A Methodology to Optimize PMSM Driven Solar Water Pumps Using a Hybrid MPPT Approach in Partially Shaded Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To implement different MPPT algorithms for a PMSM-based solar water pump in PSC and investigate their performance based on convergence time, MPPT accuracy, torque ripple, and system efficiency, ultimately identifying the best-performing algorithm.
- To employ a simplified V/f control system for PMSM-based solar water pumps aiming to reduce computational overhead, minimize system complexity, and eliminate the need for additional sensors for feedback.
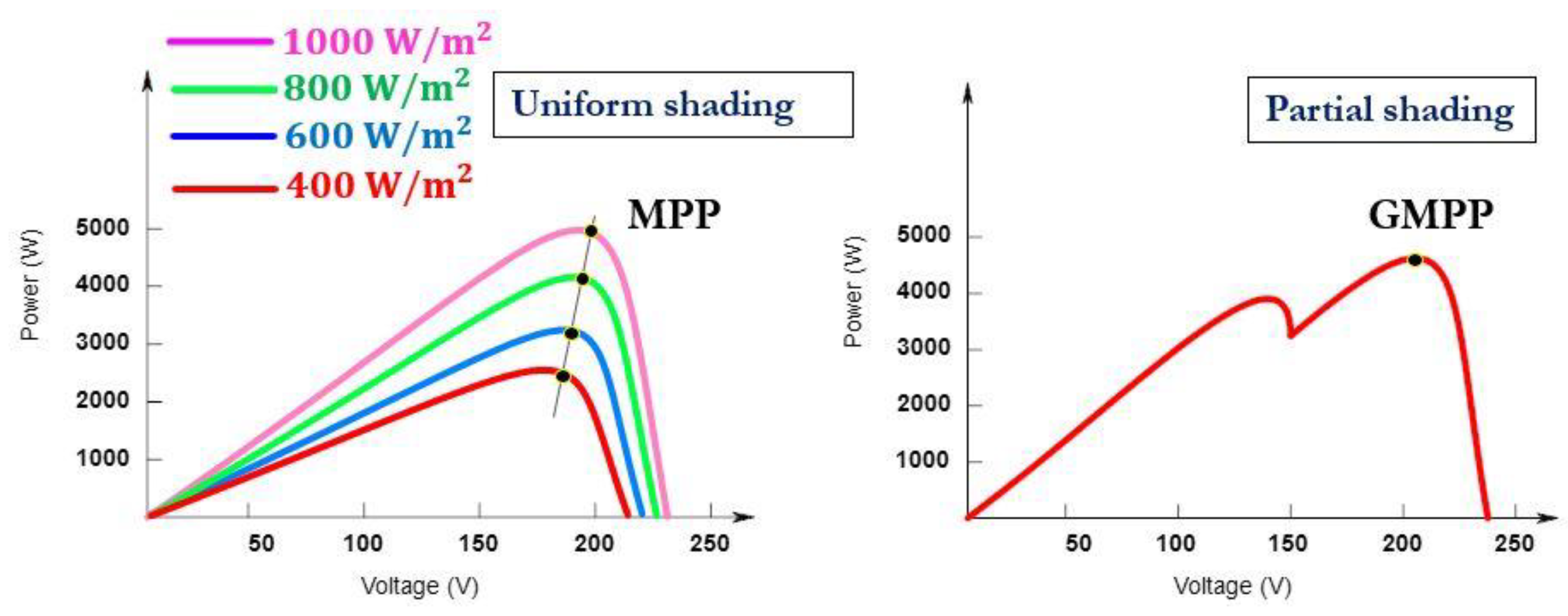
- To assess the performance of PMSM-based solar water pumps under extreme partial shading scenarios, focusing on the impact of peak power in the left region of the P-V curve on system efficiency while considering the system’s non-idealities.
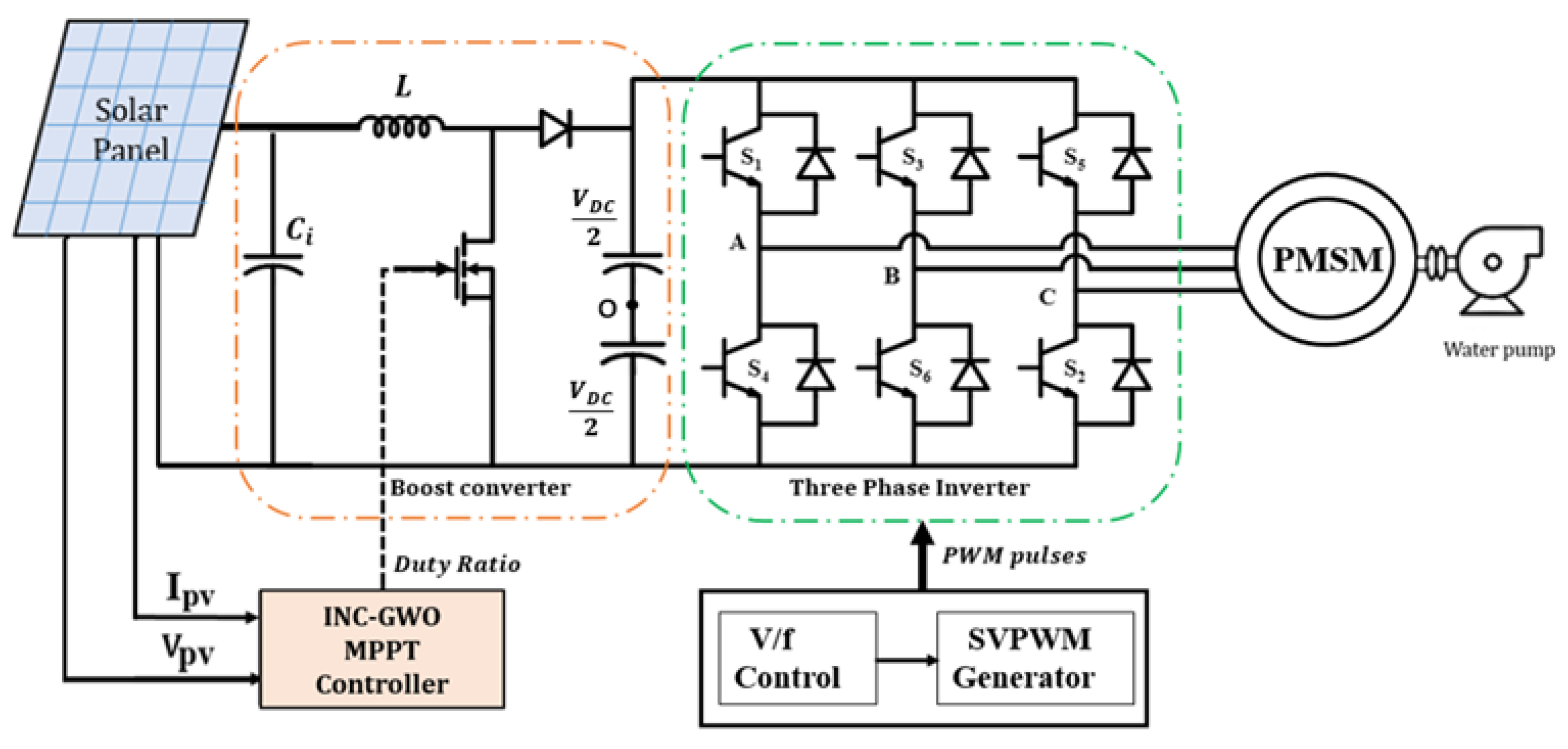
2. Modeling of the PMSM Based SWPS
2.1. Solar PV System Model
2.2. Boost Converter Model with Non-Idealities
2.3. Inverter-Powered PMSM
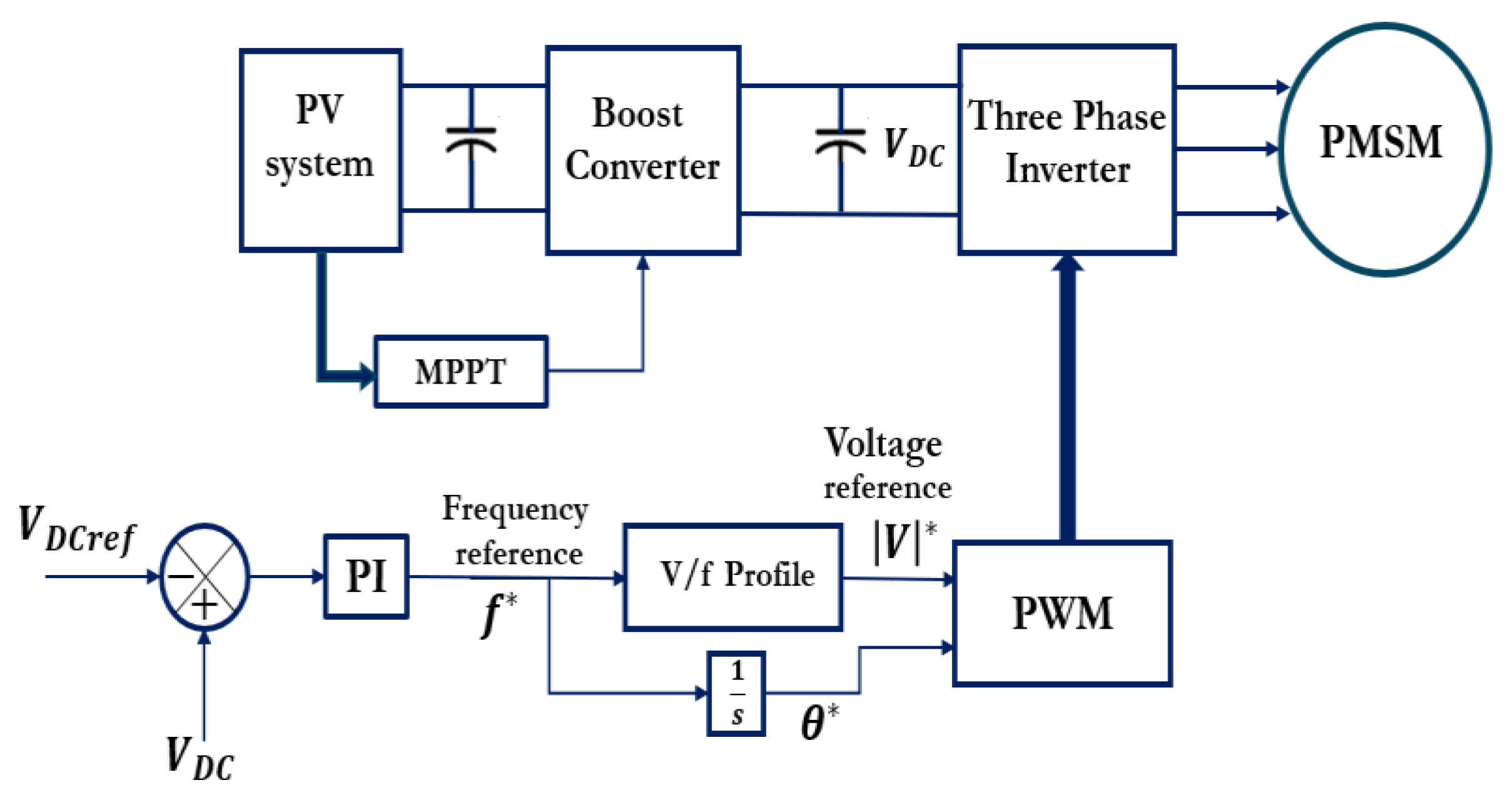
2.4. DC Link Voltage Control and V/f Control of the Solar Water Pump Drive
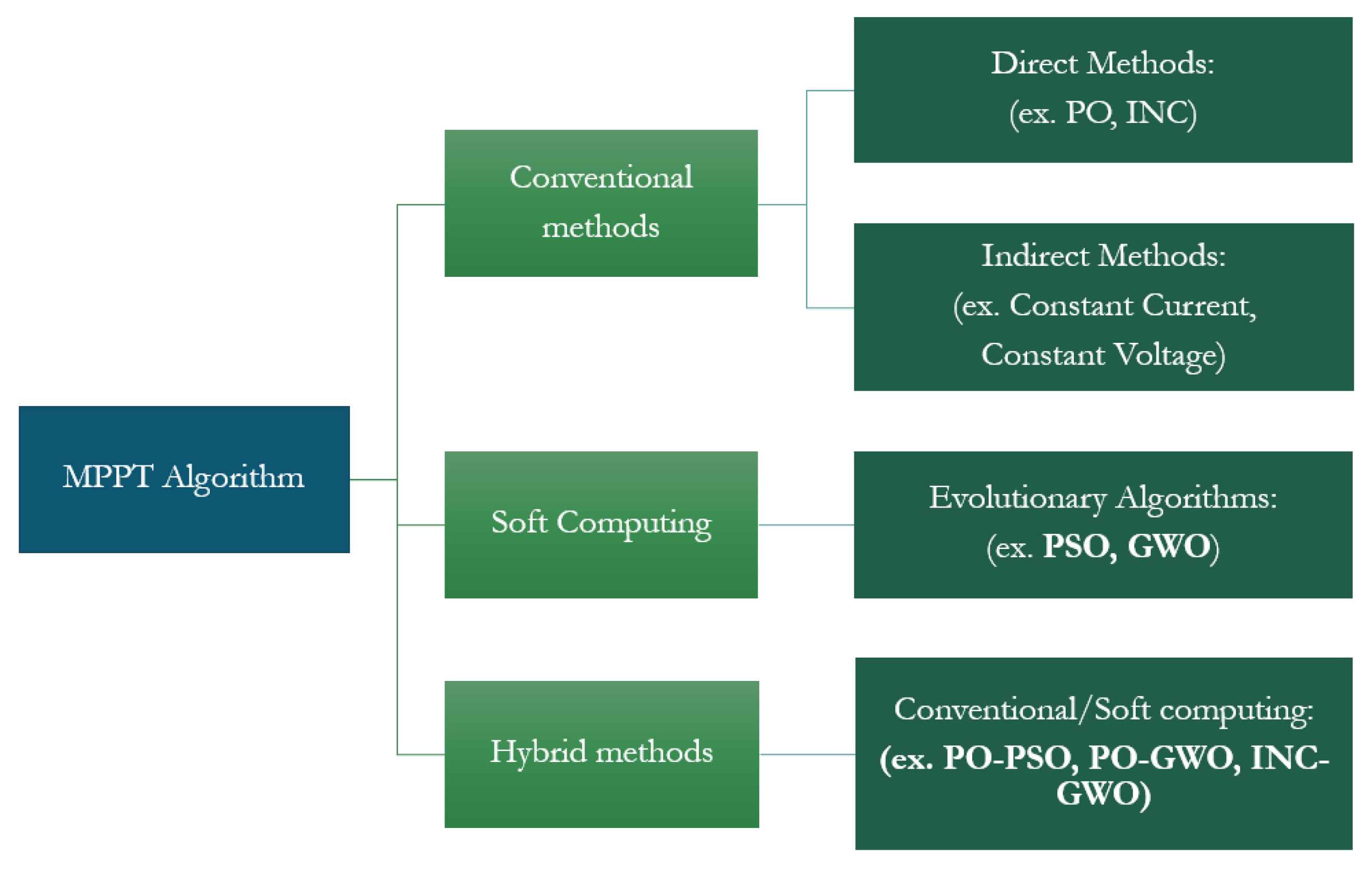
3. MPPT Algorithms
4. Results and Discussions
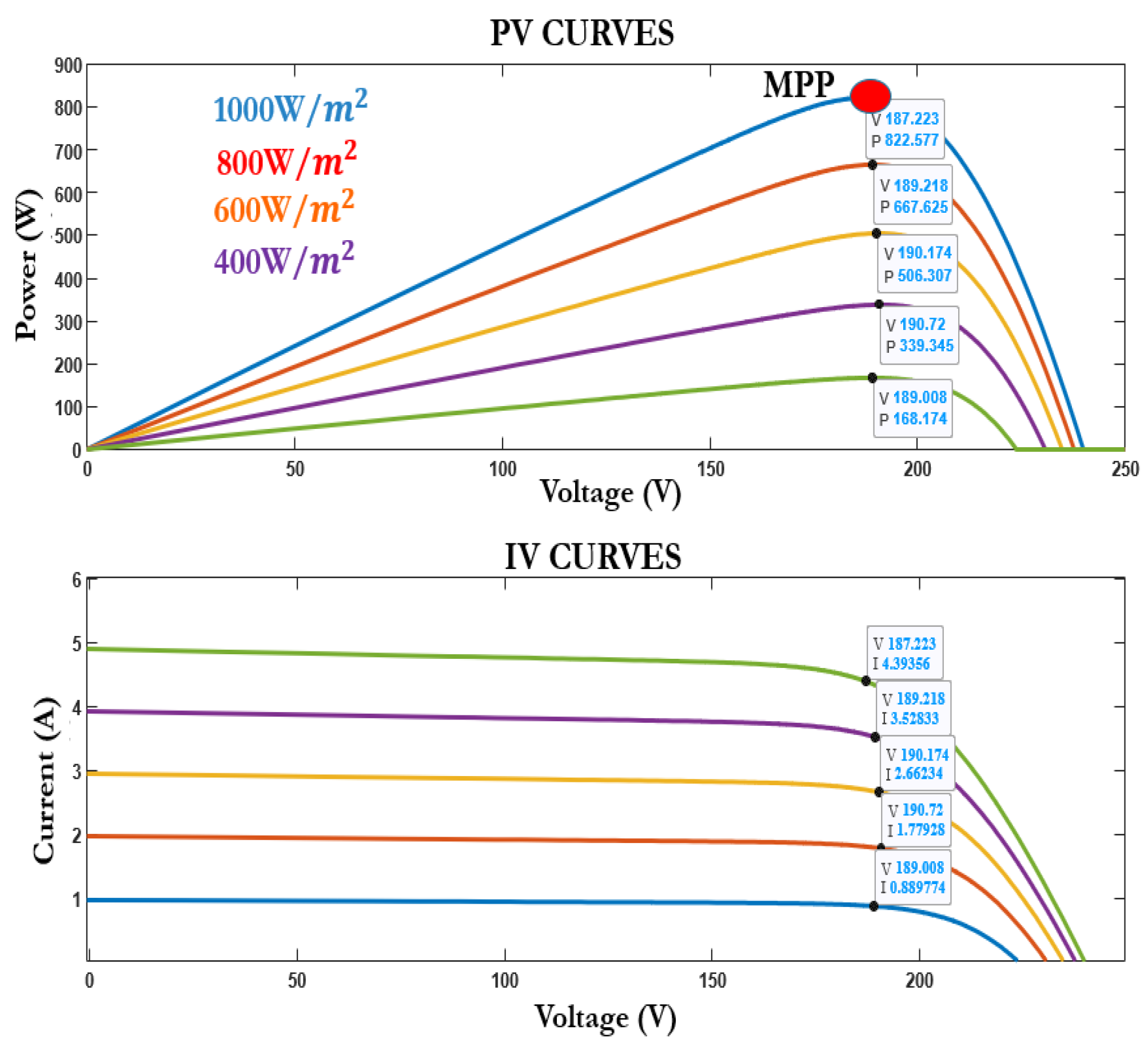
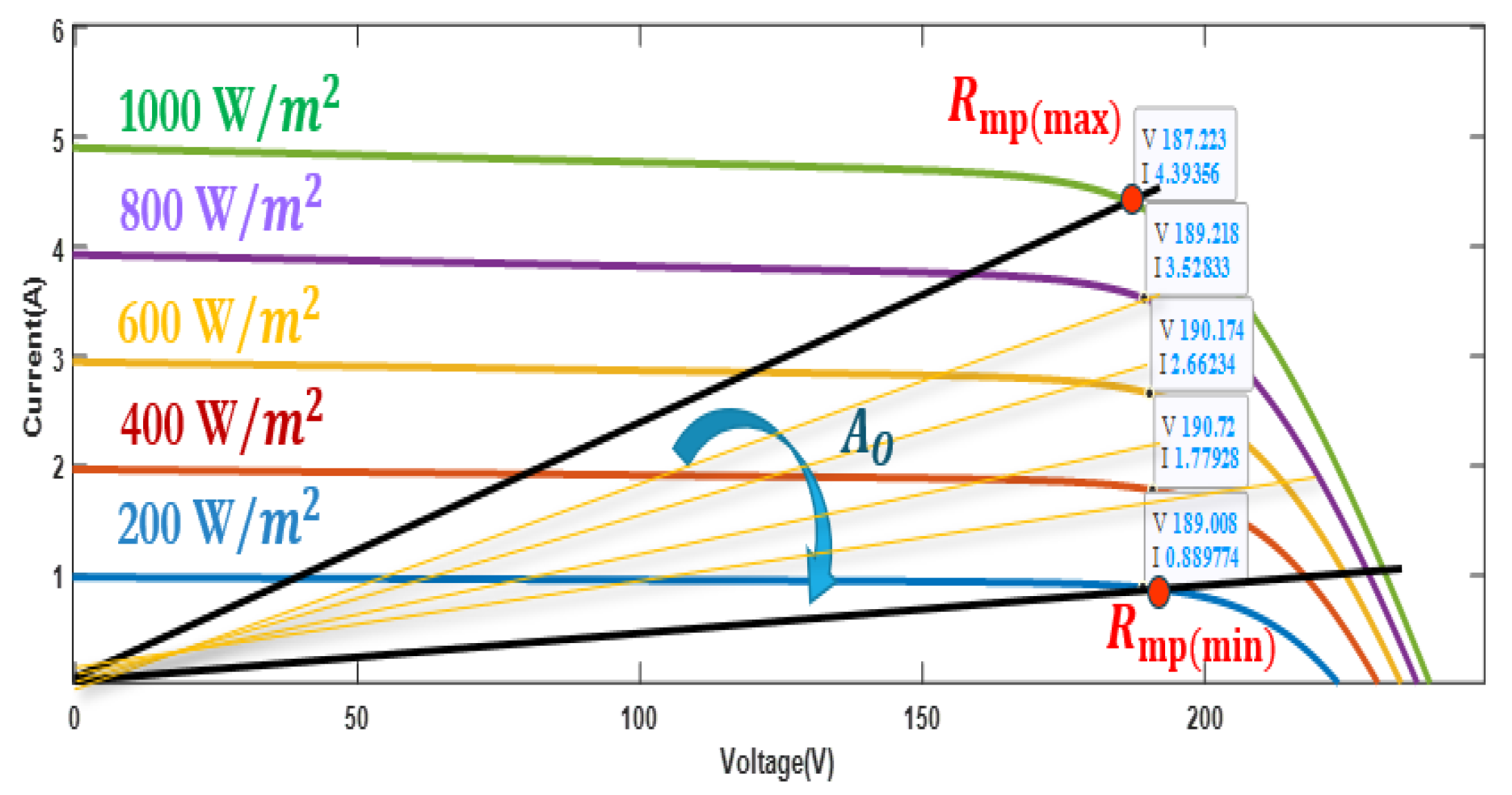
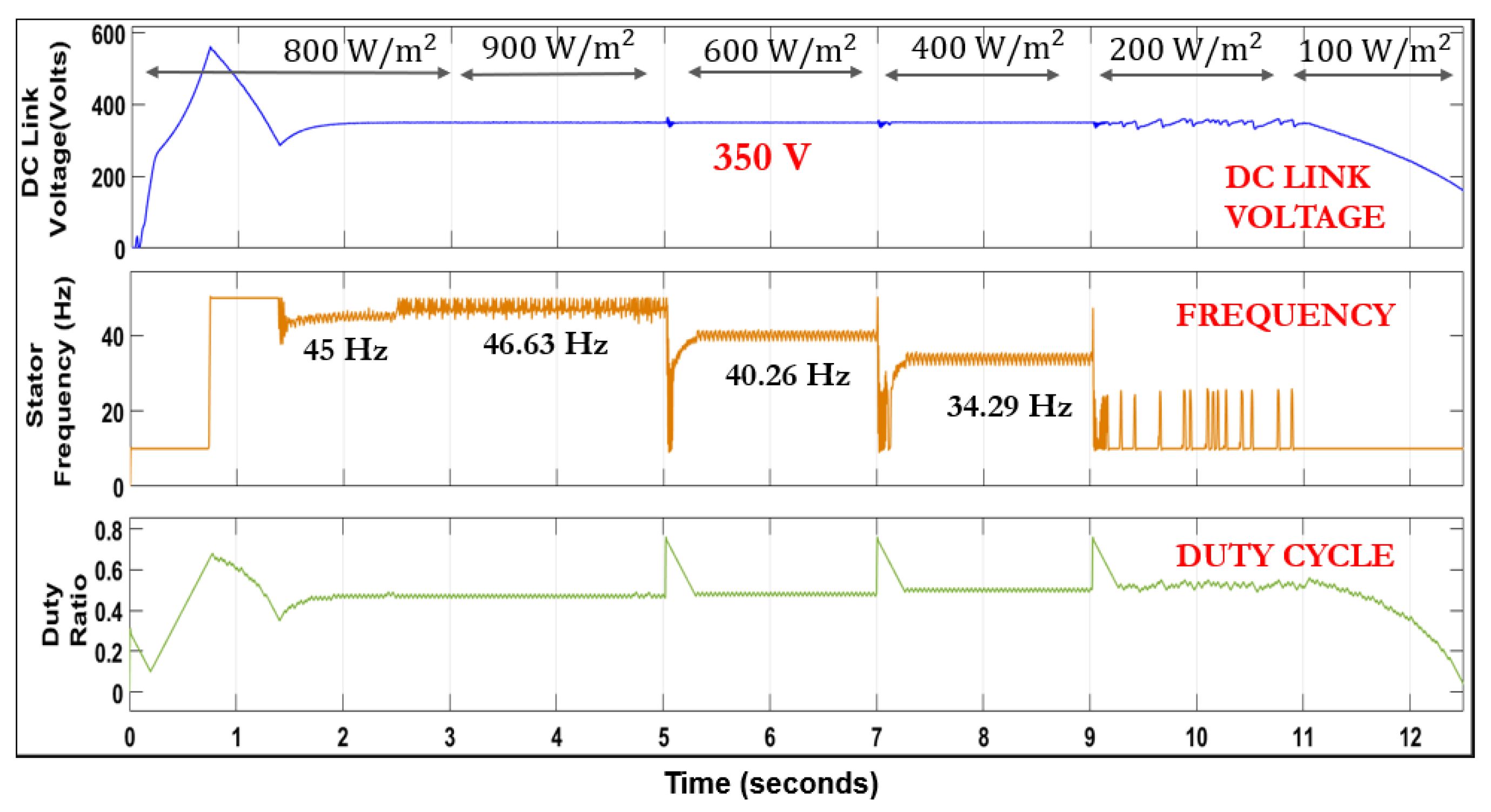
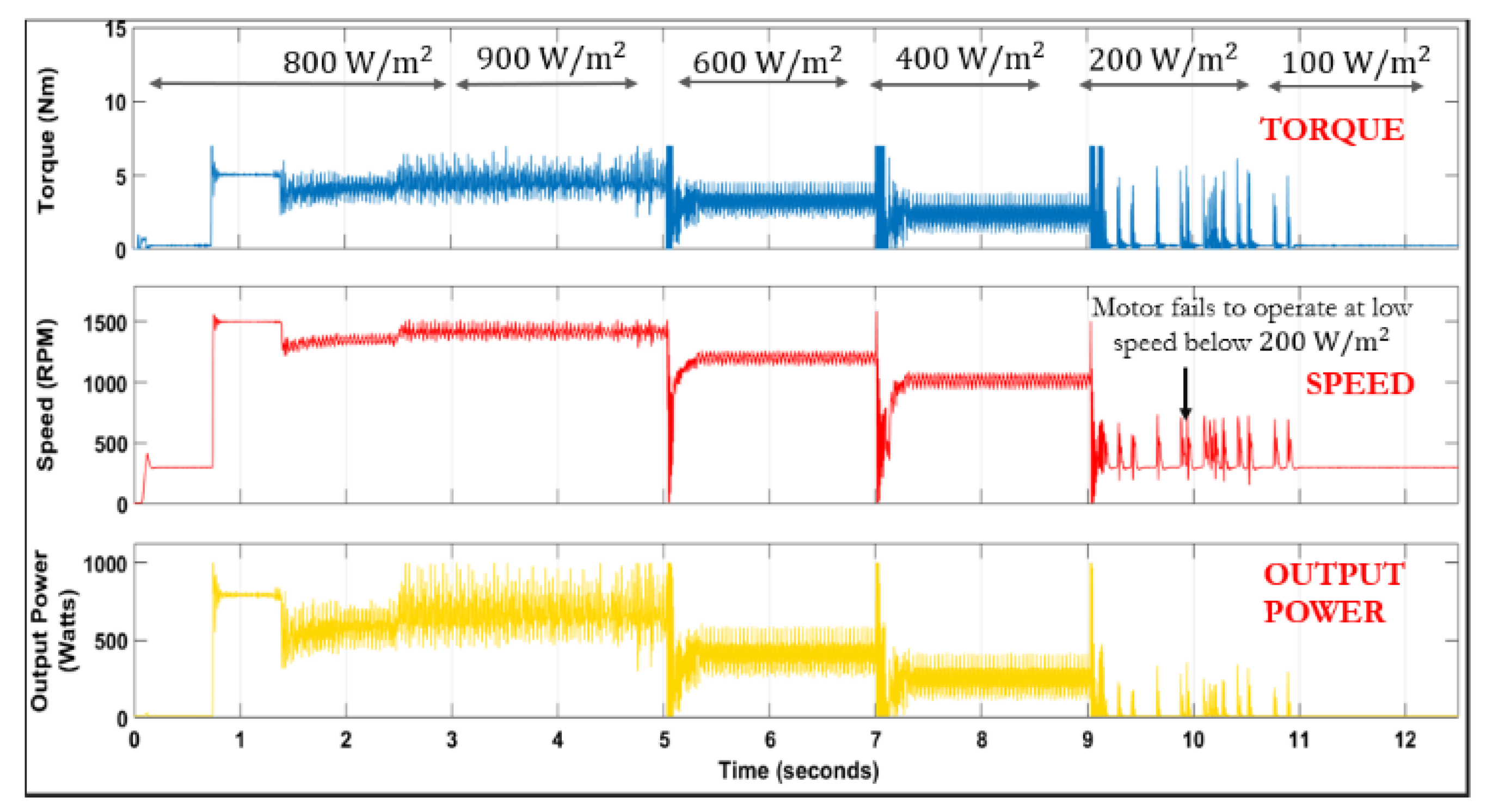
4.1. Analyzing Critical Irradiance Thresholds for PMSM Based SWPS
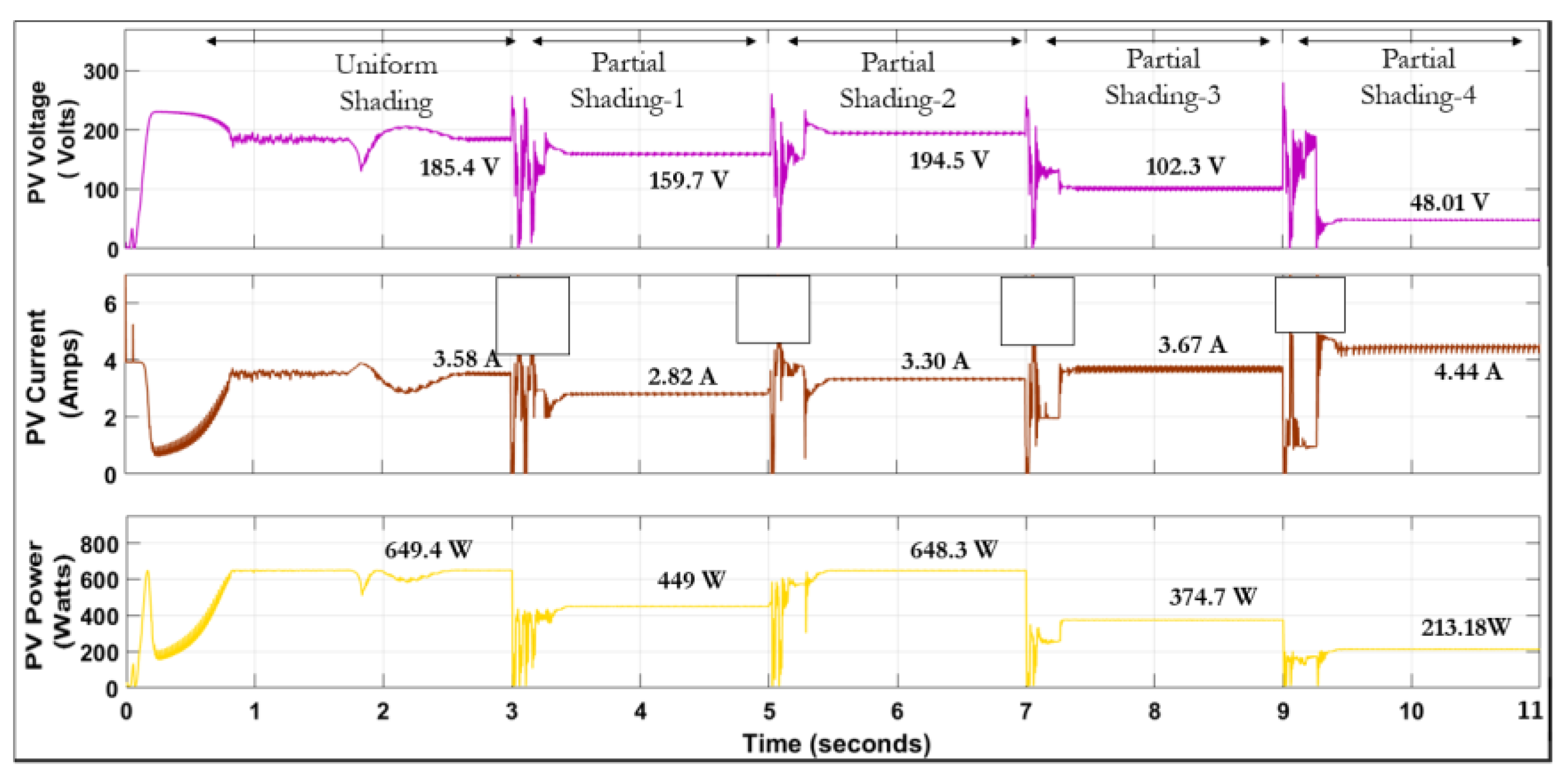
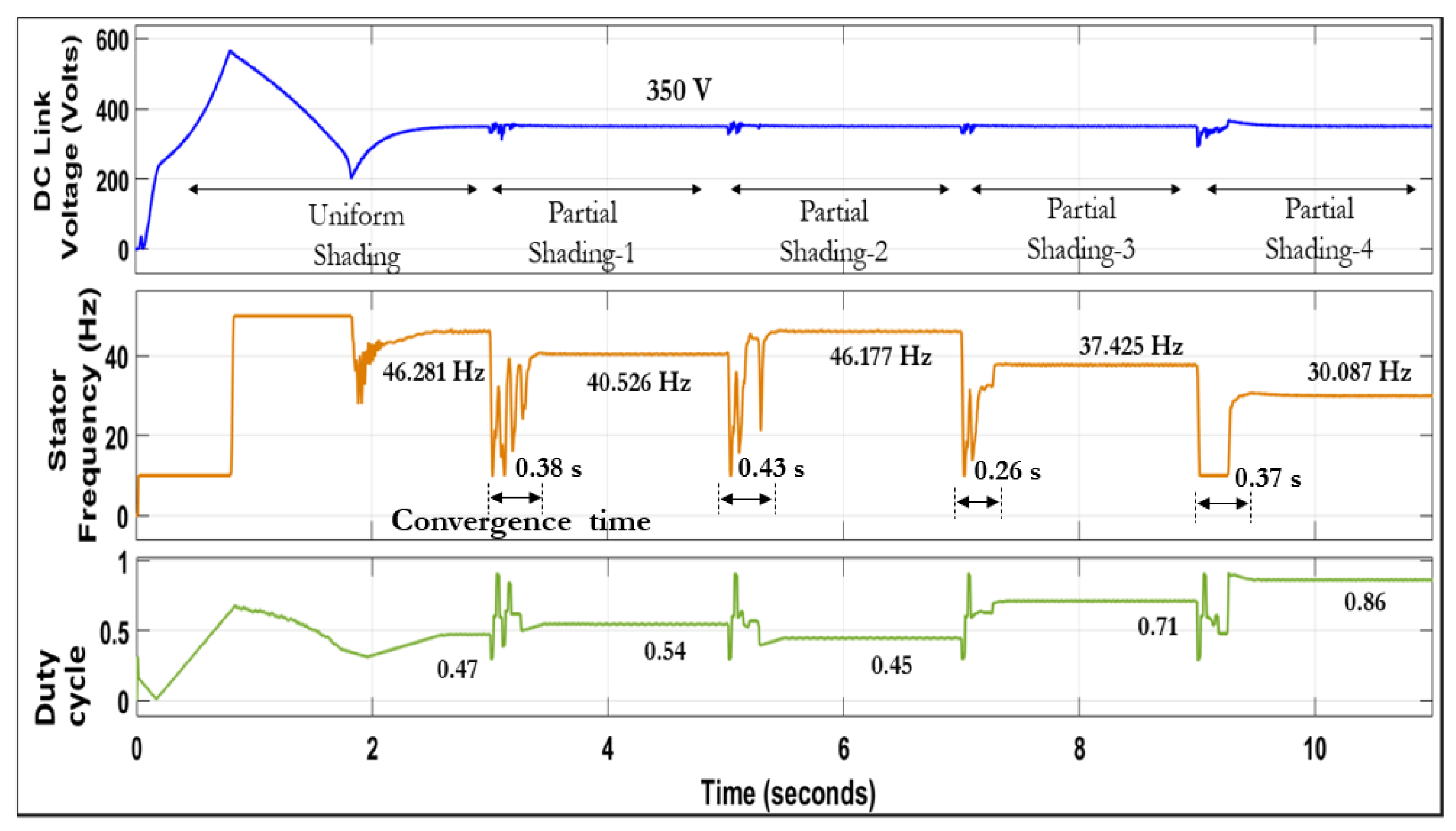
4.2. Analysis of Hybrid INC-GWO MPPT Algorithm for PMSM Based SWPS under Partial Shading
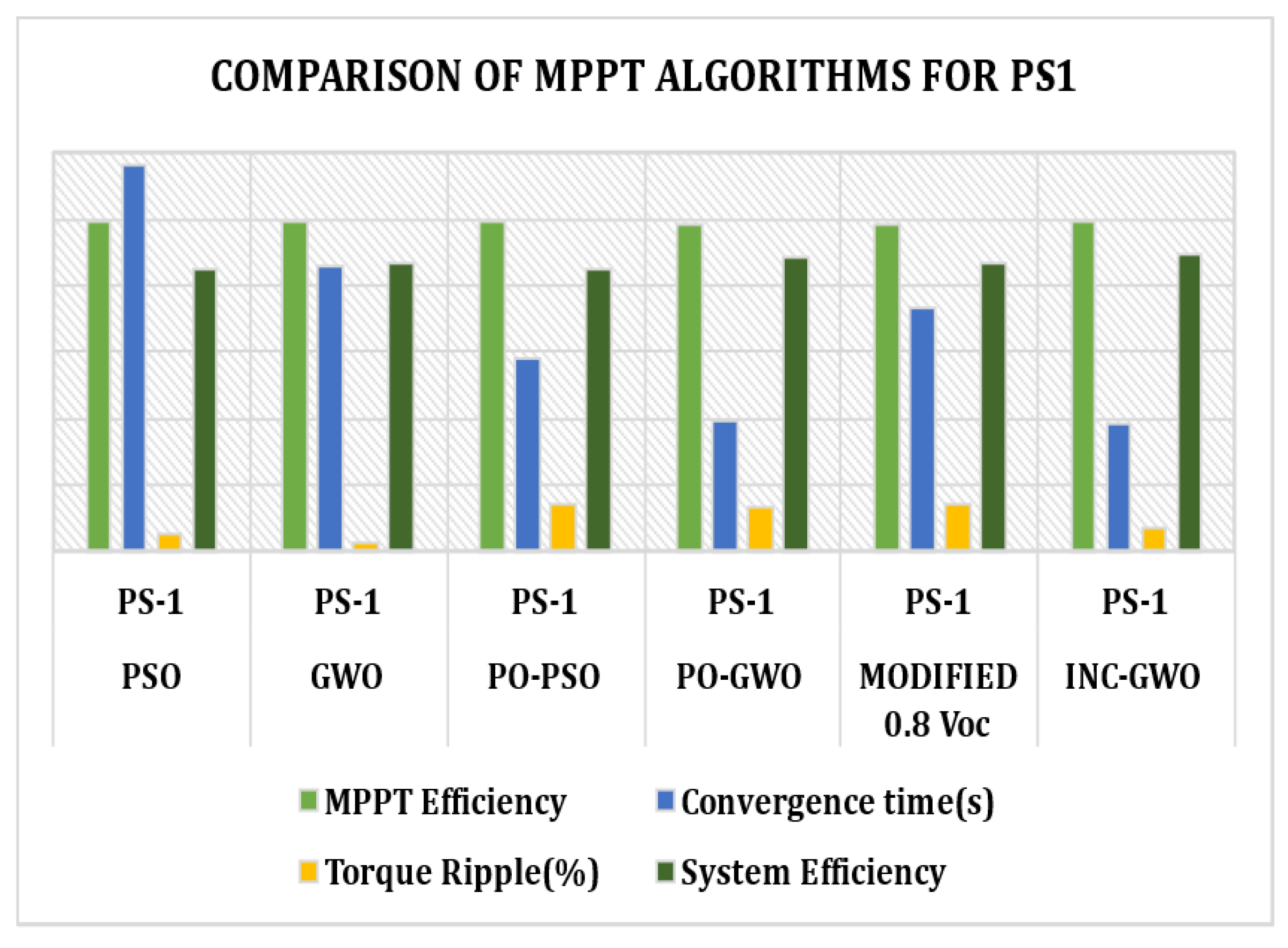
4.3. Comparing INC-GWO MPPT with Other MPPT Techniques
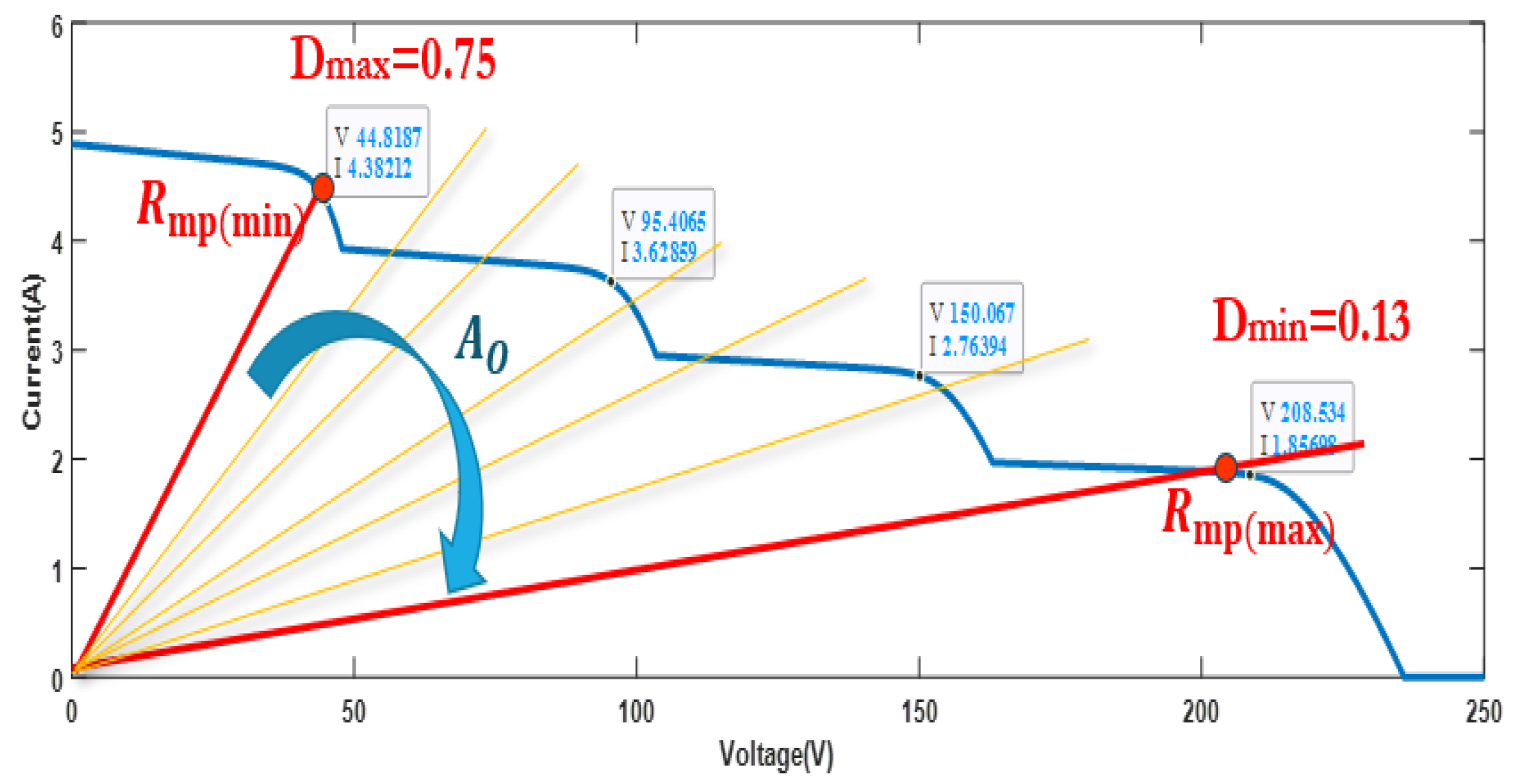
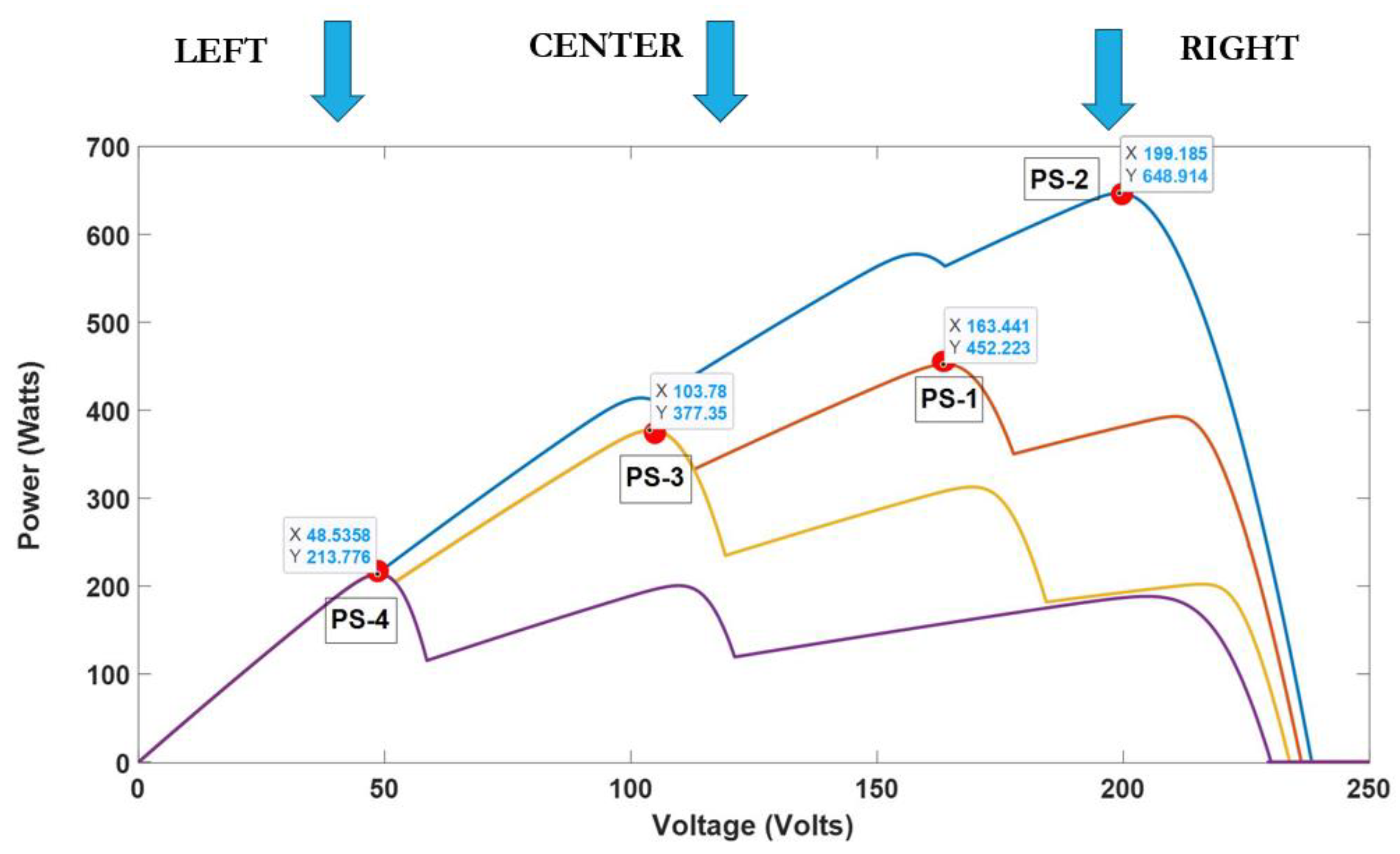
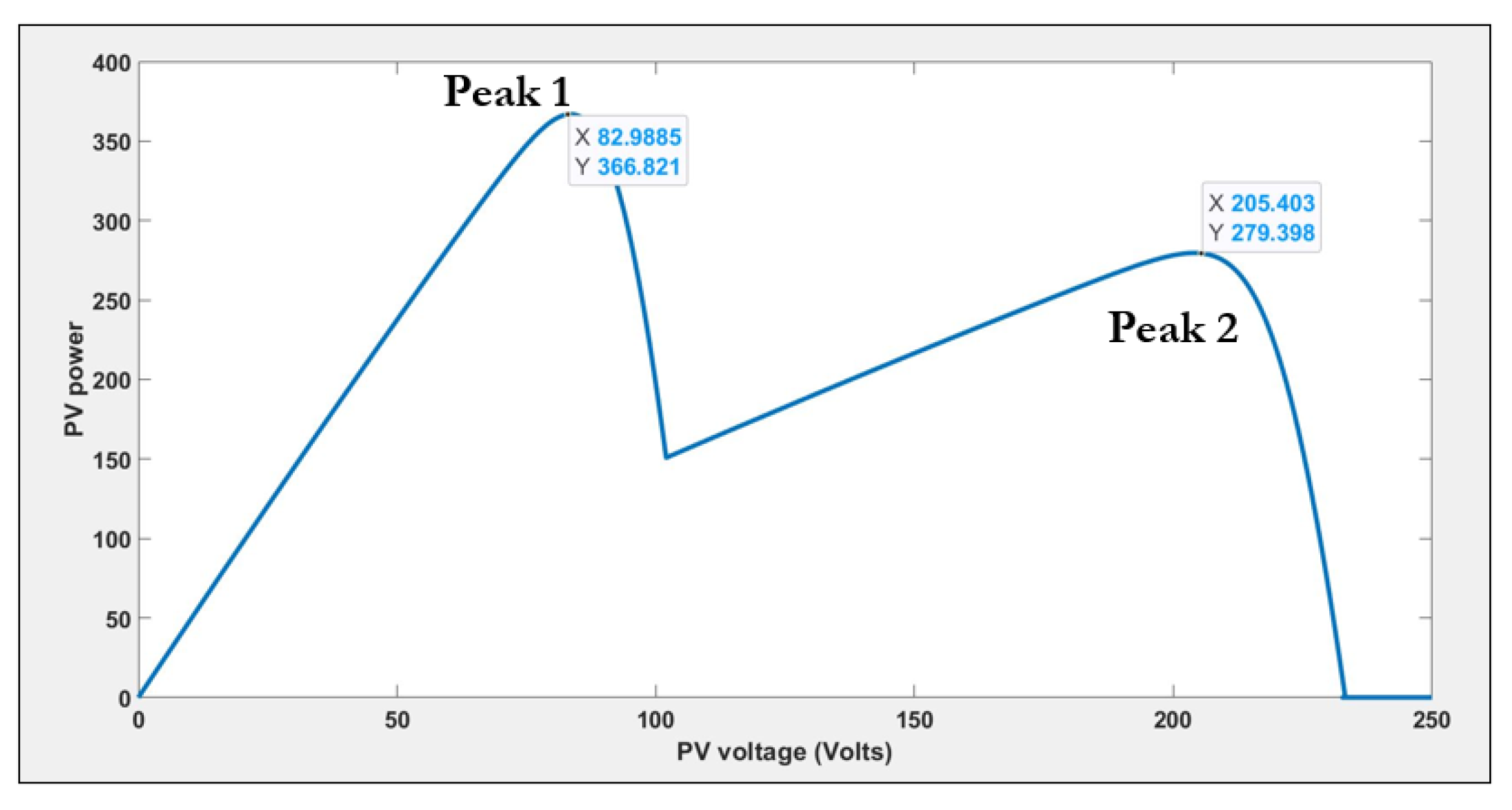
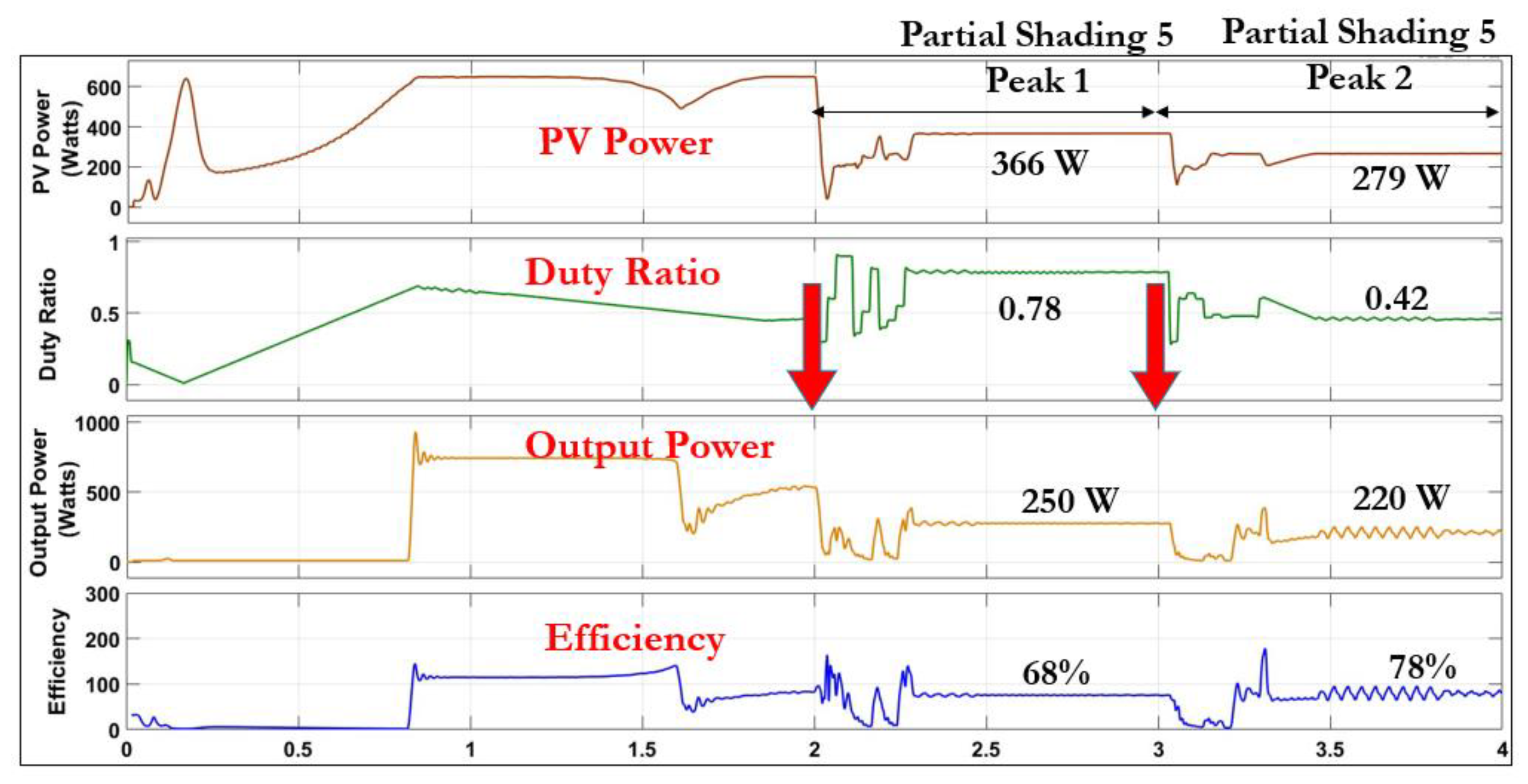
4.4. Impact of Peak Power in Left Region of P-V Curve on SWPS Efficiency
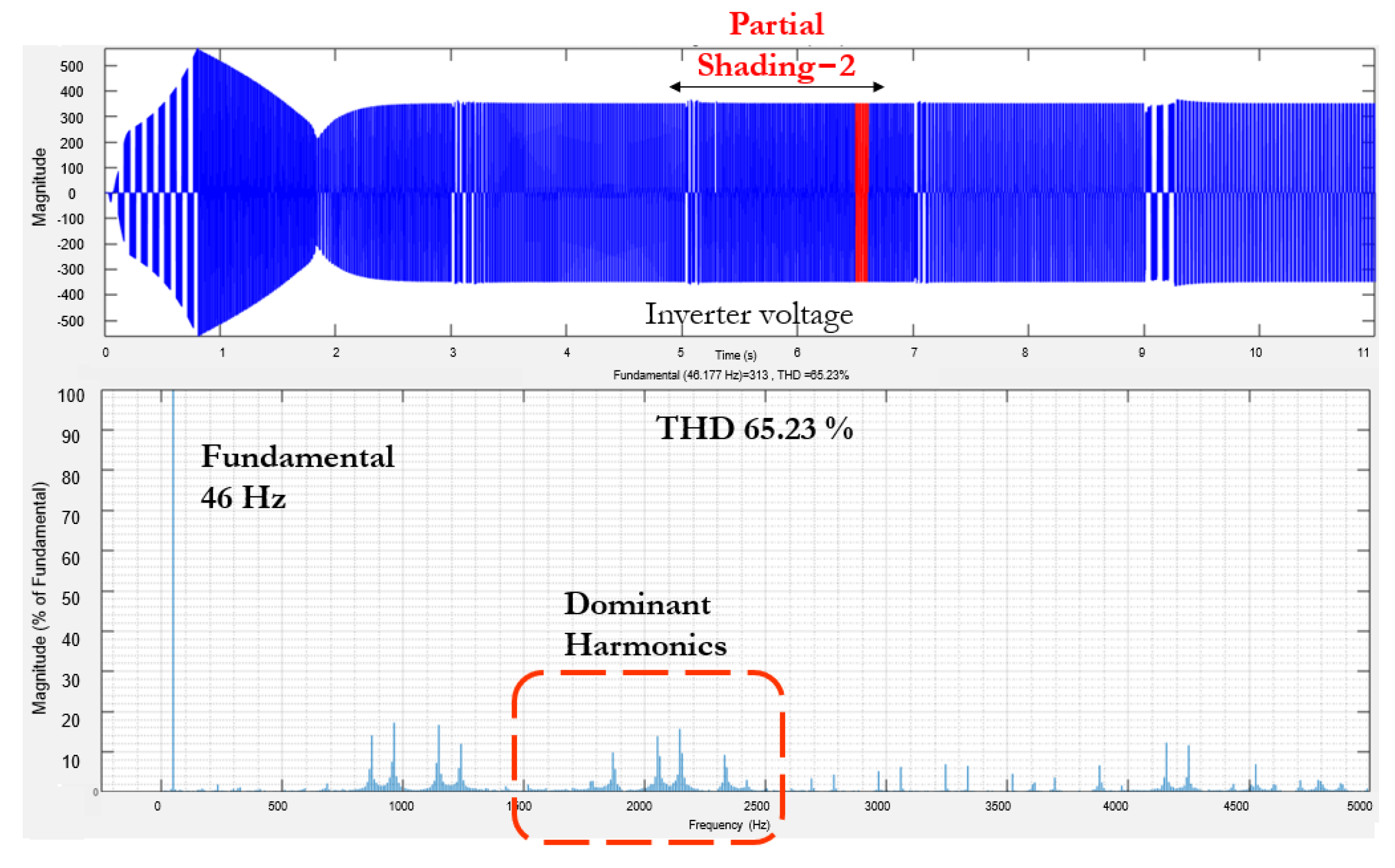
4.5. Assessment of THD of Inverter Output Voltage for Various Shading Conditions
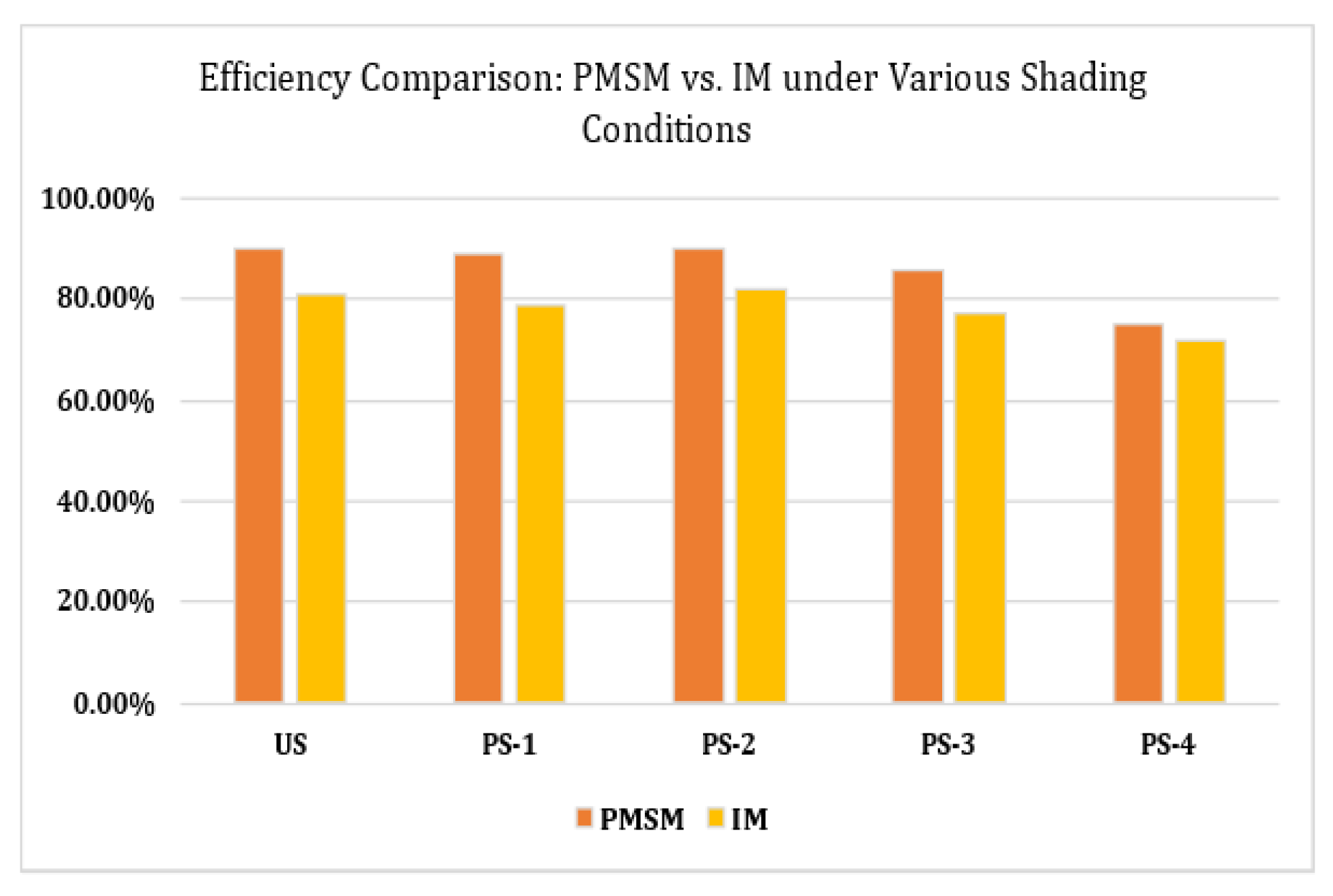
4.6. Comparative Analysis of PMSM and Induction Motor Based SWPS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandel, S.S.; Naik, M.N.; Chandel, R. Review of Solar Photovoltaic Water Pumping System Technology for Irrigation and Community Drinking Water Supplies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 49, 1084–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, M.; Hassan, G.; Said, S.A.; Siddiqui, M.U.; Alawami, A.T.; Elamin, I.M. A