An Overview on the Manufacture and Properties of Clay-Based Porous Ceramics for Water Filtration
Abstract
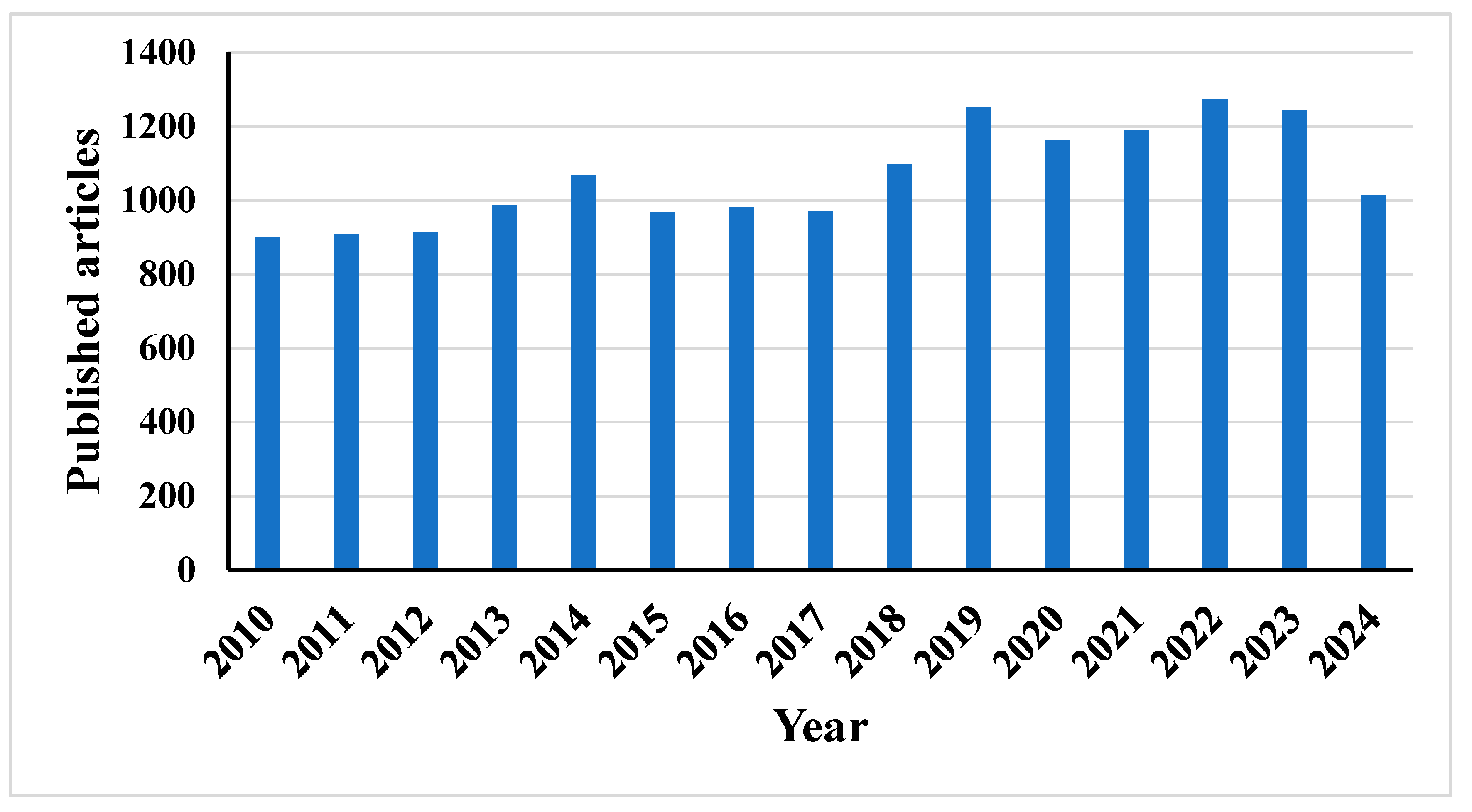
:1. Introduction
- -
- Hydraulic setting, characterized by its ease of use. This generally involves mixing a powder with excess water during the mixing stage, resulting in residual porosity after the setting reaction, followed by a drying stage.
- -
- Incomplete densification through partial sintering, used in the majority of industrial ceramics. By controlling the sintering cycle (temperature, time and/or pressure), materials with appropriate residual porosity are obtained.
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Characterization
- -
- MCT is used to form three-dimensional images, thus observing the geometry of the pore space in samples, such as the shape, connectivity, size and distribution of pores. MCT imaging is performed using a micro-focused X-ray tube that obtains shadow images of the object transmitted by multiple X-rays from different angles [39].
- -
- Mercury intrusion porosimetry method measures open porosity and is appropriate for pores with diameters ranging from 0.01 microns to 800 microns. Measuring the volume of mercury included in the sample at each pressure value gives the size distribution of its open pores. Considered a standard method of macropore analysis [40], it also enables the calculation of apparent density and total open porosity.
- -
- Porosity is calculated from the absolute (or real) ρr and apparent bulk densities ρa. The real bulk density can be determined by pycnometry on powdered materials (obtained by a fine grinding of samples), and the apparent bulk density is calculated using both dimensions and mass of the dry material. Thus, total porosity P is hence determined by Equation (1) [41].
