Sustainable Design for Geotourism Interpretation Centres: Enhancing the Santa Elena Peninsula Geopark Project Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
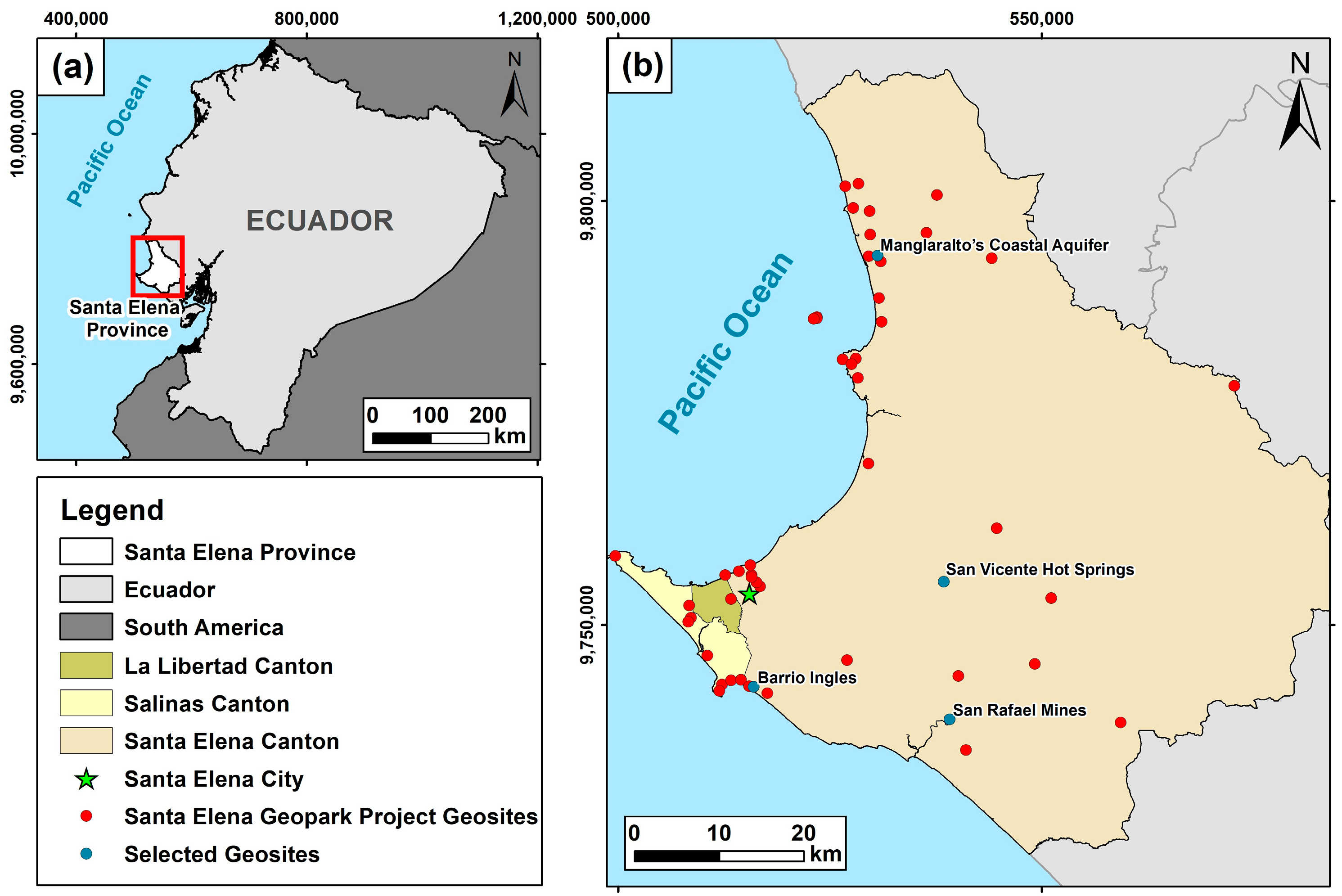
2. Study Area
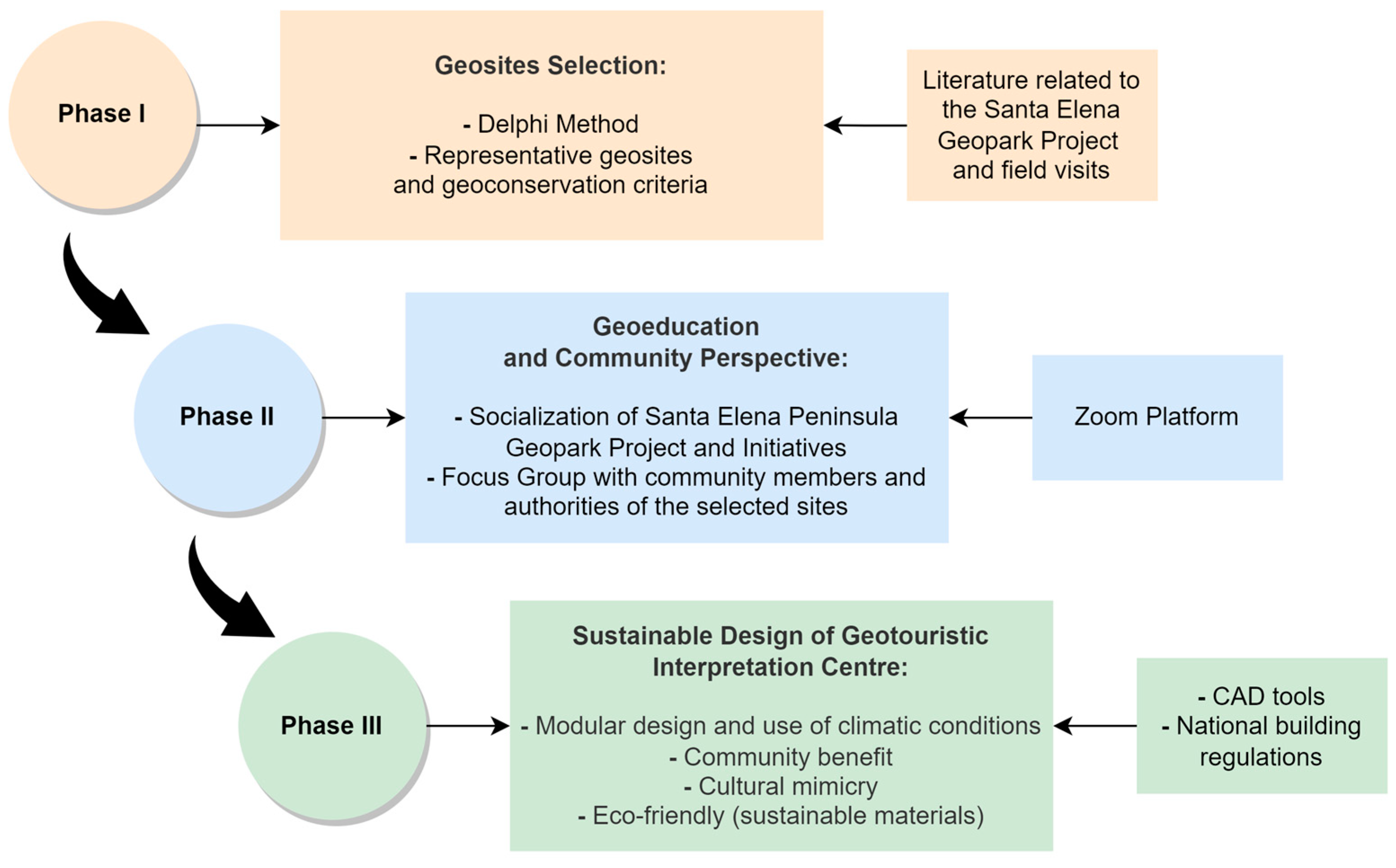
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Phase I: Geosite Selection
3.2. Phase II: Geoeducation and Community Perspective
3.3. Phase III: Sustainable Design of Geotourism Interpretation Centres
4. Results
4.1. Selected Geosites
4.2. Geoeducation and Community Perspectives
- The first is related to the present tourism limitations, in which effective public and private investment in construction projects or conditioning of tourist sites to provide facilities to different visitors stands out as a common factor. On the other hand, they highlight the need to strengthen promotion strategies that reflect the geological, cultural and historical importance of the areas and promote a greater tourist influx, representing a tool for community economic development.
- The second aspect relates to the estimated tourist statistics of the participants at each site. In general, the three identified profiles of visitors include: (i) national and international tourists, (ii) academics and researchers and (iii) businessmen or entrepreneurs who generally visit the sites on holidays or in summer with interest in ecotourism, marine tourism, gastronomy, archaeology, history and culture. A summary of the statistics provided by the focus group for each selected site is presented in Table 2.
