.; Durairaj, R. Effect of PVC on ionic conductivity, crystallographic structural, morphological and thermal characterizations in PMMA–PVC blend-based polymer electrolytes. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 511, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengwa, R.; Dhatarwal, P. Polymer nanocomposites comprising PMMA matrix and ZnO, SnO2, and TiO2 nanofillers: A comparative study of structural, optical, and dielectric properties for multifunctional technological applications. Opt. Mater. 2021, 113, 110837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.-Y.S.; Niidome, Y.; Matsuo, T.; Yamada, S. Temperature Effects on Molecular Alignments at the Surface of Ultrathin Films Studied by SHG and Fluorescence Techniques. Anal. Sci. 1997, 13, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlins, K.; Lees, A.; Fuerniss, S.; Papathomas, K. Brightly Phosphorescent Trinuclear Copper(I) Complexes of Pyrazolates: Substituent Effects on the Supramolecular Structure and Photophysics. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1540–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, S.C.; Patten, T.E. Photoluminescent Polymer/Quantum Dot Composite Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3920–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, M. Interphase in Polymer Nanocomposites. JACS Au 2022, 2, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Wen, L.C. Investigation on the effects of addition of SiO2 nanoparticles on ionic conductivity, FTIR, and thermal properties of nanocomposite PMMA–LiCF3SO3–SiO2. Ionics 2010, 16, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengwa, R.J.; Choudhary, S.; Dhatarwal, P. Investigation of alumina nanofiller impact on the structural and dielectric properties of PEO/PMMA blend matrix-based polymer nanocomposites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2019, 2, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, K.; Ahamed, M.B.; Deshmukh, R.R.; Sada Sivuni, K.K.; Ponama, D.; Pasha, S.K.K.; Almaded, M.A.A.; Polu, A.R.; Chidambaram, K. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 46, 2406–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kanchan, D.K.; Gondaliya, N.; Jayswal, M.; Joge, P. Influence of nano filler on conductivity in PEO-PMMA-AgNO3 polymer blends. Indian J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2013, 51, 346–349. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Jin, Y.; Qiu, Y. The optical and electrical characteristics of PMMA film prepared by spin coating method, IOP conference series. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 87, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.B.G.; Hayes, M. A model for dip-coating of a two liquid mixture. Int. J. Math. Math. Sci. 2002, 29, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, N.; Cui, J.; Ren, X.; Mei, H.; Xu, K.; Idrees, M.; Mei, X. Structural, optical, and electrical characterizations of silver nanowire/single-layer graphene oxide composite film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 602, 154343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengwa, R.J.; Choudhary, S.; Dhatarwal, P. Influences of ultrasonic- and microwave-irradiated preparation methods on the structural and dielectric properties of (PEO–PMMA)–LiCF3SO3–x wt% MMT nanocomposite electrolytes. Ionics 2014, 21, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.P.; Chaudhary, V.; Ahmad, F.; Manral, A. Effect of nanotoxicity and enhancement in performance of polymer compo-sites using nanofillers: A state-of-the-art review. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 2152–21270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeba, F.; Gupta, A.K.; Kulshrestha, V.; Bafna, M.; Jain, A. Analysing the dielectric properties of ZnO doped PVDF/PMMA blend composite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 23703–23713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengwa, R.; Dhatarwal, P.; Choudhary, S. Role of preparation methods on the structural and dielectric properties of plasticized polymer blend electrolytes: Correlation between ionic conductivity and dielectric parameters. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 142, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jmmal, A.Y.; Nada, Z.; Taqa, A.A. The effect of recycled PMMA on some physical and chemical properties of acrylic resin denture base. Int. J. Enhanc. Res. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2018, 7, 2319–7463. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, M.; Patidar, D.; Sharma, K.B.; Saxena, N.S. An approach to correlate experimental and theoretical thermal conductivity of MWNT/PMMA polymer composites. Mater. Res. Express 2015, 2, 095302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.K.; Gupta, A.K.; Khare, N.; Dhawan, S.K.; Gupta, H.C. Synthesis and characterization of polyaniline ZnO composite and its dielectric behavior. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, W.L. Polymer Stabilization; Wiley Inter Science: New York, NY, USA, 1972; p. 188. [Google Scholar]
- Bamford, C.H.; Tipper, C.F.H. Degradation of Polymers; Compton, R.G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; Volume 14, p. 367. ISBN 9780080868080. [Google Scholar]
- Silvia, G.; Daniele, C.; Vito, D.N.; Lidia, A.; Eugenia, T. PMMA: A key macromolecular component for dielectric low-k hybrid inorganic-organic polymer films. Eur. Polym. J. Sci. Direct. 2007, 43, 673–696. [Google Scholar]
- Schreyer, G. Kunstoffe. Polym. A Prop. Database 1972, 55, 737. [Google Scholar]
- Shindo, H.; Murakami, I.; Yamamura, H. Contemporary topics in polymer science. J. Polym. Sci. 1969, 7, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.S.; Forrest, J.A. Thickness dependence of the dynamics in thin films of isotactic poly (methylmethacrylate). Eur. Phys. J. E Soft Mater. 2003, 12, S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, S.; Tominaga, Y.; Asai, S.; Sumita, M.J. Dielectric relaxation behavior of poly(methyl methacrylate) under high-pressure carbon dioxide. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2005, 43, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, D.W. Inorganic Materials Series: Energy Materials, 1st ed.; Bruce, D.W., O’Hare, D., Walton, R.I., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2011; p. 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Hashmi, S.A. Ionic liquid based sodium ion conducting gel polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 2010, 181, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtilman, M.I. New Concepts in Polymer Science, 1st ed.; Polymeric Biomaterials; VSP B.V.: Oud-Beijerland, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 15, Available online: https://openlibrary.org/books/OL22567643M (accessed on 13 August 2022)ISBN 9067643890/9789067643894.
