Surface Formations Salinity Survey in an Estuarine Area of Northern Morocco, by Crossing Satellite Imagery, Discriminant Analysis, and Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
- A hilly area covered by xerophilous vegetation where permeable and well aerated sandy soils are developed;
- A zone covered by halophytic plants. This zone actually includes several types of halophytic vegetation and several types of soil surface conditions, which vary spatially over short distances;
- A non flooded saline bare soil zone;
- A periodically flooded barren zone;
- A frequently flooded barren zone (Figure 1a).
2.2. Soil Salinity Measurements
2.3. Statistical and Geostatistical Tools
2.3.1. Normality Test
2.3.2. ECa Data Spatial Analysis
2.3.3. Discriminant Analysis
2.3.4. Machine Learning
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. A relevant Zonation
4.2. An Effective Discrimination
4.3. Linearity as a Low-Constraining Condition
4.4. Factors Other Than Salinity and the Saline Profile
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hay, C.C.; Morrow, E.; Kopp, R.E.; Mitrovica, J.X. Probabilistic reanalysis of twentieth-century sea-level rise. Nature 2015, 517, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.A.; White, N.J. Sea-Level Rise from the Late 19th to the Early 21st Century. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 32, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mengel, M.; Levermann, A.; Frieler, K.; Robinson, A.; Marzeion, B.; Winkelmann, R. Future sea level rise constrained by observations and long-term commitment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2597–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khojasteh, D.; Glamore, W.; Heimhuber, V.; Felder, S. Sea level rise impacts on estuarine dynamics: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusek, G.; Sweet, W.V.; Widlansky, M.J.; Thompson, P.R.; Marra, J.J. A novel statistical approach to predict seasonal high tide flooding. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1073792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, L.; Janeiro, J.; Neves, A.A.S.; Martins, F. The impact of Sea level rise in the guadiana estuary. J. Comput. Sci. 2020, 44, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridd, P.V.; Stieglitz, T. Dry Season Salinity Changes in Arid Estuaries Fringed by Mangroves and Saltflats. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Rondon, L.; Carrière, S.D.; Chalikakis, K.; Valles, V. An integrative geological and geophysical approach to characterize a superficial deltaic aquifer in the Camargue plain, France. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2013, 345, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Williams, M.E.; Brown, J.M.; Thorne, P.D.; Amoudry, L.O. Salt Intrusion as a Function of Estuary Length in Periodically Weakly Stratified Estuaries. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL099082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wong, V.N.L.; Triantafilis, J. Mapping soil salinity and pH across an estuarine and alluvial plain using electromagnetic and digital elevation model data. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbiero, L.; Mohamedou, A.O.; Laperrousaz, C.; Furian, S.; Cunnac, S. Polyphasic origin of salinity in the Senegal delta and middle valley. Catena 2004, 58, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furian, S.; Mohamedou, A.O.; Hammecker, C.; Maeght, J.L.; Barbiero, L. Soil cover and landscape evolution in the Senegal floodplain: A review and synthesis of processes and interactions during the late Holocene. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 62, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, B.A.; Assaeed, A.M.; Al-Rowaily, S.L.; Al-Doss, A.A.; Abd-ElGawad, A.M. Vegetation Composition of the Halophytic Grass Aeluropus lagopoides Communities within Coastal and Inland Sabkhas of Saudi Arabia. Plants 2022, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, J.D. Electromagnetic terrain conductivity measurement at low induction numbers. Tech. note TN 1980, 6, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Durand-Delga, M.; Kornprobst, J. Carte géologique de Tanger-Al Manzla (1/50000). Notes Mémoires du Serv. Géologique du Maroc 1985, 294. [Google Scholar]
- Medioni, R.; Wernli, R. Etude géologique du bassin post-nappe mio-pliocène du Charf-el-Akab ( Province de Tanger, Maroc ). Notes Mémoires du Serv. géologique du Maroc 1978, 40, 107–133. [Google Scholar]
- Nachite, D.; Bekkali, R.; Macias, A.; Anfuso, G. El estuario de Tahadart: Integrada de un Espacio en las Bases para una Gestión Plena Transformación; Servicio Publicaciones Universidad de Cadiz: Cadiz, Spain, 2007; ISBN 9788469163504. [Google Scholar]
- Taaouati, M.; Anfuso, G.; Nachite, D. Morphological Characterization and Evolution of Tahadart Littoral Spit, Atlantic Coast of Morocco; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 289–306. [Google Scholar]
- Karrouk, M.S. Apeçu sur les mécanismes climatiques rifains. Rev. la Fac. des Lettres des Sci. Hum. Tétouan 1990, 4, 11–36. [Google Scholar]
- ONEE. Etude de Canalisation des eaux Brutes du Barrage Ibn Battouta vers la Station de Traitement de Mharhar; Office National d’Electricité et de l’Eau Potable: Rabat, Morocco, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Achab, M. Les plages et les vasières des environs des embouchures des oueds Tahaddart et Gharifa (NW du Maroc): Dynamique morphosédimentaire et impact des aménagements sur leur évolution récente. In Sandy Beaches and Coastal Zone Management, Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Sandy Beaches, Rabat, Marocco, 19–23 October 2009; Bayed, A., Ed.; Travaux de l’Institut Scientifique n°6: Rabat, Morocco, 2011; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Orbi, A.; Lakdar, J.; Zidane, H. Etude préliminaire de l’estuaire de l’Oued Tahaddart (Automne 1995-printemps et automne 1996). Trav. Doc. l’Institut Natl. Rech. Halieut. 1997, 104, 1–82. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L.; Rhoades, J.D. An Improved Technique for Determining Soil Electrical Conductivity-Depth Relations from Above-ground Electromagnetic Measurements. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoroi, J.; Grunberger, O.; Sukchan, S.; Kungklang, N. Estimation de la salinité des sols du Nord-est de la Thaïlande par électromagnétisme en domaine fréquentiel. In Proceedings of the 5eme Colloque GEOFCAN. Géophysique des Sols et des Formations Superficielles, Orléans, France, 20–21 September 2005; pp. 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades, J.D.; Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Geospatial Measurements of Soil Electrical Conductivity to Assess Soil Salinity and Diffuse Salt Loading from Irrigation. In Assessment of Non-Point Source Pollution in the Vadose Zone; American Geophysical Union (AGU): Washington, DC, USA, 1999; pp. 197–215. ISBN 9781118664698. [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades, J.D.; Corwin, D.L. Determining Soil Electrical Conductivity-Depth Relations Using an Inductive Electromagnetic Soil Conductivity Meter. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafilis, J.; Laslett, G.M.; McBratney, A.B. Calibrating an Electromagnetic Induction Instrument to Measure Salinity in Soil under Irrigated Cotton. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hamdi, A.; Morarech, M.; El Mouine, Y.; Rachid, A.; El Ghmari, A.; Yameogo, S.; Chalikakis, K.; Yachou, H.; Kacimi, I.; Zouahri, A.; et al. Sources of spatial variability of soil salinity: The case of Beni Amir irrigated command areas in the Tadla Plain, Morocco. Arid L. Res. Manag. 2022, 36, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marden, J.I. Positions and QQ Plots. Stat. Sci. 2004, 19, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heung, B.; Ho, H.C.; Zhang, J.; Knudby, A.; Bulmer, C.E.; Schmidt, M.G. An overview and comparison of machine-learning techniques for classification purposes in digital soil mapping. Geoderma 2016, 265, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, A.; Huang, J.; Wong, V.N.L.; Monteiro Santos, F.A.; Wege, R.; Triantafilis, J. Electromagnetic Conductivity Imaging of Soil Salinity in an Estuarine–Alluvial Landscape. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zucca, C.; Muhaimeed, A.S.; Al-Shafie, W.M.; Fadhil Al-Quraishi, A.M.; Nangia, V.; Zhu, M.; Liu, G. Soil salinity prediction and mapping by machine learning regression in Central Mesopotamia, Iraq. L. Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 4005–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farifteh, J.; Van der Meer, F.; Atzberger, C.; Carranza, E.J.M. Quantitative analysis of salt-affected soil reflectance spectra: A comparison of two adaptive methods (PLSR and ANN). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Minasny, B.; Sarmadian, F.; Malone, B.P. Digital mapping of soil salinity in Ardakan region, central Iran. Geoderma 2014, 213, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brungard, C.W.; Boettinger, J.L.; Duniway, M.C.; Wills, S.A.; Edwards, T.C. Machine learning for predicting soil classes in three semi-arid landscapes. Geoderma 2015, 239–240, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, S.; Kalra, A.; Stephen, H. Estimating soil moisture using remote sensing data: A machine learning approach. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouramtane, T.; Hilal, H.; Rezende-Filho, A.T.; Bouramtane, K.; Barbiero, L.; Abraham, S.; Valles, V.; Kacimi, I.; Sanhaji, H.; Torres-Rondon, L.; et al. Mapping Gully Erosion Variability and Susceptibility Using Remote Sensing, Multivariate Statistical Analysis, and Machine Learning in South Mato Grosso, Brazil. Geosciences 2022, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbiero, L.; Cunnac, S.; Mané, L.; Laperrousaz, C.; Hammecker, C.; Maeght, J.L. Salt distribution in the Senegal middle valley analysis of a saline structure on planned irrigation schemes from N’Galenka creek. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 46, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Mokhtari, A.R.; Cohen, D.R.; Monteiro Santos, F.A.; Triantafilis, J. Modelling soil salinity across a gilgai landscape by inversion of EM38 and EM31 data. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudduth, K.A.; Kitchen, N.R.; Myers, D.B.; Drummond, S.T. Mapping Depth to Argillic Soil Horizons Using Apparent Electrical Conductivity. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2010, 15, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, D.; Arshad, M.; Zare, E.; Triantafilis, J. Reconnaissance scale mapping of salinity in three-dimensions using EM38 and EM34 data and inversion modelling. L. Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2936–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, A.J.; Brown, M.J.H.; Mossman, H.L.; Grant, A. Colonization of a newly developing salt marsh: Disentangling independent effects of elevation and redox potential on halophytes. J. Ecol. 2011, 99, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellouzi, H.; Ben Hamed, K.; Hernández, I.; Cela, J.; Müller, M.; Magné, C.; Abdelly, C.; Munné-Bosch, S. A comparative study of the early osmotic, ionic, redox and hormonal signaling response in leaves and roots of two halophytes and a glycophyte to salinity. Planta 2014, 240, 1299–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, V.H.; Suprasanna, P. Prospects of Halophytes in Understanding and Managing Abiotic Stress Tolerance BT. In Environmental Adaptations and Stress Tolerance of Plants in the Era of Climate Change; Ahmad, P., Prasad, M.N.V., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 29–56. ISBN 978-1-4614-0815-4. [Google Scholar]
- Flowers, T.J.; Hajibagheri, M.A.; Clipson, N.J.W. Halophytes. Q. Rev. Biol. 1986, 61, 313–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, E.P.; Brown, J.J.; Blumwald, E. Salt Tolerance and Crop Potential of Halophytes. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1999, 18, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveringa, J.; Oost, A.P. The fractal geometry of tidal-channel systems in the Dutch Wadden Sea. Geol. en Mijnb. 1999, 78, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles, G.R.; Perillo, G.M.E.; Piccolo, M.C.; Pierini, J.O. Fractal analysis of tidal channels in the Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Geomorphology 2004, 57, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


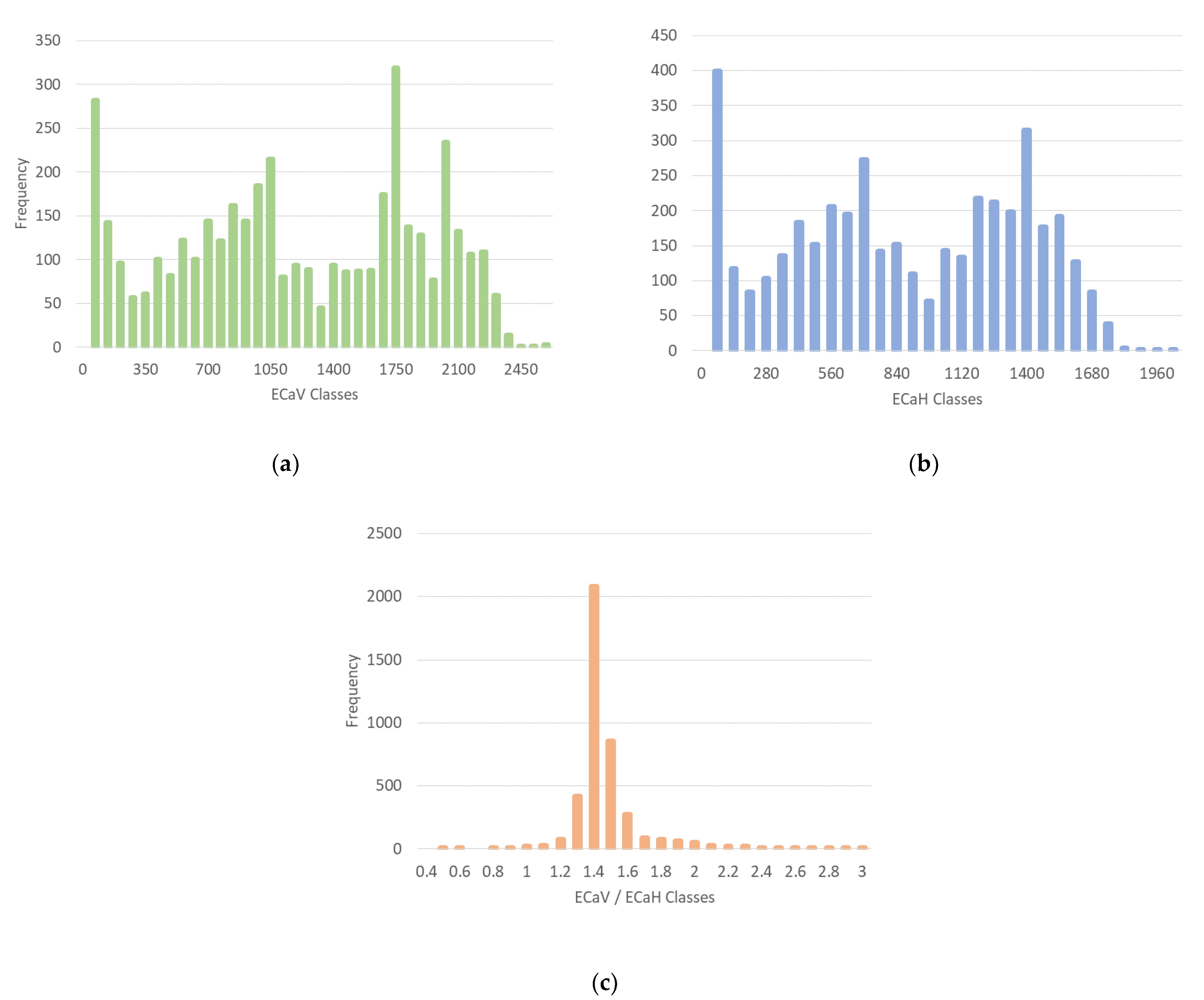




