Application End Evaluation of Electrostatic Precipitation for Control PM and NOx Emissions from Small-Scale Combustions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
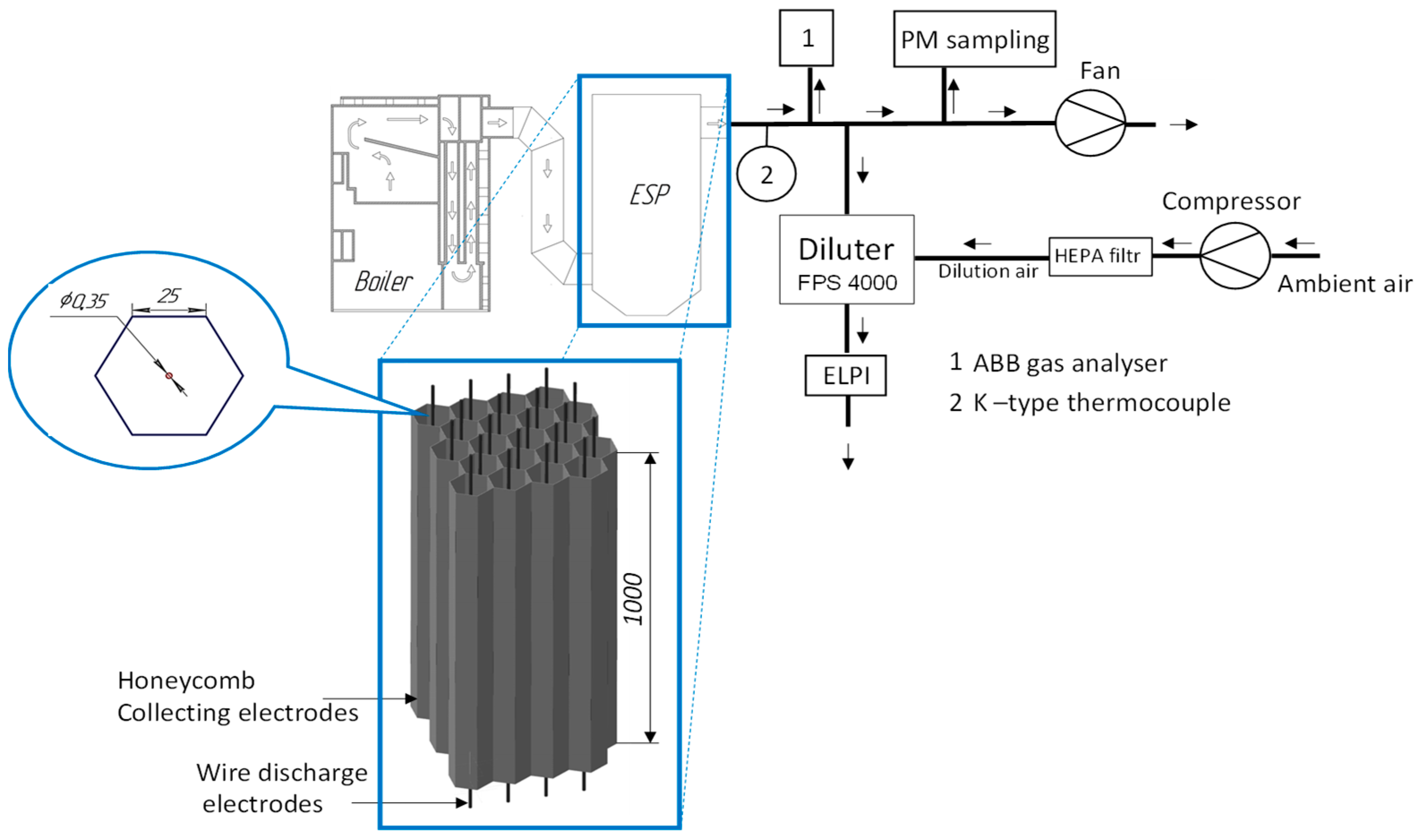
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
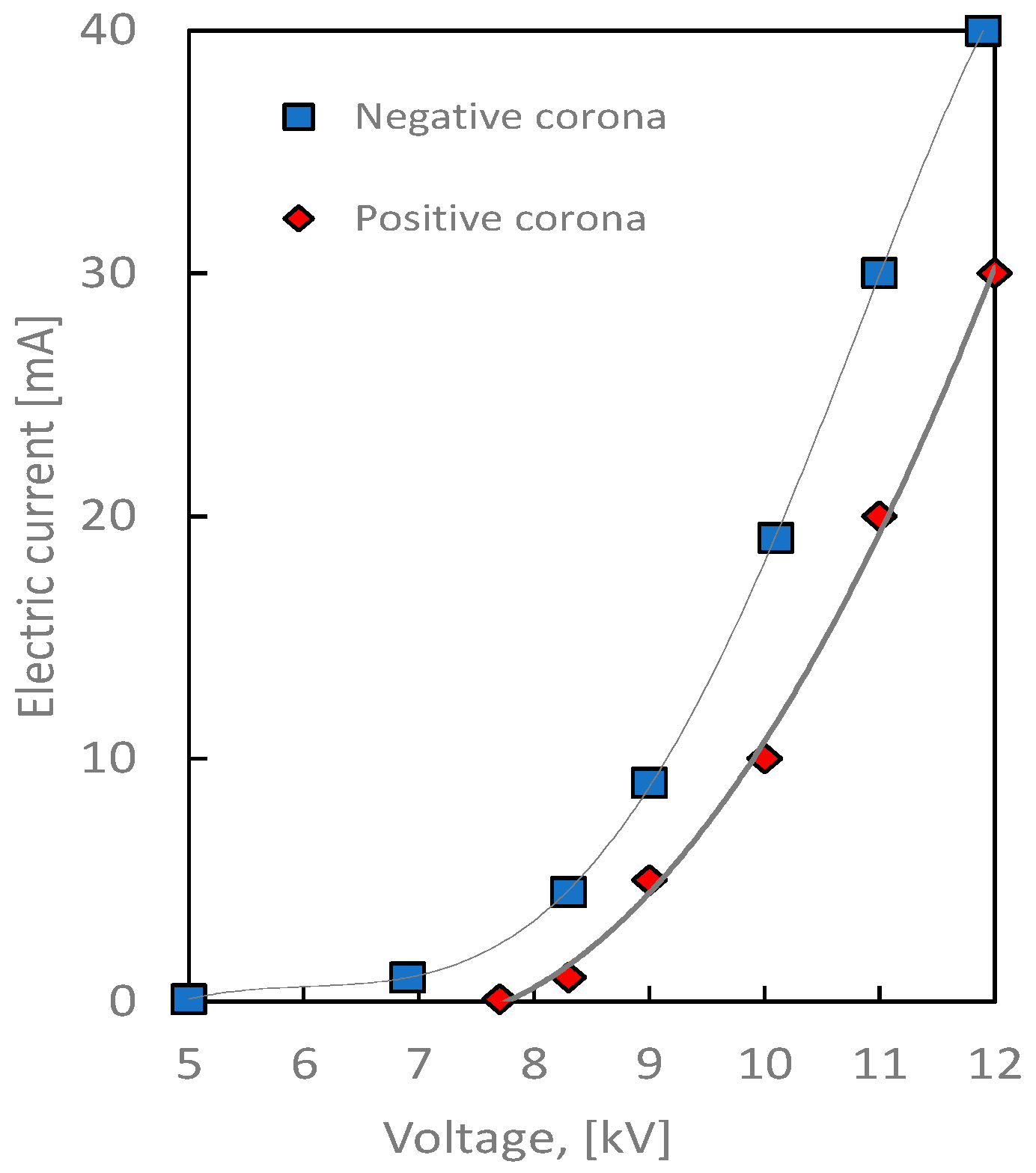
3.1. Parameters of Combustion Tests
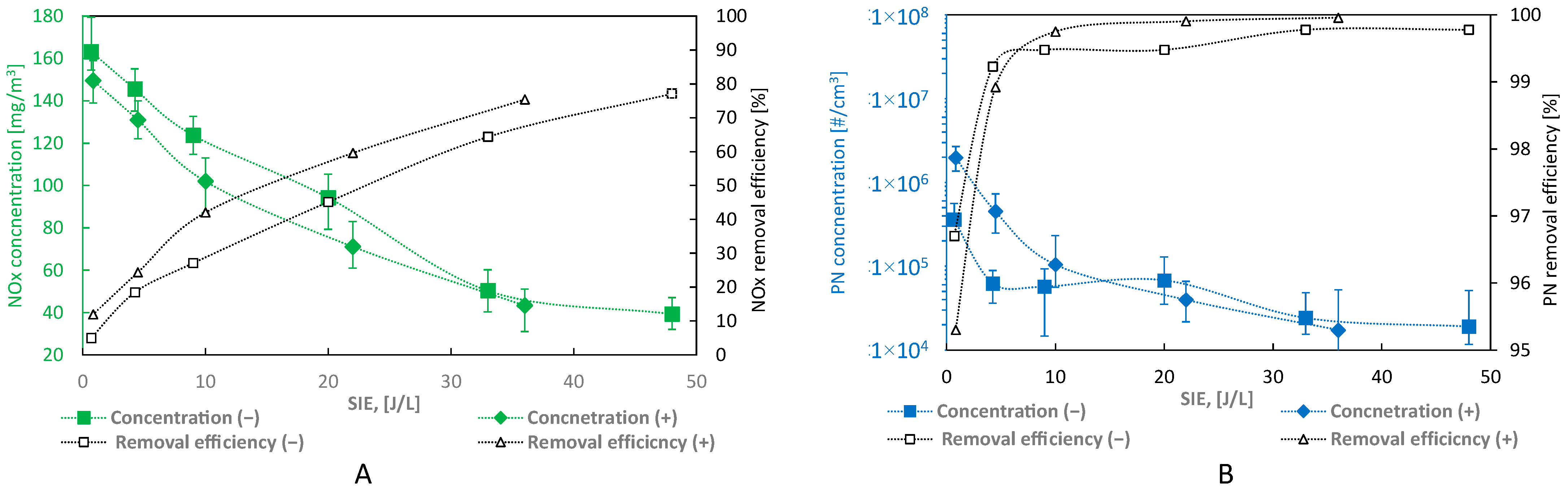
3.2. Changes in NOx and Particle Concentrations
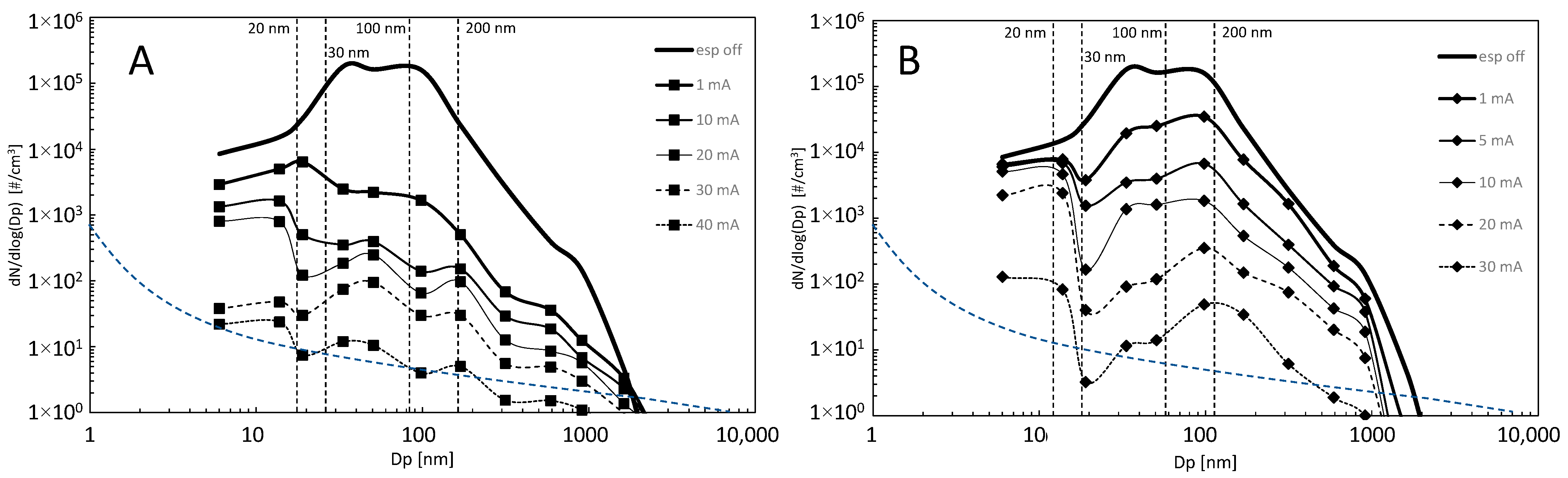
3.3. An Evaluation of the Performance of the ESP under Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Used Symbols and Abbreviations
| A | total area of collecting electrodes, [m2] |
| ESP | electrostatic precipitator |
| I | Electrostatic precipitation current, [mA] |
| PM | particle mass concentration, [mg/m3] |
| PN | particle number concentration, [#/cm3] |
| NOx | nitrogen oxides (NO and NO2) |
| [NOx]ESPon/off | NOx concentration: ESP on/off-regime, [mg/m3] |
| SIE | Specific input energy, [J/L] |
| V | Volume flow rate of combustion gases, [L/s] |
