Comparative Study of Chloride and Fluoride Induced Aluminum Pad Corrosion in Wire-Bonded Device Packaging Assembly
Abstract
:1. Introduction
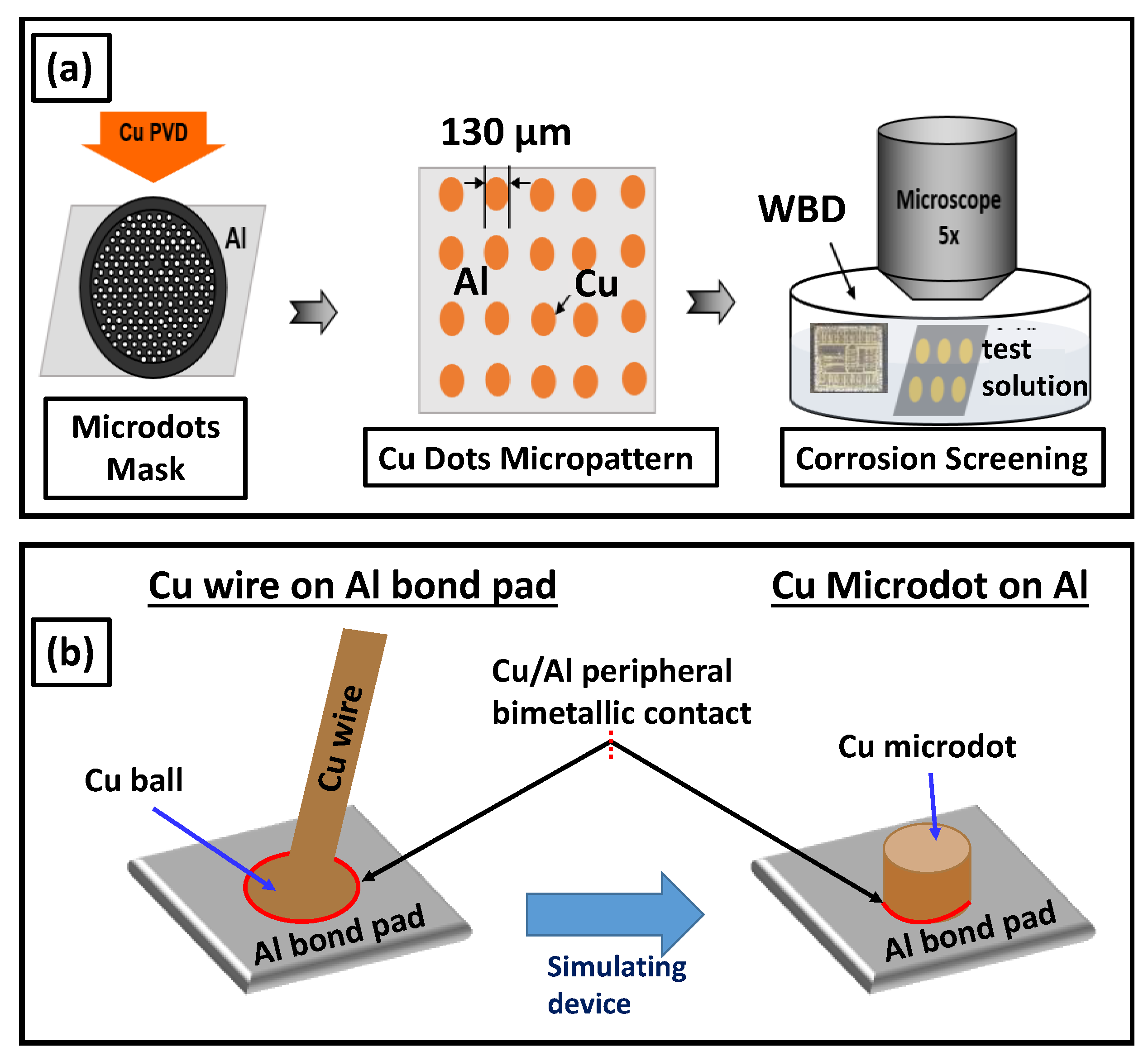
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Halide-Induced Corrosion on Blanket Al in the Absence of Cu Bimetallic Contact
3.1.1. SEM and EDS Investigation of the Corroded Blanket Al Samples
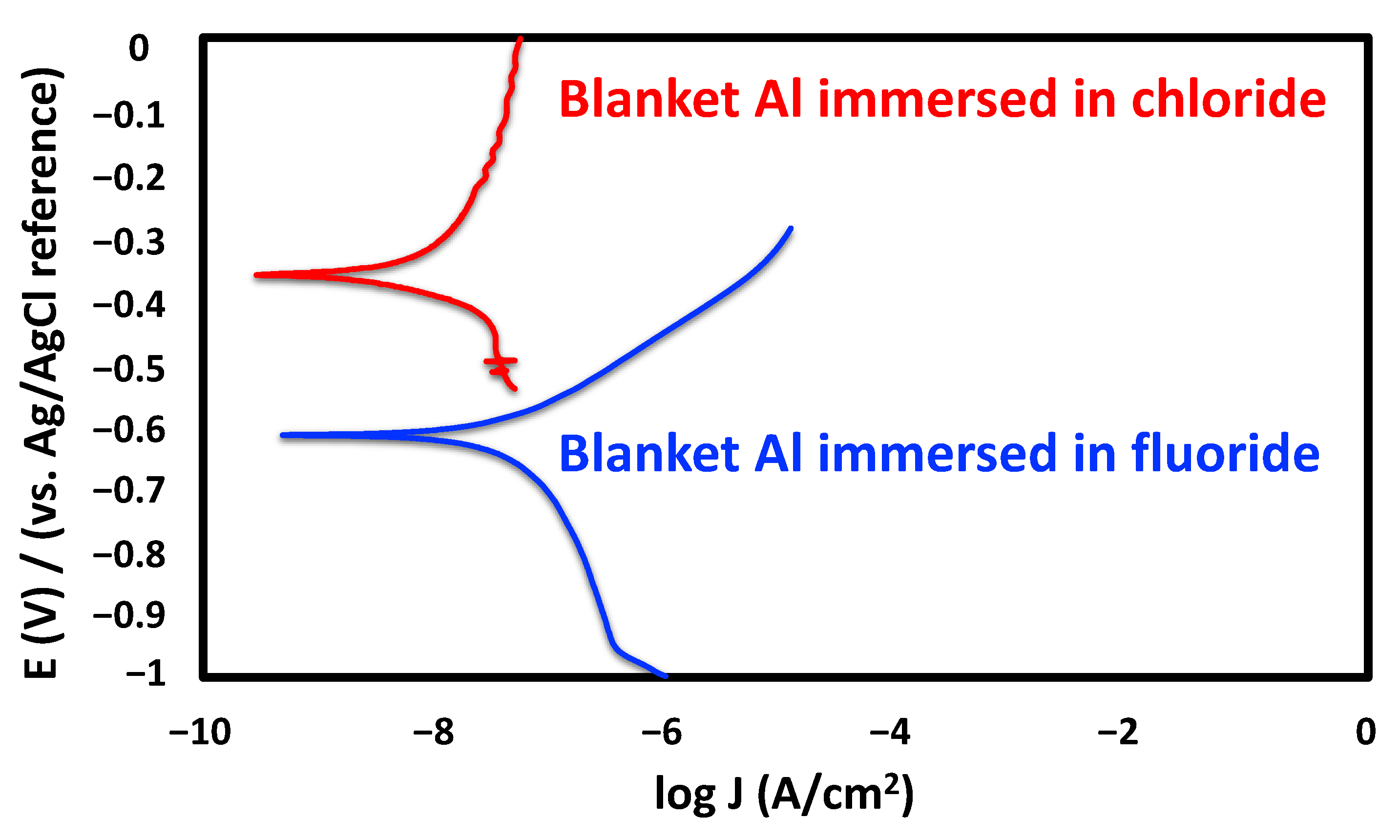
3.1.2. Electrochemical Characterization Studies
3.2. Halide-Induced Corrosion of Al with Bimetallic Contact to Cu
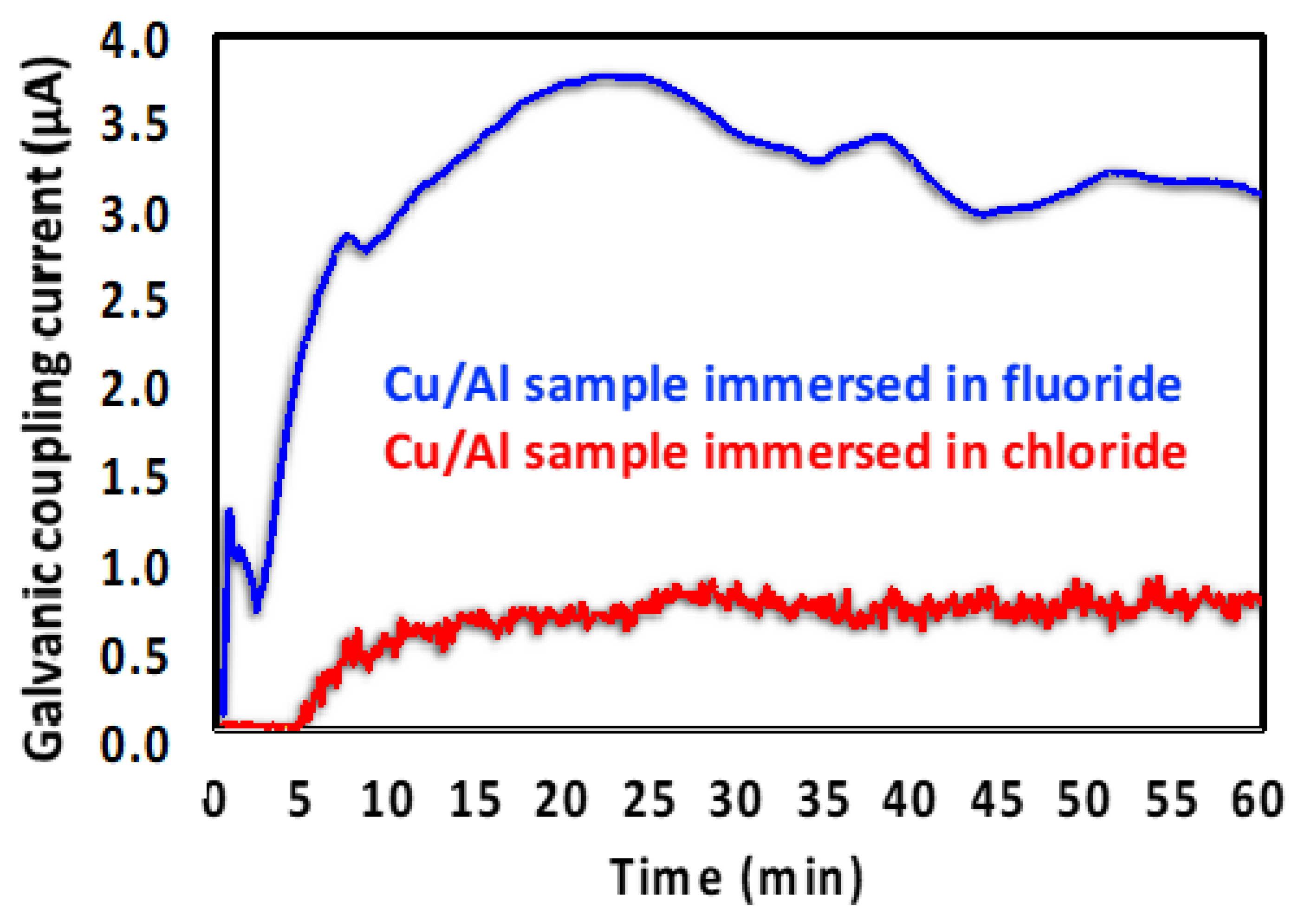
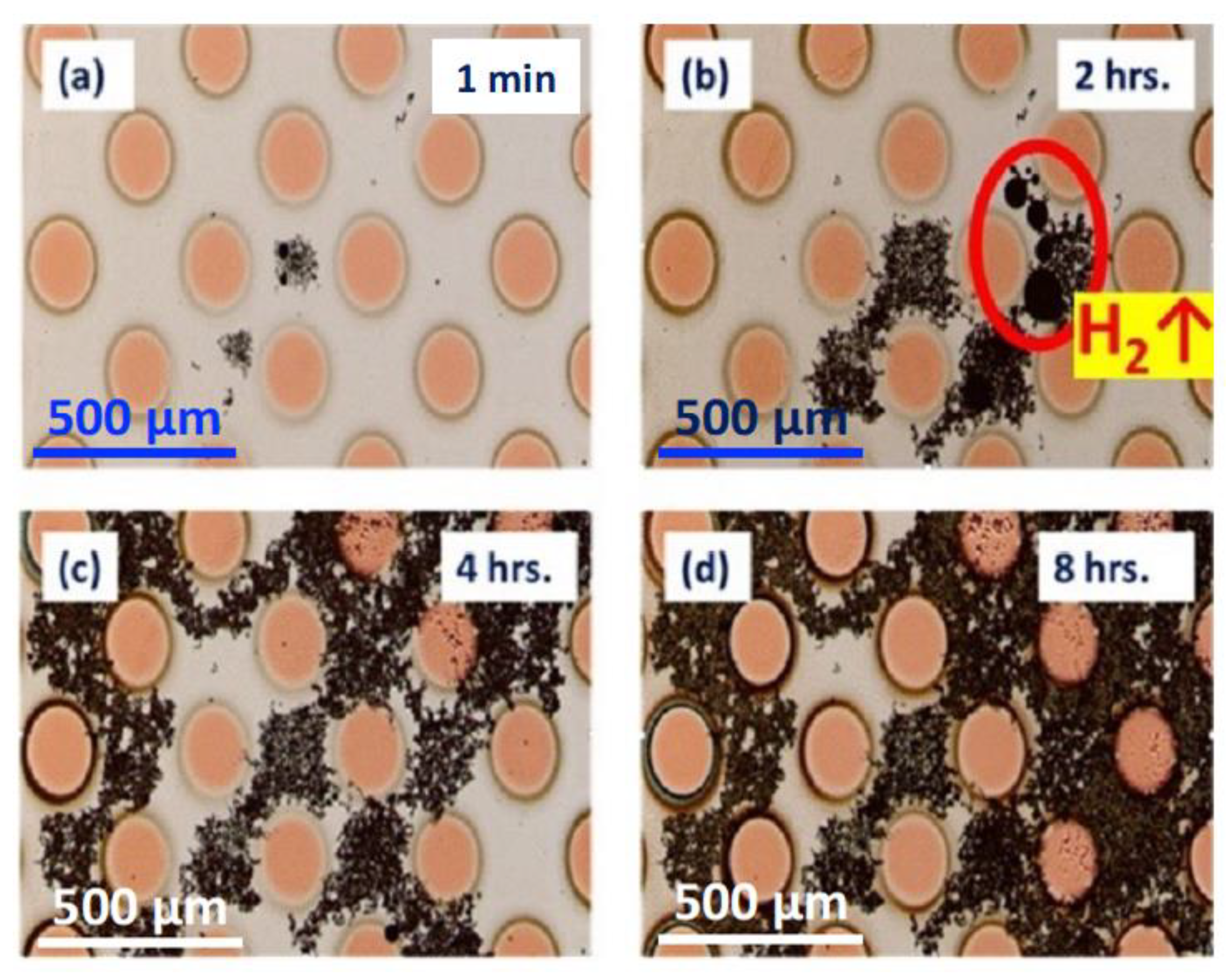
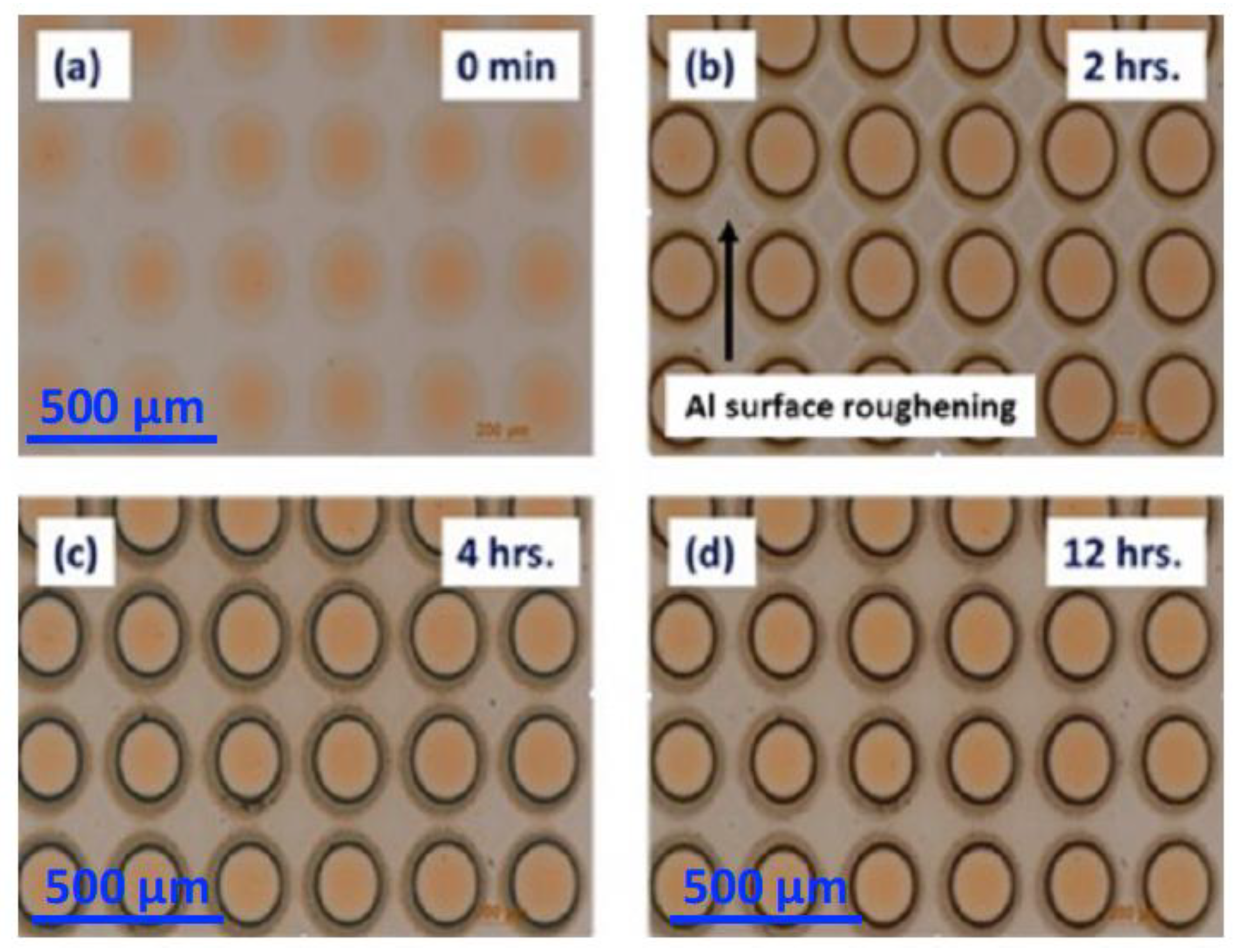
3.2.1. SEM and EDS Investigation of the Corroded Micropattern Cu/Al Samples
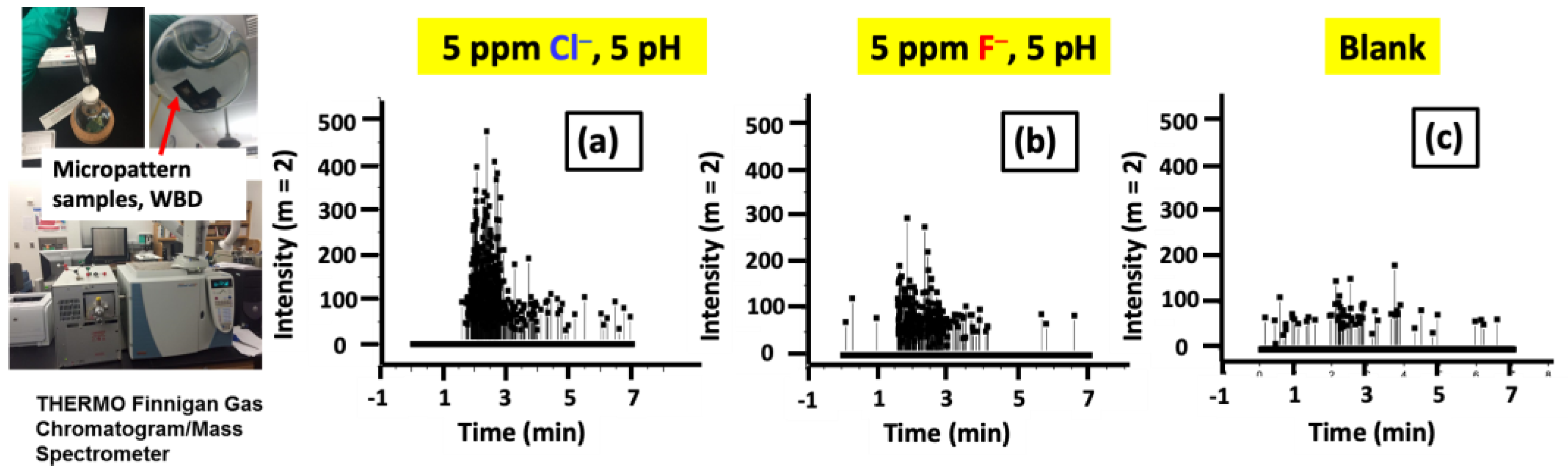
3.2.2. GC–MS Investigation of the Gas Evolution in Microdot Samples
3.3. Halide-Induced Real-Time Corrosion Investigation of WBD
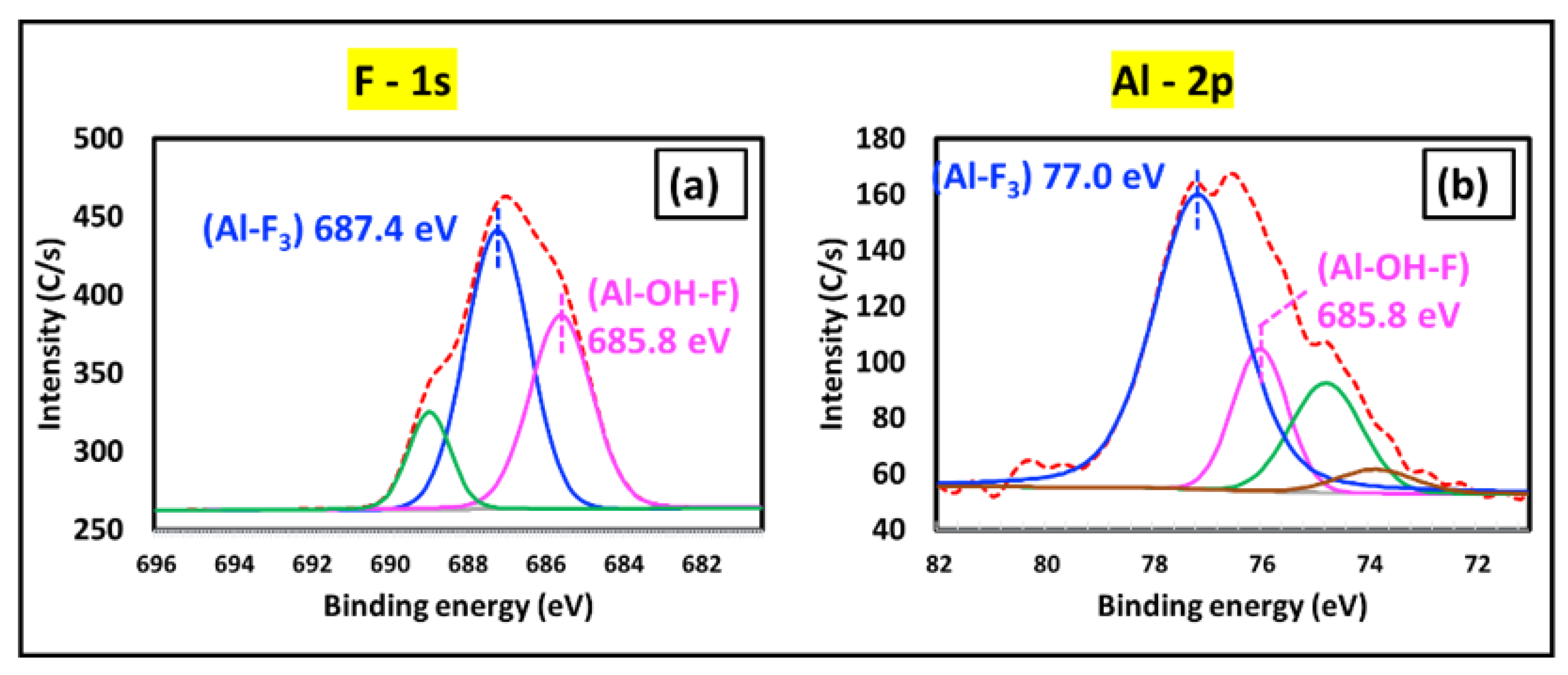
XPS Analysis of the Corroded Al Bond Pad
4. Discussion
Corrosion Mechanism Comparison of Cl− vs. F−
