Effect of Selenium–Arabinogalactan Nanocomposite on Environmental Bacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Se/AG NCs
2.2. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy of Se/AG NCs Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Emission
2.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) of Se/AG NCs
2.4. Optical Absorption of Se/AG NCs
2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering of Se/AG NCs
2.6. Microbial Strains and Cultivation Conditions
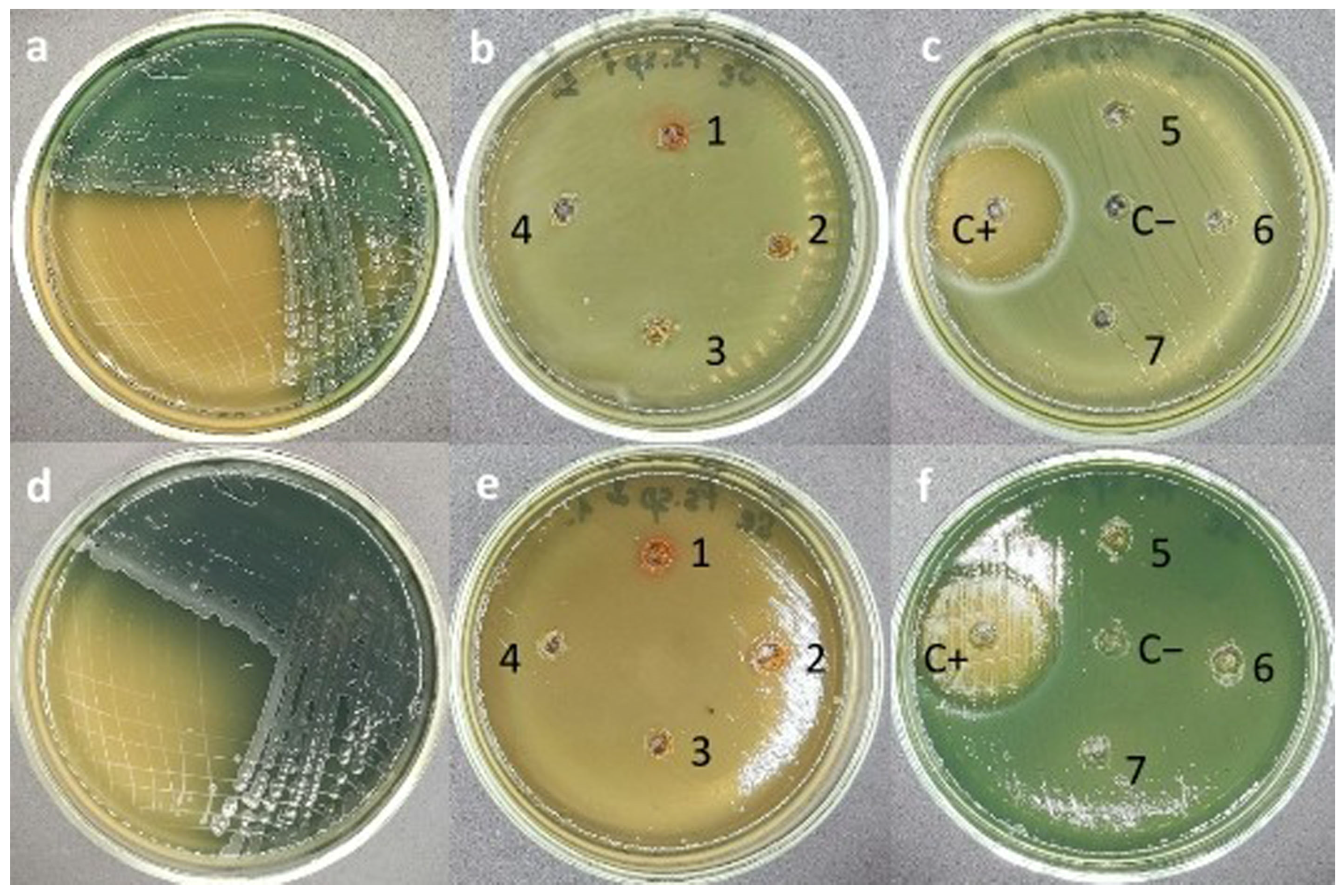
2.7. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity of Se/AG NCs by Agar Diffusion Method
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristic Se/AG NCs
3.2. Effects of Se/AG NCs on Environmental Bacteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AG | arabinogalactan |
| CFU | colony forming unit |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ICPE | inductively coupled plasma emission |
| LP | lipid peroxidation |
| NC | nanocomposite |
| NP | nanoparticle |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| Se/AG NC | Nanocomposite (NC) based on selenium (Se) and arabinogalactan (AG) |
References
- Genchi, G.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Carocci, A. Biological activity of selenium and its impact on human health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Akash, S.; Jony, M.H.; Alam, M.N.; Nowrin, F.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Thiruvengadam, M. Exploring the potential function of trace elements in human health: A therapeutic perspective. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 478, 2141–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Yu, S.; Yang, R.; Xiao, J.; Liu, J. Opportunities for the use of selenium nanoparticles in agriculture. NanoImpact 2023, 31, 100478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Wei, C.; Tu, S. The roles of selenium in protecting plants against abiotic stresses. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 87, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, I.; Skalickova, S.; Sajjad, H.; Skladanka, J.; Horky, P. Uses of selenium nanoparticles in the plant production. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, C.; Florindo, H.F.; Santos, H.A. Selenium nanoparticles for biomedical applications: From development and characterization to therapeutics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Li, Q.; Zhou, W.; Yu, S.; Liu, J. Speciation analysis of selenium nanoparticles and inorganic selenium species by dual-cloud point extraction and ICP-MS determination. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 16328–16336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfileva, A.I.; Nozhkina, O.A.; Graskova, I.A.; Sidorov, A.V.; Lesnichaya, M.V.; Aleksandrova, G.P.; Sukhov, B.G. Synthesis of selenium and silver nanobiocomposites and their influence on phytopathogenic bacterium Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2018, 67, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfileva, A.I.; Nozhkina, O.A.; Ganenko, T.V.; Graskova, I.A.; Sukhov, B.G.; Artem’ev, A.V.; Krutovsky, K.V. Selenium nanocomposites in natural matrices as potato recovery agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfileva, A.I.; Kharasova, A.R.; Nozhkina, O.A.; Sidorov, A.V.; Graskova, I.A.; Krutovsky, K.V. Effect of nanopriming with selenium nanocomposites on potato productivity in a field experiment, soybean germination and viability of Pectobacterium carotovorum. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, H.; Cheng, W.H. Beneficial and paradoxical roles of selenium at nutritional levels of intake in healthspan and longevity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 127, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, M.; Soni, K.; Kohli, K. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles from broccoli, characterization, application and toxicity. Adv. Tech. Biol. Med. 2017, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, B.A.; Sukhov, B.G.; Aleksandrova, G.P.; Medvedeva, S.A.; Grishchenko, L.A.; Mal’kina, A.G.; Feoktistova, L.P.; Sapozhnikov, A.N.; Dubrovina, V.I.; Martynovich, E.F.; et al. Arabinogalactan-based nanocomposites with magnetic, optical, catalytic and biologically active properties. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. 2003, 393, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnikova, L.I.; Karpova, E.A.; Vlasov, B.Y.; Sukhov, B.G.; Trofimov, B.A. Lipid peroxidation–antioxidant defense system during toxic liver damage and its correction with a composite substance containing selenium and arabinogalactan. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 159, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesnichaya, M.V.; Karpova, E.A.; Sukhov, B.G. Effect of high dose of selenium nanoparticles on antioxidant system and biochemical profile of rats in correction of carbon tetrachloride-induced toxic damage of liver. Coll. Surf. B Biointerface 2021, 197, 111381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesnichaya, M.V.; Shendrik, R.Y.; Sukhov, B.G. Relation between excitation dependent luminescence and particle size distributions for the selenium nanoparticles in κ-carrageenan shell. J. Lumin. 2019, 211, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graskova, I.A.; Perfilieva, A.I.; Nozhkina, O.A.; Sukhov, B.G.; Aleksandrova, G.P.; Trofimov, B.A. Silver-containing nanocomposites of humic substances, agents for healing of potatoes from the ring rot. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2018, 483, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khutsishvili, S.S.; Perfileva, A.I.; Nozhkina, O.A.; Karepova, M.S.; Ganenko, T.V.; Sukhov, B.G.; Trofimov, B.A.; Krutovsky, K.V. Novel nanobiocomposites based on natural polysaccharides as universal trophic low-dose micronutrients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khutsishvili, S.S.; Perfileva, A.I.; Kon’kova, T.V.; Lobanova, N.A.; Sadykov, E.K.; Sukhov, B.G. Copper-containing bionanocomposites based on natural raw arabinogalactan as effective vegetation stimulators and agents against phytopathogens. Polymers 2024, 16, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfileva, A.I.; Krutovsky, K.V. Effect of manganese- and selenium-containing nanocomposites on soybean resistance to Pectobacterium carotovorum and microbial landscape of soybean seedlings. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 104, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfileva, A.I.; Moty’leva, S.M.; Klimenkov, I.V.; Arsent’ev, K.Y.; Graskova, I.A.; Sukhov, B.G.; Trofimov, B.A. Development of Antimicrobial Nano-Selenium Biocomposite for Protecting Potatoes from Bacterial Phytopathogens. Nanotechnol. Russ. 2017, 12, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfileva, A.I.; Tsivileva, O.M.; Nozhkina, O.A.; Karepova, M.S.; Graskova, I.A.; Ganenko, T.V.; Sukhov, B.G.; Krutovsky, K.V. Effect of natural polysaccharide matrix-based selenium nanocomposites on Phytophthora cactorum and rhizospheric microorganisms. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurminsky, V.N.; Perfileva, A.I.; Kapustina, I.S.; Graskova, I.A.; Sukhov, B.G.; Trofimov, B.A. Growth-stimulating activity of natural polymer-based nanocomposites of selenium during the germination of cultivated plant seeds. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 495, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graskova, I.A.; Perfileva, A.I.; Nozhkina, O.A.; Dyakova, A.V.; Nurminsky, V.N.; Klimenkov, I.V.; Sudakov, N.P.; Borodina, T.M.; Aleksandrova, G.P.; Lesnichaya, M.V.; et al. The effect of nanoscale selenium on the causative agent of rot pathogen and potato in vitro. Khimiya Rastit. Syr’ya 2019, 3, 345–354, (In Russian with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, S.A.; Scheringer, M.; MacLeod, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Estimation of cumulative aquatic exposure and risk due to silver: Contribution of nano-functionalized plastics and textiles. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.C.; Nowack, B. Exposure modeling of engineered nanoparticles in the environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4447–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, F.; Sonderer, T.; Scholz, R.W.; Nowack, B. Modeled environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials (TiO2, ZnO, Ag, CNT, fullerenes) for different regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9216–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiser, M.A.; Westerhoff, P.; Benn, T.; Wang, Y.; Perez-Rivera, J.; Hristovski, K. Titanium nanomaterial removal and release from wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6757–6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidsson, R.; Molander, S.; Sandén, B.A.; Hassellöv, M. Challenges in exposure modeling of nanoparticles in aquatic environments. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2011, 17, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; Song, G.; Hristovski, K.; Kiser, M.A. Occurrence and removal of titanium at full scale wastewater treatment plants: Implications for TiO2 nanomaterials. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praetorius, A.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Development of environmental fate models for engineered nanoparticles—A case study of TiO2 nanoparticles in the rhine river. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6705–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer-Jones, M.A.; Gunsolus, I.L.; Murphy, C.J.; Haynes, C.L. Toxicity of engineered nanoparticles in the environment. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3036–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Johnston, M.; Wang, G.S.; Huang, C.P. A seasonal observation on the distribution of engineered nanoparticles in municipal wastewater treatment systems exemplified by TiO2 and ZnO. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syafiuddin, A.; Salmiati, S.; Hadibarata, T.; Kueh, A.B.; Salim, M.R.; Zaini, M.A. Silver nanoparticles in the water environment in Malaysia: Inspection, characterization, removal, modeling, and future perspective. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathi, J.R.; Moazeni, F.; Upadhyayula, V.K.; Chowdhury, I.; Palchoudhury, S.; Potts, G.E.; Gadhamshetty, V. Behavior of engineered nanoparticles in aquatic environmental samples: Current status and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesnichaya, M.V.; Malysheva, S.F.; Belogorlova, N.A.; Graskova, I.A.; Gazizova, A.V.; Perfilyeva, A.I.; Nozhkina, O.A.; Sukhov, B.G. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of arabi-nogalactan-stabilized selenium nanoparticles from sodium bis(2-phenylethyl)diselenophosphinate. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2019, 68, 2245–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Yue, L.; Jiang, Q.; Xia, W. Synthesis and antioxidant properties of chitosan and carboxymethyl chitosan-stabilized selenium nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, P.; Murray, R.G.E.; Costilow, R.N.; Nester, E.W.; Wood, W.A.; Krieg, N.R.; Phillips, G.B. (Eds.) Manual of Methods for General Bacteriology, 1st ed.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1981; Volume 1, 524p. [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielyan, L.; Badalyan, H.; Gevorgyan, V.; Trchounian, A. Comparable antibacterial effects and action mechanisms of silver and iron oxide nanoparticles on Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islama, M.M.; Masumb, S.M.; Mahbuba, K.R.; Haquea, M.Z. Antibacterial activity of crab-chitosan against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2011, 2, 63–66. Available online: https://www.sciensage.info/index.php/JASR/article/view/61 (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Aliasghari, A.; Khorasgani, M.R.; Vaezifar, S.; Rahimi, F.; Younesi, H.; Khoroushi, M. Evaluation of antibacterial efficiency of chitosan and chitosan nanoparticles on cariogenic streptococci: An in vitro study. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2016, 8, 93–100. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4906725 (accessed on 16 February 2025). [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Singh, S.C.; Mishra, S.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Gopal, R. Optical properties of selenium quantum dots produced with laser irradiation of water suspended Se nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 17374–17384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunik, T.V.; Nemchenko, U.M.; Ganenko, T.V.; Yurinova, G.V.; Dzhioev, Y.P.; Sukhov, B.G.; Zlobin, V.I.; Trofimov, B.A. Synthesis and spectral characterization of new biodegradable arabinogalactan derivatives for diagnosis and therapy. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. Phys. 2019, 83, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domokos-Szabolcsy, E.; Márton, L.; Sztrik, A.; Babka, B.; Prokisch, J.; Fari, M. Accumulation of red elemental selenium nanoparticles and their biological effects in Nicotinia tabacum. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 68, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudkov, S.V.; Shafeev, G.A.; Glinushkin, A.P.; Shkirin, A.V.; Barmina, E.V.; Rakov, I.I.; Kalinitchenko, V.P. Production and use of selenium nanoparticles as fertilizers. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17767–17774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Batal, A.I.; Sidkey, N.M.; Ismail, A.A.; Arafa, R.A.; Fathy, R.M. Impact of silver and selenium nanoparticles synthesized by gamma irradiation and their physiological response on early blight disease of potato. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2016, 8, 934–951. [Google Scholar]
- Quiterio-Gutiérrez, T.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Hernández-Fuentes, A.D.; Sandoval-Rangel, A.; Benavides-Mendoza, A.; Cabrera-de la Fuente, M.; Juárez-Maldonado, A. The application of selenium and copper nanoparticles modifies the biochemical responses of tomato plants under stress by Alternaria solani. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubkina, N.A.; Folmanis, G.E.; Tananaev, I.G. Comparative evaluation of selenium accumulation by allium species after foliar application of selenium nanoparticles, sodium selenite and sodium selenite. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2012, 444, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubkina, N.A.; Folmanis, G.E.; Tananaev, I.G.; Krivenkov, L.V.; Kosheleva, O.V.; Soldatenko, A.V. Comparative Evaluation of Spinach Biofortification with Selenium Nanoparticles and Ionic Forms of the Element. Nanotechnol. Russ. 2017, 12, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, H. Uptake, translocation and biotransformation of selenium nanoparticles in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.). J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, G.; Wu, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y. Absorption and bio-transformation of selenium nanoparticles by wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-García, J.J.; Hernández-Díaz, J.A.; Zamudio-Ojeda, A.; León-Morales, J.M.; Guerrero-Guzmán, A.; Sánchez-Chiprés, D.R.; García-Morales, S. The role of selenium nanoparticles in agriculture and food technology. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 2528–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udalova, Z.V.; Folmanis, G.E.; Khasanov, F.K.; Zinovieva, S.V. Selenium nanoparticles–an inducer of tomato resistance to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita (Kofoid et White, 1919) Chitwood 1949. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 482, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowndarya, P.; Ramkumar, G.; Shivakumar, M.S. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles conjugated Clausena dentata plant leaf extract and their insecticidal potential against mosquito vectors. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, M.; Ranganathan, K.; Maadhu, P.; Thangavelu, P.; Kundan, S.; Arjunan, N. Leaf extract of Dillenia indica as a source of selenium nanoparticles with larvicidal and antimicrobial potential toward vector mosquitoes and pathogenic microbes. Coatings 2020, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Fouda, A.; Awad, M.A.; Al-Olayan, E.M.; Allam, A.A.; Shaheen, T.I. Antibacterial, cytotoxicity and larvicidal activity of green synthesized selenium nanoparticles using Penicillium corylophilum. J. Clust. Sci. 2021, 32, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandini, B.; Hariprasad, P.; Prakash, H.S.; Shetty, H.S.; Geetha, N. Trichogenic-selenium nanoparticles enhance disease suppressive ability of Trichoderma against downy mildew disease caused by Sclerospora graminicola in pearl millet. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrandečić, K.; Ćosić, J.; Ilić, J.; Ravnjak, B.; Selmani, A.; Galić, E.; Vinković, T. Antifungal activities of silver and selenium nanoparticles stabilized with different surface coating agents. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Yu, Q.; Sun, D.; Liu, J. Investigation of functional selenium nanoparticles as potent antimicrobial agents against superbugs. Acta Biomater. 2016, 30, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagesan, V.; Venugopal, S. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticle using leaves extract of Withania somnifera and its biological applications and photocatalytic activities. Bionanoscience 2019, 9, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Dai, C.; Wang, P.; Fan, S.; Yu, B.; Qu, Y. Antibacterial properties and mechanism of selenium nanoparticles synthesized by Providencia sp. DCX. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, A.F.; Quendera, A.P.; Sousa, J.P.; Silva, A.F.Q.; Arraiano, C.M.; Andrade, J.M. Bacterial Response to Oxidative Stress and RNA Oxidation. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 821535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang-Bao, T.; Ho, T.G.; Do, B.L.; Phung Anh, N.; Phan, T.D.T.; Tran, T.B.Y.; Duong, N.L.; Hong Phuong, P.; Nguyen, T. Green orange peel-mediated bioinspired synthesis of nanoselenium and its antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 36037–36046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Holden, J.A.; Heath, D.E.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; O’Connor, A.J. Engineering highly effective antimicrobial selenium nanoparticles through control of particle size. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 14937–14951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, P.L.; Hammond, A.A.; Mosley, T.; Cortez, J.; Gray, T.; Colmer-Hamood, J.A.; Shashtri, M.; Spallholz, J.E.; Hamood, A.N.; Reid, T.W. Organo selenium coating on cellulose inhibits the formation of biofilms by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 3586–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremonini, E.; Boaretti, M.; Vandecandelaere, I.; Zonaro, E.; Coenye, T.; Lleo, M.M.; Lampis, S.; Vallini, G. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles synthesized by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia SeITE02 loose antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy as a result of the progressive alteration of their organic coating layer. Microb. Biotechnol. 2018, 11, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Ullah, M.W.; Liu, L.