- -
- The principle of Archimedes states that the force exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially, is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces. Thus, the tripled weighed method consists of weighing three different masses (M1, M2 and M3) based on the Archimedes system, where M1 is the dry mass of samples, M2 is the mass of the sample completely immersed in liquid and M3 is the wet mass of the samples. Hence, with clearly defined formulae, the open porosity Po of the sample can be calculated using Equation (2) below [42]:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Porous Ceramics Obtained from Raw Materials
3.2. Porous Ceramics Obtained from Synthesized Materials
3.3. Porous Ceramics Obtained from Raw Materials and Waste
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Programme solidarité eau Conservation et Traitement de l’eau à Domicile. Available online: https://www.pseau.org/outils/ouvrages/ps_eau_conservation_et_traitement_de_l_eau_a_domicile_2018.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Misrar, W.; Loutou, M.; Saadi, L.; Mansori, M.; Waqif, M.; Favotto, C. Cordierite Containing Ceramic Membranes from Smectetic Clay Using Natural Organic Wastes as Pore-Forming Agents. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2017, 5, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talidi, A.; Saffaj, N.; Kacemi, K.E.; Younssi, S.A.; Albizane, A.; Chakir, A. Processing and Characterization of Tubular Ceramic Support for Microfiltration Membrane Prepared from Pyrophyllite Clay. Sci. Study Res. Chem. Chem. Eng. Biotechnol. Food Ind. 2011, 12, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Larbot, A.; Cerneaux, S. New Clay–Alumina Porous Capillary Supports for Filtration Application. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 392–393, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, J.M.; Sánchez, M.J.; Pena, P.; Rodríguez, M.A. Development of a New High Porosity Ceramic Membrane for the Treatment of Bilge Water. Desalination 2007, 214, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiou, B.; Elomari, H.; Ouammou, M.; Albizane, A.; Bennazha, J.; Alami Younssi, S.; El Amrani, I.E.; Aaddane, A. Elaboration and Characterization of Flat Ceramic Microfiltration Membrane Made from Natural Moroccan Pozzolan (Central Middle Atlas). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 196–204. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, S.K.; Abdallah, H.A.M.; Roushdy, M.H.; El-Sherbiny, S.A. An Overview of Production and Development of Ceramic Membranes. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2016, 11, 7708–7721. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.N.; Fane, A.G.; Ho, W.S.W.; Matsuura, T. Advanced Membrane Technology and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, K.; Lecomte-nana, G.L.; Seynou, M.; Faucher, M.; Blanchart, P.; Peyratout, C. Comparative Properties of Porous Phyllosilicate-Based Ceramics Shaped by Freeze-Tape Casting. Ceramics 2022, 5, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medri, V.; Mazzocchi, M.; Bellosi, A. ZrB2-Based Sponges and Lightweight Devices. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2011, 8, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P. Research Progress on Preparation of Porous Ceramics. Interceram-Int. Ceram. Rev. 2015, 64, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Neeraj, V.S.; Wilson, P.; Vijayan, S.; Prabhakaran, K. Porous Ceramics with a Duplex Pore Structure by Compression Molding of Alumina-NaCl Paste in Molten Sucrose. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 14107–14113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.-Z.; Kato, T.; Fuji, M.; Takahashi, M. Gelcasting Fabrication of Porous Ceramics Using a Continuous Process. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.; Dayirou, N.; Mohamed, H.; Andre, N.; Gisele Laure, L.N.; Daniel, N. Effect of Porogenic Agent Type and Firing Temperatures on Properties of Low-Cost Microfiltration Membranes from Kaolin. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2020, 79, 1692695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Jia, Q. A Novel Strategy for Synthesizing Porous ZrB2-SiC Ceramics via Boro/Carbothermal Reaction Process Templated Pore-Forming Approach. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 43, 3905–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Qu, Y.-N.; Xu, J.; Ma, N.; Gan, K.; Huo, W.-L.; Yang, J.-L. A Simple and Efficient Way to Prepare Porous Mullite Matrix Ceramics via Directly Sintering SiO2-Al2O3 Microspheres. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 2807–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Sui, H.; Xiao, S. Structural Design of PZT Porous Ceramics Obtained via Free-Casting by Ice-Templating and Performance Exploration. Mater. Res. Bull. 2020, 127, 110862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Guo, B.; Zuo, W.; Jiang, K.; Chen, H.; Ku, J. Effect of Sintering Temperature on Structure and Properties of Porous Ceramics from Tungsten Ore Tailings. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 287, 126315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckers, J.; Vleugels, J.; Kruth, J.-P. Additive Manufacturing of Ceramics: A Review. J. Ceram. Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 245–260. [Google Scholar]
- Zocca, A.; Colombo, P.; Gomes, C.M.; Gunster, J. Additive Manufacturing of Ceramics: Issues, Potentialities, and Opportunities. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 1983–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lv, C.; Liu, B.; Wang, G.; Duan, W.; Gu, Y. Digital Light Processing 3D Printing of Porous Ceramics Based on Multi-Materials Additive Manufacturing. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2023, 42, 100106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, C.; Moraes, A.; Oliveira Rocco, F.; Montilha, F.S.; Canto, R. A Validation Procedure for Numerical Models of Ceramic Powder Pressing. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, P.; Lenka, R.; Mahata, T. Shape Forming and Sintering of Ceramics. In Handbook on Synthesis Strategies for Advanced Materials: Volume-II: Processing and Functionalization of Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–54. ISBN 978-981-16-1802-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y. Porous Silica/Mullite Ceramics Prepared by Foam-Gelcasting Using Silicon Kerf Waste as Raw Material. Mater. Lett. 2019, 239, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maca, K.; Dobsak, P.; Boccaccini, A.R. Fabrication of Graded Porous Ceramics Using Alumina–Carbon Powder Mixtures. Ceram. Int. 2001, 27, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J. Fabrication and Properties of Porous Mulite Ceramics from Calcined Carbonaceous Kaolin and α-Al2O3. Ceram. Int. 2010, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-M.; Li, M.; Liu, S.