Power and Coherence in the EEG of the Rat: Impact of Behavioral States, Cortical Area, Lateralization and Light/Dark Phases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
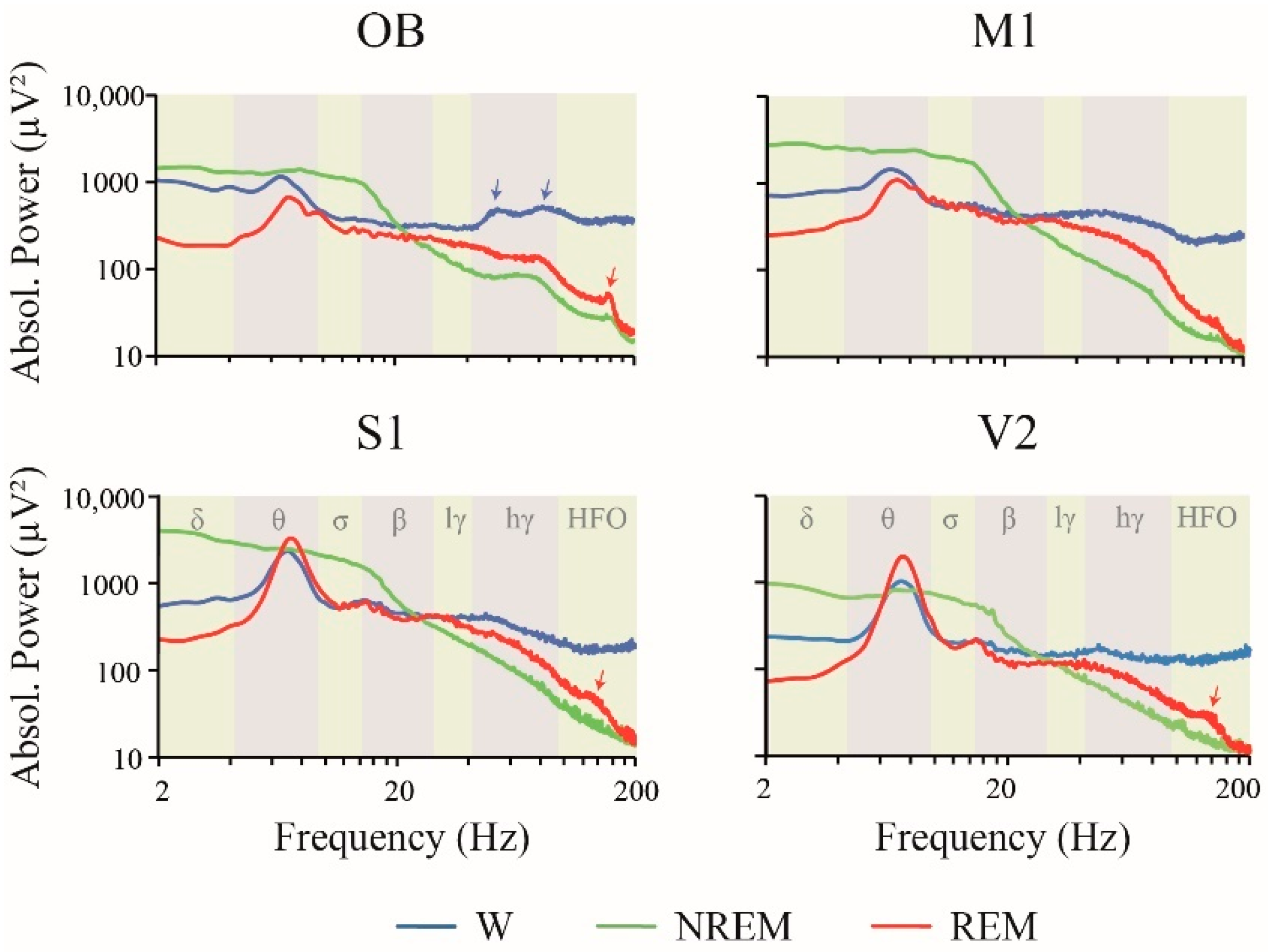
2.1. Power Spectrum: Effect of Behavioral States and Recording Site
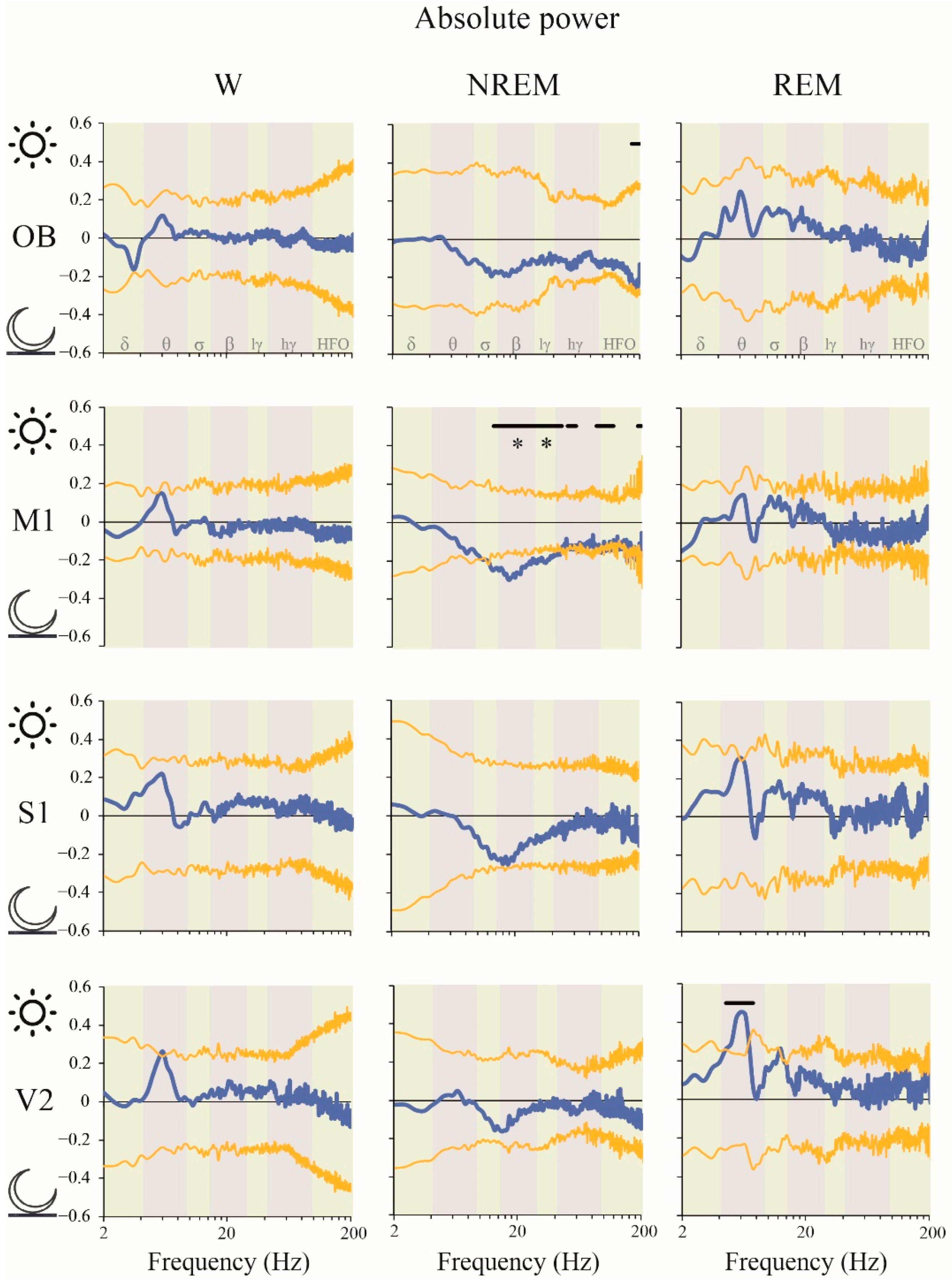
2.2. Power Spectrum: Light vs. Dark Phases
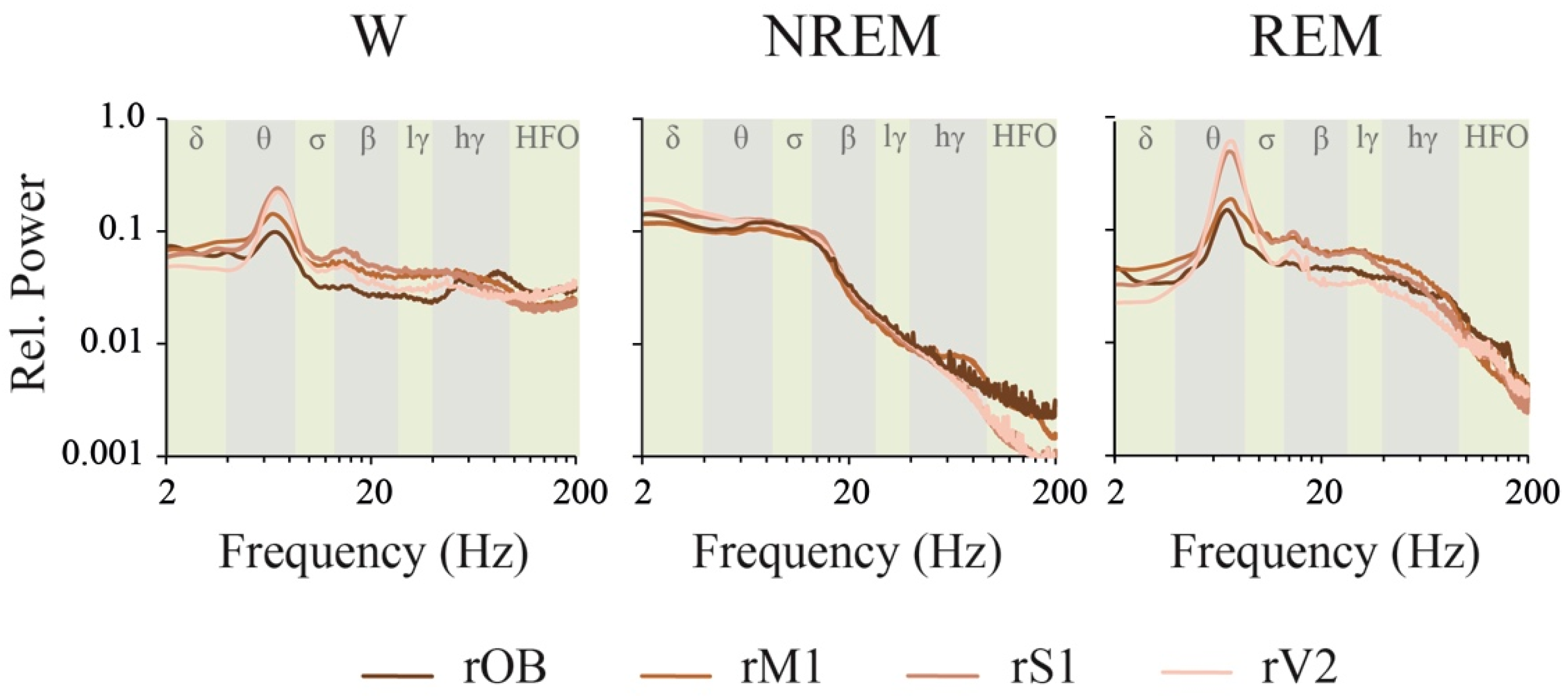
2.3. Power Spectrum: Right vs. Left Hemispheres
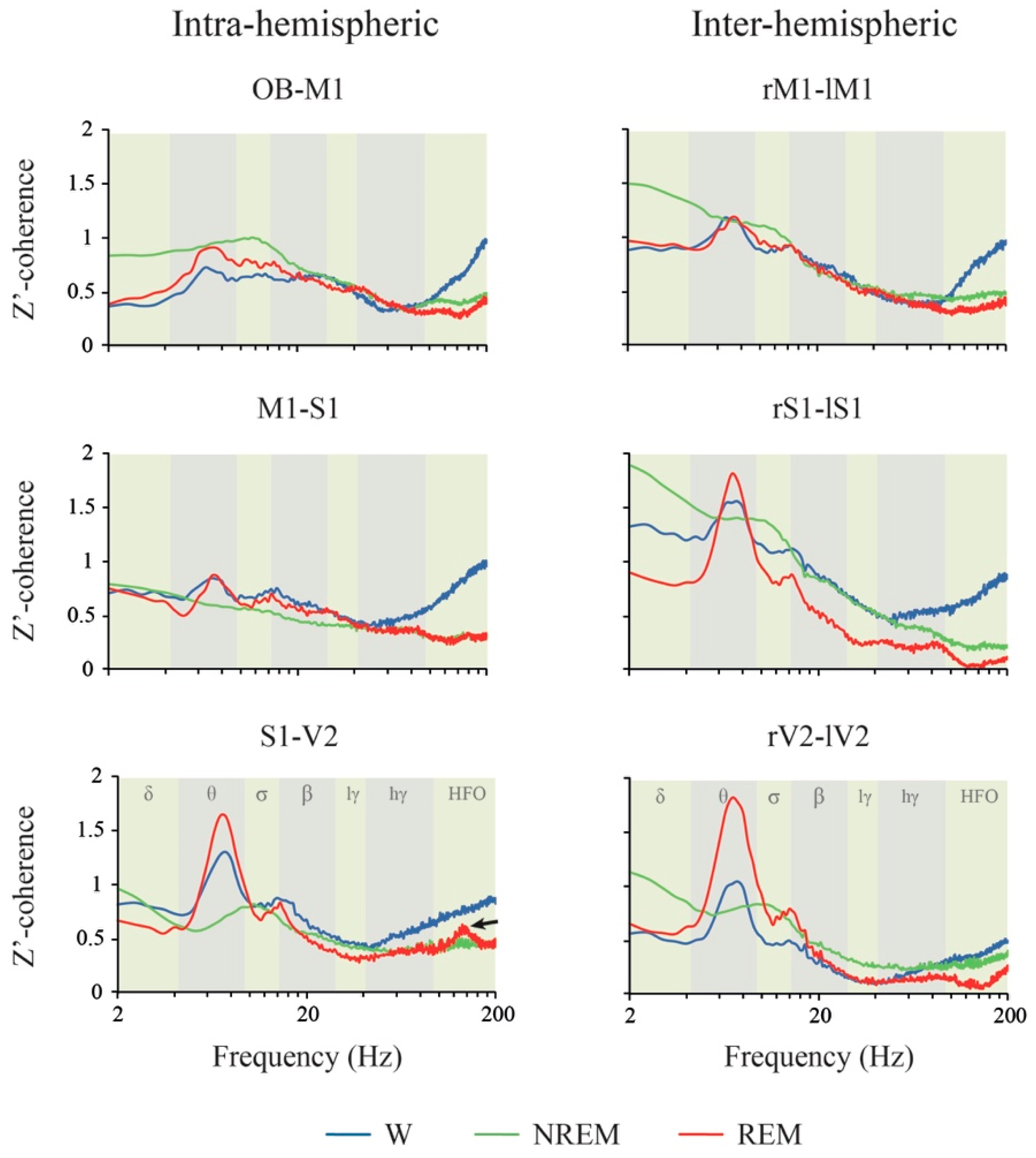
2.4. Coherence: Effects of Behavioral States and Derivations
2.5. Coherence: Light vs. Dark Phases
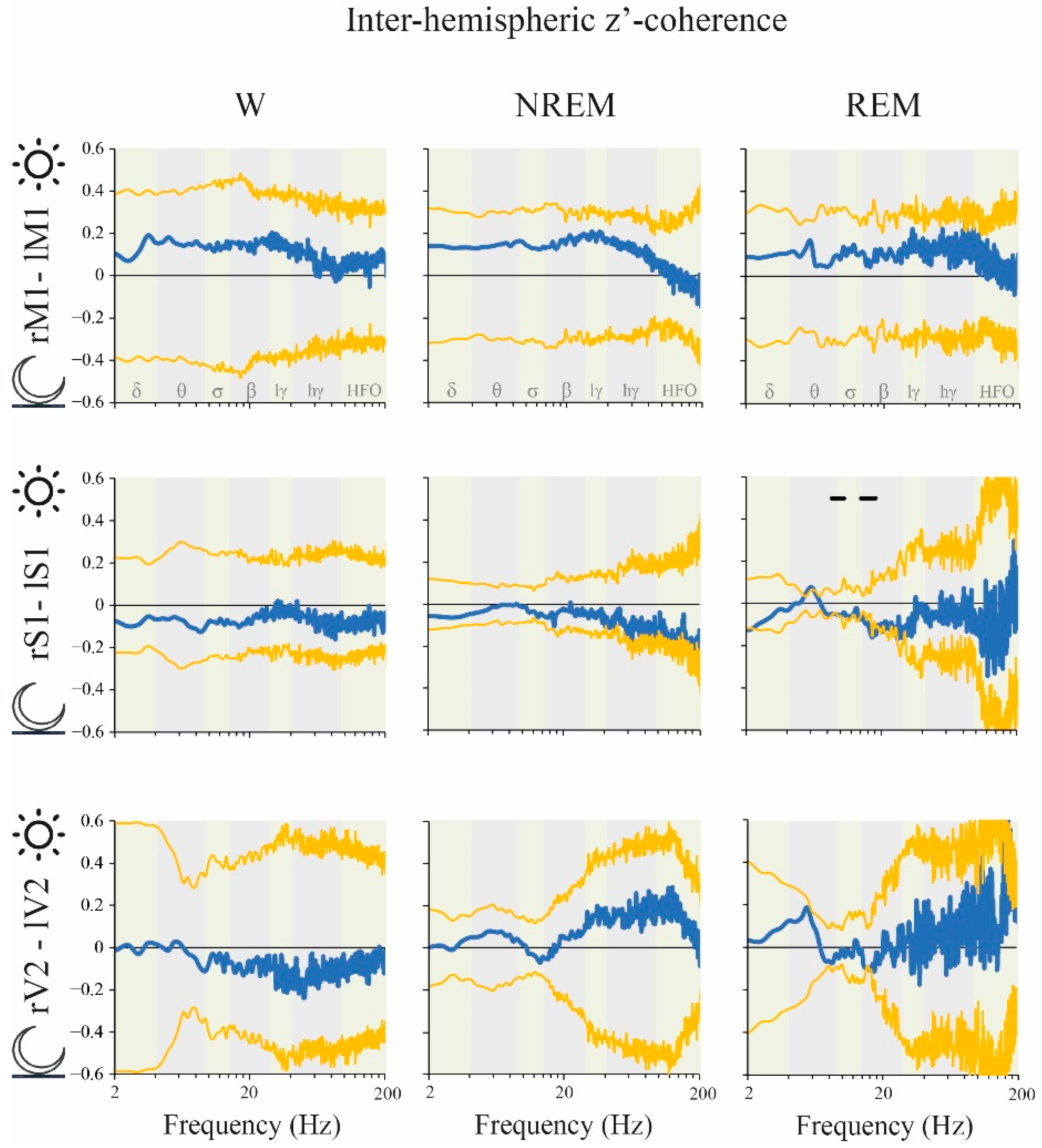
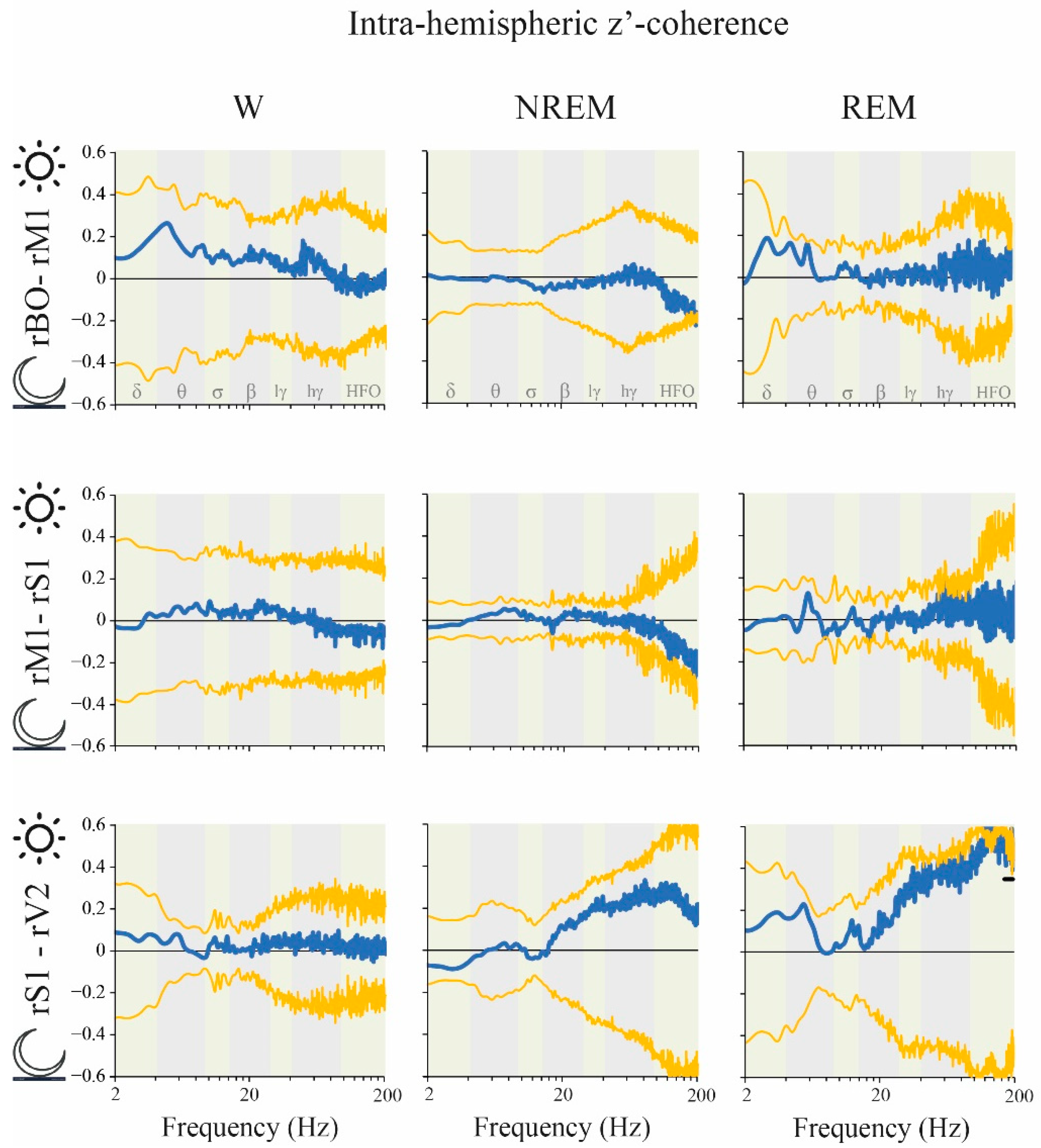
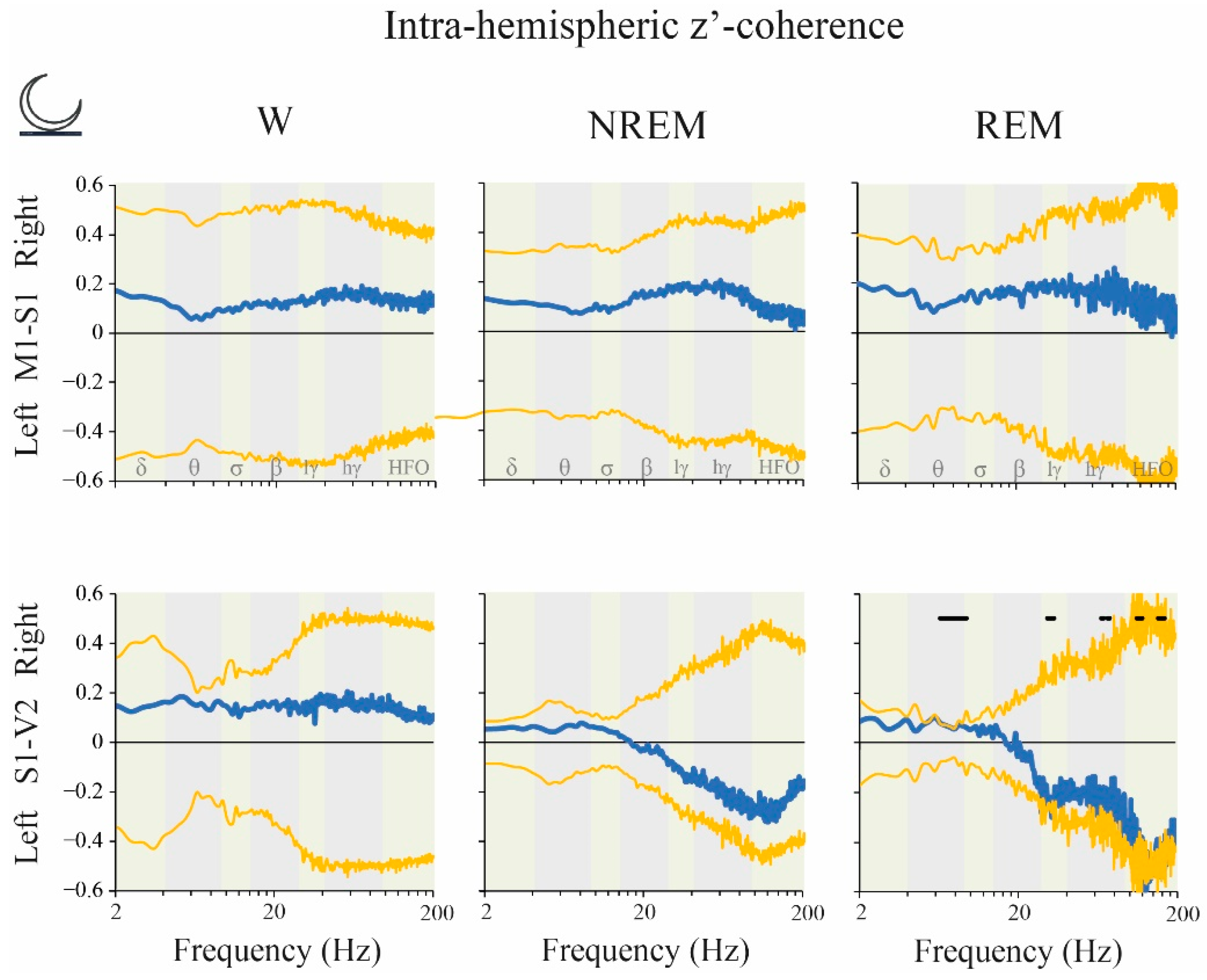
2.6. Coherence: Right vs. Left Hemispheres
3. Discussion
3.1. Technical Considerations
3.2. iEEG Power
3.3. iEEG Coherence
3.4. Impact of the Light/Dark Phases
3.5. Right/Left Hemispheric Differences in Electro-Cortical Activity
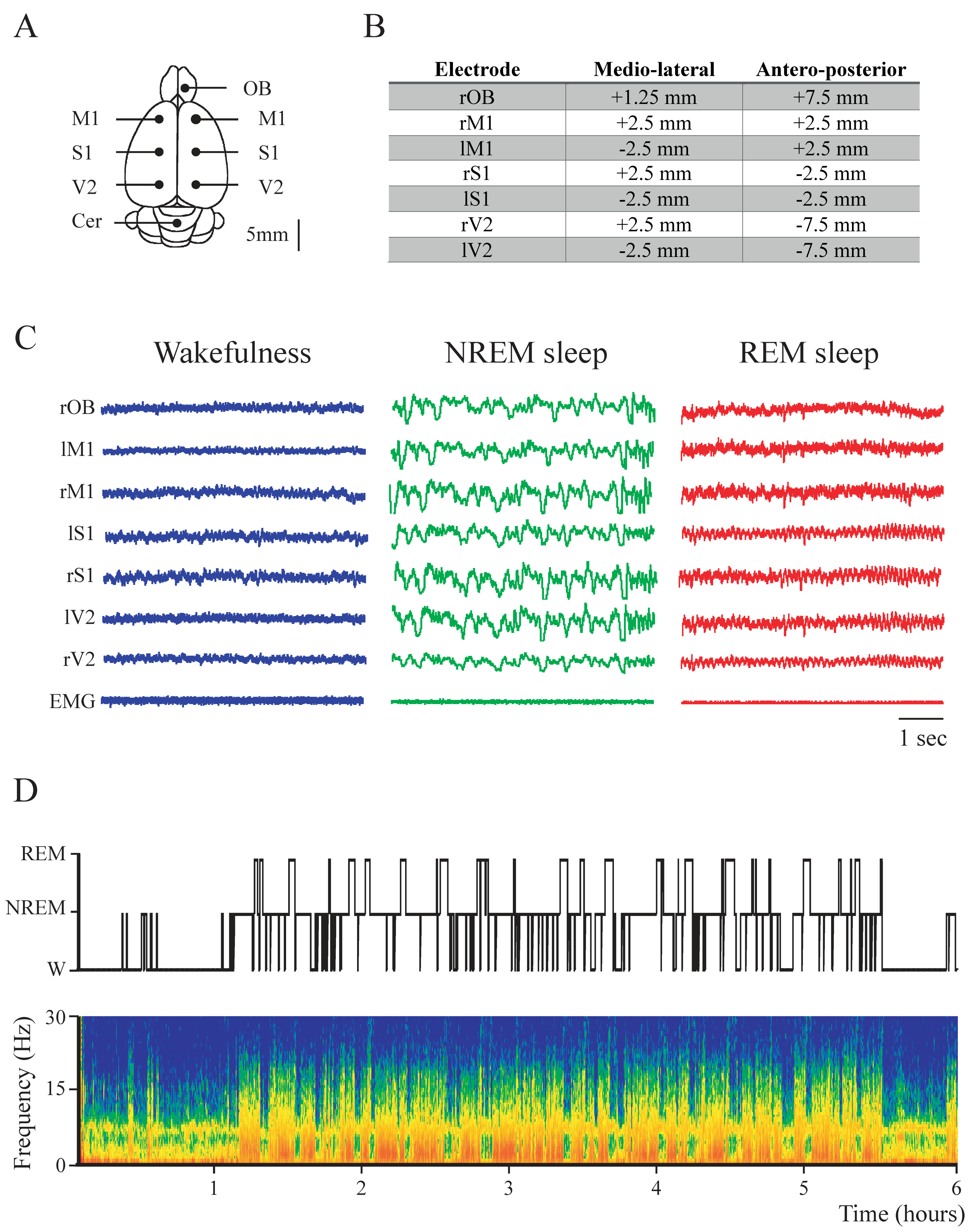
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Surgical Procedures
4.3. Sleep Recordings
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| iEEG | Intra-cranial electroencephalogram |
| HFO | High frequency oscillations |
| HG | High gamma |
| LG | Low gamma |
| M1 | Primary motor cortex |
| NREM | Non-REM |
| OB | Olfactory bulb |
| REM | Rapid eye movement |
| S1 | Primary somatosensory cortex |
| V2 | Secondary visual cortex |
| W | Wakefulness |
References
- Singer, W. Complexity as Substrate for Neuronal Computations. In Complexity and Analogy in Science; Libreria Editrice Vaticana: Vatican City, 2015; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, W. Binding by synchrony. Scholarpedia 2007, 2, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torterolo, P.; Castro-Zaballa, S.; Cavelli, M.; Gonzalez, J. Arousal and normal conscious cognition. In Arousal in Neurological and Psychiatric Diseases; Garcia-Rill, E., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade-Valenca, L.; Dubeau, F.; Mari, F.; Zelmann, R.; Gotman, J. High-Frequency Oscillations Recorded on Scalp EEG. Neurology 2011, 77, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besio, W.G.; Martinez-Juarez, I.E.; Makeyev, O.; Gaitanis, J.N.; Blum, A.S.; Fisher, R.S.; Medvedev, A.V. High-Frequency Oscillations Recorded on the Scalp of Patients With Epilepsy Using Tripolar Concentric Ring Electrodes. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2014, 2, 2000111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torterolo, P.; Monti, J.; Vanini, G. Neurochemistry and Pharmacology of Sleep. In The Behavioral, Molecular, Pharmacological, and Clinical Basis of the Sleep-Wake Cycle; Murillo, E., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 45–83. [Google Scholar]
- Steriade, M.; McCormick, D.A.; Sejnowski, T.J. Thalamocortical oscillations in the sleeping and aroused brain. Science 1993, 262, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tononi, G.; Laureys, S. (Eds.) The neurology of consciousness: An overview. In The Neurology of Consciousness: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuropathology; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 375–412. [Google Scholar]
- Crick, F.; Koch, C. Some reflections on visual awareness. In Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 55, pp. 953–962. [Google Scholar]
- Buzsaki, G.; Anastassiou, C.A.; Koch, C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents-EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavelli, M.; Castro-Zaballa, S.; Mondino, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Falconi, A.; Torterolo, P. Absence of EEG gamma coherence in a local activated neocortical state: A conserved trait of REM sleep. Transl. Brain Rhytm. 2017, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Achermann, P. EEG Analysis Applied to Sleep. Epileptologie 2009, 26, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwolf, C.H. Hippocampal electrical activity and voluntary movement in the rat. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1969, 26, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winson, J. Patterns of hippocampal theta rhythm in the freely moving rat. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1974, 36, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.R. The neurophysics of consciousness. Brain Res. Rev. 2002, 39, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, G.M.; Tononi, G. A Universe of Consciousness; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cantero, J.L.; Atienza, M.; Salas, R.M. Clinical value of EEG coherence as electrophysiological index of cortico-cortical connections during sleep. Rev. Neurol. 