Scheduling of a Microgrid with High Penetration of Electric Vehicles Considering Congestion and Operations Costs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Objective 1: Minimize Congestion
| is the MVA flow on line i in hour j | |
| is the MVA capacity of line i in hour j |
2.2. Operation Costs of a Microgrid (Objective Function 2 of the Problem to Be Solved)
2.2.1. Cost of Conventional Energy F1(x)
2.2.2. Cost of the Electric Vehicles F2(x)
2.2.3. Cost of Operation for Storage F3(x)
2.2.4. Cost of Operation Photovoltaic Generator and Wind Power Generator F4(x)
3. Optimization Methodology
Multi-Objective Particle Optimization Algorithm
4. Results
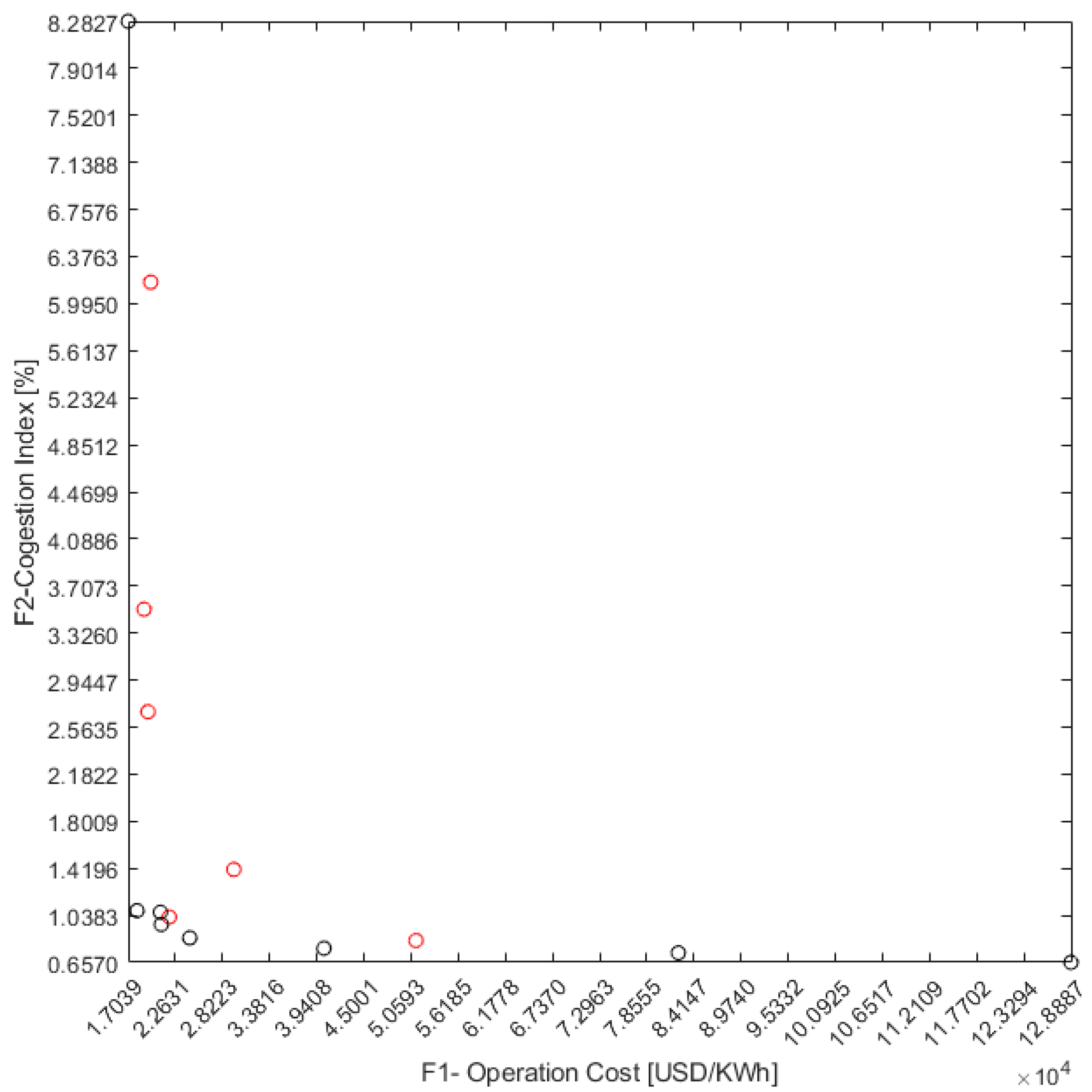
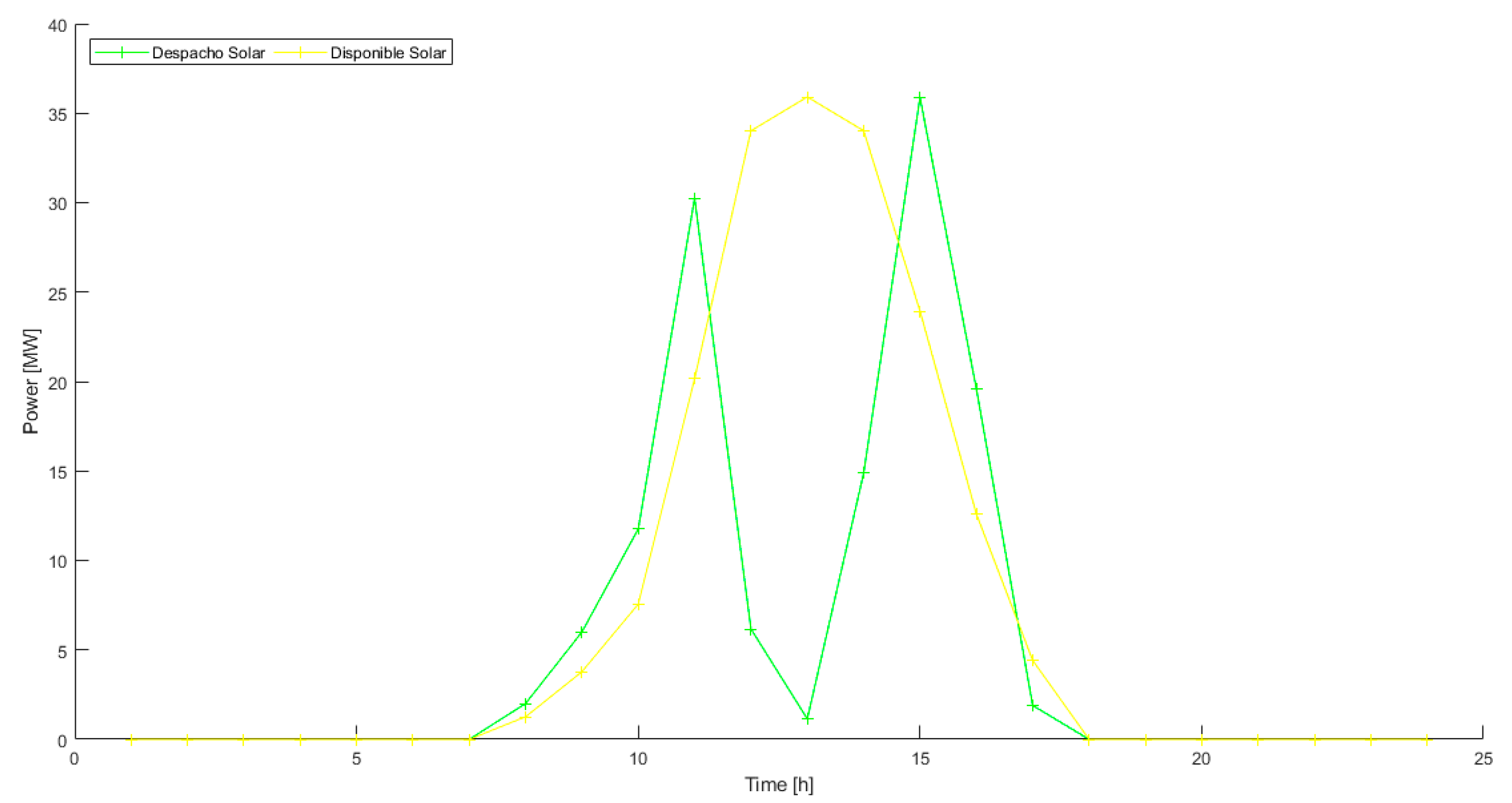
4.1. Variation of the Decision Variables at the Pareto Optimal Points
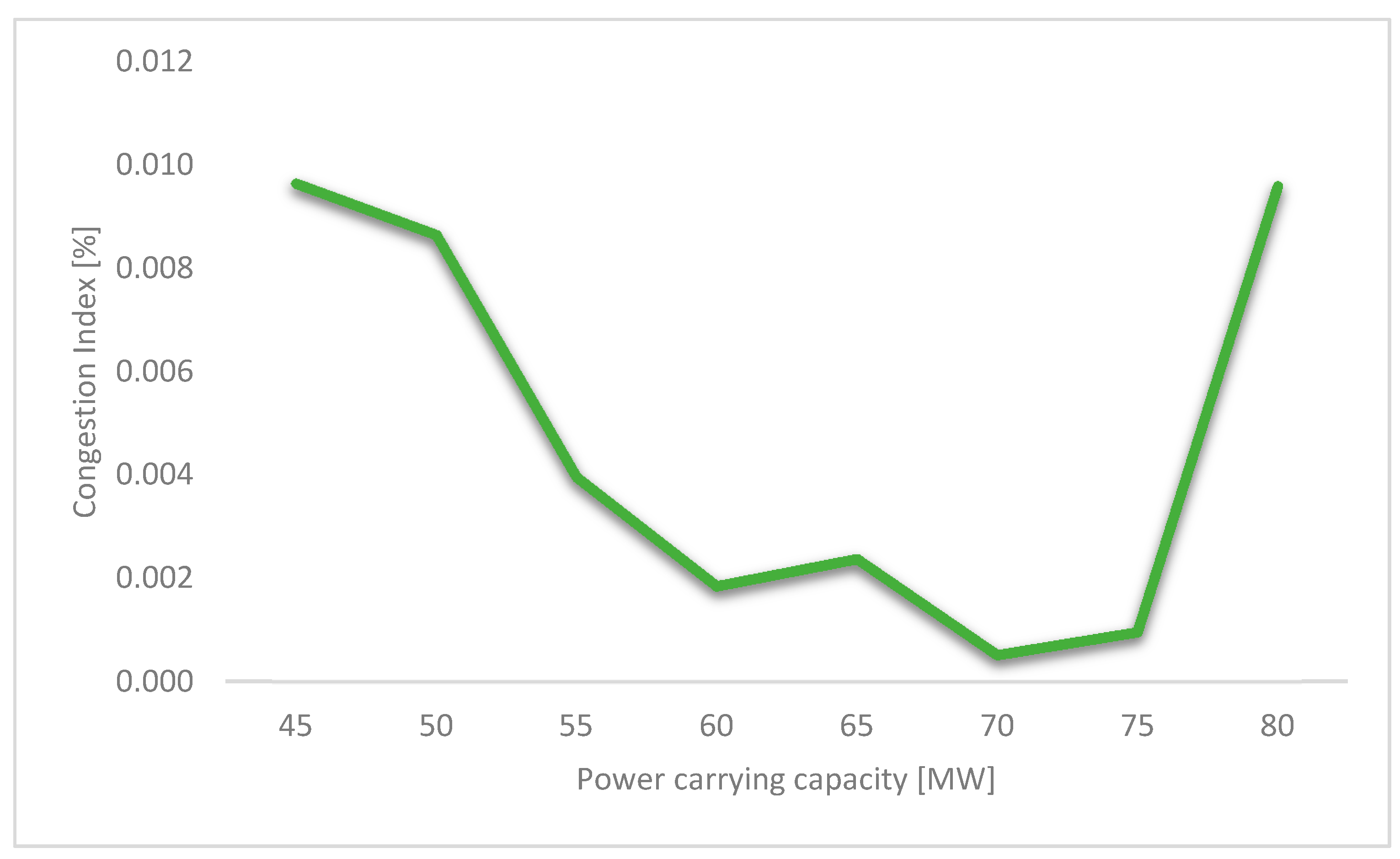
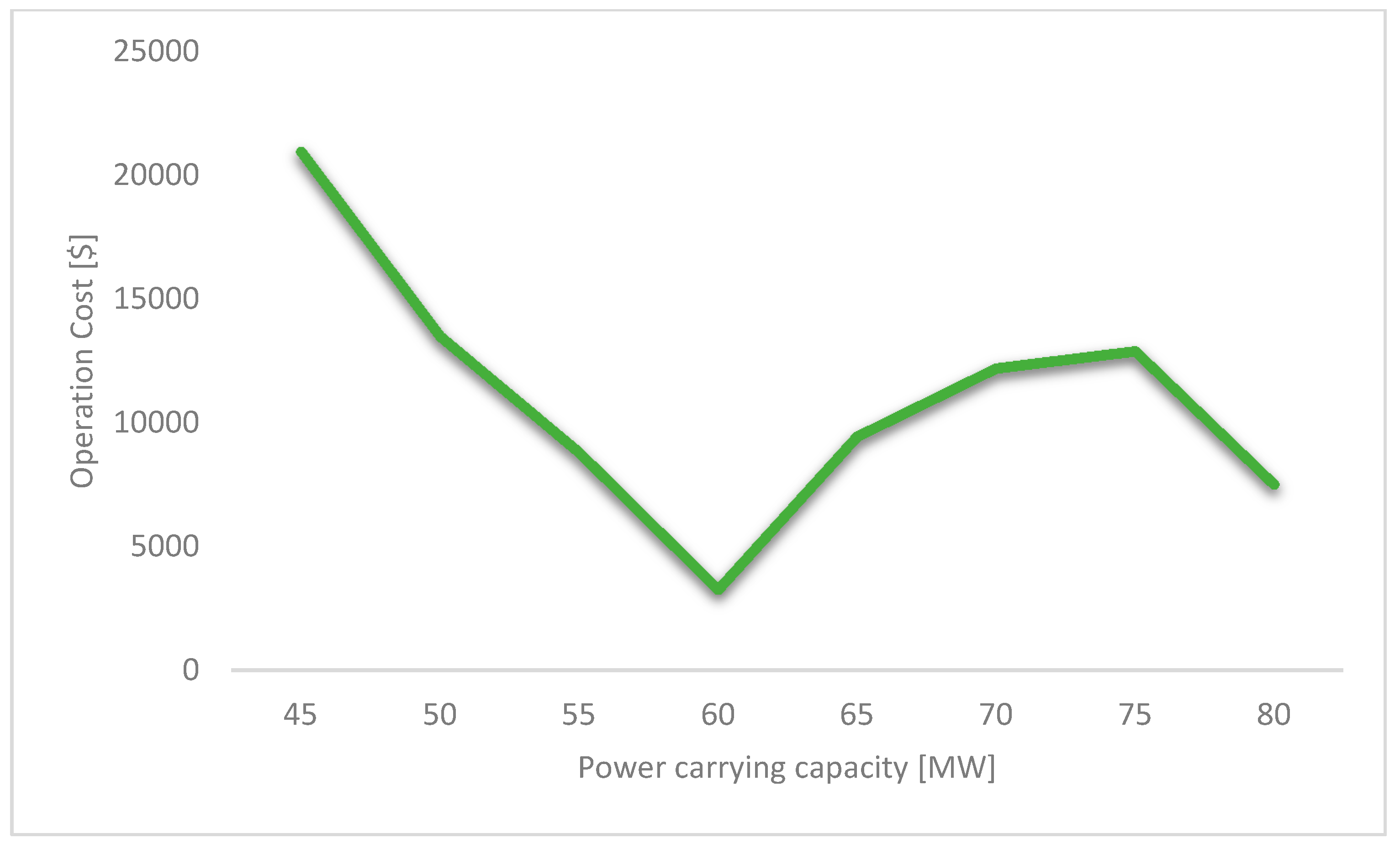
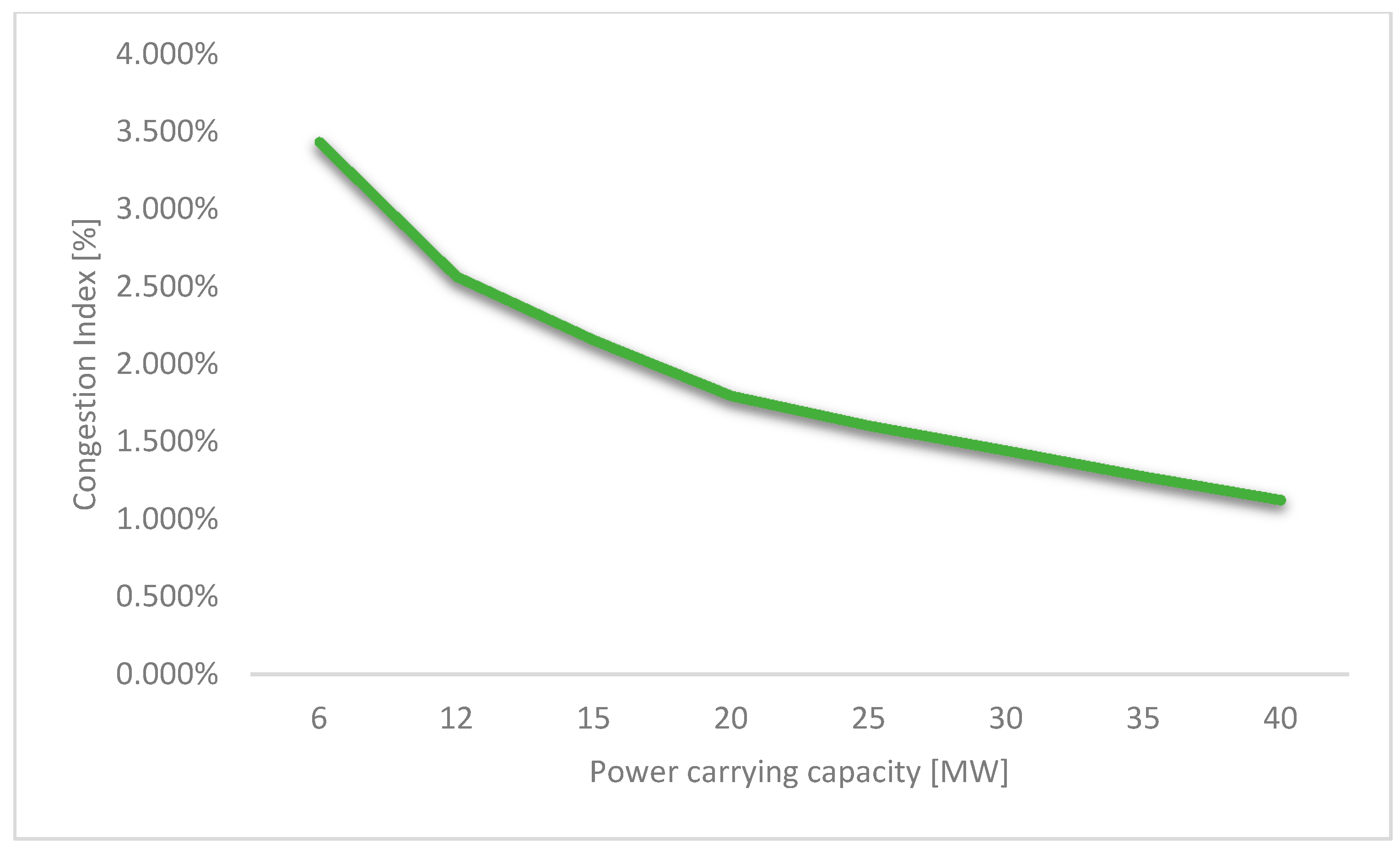
4.2. Sensibility Analysis of Line Capacity in the Modified IEEE Case No. 141
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, S.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Nielsen, A.H. Review of congestion management methods for distribution networks with high penetration of distributed energy resources. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–15 October 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdolahi, A.; Salehi, J.; Gazijahani, F.S.; Safari, A. Probabilistic multi-objective arbitrage of dispersed energy storage systems for optimal congestion management of active distribution networks including solar/wind/CHP hybrid energy system. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2018, 10, 045502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiliotis, K.; Claeys, S.; Gutierrez, A.R.; Driesen, J. Utilizing local energy storage for congestion management and investment deferral in distribution networks. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), Porto, Portugal, 6–9 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez Lezama, J.M. Propuestas Alternativas para Manejo de Congestión en el Mercado de Energía Eléctrica Colombiano. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Manizales, Colombia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gope, S.; Dawn, S.; Mitra, R.; Goswami, A.K.; Tiwari, P.K. Transmission congestion relief with integration of photovoltaic power using lion optimization algorithm. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2019, 816, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reihani, E.; Siano, P.; Genova, M. A new method for peer-to-peer energy exchange in distribution grids. Energies 2020, 13, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijayakumar, K. Multiobjective optimization methods for congestion management in deregulated power systems. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2012, 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez Lezama, J.M. Propuestas Alternativas Para Manejo De Congestión En El Mercado De Energía Eléctrica Colombiano; Universidad Nacional de Colombia Sede Manizales Departamento de Ingeniería Eléctrica, Electrónica y Computación: Manizalez, Columbia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, IEEE Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation Society. Kolkata Chapter, IEEE Power & Energy Society. Kolkata Chapter, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. Kolkata section, and North Eastern Regional Institute of Science and Technology. In Proceedings of the 2012 1st International Conference on Power and Energy in NERIST (lCPEN), Nirjuli, India, 28–29 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hazra, J.; Sinha, A.K. Congestion management using multiobjective particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2007, 22, 1726–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, I.; Sarimveis, H. Predictive control algorithms for congestion management in electric power distribution grids. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 77, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, Q.; Wen, F.; Østergaard, J. Day-ahead congestion management in distribution systems through household demand response and distribution congestion prices. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashyap, M.; Kansal, S. Hybrid approach for congestion management using optimal placement of distributed generator. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2017, 39, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, F. A congestion index considering the characteristics of generators & networks. In Proceedings of the 47th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Uxbridge, UK, 4–7 September 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Pal, B.B. A fuzzy goal programming method to solve congestion management problem using genetic algorithm. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2019, 2, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Asati, N. Congestion management using genetic algorithm. Int. Res. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2019, 7, 19–23. Available online: https://www.irjeas.org/wp-content/uploads/admin/volume7/V7I2/IRJEAS04V7I204190619000005.pdf (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Khani, H.; Zadeh, M.R.D.; Hajimiragha, A.H. Transmission congestion relief using privately owned large-scale energy storage systems in a competitive electricity market. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 31, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, K.; Sugihara, H.; Tsuji, K.; Mitani, Y. A study on power flow congestion relief by using customer-side energy storage system. IEEJ Trans. Power Energy 2005, 125, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, F.; Massucco, S.; Pongiglione, P.; Saviozzi, M.; Silvestro, F. Optimal DER regulation and storage allocation in distribution networks: Volt/Var optimization and congestion relief. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Milan PowerTech, Milan, Italy, 23–27 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, J.; Padmanaban, M.; Zaini, F.; De Silva, L.C. Congestion relief using grid scale batteries. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Power and Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 18–20 February 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Nguyen, P.; Kling, W.; Bliek, F. Congestion management in smart distribution network. In Proceedings of the 49th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 2–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.T.; Fernandez-Blanco, R.; Kozdras, K.; Kaplan, J.; Lockyear, B.; Zyskowski, J.; Kirschen, D.S. Sharing energy storage between transmission and distribution. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 34, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koeppel, G.; Geidl, M.; Andersson, G.; Koeppel, G.; Geidl, M.; Andersson, G. Value of storage devices in congestion constrained distribution networks’ value of storage devices in congestion constrained distribution networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Power System Technology, PowerCon 2004, Singapore, 21–24 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, B.K.; DE, A.; Chakrabarti, A. Impact of distributed generation for congestion relief in power networks. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Power and Energy in NERIST, ICPEN 2012, Nirjuli, India, 28–29 December 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Troitzsch, S.; Hanif, S.; Hamacher, T. Coordinated market design for peer-to-peer energy trade and ancillary services in distribution grids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 2929–2941. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338501038 (accessed on 8 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, G.; Ziras, C.; Kok, K. Aggregator Operation in the balancing market through network-constrained transactive energy. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 34, 4071–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, G.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Wu, J. Congestion management method of low-voltage active distribution networks based on distribution locational marginal price. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 32240–32255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barón Moreno, C.E. Programación de la Operación Horaria de una Microred Minimizando el Costo de Operación Usando el Algoritmo Heurístico DEEPSO. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogota, Colombia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Arévalo, J.; Santos, F.; Rivera, S. Aplicación de costos de incertidumbre analíticos de energía solar, eólica y vehículos eléctricos en el despacho óptimo de potencia. Ingeniería 2017, 22, 324–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wibowo, R.S.; Utama, F.F.; Putra, D.F.U.; Aryani, N.K. Unit commitment with non-smooth generation cost function using binary particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the International Seminar on Intelligent Technology and Its Application, ISITIA 2016: Recent Trends in Intelligent Computational Technologies for Sustainable Energy, Lombok, Indonesia, 28–30 July 2016; pp. 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ren, Z.; Ma, R.; Tang, M.; He, Z. Research on Double-Layer Optimized Configuration of Multi-Energy Storage in Regional Integrated Energy System with Connected Distributed Wind Power. Energies 2019, 12, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baron, C.; Rivera, S. Mono-objective