Review of Solar-Powered Water Pumping Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 87, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poompavai, T.; Kowsalya, M. Control and Energy Management Strategies Applied for Solar Photovoltaic and Wind Energy Fed Water Pumping System: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 107, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, S.; Yaragatti, U.R.; Suresh, Y.; Raju, A.B. Comprehensive Review on Solar, Wind and Hybrid Wind-PV Water Pumping Systems-An Electrical Engineering Perspective. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2021, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.M.S.; Singh, S.; Gupta, M.K.; Nimdeo, Y.M.; Raushan, R.; Deorankar, A.V.; Kumar, T.M.A.; Rout, P.K.; Chanotiya, C.S.; Pakhale, V.D.; et al. Solar Energy: A Promising Renewable Source for Meeting Energy Demand in Indian Agriculture Applications. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 55, 102905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, A.; Nayak, B.; Das, P.; Mohanty, K.B. A Review on MPPT Techniques of PV System under Partial Shading Condition. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhu, T.; Wang, J.; Shu, H.; Yu, T.; Zhang, X.; Yao, W.; Sun, L. Comprehensive Overview of Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithms of PV Systems under Partial Shading Condition. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, N.; Moubayed, N.; Outbib, R. General Review and Classification of Different MPPT Techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.O.; Liu, G.; Chen, X. Classification and Evaluation Review of Maximum Power Point Tracking Methods. Sustain. Futur. 2020, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, C.; Xie, B.; Wan, Y. A Hybrid Intelligent GMPPT Algorithm for Partial Shading PV System. Control Eng. Pract. 2019, 83, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Murtaza, A.F.; Sher, H.A.; Shami, U.T.; Olalekan, S. An Analytical Approach to Study Partial Shading Effects on PV Array Supported by Literature. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Agarwal, V. Maximum Power Point Tracking Scheme for PV Systems Operating under Partially Shaded Conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.; Gupta, M.; Bohre, A.K. Implementation and Comparative Analysis of P&O and INC MPPT Method for PV System. In Proceedings of the 2018 8th IEEE India International Conference on Power Electronics (IICPE), Jaipur, India, 13–15 December 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Meng, X.; Liu, C. A Review of Maximum Power Point Tracking Methods of PV Power System at Uniform and Partial Shading. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K.Y.; Sarimuthu, C.R.; Lim, J.M.Y. Artificial Intelligence Based MPPT Techniques for Solar Power System: A Review. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2020, 8, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, H.; Fathy, A.; Abdelaziz, A.Y. A Comparison of Different Global MPPT Techniques Based on Meta-Heuristic Algorithms for Photovoltaic System Subjected to Partial Shading Conditions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Subudhi, B.; Ray, P.K. A New MPPT Design Using Grey Wolf Optimization Technique for Photovoltaic System under Partial Shading Conditions. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 7, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Horan, B.; Soon, T.K.; Rahmani, R.; Oo, A.M.T.; Mekhilef, S.; Stojcevski, A. State of the Art Artificial Intelligence-Based MPPT Techniques for Mitigating Partial Shading Effects on PV Systems—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhachat, F.; Larbes, C. A Review of Global Maximum Power Point Tracking Techniques of Photovoltaic System under Partial Shading Conditions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 92, 513–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basoglu, M.E.; Çakir, B. Hybrid Global Maximum Power Point Tracking Approach for Photovoltaic Power Optimisers. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2018, 12, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollipo, R.B.; Mikkili, S.; Bonthagorla, P.K. Hybrid, Optimal, Intelligent and Classical PV MPPT Techniques: A Review. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 7, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundareswaran, K.; Vignesh Kumar, V.; Palani, S. Application of a Combined Particle Swarm Optimization and Perturb and Observe Method for MPPT in PV Systems under Partial Shading Conditions. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Subudhi, B.; Ray, P.K. A Grey Wolf-Assisted Perturb & Observe MPPT Algorithm for a PV System. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkadir, M.; Yatim, A.H.M. Hybrid Maximum Power Point Tracking Technique Based on PSO and Incremental Conductance. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Energy Conversion (CENCON), Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 13–14 October 2014; pp. 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, D.; Sabhahit, J.N. Grey Wolf Optimization and Incremental Conductance Based Hybrid MPPT Technique for Solar Powered Induction Motor Driven Water Pump. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2024, 13, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, A.; Naik, N.V.; Panda, A.K.; Tiwary, N. A Comprehensive Review of PV Driven Electrical Motors. Sol. Energy 2020, 195, 278–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidhar, K.; Rajasekar, N. A Review of Various Components of Solar Water-Pumping System: Configuration, Characteristics, and Performance. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2021, 31, e13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinner, T.R.; McCoy, R.H.; Kopecky, T. Induction versus Permanent-Magnet Motors for Electric Submersible Pump Field and Laboratory Comparisons. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, R.; Carraro, M.; Costabeber, A.; Tinazzi, F.; Zigliotto, M. Energy-Efficient Autonomous Solar Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzeria, H.; Fetha, C.; Bahi, T.; Abadlia, I.; Layate, Z.; Lekhchine, S. Fuzzy Logic Space Vector Direct Torque Control of PMSM for Photovoltaic Water Pumping System. Energy Procedia 2015, 74, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- System, M.S.W.; Singh, B.; Murshid, S. A Grid-Interactive Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor-Driven Solar Water-Pumping System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 5549–5561. [Google Scholar]
- Murshid, S.; Singh, B. Implementation of PMSM Drive for a Solar Water Pumping System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 4956–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshid, S.; Singh, B. Analysis and Control of Weak Grid Interfaced Autonomous Solar Water Pumping System for Industrial and Commercial Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 7207–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshid, S.; Singh, B. Reduced Sensor-Based PMSM Driven Autonomous Solar Water Pumping System. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 11, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taibi, D.; Amieur, T.; Laamayad, T.; Sedraoui, M. Improvement of the Standard Perturb & Observe MPPT Control Strategy by the Proposed Fuzzy Logic Mechanism for a Cascade Regulation of a PMSM-Based PV Pumping System. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 6631–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifi, B.; Salem, F.B.; Zdiri, M.A.; Abdallah, H.H. A Stand-Alone PV-PEMFC System Based SMANN-MPPT Controller: Solar Pumping Application Using PMSM. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2021, 11, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, N.; Maroti, P.K.; Hussien, M.G. Extensive Performance Investigation of Luo Converter-Based Modified Firefly Maximum Point Tracking Algorithm for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor-Driven Photovoltaic Pumping System. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashif, M.; Singh, B. Modified Active-Power MRAS Based Adaptive Control with Reduced Sensors for PMSM Operated Solar Water Pump. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Singh, B. Solar Powered Position Sensor Free PMBLDC Motor Drive with Dynamic Observer Control. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2023, 5, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, S.G.; Malla, P.; Malla, J.M.R.; Singla, R.; Choudekar, P.; Koilada, R.; Sahu, M.K. Whale Optimization Algorithm for PV Based Water Pumping System Driven by BLDC Motor Using Sliding Mode Controller. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 4832–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, A.; Hamraoui, K.; Belguellaoui, M.; Kheldoun, A. Performance Enhancement of Photovoltaic Water Pumping System Based on BLDC Motor under Partial Shading Condition. Eng. Proc. 2022, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadija, S.; Ouadia, E.M.; Abdelmajid, F. Tracking the GMPP of a Solar Photovoltaic Water Pumping System with an SMC Controller in Partial Shading Conditions. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2023, 12, 3298–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.N.; Rezk, H.; Al-Dhaifallah, M.; Sergeant, P. Solar Array Fed Synchronous Reluctance Motor Driven Water Pump: An Improved Performance under Partial Shading Conditions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 77100–77115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, N.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Padmanaban, S.; Blaabjerg, F.; Azam, F. New CUK—SEPIC Converter Based Photovoltaic Power System with Hybrid GSA—PSO Algorithm Employing MPPT for Water Pumping Applications. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 2824–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, N.; Padmanaban, S.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Azam, F.; Khan, B.; Hussien, M.G. A Novel Hybrid Grey Wolf Optimized Fuzzy Logic Control Based Photovoltaic Water Pumping System. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudlapur, A.; Ramana, V.V.; Damodaran, R.V.; Balasubramanian, V.; Mishra, S. Effect of Partial Shading on PV Fed Induction Motor Water Pumping Systems. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Singh, B. Single-Stage PV Array Fed Speed Sensorless Vector Control of Induction Motor Drive for Water Pumping. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 3575–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadiraju, H.K.V. Improved Performance of PV Water Pumping System Using Dynamic Reconfiguration Algorithm under Partial Shading Conditions. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2022, 7, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaoui, J.; Rezk, H.; Al-Dhaifallah, M.; Elyes, F.; Abdelkader, M. Numerical Performance Evaluation of Solar Photovoltaic Water Pumping System under Partial Shading Condition Using Modern Optimization. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, P.D.C.; Blaabjerg, F.; Pedersen, J.K.; Thøgersen, P. A Sensorless, Stable V/f Control Method for Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarlita, S.C.; Coman, C.E.; Andreescu, G.D.; Boldea, I. Stable V/f Control System with Controlled Power Factor Angle for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2013, 7, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuki, Y.; Doki, S. High-Performance V/f Control of PMSM Using State Feedback Control Based on n–t Coordinate System. Electr. Eng. Jpn. (Denki Gakkai Ronbunshi) 2019, 206, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Kim, S.H. A Simple MTPA Operation Scheme for V/f Control of PMSMs. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Power Electronics and ECCE Asia (ICPE 2019-ECCE Asia), Busan, Republic of Korea, 27–30 May 2019; Volume 3, pp. 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidlak, M.; Gorel, L.; Makys, P. Performance Evaluation, Analysis, and Comparison of the Back-EMF-Based Sensorless FOC and Stable V/f Control for PMSM. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Sorrento, Italy, 22–24 June 2022; pp. 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.G.; Hong, C.; Lee, J.; Lee, W.J. Simple Position Sensorless V/f Scalar Control Method for Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives. J. Power Electron. 2021, 21, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Bian, X.; Liu, H.; Peng, T. A MATLAB-Simulink-Based PV Module Model and Its Application under Conditions of Nonuniform Irradiance. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2012, 27, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayop, R.; Tan, C.W. Design of Boost Converter Based on Maximum Power Point Resistance for Photovoltaic Applications. Sol. Energy 2018, 160, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R. Permanent Magnet Synchronous and Brushless DC Motor Drives; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 9780824753849. [Google Scholar]