- Vaishya, R.; Chauhan, M.; Vaish, A. Bone cement: Review article. J. Clin. Ortho Paedics Trauma 2013, 4, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, B.A.; Satgunam, M.; Abreeza, N.M.; Abed, A.N. A review on enhancements of PMMA denture base material with different nano-fillers. Cogent Eng. 2021, 8, 1875968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S. Structural and dielectric properties of (PEO–PMMA)–SnO2 nanocomposites. Compos. Commun. 2017, 5, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Agnihotry, S.A. Nanocomposite electrolytes with fumed silica in poly(methyl methacrylate): Thermal, rheological and conductivity studies. J. Power Sources 2005, 140, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, M.O. Tin Oxide Materials: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications, 1st ed.; Orlandi, M.O., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 978-0-12-815924-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T. Dielectric Nanocomposites with Insulating properties. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2005, 12, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aashis, S.; Roy, S.; Gupta, S.; Sindhu, A.; Parveen, C.; Ramamurthy, P. Dielectric properties of novel PEO/ZnO hybrid nanocomposites films. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 47, 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Bafna, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Khanna, R.K. Dielectric properties of potassium permangnate PMMA composite films. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2018, 5, 433. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, L.N.; Farahiyah, S.A.; Habibah, Z.; Herman, S.H.; Rusop, M. Dielectric and physical properties of PMMA: TiO2 thin films by varying TiO2 concentration. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Humanities, Science and Engineering Research, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 24–27 June 2012; pp. 259–262, ISBN 978-1-4673-1311-7. [Google Scholar]
- Dhatarwal, P.; Sengwa, R.J. Dielectric polarisation and relaxation process of the lithium ion conducting polymer blend matrix based electrolyte; effect of TiO2 nano filler. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebahr, J.; Byrne, N.; Forsyth, M.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Jacobson, P. Enhancement of ion dynamics in PMMA–based gels with addition of TiO2 nano–particles. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, A.; Bobowska, I.; Tracz, M.; Opasinska, A.; Kadlubowski, S.; Kaliszewska, A.K.; Grobelny, J.; Wojciechowski, P. Dielectric properties and characterization of titanium dioxide obtained by different chemistry methods. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 124814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, H.; Ghallabi, Z.; Royaud, I.; Arous, M.; Seytre, G.; Boiteux, G.; Kallel, A. Dielectric relaxation behavior in semicrystalline polymer PVDF/TiO2 nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 45, 1119–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.D.; Levich, B.G. Dragging of a liquid by a moving plate. Acta Physiochim. 1942, 17, 42–54. [Google Scholar]