- Finally, the third aspect is related to the community’s interest in geotourism interpretation centres. According to the people who participated in the questionnaire, the community of the province and country need strategies to disseminate scientific wealth, in which community participation is a key aspect. The importance of designing an infrastructure where interpretive panels are implemented to geoeducate tourists at different levels of education or tourist profiles was highlighted. In accordance with their culture, the need for sustainable designs that use local materials and adapt to the environment was expressed. The community and authorities of the different sites consider that the conditioning project will attract more tourists as long as dissemination is strengthened, as well as community, academic and business participation in the social, cultural, economic and environmental axes.
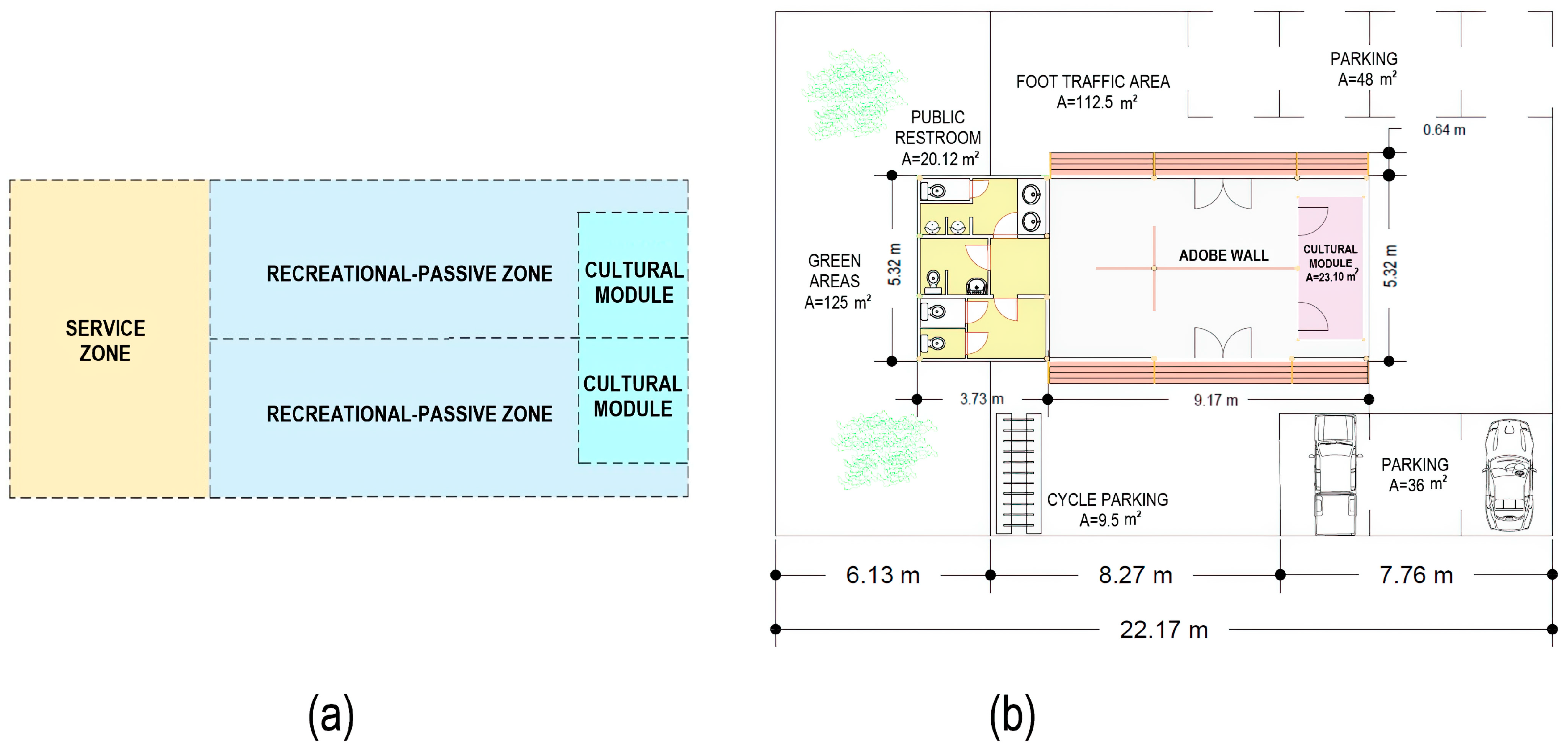
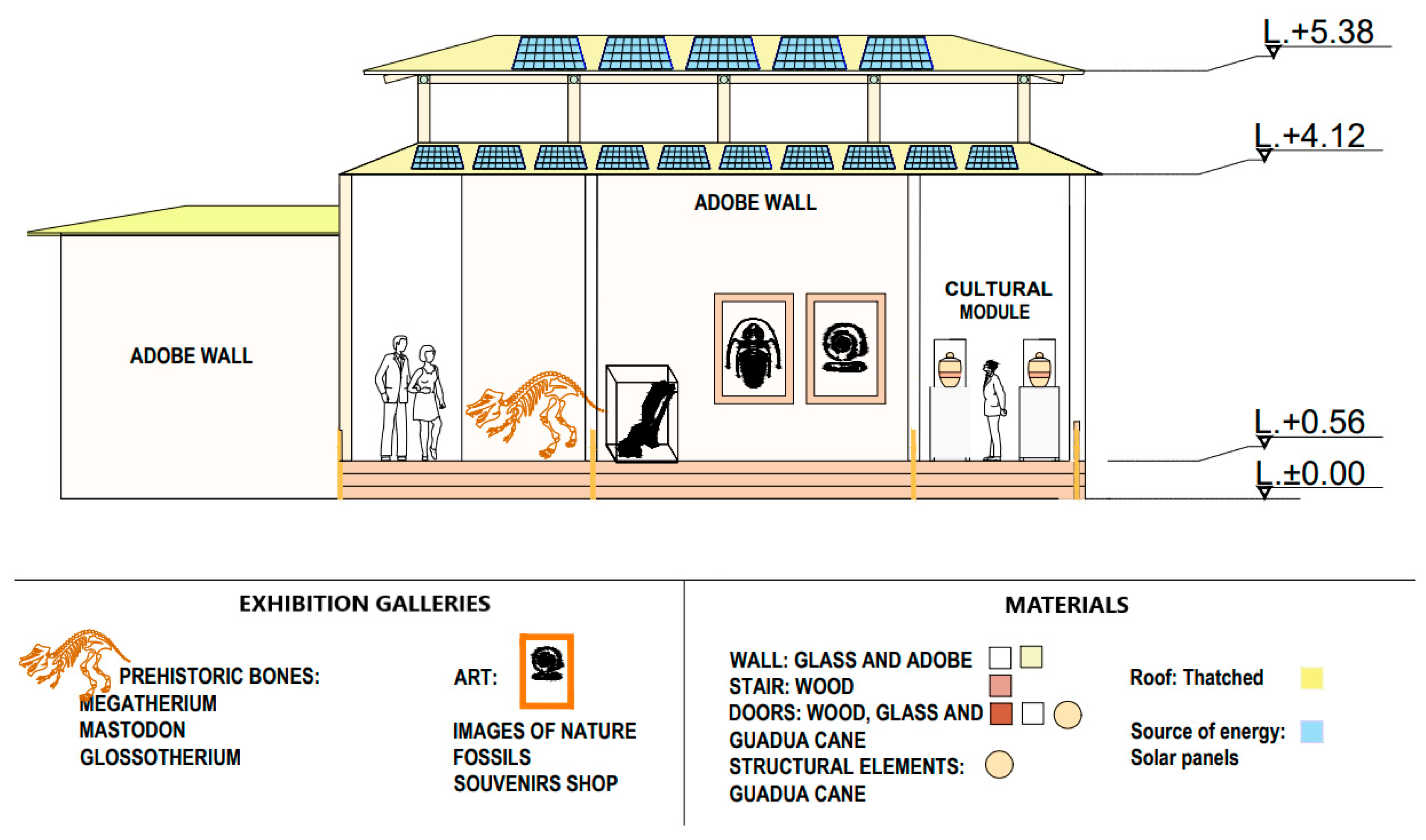
4.3. Proposed Design of Geotourism Interpretation Centres
- Component A, “terrace”: corresponds to an area designed for passive contemplation and the rest of visitors and shelter from solar radiation.
- Component B, “public bathrooms”: corresponds to the area of hygienic services for men, women, children and people with disabilities under the requirements of Ecuadorian regulations for public spaces [23].
- Component C, “cultural station”: corresponds to an area for geoeducation, designed for the exhibition of information panels, photographic galleries, models and samples of the local geology of each site to promote its dissemination.
- Furthermore, these three modules can be used individually or together, depending on each place’s geotourism needs and requirements.
- Economic–Political Sustainability: A general design adaptable to all geosites was considered, with a simple, modular and versatile structure, ensuring savings and economic viability, as well as the possible attraction of public and private investment.
- Social Sustainability: The design emphasizes community contribution to create a place suitable for community meetings, considering the rural lifestyle and integration into social customs. These spaces promote the tourist attractiveness of the sectors, improving the tourism industry and local development opportunities (e.g., development of local entrepreneurship, such as souvenir shops (geoproducts), catering services, transportation and cultural performances, and promotion of geotour guides that meet the needs of visitors). Its inclusive design guarantees the accessibility and comfort of any user, with minimum circulation spaces and access ramps, ensuring the free movement of people with reduced mobility and visual disabilities, according to Ecuadorian regulations [65].
