Obtaining Foamed Glass-Ceramics from Diamond Concentration Tailings
Abstract
1. Introduction
- −
- A transition to a new level of energy efficiency of production;
- −
- A reduction in the negative impact on the environment;
- −
- The involvement of waste in the production of building materials and increasing the processing depth of natural resources;
- −
- The production of new types (innovative and composite) of building materials that improve energy efficiency, reliability, durability, and internal environment quality in buildings and structures and reduce material consumption.
2. Materials and Methods
4FeO + O2 = 2Fe2O3.
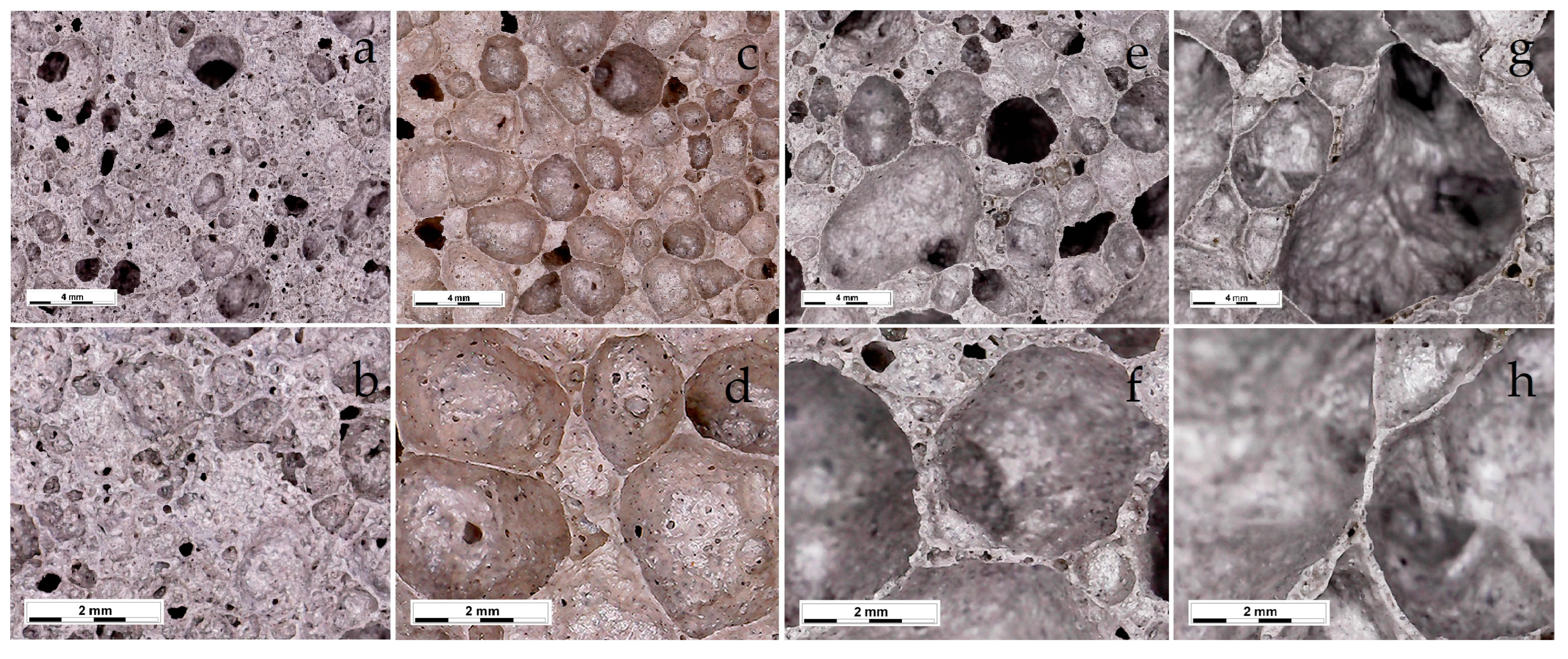
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Order 868-r of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 10 May 2016 (as Amended on 23 November 2016) “On the Strategy for the Development of the Building Materials Industry for the Period through 2020 and Long-Term Prospects through 2030”. Available online: http//www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_197766/ (accessed on 18 January 2023).