minimization of operation cost for a microgrid with renewable power generation, energy storage and electric vehicles. Rev. Int. Métodos Numéricos Cálculo Diseño Ing. 2019, 35, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, J.C.; Santos, F.; Rivera, S. Uncertainty cost functions for solar photovoltaic generation, wind energy generation, and plug-in electric vehicles: Mathematical expected value and verification by Monte Carlo simulation. Int. J. Power Energy Convers. 2019, 10, 171–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y. Coordination of PEVs charging across multiple aggregators. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpi, A.; Porru, M. Modelling and design of real-time energy management systems for fuel cell/battery electric vehicles. Energies 2019, 12, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, A.; Bui, V.-H.; Baek, J.-W.; Kim, H.-M. Stationary energy storage system for fast EV charging stations: Simultaneous sizing of battery and converter. Energies 2019, 12, 4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dufo-López, R.; Agustín, J.L.B. Multi-objective design of PV-wind-diesel-hydrogen-battery systems. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 2559–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, F.; Zaferanlouei, S.; Korpås, M.; Uhlen, K. Optimal operation of battery storage for a subscribed capacity-based power tariff prosumer—A norwegian case study. Energies 2019, 12, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jankowiak, C.; Zacharopoulos, A.; Brandoni, C.; Keatley, P.; MacArtain, P.; Hewitt, N. The role of domestic integrated battery energy storage systems for electricity network performance enhancement. Energies 2019, 12, 3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, L. Operation optimization of standalone microgrids considering lifetime characteristics of battery energy storage system. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, T.; Jasiński, M.; Ropuszyńska-Surma, E.; Węglarz, M.; Kaczorowska, D.; Kostyła, P.; Leonowicz, Z.; Lis, R.; Rezmer, J.; Rojewski, W.; et al. A case study on distributed energy resources and energy-storage systems in a virtual power plant concept: Economic aspects. Energies 2019, 12, 4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coello, C.A.C.; Lamont, G.B.; Van Veldhuizen, D.A. Evolutionary Algorithms for Solving Multi-Objective Problems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gallego Rendon, R.A.; Escobar Zuluaga, A.H.; Toro Ocampo, E.M.; Lazaro, R.A.R. Tecnicas Heuristicas y Metaheuristicas de Optimizacion, 2nd ed.; Universidad Tecnologica de Pereira: Pereira, Colombia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vélez Gallego, M.C.; Montoya, J.A. Metaheurísticos: Una alternativa para la solución de problemas combinatorios en administración de operaciones. Revista EIA Esc. Ing. Antioq. 2007, 8, 99–115. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1794-12372007000200009&lng=en&nrm=iso (accessed on 7 June 2021). [CrossRef]






| Buses | 141 |
| Generators | 3 |
| Loads | 84 |
| Fixed | 84 |
| Dispatchable | 0 |
| Shunts | 0 |
| Branches | 140 |
| Transformers | 0 |
| 0 | |
| Areas | 1 |
| Total Generation Capacity | P (MW) | Q (MVAr) |
|---|---|---|
| Total generation capacity | 2997.0 | −2997.0 to 2997.0 |
| Current generation | 89.1 | 59.9 |
| Load | 59.5 | 36.9 |
| Fixed | 59.5 | 36.9 |
| Dispatchable | −0.0 of −0.0 | −0.0 |
| Shunt (inj) | 29.64 | 0.0 |
| Losses (I2 * Z) | 29.64 | 23.04 |
| Branch load (ing) | 89.1 | 0.0 |
| Total flow between links | 0 | 0.0 |
| Parameters | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| params.Np | 10 | Population size |
| params.Nr | 10 | Repository size |
| params.maxgen | 50 | Maximum number of generations |
| params.W | 0.4 | Inertia weight |
