A Comprehensive Review on Intumescent Coatings: Formulation, Manufacturing Methods, Research Development, and Issues
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
3. Fundamentals of Intumescent Coating
3.1. Chemical Composition
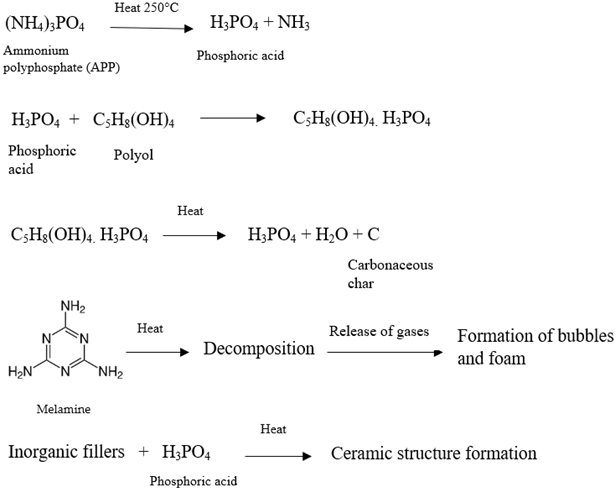
- Ammonium polyphosphate (APP):
- Monopentaerythritol (PER):
- Melamine:
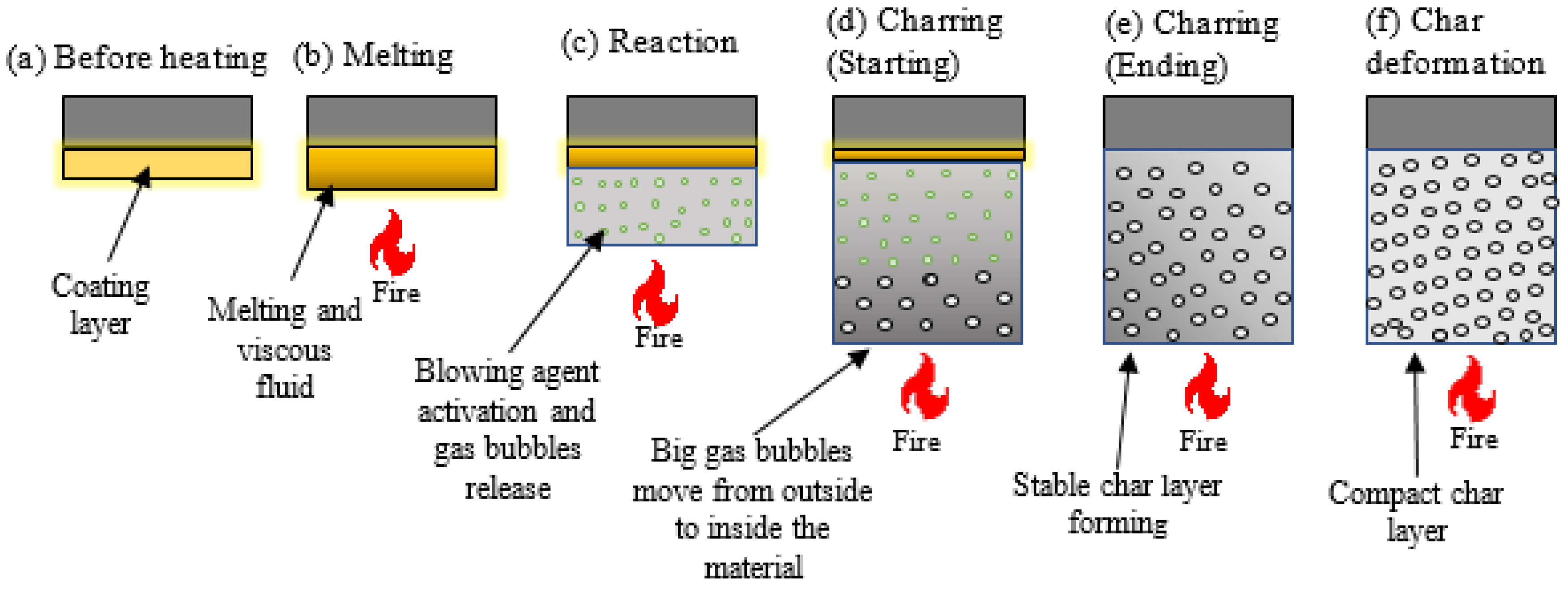
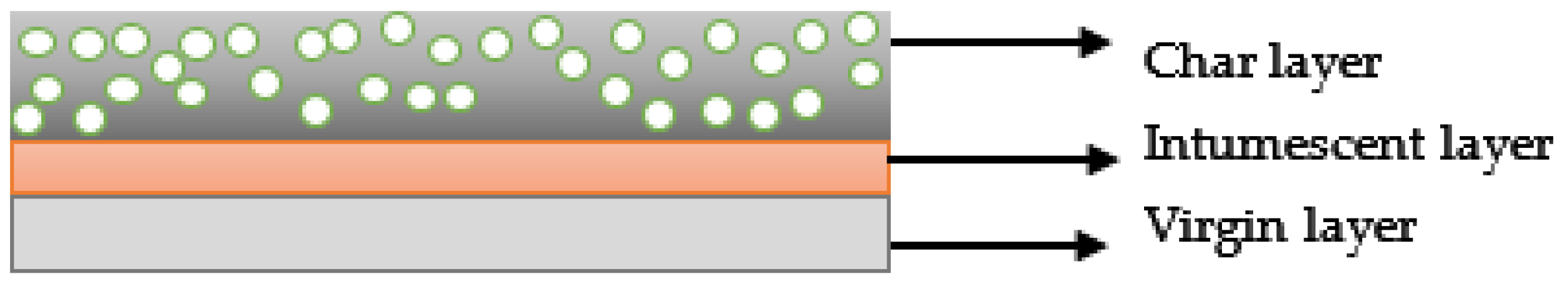
3.2. Intumescent Process
3.3. Working Mechanism and Chemical Reaction Steps
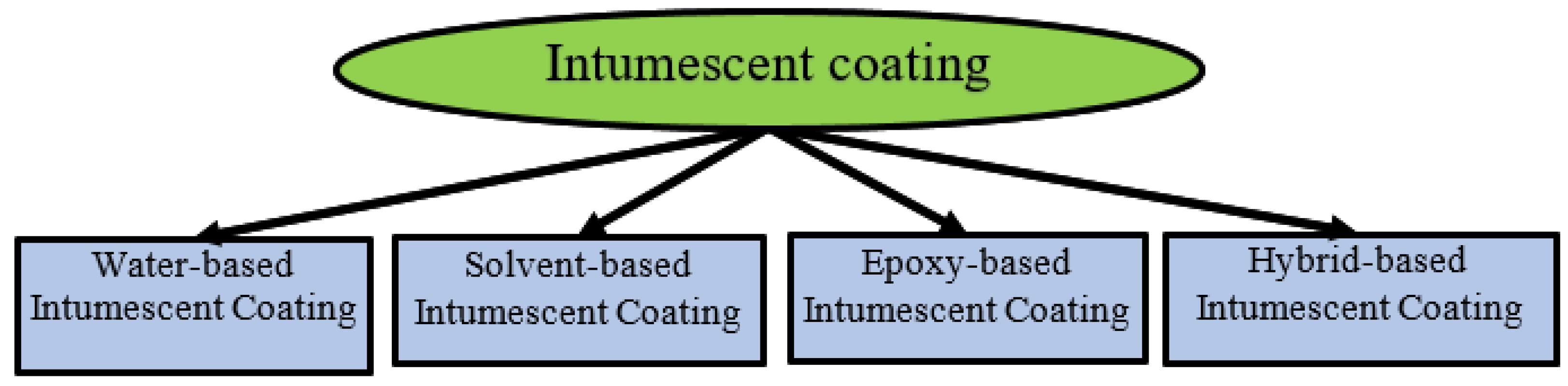
4. Manufacturing Methods
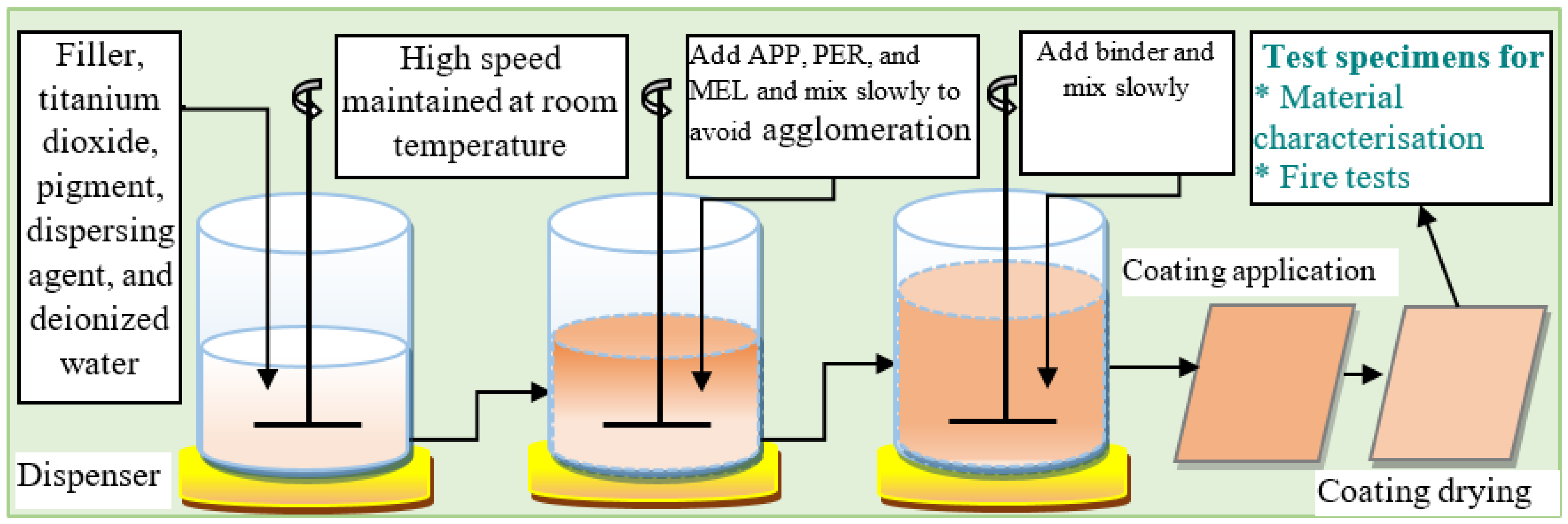
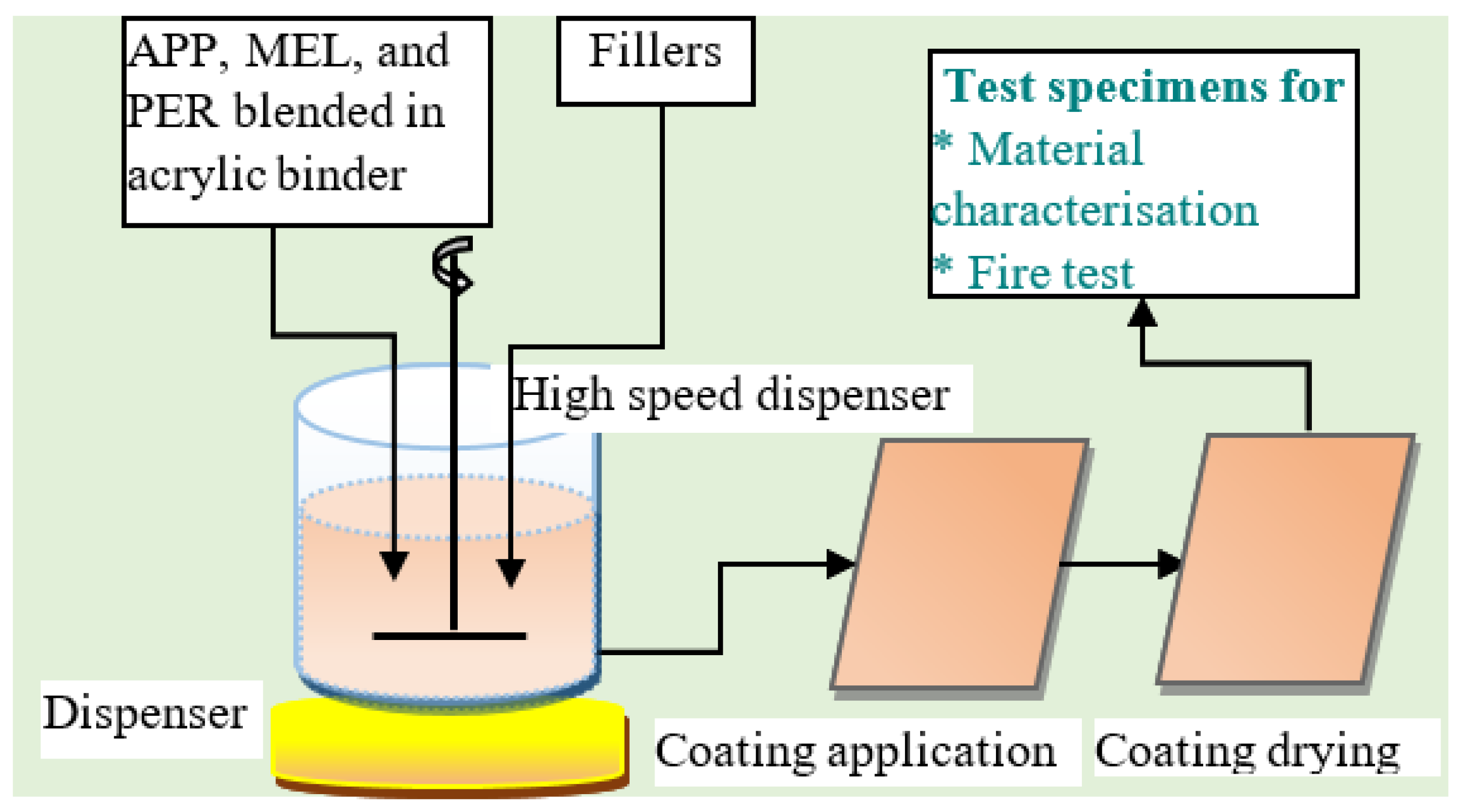
4.1. Water-Based Intumescent Coating
4.2. Solvent-Based Intumescent Coating
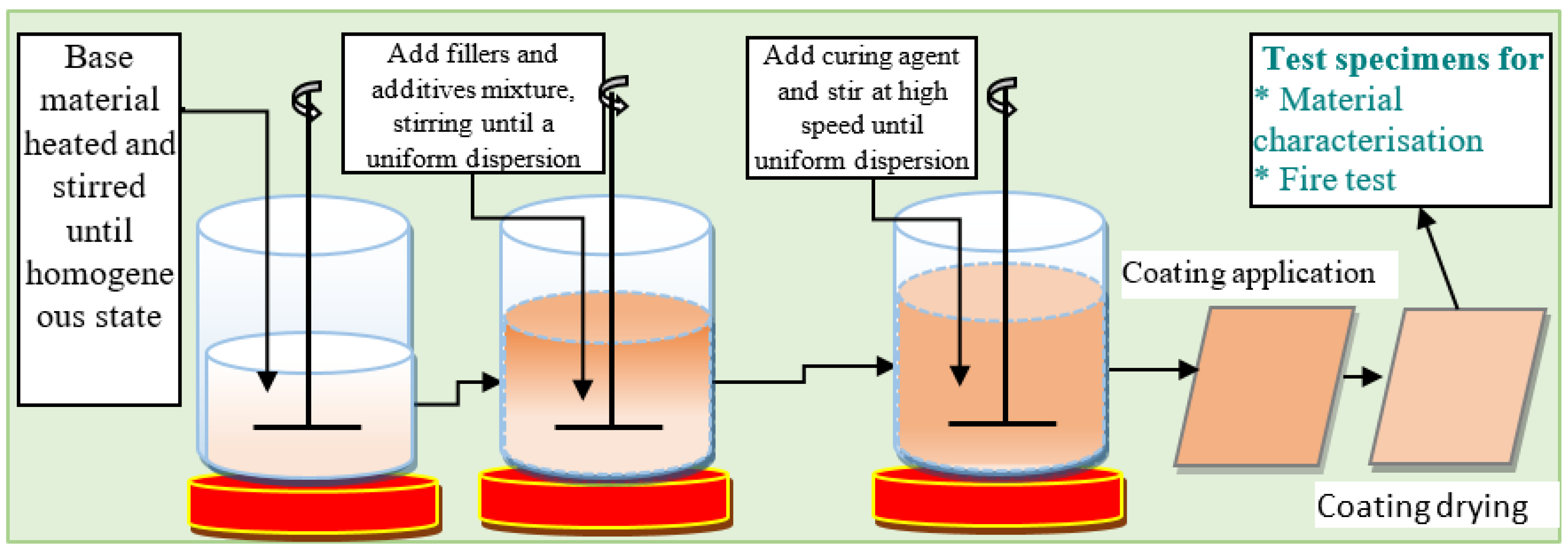
4.3. Epoxy-Based Intumescent Coating
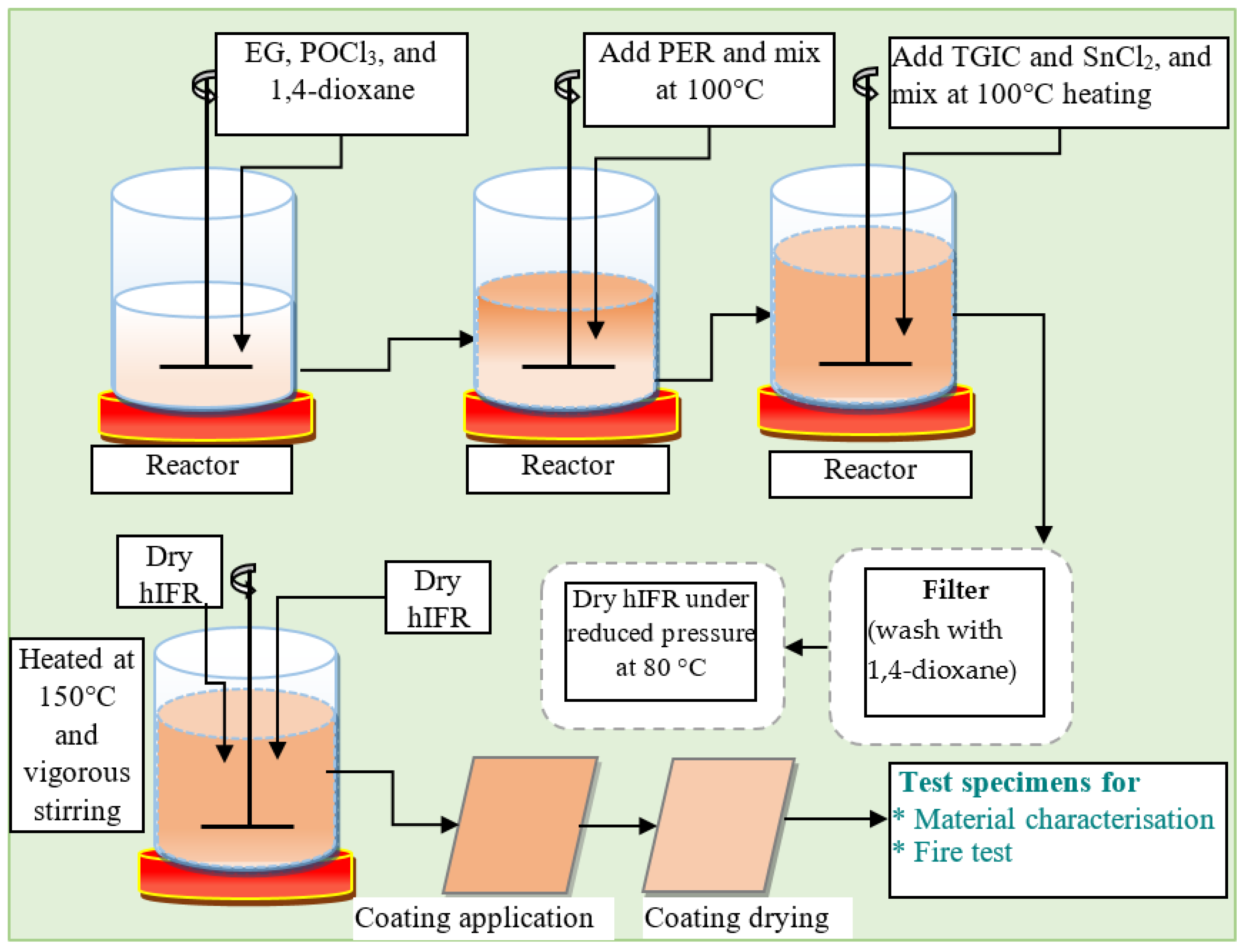
4.4. Hybrid Intumescent Coating
5. Fire Testing Methods and Standards
5.1. Ignitability Tests (Or UL94)
5.2. Flame Spread Tests
5.3. Limiting Oxygen Index
5.4. Heat Release Tests (Cone Calorimeter)
5.5. Smoke Tests
5.6. Full-Scale Fire Test
5.7. Others
6. Research and Development on Intumescent Coating
6.1. Application of Intumescent Coating
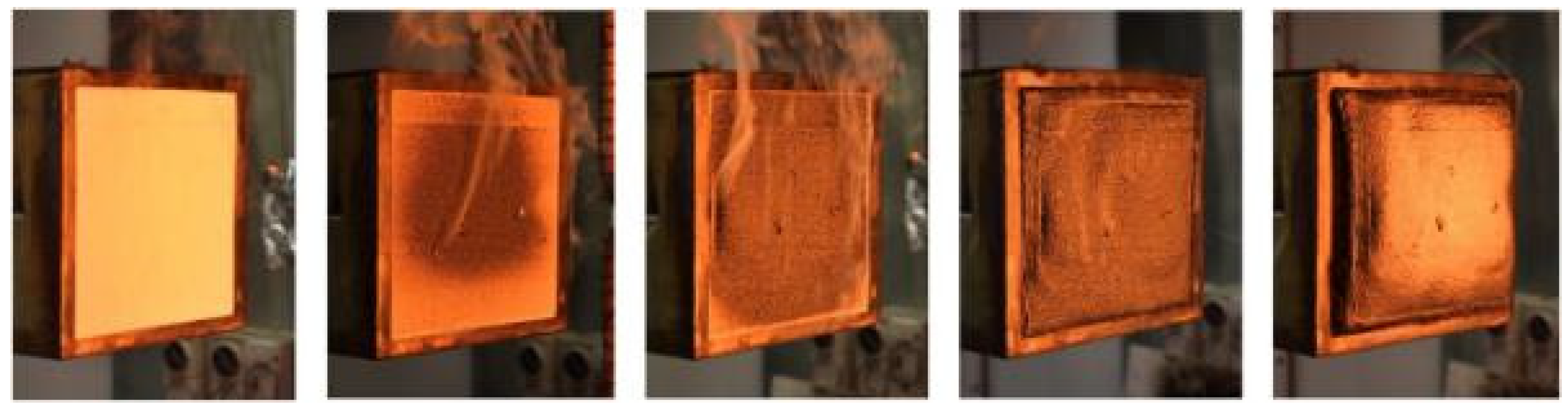
6.1.1. Structural Steel
6.1.2. Timber
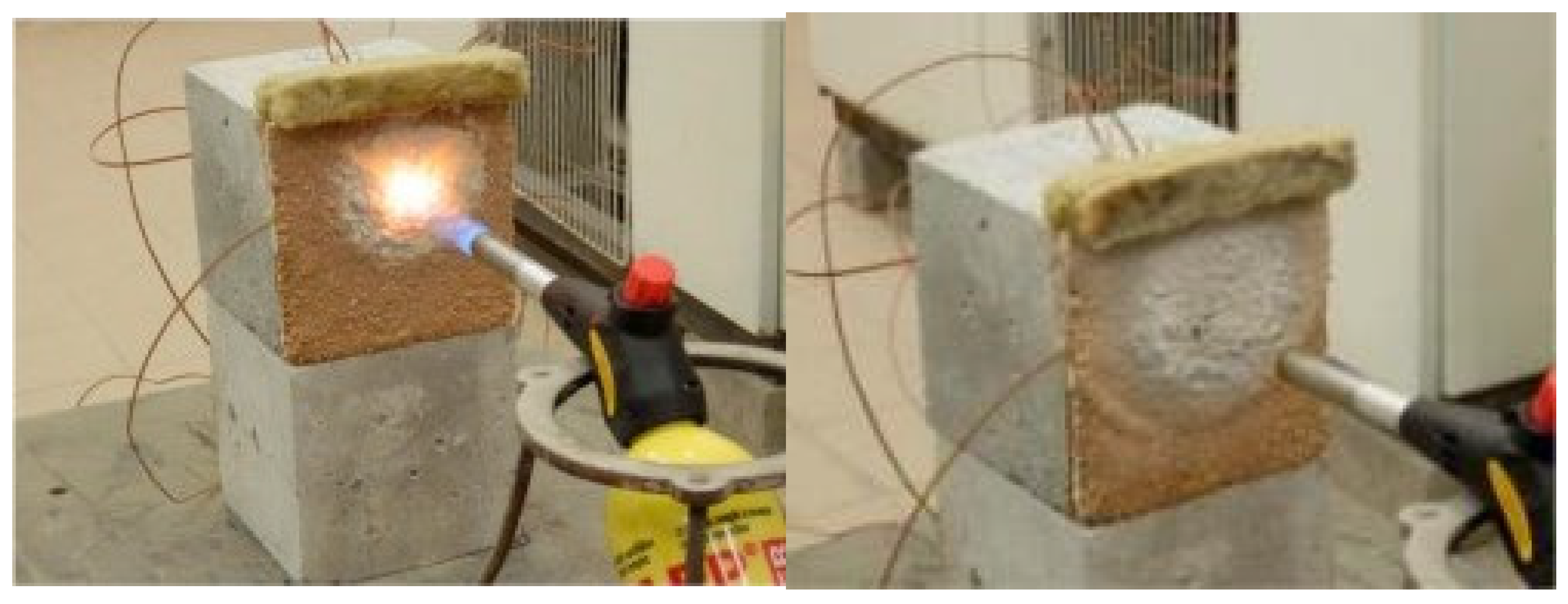
6.1.3. Concrete Material
6.2. Flame-Retardant Coating Development
| Source | Materials | % | Decomposition Temperature | Chemical Structure | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid source | Ammonium polyphosphate (APP) | 5.76–45 | 250–450 °C | 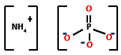 | [55,164,165] |
| Carbon source | Pentaerythritol (PER) | 6.5–13 | 187–189 °C | 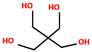 | [166,167,168] |
| Expandable graphite (EG) | 5.5–45 | 150–300 °C | 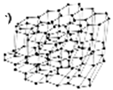 | [55,169,170] | |
| Blowing agent | Melamine (MEL) | 5.5–15 | 250 °C | 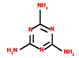 | [70,171,172] |
| Binders | Vinyl acetate copolymer | 45–50 | 180–380 °C | 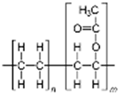 | [57,134,173,174,175] |
| Acrylic resin | 20–60 | - | - | [55,176] | |
| Epoxy resin | 39.80–70.57 | - | - | [164,177] | |
| Fillers | Mg(OH)2 | 0.5–20 | 350 °C | 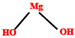 | [178,179,180] |
| Al(OH)3 (ATH) | 2.5–7.4 | 260–400 °C | 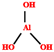 | [71,151,181] | |
| Alumina | 0.1–5 | 700–1200 °C | 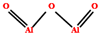 | [182,183] | |
| Cenosphere | 1–10 | - | - | [57] | |
| Boric acid | 0–11.76 | 500–650 °C |  | [55,171,184] | |