- Strategy for the Innovative Development of the Construction Industry in the Russian Federation for the Period through 2030. Available online: https://www.minstroyrf.gov.ru/docs/?date_from=&t%5B%5D=&d%5B%5D=&q=%D0%A1%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%B3%D0%B8%D1%8F&active%5B%5D=65&active%5B%5D=66 (accessed on 17 May 2023). (In Russian)
- Lotov, V.A. Making foam glass based on natural and technogenic aluminosilicates. Glass Ceram. 2012, 68, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorova, O.V.; Manakova, N.K.; Makarov, D.V. Use of bulk industrial wastes in the production of glass foam materials. Glass Ceram. 2021, 77, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minenko, V.G. Justification and design of electrochemical recovery of saponite from recycled water. J. Mining Sci. 2014, 50, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanturiya, V.; Minenko, V.; Suvorova, O.; Pletneva, V.; Makarov, D. Electrochemical modification of saponite for manufacture of ceramic building materials. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, R.D.; Wu, J.P.; Boccaccini, A.R. Glass-ceramics: Their production from wastes—A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 733–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsot, I.; Bernardo, E. Self glazed glass ceramic foams from metallurgical slag and recycled glass. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 59, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ma, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, X. Preparation of sintered foamed ceramics derived entirely from coal fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 163, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Zheng, F.; Xu, J.; Yang, W.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Zhen, Q.; Bashir, S.; Liu, J.L. Preparation of glass-ceramic foams using extracted titanium tailing and glass waste as raw materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Ji, R.; Liu, L.; Cheeseman, C.; Wang, X. Reuse of mineral wool waste and recycled glass in ceramic foams. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 15057–15064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min’ko, N.I.; Puchka, O.V.; Stepanova, M.S.; Vaysera, S.S. Heat-Insulating Glass Materials: Foam Glass, Izd; BGTU: Belgorod, Russia, 2016; 262p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Suvorova, O.V.; Makarov, D.V.; Pletneva, V.E. Ceramic materials based on tailings from enrichment of vermiculite and apatite-nepheline ores. Glass Ceram. 2009, 66, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manakova, N.K.; Suvorova, O.V. Heat-insulating material on the basis of silica-containing wastes formed in crude ore recovery in Kola Peninsula. Rus. J. App. Chem. 2012, 85, 1654–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmina, O.V.; Tokareva, A.Y.; Vereshchagin, V.I. Using quartzofeldspathic waste to obtain foamed glass material. Res-Eff. Technol. 2016, 2, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Manakova, N.K.; Suvorova, O.V.; Makarov, D.V. Influence of mineral additives on the structure and properties of heat-insulating materialsbased on silica-containing raw material. Glass Ceram. 2021, 78, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.V.; Manakova, N.K.; Suvorova, O.V. Production of rock-based foam-glass materials (review). Glass Ceram. 2023, 79, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manakova, N.K.; Suvorova, O.V.; Semushin, V.V. Physicochemical substantiation of obtaining porous glass materials from silica-containing raw materials. Glass Phys. Chem. 2023, 49, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Spiridonov, Y.A.; Orlova, L.A. Problems of foam glass production. Glass Ceram. 2003, 60, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshchenko, I.M.; Zhikh, B.P.; Kravchuk, A.P. Production of efficient heat-insulating materials on the basis of silica gel. Build. Mater. 2016, 7, 45–48. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tereshchenko, I.M.; Dormeshkin, O.B.; Kravchuk, A.P.; Zhikh, B.P. Status and prospects of development of production of gassy foamed heat-insulation materials. Glass Ceram. 2017, 74, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokareva, A.Y. Study of copper-zinc ore dressing tailings as a raw material for producing foam glass. In Chemistry and Chemical Technology in the 21st Century; Tomsk Polytechnic University: Tomsk, Russia, 2016; pp. 127–128. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kazmina, O.V.; Semke, A.P.; Miskovets, A.Y. Preparation of porous glass ceramics on the basis of copper-zinc ore dressing wastes. In Problems of Geology and Development of Mineral Resources; Tomsk Polytechnic University: Tomsk, Russia, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 374–375. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; He, F.; Shu, H.; Qiao, Y.; Mei, S.; Jin, M.; Xie, J. Preparation of high strength glass ceramic foams from waste cathode ray tube and germanium tailings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemougna, P.N.; Yliniemi, J.; Adediran, A.; Luukkonen, T.; Tanskanen, P.; Finnil, M.; Illikainen, M. Synthesis and characterization of porous ceramics from spodumene tailings and waste glass wool. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 33286–33297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, A.; Qu, G. Preparation and characterization of foam ceramics from red mud and fly ash using sodium silicate as foaming agent. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhangn, Y.; Huangn, H.; Meng, K.; Hu, K.; Hu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, X. Novel glass ceramic foams materials based on red mud. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 6677–6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lin, C.; Liu, J.; Han, L.; Gui, H.; Li, C.; Zhou, X.; Tang, H.; Yang, Q.; Lu, A. Phase evolution, pore morphology and microstructure of glass ceramic foams derived from tailings wastes. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 14393–14400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Cui, S.; Pu, X. Performance study of foam ceramics prepared by direct foaming method using red mud and K-feldspar washed waste. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 5197–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, K.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Q.; Shi, H. Effects of Na2B4O7·5H2O on the properties of foam glass from waste glass and titania-bearing blast furnace slag. Mater. Lett. 2014, 132, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Ning, W.; Wang, Q.; Shi, D.; Luo, L. Preparation and characterization of glass-ceramic foams from blast furnace slag and waste glass. Mater. Lett. 2015, 141, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heriyanto; Pahlevani, F.; Sahajwalla, V. From waste glass to building materialsAn innovative sustainable solution for waste glass. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 191, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducman, V.; Kovačević, M. The foaming of waste glass. Key Eng. Mater. 1997, 132–136, 2264–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, H.R.; Tulyaganov, D.U.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Production and characterization of glass ceramic foams from recycled raw materials. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2009, 108, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancea, C.; Lazău, I. Glass foam from window panes and bottle glass wastes. Centr. Eur. J. Chem. 2014, 12, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, E.; Scarinci, G.; Bertuzzi, P.; Ercole, P.; Ramon, L. Recycling of waste glasses into partially crystallized glass foams. J. Porous. Mater. 2010, 17, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Mirkazemi, S.M.; Ziaee, A.; Saeedi Heydari, M. The Effects of Fe2O3 and Co3O4 on Microstructure and properties of foam glass from soda lime waste glasses. Glass. Phys. Chem. 2014, 40, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoescu, M.F.; Paunescu, L.; Axinte, S.M.; Fiti, A. Influence of the color of bottle glass waste on the characteristics of foam glass produced in microwave field. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Inv. 2018, 7, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Attila, Y.; Güden, M.; Taşdemirci, A. Foam glass processing using a polishing glass powder residue. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 5869–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci, M.; Cicek, B. E-waste: A review of CRT (cathode ray tube) recycling. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.W.; Gong, Y.X.; Gao, S.Y. Preparation of high strength foam glass-ceramics from waste cathode ray tube. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 997–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-T. Production of alumino-borosilicate foamed glass body from waste LCD glass. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, H.; Andreola, F.; Barbieri, L.; Lancellotti, I.; Pascual, M.J.; Ferreira, J.M.F. The use of egg shells to produce cathode ray tube glass foams. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 9071–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.R.; König, J.; Smedskjaer, M.M.; Yue, Y. Effect of Na2CO3 as foaming agent on dynamics and structure of foam glass melts. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 2014, 400, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucsi, G.; Csűke, B.; Kertész, M.; Hoffmann, L. Physical characteristics and technology of glass foam from waste cathode ray tube glass. J. Mater. 2013, 2013, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, E.; Cedro, R.; Florean, M.; Hreglich, S. Reutilization and stabilization of wastes by the production of glass foams. Ceram. Int. 2007, 33, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saburit, A.; Orts, M.J.; Garcıa-Ten, J.; Bernardo, E.; Colombo, P. Foaming of flat glass cullet using Si3N4 and MnO2 powders. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar]
- García-Ten, J.; Saburit, A.; Orts, M.J.; Bernardo, E.; Colombo, P. Glass foams from oxidation/reduction reactions using SiC, Si3N4 and AlN powders. Glass Technol. Eur. J. of Glass Sci. Technol. Part A. 2011, 52, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Dushkina, M.A.; Kazmina, O.V. Effect of iron-containing additives on the process of obtaining foam glasscrystalline materials. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2014, 57, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
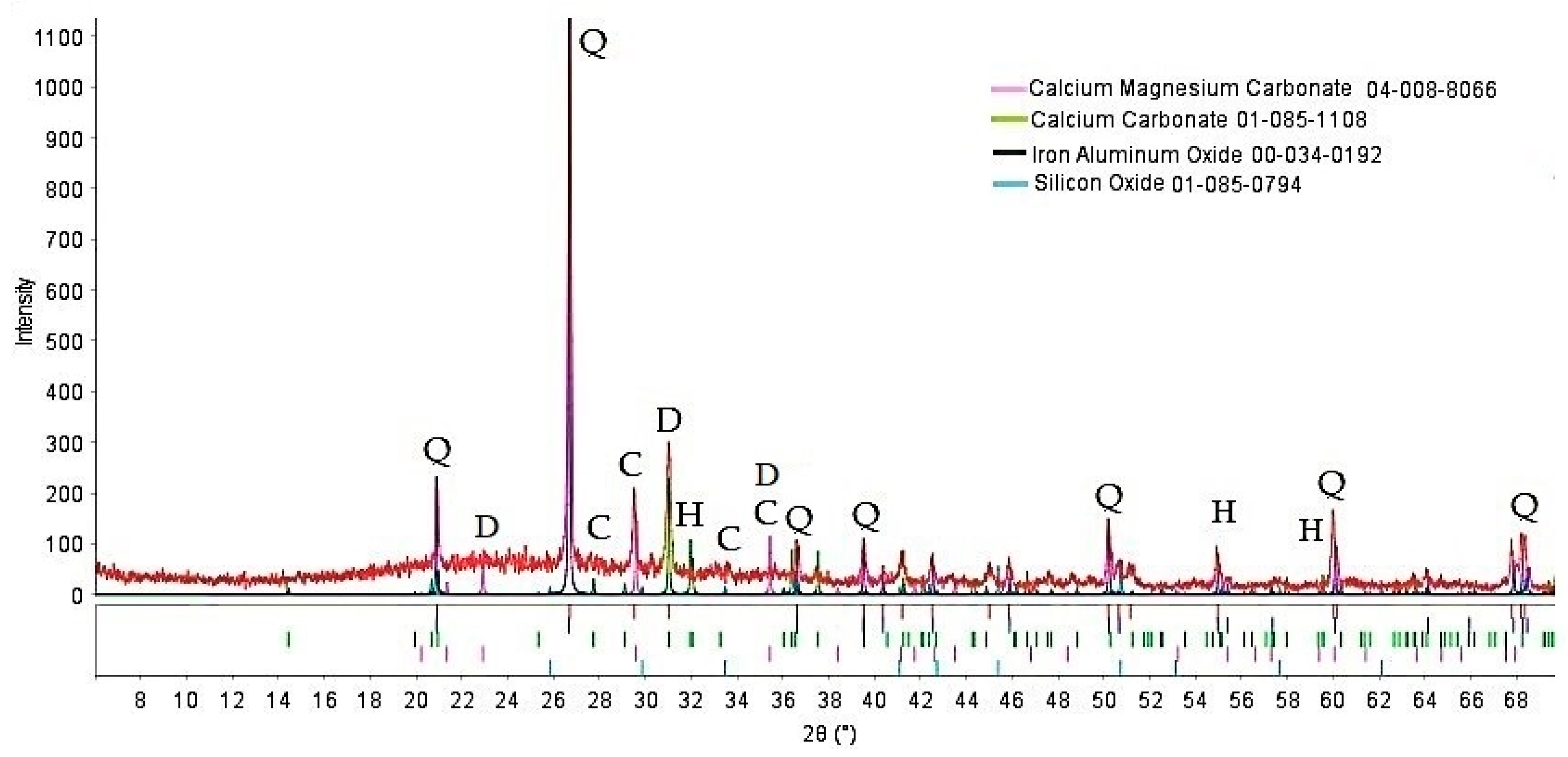
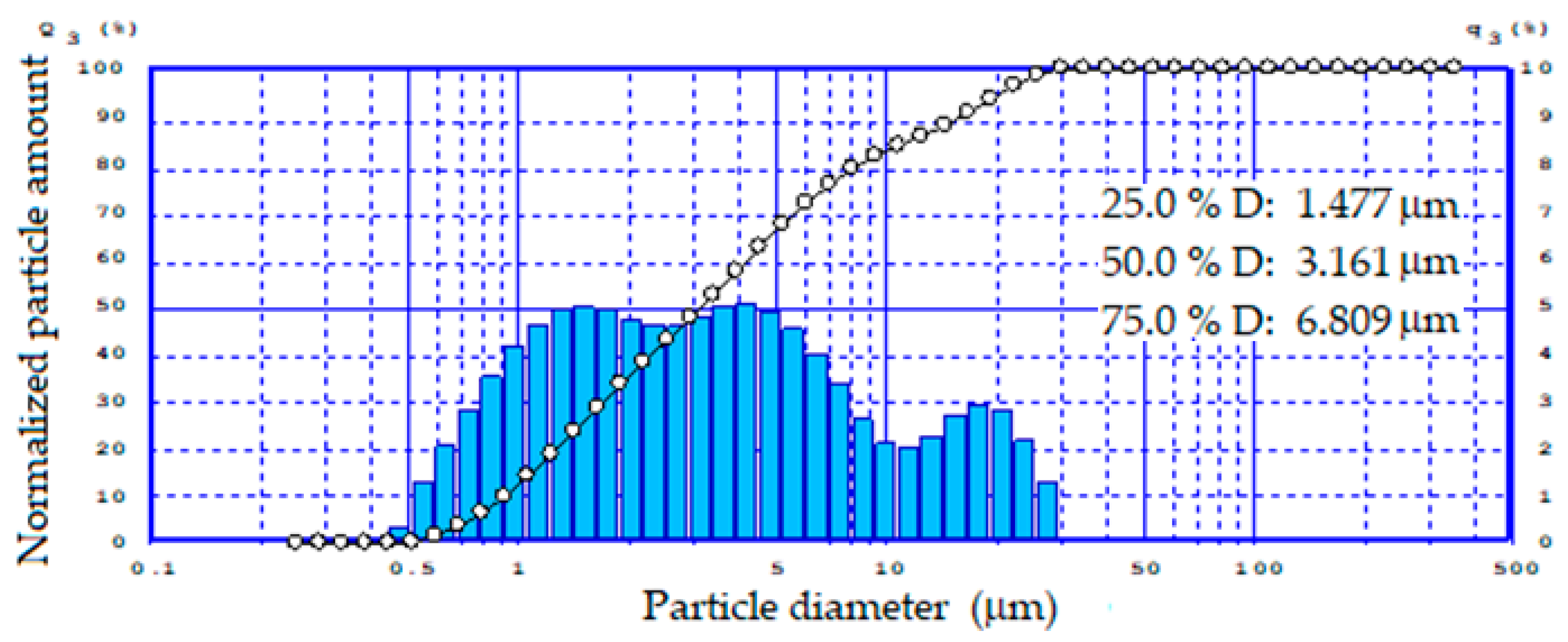
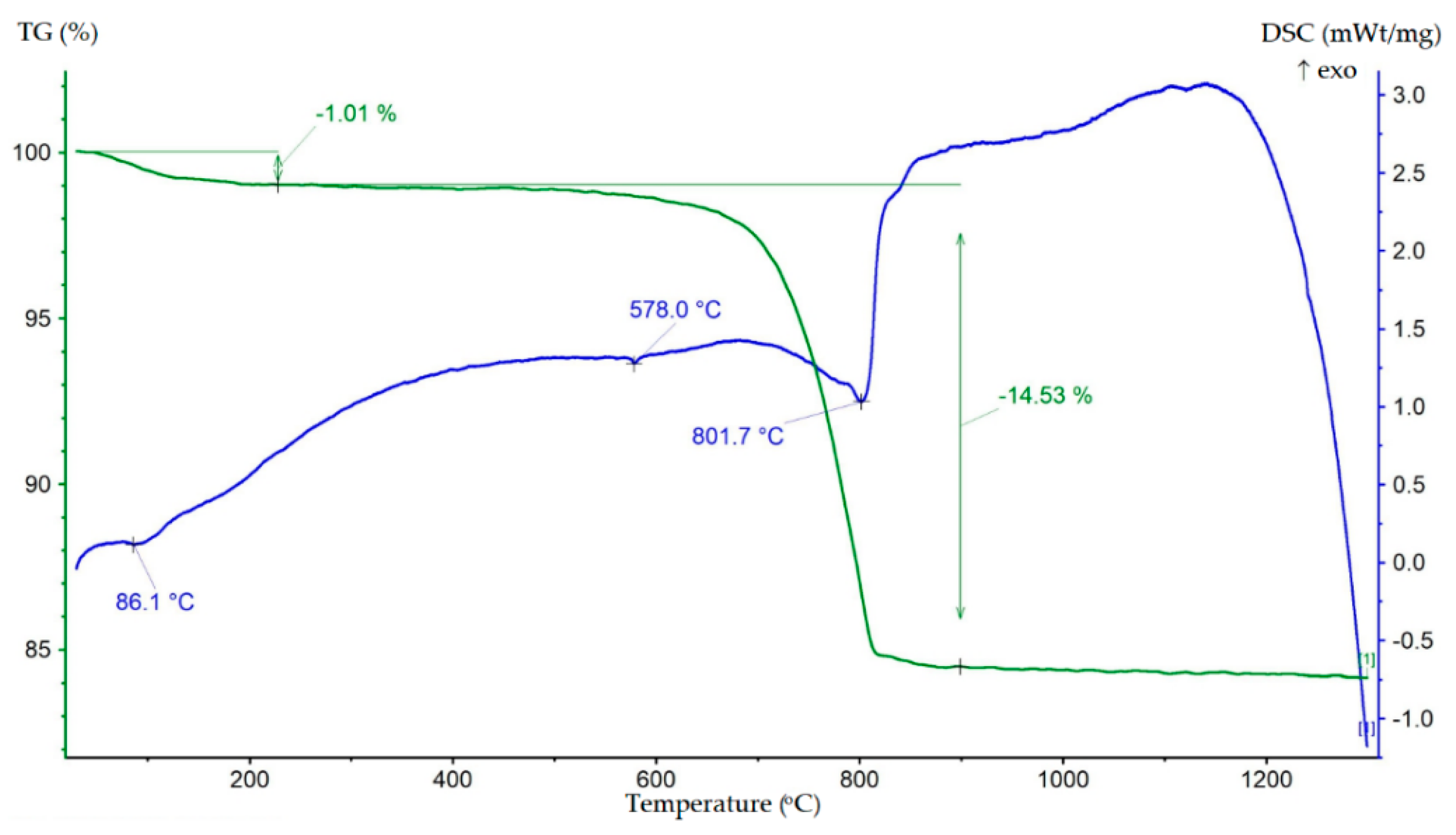

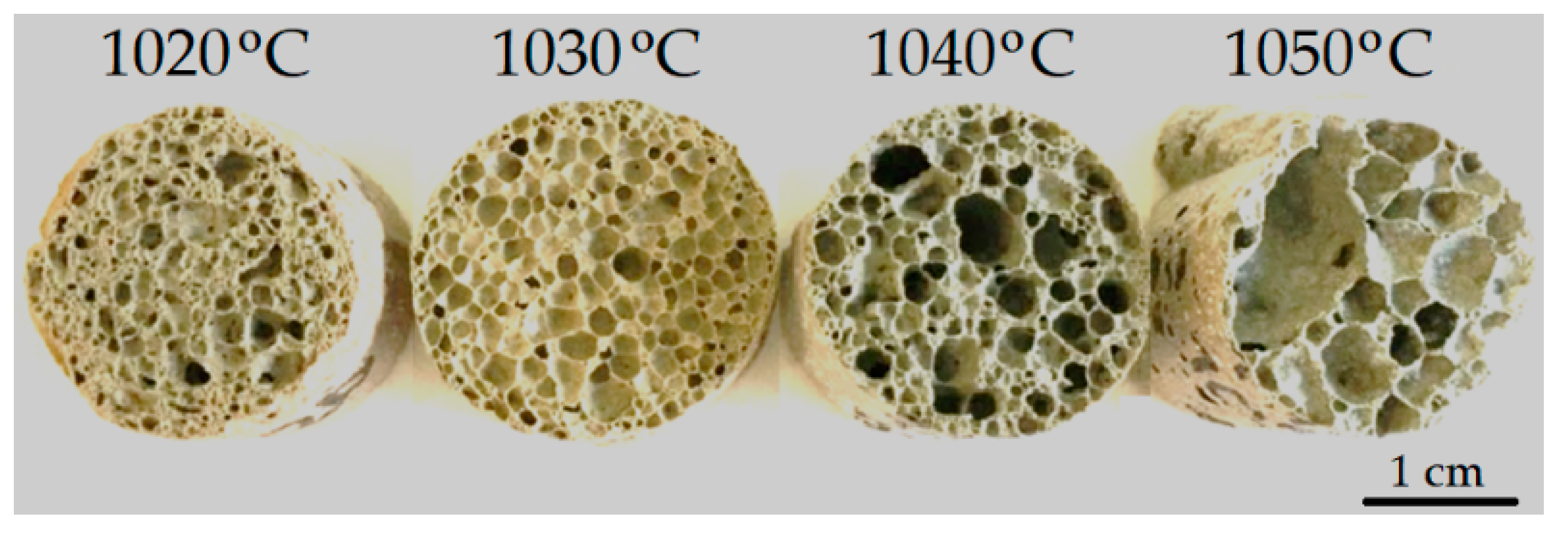
| Composition of Feed | Diamond Concentration Tailings | Clay Material for the Production of Expanded Clay Gravel, Crushed Stone, Sand, etc. (GOST 32026-2012) | Building Ceramics (GOST 32026-2012) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average composition, wt.% | |||
| Na2O + K2O | 0.49 | 1.5–6.0 | |
| Silicon dioxide SiO2 | 49.95 | No more than 70 | 53.0–81.0 |
| Al2O3 | 2.30 | 7.0–25.0 | 7.0–23.0 |
| CaO | 11.41 | Max 6.0 | |
| MgO | 7.35 | No more than 4.0 | |
| MnO | 0.32 | ||
| SO3 | - | No more than 2.0 | No more than 2.0 |
| Fe2O3 + FeO | 4.82 | 2.5–12.0 | 2.5–8.0 |
| TiO2 | 0.63 | 0.1–2.0 | |
