Abstract
Carboxylato-bridged dinuclear and tetranuclear Mn(II) complexes 1–3 with ditopic ligands featuring two N3-terminal coordination sites connected by hexyl (tphn), octyl (tpon), and p-xylyl (tpxn) linkers have been synthesized and characterized through X-ray single-crystal structure analyses, infrared spectroscopy, and elemental analyses. Complex 1 is a μ-fluorido-bis-μ-acetato dinuclear Mn(II) complex where the ligand tphn coordinates to both terminal sides of a dinuclear Mn unit. In contrast, complexes 2 and 3 are tetranuclear Mn(II) complexes with a macrocyclic structure, in which two dinuclear Mn units are linked by ligands tpon or tpxn. The redox behaviors of 1 and 2 were elucidated by cyclic voltammetry, revealing two metal-centered redox processes corresponding to Mn2(II,II)/Mn2(II,III) and Mn2(II,III)/Mn2(III,III).
1. Introduction
Manganese complexes with μ-carboxylato bridges have been extensively studied in a wide range of fields, including magnetic materials, catalysis, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), and bioinorganic chemistry, due to various chemical and physical properties, which depend on changes in the oxidation states of Mn ions and the bridging ligands [1,2,3,4]. In these studies, carboxylates exhibit a variety of bridging modes. The bridges observed between two manganese ions include single [5,6], double [7,8], and triple bridges [9,10]. Not only does the number of bridges vary, but also the bridging modes of carboxylates themselves and the formation of mixed bridges combined with other bridging ligands provide a wide range of variations [11]. For example, the well-known Mn12 cluster, a single-molecule magnet, is a multinuclear manganese complex with multiple syn-syn-type carboxylates and oxo ions, and the metal core structure, including this bridging style, significantly contributes to its single-molecule magnet (SMM) properties [12]. Additionally, metalloenzymes such as arginase and manganese catalase have a dinuclear manganese active center bridged by carboxylates with both μ-O,O′ and μ-O bridging modes, and the flexibility of carboxylato bridging may contribute to enzyme function [13,14].
Dinuclear manganese complexes are often studied from a bioinorganic chemistry perspective, and many types of dinuclear manganese complexes have been reported as catalase model complexes [15]. However, unlike the Mn(III) complexes of the same type, which progress catalytic reactions via the Mn2(II,II)/Mn2(III,III) redox cycle similar to enzymes, μ-carboxylato dinuclear Mn(II) complexes have fewer reported examples due to their stability in air and labile activity of Mn(II) ions [16]. Most of these complexes have structures in which bidentate or tridentate terminal ligands are coordinated to fill the coordination sites on both sides of the carboxylate-bridged dinuclear manganese structure [17]. Due to the properties of labile Mn(II) ions, such complexes are expected to have limited catalytic activity in solution because the bridging structure cannot be maintained. To suppress the dissociation of the dinuclear structure, many complexes using dinucleating ligands that include phenoxo or alkoxo moieties in the ligand structure have been reported [18]. However, in these structures, the dissociation of phenoxo or alkoxo bridges is unlikely, so it cannot faithfully mimic the reaction mechanisms of arginase or Mn-catalase. Therefore, attempts have been made to stabilize the bridging structure and improve catalytic reaction efficiency by connecting terminal ligands on both sides of the dinuclear unit with a linker to form a cyclic structure [19].
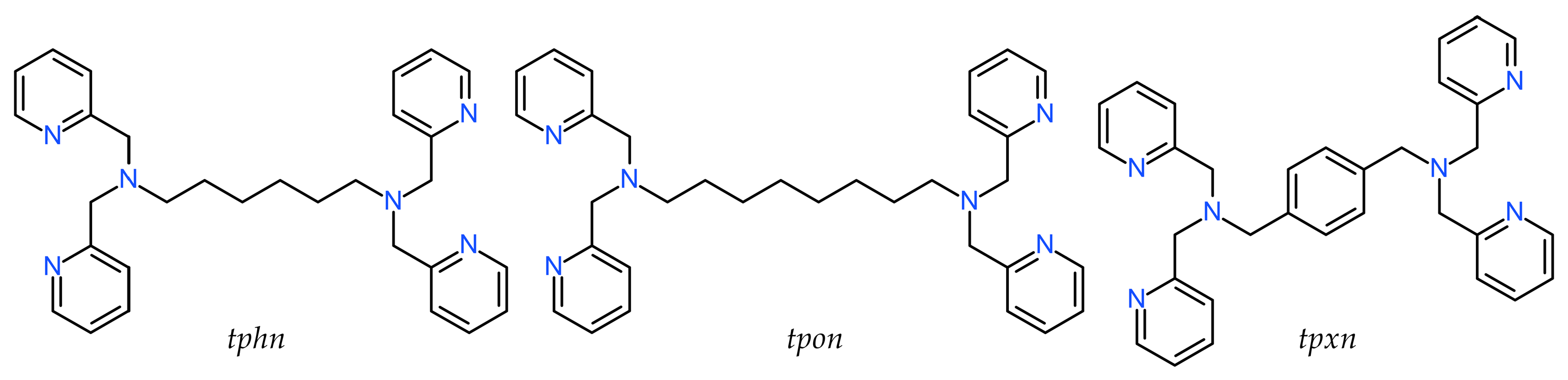
The three ditopic ligands addressed in this study, as shown in Scheme 1, all have two N3 coordination sites consisting of bis(pyridylmethyl)amine connected by a linker of six or more C atoms. The ligands tphn (N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)hexane-1,6-diamine) and tpon (N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)octane-1,8-diamine) are flexible ligands with C6 and C8 alkyl chains as linkers [20,21]. On the other hand, tpxn (N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)-p-xylene-α,α′-diamine) has a p-xylyl linker, which is considered to have a more rigid structure than the two former ligands [22]. In this study, we report the structures of newly obtained dinuclear and tetranuclear Mn(II) complexes with carboxylate bridging using these ligands, as well as their magnetic and electrochemical properties.
Scheme 1.
Chemical diagrams of ligand.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All common reagents and solvents were purchased and used as received, unless stated otherwise. Methanol was purified by distillation over magnesium turnings, while acetonitrile was dehydrated with P2O5 and distilled before use. Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate (TBAP), used as the supporting electrolyte, was recrystallized three times in a mixed solvent of dichloromethane and hexane. (Caution: TBAP is explosive and should be handled with great care!). The ligands tphn [20], tpon [21], and tpxn [22] were obtained by the literature method.
2.2. Preparation
2.2.1. [Mn2F(OAc)2(tphn)]BF4 (1)
Manganese(II) tetrafluoroborate hexahydrate (0.336 g, 1.0 mmol) was dissolved in 6.0 mL of methanol, followed by the addition of a 4.0 mL aqueous solution of sodium acetate trihydrate (0.204 g, 1.5 mmol). After stirring for 15 min, 1.0 mL of a methanol solution of tphn (0.24 g, 0.50 mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight, yielding a white precipitate. Yield 0.130 g, 31.1%.
Single crystals suitable for X-ray crystallography were obtained as colorless transparent plate crystals by recrystallization from a mixed solvent of dichloromethane/toluene (v/v = 1/1). Complex 1: C34H41BF5Mn2N6O4 (814.41): calcd. C 50.14, H 5.20, N 10.32; found C 49.76, H 5.17, N 10.13. IR (ATR) [cm−1]: 1597, 1417 (COO), 1049 (BF4−), 766 (py).
2.2.2. [{Mn2(OAc)3(tpon)}2](BPh4)2 (2)
A solution of manganese(II) acetate tetrahydrate (0.124 g, 0.50 mmol) in methanol (5 mL) was mixed with a solution of sodium acetate trihydrate (0.104 g, 0.76 mmol) in water (1 mL) and a solution of tpon (0.127 g, 0.25 mmol) in methanol (5 mL). The mixture was stirred for 30 min. To this solution, a solution of sodium tetraphenylborate (0.082 g, 0.24 mmol) in methanol (5 mL) was added and stirred for 30 min. The resulting white precipitate was collected by suction filtration. The crude product was recrystallized in a mixed solvent of THF/toluene, yielding colorless microcrystals. Yield: 0.185 g, 69.1%.
Single crystals suitable for X-ray crystallography were obtained as colorless transparent block crystals by recrystallization from a mixed solvent of THF/toluene (v/v = 1/2). Complex 2: C124H138B2Mn4N12O12 (2229.87): calcd. C 66.79, H 6.24, N 7.54; found C 67.05, H 6.22, N 7.52%. IR (ATR) [cm−1]: 1620, 1602, 1422 (COO), 758 (py), 703 (BPh4−).
2.2.3. [{Mn2(OAc)2(tpxn)(CH3OH)(H2O)2}2][{Mn2(OAc)3(tpxn)(CH3OH)(H2O)}2](PF6)6 (3)
A solution of manganese(II) acetate tetrahydrate (0.125 g, 0.51 mmol) in methanol (5 mL) was mixed with a solution of sodium acetate trihydrate (0.104 g, 0.76 mmol) in water (1 mL) and stirred for 15 min. To this solution, 3 mL of a methanol solution of tpxn (0.122 g, 0.24 mmol) was added, and the resulting dark brown solution was further stirred for 15 min. Finally, a solution of potassium hexafluorophosphate (0.052 g, 0.28 mmol) in water (3 mL) was added and stirred for 30 min. The mixture was then filtered and allowed to stand for 24 h at room temperature. The dark brown precipitate was removed by filtration, and upon further incubation at 10 °C for another 24 h, colorless plate crystals suitable for X-ray crystallography were collected. Yield 0.008 g, 4%. Complex 3∙12H2O: C152H186F36Mn8N24O30P6 (4138.54): calcd. C 44.11, H 4.53, N 8.12; found C 43.88, H 4.28, N 8.32%. IR (ATR) [cm−1]: 1603, 1549, 1445, 1421 (COO), 834 (PF6−), 764 (py).