- Basoglu, M.E. An Improved 0.8 VOC Model Based GMPPT Technique for Module Level Photovoltaic Power Optimizers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antivachis, M.; Niklaus, P.S.; Bortis, D.; Kolar, J.W. Input/Output EMI Filter Design for Three-Phase. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2021, 6, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



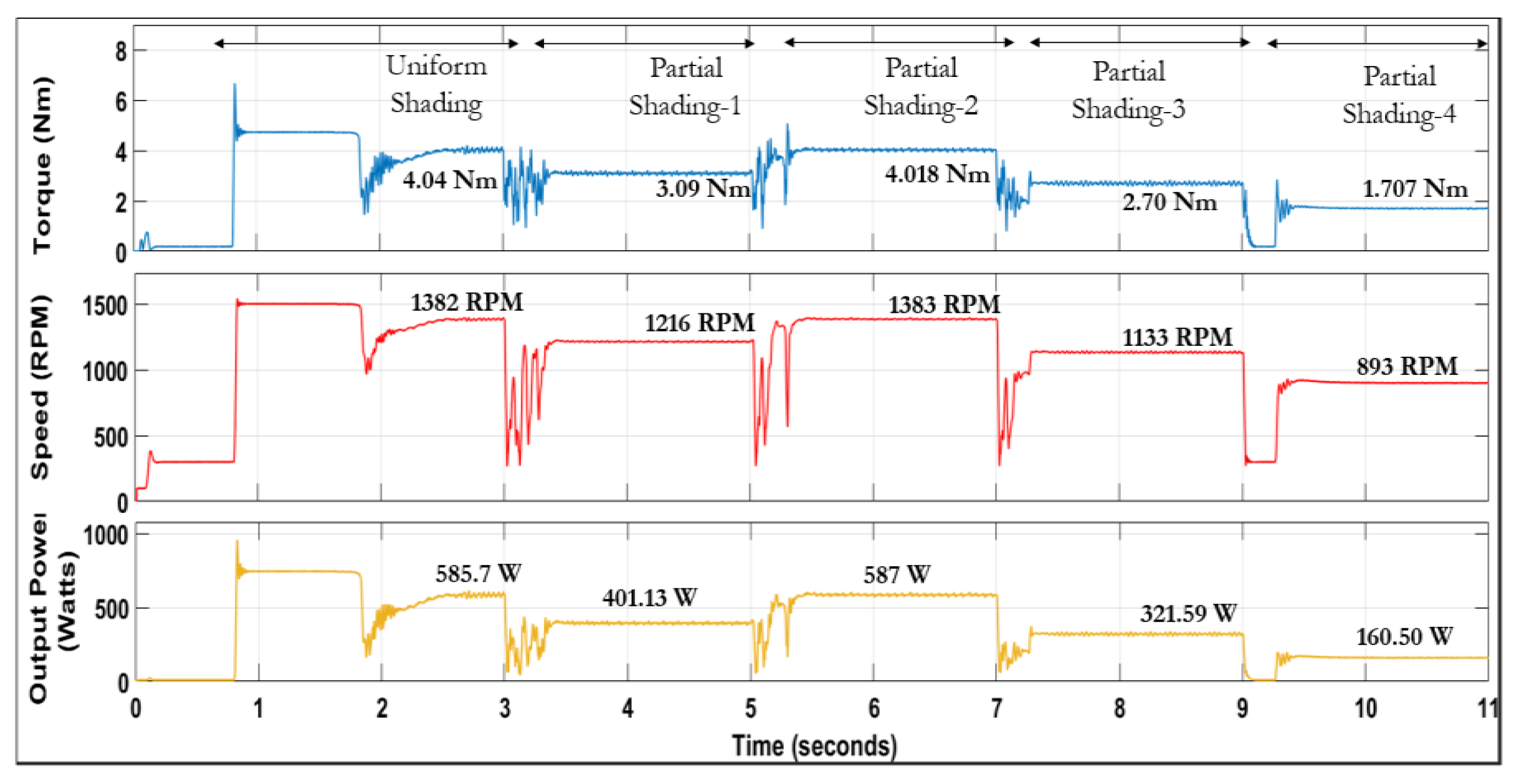

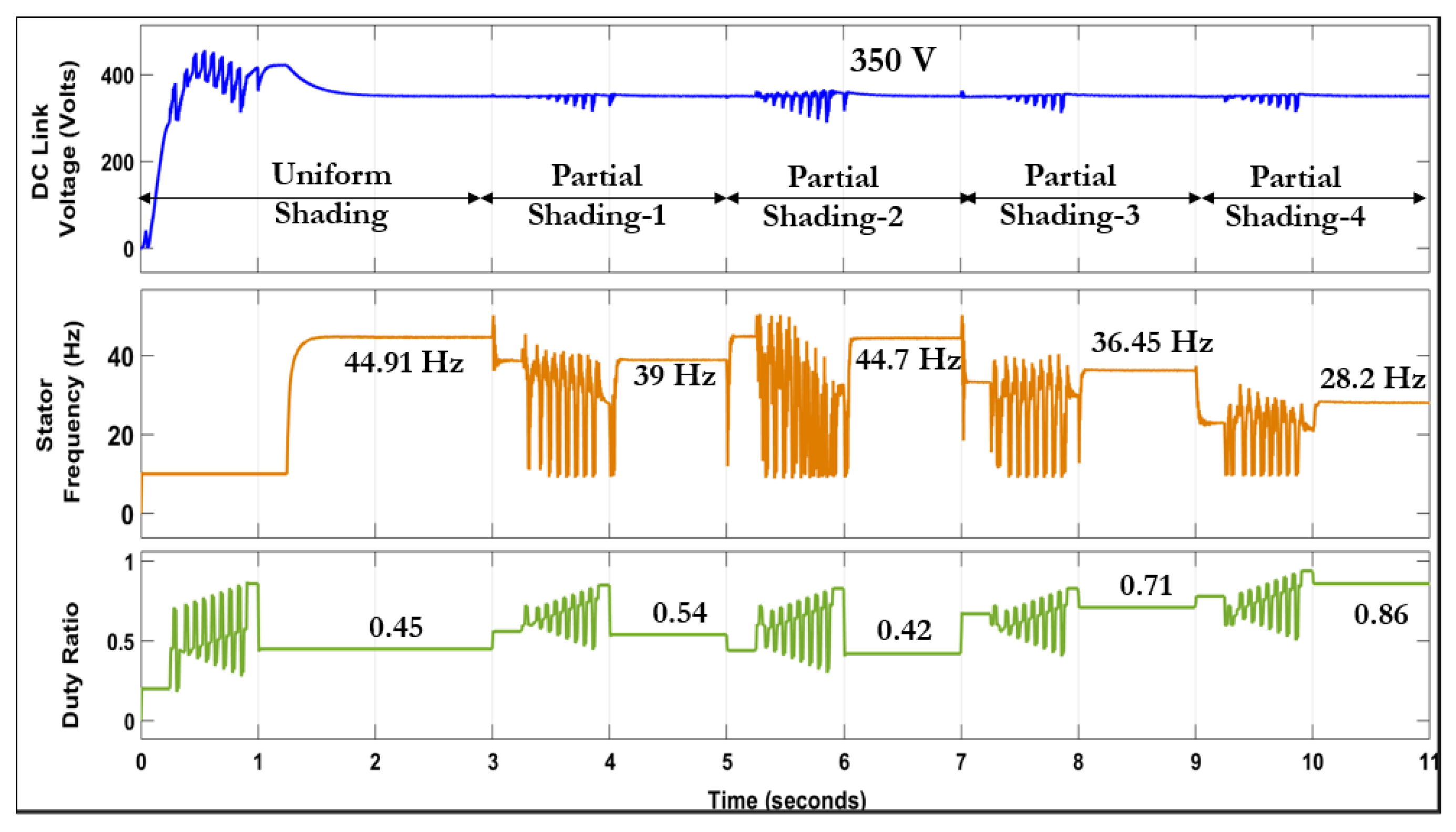
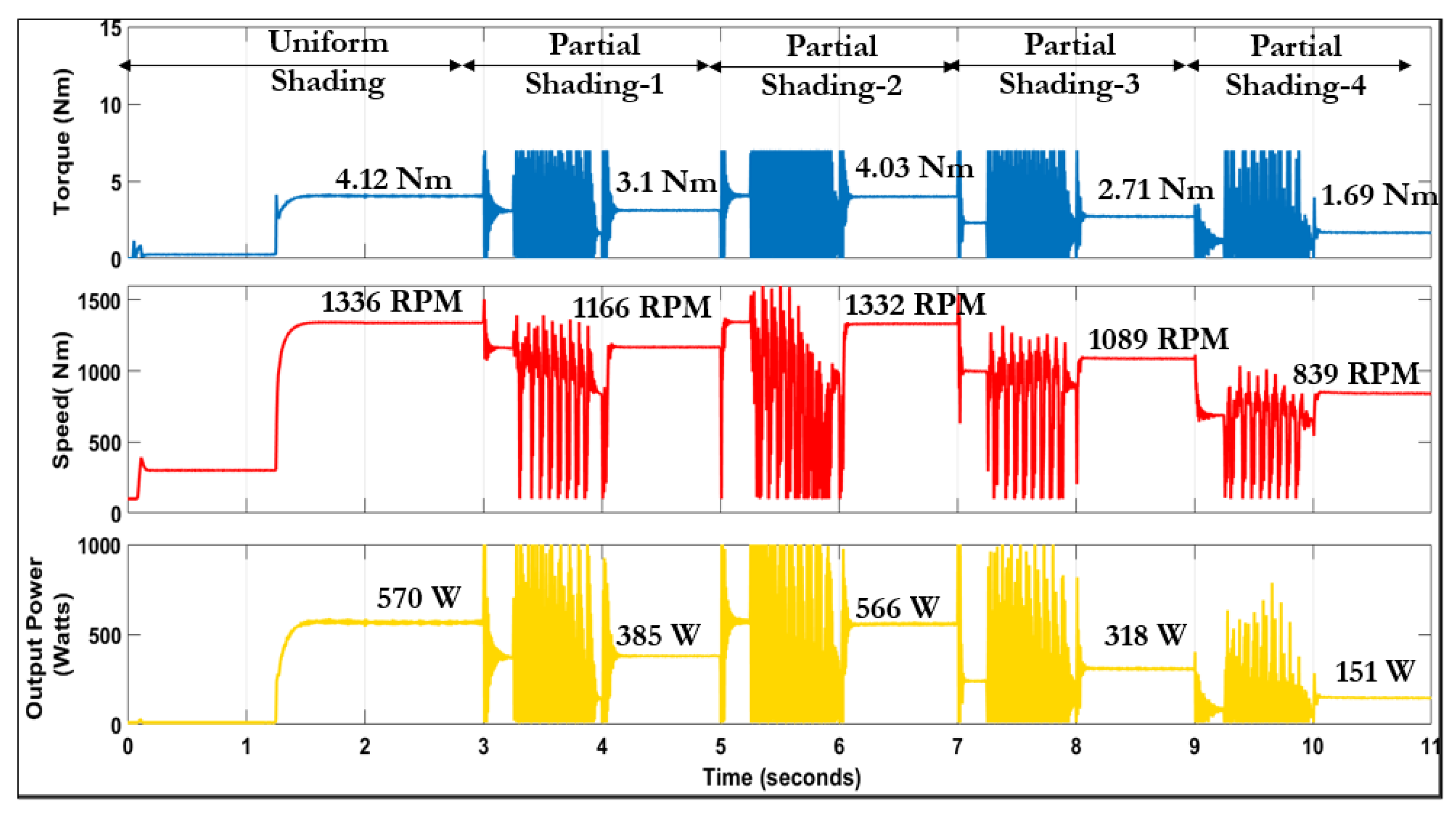
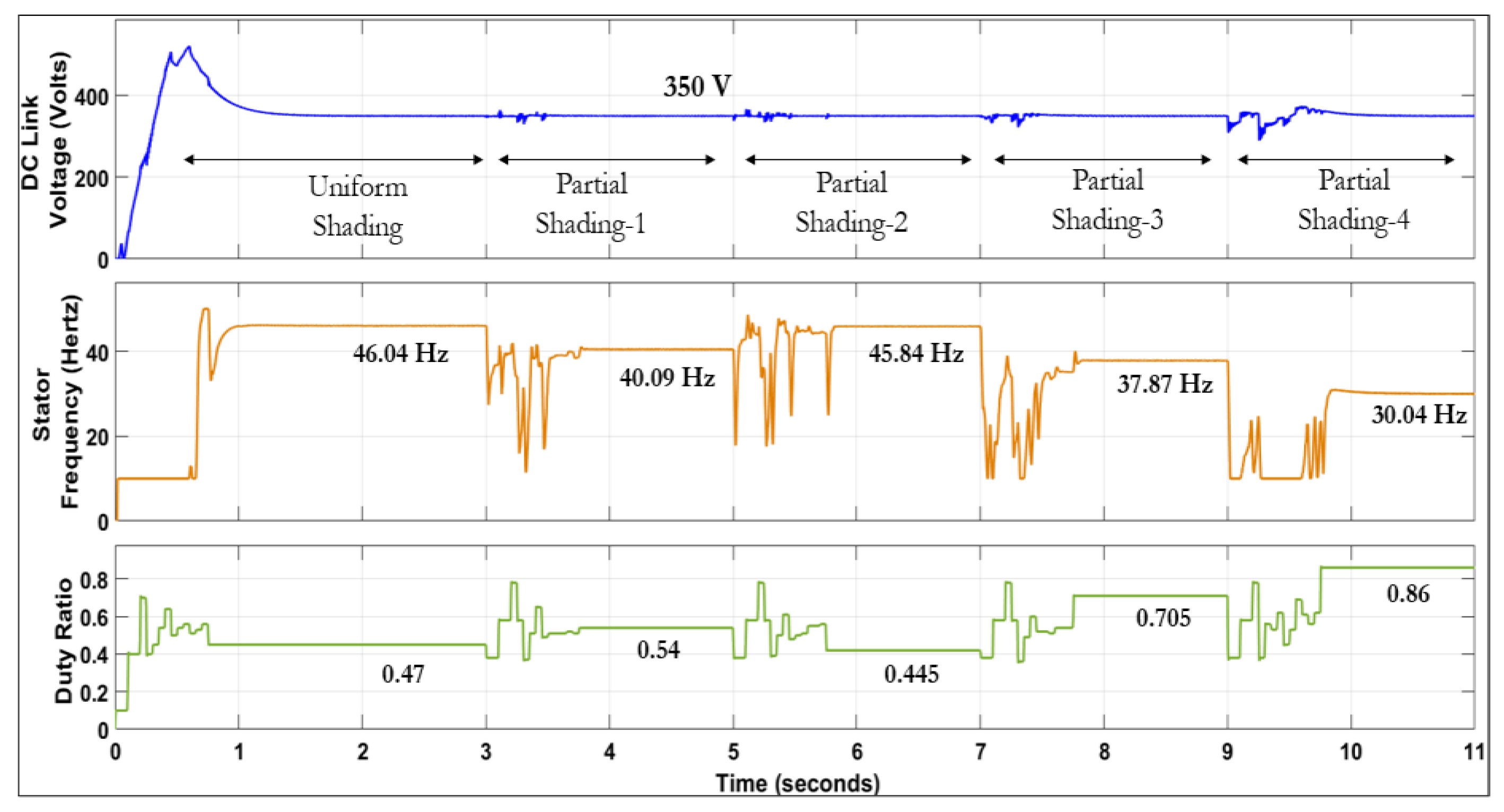



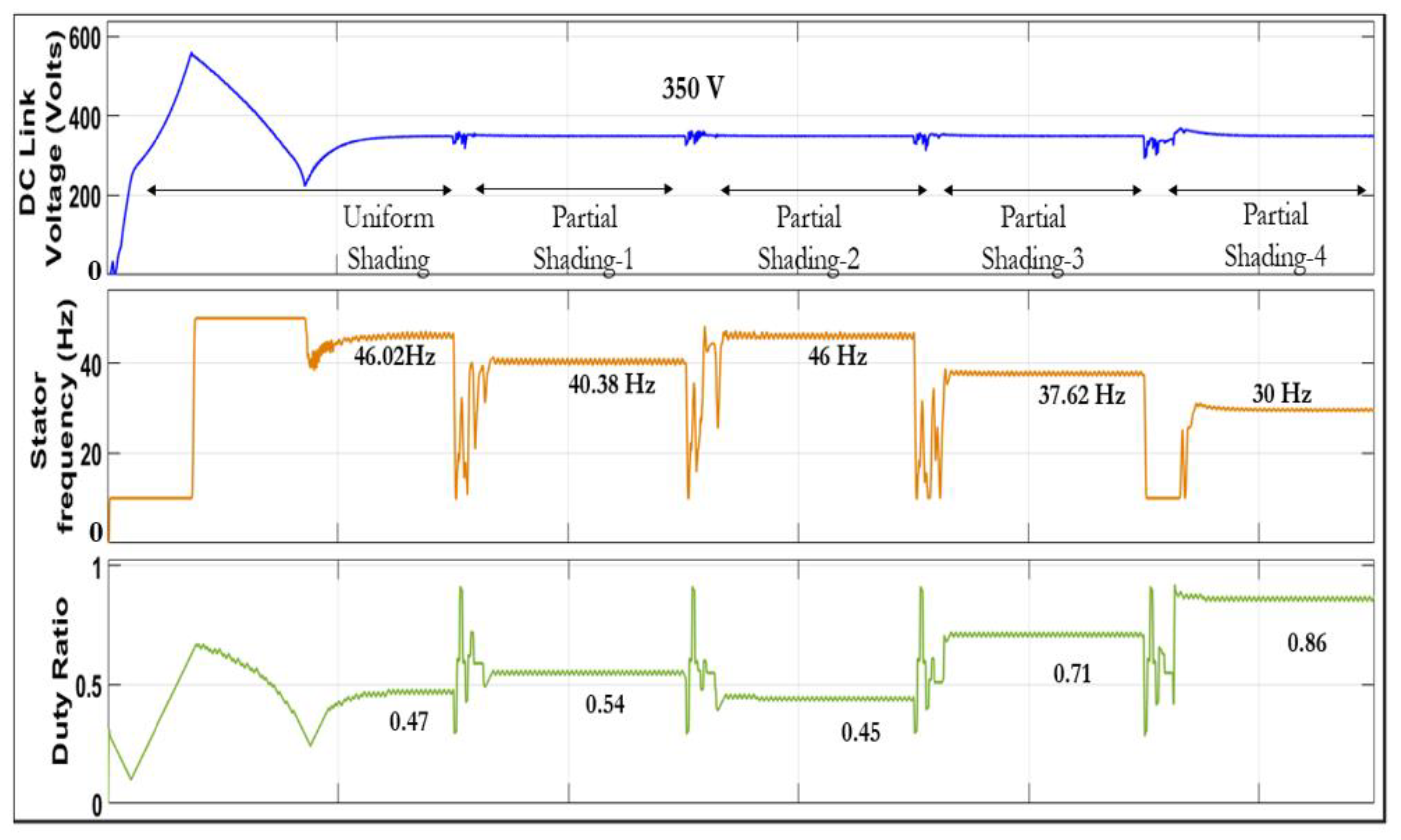
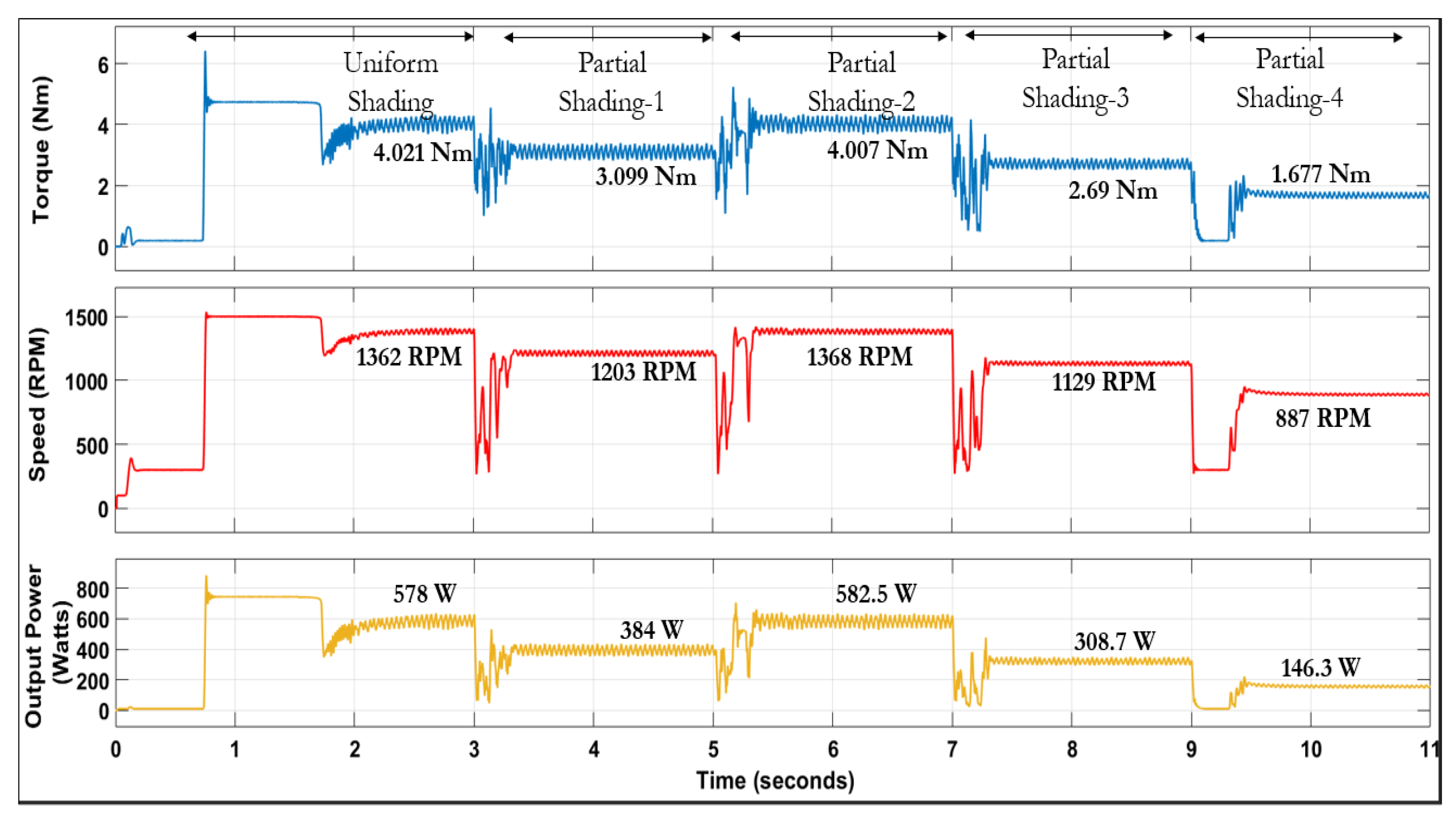
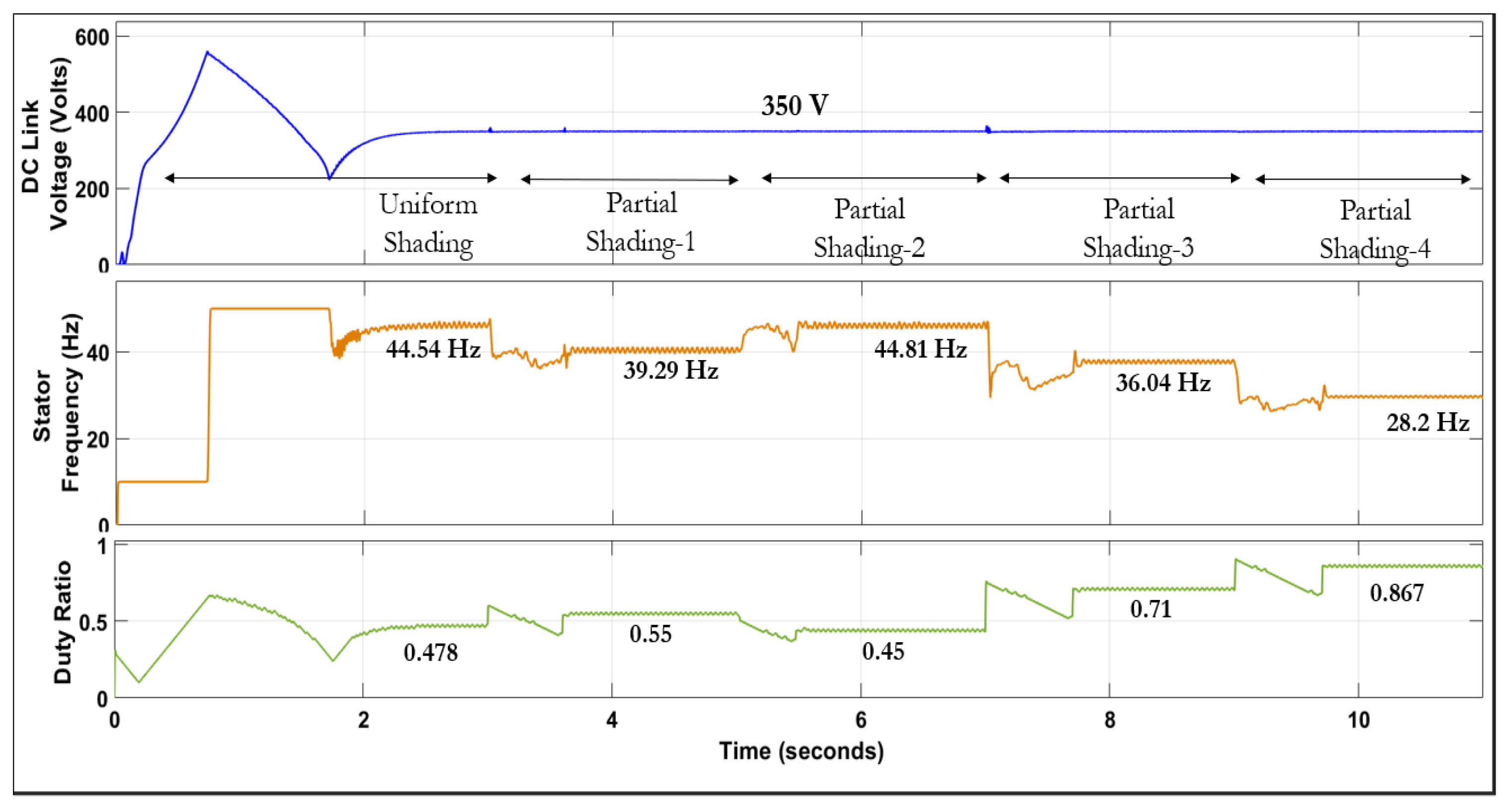
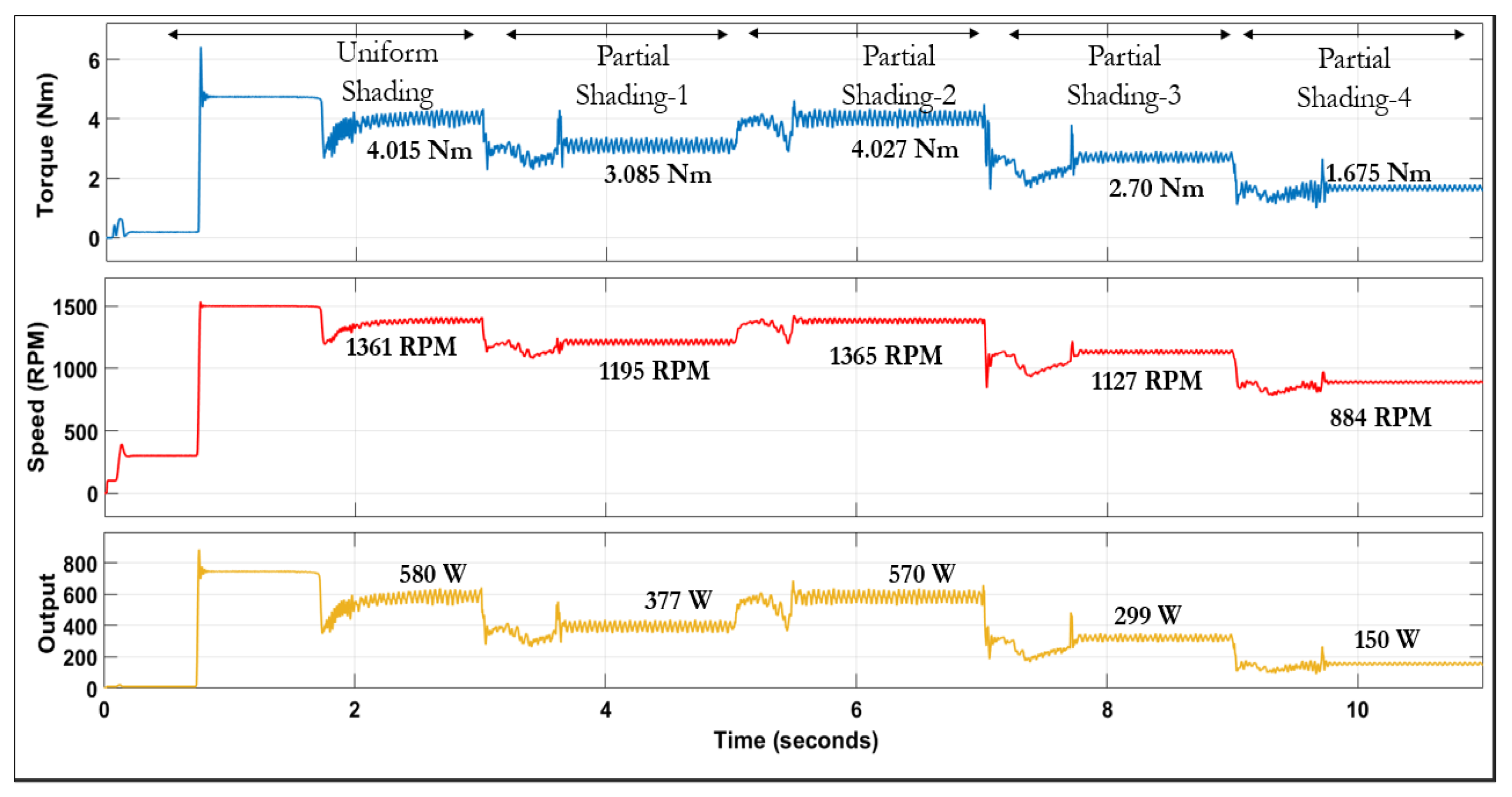

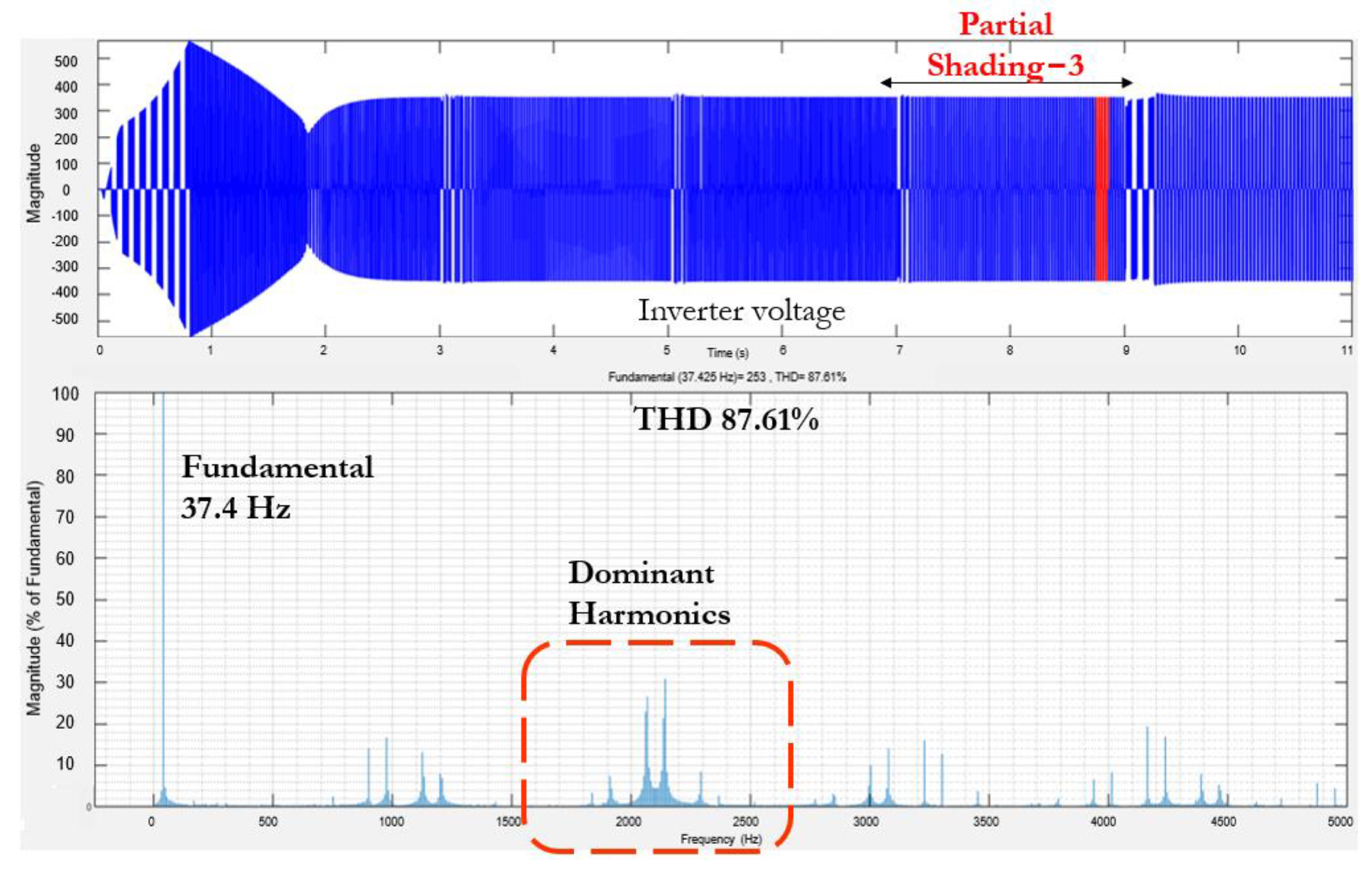


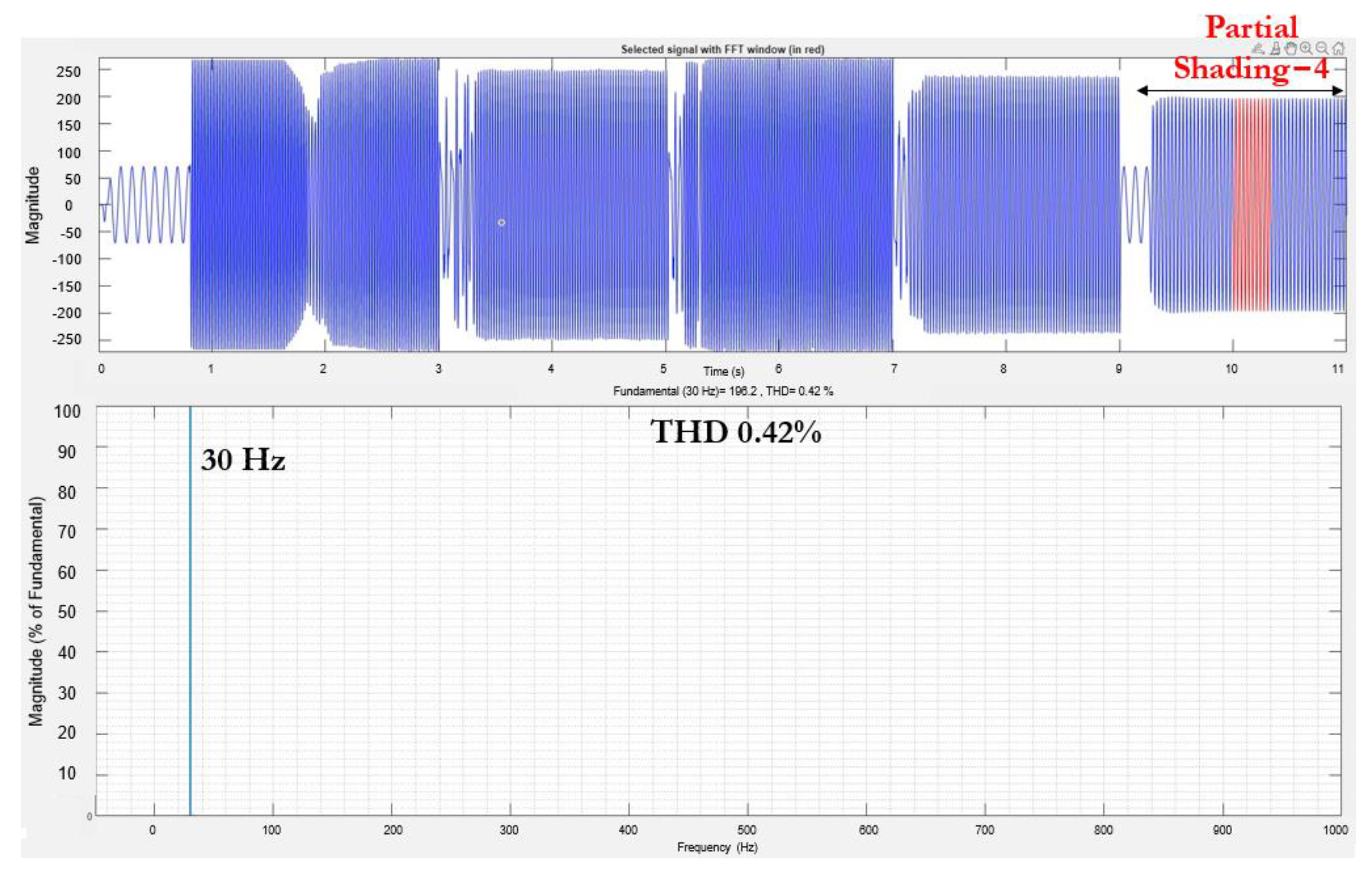
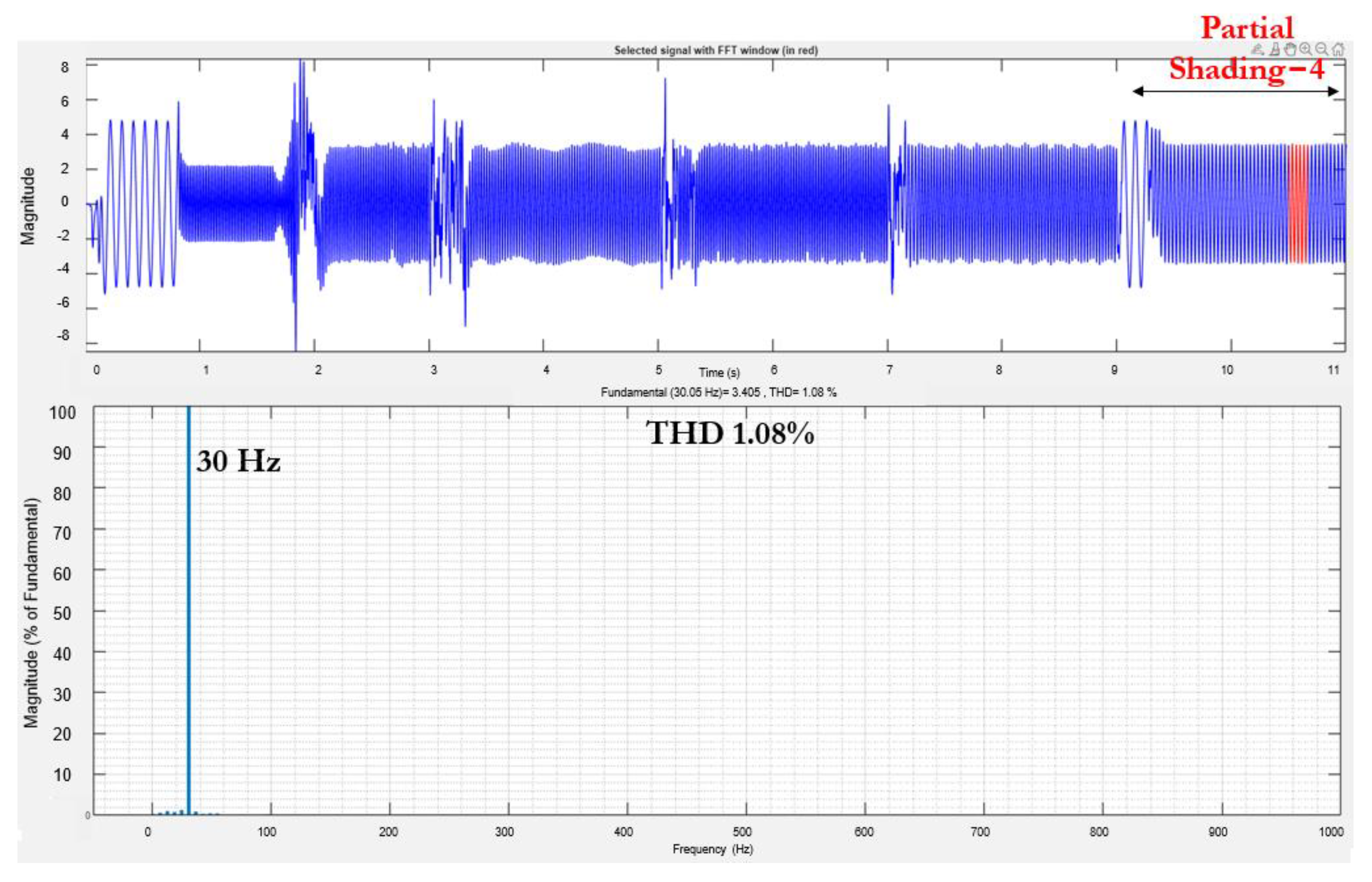

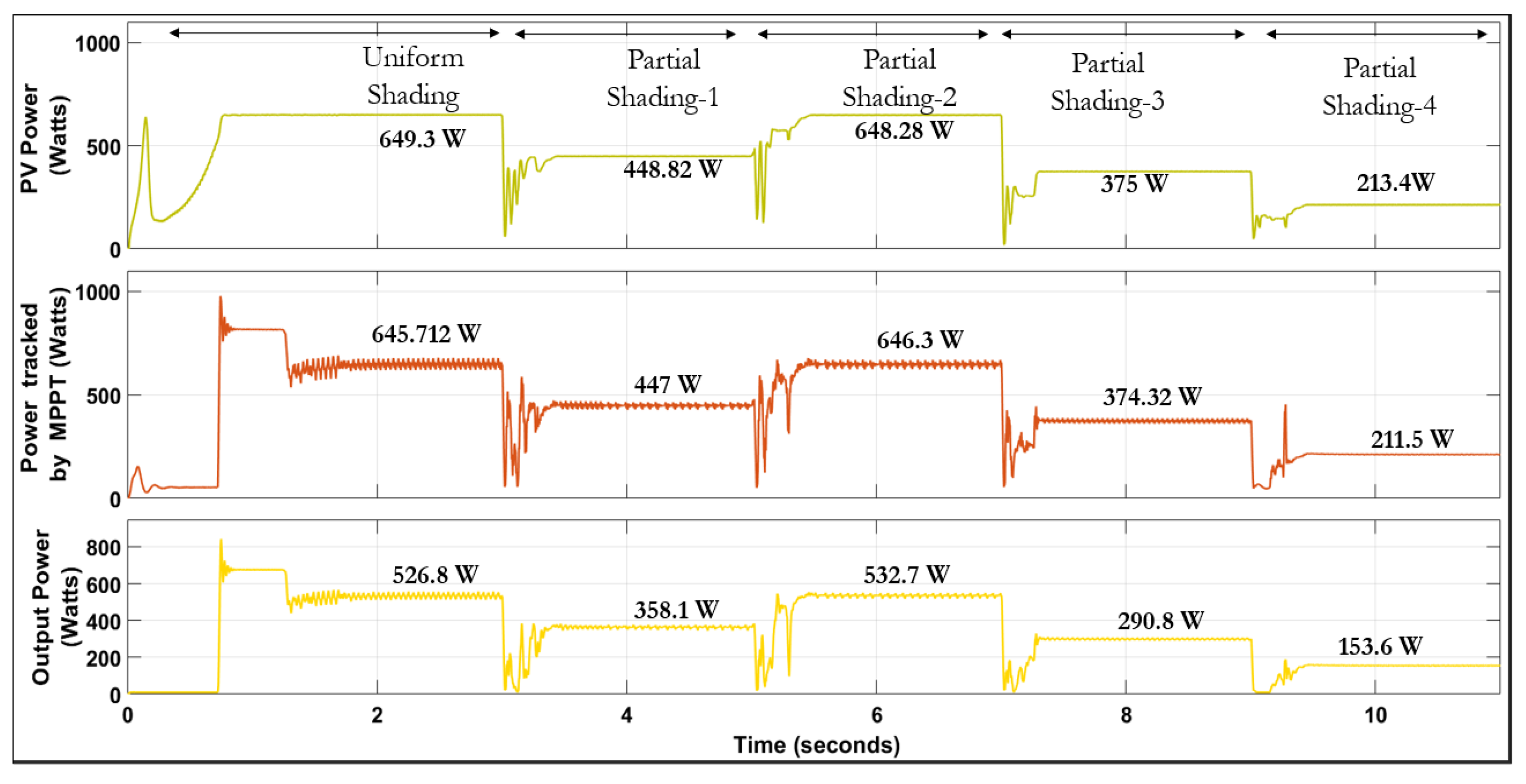
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Solar PV Panels | 11 |
| Reference Solar Insolation (Sref) | 1000 W/m2 |
| Reference Module Temperature (Tref) | 25 °C |
| Reference Short Circuit Current (Iscref) | 4.9 A |
| Reference Open Circuit Voltage (Vocref) | 20 V |
| Reference MPP Power | 68.55 W |
| Reference MPP Current | 4.4 A |
| Reference MPP Voltage | 15.6 V |
| Temperature Coefficient of Voc (β) | 0.0033 |
| Number of Solar PV Panels | 11 |
| Temperature Coefficient of Isc (α) | 0.0004 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage (PV output) | 187 V |
| Output Voltage | 350 V |
| Output Current | 2.35 A |
| Output Power | 882.8 W |
| Inductor | 10 mH |
| Capacitor | 100 µF |
| Inductor Current Ripple | 10% |
| Output Voltage Ripple | 1% |
| Inductor Resistance (rL) | 0.09 Ω |
| Capacitor ESR (rc) | 0.01 Ω |
| Diode Forward Voltage Drop (Vfd) | 1 V |
| Diode Resistance (rd) | 0.01 Ω |
| MOSFET Resistance (rON) | 0.01 Ω |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated power output | 750 W |
| Rated supply voltage | 220 V |
| Rated speed | 1500 rpm |
| Rated torque | 5 Nm |
| Stator resistance | 3.7 Ω |
| d axes winding inductance | 0.030 H |
| q axis winding inductance | 0.038 H |
| Mutual flux linkage | 0.93 Volt-sec/rad |
| Inertia (J) | 0.0001584 Kg m2 |
| Viscous coefficient (B) | 2 × 10−3 Nm/rad/s |
| Parameter | Description | Value/Range |
|---|---|---|
| Objective Function | Power from PV array (Ppv) | Ppv = Vpv Ipv |
| Constraint 1 | Number of wolves (i) | 3 |
| Constraint 2 | Duty cycle (di) | 0.1< di < 0.75 |