| U | ESP voltage, [kV] |
| η | ESP removal efficiency, [%] |
References
- Mok, Y.S.; Ham, S.W. Conversion of NO to NO2 in air by a pulsed corona discharge process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1998, 53, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanaka, R.B.; Mutlu, G.M. Particulate Matter Air Pollution: Effects on the Cardiovascular System. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Jones, R.; Pantea, C.; Özkaynak, H.; Rao, S.T.; Hwang, S.-A.; Garcia, V.C. Impact of NOx emissions reduction policy on hospitalizations for respiratory disease in New York State. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworek, A.; Krupa, A.; Czech, T. Modern electrostatic devices and methods for exhaust gas cleaning: A brief review. J. Electrost. 2007, 65, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albonetti, S.; Blasioli, S.; Bugani, M.; Lehaut-Burnouf, C.; Augustine, S.; Roncari, E.; Trifirò, F. Effect of silica additive on the thermal stability of catalysts for NOx abatement. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2003, 1, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, E.D.; Duarte, M.A.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Alves, C.A. Efficiency of Emission Reduction Technologies for Residential Biomass Combustion Appliances: Electrostatic Precipitator and Catalyst. Energies 2022, 15, 4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, S.; Nakao, H. Control of NO/sub x/ by positive and negative pulsed corona discharges. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1990, 26, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O.; Krpec, K.; Horák, J.; Kuboňová, L.; Hopan, F. The turbulence consideration in predicting efficiency of electrostatic precipitation for ultrafine aerosols from small-scale biomass combustion. Measurement 2022, 188, 110412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, T. Removal of NOx, SO2, and Hg from Simulated Flue Gas by Plasma-Absorption Hybrid System. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2013, 41, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Gao, X.; Luo, Z.Y.; Wei, E.Z.; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhang, J.Z.; Ni, M.J.; Cen, K.F. NOx treatment by DC corona radical shower with different geometric nozzle electrodes. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O.; Krpec, K.; Horák, J.; Kubonová, L.; Hopan, F.; Ryšavý, J. Combined control of PM and NOx emissions by corona discharge. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 345, 127359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13284-1:2017; Stationary Source Emissions—Determination of Low Range Mass Concentration of Dust-Part 1: Manual Gravimetric Method. Ente Nazionale Italiano di Unificazione (UNI): Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2017.
- EN 303-5:2012; Heating Boilers-Part 5: Heating Boilers for Solid Fuels, Manually and Automatically Stoked, Nominal Heat Output of up to 500 kW—Terminology, Requirements, Testing and Marking. National Standards Authority of Ireland: Dublin, Ireland, 2022.