-S.; Shi, Y.-S.; Li, C.-H.; Wang, W. Selective Laser Sintering of Porous Al2O3-Based Ceramics Using Both Al2O3 and SiO2 Poly-Hollow Microspheres as Raw Materials. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 15313–15318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fu, R.; Chen, K.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Cost-Effective Fabrication of Porous α-SiAlON Bonded β-SiAlON Ceramics. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 2601–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Wei, C.; Meng, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Du, Q.; Tang, Z. Fabrication of Porous Al2O3–MgAl2O4 Ceramics Using Combustion-Synthesized Powders Containing in Situ Produced Pore-Forming Agents. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1559–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Xu, J.; Yang, R.; Lin, L.; Wang, H.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Gao, F. Enhanced Thermal Insulation and Mechanical Properties of Y-α-SiAlON Porous Ceramics with Sr Doping. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 6074–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Wang, Z.J.W. Preparation of Porous SiC Ceramics from Waste Cotton Linter by Reactive Liquid Si Infiltration Technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 7294–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Xia, B.; Hu, T.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M. Effect of MoO3 Addition on Fly Ash Based Porous and High-Strength Mullite Ceramics: In Situ Whisker Growth and Self-Enhancement Mechanism. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 21069–21077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndzana, E.J.A.; Njuhou, S.; Pountouenchi, A.; Lecomte-Nana, G.; Njoya, D. Comparative Study of Alluvial Clay-Based Stoneware Ceramic’s Properties Using Cocoa Cortex Ash and Syenite as Fluxing Agents. Open Ceram. 2024, 17, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winans, K.; Kendall, A.; Deng, H. The History and Current Applications of the Circular Economy Concept. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wietschel, L.; Halter, F.; Thorenz, A.; Schüppel, D.; Koch, D. Literature Review on the State of the Art of the Circular Economy of Ceramic Matrix Composites. Open Ceram. 2023, 14, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonon, M. Case Studies in the X-Ray Diffraction of Ceramics. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Technical Ceramics and Glasses; Pomeroy, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 560–577. ISBN 978-0-12-822233-1. [Google Scholar]