- Cultural Sustainability: The design serves as a contribution to the geopark project, seeking the preservation of heritage, geoeducation and the cultural roots of the four geosites: the Barrio Ingles Ancon Parish, recognized for its oil legacy of English origin; Manglaralto’s Coastal Aquifer, a place of culture and awareness about underground water resources as an alternative source of water supply; San Vicente Hot Springs, with a cultural legacy of medicinal waters and muds; and San Rafael Mines, with a historic community artisanal mining culture dating back to 1968 [66], representing the main economic support of this community. In addition, the construction has community participation for the workforce, promoting the unity and integration of the inhabitants.
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeMiguel, D.; Brilha, J.; Alegret, L.; Arenillas, I.; Arz, J.A.; Gilabert, V.; Strani, F.; Valenciano, A.; Villas, E.; Azanza, B. Linking Geological Heritage and Geoethics with a Particular Emphasis on Palaeontological Heritage: The New Concept of ‘Palaeontoethics’. Geoheritage 2021, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilha, J. Inventory and Quantitative Assessment of Geosites and Geodiversity Sites: A Review. Geoheritage 2016, 8, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Franco, G.; Carrión-Mero, P.; Montalván-Burbano, N.; Caicedo-Potosí, J.; Berrezueta, E. Geoheritage and Geosites: A Bibliometric Analysis and Literature Review. Geosciences 2022, 12, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión-Mero, P.; Herrera-Franco, G.; Briones-Bitar, J.; Caldevilla, P.; Domínguez-Cuesta, M.J.; Berrezueta, E. Geotourism and Local Development Based on Geological and Mining Sites Utilization, Zaruma-Portovelo, Ecuador. Geosciences 2018, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Perelló, J.; Carrión, P.; Molina, J.; Villas-Boas, R. Geomining heritage as a tool to promote the social development of rural communities. In Geoheritage; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 167–177. [Google Scholar]
- Özdemir, M.A.; Kaymak, H.; Kulaksız, E.E. Inventory of Geomorphosites and Cultural Assets for the Development of Tourism in the Ayazini Region of the Mountainous Phrygia (Afyonkarahisar, Turkey). Geoheritage 2023, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite Mansur, K.; de Souza Carvalho, I. Characterization and Valuation of the Geological Heritage Identified in the Peró Dune Field, State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Geoheritage 2011, 3, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frassi, C.; Amorfini, A.; Bartelletti, A.; Ottria, G. Popularizing Structural Geology: Exemplary Structural Geosites from the Apuan Alps UNESCO Global Geopark (Northern Apennines, Italy). Land 2022, 11, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Golani, P.R. Unique Geosites around Zawar, Rajasthan, Western India: Its Linkage with Ancient Mining-Metallurgy and Archaeological Geodiversity. Geoheritage 2023, 15, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancello, D.; Columbu, S.; Cruciani, G.; Dulcetta, L.; Franceschelli, M. Geological and Archaeological Heritage in the Mediterranean Coasts: Proposal and Quantitative Assessment of New Geosites in SW Sardinia (Italy). Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 910990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wu, W. Geoparks and Geotourism in China: A Sustainable Approach to Geoheritage Conservation and Local Development—A Review. Land 2022, 11, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, D.; Dowling, R.K. Geotourism: The Tourism of Geology and Landscape; Goodfellow Publishers Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ateş, H.Ç.; Ateş, Y. Geotourism and Rural Tourism Synergy for Sustainable Development—Marçik Valley Case—Tunceli, Turkey. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M. Geodiversity: Developing the Paradigm. Proc. Geol. Assoc. 2008, 119, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. UNESCO Guidelines and Criteria for National Geoparks Seeking UNESCO’s Assistance to Join the Global Geoparks Network (GGN); United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 2014; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Aytaç, A.S.; Demir, T.; Maddy, D.; Bridgland, D.R. The Kula–Salihli UNESCO Geopark: Spectacular Records of Quaternary Volcanism, Fluvial and Landscape Evolution and Quaternary Environmental Change. Proc. Geol. Assoc. 2023, 134, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilha, J. Geoheritage and geoparks. In Geoheritage Assessment, Protection, and Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 323–335. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Estatuto Del Programa Internacional de Ciencias de La Tierra y Geoparques; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2015; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. List of UNESCO Global Geoparks and Regional Networks. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/en/iggp/geoparks (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Global Geoparks Network Latin America and Caribbean Geoparks Network. Available online: https://globalgeoparksnetwork.org/?page_id=228 (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Ren, F.; Simonson, L.; Pan, Z. Interpretation of Geoheritage for Geotourism—A Comparison of Chinese Geoparks and National Parks in the United States. Czech J. Tour. 2014, 2, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S. Design for Outdoor Recreation; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780415441728. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Checklist Explanatory Notes to Define an Aspiring UNESCO Global Geopark (AUGGp); UNESCO: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Began, M.; Višnić, T.; Djokić, M.; Vasiljevic, D.A. Interpretation Possibilites of Geoheritage in Southeastern Serbia—Gorge and Canyon Study. Geoheritage 2017, 9, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.C. Community Destination Management in Developing Economies; Jamieson, W., Ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA; Cantay Road Mississauga, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquaré Mariotto, F.; Bonali, F.L.; Venturini, C. Iceland, an Open-Air Museum for Geoheritage and Earth Science Communication Purposes. Resources 2020, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlongwane, A.K.; Ndlovu, S.M. Weaving stories, memories, public history, visual art and place: The 16 June 1976 interpretation centre, Central Western Jabavu, Soweto. In Public History and Culture in South Africa. African Histories and Modernities; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 155–196. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, R.G.P.; Mansur, K.L.; de Castro, A.S.F.d.R.d.S. Methodological Proposal for Inventory and Quantitative Valuation of Ex Situ Geological Heritage, a Case Study at the Museu Da Geodiversidade (MGeo/IGEO/UFRJ). Geoheritage 2023, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, T.; de Mascarenhas, J.M.; Mendes, P. Guidelines for the Integration of Biological and Cultural Values in a Landscape Interpretation Centre: Application in Southern Portugal. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 3367–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkaya de Juanas, S.; Barroso-Barcenilla, F.; Berrocal-Casero, M.; Callapez, P.M. Virtual Fossils for Widening Geoeducation Approaches: A Case Study Based on the Cretaceous Sites of Figueira Da Foz (Portugal) and Tamajón (Spain). Geosciences 2023, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B.G.; Cleal, C.J.; Thomas, B.A. Geotourism in an Industrial Setting: The South Wales Coalfield Geoheritage Network. Geoheritage 2018, 10, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catana, M.M.; Brilha, J.B. The Role of UNESCO Global Geoparks in Promoting Geosciences Education for Sustainability. Geoheritage 2020, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayla, N.; Megerle, H.E. Dinosaur geotourism in Europe, a booming tourism niche. In Global Geographical Heritage, Geoparks and Geotourism. Advances in Geographical and Environmental Sciences; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 359–379. [Google Scholar]
- Naturpark Mëllerdall Geopark. Available online: https://www.naturpark-mellerdall.lu/en/the-nature-parc/about-us/ (accessed on 30 September 2023).