| Pigment | TiO2 | 2–10 | - | 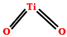 | [55,185] |
| Name | Composition of Intumescent Coating | Activation Temperature | Advantages | Limitations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
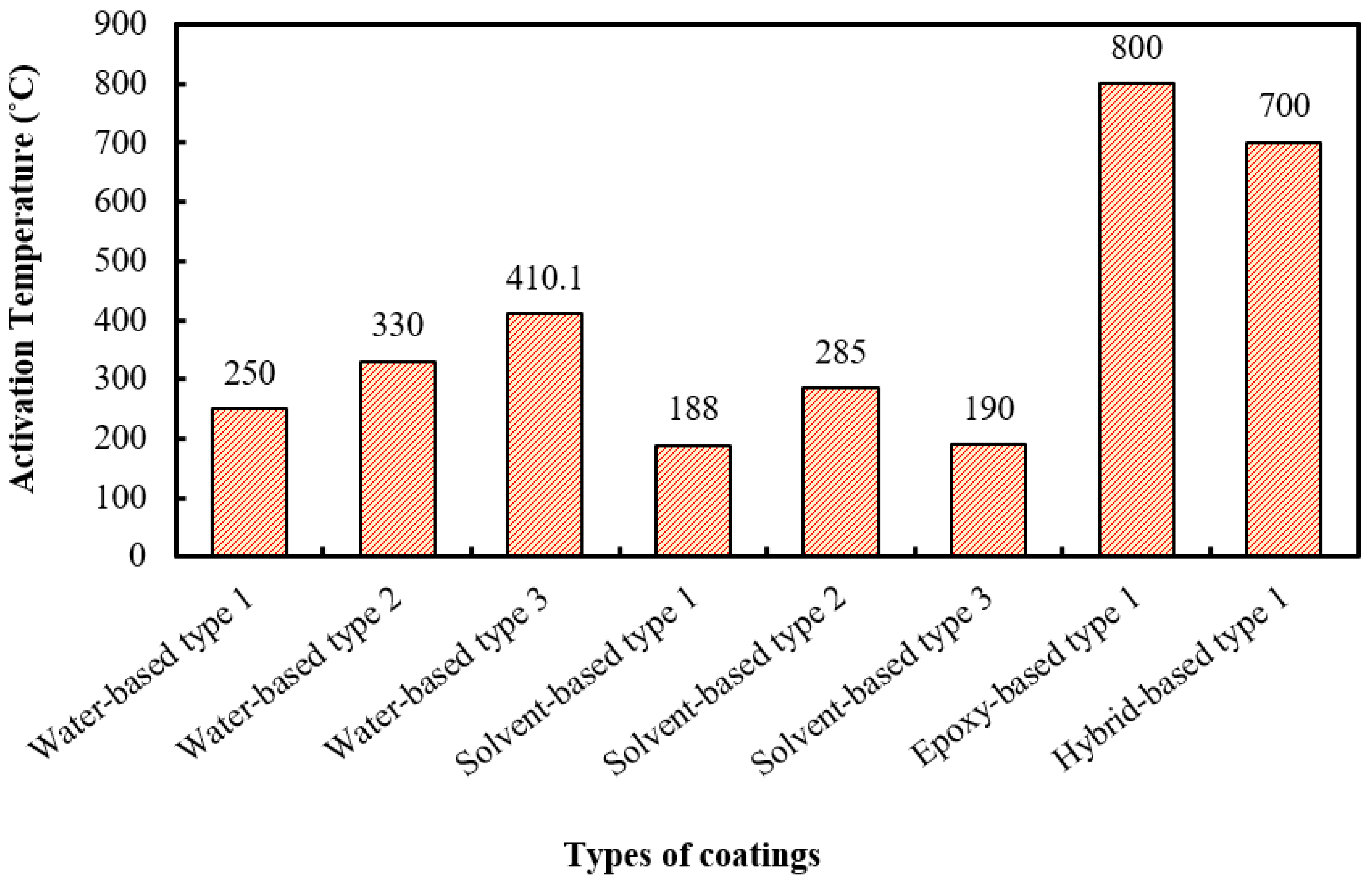
| Water-based coating (Type 1) | Vinyl acetate/vinyl ester dispersion, APP, PER, polyols, MEL, rutile TiO2, pigment, vermiculite (Ver), celite, ATH, deionised water, bondox T-80 (dispersing agents), texanol (coalescing agents), and tylose (thickener). | Below 250 °C | Showed effective heat insulation, which is crucial for protecting structural materials in the event of fire. | After time passed, the coatings showed signs of deterioration where distinct differences among samples are noted. | [66] |
| Water-based coating (Type 2) | Cenosphere (Grade CIL30), PER, MEL, boric acid (BA), TiO2, rutile R-902), APP 422, and binder (ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer and Vinappas LL3112). | At 330 °C | The addition of cenospheres improves fire protection by enhancing char expansion, forming a protective layer, and increasing thermal stability. | Incorporating cenospheres may increase formulation complexity and cost. | [57] |
| Water-based coating (Type 3) | Hollow glass microspheres (HGMs), MPP (melamine polyphosphate), starch, water-based acrylic emulsion (HS-6121), PVP (polyvinylpyrrolidone)—K90 grade, aluminium isopropoxide (AIP), CaCO3, mica flakes, defoamer (DP-633), 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane, anhydrous ethanol, isopropanol, and deionised water. | At 410.1 °C | HGMs@Al2O3 composite microspheres of the coating: reduces thermal conductivity, enhancing the coating’s thermal insulation properties. | The coating formulation is its complexity, involving multiple steps, which may lead to increased production costs. | [186] |
| Solvent-based coating (Type 1) | acrylic resin (binder), APP phase II, MEL, PER, (Mg(OH)2), and titanium dioxide (TiO2). | Relatively at 188 °C | Mg(OH)2 and TiO2 improved the coating’s fire protection and foam structure, yielding a thicker char layer. | This coating has less water resistance. | [67] |
| Solvent-based coating (Type 2) | Epoxy resin (binder), APP phase II, MEL, PER, Mg(OH)2, and TiO2. | Relatively at 285 °C | Higher epoxy content improved adhesion strength and water resistance, maximising bonding to the metal surface. | Char formation is not uniform and porous, causing heat transfer. | [67] |