- Carty, W.M.; Senapati, U. Porcelain - Raw Materials, Processing, Phase Evolution, and Mechanical Behavior. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1998, 81, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truche, C. Caractérisation et Quantification des Minéraux Argileux dans les sols Expansifs par Spectroscopie Infrarouge aux Echelles du Terrain et du Laboratoire. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paul Sabatier-Toulouse III, Toulouse, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, M.T.Q.S.; Perretto, F.; do Rocio Cardoso, M.; Mazer, W. Porosity: Some Characterization Techniques. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquerol, J.; Baron, G.V.; Denoyel, R.; Giesche, H.; Groen, J.; Klobes, P.; Levitz, P.; Neimark, A.V.; Rigby, S.; Skudas, R.; et al. The Characterization of Macroporous Solids: An Overview of the Methodology. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 154, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubi, H.G.; Kouamé, A.N.; Konan, L.K.; Tognonvi, M.; Oyetola, S. Thermal Conductivity of Compressed Earth Bricks Strengthening by Shea Butter Wastes with Cement. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2017, 7, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, B.; Ren, X.; Yu, C.; Tian, J.; Liu, C.; Deng, C.; Hu, C.; Liu, Z.; Yu, J.; et al. Phase-Engineering Strategy of ZrO2 for Enhancing the Mechanical Properties of Porous Cordierite Ceramics. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 30, 103032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamgang, S.P.; Njoya, D.; Kamseu, E.; Cyr, L.C. de S.; Marcano-Zerpa, A.; Balme, S.; Bechelany, M.; Soussan, L. Elaboration of a New Ceramic Membrane Support from Cameroonian Clays, Coconut Husks and Eggshells: Application for Escherichia coli Bacteria Retention. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 198, 105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarinci, G.; Brusatin, G.; Barbieri, L.; Corradi, A.; Lancellotti, I.; Colombo, P.; Hreglich, S.; Dall’Igna, R. Vitrification of Industrial and Natural Wastes with Production of Glass Fibres. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 20, 2485–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görhan, G.; Şimşek, O. Porous Clay Bricks Manufactured with Rice Husks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, Q.; Meng, G. Preparation of Cordierite-Based Porous Ceramic Micro-Filtration Membranes Using Waste Fly Ash as the Main Raw Materials. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 285, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dong, Y.; Hampshire, S.; Cerneaux, S.; Winnubst, L. Waste-to-Resource Preparation of a Porous Ceramic Membrane Support Featuring Elongated Mullite Whiskers with Enhanced Porosity and Permeance. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, A.; El Haddar, A.; El Amrani El Hassani, I.-E.; El Bouari, A.; Sadik, C. Valorization of Coffee Waste with Moroccan Clay to Produce a Porous Red Ceramics (Class BIII). Bol. Soc. Esp. Ceram. Vidr. 2019, 58, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigay, P.M.; Sani, R.; Cutard, T.; Nzihou, A. Modeling of the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Clay Ceramics Incorporating Organic Additives. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 708, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, N. Novel Applications of Waste Ceramics on the Fabrication of Foamed Materials for Exterior Building Walls Insulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monich, P.R.; Romero, A.R.; Rambaldi, E.; Bernardo, E. Case Studies of Up-Cycling of Partially Crystallized Ceramic Waste in Highly Porous Glass-Ceramics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 119971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonis, J.J.; Basson, A.K. Manufacturing a Low-Cost Ceramic Water Filter and Filter System for the Elimination of Common Pathogenic Bacteria. Phys. Chem. Earth 2012, 50–52, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, E.C.; Ighodaro, O.L.-R.; Okoli, O.I. Processing and Properties of Advanced Porous Ceramics: An Application Based Review. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 15351–15370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobsey, M.D.; Stauber, C.E.; Casanova, L.M.; Brown, J.M.; Elliott, M.A. Point of Use Household Drinking Water Filtration: A Practical, Effective Solution for Providing Sustained Access to Safe Drinking Water in the Developing World. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4261–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirasaki, N.; Matsushita, T.; Matsui, Y.; Urasaki, T.; Oshiba, A.; Ohno, K. Evaluation of Norovirus Removal Performance in a Coagulation-Ceramic Microfiltration Process by Using Recombinant Norovirus Virus-like Particles. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, K.; Lecomte-Nana, G.L.; Sory, N.; Ouedraogo, M.; Sawadogo, L.; Sawadogo, M.; Sanou, I.; Seynou, M.; Zerbo, L.; Blanchart, P. Mullite Effect on the Ceramic Filters Effectiveness in the Removal of Arsenic from Borehole Water from Burkina Faso. Open Ceram. 2024, 20, 100679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, H.B.; Boughzala, U.; Dridi, D.; Barillier, D.; Chekir-Ghedira, L.; Mosrati, R. Textiles Dyes as a Source of Wastewater Contamination: Screening of the Toxicity and Treatment Methods; [Les Colorants Textiles Sources de Contamination de l’eau: CRI BLAGE de La Toxicité et Des Methods Detraitement]. Rev. Sci. L’eau 2011, 24, 209–238. [Google Scholar]
- Pei Ling, Y.; Ooi, C.-H.; Matsumoto, A.; Yeoh, F.-Y. Properties Evaluation and Fabrication of Green Clay Reformulated from Water Sludge. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartal, O.; Madinzi, A.; Khattabi Rifi, S.; Haddaji, C.; Agustiono Kurniawan, T.; Anouzla, A.; Souabi, S. Optimization of Coagulation-Flocculation Process for Wastewater Treatment from Vegetable Oil Refineries Using Chitosan as a Natural Flocculant. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romphophak, P.; Chamnanmor, R.; Fagkaew, P.; Sairiam, S.; Painmanakul, P. Modelling the Predictive Analysis of Turbidity Removal Efficiency in the In-Line Coagulation and Flocculation Process. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 210, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
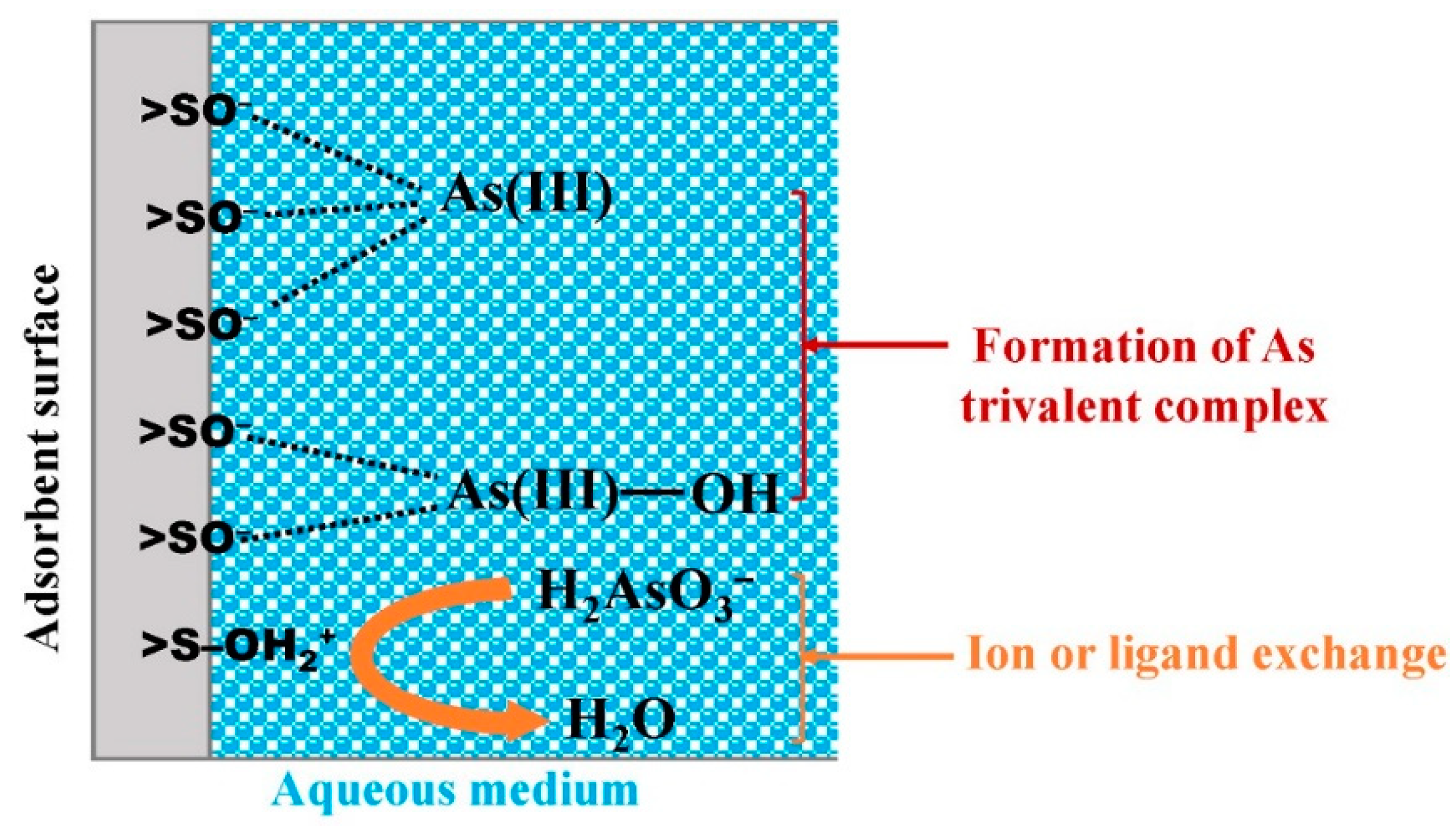
