- Article
An Adaptive Full-Order Sliding-Mode Observer Based-Sensorless Control for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Propulsion Motors Drives
- Shengqi Huang,
- Yuqing Huang and
- Junwu Zhang
- + 2 authors
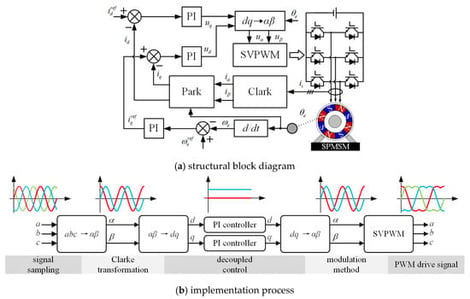
In electric vehicle and marine propulsion applications, the stable operation of permanent-magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) drive systems relies on accurate rotor position information. Such information is typically obtained from position sensors, which are prone to high temperature, humidity, vibration, and electromagnetic interference, leading to elevated failure rates; moreover, sensor installation introduces additional interfaces and wiring, thereby reducing system reliability. To address these issues, this paper proposes a sensorless control method based on an adaptive full-order sliding-mode observer (SMO). The proposed method employs the SMO output as the observer feedback correction term rather than the estimated back EMF, thereby avoiding substantial high-frequency noise. Furthermore, an S-shaped nonlinear function is designed to replace the conventional switching function, mitigating high-frequency chattering when the system operates in sliding mode; an adaptive sliding-mode gain function is designed, the sliding-mode gain and the boundary-layer thickness are adaptively tuned as a function of motor speed, which effectively enhances the back EMF estimation accuracy over a wide operating-speed range. The effectiveness of the proposed method is validated on a 2.3-kW PMSM experimental platform.
7 February 2026