Ketosis an Old Story Under a New Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ketosis and Its Impact on the Dairy Industry
2.1. Conventional View of Ketosis
2.2. Classification of Ketosis
2.3. Impact of Ketosis on Dairy Cows and the Dairy Industry
3. Current Diagnostic Approaches and Biomarkers for Ketosis
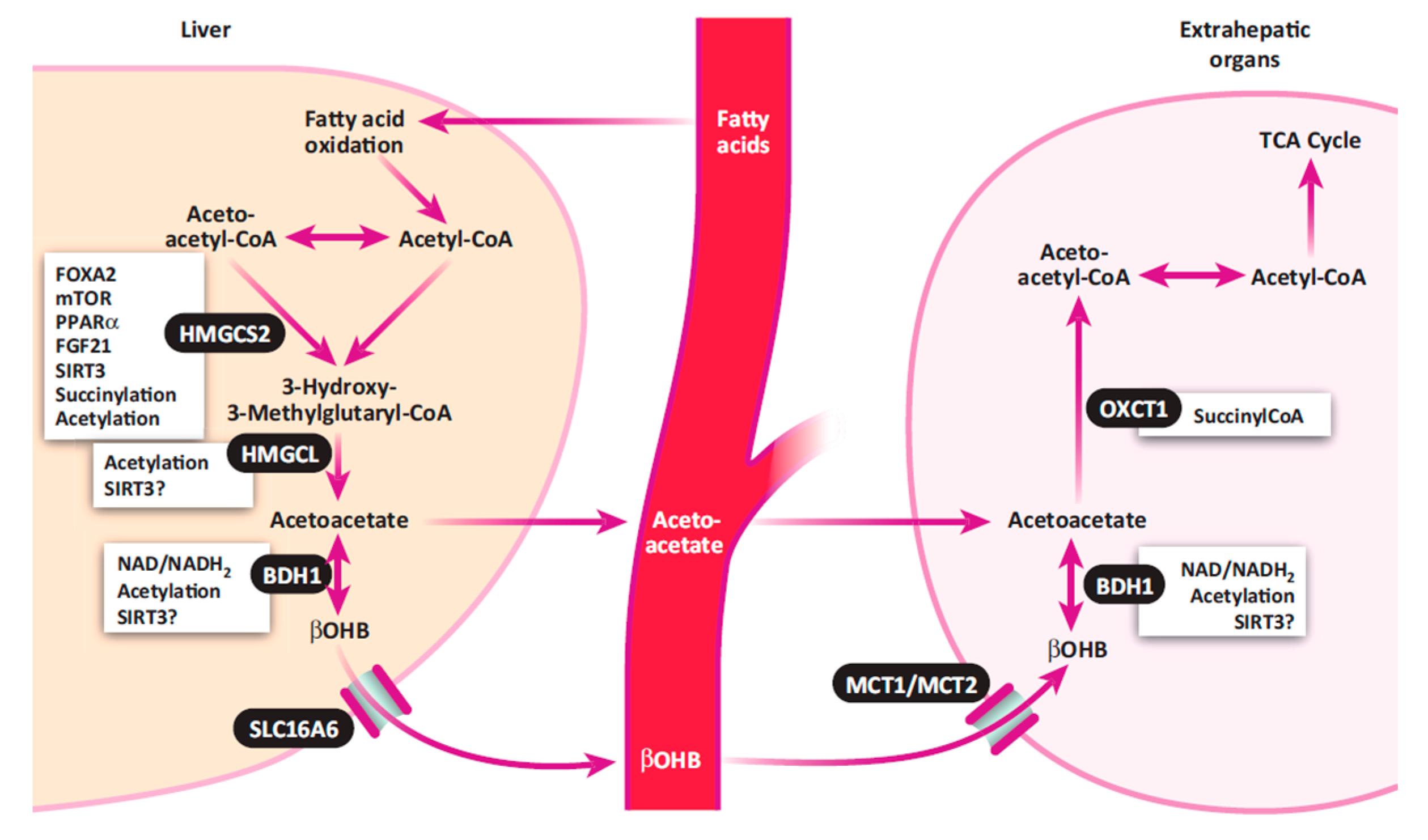
3.1. Ketone Bodies in the Blood, Urine, and Milk
3.2. Cow-side Tests for Ketosis
3.3. Some Newly Identified Diagnostic Biomarkers
4. Metabolomics: A New Approach to an Old Disease
4.1. NMR Spectroscopy and MS-Based Metabolomics
4.2. Metabolomic Databases and Bioinformatics Tools for Metabolomics Data Analyses and Interpretation
4.3. Application of Metabolomics in Studying Ketosis
4.4. Using Blood Metabolomics to Screen and Diagnose Diseases
4.5. Using Urine Metabolomics to Screen and Diagnose Diseases
4.6. Using Milk Metabolomics to Diagnose Diseases
5. Proposed Etiopathology of Ketosis in Dairy Cows
5.1. Importance of Dairy Cow Management during the Dry-Off Period
5.2. Involvement of Chronic Systemic Inflammatory Insult in Susceptibility to Ketosis
5.3. Protein Mobilization, Lipid Metabolism, and Gluconeogenesis
5.4. Understanding Ketosis at the Level of Systems Biology
5.5. Is Ketosis a Host Response to Systemic Inflammation?
5.6. Novel Predictive Serum and Urinary Biomarkers for Ketosis Identified during the Dry-Off Period
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oetzel, G.R. Monitoring and testing dairy herds for metabolic disease. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. 2004, 20, 651–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani-Sharif, M.; Hadadi, M.; Noughabi, H.H.; Mohammadi, A.; Rostami, F.; Sharifi, H. Bovine subclinical ketosis in dairy herds in Nishaboor, Iran. Comp. Clin Pathol. 2011, 21, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oetzel, G.R. Herd-level ketosis–diagnosis and risk factors. American Association of Bovine Practitioners. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–6 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Duffield, T.F. Subclinical ketosis in lactating dairy cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2000, 16, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffield, T.F.; Lissemore, K.D.; McBride, B.W.; Leslie, K.E. Impact of hyperketonemia in early lactation dairy cows on health and production. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McArt, J.A.; Nydam, D.V.; Ospina, P.A.; Oetzel, G.R. A field trial on the effect of propylene glycol on milk yield and resolution of ketosis in fresh cows diagnosed with subclinical ketosis. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 6011–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ospina, P.A.; Nydam, D.V.; Stokol, T.; Overton, T.R. Evaluation of nonesterified fatty acids and beta-hydroxybutyrate in transition dairy cattle in the northeastern United States: Critical thresholds for prediction of clinical diseases. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboisson, D.; Mounié, M.; Maigné, E. Diseases, reproductive performance, and changes in milk production associated with subclinical ketosis in dairy cows: A meta-analysis and review. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 7547–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.L. Risk Factors for and Treatment of Ketosis in Lactating Dairy Cows. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Guelph, Guelph, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Herdt, T.H. Ruminant adaptation to negative energy balance-Influences on the etiology of ketosis and fatty liver. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2000, 16, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, J.P.; Horst, R.L. Physiological changes at parturition and their relationship to metabolic disorders. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grummer, R.R. Nutritional and management strategies for the prevention of fatty liver in dairy cattle. Vet. J. 2008, 176, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, K.F.; Dawson, T.E.; Glenn, B.P.; Huntingto, G.B.; Erdman, R.A. Glucose metabolism and milk yield of cows infused abomasally or ruminally with starch. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 3248–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyle, R.R. Glucose Kinetics and Hepatic Gluconeogenesis in Ketotic and Fasted Steers. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University Ames, Iowa, IA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, J.C.; Verdin, E. Ketone bodies as signaling metabolites. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drackley, J.K.; Overton, T.R.; Douglas, G.N. 2001. Adaptations of glucose and long-chain fatty acid metabolism in liver of dairy cows during the periparturient period. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, E100–E112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayirli, A. The role of exogenous insulin in the complex of hepatic lipidosis and ketosis associated with insulin resistance phenomenon in postpartum dairy cattle. Vet. Res. Commun. 2006, 30, 749–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, V.S.; Canelas-Raposo, J.; Deniz, A.; Heuwieser, W. Prevalence of subclinical ketosis and relationships with postpartum diseases in European dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2925–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, J.L.; LeBlanc, S.J.; Duffield, T.F. Ketosis treatment in lactating dairy cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2013, 29, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtenius, P.; Holtenius, K. New aspects of ketone bodies in energy metabolism of dairy cows: A review. J. Vet. Med. A 1996, 43, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveit, B.; Lingaas, F.; Svendsen, M.; Sjaastad, O.V. Etiology of acetonemia in Norwegian cattle. 1. Effect of ketogenic silage, season, energy level, and genetic factors. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffield, T.F. Minimizing subclinical metabolic diseases in dairy cows. WCDS Adv. Dairy Technol. 2005, 18, 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc, S.J.; Leslie, K.; Duffield, T.F. Metabolic predictors of displaced abomasum in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammon, D.S.; Evjen, I.M.; Dhiman, T.R.; Goff, J.P.; Walters, J.L. Neutrophil function and energy status in Holstein cows with uterine health disorders. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2006, 113, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArt, J.A.; Nydam, D.V.; Oetzel, G.R. Epidemiology of subclinical ketosis in early lactation dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 5056–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dohoo, I.R.; Martin, S.W. Subclinical ketosis: Prevalence and associations with production and disease. Can. J. Comp. Med. 1984, 48, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kauppinen, K. Annual milk yield and reproductive performance of ketotic and non-ketotic dairy cows. Zbl. Vet. Med. A 1984, 31, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, P.V.A. Relationship between milk acetone and milk yield in individual cows. J. Vet. Med. A 1994, 41, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, P.V.A.; Setala, J.J. Relationships between subclinical ketosis, milk production and fertility in Finnish dairy cattle. Prev. Vet. Med. 1993, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geishauser, T.; Leslie, K.; Kelton, D.; Duffield, T. Monitoring for subclinical ketosis in dairy herds. Compend. Contin. Educ. Pract. Vet. 2001, 23, S65–S71. [Google Scholar]