- Geoparkea. Available online: https://geoparkea.eus/en/ (accessed on 30 September 2023).
- Sanz, J.; Zamalloa, T.; Maguregi, G.; Fernandez, L.; Echevarria, I. Educational Potential Assessment of Geodiversity Sites: A Proposal and a Case Study in the Basque Country (Spain). Geoheritage 2020, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusté-Forné, F. A Slow Tourist in the Basque Coast Geopark (Spain). Int. J. Geoheritage Park. 2023, 11, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez Taset, Y.M. Imbabura: The First UNESCO Geopark in Ecuador. Bionatura 2019, 4, 830–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cortez, J.L. Conservation of Geoheritage in Ecuador: Situation and Perspectives. Int. J. Geoheritage Park. 2019, 7, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, D.; Simbaña-Tasiguano, M.; Guzmán, O.; Cabascango, E.; Sánchez-Cortez, J.L.; Campos, C.; Grefa, H. Quantitative Assessment of Geodiversity in Ecuadorian Amazon—Case Study: Napo Sumaco Aspiring UNESCO Geopark. Geoheritage 2023, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrezueta, E.; Aguilar-Aguilar, M.; Sánchez-Cortés, J.L. Inventory and Characterization of Geosites in Ecuador: A Review. Geoheritage 2021, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Carrión, P.; Briones, J. Geotourism Potential in the Context of the Geopark Project for the Development of Santa Elena Province, Ecuador. In Proceedings of the WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment, Rome, Italy, 4 September 2018; pp. 557–568. [Google Scholar]
- Heriyanto; Shodiqin, M.A.; Sasmito, K.; Putri, R.I. Prospect Analysis of Geosite at Bukit Biru Area in Kutai Kartanegara, East Kalimantan. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1134, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, N.; Marković, S.B.; Antić, A.; Tešić, D. Exploring the Potential for Geotourism Development in the Danube Region of Serbia. Int. J. Geoheritage Park. 2020, 8, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feria, M.; Amado, M. Architectural Design: Sustainability in the Decision-Making Process. Buildings 2019, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GADP Santa Elena. Plan de Desarrollo y Ordenamiento Territorial 2019–2023 Alineación; GADP Santa Elena: Santa Elena, Ecuador, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sarabia-Molina, M.Y.; Soares, J.R.R.; Lois-González, R.C. Innovations in Community-Based Tourism: Social Responsibility Actions in the Rural Tourism in the Province of Santa Elena–Ecuador. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Franco, G.; Carrión-Mero, P.; Alvarado, N.; Morante-Carballo, F.; Maldonado, A.; Caldevilla, P.; Briones-Bitar, J.; Berrezueta, E. Geosites and Georesources to Foster Geotourism in Communities: Case Study of the Santa Elena Peninsula Geopark Project in Ecuador. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Franco, G.; Erazo, K.; Mora-Frank, C.; Carrión-Mero, P.; Berrezueta, E. Evaluation of a Paleontological Museum as Geosite and Base for Geotourism. A Case Study. Heritage 2021, 4, 1208–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvache-Franco, M.; Carvache-Franco, W.; Carvache-Franco, O.; Borja-Morán, J. Ecotourism Motivations and Segmentation in a Fauna Production Reserve in Ecuador. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 4, 983–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza Tarabó, A.E.; Yumisaca Tuquinga, J.E.; Peralta Mendoza, S.P. Diversification of Tourism through Cultural Routes in Manglaralto County, in the Province of Santa Elena. Smart Tour. 2022, 3, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Franco, G.; Carrión-Mero, P.; Mora-Frank, C.; Caicedo-Potosí, J. Comparative Analysis of Methodologies for the Evaluation of Geosites in the Context of the Santa Elena-Ancón Geopark Project. Int. J. Des. Nat. Ecodynamics 2020, 15, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Álvarez, A.; Alvarado, N. Geoparque Ancón-Santa Elena: Una Vía Para El Desarrollo Local. In La Minería y la Geología Ambiental: Herramientas para el Desarrollo Sostenible, Para el Presente y el Futuro; Sociedad Española para la Defensa del Patrimonio Geológico y Minero (SEDPGYM): Molina de Aragón, Guadalajara, Spain, 2016; pp. 355–369. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Franco, G.; Mora-Frank, C.; Kovács, T.; Berrezueta, E. Georoutes as a Basis for Territorial Development of the Pacific Coast of South America: A Case Study. Geoheritage 2022, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendón, S.; Álvarez, H.; Rendón, N.; Yumisaca, J. Patrimonio Cultural Ancestral de La Parroquia de San José de Ancón, Año 2022. Pro Sci. Rev. Prod. Ciencias Investig. 2022, 6, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Franco, G.; Montalván-Burbano, N.; Mora-Frank, C.; Moreno-Alcívar, L. Research in Petroleum and Environment: A Bibliometric Analysis in South America. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2021, 16, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamzadeh, A.; Ebrahimi, P.; Soleimani, M.; Fekete-Farkas, M. An AHP Approach to Identify the Barriers of Sustainable Geotourism Development in Iran: An Economic View. Geoheritage 2021, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Desarrollo Urbano y Vivienda. Viviendas De Hasta 2 Pisos Con Luces De Hasta 5 m. NEC-SE-VIVIENDA: Viviendas; Ministerio de Desarrollo Urbano y Vivienda: Quito, Ecuador, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Desarrollo Urbano y Vivienda. NEC-SE-GUADÚA: Estructuras de Guadúa; Ministerio de Desarrollo Urbano y Vivienda: Quito, Ecuador, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiar, R.; Rivas-Medina, A.; Caiza, P.; Quizanga, D. Control Spectra for Quito. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morante-Carballo, F.; Gurumendi-Noriega, M.; Cumbe-Vásquez, J.; Bravo-Montero, L.; Carrión-Mero, P. Georesources as an Alternative for Sustainable Development in COVID-19 Times—A Study Case in Ecuador. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión-Mero, P.; Morante-Carballo, F.; Herrera-Franco, G.; Jaya-Montalvo, M.; Rodríguez, D.; Loor-Flores de Valgas, C.; Berrezueta, E. Community-University Partnership in Water Education and Linkage Process. Study Case: Manglaralto, Santa Elena, Ecuador. Water 2021, 13, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quimí Quimí, L.R. Lady Plan de Desarrollo Turístico Para La Comuna San Rafael, Parroquia Chanduy, Provincia Santa Elena, Año 2016. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Estatal Península de Santa Elena, Santa Elena, Ecuador, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Franco, G.; Carrión-Mero, P.; Aguilar-Aguilar, M.; Morante-Carballo, F.; Jaya-Montalvo, M.; Morillo-Balsera, M.C. Groundwater Resilience Assessment in a Communal Coastal Aquifer System. The Case of Manglaralto in Santa Elena, Ecuador. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Ecuatoriano de Normalización NTE INEN. Accesibilidad de Las Personas Con Discapacidad y Movilidad Reducida Al Medio Físico: Área Higiénico Sanitaria; Instituto Ecuatoriano de Normalización: Quito, Ecuador, 2000; pp. 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Baquerizo, M.; Reyes, J. Estudio de Factibilidad Para La Creación de La Microempresa Industrial de Procesamiento y Comercialización de Baldosas y Adoquines de Piedra Granito, Para La “Asociaicón de Mineros En Canteras y Graveras de La Comuna San Rafael”, Provincia de Santa Elena; Universidad Estatal Península de Santa Elena: Santa Elena, Ecuador, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo Zambrano, R.V.; Milanes, C.B.; Pérez Montero, O.; Mestanza-Ramón, C.; Nexar Bolivar, L.O.; Cobeña Loor, D.; García Flores De Válgaz, R.G.; Cuker, B. A Sustainable Proposal for a Cultural Heritage Declaration in Ecuador: Vernacular Housing of Portoviejo. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassin, N.S.F.N.; Misni, A. Sustainable Architectural Design Features of Negeri Sembilan Malay Houses: An Analysis of Indoor Thermal Comfort. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1217, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugelaite, A.; Grazuleviciute-Vileniske, I. Aesthetics of Sustainability and Architecture: An Overview. Archit. Urban Plan. 2020, 16, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, L.E.; da Silva, F.J.; Rodrigues, F.C. Bamboo Mast for Lightweight Arquitecture. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 600, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Obaldia, M.; Cortes Chavez, F.; Rossa-Sierra, A.; Garcia-Hernandez, M. The Importance of the Adobe Brick for a Sustainable Architecture in Mexico. Hum. Factors Archit. Sustain. Urban Plan. Infrastruct. 2022, 58, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Carrión, P.; Herrera, G.; Briones, J.; Sánchez, C.; Limón, J. Practical Adaptations of Ancestral Knowledge for Groundwater Artificial Recharge Management of Manglaralto Coast. In WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 2018; pp. 375–386. [Google Scholar]