- Farheen, S.; Mathad, R.D. Effect of Nano Filler(TiO2) on conductivity in PEO-PMMA-LiClO4 polymer electrolyte. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 81, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanje, A.S.; Sharma, S.J.; Ningthoujam, R.S.; Ahn, J.S.; Pode, R.B. Low temperature dielectric studies of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles prepared by precipitation method. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Uang, X.; Li, S.; Jiang, P.; Toshikatsu, T. Novel three-dimensional zinc oxide super structures for high dielectric constant polymer composites capable of withstanding high electric field. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2012, 116, 24887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaad, A.M.; AlDairy, A.R.; Ahmad, A.A.; Al Anbar, S.A.; Al B’ataineh, M.Q. Synthesis and characterization of as-grown doped polymerized (PMMA/PVA)/ZnO NPs hybrid thin films. Artic. Polym. Bull. Res. Gate 2022, 79, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, V.D.; Lavina, S.; Negro, E.; Pace, G.; Gross, S.; Depaoli, G.; Vidali, M. Dielectric low-k composite films based on PMMA, PVC and methylsiloxane-silica: Synthesis. Elsevier J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 2878–2888. [Google Scholar]
- Sengwa, R.J.; Dhatarwal, P. Predominantly chain segmental relaxation dependent ionic conductivity of multi-phase semicrystalline PVDF/PEO/LiClO4 solid polymer elctrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 338, 135890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhatarwala, P.; Choudharya, S.; Sengwaa, R.J. Electrochemical performance of Li+-ion conducting solid polymer electrolytes based on PEO–PMMA blend matrix incorporated with various inorganic nano particles for the lithium ion batteries. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobhna, C.; Sengwa, R.J.; Choudhary, S. Dielectric properties and structural dynamics of melt compounded hot-pressed poly(ethylene oxide)–organophilic montmorillonite clay nanocomposite films. Indian Academy of Sciences. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2012, 35, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Achari, V.B.; Reddy, T.J.R.; Sharma, A.K.; Rao, V.V.R.N. Electrical, optical, and structural characterization of polymer blend (PVC/PMMA) electrolyte films. Ionics 2007, 13, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Bama, V.S.; Prabhu, M.R. Effect of lithium salt concentration in PVA-PMMA based gel polymer electrolytes. Ionics 2010, 16, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.; Dakshayini, B.S.; Kushwaha, H.S.; Vaish, R. Effect of Sr2TiMnO6 fillers on mechanical, dielectric and thermal behaviour of PMMA polymer. J. Adv. Dielectr. 2015, 5, 155001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.; Ravindran, R.S.E.; Varma, K.B.R. Dielectric properties of Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)/CaCu3Ti4O12 composites. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 10th International Conference on Properties and Applications of Dielectric Materials, Banglore, India, 24–28 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, J.; Deshmuk, K.; Chidambaram, K.K.; Faisal, M.; Selvarajan, E.