Game-Theoretic Cooperative Task Allocation for Multiple-Mobile-Robot Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation and Incitement
1.2. Related Work
1.2.1. Centralized Methods
1.2.2. Distributed Methods
1.2.3. Learning-Based Methods
1.3. Contributions and Paper Organization
- Existing research on multi-robot task allocation primarily focuses on task allocation and path planning, with limited attention to cooperative coalitions among robots and the optimization of resource utilization. In traditional approaches, robots are often treated as independent entities executing tasks, with task allocation based mainly on factors such as cost, distance, or completion time. However, these methods overlook the diverse resource needs of tasks and the potentiality for collaboration between robots. To address this issue, this study proposes a distributed multi-robot task allocation model which focuses on optimizing the resource utilization. Unlike previous methods, we not only consider the task allocation but also introduce the concept of robot coalitions, and this allows robots to share resources and collaboratively complete complex tasks. Specifically, we construct resource supply vectors for robots and resource demand vectors for tasks, while incorporating spatiotemporal constraints to ensure efficient task execution and fulfillment of resource requirements.
- We construct a task allocation model based on game theory and demonstrate that the game is an exact potential game. Then, we propose a coalition formation algorithm based on game theory to maximize the resource utilization. The effectiveness of the algorithm is validated via simulation experiments. This method improves overall resource utilization by using collaboration and resource sharing among mobile robots through distributed strategy updating and interactions. Unlike traditional centralized optimization methods, this algorithm allows robots to dynamically adjust the task allocation. Through the adaptive collaboration without central control, the algorithm enables more efficient resource utilization. This distributed strategy updating approach allows each robot to interact effectively with other robots. Based on its own resource status and task requirements, each robot maximizes the overall resource utilization of the system. Experimental results show that, compared to classic heuristic algorithms and the latest swarm intelligence optimization methods proposed for multiple robot task allocation, the proposed approach achieves better allocation solutions under different task scales and resource configurations, significantly improving the resource utilization and task completion efficiency.
2. Problem Formulation of Multi-Robot Task Allocation
2.1. Task
2.2. Mobile Robot
2.3. Coalition
2.4. Resources
2.5. Constraints
2.6. Objective Function
3. Game Model of the Task Allocation Problem
3.1. Introduction to the Game
3.2. Player
3.3. Strategy
3.4. Utility Function
3.5. Potential Game
3.6. Nash Equilibrium
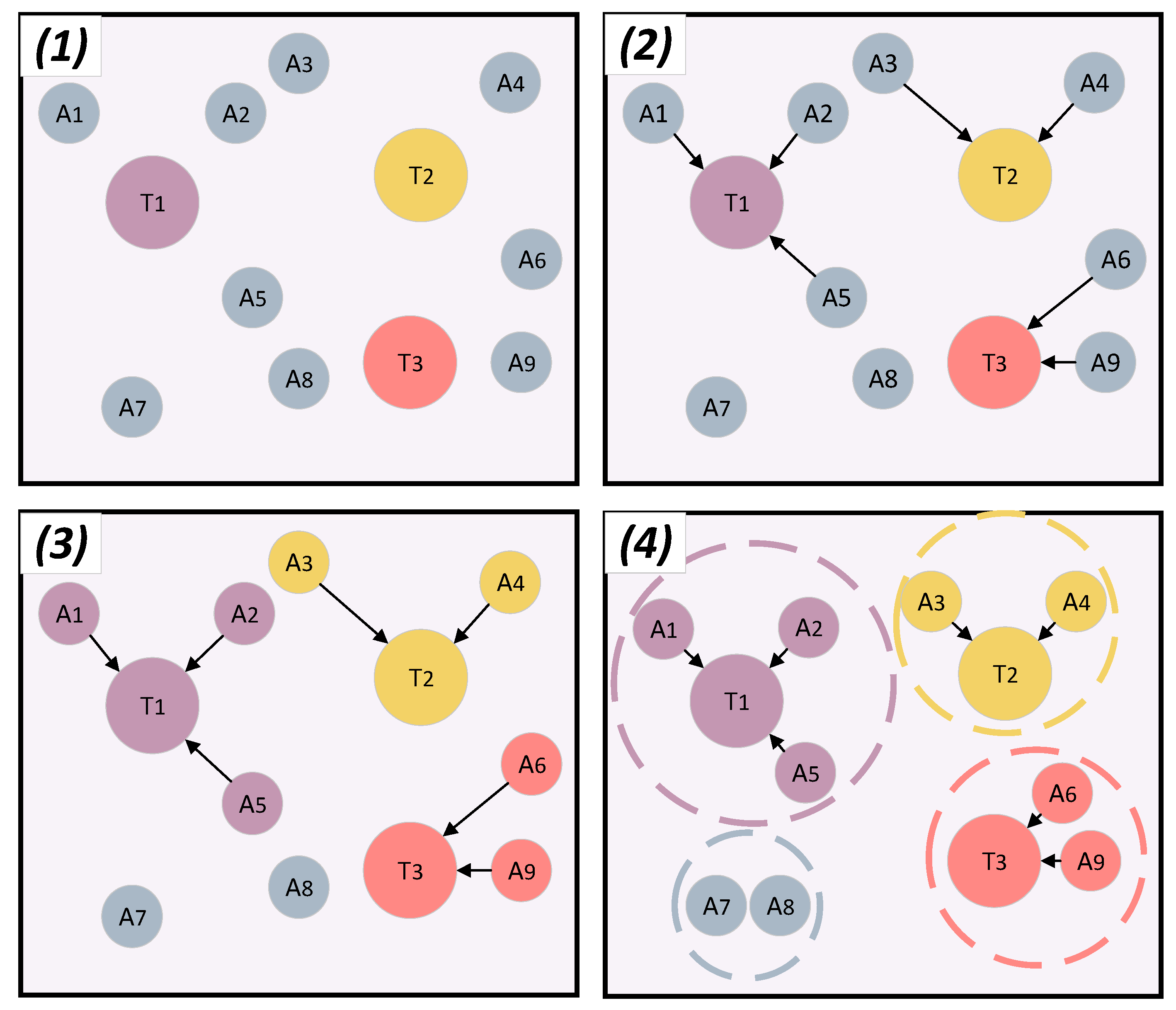
4. The Proposed Coalition Formation Algorithm
4.1. Algorithm Introduction
4.2. Algorithm Innovation
4.3. Algorithm Implementation and Pseudocode
- Stage 1. Initialization: Assign an initial strategy to each robot.