| MPPT | Shading Pattern | MPPT η (%) | Convergence Time (seconds) | Torque Ripple (%) | System η (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | US | 96.70% | 1.15 | 5.30% | 89.92% |
| PS1 | 99.33% | 1.16 | 5.45% | 84.63% | |
| PS2 | 98.60% | 1.13 | 5.59% | 88.22% | |
| PS3 | 99.64% | 1.17 | 5.96% | 82.44% | |
| PS4 | 99.82% | 1.19 | 3.13% | 67.94% | |
| GWO | US | 96.40% | 0.80 | 5.42% | 90.01% |
| PS1 | 99.33% | 0.86 | 2.35% | 86.41% | |
| PS2 | 98.60% | 0.84 | 2.15% | 89.26% | |
| PS3 | 99.64% | 0.84 | 2.73% | 85.10% | |
| PS4 | 99.84% | 0.89 | 1.73% | 72.25% | |
| PO PSO | US | 97.15% | 0.55 | 10.68% | 88.73% |
| PS1 | 98.89% | 0.58 | 13.62% | 84.78% | |
| PS2 | 99.84% | 0.78 | 13.56% | 86.82% | |
| PS3 | 99.11% | 0.65 | 12.47% | 82.62% | |
| PS4 | 97.30% | 0.91 | 16.39% | 67.78% | |
| PO GWO | US | 97.15% | 0.34 | 10.73% | 89.96% |
| PS1 | 98.23% | 0.39 | 13.07% | 88.73% | |
| PS2 | 99.22% | 0.43 | 12.77% | 89.63% | |
| PS3 | 98.05% | 0.35 | 11.92% | 85.29% | |
| PS4 | 95.89% | 0.42 | 12.57% | 68.24% | |
| 0.8 Voc | US | 97.15% | 2.30 | 11.48% | 86.88% |
| PS1 | 98.23% | 0.73 | 14.33% | 86.93% | |
| PS2 | 99.07% | 0.77 | 12.71% | 87.57% | |
| PS3 | 98.05% | 0.78 | 13.59% | 85.67% | |
| PS4 | 94.96% | 0.86 | 12.05% | 68.47% | |
| INC-GWO | US | 99.53% | 2.41 | 5.66% | 90.19% |
| PS1 | 99.56% | 0.38 | 6.92% | 89.34% | |
| PS2 | 99.80% | 0.43 | 4.57% | 90.53% | |
| PS3 | 99.92% | 0.26 | 7.51% | 85.81% | |
| PS4 | 99.62% | 0.38 | 1.17% | 75.28% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shetty, D.; Sabhahit, J.N.; Kudva, G. A Methodology to Optimize PMSM Driven Solar Water Pumps Using a Hybrid MPPT Approach in Partially Shaded Conditions. Clean Technol. 2024, 6, 1229-1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol6030060
Shetty D, Sabhahit JN, Kudva G. A Methodology to Optimize PMSM Driven Solar Water Pumps Using a Hybrid MPPT Approach in Partially Shaded Conditions. Clean Technologies. 2024; 6(3):1229-1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol6030060
Chicago/Turabian StyleShetty, Divya, Jayalakshmi N. Sabhahit, and Ganesh Kudva. 2024. "A Methodology to Optimize PMSM Driven Solar Water Pumps Using a Hybrid MPPT Approach in Partially Shaded Conditions" Clean Technologies 6, no. 3: 1229-1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol6030060
APA StyleShetty, D., Sabhahit, J. N., & Kudva, G. (2024). A Methodology to Optimize PMSM Driven Solar Water Pumps Using a Hybrid MPPT Approach in Partially Shaded Conditions. Clean Technologies, 6(3), 1229-1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol6030060