- Oetzel, G.R. Understanding the Impact of Subclinical Ketosis. In Proceedings of the 24th Florida Ruminant Nutrition Symposium, Gainesville, FL, USA, 3–5 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D. Estimating the Economic Losses from Diseases and Extended Days Open with a Farm-level Stochastic Model. Master’s Thesis, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Työppönen, J.; Kauppinen, K. The stability and automatic determination of ketone bodies in blood samples taken in field conditions. Acta Vet. Scand. 1980, 21, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kronfeld, D.S.; Raggi, F.; Ramberg, C.F., Jr. Mammary blood flow and ketone metabolism in normal, fasted, and ketotic cows. Am. J. Physiol. 1968, 215, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Detection of subclinical ketosis in dairy cows. Pak. Vet. J. 2012, 32, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Hailemariam, D.; Dervishi, E.; Deng, Q.; Goldansaz, S.A.; Dunn, S.M.; Ametaj, B.N. Alterations of innate immunity reactants in transition dairy cows before clinical signs of lameness. Animals 2015, 5, 717–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, T.; Nielsen, N. Fluorometric determination of β-hydroxybutyrate in milk and blood plasma. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2004–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, M.S.; Almstetter, M.F.; Schlamberger, G.; Nürnberger, N.; Dettmer, K.; Oefner, P.J.; Meyer, H.H.D.; Wiedemann, S.; Gronwald, W. Nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry-based milk metabolomics in dairy cows during early and late lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Roos, A.P.W.; van den Bijgaart, H.J.; Hørlyk, J.; de Jong, G. 2007. Screening for subclinical ketosis in dairy cattle by Fourier transform infrared spectrometry. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heuer, C.; Luinge, H.J.; Lutz, E.T.G.; Schukken, Y.H.; van der Maas, J.H.; Wilmink, H.; Noordhuizen, J.P.T.M. Determination of Ac in cow milk by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for the detection of subclinical ketosis. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffield, T.F.; Kelton, D.F.; Leslie, K.E.; Lissemore, K.D.; Lumsden, J.H. Use of test day milk fat and milk protein to detect subclinical ketosis in dairy cattle in Ontario. Can. Vet. J. 1997, 38, 713–718. [Google Scholar]
- Gantner, V.; Potocnik, K.; Jovanovac, S. Test-day records as a tool for subclinical ketosis detection. Acta Vet. Beogr. 2009, 59, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Čejna, V.; Chládek, G. The importance of monitoring changes in milk fat to milk protein ratio in Holstein cows during lactation. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2005, 6, 539–546. [Google Scholar]
- Heuwieser, W.; Falkenberg, U.; Iwersen, M.; Voigtsberger, R.; Padberg, W. Evaluation and use of an automated human β-hydroxybuturate (BHBA) test for cowside detection of subclinical ketosis in dairy cattle. In Proceedings of the Fortieth Annual Conference, American Association of Bovine Practitioners, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–22 September 2007; pp. 253–254. [Google Scholar]
- Nielen, M.; Aarts, M.G.A.; Jonkers, A.G.M.; Wensing, T.; Schukken, Y.H. Evaluation of two cowside tests for the detection of subclinical ketosis in dairy cows. Can. Vet. J. 1994, 35, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Geishauser, T.; Leslie, K.; Tenhag, J.; Bashiri, A. Evaluation of eight cowside ketone tests in milk for detection of subclinical ketosis in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, T.M.; Leslie, K.E.; Duffield, T.F.; Petersson, C.S.; TenHag, J.; Okada, Y. Evaluation of Keto-Test in urine and milk for the detection of subclinical ketosis in periparturient Holstein dairy cattle. In Proceedings of the 35th Conference of the American Association of Bovine Practitioners, Rome, GA, USA, 26–28 September 2002; pp. 188–189. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, N.T.; Peña, G.; Risco, C.; Barbosa, C.C.; Vieira-Neto, A.; Galvão, K.N. Utility of inline milk fat and protein ratio to diagnose subclinical ketosis and to assign propylene glycol treatment in lactating dairy cows. Can. Vet. J. 2015, 56, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tatone, E.H.; Gordon, J.L.; Hubbs, J.; LeBlanc, S.J.; DeVries, T.J.; Duffield, T.F. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care tests for the detection of hyperketonemia in dairy cows. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 130, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Knegsel, A.T.M.; Drift, S.G.A.; Horneman, M.; Roos, A.P.W.d.; Kemp, B.; Graat, E.A.M. Short communication: Ketone body concentration in milk determined by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: Value for the detection of hyperketonemia in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 3065–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Drift, S.G.A.; Jorritsma, R.; Schonewille, J.T.; Knijn, H.M.; Stegeman, J.A. Routine detection of hyperketonemia in dairy cows using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis of beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetone in milk in combination with test-day information. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 4886–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denis-Robichaud, J.; DesCôteaux, L.; Dubuc, J. Accuracy of a new milk strip cow-side test for diagnosis of hyperketonemia. Bovine Pract. Summer 2011, 45, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Jorjong, S.; van Knegsel, A.T.; Verwaeren, J.; Bruckmaier, R.M.; De Baets, B.; Kemp, B.; Fievez, V. Milk fatty acids as possible biomarkers to diagnose hyperketonemia in early lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 5211–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; Xie, G.; Xia, C.; Zhang, H.Y. Metabolic characteristic of the liver of dairy cows during ketosis based on comparative proteomics. Asian Aust. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 21, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Shu, S.; Xia, C.; Wang, P.; Sun, Y.; Xu, C.; Li, C. Mass spectral analysis of urine proteomic profiles of dairy cows suffering from clinical ketosis. Vet. Q. 2015, 35, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Xu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Xia, C.; Yu, H.; Zhu, K.; Shen, T.; Zhang, Z. FGF-21: Promising biomarker for detecting ketosis in dairy cows. Vet. Res. Commun. 2016, 40, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Wilson, M.; Wishart, D.S. Translational biomarker discovery in clinical metabolomics: An introductory tutorial. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 280–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, F.P.J.; Collino, S.; Rezzi, S.; Kochhar, S. Metabolomic applications to decipher gut microbial metabolic influence in health and disease. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, Q.T.; Merlo, M.E.; Medema, M.H.; Jankevics, A.; Breitling, R.; Takano, E. Metabolomics methods for the synthetic biology of secondary metabolism. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2177–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Atherton, H.J.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L. Systems level studies of mammalian metabolomes: The roles of mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 387–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Vallejo, M.; García, A.; Barbas, C. Method validation strategies involved in non-targeted metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. A. 2014, 1353, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.D.; Souza, A.L.; Gerszten, R.E.; Clish, C.B. Targeted Metabolomics. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2012, 30, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmer, K.; Aronov, P.A.; Hammock, B.D. Mass spectrometry–based metabolomics. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2007, 26, 51–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.N. Principles of NMR for Applications in Metabolomics. In The Handbook of Metabolomics, Methods in Pharmacology and Toxicology; Fan, T.W.M., Lane, A.N., Higashi, R.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 127–197. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, F. The Use of Modern Metabolomics and Proteomics to Address the Health Challenges Facing the Canadian Cattle Industry. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bloch, F.; Hansen, W.W.; Packard, M. The nuclear induction experiment. Phys. Rev. 1946, 70, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, E.M.; Torrey, H.C.; Pound, R.V. Resonance absorption by nuclear magnetic moments in a solid. Phys. Rev. 1946, 69, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larive, C.K.; Barding, G.A., Jr.; Dinges, M.M. NMR spectroscopy for metabolomics and metabolic profiling. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hoffmann, E.; Stroobant, V. Mass Spectrometry: Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 85–167. [Google Scholar]
- Boernsen, K.O.; Gatzek, S.; Imbert, G. Controlled protein precipitation in combination with chip-based nanospray infusion mass spectrometry. An approach for metabolomics profiling of plasma. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 7255–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouatra, S.; Aziat, F.; Mandal, R.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.R.; Knox, C.; Bjorndahl, T.C.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Saleem, F.; Liu, P.; et al. The human urine metabolome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Psychogios, N.; Hau, D.D.; Peng, J.; Guo, A.C.; Mandal, R.; Bouatra, S.; Sinelnikov, I.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Eisner, B.; Gautam, N.; et al. The human metabolome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pham-Tuan, H.; Kaskavelis, L.; Daykin, C.A.; Janssen, H.G. Method development in high-performance liquid chromatography for high-throughput profiling and metabonomic studies of biofluid samples. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2003, 789, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S.; et al. HMDB: The Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D521–D526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Knox, C.; Guo, A.C.; Eisner, R.; Young, N.; Gautam, B.; Hau, D.D.; Psychogios, N.; Dong, E.; Bouatra, S.; et al. HMDB: A knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D603–D610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E.; et al. HMDB 3.0–The Human Metabolome Database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Mandal, R.; Sinelnikov, I.V.; Broadhurst, D.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst 2.0-a comprehensive server for metabolomic data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W127–W133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.; Sinelnikov, I.V.; Han, B.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst 3.0-making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W251–W257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C. Systems biology: Metabonomics. Nature 2008, 455, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, G.A.N.; Zhang, S.; Gu, H.; Asiago, V.; Shanaiah, N.; Raftery, D. Metabolomics-based methods for early disease diagnostics: A review. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 8, 317–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Xia, C.; Zhang, H.Y.; Sun, L.W.; Gao, Y. Plasma metabolic profiling of dairy cows affected with clinical ketosis using LC/MS technology. Vet. Q. 2014, 34, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wu, L.; Shu, S.; Xia, C.; Xu, C.; Zheng, J.S. 1H-Nuclear magnetic resonance-based plasma metabolic profiling of dairy cows with clinical and subclinical ketosis. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 97, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Xu, C.; Xia, C.; Sun, L.; Shu, S. Plasma metabolomic profiling of dairy cows affected with ketosis using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Xia, C.; Zhang, H.Y.; Sun, L.; Xu, C. 1H NMR-based plasma metabolic profiling of dairy cows with Type I and Type II ketosis. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2015, 6, 1000328. [Google Scholar]