2000, 31, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siegel, M.; Donner, T.H.; Engel, A.K. Spectral fingerprints of large-scale neuronal interactions. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, S.; Falconi, A.; Chase, M.H.; Torterolo, P. Coherent neocortical 40-Hz oscillations are not present during REM sleep. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 37, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavelli, M.; Castro, S.; Schwarzkopf, N.; Chase, M.H.; Falconi, A.; Torterolo, P. Coherent neocortical gamma oscillations decrease during REM sleep in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 281, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavelli, M.; Rojas-Libano, D.; Schwarzkopf, N.; Castro-Zaballa, S.; Gonzalez, J.; Mondino, A.; Santana, N.; Benedetto, L.; Falconi, A.; Torterolo, P. Power and coherence of cortical high-frequency oscillations during wakefulness and sleep. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 2728–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achermann, P.; Borbely, A.A. Coherence analysis of the human sleep electroencephalogram. Neuroscience 1998, 85, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Wang, Y.; Fang, G.; Chen, M.; Xue, M.; Guo, D.; Yao, D.; Xia, Y. EEG Bands of Wakeful Rest, Slow-Wave and Rapid-Eye-Movement Sleep at Different Brain Areas in Rats. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazovskiy, V.V.; Tobler, I. Handedness leads to interhemispheric EEG asymmetry during sleep in the rat. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 99, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Swift, K.M.; Keus, K.; Echeverria, C.G.; Cabrera, Y.; Jimenez, J.; Holloway, J.; Clawson, B.C.; Poe, G.R. Sex differences within sleep in gonadally intact rats. Sleep 2020, 43, zsz289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, S.; Cavelli, M.; Vollono, P.; Chase, M.H.; Falconi, A.; Torterolo, P. Inter-hemispheric coherence of neocortical gamma oscillations during sleep and wakefulness. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 578, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyhus, E.; Curran, T. Functional role of gamma and theta oscillations in episodic memory. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahjoory, K.; Cesnaite, E.; Hohlefeld, F.U.; Villringer, A.; Nikulin, V.V. Power and temporal dynamics of alpha oscillations at rest differentiate cognitive performance involving sustained and phasic cognitive control. Neuroimage 2019, 188, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrden, A.; Chau, T. Feature clustering for robust frequency-domain classification of EEG activity. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 262, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrian, E.D. Olfactory reactions in the brain of the hedgehog. J. Physiol. 1942, 100, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavelli, M.; Castro-Zaballa, S.; Gonzalez, J.; Rojas-Libano, D.; Rubido, N.; Velasquez, N.; Torterolo, P. Nasal respiration entrains neocortical long-range gamma coherence during wakefulness. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 51, 1463–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Zhang, B.; Qin, Z.; Wang, P. Nasal Respiration is Necessary for the Generation of gamma Oscillation in the Olfactory Bulb. Neuroscience 2019, 398, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirota, A.; Montgomery, S.; Fujisawa, S.; Isomura, Y.; Zugaro, M.; Buzsaki, G. Entrainment of neocortical neurons and gamma oscillations by the hippocampal theta rhythm. Neuron 2008, 60, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.; Cavelli, M.; Mondino, A.; Rubido, N.; Tort, A.B.L.; Torterolo, P. Communication through coherence by means of cross-frequency coupling. Neuroscience 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Stenner, M.P.; Friston, K.J.; Dolan, R.J. Attentional modulation of alpha/beta and gamma oscillations reflect functionally distinct processes. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 16117–16125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, M.J.; Adams, N.E.; Sredniawa, W.; Wojcik, D.K.; Simon, A.; Kasicki, S.; Whittington, M.A. The olfactory bulb is a source of high-frequency oscillations (130–180 Hz) associated with a subanesthetic dose of ketamine in rodents. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, T.H.; McClune, M.C. Lateral coherence of the electrocorticogram: A new measure of brain synchrony. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1989, 73, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Silverstein, B.H.; Lee, H.; Mashour, G.A. Neural Correlates of Wakefulness, Sleep, and General Anesthesia: An Experimental Study in Rat. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio, L.; Mondino, A.; Cavelli, M.; Gonzalez, J.; Torterolo, P.; Costa, A. EEG power spectrum daily variations in sleep and wakefulness. Sleep Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazovskiy, V.V.; Borbely, A.A.; Tobler, I. Interhemispheric sleep EEG asymmetry in the rat is enhanced by sleep deprivation. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 88, 2280–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trachsel, L.; Tobler, I.; Achermann, P.; Borbely, A.A. Sleep continuity and the REM-nonREM cycle in the rat under baseline conditions and after sleep deprivation. Physiol. Behav. 1991, 49, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Hobson, J.A. The rat as an experimental model for sleep neurophysiology. Behav. Neurosci. 2000, 114, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, R.; Lim, J.; Famina, S.; Caron, A.M.; Dowse, H.B. Sleep-wake behavior in the rat: Ultradian rhythms in a light-dark cycle and continuous bright light. J. Biol. Rhythms 2012, 27, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poe, G.R. Sleep Is for Forgetting. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara, S.J. Sleep to Remember. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldyreva, G.N.; Zhavoronkova, L.A. Interhemispheric asymmetry of EEG coherence as a reflection of different functional states of the human brain. Biomed. Sci. 1991, 2, 266–270. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, D.; Hambrecht-Wiedbusch, V.S.; Silverstein, B.H.; Mashour, G.A. Electroencephalographic coherence and cortical acetylcholine during ketamine-induced unconsciousness. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidera, J.A.; Taylor, N.E.; Lee, J.T.; Vlasov, K.Y.; Pei, J.; Stephen, E.P.; Mayo, J.P.; Brown, E.N.; Solt, K. Sevoflurane Induces Coherent Slow-Delta Oscillations in Rats. Front. Neural Circuits 2017, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondino, A.; Cavelli, M.; Gonzalez, J.; Santana, N.; Castro-Zaballa, S.; Mechoso, B.; Bracesco, N.; Fernandez, S.; Garcia-Carnelli, C.; Castro, M.J.; et al. Acute effect of vaporized Cannabis on sleep and electrocortical activity. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 179, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.; Cavelli, M.; Mondino, A.; Pascovich, C.; Castro-Zaballa, S.; Torterolo, P.; Rubido, N. Decreased electrocortical temporal complexity distinguishes sleep from wakefulness. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: A practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegens, S.; Cousijn, H.; Wallis, G.; Harrison, P.J.; Nobre, A.C. Inter- and intra-individual variability in alpha peak frequency. Neuroimage 2014, 92, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.; Cavelli, M.; Castro-Zaballa, S.; Mondino, A.; Tort, A.B.L.; Rubido, N.; Carrera, I.; Torterolo, P. Gamma band alterations and REM-like traits underpin the acute effect of the atypical psychedelic ibogaine. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, J.; Nelson, L.; Simonsohn, U. A 21 word solution. Dialogue 2012, 26, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Frequency | Cortex | Behavioral State | Cortex × State | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | p | F | ηp2 | df | p | F | ηp2 | df | p | F | ηp2 | |
| Delta | 3, 30 | 0.0010 | 7.1 | 0.415 | 2, 20 | <0.0001 | 25.0 | 0.714 | 6, 57 | <0.0001 | 6.9 | 0.421 |
| Theta | 3, 30 | 0.0003 | 8.5 | 0.459 | 2, 20 | 0.0047 | 7.1 | 0.415 | 6, 57 | 0.0010 | 4.4 | 0.316 |
| Sigma | 3, 30 | 0.0003 | 8.5 | 0.459 | 2, 20 | <0.0001 | 24.6 | 0.711 | 6, 57 | 0.0608 | 2.2 | 0.188 |
| Beta | 3, 30 | <0.0001 | 12.6 | 0.557 | 2, 20 | 0.0488 | 3.5 | 0.259 | 6, 57 | 0.4312 | 1.0 | 0.095 |
| LG | 3, 30 | 0.0066 | 4.9 | 0.328 | 2, 20 | 0.0017 | 8.9 | 0.471 | 6, 57 | 0.5688 | 0.8 | 0.077 |
| HG | 3, 30 | 0.0001 | 9.8 | 0.495 | 2, 20 | <0.0001 | 59.2 | 0.855 | 6, 57 | <0.0001 | 15.5 | 0.620 |
| HFO | 3, 30 | 0.0002 | 9.0 | 0.474 | 2, 20 | <0.0001 | 57.9 | 0.852 | 6, 57 | 0.0007 | 4.6 | 0.326 |
| Frequency | Cortex | Behavioral State | Cortex × State | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | p | F | ηp2 | df | p | F | ηp2 | df | p | F | ηp2 | |
| Delta | 3, 30 | 0.5710 | 0.7 | 0.065 | 2, 20 | <0.0001 | 41.4 | 0.805 | 6, 57 | <0.0001 | 14.9 | 0.611 |