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gan, C.L.; Hashim, U. Evolutions of bonding wires used in semiconductor electronics: Perspective over 25 years. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 4412–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Then, E. Corrosion Behavior of Cu-Al Intermetallic Compounds in Copper Wire Bonding in Chloride-Containing Accelerated Humidity Testing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 66th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 May–3 June 2016; pp. 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-W.; Lee, C.C. A corrosion study of Ag–Al intermetallic compounds in chlorine-containing epoxy molding compounds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 15739–15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Nistala, R.R.; Zhao, S.; Xu, J. A method to simulate fluorine outgas and Al bond pad corrosion in wafer fab. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits (IPFA), Singapore, 18–21 July 2016; pp. 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younan, H.; Xiang, X.Z.; Xiaomin, L. Characterization studies of fluorine-induced corrosion crystal defects on microchip Al bondpads using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 21th International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits (IPFA), Singapore, 30 June–4 July 2014; pp. 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Mathew, V.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Han, M.C.; Song, Y.; Descartin, A.M. A New Finding of Cu-Al IMC Corrosion and Investigation of Fluorine Contamination Influence on Cu-Al IMC Corrosion. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT), Hong Kong, China, 11–15 August 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrah, H.; Slavek, J.; Pickering, W. Fluoride interactions with hydrous aluminum oxides and alumina. Soil Res. 1987, 25, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proost, J.; Baklanov, M.; Verbeeck, R.; Maex, K. Morphology of corrosion pits in aluminum thin film metallizations. J. Solid State Electrochem. 1998, 2, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loto, R.T. Investigation of the Localized Corrosion Resistance of 4044 Aluminum Alloy in Acid Chloride and Neutral Chloride Solutions. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2018, 18, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, P.; Luo, Y.; Nguyen, L. Chlorine-Ion Related Corrosion in Cu-Al Wirebond Microelectronic Packages. In International Electronic Packaging Technical Conference and