| P2O5 | 0.30 | ||
| LOI | 16.20 | ||
| Sample | Starting Temperature of Sample Size Increase, °C | Sintering Temperature, °C | Foaming Ratio | Sample Properties after Heat Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tailings (<0.63>0.05 mm) 50 wt.% − Waste glass 50 wt.% | ||||
| 1 | 800 | 800 | 1.30 | Bulk sintering, increase in size. |
| 2 | 900 | 1.30 | Sintering, increase in size, open porosity. | |
| 3 | 1000 | 1.40 | Surface melting, swelling, ball shape. | |
| 4 | 1100 | 1.33 | Surface melting, gaseous phase breakthrough, ball shape. | |
| Tailings (<0.63>0.05 mm) 50 wt.% − Waste glass 50 wt.% + SiC 0.5 wt.% (over 100 wt.%) | ||||
| 5 | 840 | 800 | 1.30 | Sintering, increase in size, open porosity. |
| 6 | 900 | 1.50 | Increase in size, surface melting, gaseous phase breakthrough, ball shape. | |
| 7 | 1000 | 1.40 | Increase in size, surface melting, minor gaseous phase breakthrough, ball shape. | |
| 8 | 1100 | 1.30 | Increase in size, surface melting, gas phase breakthrough, brittle, ball shape. | |
| Tailings (<0.05 mm) 50 wt.% − Waste glass 50 wt.% + SiC 0.5 wt.% (over 100 wt.%) | ||||
| 9 | 780 | 800 | 1.25 | Sintering, increase in size, cubic shape. |
| 10 | 900 | 1.30 | Sintering, increase in size, cubic shape. | |
| 11 | 1000 | 1.55 | Surface melting, increase in size, gaseous phase breakthrough, ball shape. | |
| 12 | 1100 | 1.50 | Surface melting, increase in size, minor gaseous phase breakthrough, ball shape. | |
| Tailings (<0.05 mm) 50 wt.% − Waste glass 50 wt.% + SiC 0.5 wt.% (over 100 wt.%) + Fe2O3 1 wt.% (over 100 wt.%) | ||||
| 13 | 800 | 950 | 1.20 | Sintering, slight increase in size. |
| 14 | 1000 | 1.20 | Initial surface melting, slight increase in size, cubic shape. | |
| 15 | 1050 | 1.35 | Surface melting, swelling, minor gaseous phase breakthrough, ball shape. | |
| 16 | 1100 | 1.60 | Surface melting, swelling, ball shape. | |
| Tailings (<0.05 mm) 50 wt.% − Waste glass 50 wt.% + SiC 0.5 wt.% (over 100 wt.%) + Fe2O3 3 wt.% (over 100 wt.%) | ||||
| 17 | 840 | 800 | 1.26 | Sintering, slight increase in size, cubic shape. |
| 18 | 900 | 1.20 | Sintering, slight increase in size, cubic shape. | |
| 19 | 950 | 1.25 | Slight melting, increase in size, cubic shape. | |
| 20 | 970 | 1.30 | Surface melting, swelling, ball shape. | |