| Theta | 3, 30 | <0.0001 | 35.7 | 0.781 | 2, 20 | 0.0009 | 10.2 | 0.504 | 6, 57 | <0.0001 | 61.2 | 0.866 |
| Sigma | 3, 30 | 0.0005 | 8.0 | 0.444 | 2, 20 | <0.0001 | 15.9 | 0.613 | 6, 57 | 0.2353 | 1.4 | 0.128 |
| Beta | 3, 30 | 0.0389 | 3.2 | 0.242 | 2, 20 | 0.0084 | 6.1 | 0.379 | 6, 57 | 0.0166 | 2.9 | 0.233 |
| LG | 3, 30 | 0.0544 | 2.8 | 0.219 | 2, 20 | <0.0001 | 26.8 | 0.728 | 6, 57 | <0.0001 | 4.4 | 0.316 |
| HG | 3, 30 | 0.0162 | 4.0 | 0.286 | 2, 20 | <0.0001 | 22.5 | 0.692 | 6, 57 | 0.0213 | 2.7 | 0.221 |
| HFO | 3, 30 | 0.0052 | 5.2 | 0.342 | 2, 20 | <0.0001 | 33.6 | 0.770 | 6, 57 | 0.1817 | 1.5 | 0.136 |
| State | Comparison | Delta | Theta | Sigma | Beta | LG | HG | HFO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | OB vs. M1 | 0.9621 | 0.8365 | 0.2279 | 0.7908 | 0.0485 | 0.9294 | 0.0334 |
| OB vs. S1 | 0.6436 | 0.0452 | 0.0613 | 0.0274 | 0.0494 | 0.0366 | 0.0014 | |
| OB vs. V2 | 0.2194 | 0.1459 | 0.6616 | 0.7521 | 0.7853 | 0.0173 | 0.9786 | |
| M1 vs. S1 | 0.9897 | 0.4926 | 0.9954 | 0.4594 | >0.9999 | 0.3488 | 0.9120 | |
| M1 vs. V2 | 0.7637 | 0.8360 | 0.9809 | >0.9999 | 0.5783 | 0.2254 | 0.1934 | |
| S1 vs. V2 | 0.9919 | 0.9958 | 0.7595 | 0.4585 | 0.5776 | >0.9999 | 0.0137 | |
| NREM | OB vs. M1 | 0.6010 | 0.9957 | 0.2926 | 0.1330 | >0.9999 | 0.9631 | 0.9925 |
| OB vs. S1 | 0.0054 | <0.0001 | >0.9999 | 0.9986 | >0.9999 | 0.9711 | 0.9987 | |
| OB vs. V2 | 0.8876 | 0.09998 | 0.9974 | >0.9999 | 0.9998 | 0.9986 | >0.9999 | |
| M1 vs. S1 | 0.2591 | <0.0001 | 0.4462 | 0.3735 | >0.9999 | >0.9999 | >0.9999 | |
| M1 vs. V2 | 0.9983 | 0.9957 | 0.6233 | 0.0928 | 0.9998 | 0.9994 | 0.9944 | |
| S1 vs. V2 | 0.0970 | <0.0001 | 0.9999 | 0.9931 | >0.9999 | 0.9996 | 0.9991 | |
| REM | OB vs. M1 | 0.9979 | 0.7428 | 0.0018 | 0.0698 | 0.0872 | >0.9999 | 0.2567 |
| OB vs. S1 | 0.5279 | <0.0001 | 0.0318 | 0.0130 | >0.9999 | 0.1355 | 0.4773 | |
| OB vs. V2 | 0.2539 | <0.0001 | 0.9989 | 0.6463 | 0.0977 | 0.0106 | 0.4965 | |
| M1 vs. S1 | 0.8384 | 0.0001 | 0.9651 | 0.9854 | 0.1181 | 0.0787 | 0.9999 | |
| M1 vs. V2 | 0.5548 | <0.0001 | 0.0072 | 0.8287 | <0.0001 | 0.0051 | 0.9993 | |
| S1 vs. V2 | 0.9994 | 0.3830 | 0.0930 | 0.3875 | 0.1020 | 0.9561 | >0.9999 |