2.3. Measurements
Elemental analyses for C, H, and N were conducted at the Elemental Analysis Service Center, Kyushu University. Infrared spectra were recorded using a VERTEX70-S FT-IR Spectrometer (Bruker, Corp., Billerica, MA, USA) with the ATR (Attenuated Total Reflection) method. The magnetic susceptibilities were measured on a MPMS-XL5R SQUID (Superconducting Quantum Interference Device) susceptometer (Quantum Design, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) under an applied magnetic field of 0.1 T in the temperature range 2–300 K for 1 and 2. The susceptibilities were corrected for the diamagnetism of the constituent atoms using Pascal’s constant [23]. The DC-magnetic data were fitted using the PHI program [24]. The cyclic voltammogram (CV) was obtained with an ALS Electrochemical Analyzer Model832A (BAS, Inc., Tokyo, Japan). CV measurements were carried out in dichloromethane containing 0.1 M TBAP as a supporting electrolyte. A three-electrode cell was used, equipped with a glassy carbon (ϕ = 1 mm) working electrode, a platinum wire counter electrode, and an Ag/Ag+ reference electrode.
2.4. Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction
Diffraction data were measured on a Vari-Max Saturn CCD 724 diffractometer (Rigaku, Corp, Tokyo, Japan) using graphite monochromated Mo Ka radiation (λ = 0.71069 Å) at the Analytical Research Center for Experimental Sciences, Saga University. Data were collected using CrystalClear [25]. Data processing was performed using CrysAlisPro [26] for 1 and CrystalClear for 2 and 3. A multi-scan correction for absorption was applied. The crystal data and experimental parameters are summarized in Table 1. Structures were solved by direct methods (ShelXT) and expanded using Fourier techniques [27]. Non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically. Hydrogen atoms were placed geometrically in calculated positions and refined with a riding model. Appropriate restrictions using fragment data were applied to the disordered components in 1 (BF4−) and 2 (THF). The final cycle of full-matrix least-squares refinement on F2 using ShelXL [28] was based on observed reflections and variable parameters and converged with unweighted and weighted agreement factors of R and Rw. Olex2 [29] was used as an interface to the ShelX program package. Molecular structure drawings were performed using Mercury [30]. The Hirshfeld surface was generated using Crystal Explorer 3.1 [31].

Table 1.
Crystallographic data and refinement parameters.
2.5. Study of Catalase Activity
A volumetric method was employed to determine the evolution of dioxygen. A 10 mL test tube, sealed with a silicone stopper, was connected to a 25 mL burette with a precision of 0.1 mL. A chosen concentration (1.2, 1.0, 0.85, and 0.67 mM) of aqueous H2O2 (1.0 mL) was injected through the sealed silicon stopper into the closed test tube containing 1.0 mL of an acetonitrile solution of the complex (1.0 mM), thermostatized at 25 °C. The volume of evolved oxygen was measured as a function of time.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthetic Aspects
The reaction of Mn(II) ions with three types of ditopic ligands in the presence of acetate ions yielded colorless Mn complexes 1–3. Elemental analysis suggests that these complexes have the following composition: [Mn2F(OAc)2(tphn)]BF4, [Mn2(OAc)3(tpon)]BPh4, and [Mn4(OAc)5(tpxn)2(CH3OH)2(H2O)3](PF6)3∙6H2O, respectively. Even with a composition in which the fluoride ion of 1 is replaced with a hydroxy ion, the elemental analysis values are sufficiently close. However, the characteristic sharp ν(OH) vibration of the μ-hydroxo bridge is not observed in the IR spectrum, indicating the presence of the fluoride ion generated by the hydrolysis of the tetrafluoroborate ion. Single crystals of 1 and 3 were obtained directly during synthesis, whereas single crystals of 2 were obtained by recrystallization from a mixed solvent (THF/toluene) different from that used during synthesis. Complex 3 has very high solubility in various solvents, making it difficult to crystallize. However, we confirmed that single crystals can be reproduced by following the synthetic procedure described in Section 2.2.3, although the yield is extremely low.
3.2. Crystal Structures
3.2.1. Complex 1
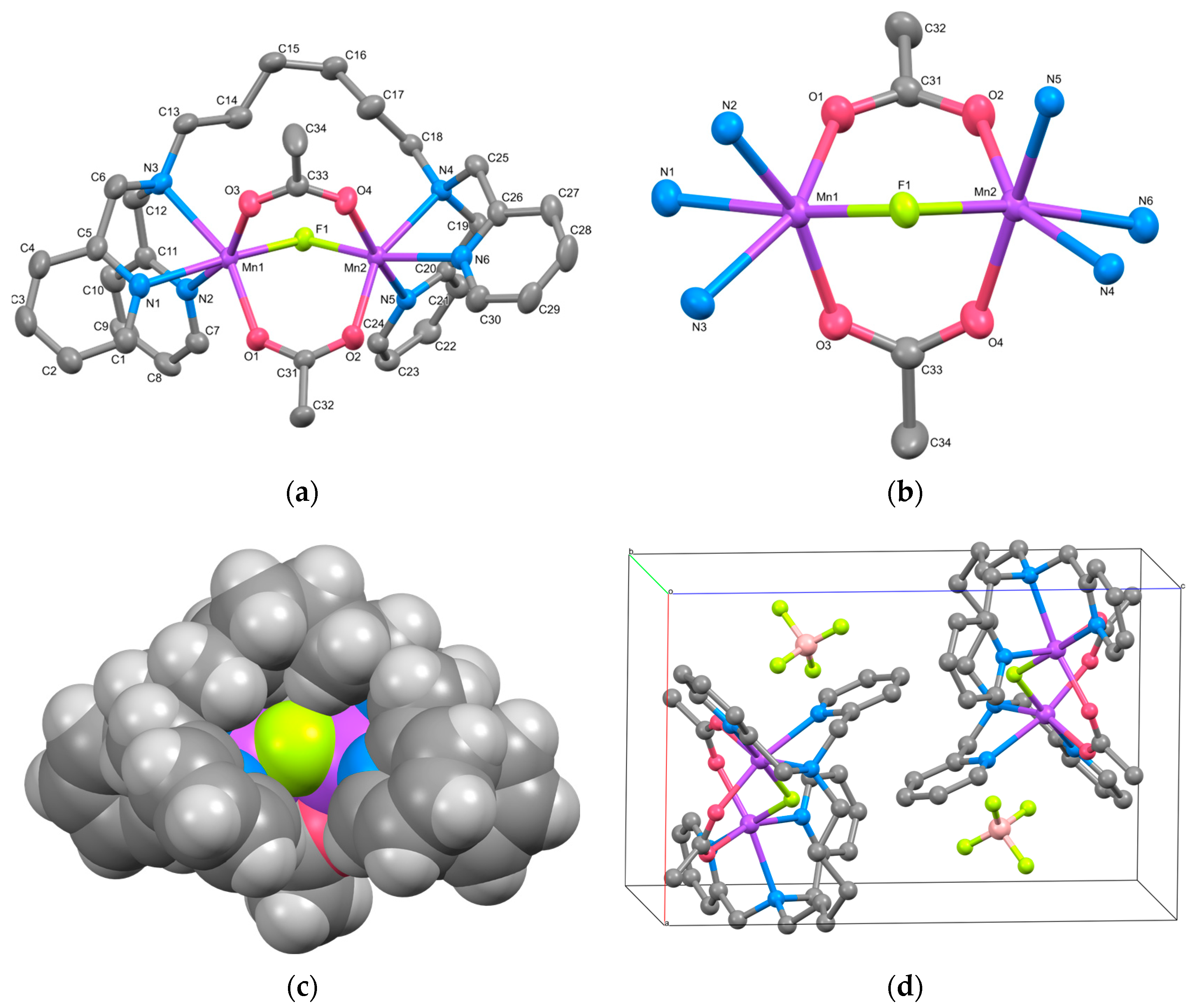
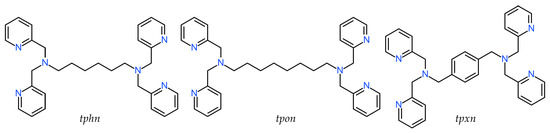
The cation structure of 1 is shown in Figure 1a, and the selected bond lengths and angles are listed in Table 2. Complex 1 was identified as a triply bridged dinuclear Mn(II) complex, [Mn2(μ-F)(μ-acetato-O,O′)2(tphn)]BF4. The BF4− anion was treated as disordered, with occupancies of 0.51 and 0.49.