- Järvinen, A.; Heikkilä, P.; Keskinen, J.; Yli-Ojanperä, J. Particle charge-size distribution measurement using a differential mobility analyzer and an electrical low pressure impactor. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusasco, R.M.; Merritt, B.T.; Penetrante, B.; Pitz, W.J.; Vogtlin, G.E. Feasibility of Plasma Aftertreatment for Simultaneous Control of NOx and Particulates; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Obradović, B.M.; Sretenović, G.B.; Kuraica, M.M. A dual-use of DBD plasma for simultaneous NOx and SO2 removal from coal-combustion flue gas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Research progress of pollutants removal from coal-fired flue gas using non-thermal plasma. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 791–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O.; Krpec, K.; Horák, J. Nox removal from Small-Scale biomass combustion in DC Corona: Influence of discharge polarity on plasma chemical kinetics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 300, 120597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mätzing, H. Chemical Kinetics of Flue Gas Cleaning by Irradiation with Electrons. In Advances in Chemical Physics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991; pp. 315–402. [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson, B.; Kogelshatz, U. Basic Data for Modeling of Electrical Discharges in Gases: Oxygen Report; Technical Report; ABB Asea Brown Boveri: Zurich, Switzerland, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Skalska, K.; Miller, J.S.; Ledakowicz, S. Trends in NOx abatement: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young Sun, M.; Sung Won, H.; In-Sik, N. Mathematical analysis of positive pulsed corona discharge process employed for removal of nitrogen oxides. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1998, 26, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, Y.S.; Nam, I.-S. Modeling of pulsed corona discharge process for the removal of nitric oxide and sulfur dioxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 85, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskooei, A.B.; Koohsorkhi, J.; Mehrpooya, M. Simulation of plasma-assisted catalytic reduction of NOx, CO, and HC from diesel engine exhaust with COMSOL. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 197, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizer, Y.P.; Allen, J.E. Gas Discharge Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Manion, J.A.; Huie, R.E.; Levin, R.D.; Burgess, D.R.; Orkin, V.L.; Tsang, W.; McGivern, W.S.; Hudgens, J.W.; Knyazev, V.D.; Atkinson, D.B. Chemical Kinetics Database Standard Reference Database 17; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2015.
- Borra, J.P. Charging of aerosol and nucleation in atmospheric pressure electrical discharges. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2008, 50, 124036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamero-Castaño, M.; de la Mora, J.F. Ion-induced nucleation: Measurement of the effect of embryo’s size and charge state on the critical supersaturation. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 3345–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-S. Aerosol particle growth rates in an ionized environment. J. Aerosol Sci. 1983, 14, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjamäki, M.; Keskinen, J.; Chen, D.-R.; Pui, D.Y.H. PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF THE ELECTRICAL LOW-PRESSURE IMPACTOR (ELPI). J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleksandr, M.; Kamil, K.; Jiří, H.; Lenka, K.; František, H.; Jiří, R. Coagulation contributing to electrostatic precipitation of ultrafine fly ash from small-scale biomass combustions. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, E.D.; Duarte, M.A.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Nunes, T.F.; Amato, F.; Querol, X.; Colombi, C.; Gianelle, V.; Alves, C.A. Particulate and gaseous emissions from the combustion of different biofuels in a pellet stove. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penetrante, B.M.; Hsiao, M.C.; Merritt, B.T.; Vogtlin, G.E.; Wallman, P.H.; Neiger, M.; Wolf, O.; Hammer, T.; Broer, S. Pulsed corona and dielectric-barrier discharge processing of NO in N2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 68, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, A.; Shimizu, K.; Chakrabarti, A.; Dascalescu, L.; Furuta, S. NO/sub x/removal process using pulsed discharge plasma. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1993 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Twenty-Eighth IAS Annual Meeting, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–8 October 1993; Volume 1973, pp. 1977–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Chang, C.; Ji, Y. Nitrogen Oxides Removal and Mechanism Research for Dielectric Barrier Discharge with NaCl Solution Grounded Electrode. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2023, 43, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewski, A.G.; Licki, J.; Pawelec, A.; Tymiński, B.; Zimek, Z. Operational experience of the industrial plant for electron beam flue gas treatment. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2004, 71, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forzatti, P. Present status and perspectives in de-NOx SCR catalysis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 222, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Badiwal, A.; Shenoy, K.T. Removal of NOx using ozone injection and subsequent absorption in water. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 15, 100511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, Y.S.; Koh, D.J.; Shin, D.N.; Kim, K.T. Reduction of nitrogen oxides from simulated exhaust gas by using plasma–catalytic process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2004, 86, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-S.; Kim, D.-I.; Lee, H.-S.; Chun, K.M.; Chun, B.-H. Effect of various hydrocarbons on the plasma DeNOx process. SAE Trans. 2001, 110, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, H.; Janssen, F. Catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides-a review on the fundamentals and technology. Catal. Today 1988, 2, 369–531. [Google Scholar]
- Koebel, M.; Elsener, M.; Kleemann, M. Urea-SCR: A promising technique to reduce NOx emissions from automotive diesel engines. Catal. Today 2000, 59, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, W.; Wang, J.; Wen, J.; Wang, S.; Tan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, K.; Zhang, R.; Li, W. Research landscape and hotspots of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) for NOx removal: Insights from a comprehensive bibliometric analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 65482–65499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, W. Industrial Gas Cleaning; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-H. Nonthermal Plasma Processing for Air-Pollution Control: A Historical Review, Current Issues, and Future Prospects. Plasma Process. Polym. 2004, 1, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Liu, J.; Cen, K. Simultaneous removal of NOx, SO2 and Hg in nitrogen flow in a narrow reactor by ozone injection: Experimental results. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalska, K.; Ledakowicz, S.; Louwe, R.; Szymczak, R. Nitrogen oxides pre-ozonation in flue gases from phosphate rock digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 318, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Unit | Negative/Positive Corona | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flue gas temperature | °C | 130 | |||||
| Gas flow rate | L/s | 10 | |||||
| H2O content | vol% | 10.3 | |||||
| O2 content | vol% | 12 | |||||
| NOx * ESP-off regime | mg/m3 | 178 | |||||
| PM * ESP-off regime | mg/m3 | 48 | |||||
| PN * ESP-off regime | #/cm3 | 1.5 × 107 | |||||
| Electric current in ESP | mA | 1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| Voltage value | kV | 7/8.5 | 8.5/9 | 9/10 | 10/11 | 11/12 | 12/- |
| Specific input energy | J/L | 0.7/0.85 | 4.25/4.5 | 9/10 | 20/22 | 33/36 | 48/- |
| Technology | Capital Cost | Operating Cost * | SIE | Efficiency | Additional Considerations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Presented ESP | Moderate | Low | 36–48 J/L | PM: Up to 99.99% NOx: Up to 78% |
| |
| Selective Catalytic Reduction | High | Moderate to High | NOx: 80–90% |
| [37,41,42,43] | |
| Wet Scrubbing Systems | Moderate to High | High | Generally higher than ESP | PM and NOx: 60–95% |
| [21,44] |
| Pulsed Corona and Dielectric Barrier Discharge | Moderate to High | Moderate | 60–150 J/L | NOx: 60–70% |
| [33,34,35] |
| Electron Beam Technology | Very High | High | 28.8–43.2 J/L | NOx: Up to 70% |
| [36,45] |
| Low-Temperature Oxidation | High | High | Generally higher than ESP | NOx: Up to 95% |
| [38,46,47] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molchanov, O.; Krpec, K.; Horák, J.; Kuboňová, L.; Hopan, F.; Ryšavý, J. Application End Evaluation of Electrostatic Precipitation for Control PM and NOx Emissions from Small-Scale Combustions. Fire 2024, 7, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7100356
Molchanov O, Krpec K, Horák J, Kuboňová L, Hopan F, Ryšavý J. Application End Evaluation of Electrostatic Precipitation for Control PM and NOx Emissions from Small-Scale Combustions. Fire. 2024; 7(10):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7100356
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolchanov, Oleksandr, Kamil Krpec, Jiří Horák, Lenka Kuboňová, František Hopan, and Jiří Ryšavý. 2024. "Application End Evaluation of Electrostatic Precipitation for Control PM and NOx Emissions from Small-Scale Combustions" Fire 7, no. 10: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7100356
APA StyleMolchanov, O., Krpec, K., Horák, J., Kuboňová, L., Hopan, F., & Ryšavý, J. (2024). Application End Evaluation of Electrostatic Precipitation for Control PM and NOx Emissions from Small-Scale Combustions. Fire, 7(10), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7100356