- Stage 2. Strategy Update: In each iteration, a robot is selected for strategy updating. The robot calculates the utility of each task in its strategy set. Then the task with the highest utility is selected as the new strategy.
- Stage 3. Nash Equilibrium Check: The strategy updating ends when all robot strategies are optimal given the strategies of the other robots, i.e., when the Nash equilibrium is reached. Otherwise, the strategy updating continues.
- Stage 4. Cost Optimization: Based on the Nash equilibrium, if a robot has zero utility but is not in an empty coalition, its strategy will be adjusted to join the empty coalition, thus optimizing the cost of the multi-robot system.
| Algorithm 1: Coalition Formation algorithm |
| Input: Output: strategy profile s 1: 2: while is_not_Nash Equilibrium do 3: choose player i from N 4: for j = 1:m do 5: if i can perform tj do |
| 6: compute 7: end if 8: end for 9: 10: end while 11: for i = 1:n do 12: if do 13: 14: end if 15: end for 16: return s |
5. Simulation Experiment
5.1. Benchmark Algorithms and Simulation Settings
5.2. Comparative Experiments
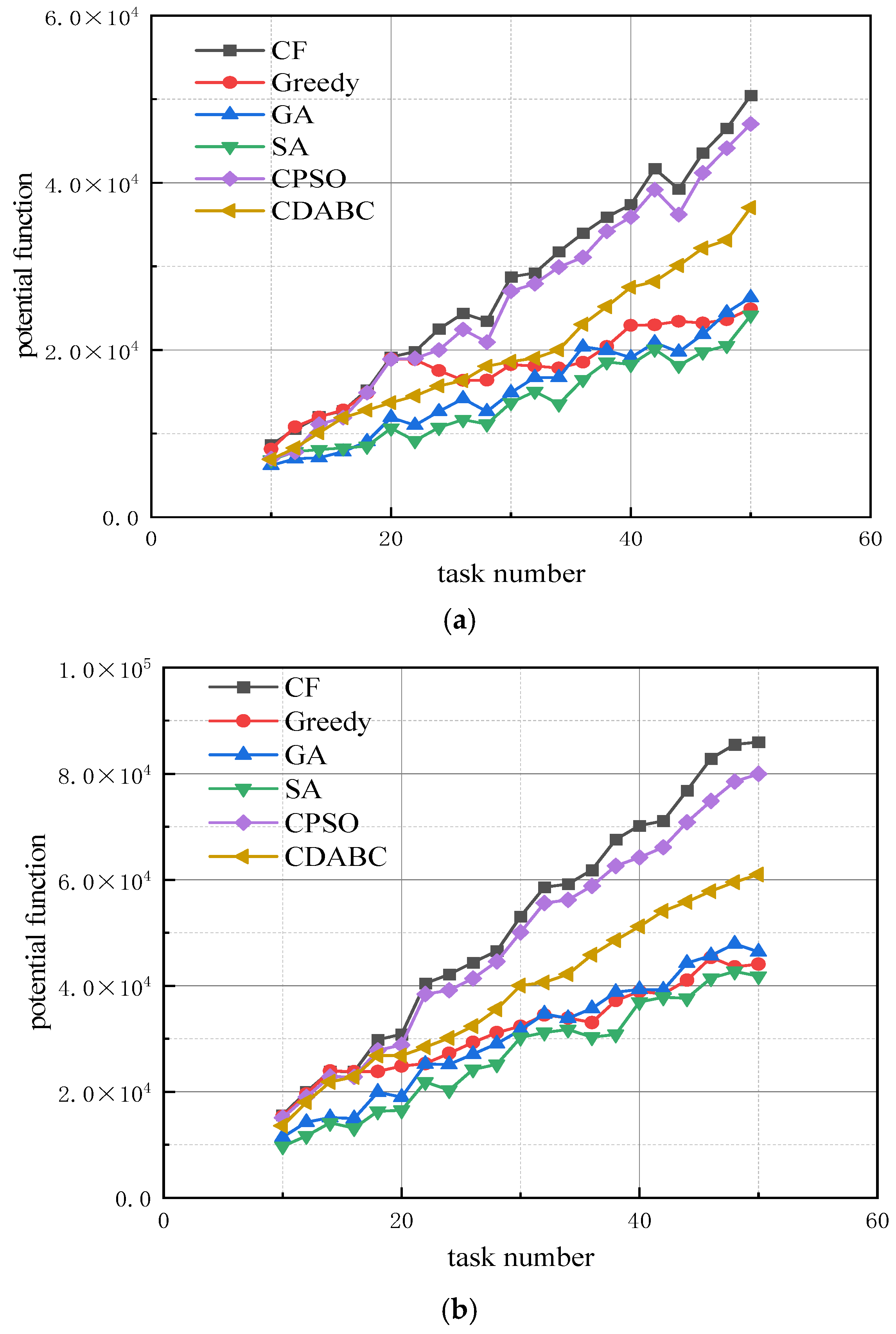
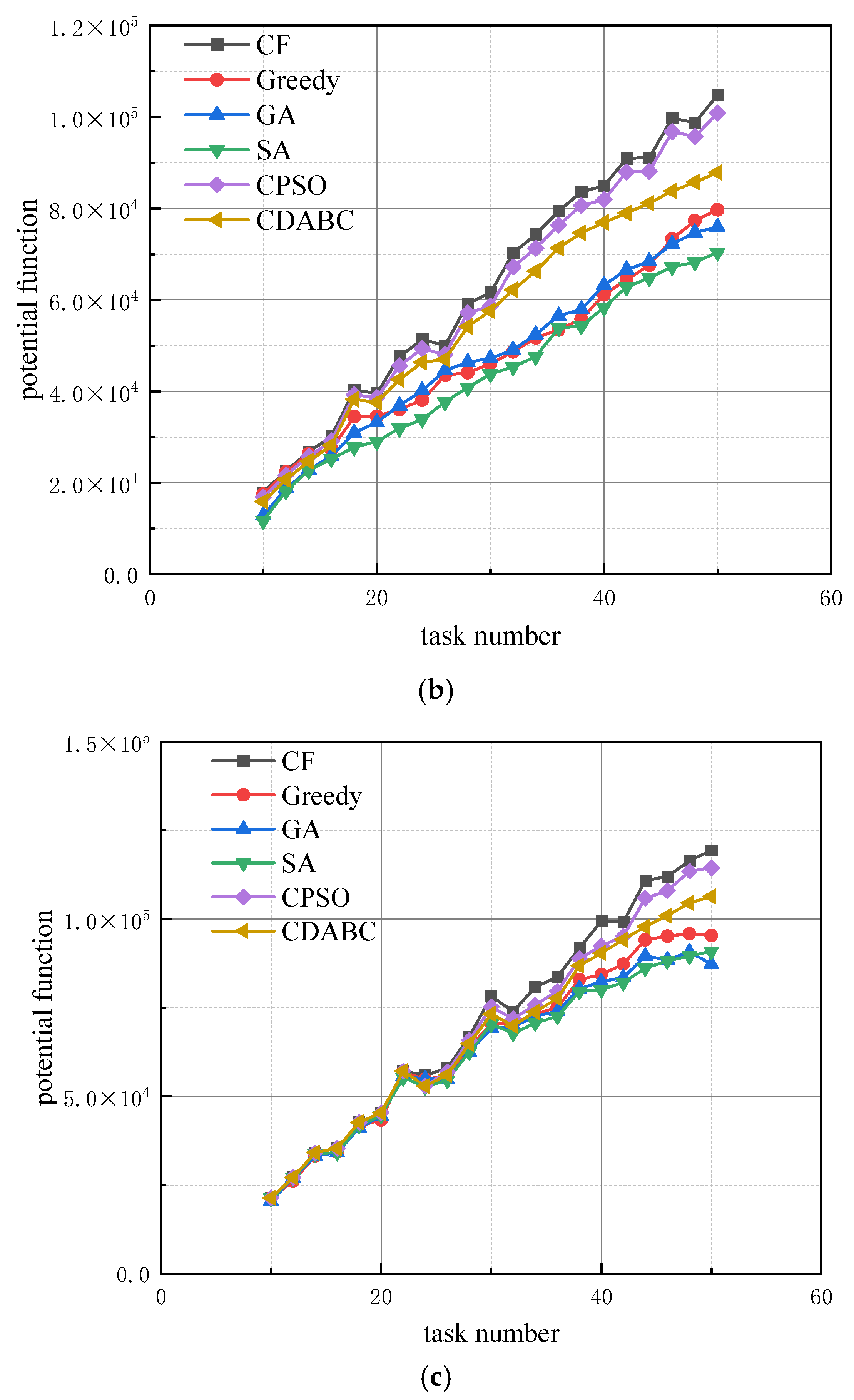
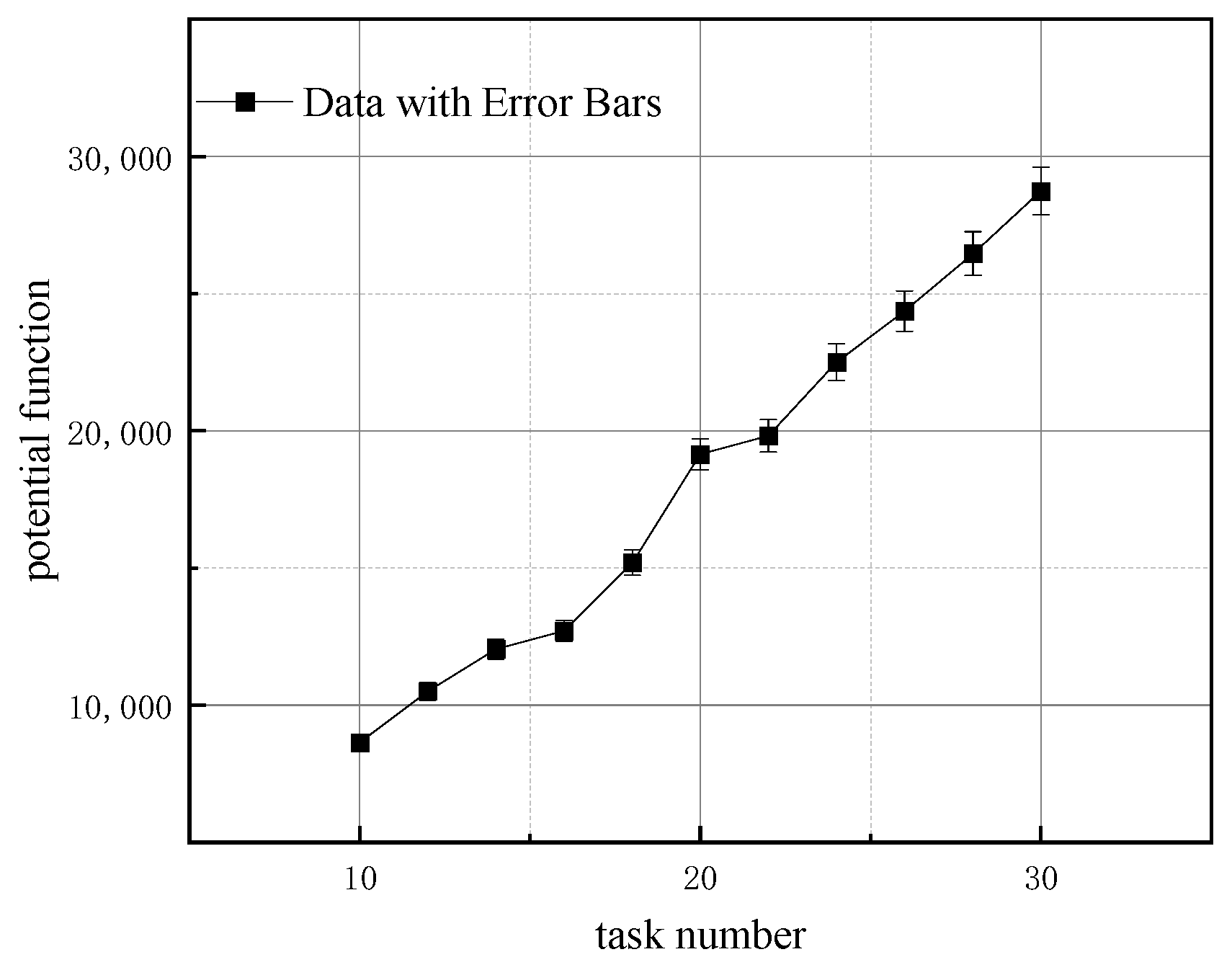
- Experiment 1: We analyze the impact of resource dimension on the algorithm’s performance. The running time of all four algorithms is set to 10 s, with the number of robots being three times the number of tasks. The resource dimension r is set to 5, 10, and 15, respectively. The effect of the number of tasks on the algorithm’s objective function is shown in Figure 3.