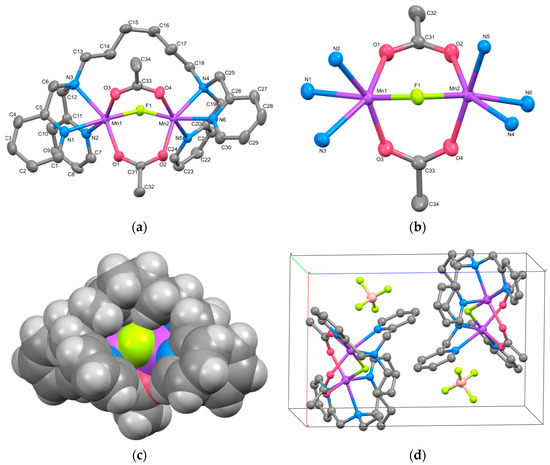
Figure 1.
(a) X-ray crystal structure for the complex cation of 1, showing thermal ellipsoids at a 30% probability level. Hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity. (b) Metal core structure. (c) CPK model. (d) Crystal packing view. For the disordered BF4− ion, only the highly occupied part is shown for clarity.

Table 2.
Selected bond distances and angles of 1.
Two Mn atoms are bridged by two acetate ions and a fluoride ion. The bridging fluoride ion is believed to result from the partially hydrolyzed BF4− during synthesis. The tridentate N3-coordination sites at both ends of the tphn ligand coordinate in a fac-manner at both sides of the dinuclear Mn core, forming a characteristic metallacyclic structure. The coordination environments of the two Mn atoms are similar, with average bond distances to each coordinating atom being Mn–F = 2.0533(8), Mn–O = 2.1346(10), and Mn–N = 2.3288(12) Å, respectively, suggesting an oxidation state of +2 for Mn. The difference of approximately 0.2 Å between the Mn–N distances and those of other bonds suggests a distorted octahedral geometry for the Mn ion.
The bond lengths, bond angles, and torsion angles of the two bridging acetate ions are summarized in Table 3. The bridging modes of carboxylate groups are classified based on the differences between these parameters [32]. The torsion angles defined by Mn–O–C–C and Mn–O∙∙∙O–Mn range from 165.71(12) to 175.15(11)° and 3.07(6) to 6.67(6)°, respectively. These parameters fit well with the syn-syn coplanar bridging mode. The bridging structure of 1, as shown in Figure 1b, resembles those of μ-alkoxo/carboxylato-O-bis-μ-carboxylato-O,O′ bridged dinuclear Mn(II) complexes, except for the fluoride bridge [33]. The distance between the two Mn atoms is 3.4309(3) Å, which is shorter than reported tris-μ-carboxylato bridged Mn(II) complexes (~4 Å) [9,10].

Table 3.
Structural parameters and bridging modes of carboxylato bridges in Complex 1.
The CPK model for 1 is presented in Figure 1c. Although the dinuclear Mn core appears to be surrounded and shielded by pyridyl groups and the alkyl linker, it is evident that the bridging fluoride ion remains unshielded. The Hirshfeld surface and 2D fingerprint plots for the complex cation of 1 are illustrated in Figure S4. The contact between the bridging F atom and the outer atom is about 0.6%, which is not large, but it indicates the possibility of external contact. Consequently, the dissociation of the fluoride ion may create a pathway for accessing the Mn ions, suggesting the potential for catalytic reactions.
Figure 1d illustrates the packing diagram of 1. Each dinuclear complex cation is stacked through weak π-π stacking interactions involving the pyridyl group, including N2, of tphn (centroid distance: 3.9103(12) Å).
3.2.2. Complex 2
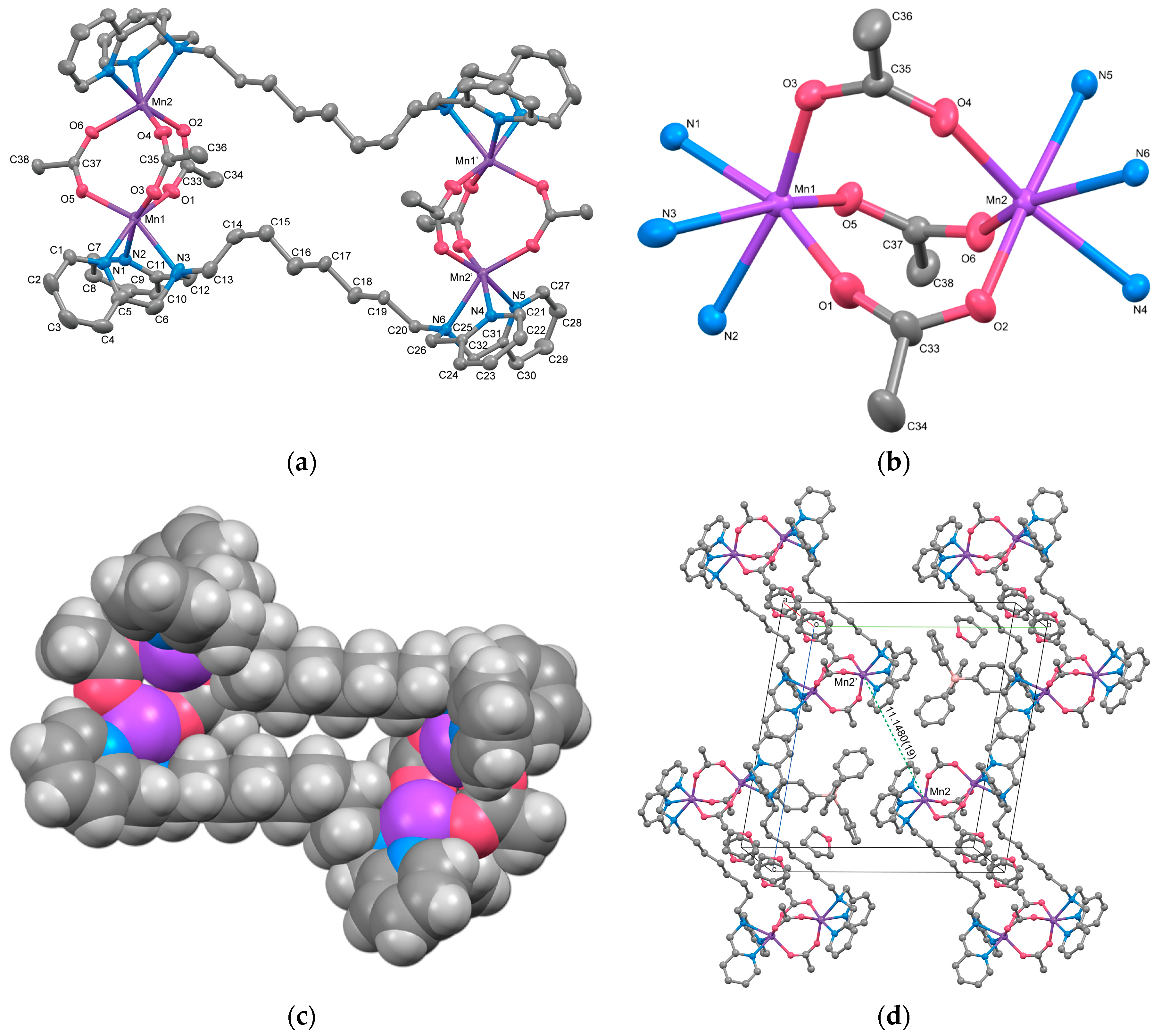
The cation structure of 2 is depicted in Figure 2a, and selected bond lengths and angles are listed in Table 4. Complex 2 was identified as a cyclic tetranuclear Mn complex, [{Mn2(μ-acetato-O,O′)3(tpon)}2](BPh4)2·3THF, with an inversion center. Within the complex cation, two tris-μ-carboxylato triple-bridged dinuclear Mn units are present. One of the three THF molecules present as the crystal solvent was found to be disordered with an occupancy of 0.5 at a crystallographically special position.
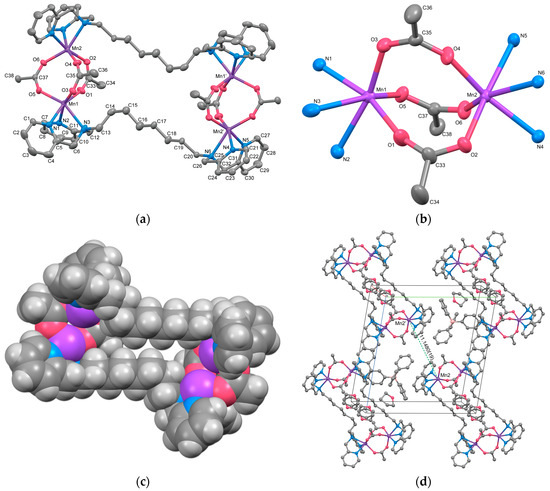
Figure 2.
(a) X-ray crystal structure for the complex cation of 2, showing thermal ellipsoids at a 50% probability level. Hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity. (b) Metal core structure of 2. (c) CPK model of 2, with the bridging acetates overlapping the alkyl chain hidden for clarity. (d) Crystal packing view of 2.

Table 4.
Selected bond distances and angles of 2.
The dinuclear Mn unit in 2 is illustrated in Figure 2b. Each Mn is hexacoordinated, with three oxygen atoms originating from acetate ions, three nitrogen atoms from two pyridyl groups, and one tertiary amine from the tpon ligand. The coordination geometry adopts a distorted octahedral structure. The Mn–N bond lengths range from 2.253(2) to 2.411(3) Å for Mn1 and from 2.268(2) to 2.381(2) Å for Mn2, while the Mn–O bond lengths range from 2.095(2) to 2.1339(19) Å and 2.1176(19) to 2.137(7) Å, respectively. These values closely resemble those reported for Mn(II) complexes, indicating that both Mn1 and Mn2 ions exist in the +2 oxidation state. The metal-to-metal distance Mn1···Mn2 is 4.0293(9) Å, similar to the distances observed in reported dinuclear Mn(II) complexes with tris-μ-carboxylato bridges (~4 Å) [9,10].