| params.C1 | 2 | Individual confidence factor |
| params.C2 | 2 | Swarm confidence factor |
| params.ngrid | 20 | Number of grids in each dimension |
| params.maxvel | 5 | Maximum vel in percentage |
| params.u_mut | 0.5 | Uniform mutation percentage |
| Notation | Value | Description and Units |
|---|---|---|
| Costdiesel | 0.8 | Taken from the Energy Information Administration of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)-(USD/KWh) |
| CUbat | 180 | Battery cost (USD/KWh) (from reference [27]) |
| Ctransbat | 1.05 | Cost overrun due to the transportation of the batteries |
| Cinit | Cbat × Ubat × Ctransbat | Initial cost of the batteries, in dollars. |
| CostSolar | 0.0803 | Solar energy cost (USD/kWh) (from reference [28]) |
| CostWind | 0.130 | Cost of wind energy (USD/kWh [28]) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nitola, A.; Marin, J.; Rivera, S. Scheduling of a Microgrid with High Penetration of Electric Vehicles Considering Congestion and Operations Costs. Vehicles 2021, 3, 578-594. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles3030035
Nitola A, Marin J, Rivera S. Scheduling of a Microgrid with High Penetration of Electric Vehicles Considering Congestion and Operations Costs. Vehicles. 2021; 3(3):578-594. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles3030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleNitola, Alejandra, Jennyfer Marin, and Sergio Rivera. 2021. "Scheduling of a Microgrid with High Penetration of Electric Vehicles Considering Congestion and Operations Costs" Vehicles 3, no. 3: 578-594. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles3030035
APA StyleNitola, A., Marin, J., & Rivera, S. (2021). Scheduling of a Microgrid with High Penetration of Electric Vehicles Considering Congestion and Operations Costs. Vehicles, 3(3), 578-594. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles3030035






