- Article
Beyond Static Barriers: Modelling the Effects of Water Drop Suppression on Wildfire Spread
- Leonardo Martins,
- António Maia and
- Pedro Vieira
Wildfire suppression is often represented in fire spread simulators as static barriers that completely stop fire propagation and are placed at the start of the simulation. Recent works have begun to simulate barriers introduced at different time frames, but these normally act as static barriers. In reality, many water-based suppression tactics (aerial and ground) only slow the fire spread by temporarily increasing fuel moisture and cooling the fuel bed. To address this limitation, we present a new simulation feature: the Dynamic Water Barrier. Unlike static barriers, this representation captures the temporal transient effect of water application, since it is modeled using a simplified water load and evaporation dynamics to estimate changes in live fuel moisture content (LFMC). Implemented using the Fire Area Simulator (FARSITE), the Dynamic Water Barrier reduces the rate of spread and fireline intensity, delaying but not fully preventing fire propagation, providing a transient influence of water-based suppression. The approach was tested on one North American (NA) and one Portuguese fire, where suppression missions were available. The dynamic barriers led to reductions in Relative Area Difference, reaching 0.234 for the Portuguese fire and 0.006 for the NA fire, outperforming the scenario of no combat and having a comparable performance with the full static barrier (RAD 0.108 and 0.024, respectively), while limiting the creation of unburned areas behind the firefront. Although the validation is limited, these findings illustrate the potential to improve tactical decision support and dynamic suppression planning in wildfire management, requiring further studies of other fires and controlled fire suppression missions.
6 February 2026



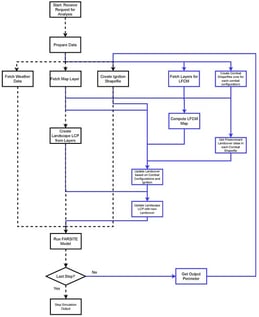
![Conceptual framework for joint action, with its elements (boxes), their related working rules in [], the identified joint forest management challenges (normal), and key related variables (italics). Adapted from [21].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/fire/fire-09-00070/article_deploy/html/images/fire-09-00070-g001-550.jpg)