The intermetallic distances between two dinuclear units, Mn1···Mn1i, Mn1···Mn2i, and Mn2···Mn2i (symmetry code i: 1−x, −y, −z) are 13.368(3), 13.348(2), and 14.496(3) Å, respectively, which are more than three times longer than the distance between Mn1 and Mn2. As evident from the CPK model of the complex cation shown in Figure 2c, the alkyl linker moieties of the tpon ligands extend straight, indicating the presence of a “fastener effect” between the alkyl chains [34]. One reason for the structural differences between complexes 1 and 2 is believed to be the strong fastener effect due to the extension of the methylene chain of the linker moiety from C6 to C8.
The bridging acetate ions exhibit significant variations in bond angles and torsion angles with the Mn ions. The structural parameters related to the carboxylate-bridging mode are summarized in Table 5. This table shows significant differences in the Mn–O–C bond angle and in the torsion angles M–O–C–C and M–O∙∙∙O–M. The three acetato bridges in this complex are classified as a syn-syn coplanar type with a small torsion angle (bridge A) and as syn-skew nonplanar types with larger torsion angles (bridges B and C). Even in similar complexes with tris-μ-acetato bridges, two of the three bridging acetate ions are often twisted by about 15 to 35°, which is thought to be a common structure in tris-μ-acetato dinuclear structures [9,10].

Table 5.
Structural parameters and bridging modes of carboxylato bridges in Complex 2.
The crystal packing diagram (Figure 2d) reveals the shortest intermolecular metal-to-metal distance between the complex cations to be 11.1480(19) Å, shorter than the intramolecular distance between the dinuclear units. No interactions such as hydrogen bonding or π–π stacking were observed in the crystal packing. The components in 2 are largely covered with hydrogen atoms, so the Hirshfeld surface analysis does not reveal any significant features (Figure S5).
3.2.3. Complex 3
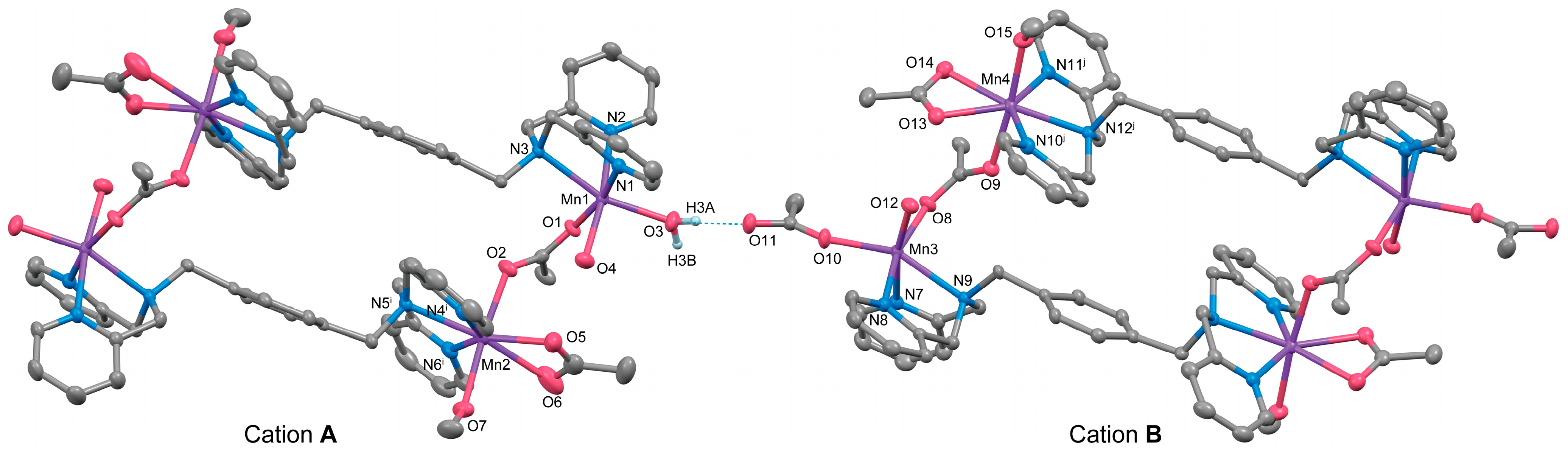
Complex 3 is a double salt composed of two types of complex cations with different charges, [{Mn2(μ-acetato-O,O′)(acetato-O,O′)(tpxn)(CH3OH)(H2O)2}2]4+ (Cation A) and [{Mn2(μ-acetato-O,O′)(acetato-O,O′)(acetato-O)(tpxn)(CH3OH)(H2O)}2]2+ (Cation B), along with six PF6− counter anions. Both complex cations form a cyclic tetranuclear structure in which two μ-acetato single bridged dinuclear Mn units are connected by two tpxn ligands. The composition and charge of the cations differ depending on the combination of non-bridging ligands (H2O, CH3OH, and CH3COO−). The structures of cations A and B of Complex 3 are illustrated in Figure 3, and the selected bond lengths and angles are listed in Table 6. Aside from differences in the ditopic ligands and acetate bridging moieties, the fundamental structures of the tetranuclear complex cations closely resemble those of Complex 2.
Figure 3.
The X-ray crystal structure for the complex cations (A and B) of 3 showing thermal ellipsoids at a 50% probability level. The dotted line shows a hydrogen bond. Hydrogen atoms except for H3A and H3B have been omitted for clarity.

Table 6.
Selected bond distances and angles of 3.
Each Mn has two coordination sites in addition to the coordination of the bridging acetate ion and tpxn. Mn1 in Cation A and Mn3 in Cation B exhibit six-coordinate octahedral structures with two monodentate ligands (H2O or CH3OH) binding. In contrast, Mn2 and Mn4 form seven-coordinate pentagonal bipyramidal structures with bidentate-chelating acetate ions and monodentate-coordinating methanol. This difference appears to correlate with the coordination modes of the tpxn ligands, where each N3 site of tpxn coordinates in a fac-mode with the six-coordinate Mn1 and Mn3, whereas Mn2 and Mn4 are coordinated in a mer-mode within the equatorial plane of the pentagonal bipyramid. The average bond lengths around Mn are Mn–O = 2.218(2) and Mn–N = 2.327(2) Å, respectively, suggesting an oxidation state of +2 for all Mn ions. The metal-to-metal distances within the dinuclear unit were 5.3487(13) for Cation A and 5.3389(13) Å for Cation B, respectively. The distances are significantly longer than those observed in 1 and 2 due to the single acetato bridge in a syn-anti mode [5,6]. Therefore, although the phenyl rings of tpxn ligands are located in parallel, they are not close enough to allow π-stacking interactions between the phenyl rings [Cation A: 6.306(3) Å, Cation B: 6.316(3) Å]. When comparing the structures of 1–3 with previously reported dinuclear Mn complexes featuring shorter linkers such as tptn or tpbn [35], it can be concluded that when the linker length is shorter than C6, dinuclear Mn complexes are formed, whereas when it becomes longer or includes rigid structures like a phenyl ring, tetranuclear structures are formed.