| Solvent-based coating (Type 3) | APP, MEL, PER, acrylic resin (binder), TiO2, nano-CES, expandable graphite, zinc borate, and calcium silicate. | At 190 °C | The ingredient cost is low. | Multiple flame retardants are required in this formulation. | [187] |
| Epoxy-based coating (Type 1) | Epichlorohydrin based epoxy resin, cycloaliphatic polyamine-based hardener (CeTePox 1393 H, 93 g/eq), Exolit AP 750, zinc borate (ZB 467), boric acid, and MEL. | At 800 °C | Fire-protection properties of the coating increase with the proper proportion of ingredients. | Antagonistic effects observed with ZB complicate the formulation despite increased char yield. | [68] |
| Epoxy-based coating (Type 2) | Epoxy resin (NPEL-128), polyamide amine (hardener H-2310), APP, expandable graphite (EG), boric acid, MEL, basalt chopped strands, ethanol, and mild steel plates S355. | _ | Ethanol as a dispersing agent enhances the dispersion of basalt that helps to achieve high thermal stability, insulation, and fire protection. | Ethanol is flammable. | [130] |
| Hybrid-based coating (Type 1) | 2,2′-bis(4-cyanatophenyl) isopropylidene, expandable graphite (EG), POCl3, and PER, 1,3,5-triglycidyl isocyanurate (TGIC). | At 700 °C | This coating offers improved resistance to high temperatures, effectively slowing down the spread of fire. | The production process may be costly. | [92] |
| Hybrid-based coating (Type 2) | 4,4′-diaminodiphenyl ether (ODA), 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane (DDM), hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene (HCCP), anhydrous ethanol, MEL, pyridine, acetone, APP-II, and epoxy resin (EP or DGEBA, E-44). | _ | PZMA@APP works great to enhance flame retardancy and the mechanical performance of EP composites. | PZMA@APP is a complex synthesis and incorporation process that may increase production costs and limit scalability. | [188] |
6.3. Adhesive or Bonding Performance
6.4. Corrosion and Chemical Resistance Performance
6.5. Durability and Weather Performance
6.6. Fire Resistance
6.7. Cost-Effectiveness
7. Challenges and Issues
7.1. Fire Protection Time and Flame Spread
7.2. Char Activation Temperature
7.3. Toxicity
8. Conclusions and Recommendations
- Chemical formulation greatly controls the fire resistance performance of the intumescent coating where the acid donor, carbon or char source, and foaming/blowing agent play a crucial role. Further studies are needed to fully understand the potential of intumescent coatings, optimise their formulations for efficient char activation temperature with reduced flame hazard, and ensure their successful integration into comprehensive fire protection strategies for building materials.