- Halim, M.A.; Waliul Hoque, S.A.M.; Hossain, M.K.; Saadat, A.H.M.; Goni, M.A.; Saiful Islam, M. Arsenic Removal Properties of Laterite Soil by Adsorption Filtration Method. J. Appl. Sci. 2008, 8, 3757–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Konadu-Amoah, B.; Gatcha-Bandjun, N.; Hu, R.; Gwenzi, W.; Noubactep, C. Kanchan Arsenic Filters for Household Water Treatment: Unsuitable or Unsustainable? Water 2022, 14, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiquzzaman, M.; Hasan, M.M.; Haider, H.; Bari, Q.H.; EL-Ghoul, Y.; Nakajima, J. Arsenic Removal by Household-Based Ceramic Filters: Evaluating Mode of Operations and Influence of Groundwater Compositions. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, N.H.; Harun, Z.; Othman, M.H.D.; Abdullahi, T.; Syamsul Bahri, S.; Kamarudin, N.H.; Yunos, M.Z.; Wan Salleh, W.N. Waste Environmental Sources of Metakaolin and Corn Cob Ash for Preparation and Characterisation of Green Ceramic Hollow Fibre Membrane (h-MCa) for Oil-Water Separation. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 1512–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouafon, M.; Lecomte-Nana, G.L.; Tessier-Doyen, N.; Njoya, A.; Njoya, D.; Njopwouo, D. Processing and Characterization of Low-Thermal Conductivity, Clay-Based Ceramic Membranes for Filtering Drinking Water. Clays Clay Miner. 2021, 69, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiquzzaman, M.; Azam, M.S.; Nakajima, J.; Bari, Q.H. Arsenic Leaching Characteristics of the Sludges from Iron Based Removal Process. Desalination 2010, 261, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayral, A.; Hulea, V.; Jean-Pierre, J.; Julbe, A. Céramiques Pour l’environnement: Filtres, Membranes, Adsorbants et Catalyseurs. Chim. Verte 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, J.; Skinner, B.; Lantagne, D. Current Practices in Manufacturing Locally-Made Ceramic Pot Filters for Water Treatment in Developing Countries. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2013, 3, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvinelli, C.; Elmore, A.C.; Reidmeyer, M.R.; Drake, K.D.; Ahmad, K.I. Characterization of the Relationship between Ceramic Pot Filter Water Production and Turbidity in Source Water. Water Res. 2016, 104, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
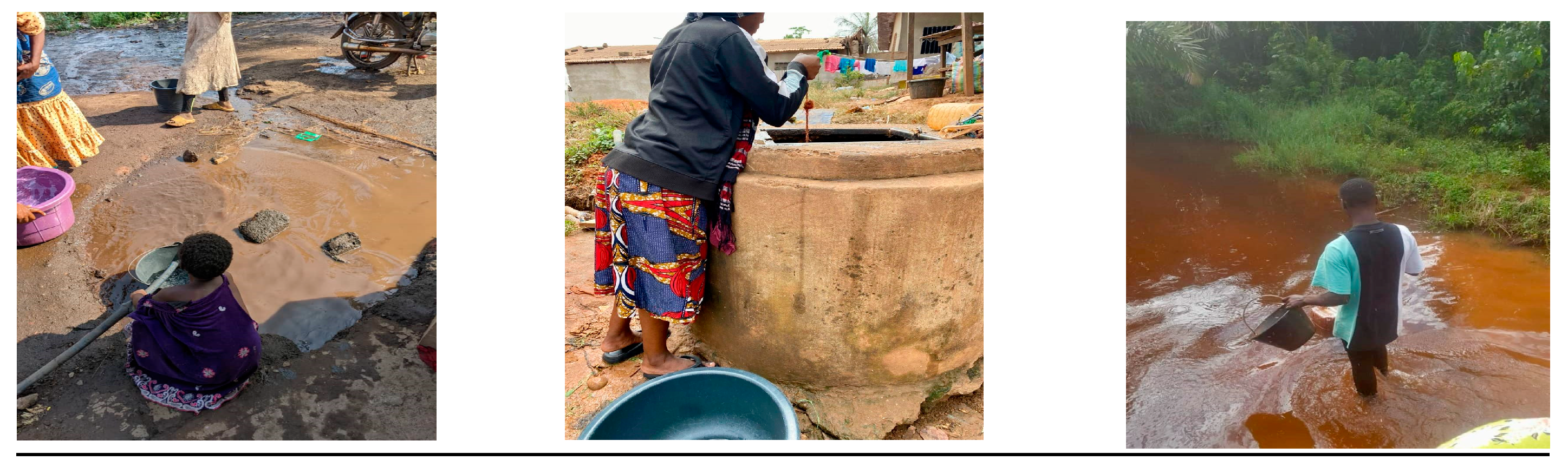
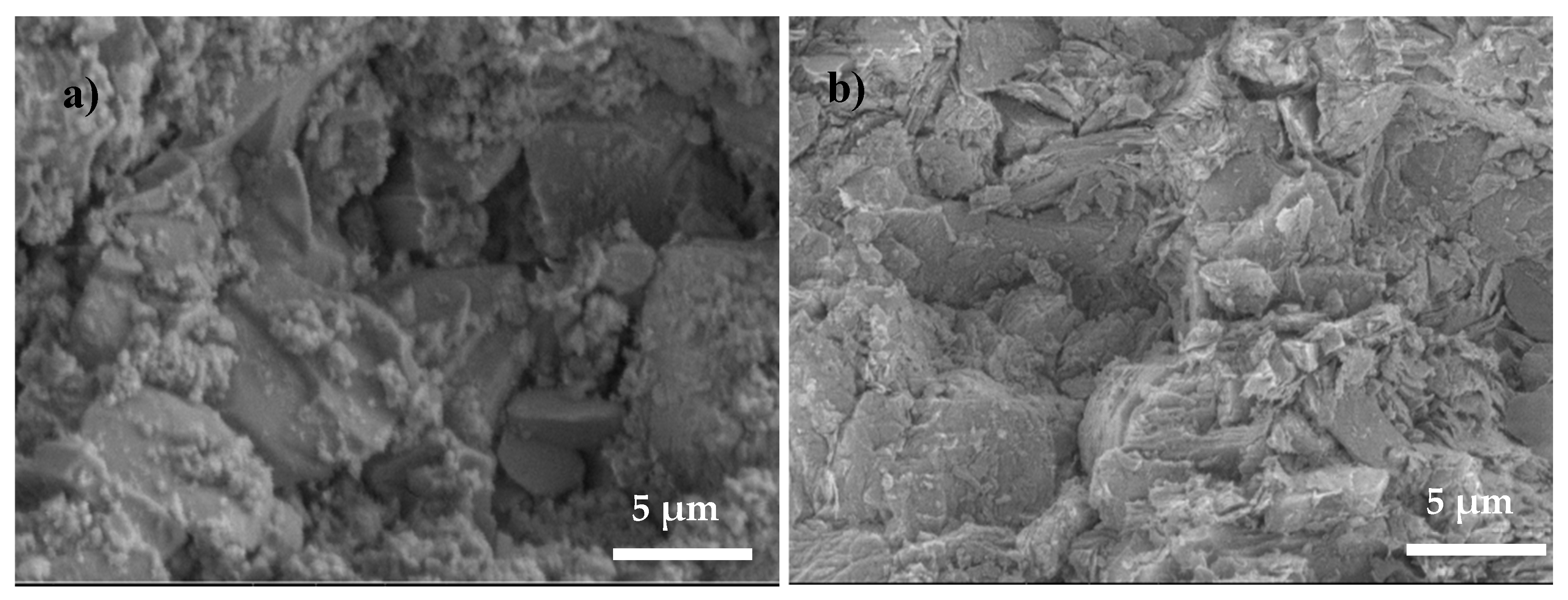
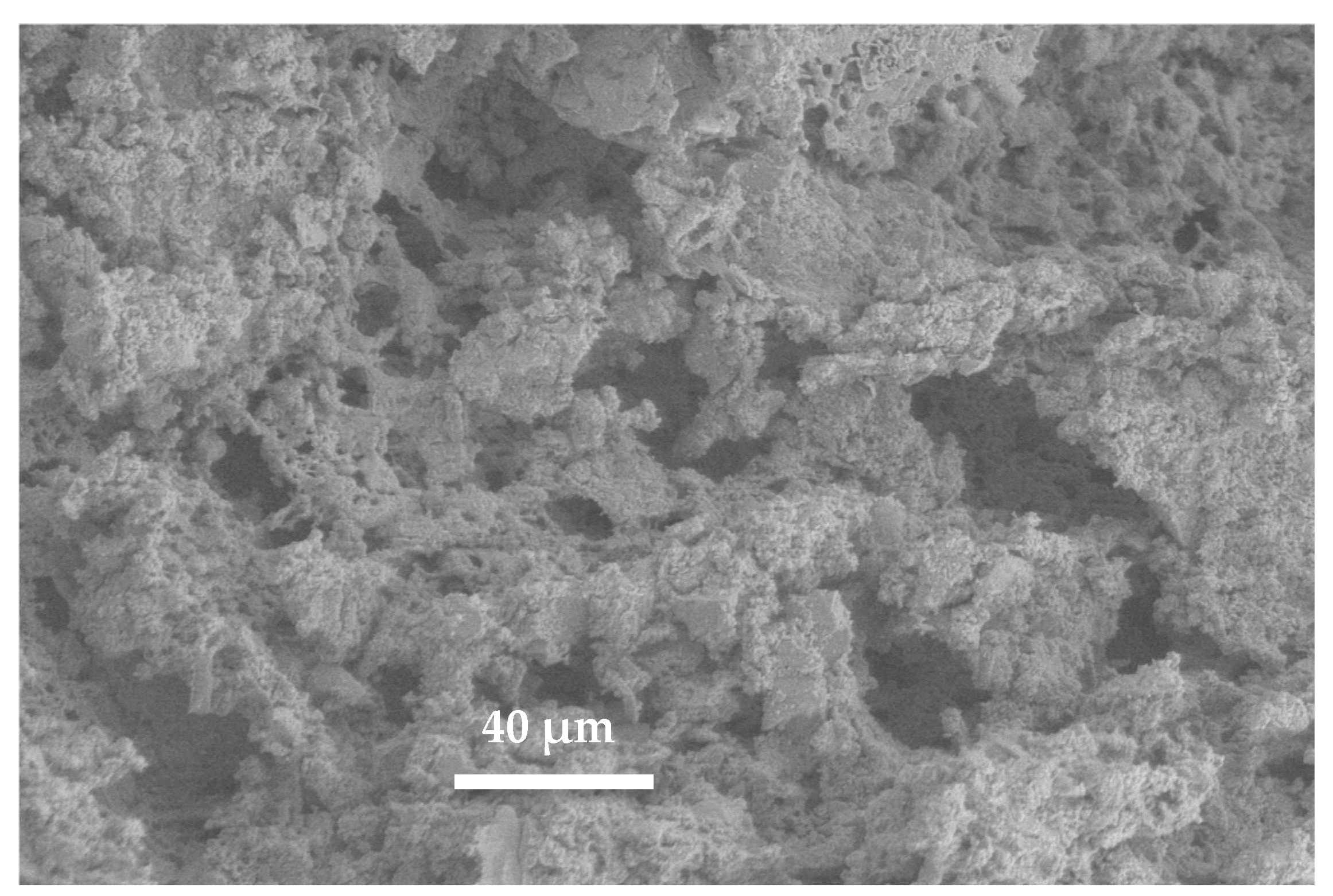




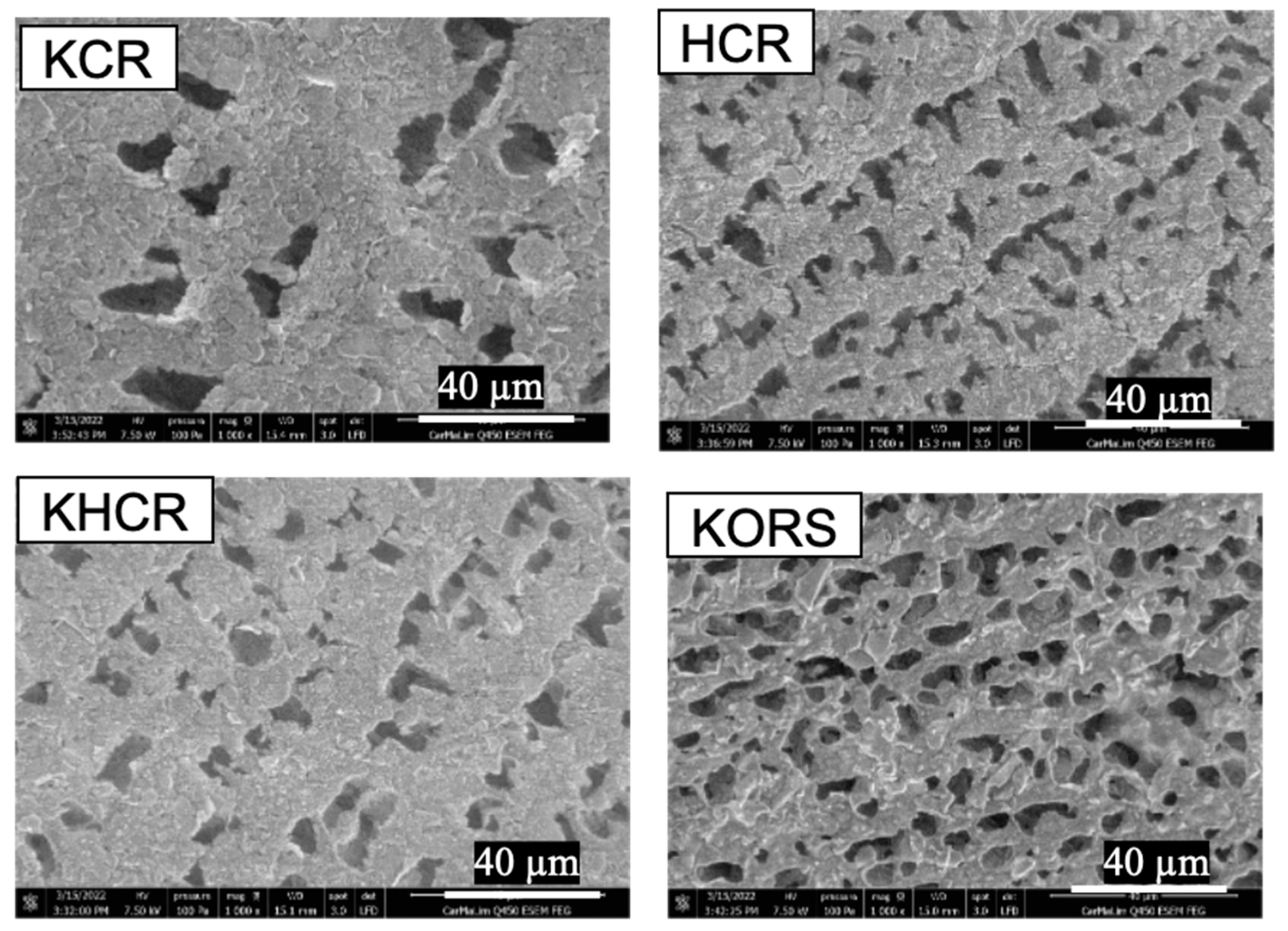

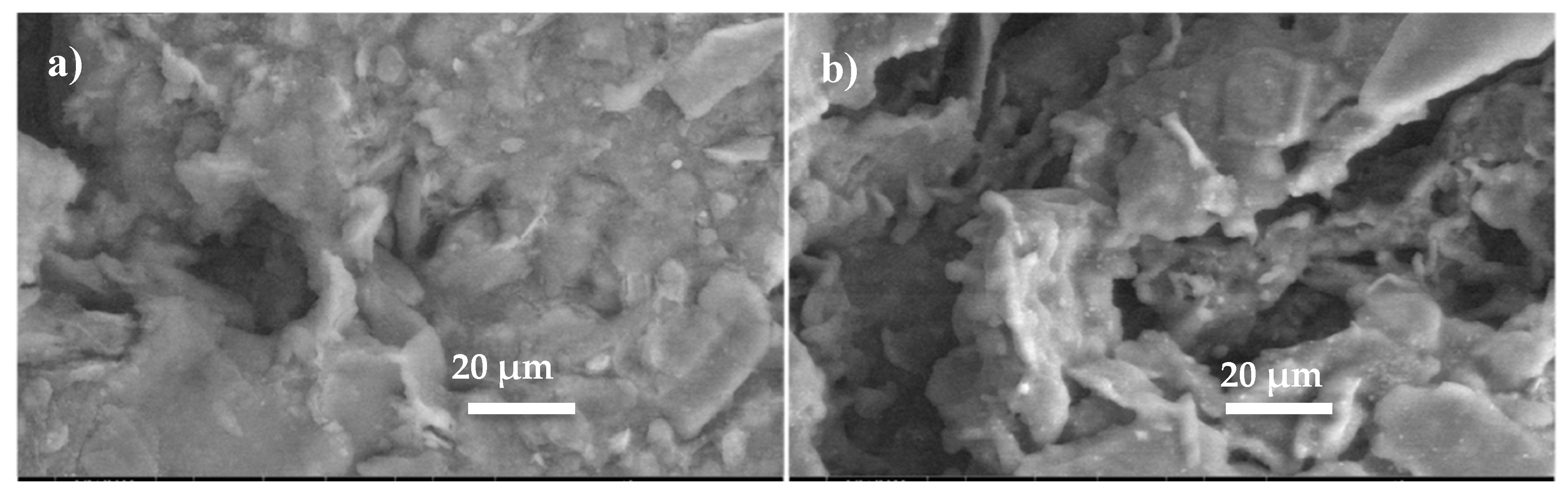
| Composition | Final Product | Sintering Conditions | Apparent Porosity (%) | Pore Size (µm) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZrO2 powder + SiO2 + boron carbide + carbon black | Porous ZrB2-SiC ceramic | 1500 °C/2 h | 67–78 | 0.2–9.8 | [15] | |
| Quartz powder + alumina powder + glass powder + ammonium polycrylates solution + propyl gallate | Porous mullite matrix ceramic | 1200 °C/1 h 1300 °C/1 h 1400 °C/1 h 1500 °C/1 h 1550 °C/1 h 1600 °C/1 h 1650 °C/1 h | ~45 ~80 ~82 ~83 81.37 ~81.4 ~88 | ~750 | 88.3 ± 13.61 - - - 6.25 ± 0.91 - - | [16] |
| Tungsten ore tailing (75 wt%) + CaO + Kaolin + polymethyl methacrylate (18 wt%) | Porous ceramics | 1200 °C/60 min | 44.85 | 180 | 14.10 | [18] |
| Alumina powder + milled carbon coal + stearin | Porous ceramic | 1530 °C/2 h | - | 60 × 20 | - | [25] |
| Carbonaceous kaolinite clay + alumina powder | Porous ceramic | 1400 °C/4 h 1450 °C/4 h 1500 °C/4 h 1550 °C/4 h | ~43–46 ~44–48 ~36–38 ~17–32 | - - - - | - - 42.1 75.9 | [26] |
| Al2O3 + SiO2 PHMs (0–40 wt%) + epoxy resin | Porous Al2O3 Ploy-hollow microspheres (PHM) ceramic | 1550 °C/4 h | ~77 ~76 ~71 65.0 ~66 | 51.95 45.51 38.25 38.25 30.14 | ~0.2 ~0.1 ~1 4 ~1.8 | [27] |