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Ahamed, M.B.; Pasha, S.K.K. Dielectric and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of germanium dioxide nanoparticle reinforced poly(vinyl chloride) and poly(methylmethacrylate) blend nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 20172–20188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Batool, S.; Javed, M.S.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, Q.U.; Imran, M.; Rasaki, S.A.; Mwizerwa, J.P.; Chen, Z. Adsorption and electrochemical facet of polymer precursor to yield meso porous carbon ceramic. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.W.; Zheng, M.S.; Fan, B.; Dang, Z.M. Polymer-based dielectrics with high permittivity for electric energy storage: A review. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafna, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Khanna, R.K. Effect of potassium chromate nanoparticles on the optical properties of poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) films. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeba, F.; Bafna, M.; Jain, A. Tuning of electrical properties of polymer blends or composites by doping of salts and inorganic fillers: A review. SGVU Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 8, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Chitra, S.; Mahalakshmi, P.; Radha, K.P. Vibrational and Impedance analysis of polymer electrolyte based on PMMA complexed with adipic acid. Int. J. Multidiscip. Educ. Res. 2016, 1, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Kanchan, D.K.; Gondaliya, N. Effect of nano-filler on structural and Ionic transport properties of plasticized polymer electrolyte. Sci. Res. 2012, 2, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.J.; Zhao, X.H. Polymer Nanocomp, Polymer Nanocomposites for Pressure Sensors, 1st ed.; Zhou, Y., Ding, G., Eds.; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouknaitir, I.; Panniello, A.; Teixeira, S.S.; Kreit, L.; Corricelli, M.; Striccoli, M.; Costa, L.C.; Achour, M.E. Optical and dielectric properties of PMMA (poly(methyl methacrylate))/carbon dots composites. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, C.W.; Ramesh, S.; Durairaj, R. Impact of low viscosity ionic liquid on PMMA-PVC-LiTFSI polymer electrolytes based on AC impedance, dielectric behavior and HATR-FTIR characteristics. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 2996–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, D.; Kinoshita, T.; Watanabe, A.; Konno, M. Fabrication of highly refractive, transparent BaTiO3/poly (methyl methacrylate) composite films with high permittivities. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathesh, R.; Sebastian, M.T. Polymer Ceramic Composites for Microwave Applications. In Microwave Materials and Applications; Sebastian, M.T., Jantunen, H., Ubic, R., Eds.; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Chapter 11; p. 481. ISBN 978111920854. [Google Scholar]
- Strawbridge, I.; James, P.F. Study of polymer films. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1986, 82, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Sengwa, R.J. Structural and dielectric studies of amorphous and semi crystalline polymers blend-based polymer nanocomposites electrolytes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