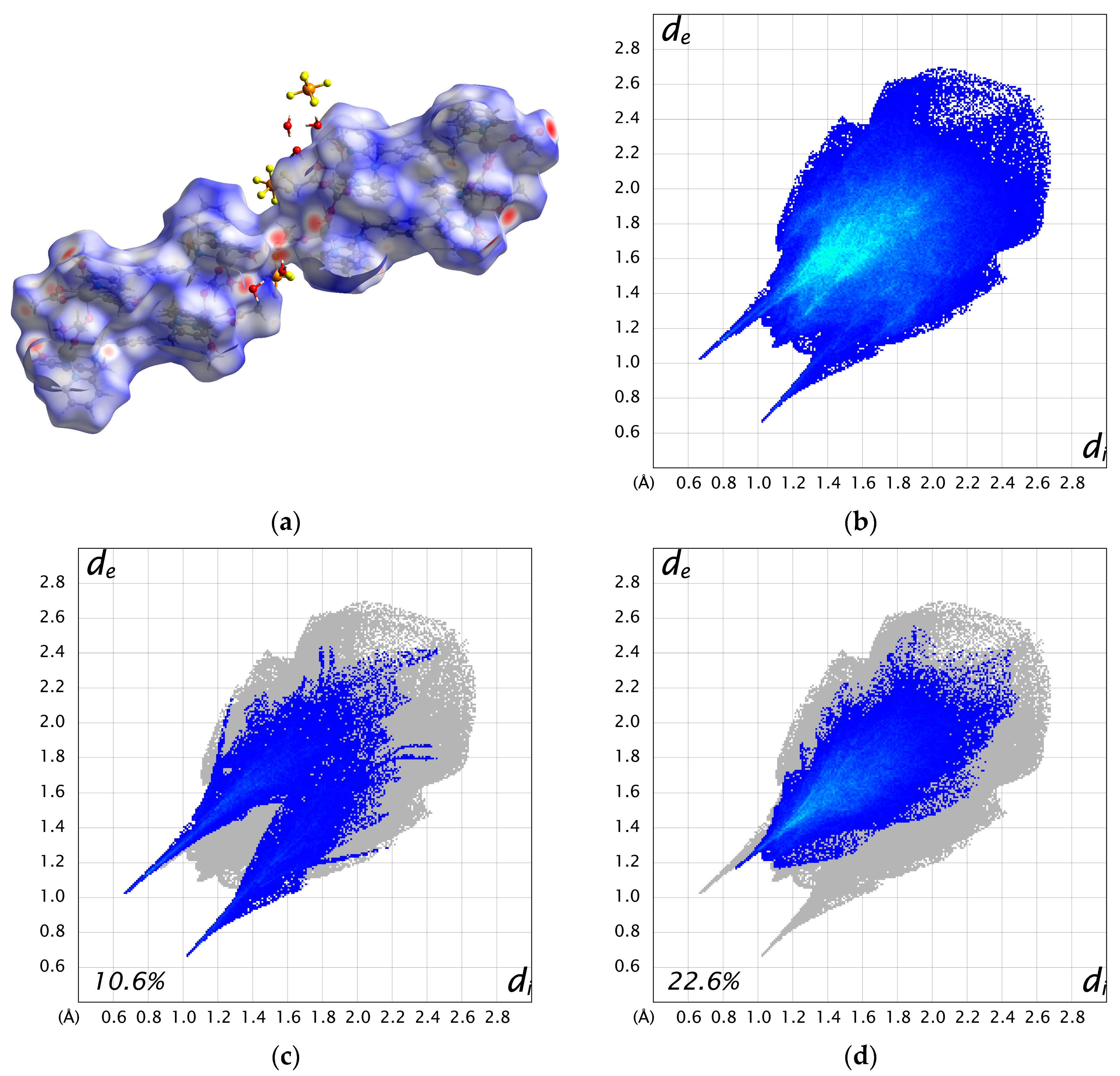
The two cations are weakly connected by a hydrogen bond between the water molecule bound to Mn1 and the acetate ion bound to Mn3 (O3–H3A···O11 = 2.663 Å), forming a 1D chain structure. As a result, the intermetallic distance between dinuclear units is shorter between adjacent cations (Mn1···Mn3 = 8.6610(17) Å) than the distance within a cation (10.826(2)—15.039(2) Å). Additionally, numerous hydrogen bonds are formed between the crystal solvents, counter ions, and complex cations (Figure S6). The Hirshfeld surface analysis was performed on 3. The resulting Hirshfeld surface (dnorm) is shown in Figure 4a. Furthermore, 2D fingerprint plots of all atoms, H···O, and H···F are shown in Figure 4b–d. The Hirshfeld surface of the complex cation is mapped in red near the water molecules and PF6 ions, visualizing the presence of these strong interactions. The fingerprint plots show two characteristic sharp spikes, which are specific contacts between complex cations and water molecules, as seen in Figure 4a,c, indicating the network structure constructed by H···O contacts. The H···F contacts (Figure 4d) are distributed throughout (22.6%), likely because they are scattered throughout the 1D structure of the complex cation rather than being specific.
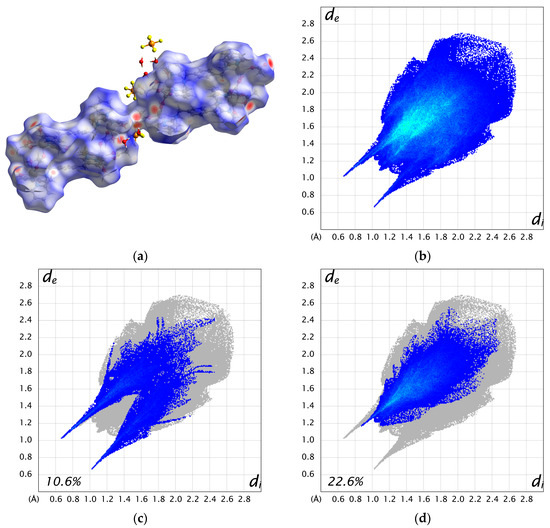
Figure 4.
(a) Hirshfeld surface (dnorm) for complex cation A and B. (b) 2D fingerprint plot for all atoms. (c) H···O contacts. (d) H···F contacts.
3.3. IR Spectroscopy
Infrared spectra of 1–3 are shown in Figures S1, S2, and S3, respectively. The γ(CH) vibrations of the pyridyl group are observed in the range of 764 to 759 cm−1 in all complexes, indicating the presence of the pyridyl groups as terminal ligands. Intense peaks attributed to the symmetric (νs) and antisymmetric (νas) stretching vibrations of the carboxylate (COO) groups were observed in all complexes. As revealed by X-ray crystal structure analysis, these complexes exhibit significant differences in the coordination mode of acetate ions, which is reflected in the IR spectra. These differences are typically detected by the peak separation between νas and νs (Δν = νas − νs) [36]. In Complex 1, two intense peaks at 1597 and 1417 cm−1 are assigned to νas and νs, respectively. The Δν value (180 cm−1) indicates the presence of syn-syn type carboxylato bridges. For Complex 2, two νas vibrations and a slightly broad νs band are observed at 1620, 1602, and 1422 cm−1, respectively. According to the X-ray results, separations of 198 cm–1 and 180 cm–1 suggest their assignment to syn-skew and syn-syn bridging coordination, respectively. In the case of Complex 3, two sets of νas and νs vibrations are observed at 1603, 1421 cm−1 and 1549, 1445 cm−1, respectively. Each Δν is 182 and 104 cm–1, corresponding to syn-anti bridging and chelating bidentate coordination. Additionally, characteristic peaks originating from the counter anions, BF4−, BPh4−, and PF6−, were observed around 1049, 703, and 834 cm−1, respectively.
3.4. Magnetic Measurements
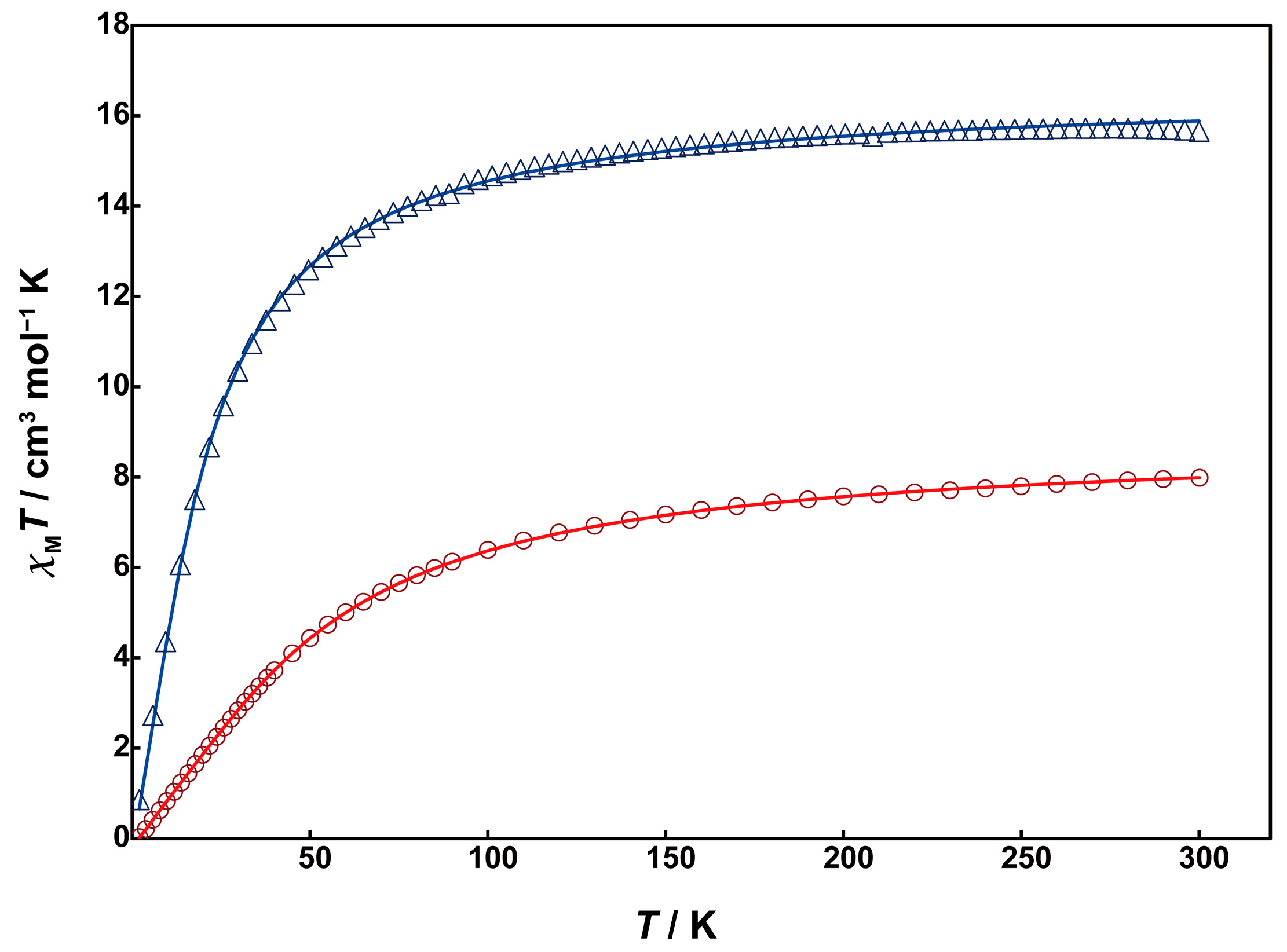
Magnetic susceptibility measurements for 1 and 2 were performed using a SQUID magnetometer. Unfortunately, due to the low yield of 3, magnetic and electrochemical measurements could not be conducted for it. The temperature dependence of magnetic susceptibility was measured in the temperature range of 2 to 300 K. Figure 5 shows χMT vs. T plots for 1 (red circles) and 2 (blue triangles).