| Frequency | Derivation | Behavioral State | Derivation × State | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | p | F | ηp2 | df | p | F | ηp2 | df | p | F | ηp2 | |
| Delta | 5, 50 | 0.0411 | 2.5 | 0.200 | 2, 20 | <0.0001 | 23.1 | 0.698 | 10, 82 | 0.0121 | 2.5 | 0.233 |
| Theta | 5, 50 | 0.0423 | 2.5 | 0.200 | 2, 20 | 0.0015 | 9.2 | 0.479 | 10, 82 | <0.0001 | 10.7 | 0.566 |
| Sigma | 5, 50 | 0.1992 | 1.5 | 0.130 | 2, 20 | 0.0221 | 4.6 | 0.315 | 10, 82 | 0.0018 | 3.2 | 0.280 |
| Beta | 5, 50 | 0.3609 | 1.86 | 0.157 | 2, 20 | 0.0356 | 3.9 | 0.280 | 10, 82 | 0.0129 | 2.4 | 0.226 |
| LG | 5, 50 | 0.3687 | 1.1 | 0.099 | 2, 20 | 0.0058 | 6.7 | 0.401 | 10, 82 | 0.0094 | 2.6 | 0.240 |
| HG | 5, 50 | 0.2258 | 1.4 | 0.123 | 2, 20 | 0.0004 | 11.7 | 0.539 | 10, 82 | <0.0001 | 4.3 | 0.344 |
| HFO | 5, 50 | 0.0600 | 2.3 | 0.187 | 2, 20 | <0.0001 | 32.1 | 0.762 | 10, 82 | <0.0001 | 5.5 | 0.401 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mondino, A.; Cavelli, M.; González, J.; Osorio, L.; Castro-Zaballa, S.; Costa, A.; Vanini, G.; Torterolo, P. Power and Coherence in the EEG of the Rat: Impact of Behavioral States, Cortical Area, Lateralization and Light/Dark Phases. Clocks & Sleep 2020, 2, 536-556. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep2040039
Mondino A, Cavelli M, González J, Osorio L, Castro-Zaballa S, Costa A, Vanini G, Torterolo P. Power and Coherence in the EEG of the Rat: Impact of Behavioral States, Cortical Area, Lateralization and Light/Dark Phases. Clocks & Sleep. 2020; 2(4):536-556. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep2040039
Chicago/Turabian StyleMondino, Alejandra, Matías Cavelli, Joaquín González, Lucía Osorio, Santiago Castro-Zaballa, Alicia Costa, Giancarlo Vanini, and Pablo Torterolo. 2020. "Power and Coherence in the EEG of the Rat: Impact of Behavioral States, Cortical Area, Lateralization and Light/Dark Phases" Clocks & Sleep 2, no. 4: 536-556. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep2040039
APA StyleMondino, A., Cavelli, M., González, J., Osorio, L., Castro-Zaballa, S., Costa, A., Vanini, G., & Torterolo, P. (2020). Power and Coherence in the EEG of the Rat: Impact of Behavioral States, Cortical Area, Lateralization and Light/Dark Phases. Clocks & Sleep, 2(4), 536-556. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep2040039