- Emwas, A.H.; Luchinat, C.; Turano, P.; Tenori, L.; Roy, R.; Salek, R.M.; Ryan, D.; Merzaban, J.S.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; Zeri, A.C.; et al. Standardizing the experimental conditions for using urine in NMR-based metabolomic studies with a particular focus on diagnostic studies: A review. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 872–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, M.S.; Buttchereit, N.; Miemczyk, S.P.; Immervoll, A.K.; Louis, C.; Wiedemann, S.; Junge, W.; Thaller, G.; Oefner, P.J.; Gronwald, W. NMR metabolomic analysis of dairy cows reveals mlk glycerophosphocholine to phosphocholine ratio as prognostic biomarker for risk of ketosis. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundekilde, U.K.; Poulsen, N.A.; Larsen, L.B.; Bertram, H.C. Nuclear magnetic resonance metabonomics reveals strong association between milk metabolites and somatic cell count in bovine milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, R. Proteomics and Metabolomicsstudies on Milk during Bovine Mastitis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dingwell, R.T.; Kelton, D.F.; Leslie, K.E.; Edge, V.L. Deciding to dry-off: Does level of production matter? In Proceedings of the National Mastitis Council Annual Meeting Proceedings, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11–14 February 2001; pp. 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Leelahapongsathon, K.; Piroon, T.; Chaisri, W.; Suriyasathaporn, W. Factors in dry period associated with intramammary infection and subsequent clinical mastitis in early postpartum cows. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 580–585. [Google Scholar]
- Erb, H.N.; GroÈhn, Y.T. Epidemiology of metabolic disorders in the periparturient dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1988, 71, 2557–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ametaj, B.N.; Bradford, B.J.; Bobe, G.; Nafikov, R.A.; Lu, Y.; Young, J.W.; Beitz, D.C. Strong relationships between mediators of the acute phase response and fatty liver in dairy cows. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 85, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ametaj, B.N. A new understanding of the causes of fatty liver in dairy cows. Adv. Dairy Technol. 2005, 17, 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Hailemariam, D.; Dervishi, E.; Deng, Q.; Goldansaz, S.A.; Dunn, S.M.; Ametaj, B.N. Dairy cows affected by ketosis show alterations in innate immunity and lipid and carbohydrate metabolism during the dry off period and postpartum. Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 107, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, Y.H.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Grant, R.W.; Goldberg, E.L.; Bodogai, M.; Kim, D.; D’Agostino, D.; Planavsky, N.; Lupfer, C.; Kanneganti, T.D.; et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harte, C.; Gorman, A.L.; McCluskey, S.; Carty, M.; Bowie, A.G.; Scott, C.J.; Meade, K.G.; Lavelle, E.C. Alum Activates the Bovine NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drackley, J.K. Factors Contributing to Development of Fatty Liver and Ketosis in Lactating Dairy Cows. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zebeli, Q.; Dunn, S.M.; Ametaj, B.N. Perturbations of plasma metabolites correlated with the rise of rumen endotoxin in dairy cows fed diets rich in easily degradable carbohydrates. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 2374–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Soriano, F.J.; Williamson, D.H. Acute effects of endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide) on tissue lipid metabolism in the lactating rat. The role of delivery of intestinal glucose. Mol. Cell Biochem. 1994, 141, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feingold, K.R.; Staprans, I.; Memon, R.; AMoser, A.H.; Shigenaga, J.K.; Doerrler, W.; Dinarello, C.A.; Grunfeld, C. Endotoxin rapidly induces changes in lipid metabolism that produce hypertriglyceridemia: Low doses stimulate hepatic triglyceride production while high doses inhibit clearance. J. Lipid Res. 1992, 33, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Kremer, W.D.; Noordhuizen-Stassen, E.N.; Grommers, F.J.; Schukken, Y.H.; Heeringa, R.; Brand, A.; Burvenich, C. Severity of experimental Escherichia coli mastitis in ketonemic and nonketonemic dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1993, 76, 3428–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, T.; McCann, K.; Gilbert, D.O.; Nydam, D.V.; Overton, T.R. Associations of cytological endometritis with energy metabolism and inflammation during the periparturient period and early lactation in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 2763–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sartorelli, P.; Paltrinieri, S.; Agnes, F. Non-specific immunity and ketone bodies. I: In vitro studies on chemotaxis and phagocytosis in ovine neutrophils. J. Vet. Med. A 1999, 46, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Williams, K.L.; Oliver, T.; Vandenabeele, P.; Rajan, J.V.; Miao, E.A.; Shinohara, M.L. Interferon-beta therapy against EAE is effective only when development of the disease depends on the NLRP3 inflammasome. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, B.Z.; Xu, Z.Q.; Han, B.Z.; Su, D.F.; Liu, C. NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tóthová, C.; Nagy, O.; Kováč, G. Relationship between some variables of protein profile and indicators of lipomobilization in dairy cows after calving. Archiv. Tierzucht. 2014, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overton, T.R.; Drackley, J.K.; Douglas, G.N.; Emmert, L.S.; Clark, J.H. Hepatic gluconeogenesis and whole-body protein metabolism of periparturient dairy cows as affected by source of energy and intake of the prepartum diet. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 295. [Google Scholar]
- Loor, J.J.; Everts, R.E.; Bionaz, M.; Dann, H.M.; Morin, D.E.; Oliveira, R.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L.; Drackley, J.K.; Lewin, H.A. Nutrition-induced ketosis alters metabolic and signaling gene networks in liver of periparturient dairy cows. Physiol. Genom. 2007, 32, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Dervishi, E.; Dunn, S.M.; Mandal, R.; Liu, P.; Han, B.; Wishart, D.S.; Ametaj, B.N. Metabotyping reveals distinct metabolic alterations in ketotic cows and identifies early predictive serum biomarkers for the risk of disease. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Dervishi, E.; Mandal, R.; Wishart, D.S.; Ametaj, B.N. Metallotyping of ketotic dairy cows reveals major alterations preceding, associating, and following the disease occurrence. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Ametaj, B.N. Ketosis an Old Story Under a New Approach. Dairy 2020, 1, 42-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy1010005
Zhang G, Ametaj BN. Ketosis an Old Story Under a New Approach. Dairy. 2020; 1(1):42-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guanshi, and Burim N. Ametaj. 2020. "Ketosis an Old Story Under a New Approach" Dairy 1, no. 1: 42-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy1010005
APA StyleZhang, G., & Ametaj, B. N. (2020). Ketosis an Old Story Under a New Approach. Dairy, 1(1), 42-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy1010005