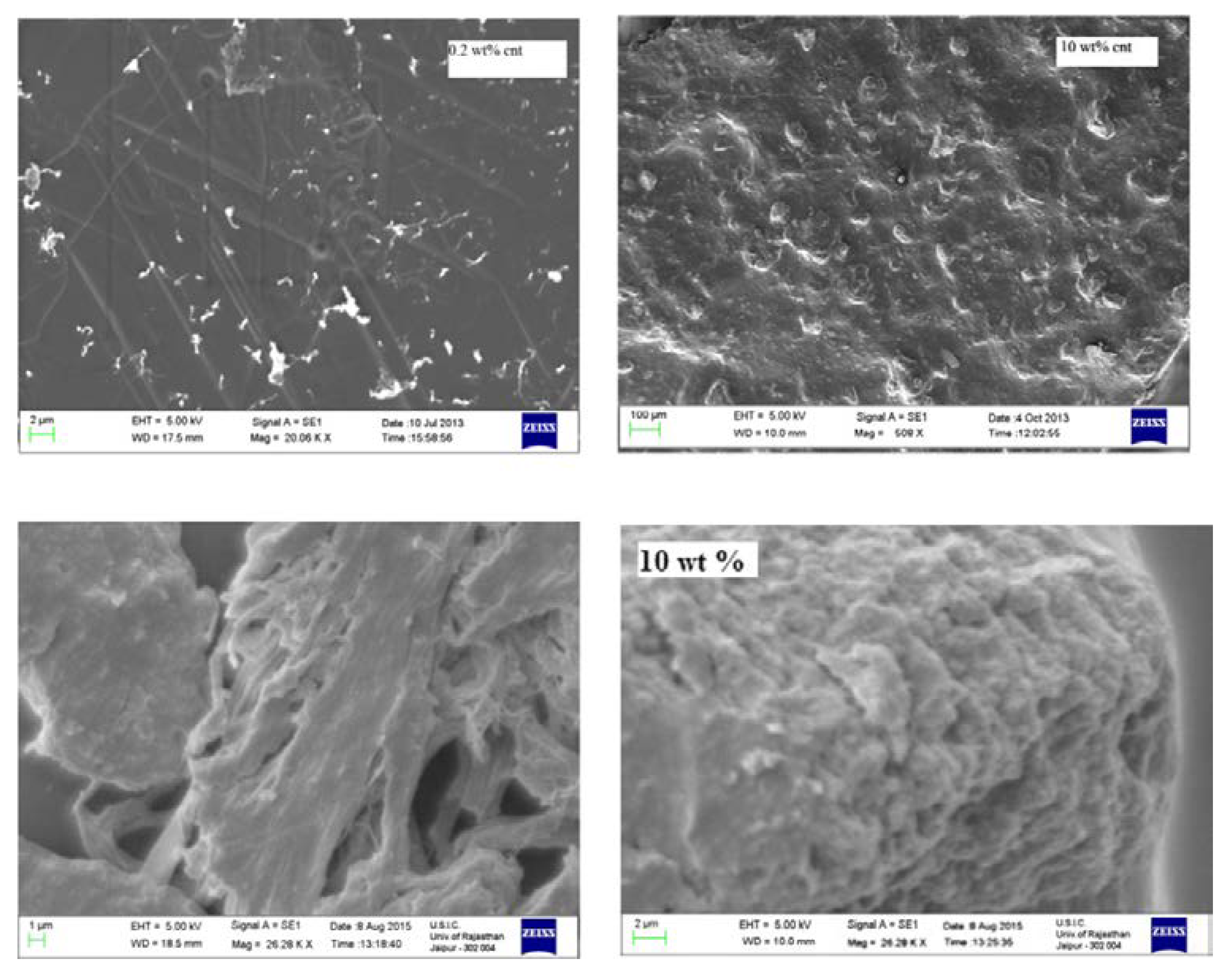



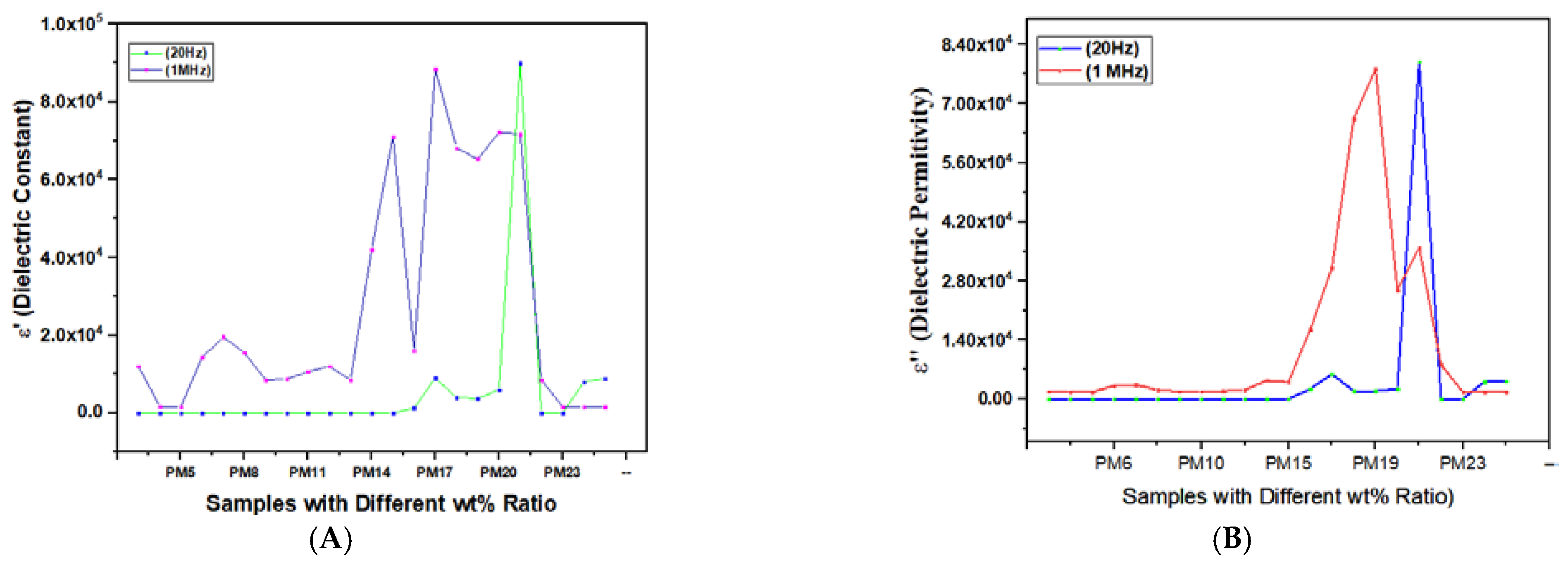

| S. No. | Polymer Composites with Differently Loaded Fillers | Samples | ε′ | E″ | tan δ | M′ | σ′ [S/cm] | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (PNCs with Inorganic Fillers) | Codes | 20 Hz | 1 MHz | 20 Hz | 1 MHz | 20 Hz | 1 MHz | 20 Hz | 1 MHz | 20 Hz | 1 MHz | ||
| 1 | PMMA + ZnO (5 wt%) | PM1 | 3.1 | 2.82 | 0.1482 | 0.0675 | 0.045 | 0.021 | 0.1482 | 0.082 | 1 × 10−12 | 4 × 10−8 | [20] |
| 2 | PMMA + SnO2 (5 wt%) | PM2 | 3.11 | 2.55 | 0.1675 | 0.67 | 0.0578 | 0.0287 | 0.02 | 0.052 | 2 × 10−12 | 6 × 10−8 | [20] |
| 3 | PMMA + TiO2 (5 wt%) | PM3 | 2.088 | 1.81 | 0.081 | 0.0189 | 0.04 | 0.012 | 0.0225 | 0.01 | 8 × 10−13 | 2 × 10−8 | [20] |
| 4 | PMMA + PVC (70/30 wt%) | PM4 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 3.5 | 0.0087 | ------ | ------ | 0.001 | 8.2 | 1 × 10−8 | 9 × 10−7 | [19] |
| 5 | PMMA + PVC (60/40 wt%) | PM5 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.008 | 0.0023 | ------ | ------ | 0.0021 | 7 | 1.1 × 10−11 | 9 × 10−8 | [19] |
| 6 | PEO/PMMA (75/2 5 wt%) + SiO2 (5 wt%) | PM6 | 10.3 | 2.2 | 3.4 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.012 | 0.028 | 0.009 | 9.8 × 10−12 | 9 × 10−9 | [69] |
| 7 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + SiO2 (5 wt%) | PM7 | 9.1 | 3.1 | 2.89 | 0.289 | 0.309 | 0.0109 | 0.0267 | 0.002 | 9 × 10−12 | 1 × 10−8 | [69] |
| 8 | PEO/PMMA (25/75 wt%) + SiO2 (5 wt%) | PM8 | 3.912 | 2.408 | 0.783 | 0.085 | 0.189 | 0.05 | 0.0487 | 0.0076 | 8.5 × 10−12 | 2 × 10−8 | [69] |
| 9 | PMMA/PVA (50/50 wt%) + Al2O3 (5 wt%) | PM9 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.022 | 0.017 | 0.018 | 0.012 | 1 × 10−13 | 7 × 10−9 | [66,72] |
| 10 | PMMA/PVA (50/50 wt%) + SiO2 (5 wt%) | PM10 | 1.4 | 1.25 | 0.04 | 0.022 | 0.025 | 0.018 | 0.028 | 0.011 | 2 × 10−13 | 8 × 10−9 | [66,72] |
| 11 | PMMA/PVA (50/50 wt%) + ZnO (5 wt%) | PM11 | 1.8 | 1.58 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.026 | 0.022 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 5 × 10−13 | 1 × 10−8 | [66,72] |
| 12 | PMMA/PVA (50/50 wt%) + SnO2 (5 wt%) | PM12 | 2.45 | 1.81 | 0.15 | 0.075 | 0.062 | 0.035 | 0.025 | 0.021 | 2 × 10−12 | 1 × 10−8 | [66,72] |
| 13 | PMMA/PEO (80/20 wt%) + LiClO4 + MMT (5 wt%) | PM13 | 20 | 1.2 | 8 | 0.467 | 0.4 | 0.21 | 0.032 | 0.0496 | ------ | ------ | [68,69,70] |
| 14 | Al-PMMA-TiO2-Al | PM14 | 14.3 | ------ | ------- | ------ | 0.1 | 0.12 | ------ | ------ | 7 × 10−11 | 2 × 10−7 | [58] |
| 15 | PMMA + LiClO4 + PEG (10 wt%) | PM15 | 51 | 12 | 60 | 0.4 | 1.125 | 0.14 | 0.013 | 0.052 | 4 × 10−10 | 5 × 10−7 | [35,42] |
| 16 | PMMA + LiClO4 + PEG (10 wt%) + MMT (5 wt%) | PM16 | 1340 | 2.5 | 2500 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 0.25 | 0.0011 | 0.123 | 5 × 10−8 | 9 × 10−7 | [35,42] |
| 17 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiClO4 (3 wt%) | PM17 | 9000 | 15 | 6000 | 5 | 0.8 | 3.89 | ------- | ------ | 4 × 10−8 | 2 × 10−5 | [32,68,69] |
| 18 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiClO4 (3 wt%) + Al2O3 (3 wt%) | PM18 | 4000 | 11.5 | 2000 | 11 | 0.51 | 1.2 | ------ | ------ | 2 × 10−8 | 7 × 10−6 | [32,68,69] |
| 19 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiClO4 (3 wt%) + SiO2 (3 wt%) | PM19 | 3800 | 11 | 2000 | 13 | 0.5 | 1.52 | ------ | ------ | 1.8 × 10−8 | 2 × 10−5 | [68,69] |