Exhibition; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2015; p. V002T02A012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, V.; Wikramanayake, E.; Chopin, S.F. Corrosion of Copper Wire bonded Packages by Chlorine Containing Foreign Particles. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 70th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA; 2020; pp. 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.J.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Hua, Y.; Fu, C.; Tee, W.; Yee, B.; Wang, B.; Mao, S. Comprehensive study of wire bond reliability impacts from wire, molding compound and bond pad contamination. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on IC Design and Technology (ICICDT), Suzhou, China, 17–19 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, T. Bond reliability under humid environment for coated copper wire and bare copper wire. Microelectron. Reliab. 2011, 51, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Zhong, Z.W.; Pecht, M. Copper Wire Bonding Concerns and Best Practices. J. Electron. Mater. 2013, 42, 2415–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Bai, K.; Jin, H. Thermodynamic study on the corrosion mechanism of copper wire bonding. Microelectron. Reliab. 2013, 53, 985–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, N.; Asokan, M.; Kumar, G.I.A.; Caperton, J.; Alptekin, J.; Salunke, A.S.; Chyan, O.M. Mechanistic study of copper wire-bonding failures on packaging devices in acidic chloride environments. Microelectron. Reliab. 2020, 113, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.I.A.; Alptekin, J.; Caperton, J.; Salunke, A.; Chyan, O. Accelerated reliability testing of Cu-Al bimetallic contact by a micropattern corrosion testing platform for wire bond device application. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiconductor Epoxy Mold Compounds. Available online: https://www.caplinq.com/semiconductor-epoxy-mold-compounds.html (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Moreno-López, J.C.; Ruano, G.; Ferrón, J.; Ayala, P.; Passeggi, M.C.G. Thermally Annealed Sub-Monolayers of AlF 3 on Cu(100): An STM and XPS Study. Phys. Status Solidi B 2018, 255, 1800389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chastain, J.; Moulder, J.F. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: A Reference Book of Standard Spectra for Identification and Interpretation of Xps Data; Physical Electronics Inc.: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1995; pp. 230–232. ISBN 0-9648124-1-X. [Google Scholar]
- Roodenko, K.; Halls, M.; Gogte, Y.; Seitz, O.; Veyan, J.-F.; Chabal, Y.J. Nature of Hydrophilic Aluminum Fluoride and Oxyaluminum Fluoride Surfaces Resulting from XeF2 Treatment of Al and Al2O3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 21351–21357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Cooper, W.C.; Pascual, R.; Saimoto, S. Effect of fluoride ions on the corrosion of aluminium in sulphuric acid and zinc electrolyte. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1991, 21, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Guan, X.; Su, T.; Gao, N.; Wang, J. Fluoride adsorption onto activated alumina: Modeling the effects of pH and some competing ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 337, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidell, A. Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds, 2nd ed.; D Van Nostrand Company: New York, NY, USA, 1919; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Millipore Sigma. Safety Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/sds/SIGMA/A8205 (accessed on 16 June 2021).