| Composition | Final Product | Sintering Conditions | Apparent Porosity (%) | Pore Size (µm) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al(NO3)3.9H2O + Mg(NO3)3.9H2O + Urea + Soluble starch | Porous ceramics | 1400 °C/2 h | 35.2–51.6 | ~0.2–20 | ~36.1–454.7 | [29] |
| Si3N4 + Y2O3 + SrCO3 +Al2O3 + premix solution + polyacrylamide + methyletylenediamine + ammonium persulfate | Porous ceramics | 1750 °C/1 h | ~47–57 | - | 52.67–106.33 | [28] |
| Composition | Final Product | Sintering Conditions | Apparent Porosity (%) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground rice husk (5–15 vol%) + brick raw material | Porous clay brick | 800 °C/1 h 900 °C/1 h 1000 °C/1 h | ~39–44.5 ~38–44 ~37–43.5 | ~9.5 ~5.75–9.25 ~6–9 | [45] |
| Coffee waste (10–30 wt%) + red clay | Porous red ceramics | 1150 °C | ~30.2–63.8 | ~1.8–19.5 | [48] |
| Wheat straw (4–8 wt%) + clay | Porous clay brick | 950 °C | ~40–50 | - | [49] |
| Ceramic waste (80%) + flux + cement + clay | Ceramic foam | 1000 °C/3 h | ~40–83 | ~0–9.3 | [50] |
| Polished stonewere residue (90%) + soda-lime glass | Highly porous glass ceramic | 900 °C/1 h | 75.1 | 2.5 | [51] |
| Filters | Price (Euro) | Pollutant Eliminated | Yield Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse osmosis filter | 60–400 | Microorganisms, particles | 85–95 |
| UV filter | 150–1000 | Parasite, viruses | >86 |
| Ion exchange filter | Heavy metals, limestone | 82 | |
| Glass fiber filter | Suspended particles | 95 | |
| Ceramic filter | 150–600 | Viruses, suspended particles, protozoaires, bacteria | 98 |
| Alkali water ionizer filter | 400–2000 | Suspended particles, bacteria, viruses | 92 |
| Composition | Permeability (L/h.m2.Bar) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Clay + coconut husk + eggshell | 14,013 | [43] |
| Kaolinitic clay + peanut shell (sintered at 1100 °C) | 53,802 | [56] |
| Kaolinitic clay + peanut shell (sintered at 900 °C) | 18,596 | [56] |
| Metakaolin + corn cob ash waste | 1359.93 | [64] |
| Clays + cassava starch + bovine bone ash | 2902 | [65] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maury Njoya, I.Q.; Lecomte-Nana, G.L.; Barry, K.; Njoya, D.; El Hafiane, Y.; Peyratout, C. An Overview on the Manufacture and Properties of Clay-Based Porous Ceramics for Water Filtration. Ceramics 2025, 8, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8010003
Maury Njoya IQ, Lecomte-Nana GL, Barry K, Njoya D, El Hafiane Y, Peyratout C. An Overview on the Manufacture and Properties of Clay-Based Porous Ceramics for Water Filtration. Ceramics. 2025; 8(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaury Njoya, Iffat Qoudsiyyah, Gisèle Laure Lecomte-Nana, Kassoum Barry, Dayirou Njoya, Youssef El Hafiane, and Claire Peyratout. 2025. "An Overview on the Manufacture and Properties of Clay-Based Porous Ceramics for Water Filtration" Ceramics 8, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8010003
APA StyleMaury Njoya, I. Q., Lecomte-Nana, G. L., Barry, K., Njoya, D., El Hafiane, Y., & Peyratout, C. (2025). An Overview on the Manufacture and Properties of Clay-Based Porous Ceramics for Water Filtration. Ceramics, 8(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8010003