- Carrión-Mero, P.; Merchán-Sanmartín, B.; Aguilar-Aguilar, M.; Morante-Carballo, F.; Suárez-Zamora, S.; Bárcenes-Campoverde, R.; Berrezueta, E. Strategies to Improve the Tourist Interest of a Geosite Respecting Its Natural Heritage. A Case Study. Geoheritage 2022, 14, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeroso, A.; Rahardjo, N.; Turgarini, D. Green Tourism Planning for Coastal Development in Gunungsewu Geopark, Indonesia. Int. J. Geoinformatics 2023, 19, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harangi, S.; Korbély, B. The Basaltic Monogenetic Volcanic Field of the Bakony–Balaton UNESCO Global Geopark, Hungary: From Science to Geoeducation and Geotourism. Geoconservation Res. 2023, 6, 70–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.K.; Brown, G. Understanding Tourist Perspectives on Geotourism Experience: Implications for Destination Development. Tour. Rev. Int. 2012, 16, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Turismo Expenditure Statistics and Number of Annual Tourist Trips in Ecuador. Available online: https://servicios.turismo.gob.ec/turismo-en-cifras/feriados-nacionales/ (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Herrera Anangonó, R.C.; Delgado Campuzano, D.V.; Moreira Espinoza, J.A.; Toala Tuarez, P.J. La Reactivación Turística Post COVID-19 de Las Áreas Naturales Protegidas y Su Incidencia En La Mejora de La Experiencia de Los Turistas En El Ecuador. Siembra 2021, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Turismo Annual Visitors to Protected Areas of Ecuador. Available online: https://servicios.turismo.gob.ec/turismo-en-cifras/areas-naturales/ (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Li, Q.J.; Ng, Y.; Wu, R.R. Strategies and Problems in Geotourism Interpretation: A Comprehensive Literature Review of an Interdisciplinary Chinese to English Translation. Int. J. Geoheritage Park. 2022, 10, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
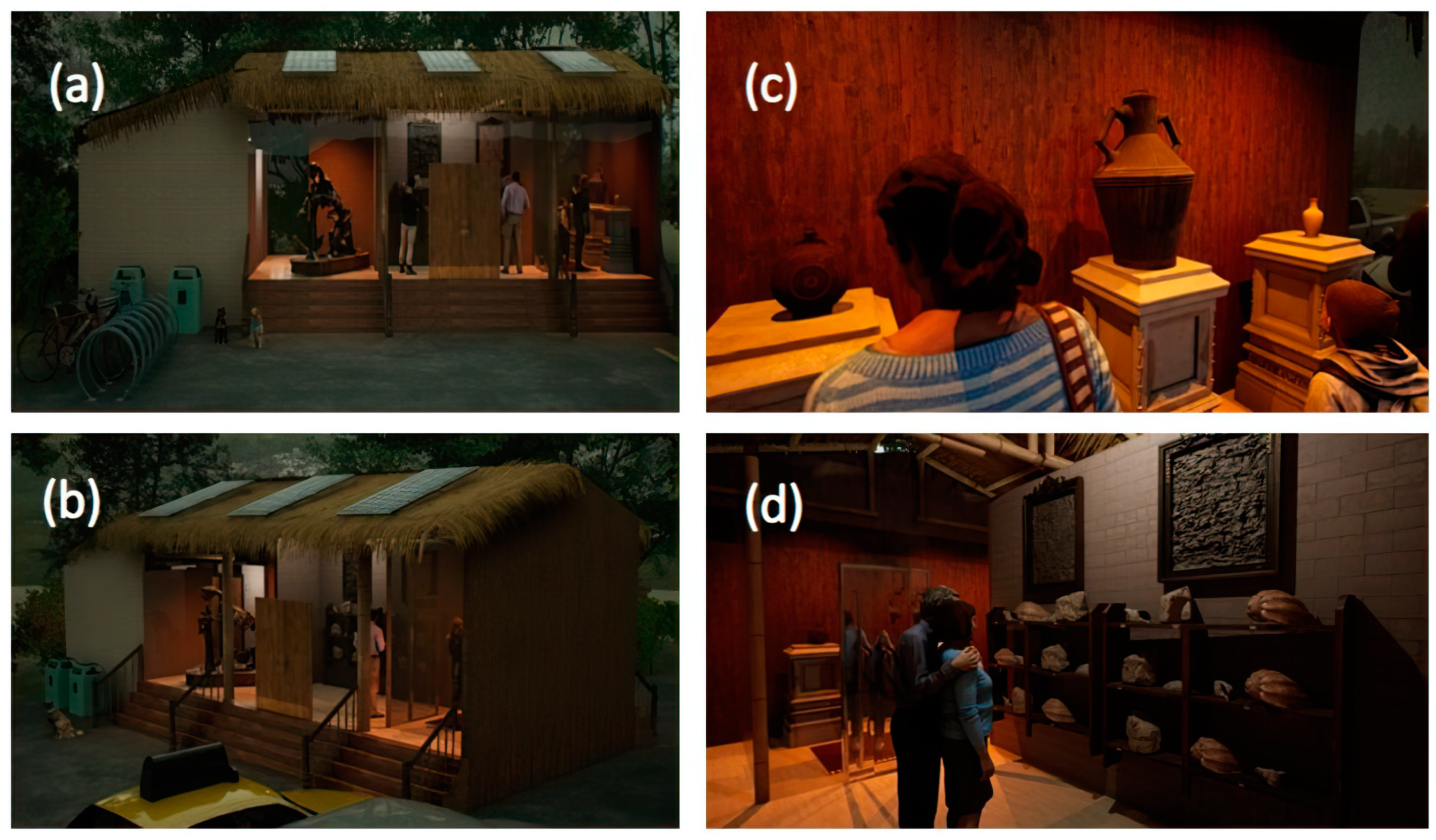




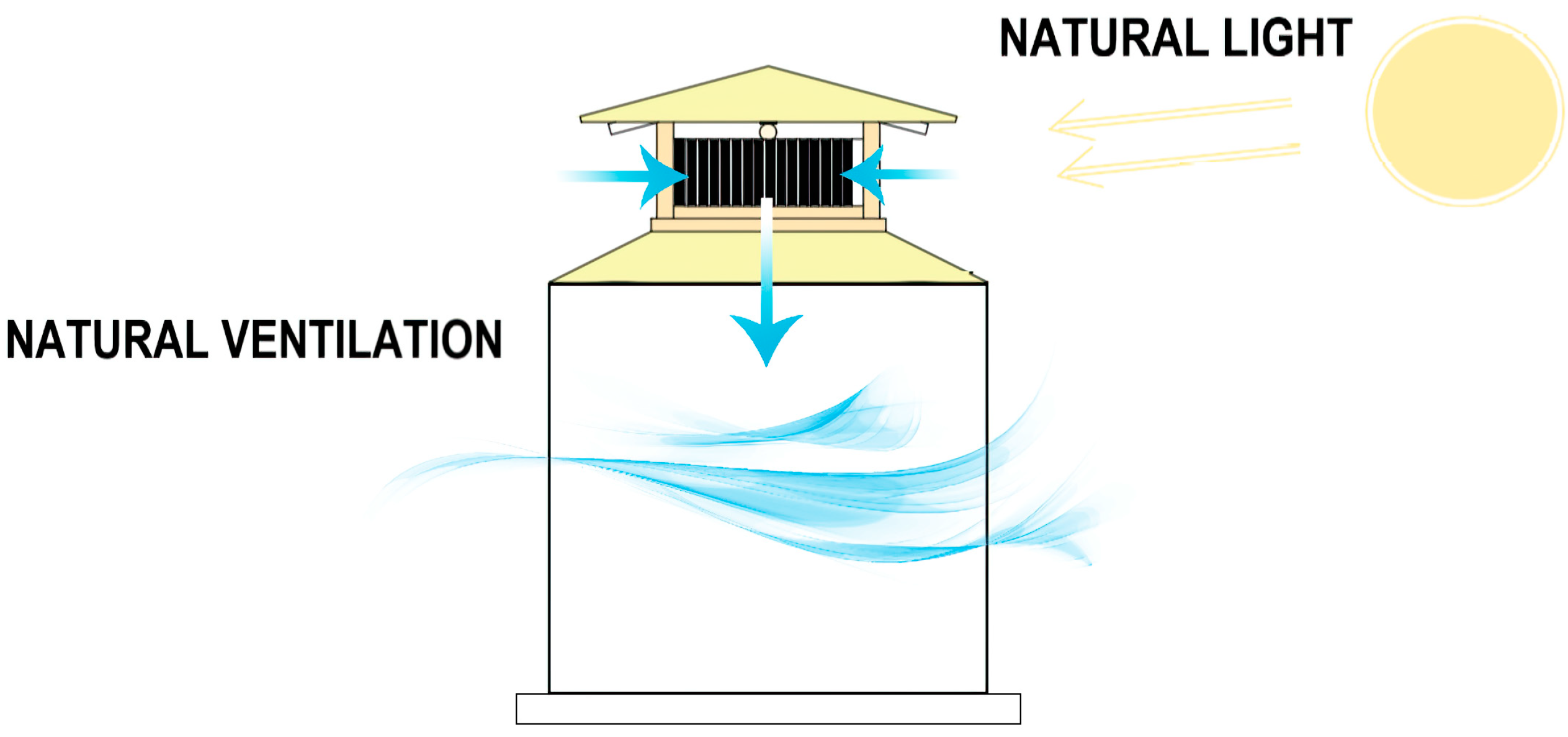
| Selected Sites | Description | Tourism Information | Heritage Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barrio Ingles Ancon Parish (Figure 3a) | Site of historical and architectural interest located in Ancon. The neighbourhood has infrastructure dating back to 1911, exhibiting the cultural legacy of the English settlement that began oil exploitation in Ecuador in the city of Ancon [53]. | The attraction comprises buildings with English-influenced architecture in wood and pumice, oil pumpjacks and proximity to a viewpoint overlooking the sea. In addition, Barrio Ingles encompasses five geosites of varied geological and geomorphological characteristics, such as bituminous exudations, the first Ancon oil well, the Anconcito badlands, Anconcito cliff and Anconcito gypsum veins [54]. | The cultural legacy of the Barrio Ingles began with the oil history in Ecuador; it is located within the San Jose de Ancon Parish, was declared a Cultural Heritage of Ecuador in 2011, and the cultural wealth is complemented by heritage houses, artisans and “paja toquilla” weavers. |
| Manglaralto’s Coastal Aquifer (Figure 3b) | Geosite of hydrogeological interest located in the parish of Manglaralto. It is the main water supply source for six communes in the parish. Among its secondary characteristics are the ecological and fluvial landscaping of the Manglaralto River [61]. | The main attraction is the technical–artisanal dam built on the Manglaralto River for damming water and recharging the aquifer. The place has become a site for fishing, recreation and university hydrogeological education [62]. | It is located in a semi-arid area of the Ecuadorian coast (Santa Elena Province), in which water supply is possible owing to the joint use of surface and underground water through ancient techniques of Water Sowing and Harvesting (WS&H) (e.g., tapes, technical–artisanal dykes and artificial wetlands (“albarradas”)) that guarantee the availability of resources to the community and control the advance of saline intrusion into the aquifer. Since 2007, these techniques have been strengthened with academic intervention (ESPOL University), in which the inclusion of technical criteria has allowed the functionality of WS&H systems to be enhanced in the long term. |