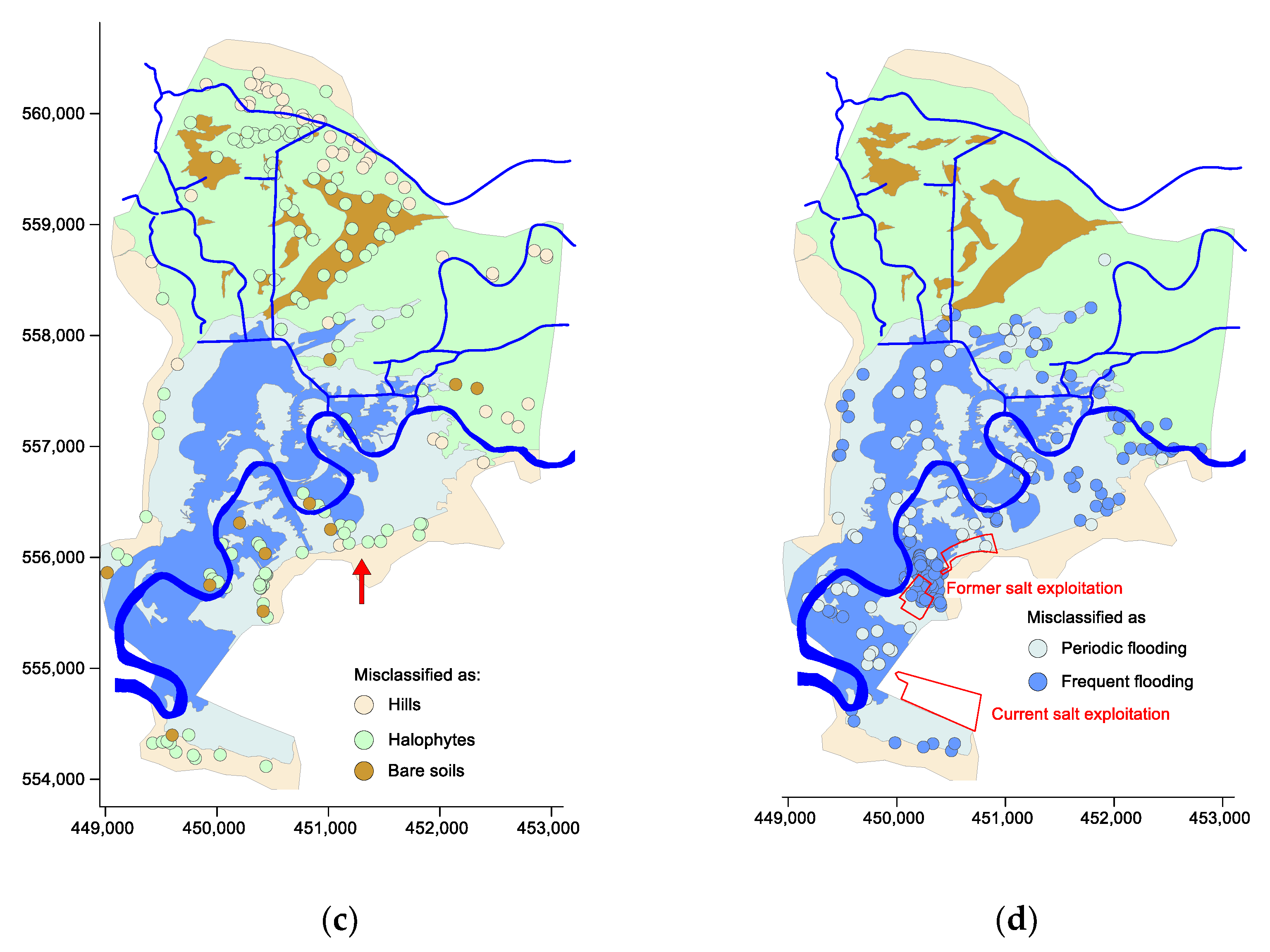
| Statistique | ECaV | ECaH | ECaV/ECaH |
|---|---|---|---|
| N. of observations | 4171 | 4171 | 4171 |
| Minimum | 3 | 1 | 0.20 |
| Maximum | 2842 | 2310 | 2.19 |
| Median | 1102 | 840 | 0.73 |
| Mean | 1165 | 858 | 0.71 |
| Variance | 459919 | 262159 | 0.01 |
| Stand. deviation | 678 | 512 | 0.10 |
| Coef. of variation | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.14 |
| Hills | Halophytes | Bare Soils | Frequent Flooding | Periodic Flooding | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECaV | Mean | 252 | 786 | 1034 | 1698 | 1792 |
| Stand. Dev | 355 | 320 | 242 | 285 | 393 | |
| ECaH | Mean | 182 | 559 | 767 | 1268 | 1333 |
| Stand. Dev | 275 | 247 | 197 | 203 | 286 |
| ECaV | ECaV, ECaH | ECaV, ECaH | Log(ECaV) | Log(ECaV), Log(ECaH) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| And | And | And | And | And | |
| ECaH | ECaV/ECaH | log(ECaV/ECaH | log(ECaH) | log(ECaV/ECaH) | |
| Well-classified | 60.66% | 59.22% | 62.29% | 56.39% | 55.26% |
| From\To | Freq. Flooding | Per. Flooding | Halophytes | Hills | Bare Soils | Total | % Correct |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freq. flooding | 760 | 46 | 10 | 1 | 51 | 868 | 87.56% |
| Per. flooding | 784 | 222 | 28 | 6 | 60 | 1100 | 20.18% |
| Halophytes | 97 | 2 | 1008 | 87 | 135 | 1329 | 75.85% |
| Hills | 16 | 3 | 100 | 537 | 31 | 687 | 78.17% |
| Bare soils | 19 | 0 | 97 | 0 | 71 | 187 | 37.97% |
| Total | 1676 | 273 | 1243 | 631 | 348 | 4171 | 62.29% |
| GMM | K-Means | KNN | NBC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numb. test points | 4171 | 4171 | 1042 | 1042 |
| Well-classified | 57.68% | 58.71% | 66.03% | 66.03% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Jarjini, Y.; Morarech, M.; Valles, V.; Touiouine, A.; Touzani, M.; Arjdal, Y.; Barry, A.A.; Barbiero, L. Surface Formations Salinity Survey in an Estuarine Area of Northern Morocco, by Crossing Satellite Imagery, Discriminant Analysis, and Machine Learning. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7020033
El Jarjini Y, Morarech M, Valles V, Touiouine A, Touzani M, Arjdal Y, Barry AA, Barbiero L. Surface Formations Salinity Survey in an Estuarine Area of Northern Morocco, by Crossing Satellite Imagery, Discriminant Analysis, and Machine Learning. Soil Systems. 2023; 7(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Jarjini, Youssouf, Moad Morarech, Vincent Valles, Abdessamad Touiouine, Meryem Touzani, Youssef Arjdal, Abdoul Azize Barry, and Laurent Barbiero. 2023. "Surface Formations Salinity Survey in an Estuarine Area of Northern Morocco, by Crossing Satellite Imagery, Discriminant Analysis, and Machine Learning" Soil Systems 7, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7020033
APA StyleEl Jarjini, Y., Morarech, M., Valles, V., Touiouine, A., Touzani, M., Arjdal, Y., Barry, A. A., & Barbiero, L. (2023). Surface Formations Salinity Survey in an Estuarine Area of Northern Morocco, by Crossing Satellite Imagery, Discriminant Analysis, and Machine Learning. Soil Systems, 7(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7020033