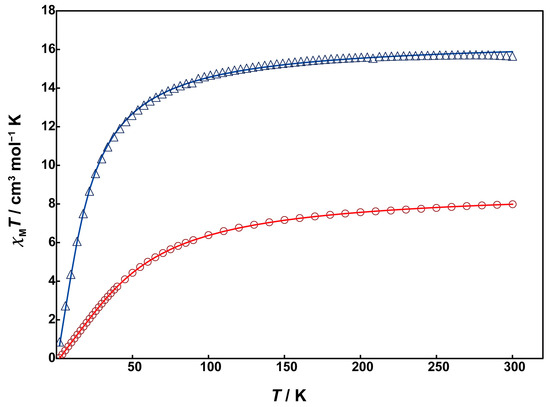
Figure 5.
Temperature dependence of χMT vs. T plots of 1 (red circles) and 2 (blue triangles). Solid lines are drawn with the best-fitted parameter values described in the text.
At 300 K, Complex 1 exhibits a χMT value of 7.99 cm3mol−1K, which is smaller than the expected spin-only value of 8.75 cm3mol−1K for two magnetically uncoupled high-spin Mn(II) (S = 5/2). As the temperature decreases from room temperature, the χMT value gradually decreases, reaching 0.35 cm3mol−1K at 2 K. This behavior indicates the presence of antiferromagnetic interaction between the Mn(II) ions. The behavior was analyzed by the PHI program [24] using the theoretical equation for the magnetic susceptibility of an S = 5/2 dinuclear model based on the isotropic Heisenberg spin-exchange Hamiltonian (H = −2JS1S2), where S1 = S2 = 5/2. The obtained magnetic parameters were J = −3.42 cm−1 and g = 2.01, indicating weak antiferromagnetic interactions between the Mn(II) ions. The absolute value of J is smaller compared to the similar dinuclear Mn(II) complexes with μ-hydroxo-bis-μ-carboxylate bridges, e.g., [Mn2(tpa)2(OH)(OAc)2] (J = −18 cm−1) [17]. This suggests that the super-exchange spin coupling between the metal ions is inhibited due to the strong electronegativity of the fluorido bridge instead of the hydroxo group.
The χMT value of 2 at 300 K is 15.7 cm3mol−1K, slightly smaller than the spin-only value of 17.5 cm3mol−1K for four magnetically uncoupled high-spin Mn(II) ions at room temperature. The χMT value gradually decreased with decreasing temperature, dropping sharply around 70 K and reaching 0.235 cm3mol−1K at 2 K. This behavior suggests that the antiferromagnetic interaction in 2 is much weaker than in 1. The data were analyzed using the PHI program based on the spin Hamiltonian in Equation (1):
H = −2J1(SMn1SMn2 + SMn1iSMn2i) − 2J2(SMn1SMn2i + SMn1iSMn2) − 2J3SMn1SMn1i − 2J4SMn2SMn2i
The obtained magnetic parameters are as follows: J1 = −1.31 cm−1, J2 = −0.07 cm−1, J3 = −0.19 cm−1, J4 = −0.02 cm−1, g = 1.95, indicating significantly weak antiferromagnetic interactions between the Mn(II) ions. The absolute value of the exchange parameter J1 for the dinuclear Mn(II) unit is close to those of reported tris-μ-carboxylato-bridged dinuclear Mn(II) complexes [10,11]. This difference in J value between complexes 1 and 2 is thought to be caused by the presence of the twisted μ-acetato bridges in 2 instead of the fluoride bridge in 1, which reduces the overlap of magnetic orbits.
3.5. Electrochemistry
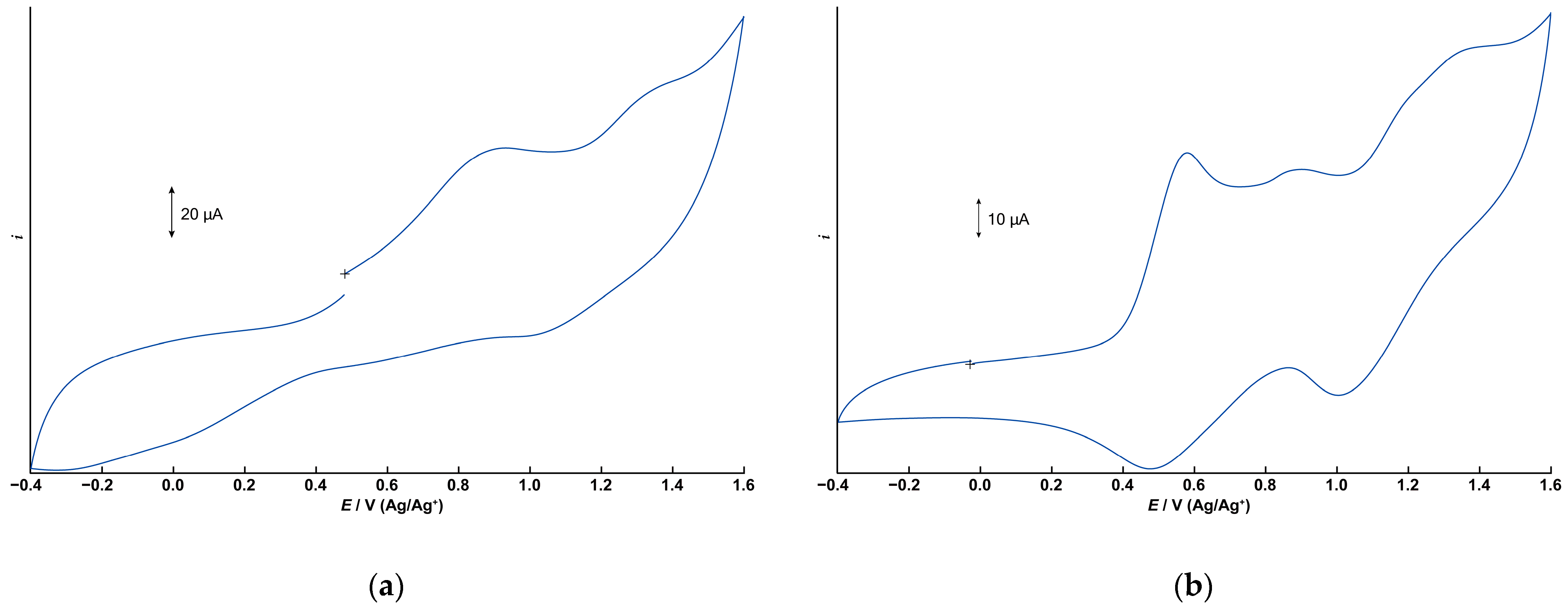
The electrochemical properties of 1 and 2 were investigated using cyclic voltammetry (CV) in dichloromethane containing tetrabutylammonium perchlorate (0.1 M) as the supporting electrolyte. Figure 6a,b depict the cyclic voltammograms for 1 and 2, respectively, measured in the range of −0.4 to +1.6 V (vs. Ag/Ag+) using a glassy carbon electrode. Differential pulse voltammograms under the same conditions are illustrated in Figure S7.
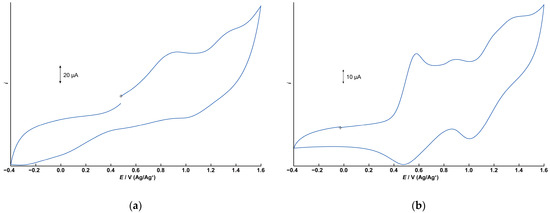
Figure 6.
Cyclic voltammograms (CVs) of 1 and 2. 1.0 × 10−3 M dichloromethane solution with 0.1 M TBAP. (a) CV of 1. Initial E: +0.480 V, High E: +1.6 V, Low E: −0.4 V, Scan speed: 100 mV, Scan direction: Positive. (b) CV of 2.Initial E: −0.025 V, High E: +1.6 V, Low E: −0.4 V, Scan speed: 50 mV, Scan direction: Positive.
The CV of 1 displays two irreversible oxidation waves at +0.932 V and approximately +1.3 V. The free tphn ligand shows an irreversible oxidation peak at +0.734 V, which is attributed to the oxidation of the tertiary amine moiety (Figures S8 and S9). However, no corresponding oxidation wave is observed in the CV of 1. Therefore, these two oxidation processes of 1 are assigned to the oxidation of manganese centers, corresponding to Mn2(II,II)/Mn2(II,III) and Mn2(II,III)/Mn2(III,III). The observed potentials are slightly higher than those of the μ-hydroxo-bis-μ-carboxylato dinuclear Mn(II) complex [Mn2(μ-OH)(μ-OAc)2(Me3-tacn)2]ClO4 [17], which features a different bridging ligand. It is suggested that the metal-centered oxidation processes are shifted to more positive potentials due to the high electronegativity of the bridging fluoride anion.