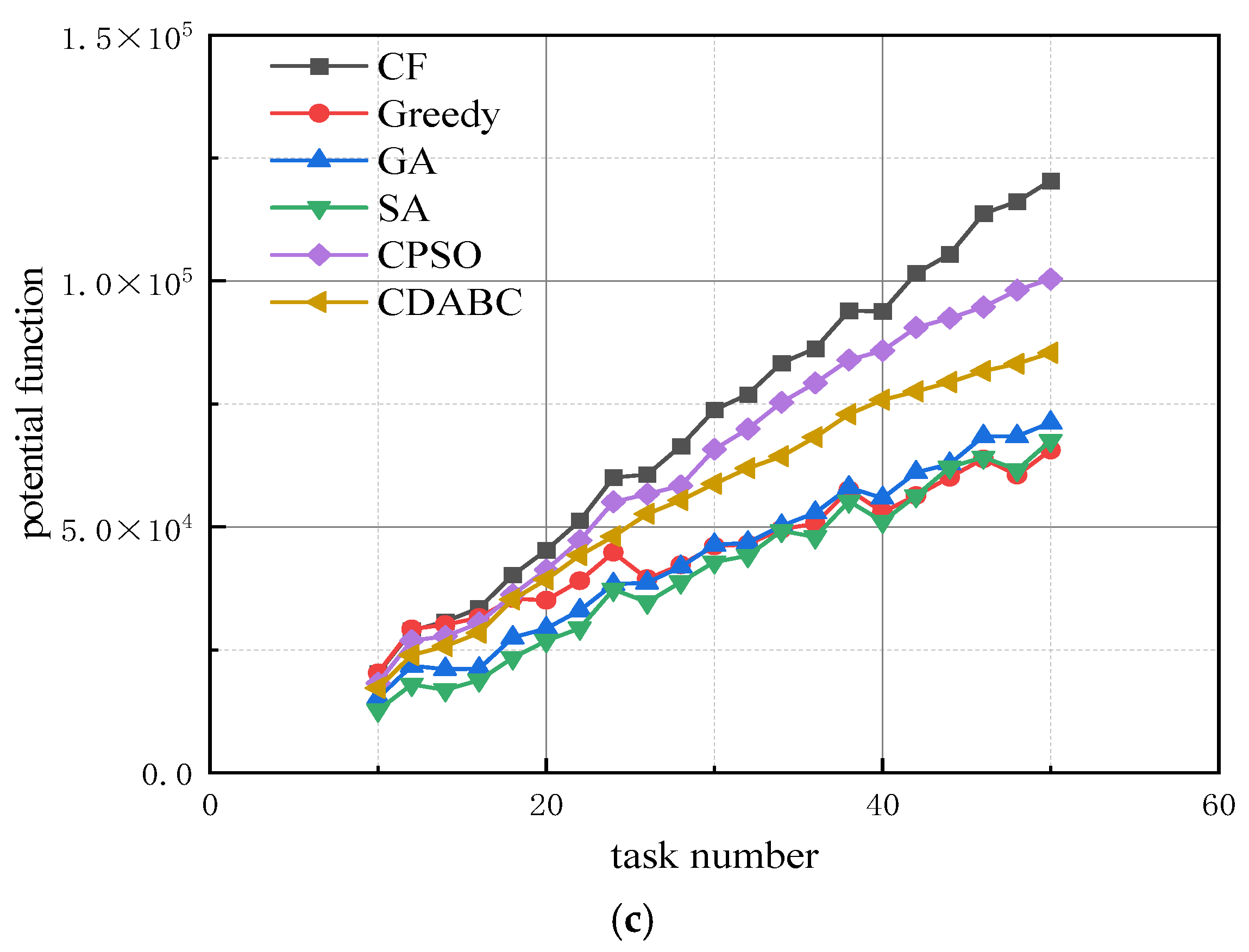
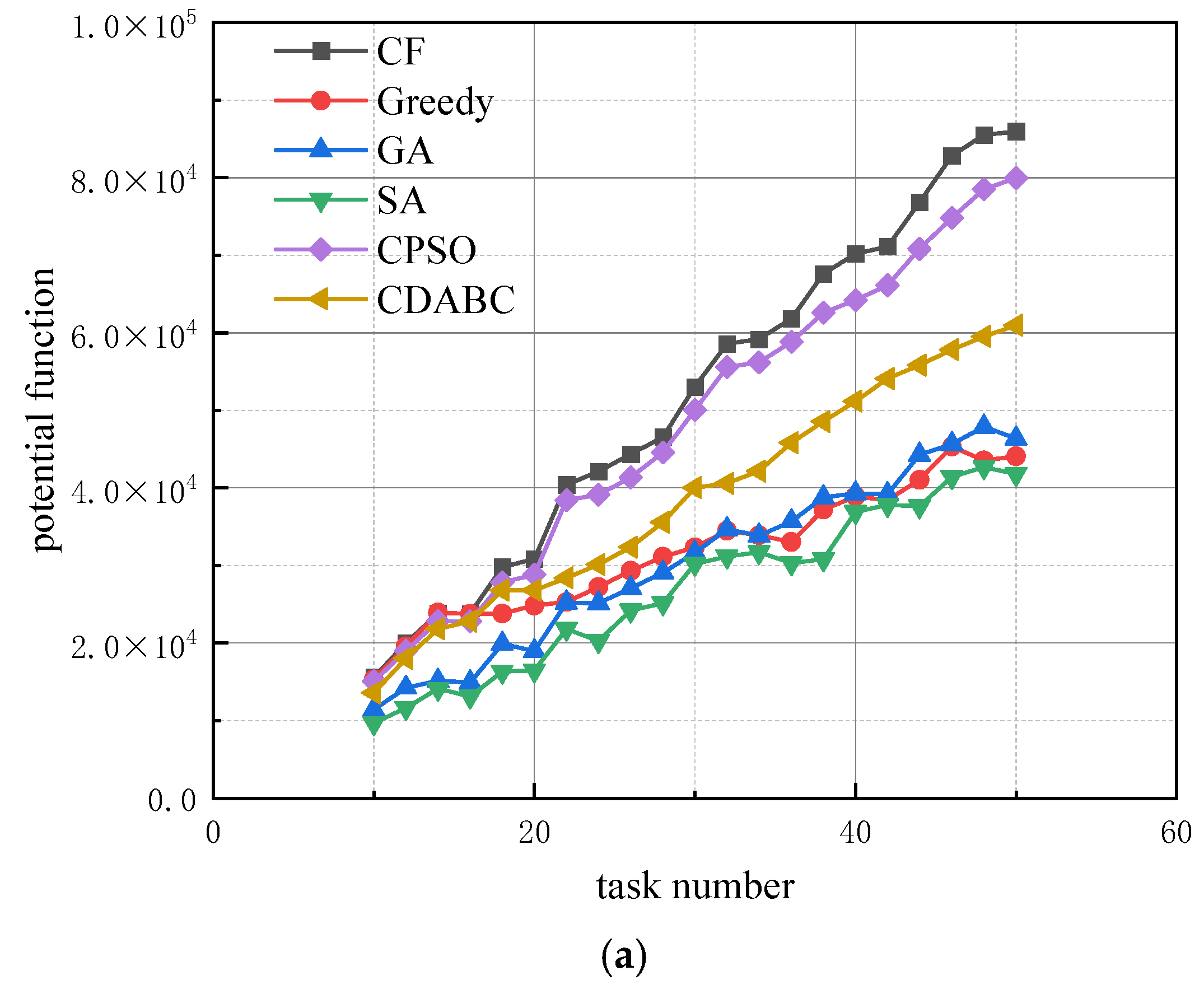
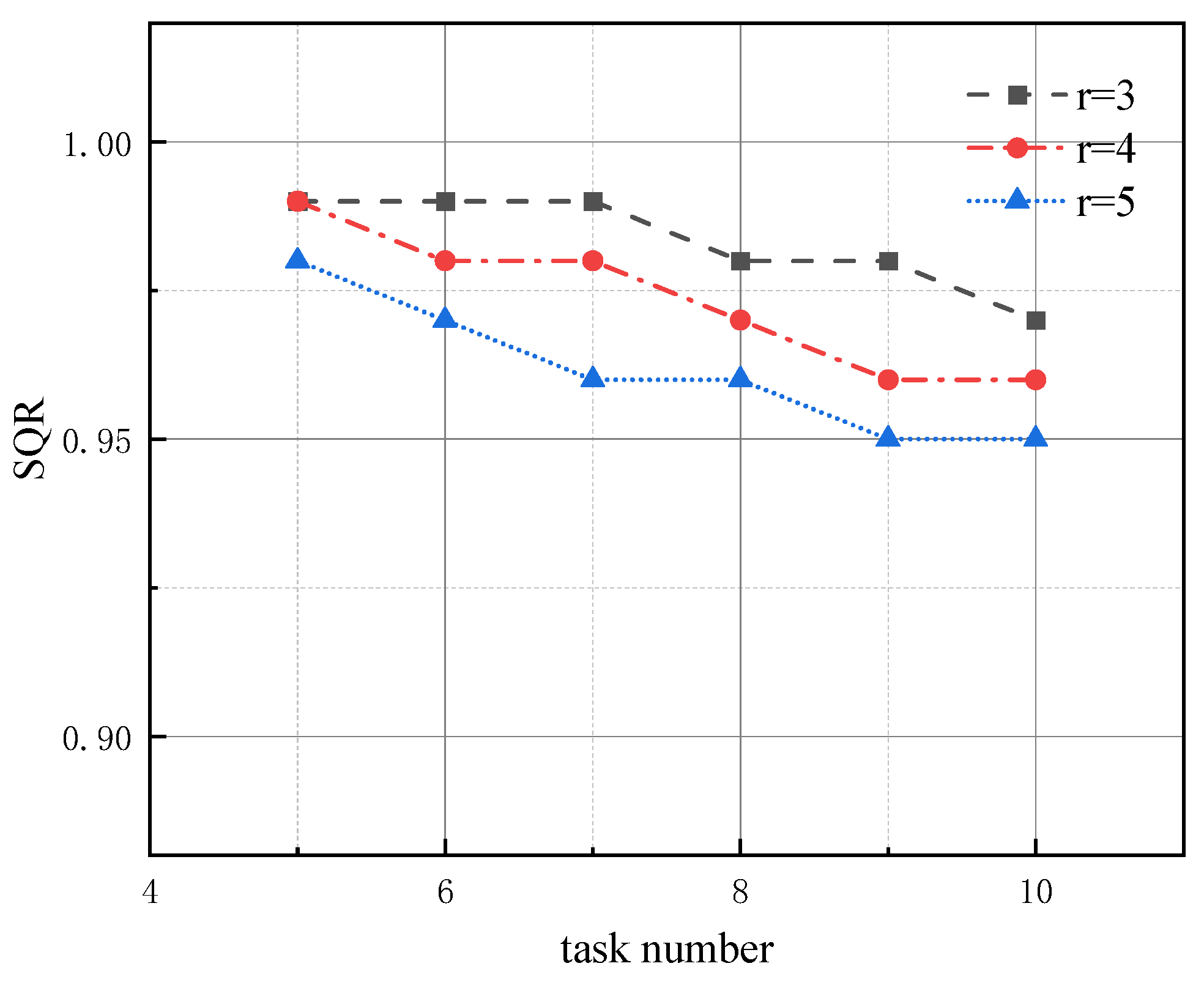
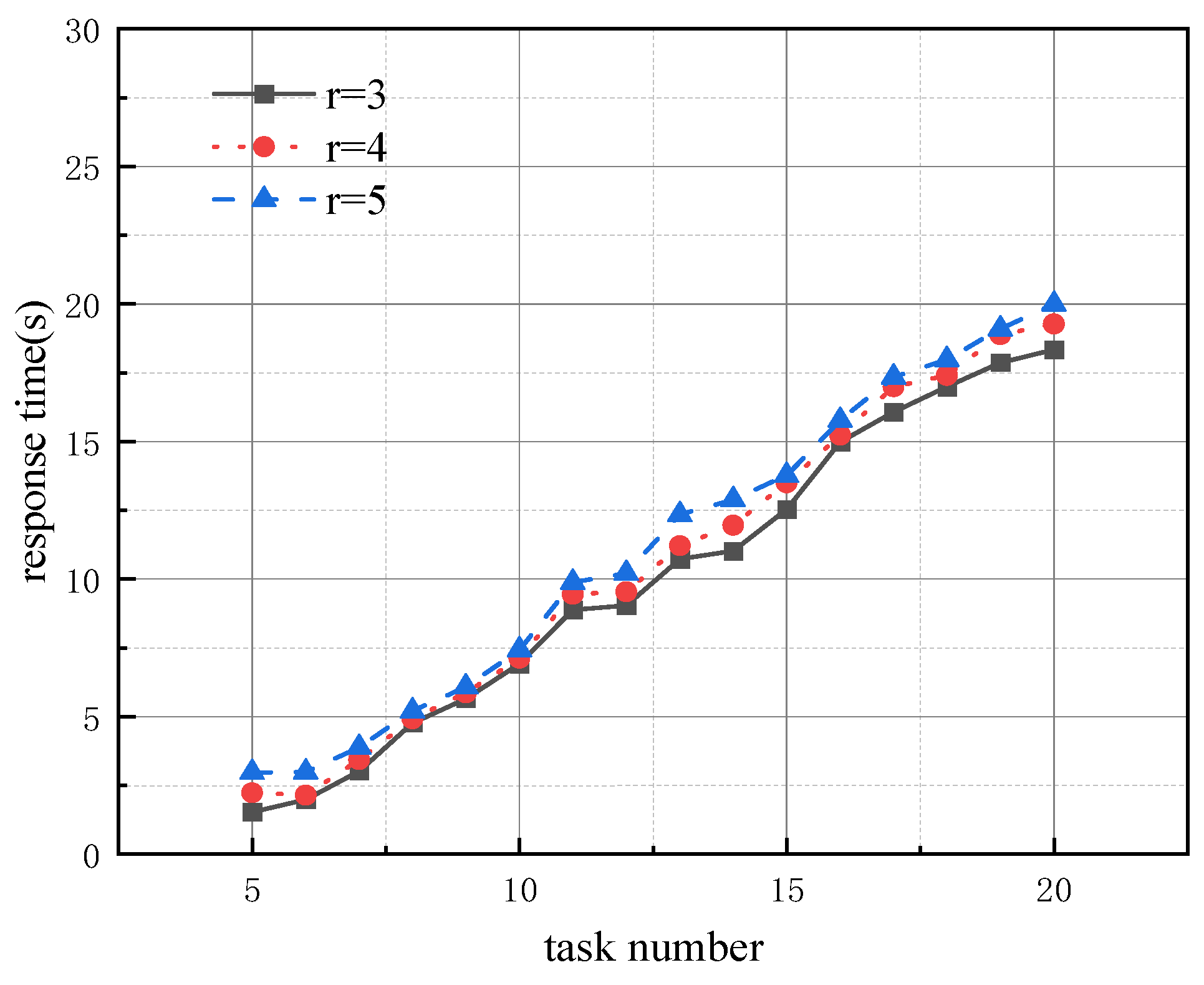
- Experiment 2: We analyze the effect of the ratio between the number of robots and the number of tasks on the algorithm’s performance. The running time of all four algorithms is set to 10 s, with the resource dimension r fixed at 10. The number of robots is set to 3, 4, and 5 times the number of tasks, respectively. The effect of changes in the number of tasks on the algorithm’s performance is shown in Figure 4.
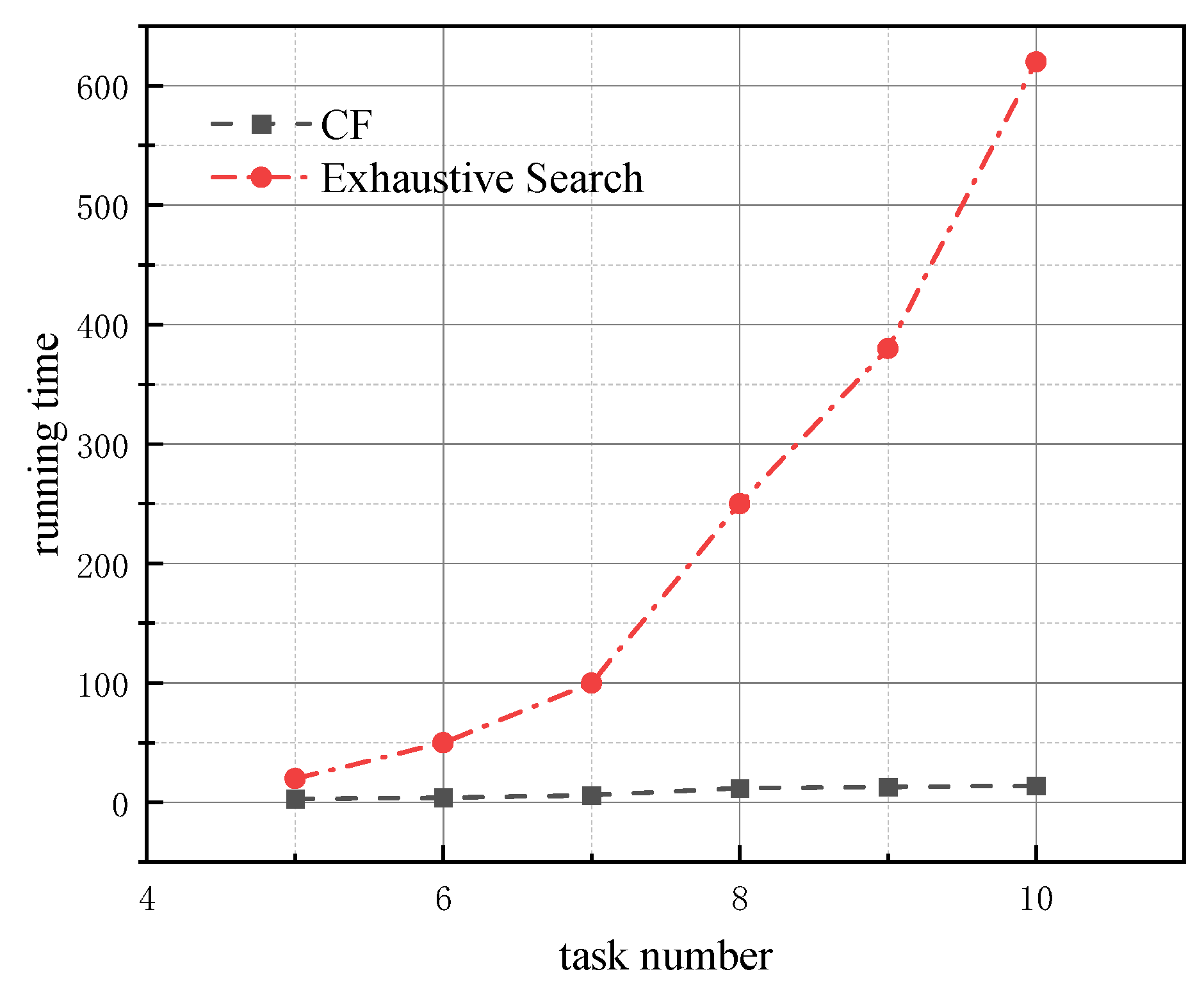
5.3. Test Experiments
5.4. Real-World Disaster Relief Application
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Son, H.I.; Franchi, A.; Chuang, L.L.; Kim, J.; Bulthoff, H.H.; Giordano, P.R. Human-centered design and evaluation of haptic cueing for teleoperation of multiple mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Zhu, W.; Yu, D.Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Multi-Depot Electric Vehicle–Drone Collaborative-Delivery Routing Optimization with Time-Varying Vehicle Travel Time. Vehicles 2024, 6, 1812–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Cabani, A.; Chafouk, H. Cooperative Vehicle Localization in Multi-Sensor Multi-Vehicle Systems Based on an Interval Split Covariance Intersection Filter with Fault Detection and Exclusion. Vehicles 2024, 6, 352–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawengkang, H.; Syahputra, M.R.; Sutarman, S.; Salhi, A. A Non-Linear Optimization Model for the Multi-Depot Multi-Supplier Vehicle Routing Problem with Relaxed Time Windows. Vehicles 2024, 6, 1482–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, F.; Grand, C.; Lesire, C. Market approaches to the multi-robot task allocation problem: A survey. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2023, 107, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seenu, N.; Kuppan Chetty, R.M.; Ramya, M.M.; Janardhanan, M.N. Review on state-of-the-art dynamic task allocation strategies for multiple-robot systems. Ind. Robot 2020, 47, 929–942. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Zavlanos, M.M. Temporal logic task allocation in heterogeneous multirobot systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 38, 3602–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomista, G.; Mayya, S.; Emam, Y.; Kroninger, C.; Bohannon, A.; Hutchinson, S.; Egerstedt, M. A resilient and energy-aware task allocation framework for heterogeneous multirobot systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 38, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, M.; Vo, B.Q.; Kowalczyk, R. An efficient algorithm for task allocation with the budget constraint. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 210, 118279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.; Gupta, J.K.; Kochenderfer, M.J.; Sadigh, D.; Bohg, J. Dynamic multi-robot task allocation under uncertainty and temporal constraints. Auton. Robots 2022, 46, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, S.; Moh, S. Task assignment algorithms for unmanned aerial vehicle networks: A comprehensive survey. Veh. Commun. 2022, 35, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Tang, D.; Zhou, T.; Gui, Y. Dynamic job shop scheduling based on deep reinforcement learning for multi-agent manufacturing systems. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2022, 78, 102412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, F. Task allocation in manufacturing: A review. J. Ind. Infor. Integr. 2019, 15, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Alonso-Mora, J.; Bai, X.; Harabor, D.D.; Stuckey, P.J. Integrated task assignment and path planning for capacitated multi-agent pickup and delivery. IEEE Robot. Autom. 2021, 6, 5816–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Duan, H. A potential game approach to multiple UAV cooperative search and surveillance. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, A.; Notarstefano, G. Generalized assignment for multi-robot systems via distributed branch-and-price. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 38, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. A survey of task allocation and load balancing in distributed systems. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2015, 27, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.G.; Frejo, J.R.D.; García, R.A.; Camacho, E.F. Multi-robot task allocation problem with multiple nonlinear criteria using branch and bound and genetic algorithms. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2021, 14, 707–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Afghah, F.; Ashdown, J.D.; Turck, K. Use of a quantum genetic algorithm for coalition formation in large-scale UAV networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2019, 87, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bänziger, T.; Kunz, A.; Wegener, K. Optimizing human–robot task allocation using a simulation tool based on standardized work descriptions. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 31, 1635–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.; Chen, Z.; Nguyen, Q.A.; Gong, D. Particle swarm optimization algorithm for the optimization of rescue task allocation with uncertain time constraints. Complex. Intell. Syst. 2021, 7, 873–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Ji, Z.; Cai, B. Particle swarm optimization for cooperative multi-robot task allocation: A multi-objective approach. IEEE Robot. Autom. 2020, 5, 2530–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huo, F.; Huangfu, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhou, J. Cooperative task allocation for multi-robot systems based on multi-objective ant colony system. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 56375–56387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Miao, Z.; Ji, J.; Pan, Q. An effective collaboration evolutionary algorithm for multi-robot task allocation and scheduling in a smart farm. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 289, 111474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Gai, L.; Xu, D. Collaborative target assignment problem for large-scale UAV swarm based on two-stage greedy auction algorithm. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 149, 109146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Fielbaum, A.; Kronmüller, M.; Knoedler, L.; Alonso-Mora, J. Group-based distributed auction algorithms for multi-robot task assignment. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otte, M.; Kuhlman, M.J.; Sofge, D. Auctions for multi-robot task allocation in communication limited environments. Auton. Robots 2020, 44, 547–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.L.; Brunet, L.; How, J.P. Consensus-based decentralized auctions for robust task allocation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2009, 25, 912–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ryck, M.; Pissoort, D.; Holvoet, T.; Demeester, E. Decentral task allocation for industrial AGV-systems with routing constraints. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 62, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wu, G. A Dynamic Task Scheduling Method for Multiple UAVs Based on Contract Net Protocol. Sensors 2022, 22, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Gu, X.; Chen, J.; Shen, L. A multi-responsibility–oriented coalition formation framework for dynamic task allocation in mobile–distributed multi-agent systems. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2018, 15, 1729881418813037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.; Shin, H.S.; Tsourdos, A. Anonymous hedonic game for task allocation in a large-scale multiple agent system. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 1534–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J. Dynamics of task allocation based on game theory in multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 2018, 66, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shang, H. Potential game for dynamic task allocation in multi-agent system. ISA Trans. 2020, 102, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, W.-A. Distributed dynamic task allocation for unmanned aerial vehicle swarm systems: A networked evolutionary game-theoretic approach. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 182–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Long, W.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Xia, Y.; Tang, Z. A game-based approach for cost-aware task assignment with QoS constraint in collaborative edge and cloud environments. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2020, 32, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandilya, S.; Szymanski, Z.; Shandilya, S.K.; Izonin, I.; Singh, K.K. Modeling and comparative analysis of multi-agent cost allocation strategies using cooperative game theory for the modern electricity market. Energies 2022, 15, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Qi, N.; Guan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Z. Joint task assignment and spectrum allocation in heterogeneous UAV communication networks: A coalition formation game-theoretic approach. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 20, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zong, Q.; Tian, B.; Zhang, B.; You, M. Fast task allocation for heterogeneous unmanned aerial vehicles through reinforcement learning. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ren, J.; Cui, Y.; Fu, D.; Cong, J. Multi-USV task planning method based on improved deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 18549–18567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, N.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, M. Deep reinforcement learning path planning and task allocation for multi-robot collaboration. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 109, 408–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, N.D.; Nahavandi, S. Deep reinforcement learning for multiagent systems: A review of challenges, solutions, and applications. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 3826–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marden, J.R.; Arslan, G.; Shamma, J.S. Cooperative control and potential games. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Part B Cybern. 2009, 39, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Liu, A.; Wang, J.; Kong, X. An improved fault-tolerant cultural-PSO with probability for multi-AGV path planning. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Notation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| m | number of tasks |
| n | number of robots |
| r | number of resources |
| T | set of tasks |
| the j-th task | |
| location of the j-th task | |
| resource requirement vector of the j-th task | |
| requirement of resource k for the j-th task | |
| the latest execution time of the j-th task | |
| set of robots | |
| set of the i-th robot | |
| location of the i-th robot | |
| resource supply vector of the i-th robot | |
| supply of resource k for the i-th robot | |
| maximum operating time of the i-th robot | |
| set of coalition | |
| set of the j-th coalition | |
| set of feasible tasks for the i-th robot | |
| set of feasible coalitions for the i-th robot | |
| weight coefficient of resource k |
| Experiment ID | Resource Dimension | Running Time (s) | Number of Tasks | Robot-to-Task Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 10 | 10–50 | 3 |
| 10 | 10 | 10–50 | 3 | |