| 20 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiClO4 (3 wt%) + SnO2 (3 wt%) | PM20 | 6000 | 12.2 | 2500 | 4.1 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 9× 10−5 | 0.0657 | 4 × 10−8 | 2 × 10−5 | [68,69] |
| 21 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiClO4 (3 wt%) + ZnO (3 wt%) | PM21 | 90,000 | 12.1 | 80,000 | 5.8 | 0.534 | 3.5 | ------ | ------ | 8.5 × 10−8 | 4 × 10−5 | [69] |
| 22 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiCF3SO3 (3 wt%) + MMT (5 wt%) | PM22 | 100 | 1.2 | 56 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.004 | 0.038 | 3 × 10−10 | 8 × 10−7 | [32,60] |
| 23 | PMMA/PVC (70 wt%) + LiTFSI (30 wt%) | PM23 | 50 | 0.002 | 88.89 | 0.0011 | ------ | ------ | 0.0009 | 17.89 | 2.1 × 10−7 | 2 × 10−6 | [20] |
| 24 | PMMA/PVC/LiTFSI (40 wt%) + BmImTFSI (60 wt%) | PM24 | 8000 | 0.011 | 4250 | 0.0123 | ------ | ------ | 0.0001 | 0.375 | 1.4 × 10−5 | 6 × 10−5 | [67] |
| 25 | PMMA/PVC/LiTFSI/BmImTFSI (92 wt%) + SiO2 (8 wt%) SiO2 (8 wt%) | PM25 | 8876 | 0.001 | 4300 | 0.012 | ------ | ------ | 0.002 | 0.248 | 1.2 × 10−5 | 8 × 10−5 | [67] |
| S. No. | Dielectric Composite Polymer | Sample Codes | Conductivity σ′ [S/cm] | Feature and Applications | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (PNCs with Inorganic Fillers) | 20 Hz | 1 MHz | |||
| 1 | PMMA + ZnO (5 wt%) | PM1 | 1 × 10−12 | 4 × 10−8 | Addition of filler content in matrix increased k values and loss factor and for low frequencies it has comparatively high values [20,34] |
| 2 | PMMA + SnO2 (5 wt%) | PM2 | 2 × 10−12 | 6 × 10−8 | ε′ values and loss factor values improved with loading fillers and conductivity is slightly high than ZnO filler [20,26,34,47] |
| 3 | PMMA + TiO2 (5 wt%) | PM3 | 8 × 10−13 | 2 × 10−8 | ε′ values and loss factor decreased with increasing content of fillers and conductivity is reduced [20,34,36,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66] |
| 4 | PMMA + PVC (70/30 wt%) | PM4 | 1 × 10−8 | 9 × 10−7 | Polymer blend without fillers has very low ε′ values [19,20,26,27] |
| 5 | PMMA + PVC (60/40 wt%) | PM5 | 1.1 × 10−11 | 9 × 10−8 | Lowering the PMMA content in polymer blend further reduced its ε′ values [19,20] |
| 6 | PEO/PMMA (75/25 wt%) + SiO2 (5 wt%) | PM6 | 9.8 × 10−12 | 9 × 10−9 | Low dielectric values demand such materials in electrical insulator, dielectric substrate layer used in fabrication of flexible organo electronic devices and sensors [69,88] |
| 7 | PEO/PMMA (50/50wt%) + SiO2 (5 wt%) | PM7 | 9 × 10−12 | 1 × 10−8 | Applicable in insulating devices due to low values of dielectric properties [52,69] |
| 8 | PEO/PMMA (25/75 wt%) + SiO2 (5 wt%) | PM8 | 8.5 × 10−12 | 2 × 10−8 | Increasing loading filler show better results in dielectric properties [19,69] |
| 9 | PMMA/PVA (50/50 wt%) + Al2O3 (5 wt%) | PM9 | 1 × 10−13 | 7 × 10−9 | Low ε′ values, electric insulator, polymeric dielectric substrate for microelectronic devices at low operating voltage [66,72] |
| 10 | PMMA/PVA (50/50 wt%) + SiO2 (5 wt%) | PM10 | 2 × 10−13 | 8 × 10−9 | Low ε′ values, insulators /dielectric substrate [66,72] |
| 11 | PMMA/PVA (50/50 wt%) + ZnO (5 wt%) | PM11 | 5 × 10−13 | 1 × 10−8 | Low ε′ values, insulators/ dielectric substrate [20,66,72] |