In contrast, the CV of 2 exhibits two distinct quasi-reversible redox couples at E1/2 = +0.529 V and +1.20 V, respectively, corresponding to the Mn2(II,II)/Mn2(II,III) and Mn2(II,III)/Mn2(III,III) processes. These potentials are consistent with those reported for tris-μ-carboxylato dinuclear Mn(II) complexes [10]. In addition to these two redox processes, a small peak appears at +0.902 V, which is believed to be due to the tpon ligand. Since the oxidation peak of the free ligand is at +0.693 V, it is believed that some of the coordination sites are partially dissociated. In acetonitrile, the two quasi-reversible redox processes become irreversible, and this small peak disappears, suggesting that partial dissociation of the tpon ligand is unlikely to occur in acetonitrile (Figure S10). These results suggest that the small peak is not simply due to contamination and that the stability of 2 is affected by the solvent.
3.6. Catalase Activity
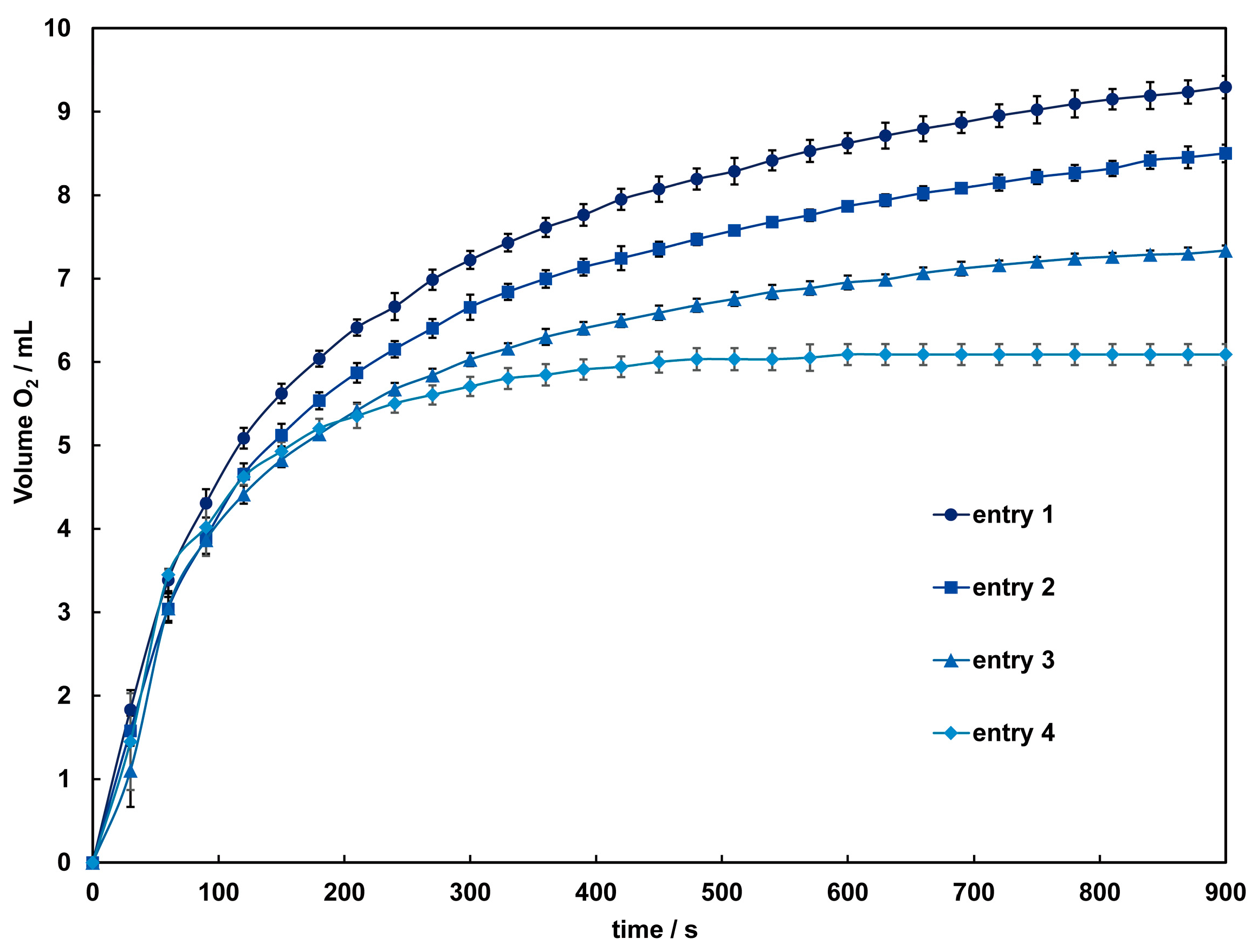
The catalytic activity of these complexes in the disproportionation of H2O2 into H2O and O2 was investigated using a volumetric method. When aqueous hydrogen peroxide is added to an acetonitrile solution of 1 and 2, bubbles due to oxygen evolution are observed only in 2, and the colorless solution gradually turns light brown. After around 60 s, the solution becomes very dark, and the evolution of oxygen intensifies. The time courses of dioxygen evolution catalyzed by 2 are shown in Figure 7. The amount of O2 evolved after 900 s under each condition was 9.3–6.09 mL, corresponding to a turnover number (TON) of 414–272, close to the TON reported for dinuclear Mn(III) complexes [37]. By the time oxygen evolution subsides, the solution color approaches colorlessness but does not fully return to it, with a slight presence of brown precipitate observed. This suggests a small amount of decomposition of 2 during the reaction. Therefore, while the initial reaction might be catalyzed by the complex cation, it is anticipated that from three minutes onward, the catalytic reaction is mediated by manganese dioxide or other manganese species formed from the decomposition of the complex. As indicated by the results of the CV measurements, the terminal ligands and acetate bridging used in this study are considered insufficient to maintain the dinuclear Mn structure adequately in such a reaction condition. To improve the reactivity, adjustments to the complex structure, such as incorporating other auxiliary ligands into the bridging moiety, are necessary.
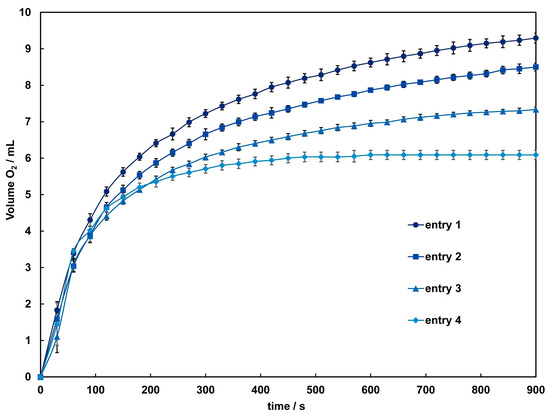
Figure 7.
Time dependence of the O2 evolution catalyzed by 2 with different concentrations of H2O2. Conditions: [complex] = 1.0 mM in acetonitrile, [H2O2] = 1.2 (entry 1 ●), 1.0 (entry 2 ■), 0.85 (entry 3 ▲), 0.67 (entry 4 ♦) mM. Solid lines are guides for the eye.