- Cowley, J.M.; Scott, T.R. Basic Fluorides of Aluminum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1948, 70, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P.; Paula, J. Chemical Equilibrium: Electrochemistry. In Elements of Physical Chemistry, 5th ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Chapter 9; p. 212. [Google Scholar]
- Curioni, M.; Scenini, F. The Mechanism of Hydrogen Evolution During Anodic Polarization of Aluminium. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 180, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrublevsky, I.; Parkoun, V.; Sokol, V.; Schreckenbach, J.; Marx, G. The study of the volume expansion of aluminum during porous oxide formation at galvanostatic regime. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 222, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

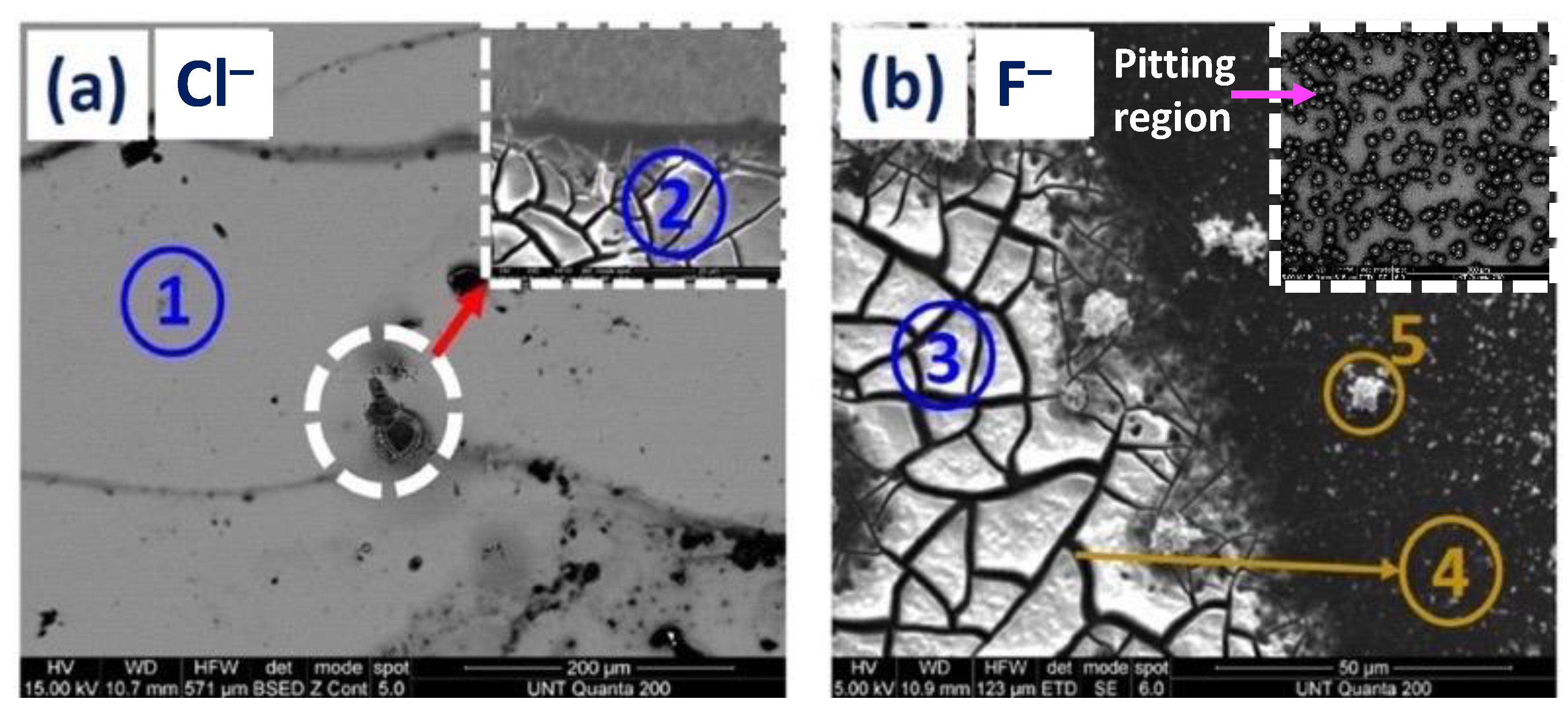
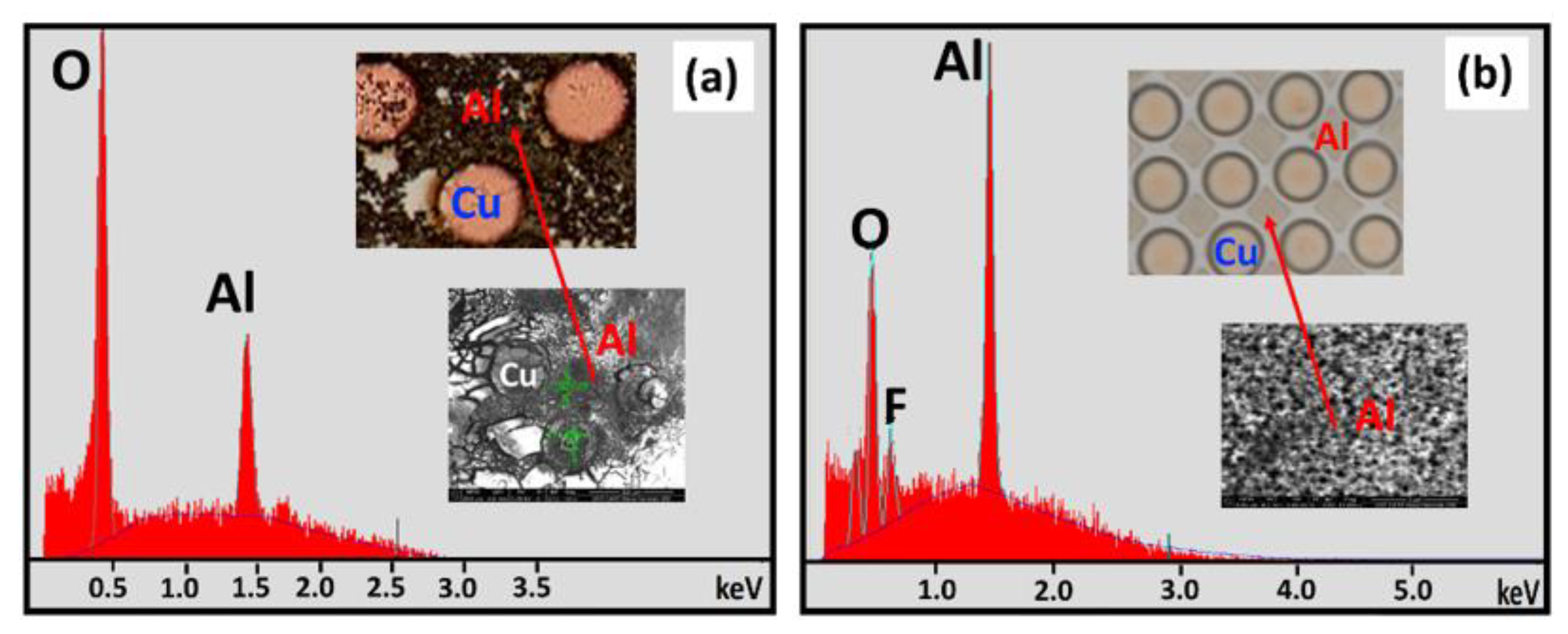



| Figure Number | EDX Spot Number | Area Description | Al Atomic % | O Atomic % | Cl Atomic % | F Atomic % | Si Atomic % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5a. | 1 | Al surface | 94.9 | 5.0 | --- | --- | 0.0 |
| 5a. | 2 | Cl−—mud crack island | 45.8 | 48.9 | --- | --- | 0.0 |
| 5b. | 5 | F−—surface precipitate | 36.5 | 57.0 | --- | 6.5 | 0.0 |
| 5b. | 3 | F−—mud crack island | 38.0 | 46.5 | --- | 15.5 | 0.0 |