| 12 | PMMA/PVA (50/50 wt%) + SnO2 (5 wt%) | PM12 | 2 × 10−12 | 1 × 10−8 | Low ε′ values, insulators /dielectric substrate [20,72] |
| 13 | PMMA/PEO (80/20 wt%) + LiClO4 + MMT (5 wt%) | PM13 | ------ | ------ | Potential applications for electro chromic devices and electrolyte material for lithium ion batteries [68,69,70] |
| 14 | Al- PMMA-TiO2 –Al | PM14 | 7 × 10−11 | 2 × 10−7 | High dielectric layer in thin film transistors [20,58] |
| 15 | PMMA + LiClO4 + PEG (10 wt%) | PM15 | 4 × 10−10 | 5 × 10−7 | Very high ε′ values in SPNCs, use as ion conducting devices [35,42,88] |
| 16 | PMMA + LiClO4 + PEG (10 wt%) + MMT (5 wt%) | PM16 | 5 × 10−8 | 9 × 10−7 | Very high ε′ values, ion conducting electro chromic devices [35,42] |
| 17 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiClO4 (3 wt%) | PM17 | 4 × 10−8 | 2 × 10−5 | Very high ε′ values, lithium ion batteries use in mobile phones [35,42] |
| 18 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiClO4 (3 wt%) + Al2O3 (3 wt%) | PM18 | 2 × 10−8 | 7 × 10−6 | Lithium ion batteries use in mobile phones (high efficiency) [32,68,69]] |
| 19 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiClO4 (3 wt%) + SiO2 (3 wt%) | PM19 | 1.8 × 10−8 | 2 × 10−5 | Bulk properties resistance indicates its use for conducting devices [65,66,67,68,69] |
| 20 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiClO4 (3 wt%) + SnO2 (3 wt%) | PM20 | 4 × 10−8 | 2 × 10−5 | Conducting devices for low values [68,69] |
| 21 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiClO4 (3 wt%) + ZnO (3 wt%) | PM21 | 8.5 × 10−8 | 4 × 10−5 | Extremely high ε′ values, use as conducting devices for more low values [34,68,69] |
| 22 | PEO/PMMA (50/50 wt%) + LiCF3SO3 (3 wt%) + MMT (5 wt%) | PM22 | 3 × 10−10 | 8 × 10−7 | Bulk resistance property makes its use in good conductivity devices [65,66,67,68] |
| 23 | PMMA/PVC (70 wt%) + LiTFSI (30 wt%) | PM23 | 2.1 × 10−7 | 2 × 10−6 | Very high ε′ values and good conductivity [80,84,85,86,87,88] |
| 24 | PMMA/PVC/LiTFSI (40 wt%) + BmImTFSI (60 wt%) | PM24 | 1.4 × 10−5 | 6 × 10−5 | Fillers further increased its ε′ values [82,83,84] |
| 25 | PMMA/PVC/LiTFSI/BmImTFSI (92 wt%) + SiO2 (8 wt%) | PM25 | 1.2 × 10−5 | 8 × 10−5 | Extremely high values of conductivity [84,88] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deeba, F.; Shrivastava, K.; Bafna, M.; Jain, A. Tuning of Dielectric Properties of Polymers by Composite Formation: The Effect of Inorganic Fillers Addition. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6120355
Deeba F, Shrivastava K, Bafna M, Jain A. Tuning of Dielectric Properties of Polymers by Composite Formation: The Effect of Inorganic Fillers Addition. Journal of Composites Science. 2022; 6(12):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6120355
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeeba, Farah, Kriti Shrivastava, Minal Bafna, and Ankur Jain. 2022. "Tuning of Dielectric Properties of Polymers by Composite Formation: The Effect of Inorganic Fillers Addition" Journal of Composites Science 6, no. 12: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6120355
APA StyleDeeba, F., Shrivastava, K., Bafna, M., & Jain, A. (2022). Tuning of Dielectric Properties of Polymers by Composite Formation: The Effect of Inorganic Fillers Addition. Journal of Composites Science, 6(12), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6120355