4. Conclusions
New carboxylate-bridged dinuclear and tetranuclear Mn(II) complexes with ditopic ligands containing two tridentate coordination sites connected by organic linkers were synthesized and characterized. Single-crystal X-ray analysis revealed that all of these complexes have macrocyclic structures. Complex 1 is a dinuclear complex where both ends of the dinuclear Mn unit are surrounded by the ligand tphn. On the other hand, complexes 2 and 3 are tetranuclear complexes where two dinuclear Mn units are dimerized by the ligands tpon and tpxn, respectively. Investigations into the magnetic properties of 1 and 2 through magnetic measurements revealed the presence of weak antiferromagnetic interactions among carboxylate-bridged dinuclear Mn(II) units. Electrochemical measurements showed that complexes 1 and 2 have redox potentials capable of carrying out catalase-like hydrogen peroxide disproportionation reactions. Indeed, when reacted with hydrogen peroxide, although signs of decomposition were observed, oxygen evolution due to the disproportionation reaction was confirmed for 2. The macrocyclic structures of these complexes can be utilized to develop substrate-selective new oxidation catalysts.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemistry6040036/s1, Figure S1. IR spectrum of 1. Figure S2. IR spectrum of 2. Figure S3. IR spectrum of 3. Figure S4. Crystal packing diagram for 3. Figure S5. Differential pulse voltammograms (DPVs) of 1 (a) and 2 (b). 1.0 × 10−3 M dichloromethane solution with 0.1 M TBAP. Figure S6. Cyclic voltammograms (CVs) of tphn and tpon. 1.0 × 10−3 M dichloromethane solution with 0.1 M TBAP. (a) CV of tphn. Initial E: +0.10 V, High E: +1.6 V, Low E: −0.4 V, Scan speed: 100 mV, Scan direction: Positive. (b) CV of tpon. Initial E: 0.00 V, High E: +1.6 V, Low E: −0.4 V, Scan speed: 100 mV, Scan direction: Positive. Figure S7. Differential pulse voltammograms (DPVs) of tphn and tpon. 1.0 × 10−3 M dichloromethane solution with 0.1 M TBAP. Figure S8. Cyclic voltammograms (CVs) of 1 and 2. 1.0 × 10−3 M acetonitrile solution with 0.1 M TBAP. (a) CV of 1. Initial E: +0.081 V, High E: +1.5 V, Low E: −1.2 V, Scan speed: 100 mV, Scan direction: Positive. (b) CV of 2.Initial E: −0.001 V, High E: +1.2 V, Low E: −0.4 V, Scan speed: 100 mV, Scan direction: Positive. Figure S9. Differential pulse voltammograms (DPVs) of tphn and tpon. 1.0 × 10−3 M dichloromethane solution with 0.1 M TBAP. Figure S10. Cyclic voltammograms (CVs) of 1 and 2. 1.0 × 10−3 M acetonitrile solution with 0.1 M TBAP. (a) CV of 1. Initial E: +0.081 V, High E: +1.5 V, Low E: −1.2 V, Scan speed: 100 mV, Scan direction: Positive. (b) CV of 2. Initial E: −0.001 V, High E: +1.2 V, Low E: −0.4 V, Scan speed: 100 mV, Scan direction: Positive.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K.; Data curation, K.Y.; Formal analysis, J.S., Y.U. and S.S.; Funding acquisition, M.K.; Investigation, J.S. and Y.U.; Project administration, M.K.; Software, M.K.; Supervision, M.K.; Visualization, M.K.; Writing—original draft, M.K. and J.S.; Writing—review and editing, M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the author upon reasonable request. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
This research was performed using the equipment (IR, SQUID, and single crystal X-ray analysis) of Analytical Research Center for Experimental Science, Saga University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Price, D.J.; Batten, S.R.; Moubaraki, B.; Murray, K.S. Synthesis, structure and magnetism of a new manganese carboxylate cluster: [Mn16O16(OMe)6(OAc)16(MeOH)3(H2O)3]·6H2O. Chem. Commun. 2002, 762–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, C.S.; Pecoraro, V.L. Reflections on small molecule manganese models that seek to mimic photosynthetic water oxidation chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 416–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.; Iqbal, N.; Noor, T.; Kariuki, B.M.; Kidwell, L.; Easun, T.L. Efficient electrochemical synthesis of a manganese-based metal–organic framework for H2 and CO2 uptake. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, J.; Albela, B.; Stoeckli-Evans, H.; Christou, G. Synthesis and magnetic properties of six new trinuclear oxo-centered manganese complexes of general formula [Mn3O(X-benzoato)6L3] (X = 2-F, 2-Cl, 2-Br, 3-F, 3-Cl, 3-Br; L = pyridine or water) and crystal structures of the 2-F, 3-Cl, and 3-Br complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, P.; Ghosh, A. Synthesis, structure and alkene epoxidation activity of an alternating phenoxido and formato bridged manganese(III)–salen complex. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2013, 395, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durot, S.; Policar, C.; Pelosi, G.; Bisceglie, F.; Mallah, T.; Mahy, J.-P. Structural and magnetic properties of carboxylato-bridged manganese(II) complexes involving tetradentate ligands: Discrete complex and 1D polymers. Dependence of J on the nature of the carboxylato bridge. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 8072–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triller, M.U.; Hsieh, W.-Y.; Pecoraro, V.L.; Rompel, A.; Krebs, B. Preparation of highly efficient manganese catalase mimics. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 41, 5544–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, V.; Corbella, M. Crystal structure and magnetic properties of the dinuclear MnII compound [Mn2(bpy)4(2-ClC6H4COO)2](ClO4)2∙2EtOH. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2011, 41, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.P.; Singh, R.; Hikichi, S.; Akita, M.; Moro-oka, Y. Characterization of a dinuclear Mn(II) tri(μ-carboxylato) complex with the hindered hydrotris(3,5-diisopropyl-1-pyrazolyl)borate (=TpiPr2) ligand: Intramolecular hydrogen bonding interaction between the protonated TpiPr2 and Mn-coordinating carboxylate ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2000, 310, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, I.; Dubois, L.; Collomb, M.-N.; Deronzier, A.; Latour, J.-M.; Pécaut, J. A Dinuclear manganese(II) complex with the {Mn2(μ-O2CCH3)3}+ core: Synthesis, structure, characterization, electroinduced transformation, and catalase-like activity. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 41, 1795–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, G.; Corbella, M.; Alfonso, M.; Stoeckli-Evans, H.; Castro, I. A comparative XAS and X-ray diffraction study of new binuclear Mn(III) complexes with catalase activity. Indirect effect of the counteranion on magnetic properties. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 6684–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessoli, R.; Gatteschi, D.; Caneschi, A.; Novak, M.A. Magnetic bistability in a metal-ion cluster. Nature 1993, 365, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanyo, Z.F.; Scolnick, L.R.; Ash, D.E.; Christianson, D.W. Structure of a unique binuclear manganese cluster in arginase. Nature 1996, 383, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barynin, V.V.; Whittaker, M.M.; Antonyuk, S.V.; Lamzin, V.S.; Harrison, P.M.; Artymiuk, P.J.; Whittaker, J.W. Crystal structure of manganese catalase from Lactobacillus plantarum. Structure 2001, 9, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakiyama, H.; Ōkawa, H.; Isobe, R. A functional model of manganese catalase. Mass spectrometric and visible spectral evidence for {MnIV(=O)}2 and MnIIMnIV(=O) intermediates. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1993, 882–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, J.W.; Browne, W.R.; Feringa, B.L.; Hage, R. Carboxylate-bridged dinuclear manganese systems—From catalases to oxidation catalysis. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2007, 10, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieghardt, K.; Bossek, U.; Nuber, B.; Weiss, J.; Bonvoisin, J.; Corbella, M.; Vitols, S.E.; Girerd, J.J. Synthesis, crystal structures, reactivity, and magnetochemistry of a series of binuclear complexes of manganese(II), -(III), and -(IV) of biological relevance. The crystal structure of [L’MnIV(μ-O)3MnIVL’](PF6)2·H2O containing an unprecedented short Mn···Mn distance of 2.296 Å. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 7398–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Haukka, M.; McKenzie, C.J.; Nordlander, E. High turnover catalase activity of a mixed-valence MnIIMnIII complex with terminal carboxylate donors. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 3485–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toftlund, H.; Markiewicz, A.; Murray, K.S. Synthesis and magnetic properties of a μ-oxo-di(μ-acetato)manganese(III) complex of a strapped tripodal pyridylamine ligand N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)-1,3-propanediamine. A model for the Mn2 site of Mn-catalase enzymes. Acta Chem. Scand. 1990, 44, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertürk, H.; Hofmann, A.; Puchta, R.; van Eldik, R. Influence of the bridging ligand on the substitution behavior of dinuclear Pt(II) complexes. An experimental and theoretical approach. Dalton Trans. 2007, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, V.; Bonomi, R.; Sissi, C.; Mancin, F. Phosphate diesters and DNA hydrolysis by dinuclear Zn(II) complexes featuring a disulfide bridge and H-bond donors. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, S.; Uchimaru, T. Dinucleotide hydrolysis promoted by dinuclear Zn complexes—The effect of the distance between Zn ions in the complexes on the hydrolysis rate. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 2001, 2437–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwood, P.W. Magnetochemistry; Interscience Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1956; pp. 78–91. [Google Scholar]
- Chilton, N.F.; Anderson, R.P.; Turner, L.D.; Soncini, A.; Murray, K.S. PHI: A powerful new program for the analysis of anisotropic monomeric and exchange-coupled polynuclear d- and f-block complexes. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaku Corporation. CrystalClear: Data Collection and Processing Software; Rigaku Corporation: Tokyo, Japan, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rigaku Oxford Diffraction. CrysAlis Pro; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction: Tokyo, Japan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, C.F.; Sovago, I.; Cottrell, S.J.; Galek, P.T.A.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Platings, M.; Shields, G.P.; Stevens, J.S.; Towler, M.; et al. Mercury 4.0: From visualization to analysis, design and prediction. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2020, 53, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spackman, M.A.; Jayatilaka, D. Hirshfeld surface analysis. CrystEngComm 2009, 11, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.-R.; Li, Q.; Leung, W.-P.; Makt, T.C.W. A dinuclear manganese(ll) complex doubly bridged by skew-skew μ-carboxylato groups: Synthesis and X-ray structure of [{Mn(bpy)2(p-Me2N+C5H4NCH2CO2−)}2](C1O4)4. Polyhedron 1997, 16, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, H.; Ishiwa, E.; Koikawa, M.; Nakashima, M.; Tokii, T. Synthesis, structure, and magnetic properties of triply carboxylato-bridged dimanganese(II) complexes. Chem. Lett. 1995, 24, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.; Ito, T.; Takahashi, K.; Koganezawa, T.; Hayashi, H.; Aratani, N.; Suzuki, M.; Yamada, H. Exploration of alkyl group effects on the molecular packing of 5,15-disubstituted tetrabenzoporphyrins toward efficient charge-carrier transport. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 32319–32329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinksma, J.; Hage, R.; Kerschner, J.; Feringa, B.L. The dinuclear manganese complex Mn2O(OAc)2(TPTN) as a catalyst for epoxidations with hydrogen peroxide. Chem. Commun. 2000, 537–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, G.B.; Phillips, R.J. Relationships between the carbon-oxygen stretching frequencies of carboxylato complexes and the type of carboxylate coordination. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1980, 33, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, V.; Corbella, M. Catalase activity of dinuclear MnIII compounds with chlorobenzoato bridges. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 3147–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).