| 5b. | 4 | F−—crack region between two islands | 13.7 | 17.4 | --- | 0.5 | 67.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashok Kumar, G.I.; Lambert, A.; Caperton, J.; Asokan, M.; Yi, W.; Chyan, O. Comparative Study of Chloride and Fluoride Induced Aluminum Pad Corrosion in Wire-Bonded Device Packaging Assembly. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2021, 2, 447-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2030023
Ashok Kumar GI, Lambert A, Caperton J, Asokan M, Yi W, Chyan O. Comparative Study of Chloride and Fluoride Induced Aluminum Pad Corrosion in Wire-Bonded Device Packaging Assembly. Corrosion and Materials Degradation. 2021; 2(3):447-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshok Kumar, Goutham Issac, Alexander Lambert, Joshua Caperton, Muthappan Asokan, William Yi, and Oliver Chyan. 2021. "Comparative Study of Chloride and Fluoride Induced Aluminum Pad Corrosion in Wire-Bonded Device Packaging Assembly" Corrosion and Materials Degradation 2, no. 3: 447-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2030023
APA StyleAshok Kumar, G. I., Lambert, A., Caperton, J., Asokan, M., Yi, W., & Chyan, O. (2021). Comparative Study of Chloride and Fluoride Induced Aluminum Pad Corrosion in Wire-Bonded Device Packaging Assembly. Corrosion and Materials Degradation, 2(3), 447-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2030023