- The manufacturing methods for conventional intumescent coatings, such as water-based, solvent-based, and epoxy-based intumescent coatings, are almost similar, whereas the process is more complex and involves more steps in the case of hybrid intumescent coatings, though they exhibit better performance.
- The fire spread due to the burning of some intumescent coatings at the early stage of fire exposure still poses a great threat by providing a gateway for a secondary fire hazard source. Smoke toxicity for some intumescent coatings can be another hazard. Silicone-based coatings release fewer toxic gases during degradation compared to traditional organic-based coatings. Further research can be conducted to minimise the toxicity level of intumescent coatings. This can be improved by using appropriate acid donors, flame retardant fillers, and binding materials.
- The corrosion and durability of intumescent coatings exposed to corrosive and wet environmental conditions are one of the key issues, which can be improved by applying an appropriate topcoat to the surface of the coating or by incorporating particles as modifiers into intumescent coatings.
- Extensive research has been conducted on the steel and timber structures using intumescent coatings. However, there is limited research on concrete using intumescent coatings. Further research can be conducted to improve the fire resistance and spalling issue of concrete.
- Intumescent coatings can also be explored for additional materials like plastics, solid aluminium panels, ACP (aluminium composite panel) cladding, and cementitious materials for high-rise buildings. A significant study is also required on the environmental aspect of sustainable application.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nazrun, T.; Hassan, M.K.; Hossain, M.D.; Ahmed, B.; Hasnat, M.R.; Saha, S. Application of Biopolymers as Sustainable Cladding Materials: A Review. Sustainability 2023, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.D.; Hassan, M.K.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; He, Y.; Saha, S.; Hittini, W. Flame behaviour, fire hazard and fire testing approach for lightweight composite claddings–a review. J. Struct. Fire Eng. 2021, 12, 257–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnat, M.R.; Hassan, M.K.; Saha, S. Flame Retardant Polymer Composite and Recent Inclusion of Magnesium Hydroxide Filler Material: A Bibliometric Analysis towards Further Study Scope. Fire 2023, 6, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A. Sharjah Fire Probable Cause Found, 150 Buildings to Have Cladding Changed. Available online: https://gulfnews.com/photos/news/photos-aftermath-of-abbco-tower-fire-in-sharjah-1.1588757069335?slide=1 (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- Milan Tower Block Fire ‘Reminiscent’ of Grenfell Disaster, Officials Say. Available online: https://www.euronews.com/2021/08/30/no-victims-in-milan-towerblock-fire-reminiscent-of-grenfell-disaster (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- New York Fire that Killed 19 Likely Began with Space Heater, Fire Chief Says. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/nation/2022/01/09/more-than-30-people-have-life-threatening-injuries-after-bronx-fire/ (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Milton, J. Huge Fire Tears Through Hong Kong Skyscraper Raining Embers on Street Below. Available online: https://metro.co.uk/2023/03/02/huge-fire-tears-through-hong-kong-skyscraper-18378312/ (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Marina Urman, D.L. Fire Engulfs High-Rise Building in Brazil. Available online: https://www.boredpanda.com/high-rise-building-engulfed-in-flames-brazil/ (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Yang, Q.; Wang, N.; Yi, L.; Yan, L. Construction of decorative, antibacterial, anti-aging and fire-retardant integrative coatings for wood substrates with super protective performances. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 219, 110620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyridakis, S.; Wiesner, F.; Orabi, A.; Maluk, C. Experimental Fire Studies Comparing the Charring Behaviour of Timber Protected with thin Intumescent Coatings and Fire Rated Plasterboard; University of Coimbra: Coimbra, Portugal, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, L.; Feng, S.; Wang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Chu, T.; Zhuang, Y. A comprehensive model to predict the fire performance of intumescent fire-retardant coating on steel substrate. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, W.; Sharma, U.K.; Shome, M. Mechanical properties of conventional structural steel and fire-resistant steel at elevated temperatures. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 181, 106615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorathia, U.; Gracik, T.; Ness, J.; Durkin, A.; Williams, F.; Hunstad, M.; Berry, F. Evaluation of intumescent coatings for shipboard fire protection. J. Fire Sci. 2003, 21, 423–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörold, A.; Schartel, B.; Trappe, V.; Gettwert, V.; Korzen, M. Protecting the structural integrity of composites in fire: Intumescent coatings in the intermediate scale. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperopoulos, E.; Scionti, G.; Atria, M.; Calabrese, L.; Valenza, A.; Proverbio, E. Optimizing Ammonium Polyphosphate–Acrylic Intumescent Coatings with Sustainable Fillers for Naval Fire Safety. Materials 2024, 17, 5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, R.G.; Khanna, A. Intumescent coatings: A review on recent progress. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2017, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.-S.; Bee, S.-T.; Sin, L.T.; Tee, T.-T.; Ratnam, C.; Hui, D.; Rahmat, A. A review of application of ammonium polyphosphate as intumescent flame retardant in thermoplastic composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 84, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.-R.; Hu, X.-M.; Cheng, W.-M.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Wang, W.; Liang, Y.-T.; Liu, T.-Y.; Feng, Y.; Xue, D. A novel intumescent flame-retardant to inhibit the spontaneous combustion of coal. Fuel 2021, 297, 120768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, G.B.; Rayner, E.; Yeadon, D.A.; Hopper, L.L.; Goldblatt, L.; Dollear, F.; Dupuy, H.; York, E. Water-resistant, oil-based, intumescing fire-retardant coatings. I. Dev. Formul. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1964, 41, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, T. Fire retardant coatings. In New Technologies in Protective Coatings; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wladyka-Przybylak, M.; Kozlowski, R. The thermal characteristics of different intumescent coatings. Fire Mater. 1999, 23, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beh, J.H.; Yew, M.C.; Saw, L.H.; Yew, M.K. Fire resistance and mechanical properties of intumescent coating using novel bioash for steel. Coatings 2020, 10, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evolution of Water Based Intumescent Coatings. Available online: https://www.newkem.com/evolution-of-water-based-intumescent-coatings/ (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Piperopoulos, E.; Grifò, G.; Scionti, G.; Atria, M.; Calabrese, L.; Consolo, G.; Proverbio, E. Study of intumescent coatings growth for fire retardant systems in naval applications: Experimental test and mathematical model. Coatings 2022, 12, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-Q.; Zhang, C.; Lou, G.-B.; Wang, Y.-C.; Wang, L.-L. Assess the fire resistance of intumescent coatings by equivalent constant thermal resistance. Fire Technol. 2012, 48, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, D. Experimental study of heat transfer in intumescent coatings exposed to non-standard furnace curves. Fire Technol. 2015, 51, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Weinell, C.E.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Ring, L.; Kiil, S. Effects of coating ingredients on the thermal properties and morphological structures of hydrocarbon intumescent coating chars. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 143, 105626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoleta, J.B.; Itao, G.B.; Resabal, V.J.T.; Lubguban, A.A.; Corpuz, R.D.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N.; Tabelin, C.B. Improved pyrolysis behavior of ammonium polyphosphate-melamine-expandable (APP-MEL-EG) intumescent fire retardant coating system using ceria and dolomite as additives for I-beam steel application. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torun, S.B.; Cavdar, A.D.; Ozdemir, T. The synergistic effect of intumescent coating containing titanium dioxide and antimony trioxide onto spruce and alder wood species. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 31, 101407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirhan, Y.; Yurtseven, R.; Usta, N. The effect of boric acid on flame retardancy of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites including nanoclay. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2023, 36, 1187–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingtipi, K.; Choudhury, B.J.; Moholkar, V.S. Kaolin-embedded cellulose hydrogel with tunable properties as a green fire retardant. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 313, 120871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Z. Montmorillonite-synergized water-based intumescent flame retardant coating for plywood. Coatings 2020, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zybina, O.; Gravit, M. Polymer Binders of Flame-Retardant Intumescent Coatings. In Intumescent Coatings for Fire Protection of Building Structures and Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 91–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Sabee, M.M.S.; Itam, Z.; Beddu, S.; Zahari, N.M.; Mohd Kamal, N.L.; Mohamad, D.; Zulkepli, N.A.; Shafiq, M.D.; Abdul Hamid, Z.A. Flame retardant coatings: Additives, binders, and fillers. Polymers 2022, 14, 2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariappan, T. Recent developments of intumescent fire protection coatings for structural steel: A review. J. Fire Sci. 2016, 34, 120–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.; Temple, A.; Maluk, C.; Bisby, L. Novel testing to study the performance of intumescent coatings under non-standard heating regimes. In Proceedings of the Fire Safety Science–Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 10–14 February 2014; pp. 652–665. [Google Scholar]
- Lucherini, A.; Maluk, C. Intumescent coatings used for the fire-safe design of steel structures: A review. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 162, 105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, C.-F.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Liu, S.-C.; Bae, J.; Tang, L.-C. Waterborne Intumescent Fire-Retardant Polymer Composite Coatings: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucherini, A.; Giuliani, L.; Jomaas, G. Experimental study of the performance of intumescent coatings exposed to standard and non-standard fire conditions. Fire Saf. J. 2018, 95, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.; Bellayer, S.; Revel, B.; Duquesne, S.; Bourbigot, S. Comprehensive study of the influence of different aging scenarios on the fire protective behavior of an epoxy based intumescent coating. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, D.; Nuzzo, I.; Nigro, E.; Occhiuzzi, A. Intumescent coatings for fire resistance of steel structures: Current approaches for qualification and design. Coatings 2022, 12, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspitasari, W.; Ahmad, F.; Ullah, S.; Hussain, P.; Megat-Yusoff, P.S.; Masset, P.J. The study of adhesion between steel substrate, primer, and char of intumescent fire retardant coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 127, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, M.C.; Ramli Sulong, N.H. Effect of epoxy binder on fire protection and bonding strength of intumescent fire protective coatings for steel. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 168, 1228–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Delichatsios, M.; McKee, M.; Ukleja, S.; Pagella, C. Experimental study of burning behaviors of intumescent coatings and nanoparticles applied on flaxboard. J. Fire Sci. 2011, 29, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morys, M.; Häßler, D.; Krüger, S.; Schartel, B.; Hothan, S. Beyond the standard time-temperature curve: Assessment of intumescent coatings under standard and deviant temperature curves. Fire Saf. J. 2020, 112, 102951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Leonidas, E.; Fisk, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Willmott, J. Investigating the fire-retardant efficiency of intumescent coatings on inclined timber: A study on application strategies and heat transfer mechanisms. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 407, 133586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirpici, B.K.; Aydin, I. Investigation of intumescent coating on the fire endurance of concrete-filled steel columns with varied characteristics. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 1959–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.B.R.S.; Junior, A.L.M.; Vieira, L.C.M. Intumescent Paint as Fire Protection Coating. Rev. IBRACON de Estruturas e Mater. 2017, 10, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreh, R.P. Intumescent Fireproofing Systems and Methods. U.S. Patent 8519024B2, 27 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Landry, V.; Blanchet, P.; Hoang, D.-T.; Dagenais, C. Fire performance of intumescent waterborne coatings with encapsulated APP for wood constructions. Coatings 2021, 11, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Han, Z.; Bourbigot, S. Intumescence: Tradition versus novelty. A comprehensive review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 51, 28–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J. Benign design of intumescent flame retardant coating incorporated various carbon sources. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaydin, K.; Laachachi, A.; Ball, V.; Jimenez, M.; Bourbigot, S.; Ruch, D. Layer-by-layer deposition of a TiO2-filled intumescent coating and its effect on the flame retardancy of polyamide and polyester fabrics. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 469, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daus, L.-H.; Korzen, M.; Schartel, B. High-throughput fire tests and weathering-induced degradation behaviour of intumescent coatings. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1107, 032014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena, J.C.; Wang, C.; Kabir, I.I.; Khalid, A.; Nazir, M.T.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Ahmad, F.; Yeoh, G.H. Fire behaviour of waterborne intumescent coatings on timber substrate for bushfire exposure. Fire Saf. J. 2023, 140, 103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zybina, O.; Gravit, M. Basic Ingredients of Intumescent Compositions. In Intumescent Coatings for Fire Protection of Building Structures and Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Puri, R.G.; Khanna, A. Effect of cenospheres on the char formation and fire protective performance of water-based intumescent coatings on structural steel. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 92, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustinov, A.; Zybina, O.; Tomakhova, A.; Pavlov, S. The enhancement of operating properties of intumescent fire-protective compositions. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 245, 11008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Qu, B. Synergistic effects of expandable graphite with some halogen-free flame retardants in polyolefin blends. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 71, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, H.J. Characterisation of Expandable Graphite and Its Flame Retardant Abilities in Flame Retardant Systems for Polyethylene; University of Pretoria: Pretoria, South Africa, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Lang, D.; Liu, S.-W.; Chi, Z.-G.; Xu, J.-R. Flame retardant mechanism of a novel intumescent flame retardant polypropylene. Procedia Eng. 2013, 52, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krassowski, D.; Hutchings, D.; Qureshi, S. Expandable graphite flake as an additive for a new flame retardant resin. In Proceedings of the Fire Retardant Chemicals Association, Fall Meeting, Naples, FL, USA, 13–16 October 1996; pp. 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Kalali, E.N.; Wan, J.-T.; Wang, D.-Y. Carbon-family materials for flame retardant polymeric materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 69, 22–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Wang, S.; Song, P.a.; Wu, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, X. Combination effect of carbon nanotubes with graphene on intumescent flame-retardant polypropylene nanocomposites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 59, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandersall, H. Intumescent coating system, their development and chemistry. J. Fire Flamm. 1971, 2, 97–140. [Google Scholar]
- Nasirzadeh, M.; Yahyaei, H.; Mohseni, M. Effects of inorganic fillers on the performance of the water-based intumescent fire-retardant coating. Fire Mater. 2023, 47, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, M.; Ramli Sulong, N.; Yew, M.; Amalina, M.; Johan, M. Investigation on solvent-borne intumescent flame-retardant coatings for steel. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, S6-S384–S6-S388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murat Unlu, S.; Tayfun, U.; Yildirim, B.; Dogan, M. Effect of boron compounds on fire protection properties of epoxy based intumescent coating. Fire Mater. 2017, 41, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horacek, H. Reactions of stoichiometric intumescent paints. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 1745–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, J.; He, T.; Wu, Y.; Liang, G. An Investigation of the thermal degradation of the intumescent coating containing MoO3 and Fe2O3. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 3121–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, M.; Sulong, N.R.; Yew, M.; Amalina, M.; Johan, M. Influences of flame-retardant fillers on fire protection and mechanical properties of intumescent coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 78, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, A.; Angeler, D. Flame retardants: Chemistry, applications, and environmental impacts. In Handbook of Combustion; Willey: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 415–439. [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas, M.; García-López, D.; Gobernado-Mitre, I.; Merino, J.; Pastor, J.; Martínez, J.d.D.; Barbeta, J.; Calveras, D. Mechanical and fire retardant properties of EVA/clay/ATH nanocomposites–Effect of particle size and surface treatment of ATH filler. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 2032–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Ullah, S.; Mohammad, W.F.; Shariff, M.F. Thermal performance of alumina filler reinforced intumescent fire retardant coating for structural application. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2014; p. 012023. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; Ahmad, F.; Shariff, A.; Bustam, M. Synergistic effects of kaolin clay on intumescent fire retardant coating composition for fire protection of structural steel substrate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 110, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X. Influence of nano-silica on the flame retardancy and smoke suppression properties of transparent intumescent fire-retardant coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 112, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbasuney, S.; Maraden, A. Novel thermoset nanocomposite intumescent coating based on hydroxyapatite nanoplates for fireproofing of steel structures. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Bailey, C.G.; Taylor, A.P. Global modelling of fire protection performance of an intumescent coating under different furnace fire conditions. J. Fire Sci. 2013, 31, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.; Duquesne, S.; Bourbigot, S. Intumescent fire protective coating: Toward a better understanding of their mechanism of action. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 449, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucherini, A.; Costa, R.-I.; Giuliani, L.; Jomaas, G. Experimental Study of the Behaviour of Steel Structures Protected by Different Intumescent Coatings and Exposed to Various Fire Scenarios; Lucherini, A., Ed.; DEStech Publications: Lancaster, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, J. Intumescent Coatings: What Are They and How Are They Used. Available online: https://www.firefree.com/blog/intumescent-coatings-what-are-they-and-how-are-they-used/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Modeling study on the combustion of intumescent fire-retardant polypropylene. Express Polym. Lett. 2007, 1, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, M.; Autrique, L.; Perez, L. Mathematical model for intumescent coatings growth: Application to fire retardant systems evaluation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Weinell, C.E.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Ring, L.; Kiil, S. A char stratification approach to characterization and quantitative thermal insulation performance of hydrocarbon intumescent coatings. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2022, 19, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arogundade, A.I.; Megat-Yussof, P.S.; Afolabi, L.O. Evaluation of compression strength of intumescent char using ASTM 1162 00. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2021, 18, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetsma, J. Intumescent Paints—The Key Ingredients.” Prospector Knowledge Center. 2022. Available online: https://www.ulprospector.com/knowledge/13245/pc-intumescent-paints-the-key-ingredients/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Camino, G.; Costa, L.; Trossarelli, L. Study of the mechanism of intumescence in fire retardant polymers: Part V—Mechanism of formation of gaseous products in the thermal degradation of ammonium polyphosphate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1985, 12, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, P. Synthesis of melamine phenyl hypophosphite and its synergistic flame retardance with SiO 2 on polypropylene. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 6207–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, R.; Yang, F.; Fan, Z. The effect of water-based primer pretreatment on the performance of water-based inkjet coatings on wood surfaces. Coatings 2023, 13, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassburger, D.; Silveira, M.; Baldissera, A.; Ferreira, C. Performance of different water-based resins in the formulation of intumescent coatings for passive fire protection. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2023, 20, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapa, S.; Sulong, N.R. Performance of solvent-borne intumescent fire protective coating with Palm oil clinker as novel bio-filler on steel. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Liang, G.; Gu, A.; Ye, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, L. A novel inorganic–organic hybridized intumescent flame retardant and its super flame retarding cyanate ester resins. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 2169–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Chow, W.K. A brief review of intumescent fire retardant coatings. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2003, 46, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wu, M.; He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qu, W. The Evolution of Intumescent Char in Flame-Retardant Coatings Based on Amino Resin. Coatings 2021, 11, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Wang, C.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z. A facile strategy to fabricate an intumescent fire-retardant coating with improved fire resistance and water tolerance for steel structure. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2020, 17, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Cai, H.; Wang, J. Synthesis of a phosphaphenanthrene/benzimidazole-based curing agent and its application in flame-retardant epoxy resin. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 163, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Hu, Q.; Huo, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z. Intumescent fire retardant coating with recycled powder from industrial effluent optimized using response surface methodology. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 140, 105494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, J.S.; Ma, B.C. Understanding the flame retardant mechanism of intumescent flame retardant on improving the fire safety of rigid polyurethane foam. Polymers 2022, 14, 4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Investigation of Water-based and Solvent-based Polymer Binders on the Fire Protection Performance and Mechanical Properties of Intumescent Coating. Doctoral Dissertation, Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman (UTAR), Kampar, Malaysia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tomczak, M.; Łopiński, J.; Kowalczyk, K.; Schmidt, B.; Rokicka, J. Vinyl intumescent coatings modified with platelet-type nanofillers. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 126, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.P.; de Sá, S.C.; Beraldo, C.H.; Hidalgo, G.E.; Ferreira, C.A. Intumescent coatings using epoxy, alkyd, acrylic, silicone, and silicone–epoxy hybrid resins for steel fire protection. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2020, 17, 1471–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Peng, H.; Esmaeili, N. Development of an epoxy-based self-intumescent fire protective coating containing an appropriate mass ratio of APP and Cu2O. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2023, 21, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otáhal, R.; Veselý, D.; Násadová, J.; Zíma, V.; Němec, P.; Kalenda, P. Intumescent coatings based on an organic-inorganic hybrid resin and the effect of mineral fibres on fire-resistant properties of intumescent coatings. Pigment. Resin Technol. 2011, 40, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odera, R.S.; Idumah, C.I.; Ezeani, E.O.; Okpechi, V.U.; Madu, I.O.; Oyeoka, H.C.; Ugwu, S.C.; Ogbu, J.E. Novel advancements in flame retardant mechanisms of halloysite nanotubes polymeric nanoarchitectures. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2023, 63, 312–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merryweather, G.; Spearpoint, M. Flame spread measurements on wood products using the ASTM E 1321 LIFT apparatus and a reduced scale adaptation of the cone calorimeter. Fire Mater. Int. J. 2010, 34, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabet, M.; Soleimani, H.; Hosseini, S. Thermal and flammable stability of radiated LDPE and composites. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 2019, 23, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-Y.; Hamerton, I. Recent developments in the chemistry of halogen-free flame retardant polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1661–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomakin, S.M.; Zaikov, G.E. Ecological Aspects of Polymer Flame Retardancy; Taylor Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1999; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, G.L. Fire and Polymers: An Overview; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- McCoy, C.G.; Stoliarov, S.I. Experimental characterization and modeling of boundary conditions and flame spread dynamics observed in the UL-94V test. Combust. Flame 2021, 225, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Niu, B.; Yan, H. Flexible water-resistant intumescent coatings: Fabrication, characterization, and fire protective performance. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 137, 105322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revaiah, R.; Kotresh, T.; Kandasubramanian, B. Effects of barrier chemicals on flame retardant properties of inherently flame retardant fabric. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 80, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.Z.S.; Losada, A.M.C.; Hernandez, J.A.G.; Quiñones, A.O. Characterization of a polypropylene and polyethylene compound for the production of bricks in non-structural walls. Inf. De La Construcción 2023, 75, e509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.; Chow, W.K. Review on four standard tests on flame spreading. Int. J. Eng. Perform. Based Fire Codes 2001, 3, 67–86. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, C.; Chalabi, R. Small scale flame-spread testing to BS 476 part 7. Fire Mater. 1976, 1, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.; Chow, W.K. Recommendation on assessing flame spreading of materials using ISO 9705. Fire Sci. Technol. 2004, 23, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Wade, C.; Baker, G. Fire hazard assessment of wall and ceiling fire spread in rooms. In Flammability Testing of Materials Used in Construction, Transport and Mining; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 127–156. [Google Scholar]
- Leventon, I.T.; Li, J.; Stoliarov, S.I. A flame spread simulation based on a comprehensive solid pyrolysis model coupled with a detailed empirical flame structure representation. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 3884–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.; Sidhu, H.; Weber, R.; Mercer, G. A dynamical systems model of the limiting oxygen index test. ANZIAM J. 2001, 43, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Nasir, K.; Ramli Sulong, N.H.; Johan, M.R.; Afifi, A.M. An investigation into waterborne intumescent coating with different fillers for steel application. Pigment. Resin. Technol. 2018, 47, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, R.J.; Tretsiakova-McNally, S.; Zhang, J. The Controlled Atmosphere Cone Calorimeter: A Literature Review. Fire Technol. 2023, 59, 2203–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovická Osvaldová, L.; Fatriasari, W. Special Test Methods. In Testing of Materials for Fire Protection Needs: European Standard Test Methods for the Building Sector; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tanchak, R.N.; Wang, Q. A review on cone calorimeter for assessment of flame-retarded polymer composites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 10209–10234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.K.; Hasnat, M.R.; Loh, K.P.; Hossain, M.D.; Rahnamayiezekavat, P.; Douglas, G.; Saha, S. Effect of Interlayer Materials on Fire Performance of Laminated Glass Used in High-Rise Building: Cone Calorimeter Testing. Fire 2023, 6, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzulkafli, H.H.; Ahmad, F.; Ullah, S.; Hussain, P.; Mamat, O.; Megat-Yusoff, P.S. Effects of talc on fire retarding, thermal degradation and water resistance of intumescent coating. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 146, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beh, J.H.; Yew, M.C.; Yew, M.K.; Saw, L.H. Fire protection performance and thermal behavior of thin film intumescent coating. Coatings 2019, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AS 3959–2009; Construction of Buildings in Bushfire-Prone Areas. Standards Australia: Sydney, NSW, Austrlia, 2009. Available online: https://hackaday.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Standards-Construction-of-buildings-in-bushfire-prone-areas.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Chaturvedi, S.; Vedrtnam, A.; Youssef, M.A.; Palou, M.T.; Barluenga, G.; Kalauni, K. Fire-resistance testing procedures for construction elements—A Review. Fire 2022, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisaenrith, P.; Taksakulvith, P.; Pavasupree, S. Effect of nano titanium dioxide in intumescent fireproof coating on thermal performance and char morphology. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 3462–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Amir, N.; Ahmad, F.; Ullah, S.; Jimenez, M. Effect of basalt fibers dispersion on steel fire protection performance of epoxy-based intumescent coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 122, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Standard BS 476 Fire Test. Available online: https://www.firesafe.org.uk/british-standard-476-fire-tests/ (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Xu, Q.; Li, G.-Q.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.C. Experimental study of the influence of topcoat on insulation performance of intumescent coatings for steel structures. Fire Saf. J. 2018, 101, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, P.; Sharma, U.K.; Kumar, V.; Bhargava, P.; Usmani, A.; Singh, B.; Singh, Y.; Torero, J.; Gillie, M.; Pankaj, P. Full-scale fire test on an earthquake-damaged reinforced concrete frame. Fire Saf. J. 2015, 73, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwang Yin, J.J.; Yew, M.C.; Yew, M.K.; Saw, L.H. Preparation of intumescent fire protective coating for fire rated timber door. Coatings 2019, 9, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, M.C.; Sulong, N.R. Fire-resistive performance of intumescent flame-retardant coatings for steel. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.; Duquesne, S.; Bourbigot, S. Characterization of the performance of an intumescent fire protective coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazaré, S.; Pitts, W.M.; Shields, J.; Davis, R. Factors for consideration in an open-flame test for assessing fire blocking performance of barrier fabrics. Polymers 2016, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazrun, T.; Hassan, M.K.; Hasnat, M.R.; Hossain, M.D.; Rahnamayiezekavat, P.; Saha, S. Comparative Study on Fire Behaviour of Solid Aluminium Sheets Coated with Intumescent Materials; International Conference on Fire Safety Engineering Research and Practice: Sydney, Australia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Havula, J.; Wald, F.; Cabova, K. Temperature analysis of steel structures protected by intumescent paint with steel claddings in fire. Fire Mater. 2020, 44, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures. Available online: https://eurocodes.jrc.ec.europa.eu/EN-Eurocodes/eurocode-3-design-steel-structures (accessed on 22 October 2024).
- de Silva, D.; Bilotta, A.; Nigro, E. Experimental investigation on steel elements protected with intumescent coating. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 205, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-Q.; Han, J.; Lou, G.-B.; Wang, Y.C. Predicting intumescent coating protected steel temperature in fire using constant thermal conductivity. Thin-Walled Struct. 2016, 98, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakumoto, Y.; Nagata, J.; Kodaira, A.; Saito, Y. Durability evaluation of intumescent coating for steel frames. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2001, 13, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, J. Influences of binder on fire protection and anticorrosion properties of intumescent fire resistive coating for steel structure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häßler, M.; Häßler, D.; Hothan, S.; Krüger, S. Fire tests of steel tension rod systems with intumescent coating. J. Struct. Fire Eng. 2020, 11, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intumescent Paints—Efficient Way of Protection of Steel Materials Against Fire. Available online: https://fireproofer.com.sg/2021/12/23/intumescent-paints-efficient-way-of-protection-of-steel-materials-against-fire/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- UPVC Spraying Experts. Available online: https://upvcspraypainters.com/intumescent-paint-coating/ (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- Häßler, M.; Häßler, D.; Hothan, S.; Krüger, S. Performance of intumescent fire protection coatings on steel tension rod systems. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Structures in Fire, Ulster University, Belfast, UK, 6–8 June 2018; pp. 649–654. [Google Scholar]
- Häßler, D.; Häßler, M.; Hothan, S.; Krüger, S. Leistungsfähigkeit reaktiver Brandschutzsysteme auf Zugstabsystemen und deren Anschlusskonstruktionen. Stahlbau 2018, 87, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar, E.A.A. Flammability and Burning Behaviour for Mass Timber Protected Using Intumescent Coatings. PhD Thesis, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Aqlibous, A.; Tretsiakova-McNally, S.; Fateh, T. Waterborne intumescent coatings containing industrial and bio-fillers for fire protection of timber materials. Polymers 2020, 12, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucherini, A.; Razzaque, Q.S.; Maluk, C. Exploring the fire behaviour of thin intumescent coatings used on timber. Fire Saf. J. 2019, 109, 102887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.-J.; Ahn, K.-S.; Kim, M.-J.; Hwang, S.-W.; Kang, S.G.; Kwak, H.W.; Yeo, H.; Oh, J.-K. Effect of Intumescent Coating on the Charring Rate of Nail-laminated Timber. BioResources 2022, 17, 5999–6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyridakis, S.; Carrascal, J.; Wiesner, F.; Barber, D.; Maluk, C. Exploring the influence of heating conditions in the charring profile of bare timber and timber protected with a thin intumescent coating. In Proceedings of the World Conference on Timber Engineering (WCTE 2023), Oslo, Norway, 19–22 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J. Preliminary study on decanoic/palmitic eutectic mixture modified silica fume geopolymer-based coating for flame retardant plywood. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 189, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Zhang, G.; He, S. Fire resistance tests on prestressed concrete box girder with intumescent fire-retardant coatings. Fire Technol. 2022, 58, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivenko, P.V.; Guzii, S.G.; Bodnarova, L.; Valek, J.; Hela, R.; Zach, J. Effect of thickness of the intumescent alkali aluminosilicate coating on temperature distribution in reinforced concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 8, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.-Y.; Han, L.-H.; Zhou, K.; Feng, Y. Fire resistance of circular concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) column protected by intumescent coating. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2018, 147, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllidis, Z.; Bisby, L.A. Fibre-reinforced intumescent fire protection coatings as a confining material for concrete columns. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 231, 117085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagdag, O.; Berisha, A.; Mehmeti, V.; Haldhar, R.; Berdimurodov, E.; Hamed, O.; Jodeh, S.; Lgaz, H.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Ebenso, E.E. Epoxy coating as effective anti-corrosive polymeric material for aluminum alloys: Formulation, electrochemical and computational approaches. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 346, 117886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Dai, M.