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Ahmed, A.A.Q.; Cheng, H.; Shi, Z.; et al. In situ synthesized selenium nanoparticles-decorated bacterial cellulose/gelatin hydrogel with enhanced antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory capabilities for facilitating skin wound healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastulyavichus, A.A.; Kudryashov, S.I.; Smirnov, N.A.; Khmel’nitskii, R.A.; Rudenko, A.A.; Mel’nik, N.N.; Kirilenko, D.A.; Brunkov, P.; Ionin, A.A. Laser formation of colloidal sulfur-and carbon-doped silicon nanoparticles. Opt. Spectrosc. 2020, 128, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papkina, A.V.; Perfileva, A.I.; Zhivet’yev, M.A.; Borovskii, G.B.; Graskova, I.A.; Klimenkov, I.V.; Lesnichaya, M.V.; Sukhov, B.G.; Trofimov, B.A. Complex effects of selenium-arabinogalactan nanocomposite on both phytopathogen Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus and potato plants. Nanotechnol. Russ. 2015, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallathamby, P.D.; Lee, K.J.; Desai, T.; Xu, X.H. Study of the multidrug membrane transporter of single living Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells using size-dependent plasmonic nanoparticle optical probes. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 5942–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strekalovskaya, E.I.; Sipkina, E.I. Nanostructured materials as hazardous wastewater micropullutants: Sources, behavior, and impact on functional bacterial community of activated sludge. Proc. Univ. Appl. Chem. Biotechnol. 2024, 14, 339–351, (In Russian with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khina, A.G.; Krutyakov, Y.A. Similarities and differences in the mechanism of antibacterial action of silver ions and nanoparticles. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2021, 57, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño-Martínez, N.; Salas Orozco, M.F.; Martínez-Castañón, G.A.; Torres Méndez, F.; Ruiz, F. Molecular mechanisms of bacterial resistance to metal and metal oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnucco, G.; Overfield, D.; Chamlee, Y.; Shuler, C.; Kassem, A.; Opara, S.; Najaf, H.; Abbas, L.; Coutinho, O.; Fortuna, A.; et al. Metal tolerance and biosorption capacities of bacterial strains isolated from an urban water-shed. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1278886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Byeon, E.; Kim, D.H.; Maszczyk, P.; Lee, J.S. Heavy metals and metalloid in aquatic invertebrates: A review of single/mixed forms, combination with other pollutants, and environmental factors. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Engineered nanoparticles in wastewater and wastewater sludge–evidence and impacts. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljerf, L.; AlMasri, N. A gateway to metal resistance: Bacterial response to heavy metal toxicity in the biological environment. Ann. Adv. Chem. 2018, 2, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Nizet, V. Color me bad: Microbial pigments as virulence factors. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleneva, I.A.; Kharchenko, U.V. Ecological and biological aspects of effect of nanoparticles and toxic forms of metals on marine and opportunistic bacteria. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2024, 50, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, L.E.; Price-Whelan, A.; Petersen, A.; Whiteley, M.; Newman, D.K. The phenazine pyocyanin is a terminal signalling factor in the quorum sensing network of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 61, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nansathit, A.; Phaosiri, C.; Pongdontri, P.; Chanthai, S.; Ruangviriyachai, C. Synthesis, isolation of phenazine derivatives and their antimicrobial activities. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 6, 79–91. Available online: https://wjst.wu.ac.th/index.php/wjst/article/view/74 (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Aziz, L.M.; Hamza, S.J.; Abdul-Rahman, I.A. Isolation and characterization of phenazine produced from mutant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Al-Anbar J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 5, 42–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Gómez, B.; Arregui, L.; Serrano, S.; Santos, A.; Pérez-Corona, T.; Madrid, Y. Unravelling mechanisms of bacterial quorum sensing disruption by metal-based nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.G.; Ansari, M.A.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Jalal, M.; AlYahya, S.; Khan, H.M. Effect of biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles on multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Bacteria/Source | Dilutions of Se/AG NCs, mg/mL | Ceftriaxone, mg/mL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 20 | 10 | 5 | 2.5 | 1.25 | 0.625 | 10 | |
| Gram-negative bacteria | ||||||||
| Escherichia coli/soil | 20.3 ± 0.5 | 19.0 ± 0.8 | 17.3 ± 0.5 | 13.3 ± 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 42.3 ± 2.1 |
| Serratia marcescens/activated sludge | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41.6 ± 0.9 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing pyoverdin/wastewater | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.6 ± 0.5 |
| P. aeruginosa producing pyocyanin/wastewater | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28.6 ± 0.5 |
| Gram-positive bacteria | ||||||||
| Micrococcus luteus/water | 26.3 ± 0.5 | 22.6 ± 0.9 | 18.0 ± 4.3 | 15.0 ± 0.8 | 11.6 ± 0.5 | 10.6 ± 0.5 | 9.3 ± 0.5 | 57.0 ± 1.4 |
| M. luteus/activated sludge | 14.3 ± 0.5 | 13.3 ± 1.2 | 13.3 ± 1.2 | 13.3 ± 1.2 | 8.3 ± 1.3 | 7.0 ± 0.0 | 0 | 59.6 ± 0.5 |
| Bacillus cereus/activated sludge | 16.3 ± 2.6 | 15.0 ± 3.7 | 13.3 ± 2.1 | 13.3 ± 1.7 | 11.0 ± 1.4 | 11.0 ± 1.4 | 8.3 ± 0.5 | 40.6 ± 0.5 |
| B. cereus/soil | 11.3 ± 0.5 | 9.0 ± 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.6 ± 0.5 |
| B. megaterium/soil | 11.6 ± 0.9 | 11.6 ± 0.9 | 8.6 ± 0.5 | 7.6 ± 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19.0 ± 0.8 |
| B. subtilis/water | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 45.3 ± 0.5 |
| Sarcina flava/water | 16.0 ± 0.8 | 15.0 ± 1.6 | 13.0 ± 3.0 | 13.0 ± 0.8 | 12.3 ± 0.5 | 11.3 ± 1.0 | 0 | 59.6 ± 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strekalovskaya, E.I.; Perfileva, A.I.; Vyatchina, O.F.; Stom, D.I.; Romashchenko, A.V.; Kasatova, A.I.; Kon’kova, T.V.; Sukhov, B.G.; Krutovsky, K.V. Effect of Selenium–Arabinogalactan Nanocomposite on Environmental Bacteria. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050210
Strekalovskaya EI, Perfileva AI, Vyatchina OF, Stom DI, Romashchenko AV, Kasatova AI, Kon’kova TV, Sukhov BG, Krutovsky KV. Effect of Selenium–Arabinogalactan Nanocomposite on Environmental Bacteria. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(5):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050210
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrekalovskaya, Elena I., Alla I. Perfileva, Olga F. Vyatchina, Devard I. Stom, Aleksander V. Romashchenko, Anna I. Kasatova, Tatyana V. Kon’kova, Boris G. Sukhov, and Konstantin V. Krutovsky. 2025. "Effect of Selenium–Arabinogalactan Nanocomposite on Environmental Bacteria" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 5: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050210
APA StyleStrekalovskaya, E. I., Perfileva, A. I., Vyatchina, O. F., Stom, D. I., Romashchenko, A. V., Kasatova, A. I., Kon’kova, T. V., Sukhov, B. G., & Krutovsky, K. V. (2025). Effect of Selenium–Arabinogalactan Nanocomposite on Environmental Bacteria. Journal of Composites Science, 9(5), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050210