| 21 | 1000 | 1.59 | Surface melting, swelling, minor gaseous phase breakthrough, ball shape. | |
| 22 | 1050 | 1.65 | Surface melting, swelling, minor gaseous phase breakthrough, ball shape. | |
| Tailings (<0.05 mm) 50 wt.% − Waste glass 50 wt.% + SiC 0.5 wt.% (over 100 wt.%) + Fe2O3 5 wt.% (over 100 wt.%) | ||||
| 23 | 880 | 900 | 1.20 | Sintering, slight increase in size, cubic shape. |
| 24 | 1000 | 1.20 | Sintering, slight increase in size, cubic shape. | |
| 25 | 1050 | 1.30 | Slight melting, hemispheric shape. | |
| 26 | 1100 | 1.30 | Slight melting, ball shape. | |
| Sintering Temperature, °C | Apparent Density, g/cm3 | Porosity, % | Compressive Strength, MPa | Water Absorption, % (by Volume) | Thermal Conductivity, W/m·K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1020 | 0.51 ± 0.02 | 77.1 ± 0.08 | 2.40 ± 0.05 | 8.7 ± 0.17 | 0.060 ± 0.004 |
| 1030 | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 88.3 ± 0.09 | 1.20 ± 0.02 | 9.5 ± 0.19 | 0.066 ± 0.005 |
| 1040 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 84.9 ± 0.09 | 1.05 ± 0.02 | 12.8 ± 0.26 | 0.062 ± 0.004 |
| 1050 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 91.3 ± 0.09 | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 19.0 ± 0.38 | 0.061 ± 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suvorova, O.V.; Manakova, N.K.; Novikov, A.I.; Makarov, D.V. Obtaining Foamed Glass-Ceramics from Diamond Concentration Tailings. Ceramics 2023, 6, 1139-1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6020068
Suvorova OV, Manakova NK, Novikov AI, Makarov DV. Obtaining Foamed Glass-Ceramics from Diamond Concentration Tailings. Ceramics. 2023; 6(2):1139-1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6020068
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuvorova, Olga V., Nadezhda K. Manakova, Andrey I. Novikov, and Dmitriy V. Makarov. 2023. "Obtaining Foamed Glass-Ceramics from Diamond Concentration Tailings" Ceramics 6, no. 2: 1139-1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6020068
APA StyleSuvorova, O. V., Manakova, N. K., Novikov, A. I., & Makarov, D. V. (2023). Obtaining Foamed Glass-Ceramics from Diamond Concentration Tailings. Ceramics, 6(2), 1139-1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6020068