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Gao, X.; Ren, F.; Zhang, Q. Effect of microencapsulated ammonium polyphosphate on the durability and fire resistance of waterborne intumescent fire-retardant coatings. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2019, 16, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, Z.; Pomázi, Á.; Toldy, A. Development of Multifunctional Flame-Retardant Gel Coatings for Automotive Applications. Coatings 2023, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sa, S.C.; de Souza, M.M.; Peres, R.S.; Zmozinski, A.V.; Braga, R.M.; de Araujo Melo, D.M.; Ferreira, C.A. Environmentally friendly intumescent coatings formulated with vegetable compounds. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 113, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ahmad, F.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Assiri, M.A.; Raza, M.R.; Irfan, A. Effect of expandable graphite and ammonium polyphosphate on the thermal degradation and weathering of intumescent fire-retardant coating. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Jia, Z.; Sun, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, J. Estimation of mechanical performance, thermal stability and flame retardancy of high-impact polystyrene/surface-modified APP/carboxylic-functionalized MWCNTs nanocomposites. Polymers 2019, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, K.; Kowalczyk, A. Intumescent coatings modified with cocoa shells as a bio-substitute for pentaerythritol. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 186, 108046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkitaraj, K.; Suresh, S. Experimental thermal degradation analysis of pentaerythritol with alumina nano additives for thermal energy storage application. J. Energy Storage 2019, 22, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.T.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Koo, S.; Jerng, D.-W.; Wongwises, S.; Ahn, H.S. Mesoporous graphene adsorbents for the removal of toluene and xylene at various concentrations and its reusability. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillani, Q.F.; Ahmad, F.; Mutalib, M.I.A.; Melor, P.S.; Ullah, S.; Arogundade, A. Effect of dolomite clay on thermal performance and char morphology of expandable graphite based intumescent fire retardant coatings. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y. Recent development of flame retardant polymeric materials containing expandable graphite. Bull. Jpn. Assoc. Fire Sci. Eng. 2006, 56, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; Ahmad, F.; Yusoff, P.M. Effect of boric acid and melamine on the intumescent fire-retardant coating composition for the fire protection of structural steel substrates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 2983–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörold, S. Phosphorus-based and intumescent flame retardants. In Polymer Green Flame Retardants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 221–254. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, S.L.; Hesse, J.; Blanchard, L.-P. Thermal decomposition of a vinyl chloride/vinyl acetate copolymer. Polymer 1975, 16, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, P.; He, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Fast quantifying collision strength index of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer coverings on the fields based on near infrared hyperspectral imaging techniques. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Almasi, H. Biodegradable polymers. Biodegrad. Life Sci. 2013, 141–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, J.T.; Gonçalves, C.; Hiliou, L.; Coelho, J.F.; Magalhaes, F.D. Effect of binder on performance of intumescent coatings. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2016, 13, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Wan, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, N.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M. Preparation and performance analysis of methyl-silicone resin-modified epoxy resin-based intumescent flame retardant thermal insulation coating. J. Micromech. Mol. Phys. 2023, 8, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Y. Influence of magnesium hydroxide on thermal decomposition of intumescent fire-retardant epoxy coatings. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2016, 29, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Kiviranta, K.; Suvanto, S.; Alvila, L.; Leskinen, J.; Lappalainen, R.; Haapala, A. Casein-magnesium composite as an intumescent fire retardant coating for wood. Fire Saf. J. 2020, 112, 102943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, G.; Diaz, L.B.; Gregory, D.H. Recent progress in the synthesis of nanostructured magnesium hydroxide. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 6067–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, B.S.; Dobra, G.; Iliev, S.; Cotet, L.; Neacsu, I.A.; Surdu, V.A.; Nicoara, A.I.; Boiangiu, A.; Filipescu, L. Thermally activated Al (OH) 3 Part II—Effect of different thermal treatments. Ceramics 2021, 4, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Zulkurnain, E.S.B.; Ullah, S.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Raza, M.R. Improved fire resistance of boron nitride/epoxy intumescent coating upon minor addition of nano-alumina. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 256, 123634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, S.; Ahmed, A.; Okonkwo, P. Alumina phase transformation from thermal decomposition of ammonium alum synthesized from kankara kaolin. Niger. J. Technol. 2017, 36, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevim, F.; Demir, F.; Bilen, M.; Okur, H. Kinetic analysis of thermal decomposition of boric acid from thermogravimetric data. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 23, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Feng, W.; Guo, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, S.; Gu, X.; Li, H.; Yang, W. Hydrophobic modification of pentaerythritol and its application in fire-retardant coatings for steel structures. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 138, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gong, G.; Gao, L.; Cui, W.; Wang, Y. Preparation and performance of intumescent water-based coatings with both thermal insulation and flame retardant functions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, M.C.; Ooi, G.J.; Yew, M.K.; Saw, L.H.; Beh, J.H.; Ng, T.C.; Yeo, W.H. Effects of hybrid flame-retardant fillers on fire-resistive and mechanical properties of solvent-borne intumescent coatings. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 012008. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Feng, X.; Yuen, R.K.; Hu, Y. Melamine-containing polyphosphazene wrapped ammonium polyphosphate: A novel multifunctional organic-inorganic hybrid flame retardant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustinov, A.; Zybina, O.; Vasiliev, M.; Suprun, W. A method to assess adhesion and durability of charred intumescent layers in non-specific conditions. In Proceedings of the EECE 2019: Energy, Environmental and Construction Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Kablov, V.; Keibal, N.; Kochetkov, V. Fire and Heat Retardant Polymer Materials and Coatings with Functionally Active Phosphorus–Boron–Nitrogen-Containing Components. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2024, 66, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, T.; Kamble, A.; Naik, S.M. An investigation of primer adhesion and topcoat compatibility on the waterborne intumescent coating to structural steel. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 131, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, X.; Yang, X. The effects to the structure and electrochemical behavior of zinc phosphate conversion coatings with ethanolamine on magnesium alloy AZ91D. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, F.; Han, E.-H.; Anjum, S.; Xu, G. The mechanism of inhibition by zinc phosphate in an epoxy coating. Corros. Sci. 2013, 69, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, W.-h.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z. Experimental study of the acid corrosion effects on an intumescent coating for steel elements. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 11249–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, G. Influences of montmorillonite on fire protection, water and corrosion resistance of waterborne intumescent fire retardant coating for steel structure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 239, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.Y.; Stahlheber, N.E.; Dyroff, D.R. Preparation and characterization of crystalline long-chain ammonium polyphosphates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1969, 91, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees, S.M.; Dasari, A. A review on the environmental durability of intumescent coatings for steels. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 124–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrani, B.; Hemmati, V.; Zhou, A.; Quarles, S.L. Effects of natural weathering on the fire properties of intumescent fire-retardant coatings. Fire Mater. 2018, 42, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Li, G.-Q. Experimental study of hydrothermal aging effects on insulative properties of intumescent coating for steel elements. Fire Saf. J. 2013, 55, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Li, G. Thermal conductivity of intumescent coating char after accelerated aging. Fire Mater. 2013, 37, 440–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotta, A.; de Silva, D.; Nigro, E. Tests on intumescent paints for fire protection of existing steel structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 121, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, E.; Ke, W. Effect of nanoparticles on the improvement in fire-resistant and anti-ageing properties of flame-retardant coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 5706–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, E.; Ke, W. Influence of expandable graphite on fire resistance and water resistance of flame-retardant coatings. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 2237–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, E.; Liu, F.; Ke, W. Fire and corrosion resistances of intumescent nano-coating containing nano-SiO2 in salt spray condition. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, J. Influences of glass flakes on fire protection and water resistance of waterborne intumescent fire resistive coating for steel structure. Prog. Org. Coat. 2011, 70, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.; Bellayer, S.; Naik, A.; Bachelet, P.; Duquesne, S.; Bourbigot, S. Topcoats versus durability of an intumescent coating. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 9625–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Li, G.-Q.; Zhang, Q.-Q. An experimental study of the effects of topcoat on aging and fire protection properties of intumescent coatings for steel elements. Fire Saf. J. 2020, 111, 102931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrulle, L.; Dubrulle, L.; Zammarano, M.; Davis, R.D. Effect of Fire-Retardant Coatings and Accelerated-Weathering on the Flammability of Wood-Based Materials in Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI) Communities; US Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2020.
- Tang, G.; Shang, C.; Qin, Y.; Lai, J. Current Advances in Flame-Retardant Performance of Tunnel Intumescent Fireproof Coatings: A Review. Coatings 2025, 15, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucherini, A.; Lam, H.Y.; Jimenez, M.; Samyn, F.; Bourbigot, S.; Maluk, C. Fire testing of intumescent coatings: Comparison between bench-scale furnace and radiant panels experimental methodologies. Fire Technol. 2022, 58, 1737–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, G.; Su, Q. Influence of degree of polymerization of ammonium polyphosphate on anti-aging property of waterborne fire resistive coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 246, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. The protective effects and aging process of the topcoat of intumescent fire-retardant coatings applied to steel structures. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2016, 13, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shaughnessy, T. Comparing Two Popular Fire-Resistant Coatings. Available online: https://www.facilitiesnet.com/paintscoatings/article/Comparing-Two-Popular-Fire-Resistant-Coatings--19197 (accessed on 29 December 2023).
- O’Shaughnessy, T. Exploring Fireproofing Options for Facility Managers. Available online: https://www.impomag.com/maintenance/article/21591127/exploring-fireproofing-options-for-facility-manager (accessed on 29 December 2023).
- Best for Steel: Intumescent or Cementitious? 2021. Available online: https://permax.com.au/steel-fireproofing-intumescent-coating-vs-cementitious-coating/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Passive Fire Protection, Intumescent vs. Lightweight Cementittious. 2021. Available online: https://protectiveemea.sherwin-williams.com/Documents/LiteratureLibrary/Brochures/en/Intumescent%20vs%20Cementious.pdf (accessed on 31 December 2023).