| San Vicente Hot Springs (Figure 3c) | It is a geosite of hydrogeological and petrological interest located in the Baños de San Vicente commune. The place contains hot springs and a mud volcano, both of underground natural origin [48]. | Since 1922, there has been a tourist complex for using the thermal waters and volcanic muds, which local people consider natural medicinal treatments. The place has an area of 4 hectares. In 2014, it was visited by around 126,000 people [48]. | San Vicente hot springs is one of the two representative hot spring sites on the Ecuadorian coast; its inhabitants attribute medicinal values to the water and mineralogical content of the volcanic mud typical of the area through hydrotherapy and thermotherapy. This type of activity is aimed at the cure and prevention of physical diseases (inflammation and muscle pain) and mental diseases (stress and anxiety). |
| San Rafael Mines (Figure 3d) | It is a geo-industrial type geosite located in the San Rafael canton. It is characterised by presenting rocks typical of the Chanduy-Playas Mountain Range, such as quartzite and granite [54]. | The largest tourist resource in the area is the granite quarries that expose the natural geology. In the place, you can see the artisanal extraction process of this material [63]. | Artisanal mining identity of the extraction of stone material is the main source of economic income for approximately 60% of the population. |
| Parameter | Barrio Ingles (Ancon Parish) | Manglaralto’s Coastal Aquifer | San Vicente Hot Springs | San Rafael Mines |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monthly tourist number | 1300 | 2000 | 900 | 2300 |
| Visit frequency | Monthly | Monthly | Daily | Daily |
| Estimated stay | 2 to 3 days | 2 to 3 days | Just a few hours | Just a few hours |
| Average expenses per day | Between $25 and $50 | More than $50 | Between $25 and $50 | Between $25 and $50 |
| Travel reasons | Tourism, education, research and work | Tourism, education and research | Tourism, research and health | Tourism, education and work |
| Environmental Sustainability | Proposals |
|---|---|
| Eco-friendly materials |
|
| Energy efficiency |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rubira-Gómez, G.; Malavé-Hernández, J.; Jaya-Montalvo, M.; Candell-Soto, J.; Caicedo-Potosí, J.; Merchán-Sanmartín, B.; Aguilar-Aguilar, M.; Morante-Carballo, F. Sustainable Design for Geotourism Interpretation Centres: Enhancing the Santa Elena Peninsula Geopark Project Experience. Heritage 2024, 7, 499-516. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage7010024
Rubira-Gómez G, Malavé-Hernández J, Jaya-Montalvo M, Candell-Soto J, Caicedo-Potosí J, Merchán-Sanmartín B, Aguilar-Aguilar M, Morante-Carballo F. Sustainable Design for Geotourism Interpretation Centres: Enhancing the Santa Elena Peninsula Geopark Project Experience. Heritage. 2024; 7(1):499-516. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage7010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleRubira-Gómez, Gilda, Jenifer Malavé-Hernández, María Jaya-Montalvo, Jimmy Candell-Soto, Jhon Caicedo-Potosí, Bethy Merchán-Sanmartín, Maribel Aguilar-Aguilar, and Fernando Morante-Carballo. 2024. "Sustainable Design for Geotourism Interpretation Centres: Enhancing the Santa Elena Peninsula Geopark Project Experience" Heritage 7, no. 1: 499-516. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage7010024
APA StyleRubira-Gómez, G., Malavé-Hernández, J., Jaya-Montalvo, M., Candell-Soto, J., Caicedo-Potosí, J., Merchán-Sanmartín, B., Aguilar-Aguilar, M., & Morante-Carballo, F. (2024). Sustainable Design for Geotourism Interpretation Centres: Enhancing the Santa Elena Peninsula Geopark Project Experience. Heritage, 7(1), 499-516. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage7010024