| 15 | 10 | 10–50 | 3 | |
| 2 | 10 | 10 | 10–50 | 3 |
| 10 | 10 | 10–50 | 4 | |
| 10 | 10 | 10–50 | 5 | |
| 3 | 10 | 10 | 10–50 | 3 |
| 10 | 15 | 10–50 | 3 | |
| 10 | 20 | 10–50 | 3 |
| Task ID | Disaster Area | Resource Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Area A | Ground robots (medical, search equipment), drones (aerial scanning), first aid kits, medicines. |
| 2 | Area B | Heavy-duty robots (transport equipment), load-carrying robots (supply transport), water, food, medical supplies. |
| 3 | Area C | Drones (real-time video transmission, infrared detection), ground robots (search, obstacle removal), first aid kits. |
| 4 | Area D | Drones (building damage detection), heavy-duty ground robots (material handling), building assessment tools. |
| 5 | Area E | Drones (area search), ground robots (emergency supplies, communication equipment), demolition tools. |
| Robot ID | Capabilities and Resources |
|---|---|
| R1 | Medical supplies, search equipment |
| R2 | Heavy transport tools, water |
| R3 | Drone (video transmission), infrared sensor |
| R4 | First aid kit, medical supplies |
| R5 | Ground search, obstacle removal tools |
| R6 | Food transport, water |
| R7 | Drone (damage assessment), building tools |
| R8 | Heavy transport tools, food |
| R9 | Search equipment, emergency medical supplies |
| R10 | Building material handling |
| R11 | Drone (real-time transmission), comms device |
| R12 | Ground transport, building tools |
| R13 | Drone (area search), emergency supplies |
| R14 | Demolition tools, communication device |
| R15 | Drone (area search), material handling |
| Task ID | Disaster Area | Assigned Robots | Resource Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Area A | R1, R4, R9 | Medical aid, search operation, first aid kit |
| 2 | Area B | R2, R6, R8 | Supply transport, heavy load handling, food, water |
| 3 | Area C | R3, R5, R11 | Drone search, video transmission, obstacle removal |
| 4 | Area D | R7, R10, R12 | Damage assessment, building evaluation, logistics |
| 5 | Area E | R13, R14, R15 | Drone search, supply transport, demolition |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Li, P. Game-Theoretic Cooperative Task Allocation for Multiple-Mobile-Robot Systems. Vehicles 2025, 7, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles7020035
Liu L, Li P. Game-Theoretic Cooperative Task Allocation for Multiple-Mobile-Robot Systems. Vehicles. 2025; 7(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles7020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lixiang, and Peng Li. 2025. "Game-Theoretic Cooperative Task Allocation for Multiple-Mobile-Robot Systems" Vehicles 7, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles7020035
APA StyleLiu, L., & Li, P. (2025). Game-Theoretic Cooperative Task Allocation for Multiple-Mobile-Robot Systems. Vehicles, 7(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles7020035