- Firetex® FX6002: A Three-Component, Intumescent Coating. Available online: https://industrial.sherwin-williams.com/na/us/en/protective-marine/catalog/product/protective-and-marine-coatings/products-by-industry.11543396/firetex-fx6002.20716667.html (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Nazrun, T.; Hassan, M.K.; Hasnat, M.R.; Hossain, M.D.; Saha, S. Improving fire performance of solid aluminium of composite cladding panels incorporating intumescent coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2025, 201, 109142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Impact of DFT on Intumescent Paint Performance in Fire Protection Services. Available online: https://www.b-line.co/the-impact-of-dft-on-intumescent-paint-performance-in-fire-protection-services/ (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Stefanidou, M.; Athanaselis, S.; Spiliopoulou, C. Health impacts of fire smoke inhalation. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubright, S. Cyanide and Hydrogen Sulfide: A Review of Two Blood Gases, Their Environmental Sources, and Potential Risks. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Raub, J.A.; Mathieu-Nolf, M.; Hampson, N.B.; Thom, S.R. Carbon monoxide poisoning—A public health perspective. Toxicology 2000, 145, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquesne, S.; Le Bras, M.; Bourbigot, S.; Delobel, R.; Poutch, F.; Camino, G.; Eling, B.; Lindsay, C.; Roels, T. Analysis of fire gases released from polyurethane and fire-retarded polyurethane coatings. J. Fire Sci. 2000, 18, 456–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielecka, M.; Rabajczyk, A.; Cygańczuk, K.; Pastuszka, Ł.; Jurecki, L. Silicone resin-based intumescent paints. Materials 2020, 13, 4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisterkamp, I.; Gartiser, S.; Kalbe, U.; Bandow, N.; Gloßmann, A. Assessment of leachates from reactive fire-retardant coatings by chemical analysis and ecotoxicity testing. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardelle, B.; Duquesne, S.; Rerat, V.; Bourbigot, S. Thermal degradation and fire performance of intumescent silicone-based coatings. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2013, 24, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, K.M. Physical modeling of intumescent fire retardant polymers. In ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Li, X.-Z.; Wu, Z.-P.; Liu, Y.-X.; Fang, C.-C.; Meng, W. Formulation of intumescent flame retardant coatings containing natural-based tea saponin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2782–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Lam, J.C.; Yang, S.; Lam, P.K. Conventional and emerging halogenated flame retardants (HFRs) in sediment of Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region, East China. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

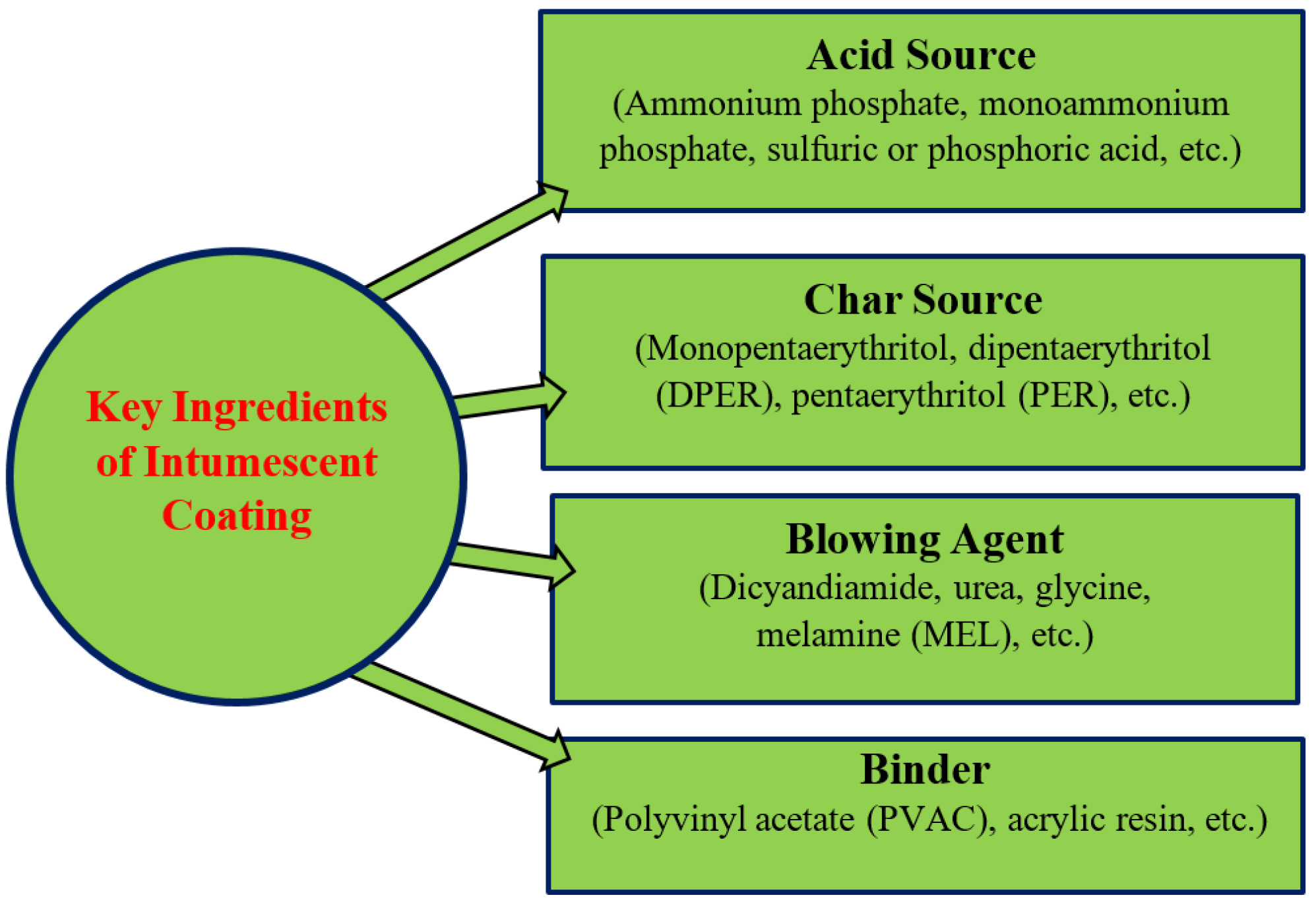
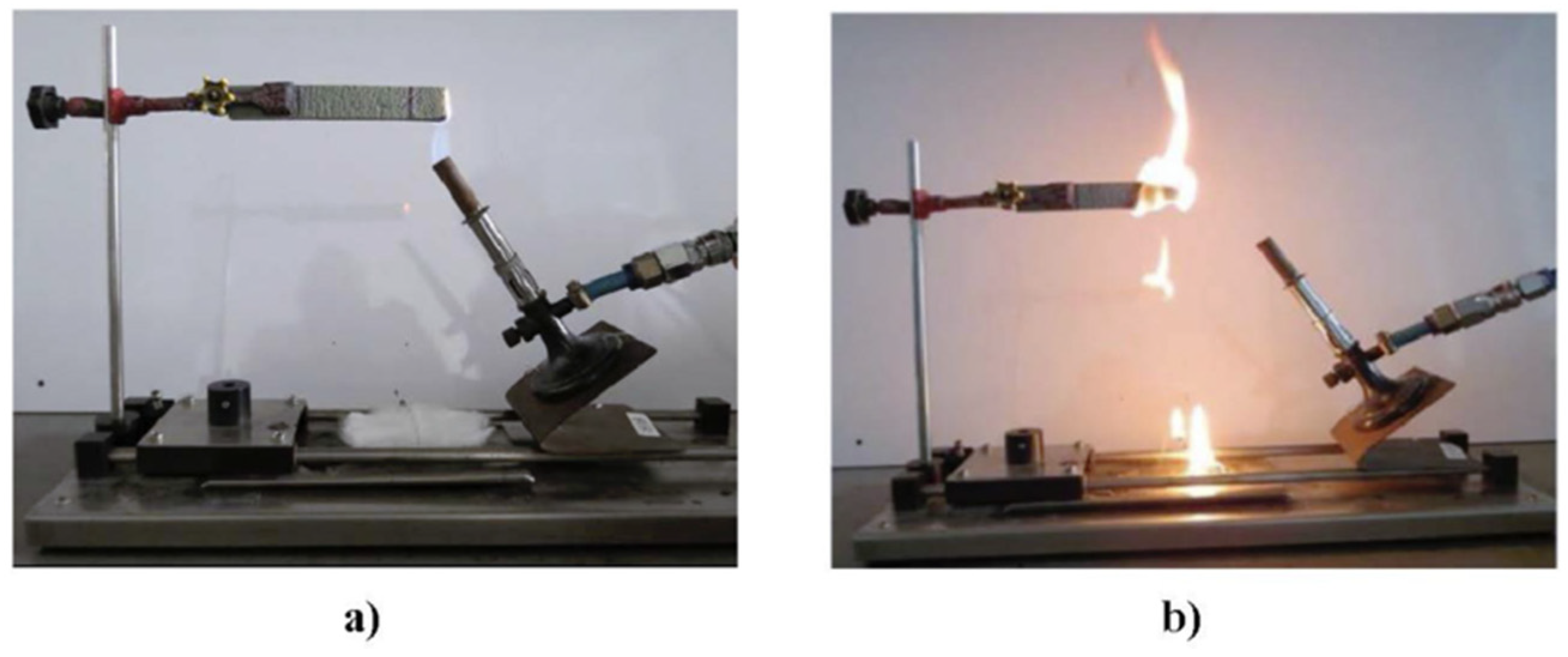



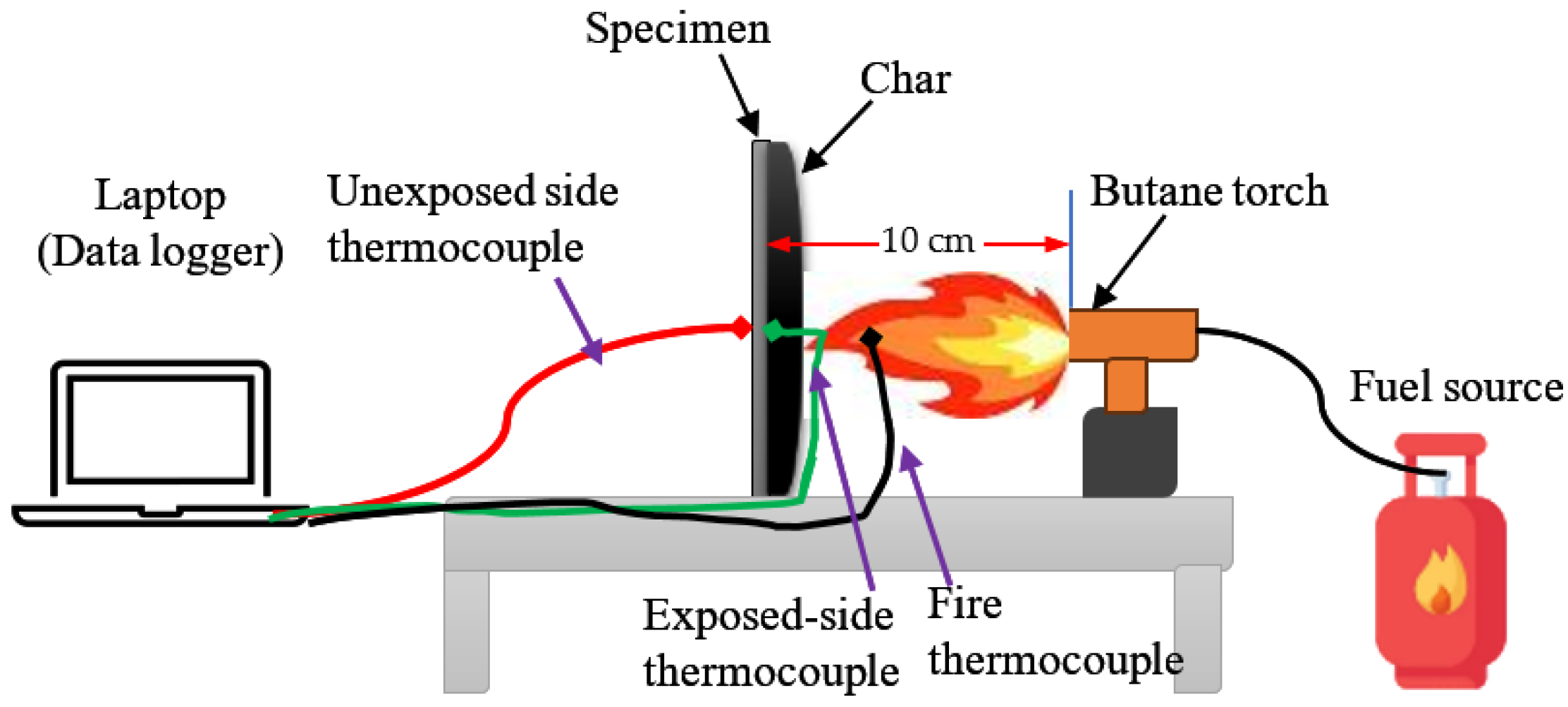


| Criteria | V-0 (Lowest Flammability) | V-1 | V-2 (Highest Flammability) |
|---|---|---|---|
| After flame time (t) (in secs) | <10 s | <30 s | <30 s |
| Whether the flame reached the top of the specimen | No | No | Yes |
| Cotton indicator (whether dripping occurred) | No | No | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazrun, T.; Hassan, M.K.; Hasnat, M.R.; Hossain, M.D.; Ahmed, B.; Saha, S. A Comprehensive Review on Intumescent Coatings: Formulation, Manufacturing Methods, Research Development, and Issues. Fire 2025, 8, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8040155
Nazrun T, Hassan MK, Hasnat MR, Hossain MD, Ahmed B, Saha S. A Comprehensive Review on Intumescent Coatings: Formulation, Manufacturing Methods, Research Development, and Issues. Fire. 2025; 8(4):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8040155
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazrun, Touha, Md Kamrul Hassan, Md Rayhan Hasnat, Md Delwar Hossain, Bulbul Ahmed, and Swapan Saha. 2025. "A Comprehensive Review on Intumescent Coatings: Formulation, Manufacturing Methods, Research Development, and Issues" Fire 8, no. 4: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8040155
APA StyleNazrun, T., Hassan, M. K., Hasnat, M. R., Hossain, M. D., Ahmed, B., & Saha, S. (2025). A Comprehensive Review on Intumescent Coatings: Formulation, Manufacturing Methods, Research Development, and Issues. Fire, 8(4), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8040155