Epinephrine in Anaphylaxis: Preclinical Study of Pharmacokinetics after Sublingual Administration of Taste-Masked Tablets for Potential Pediatric Use
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Manufacturing of Taste-Masked Rapidly-Disintegrating Sublingual Tablets (RDSTs) of Epinephrine
2.2. Quality Control Testing of Taste-Masked Rapidly-Disintegrating Sublingual Tablets (RDSTs) of Epinephrine
2.3. Animal Study Design
2.4. Measurement of Plasma Epinephrine Concentrations
2.5. Data Analysis
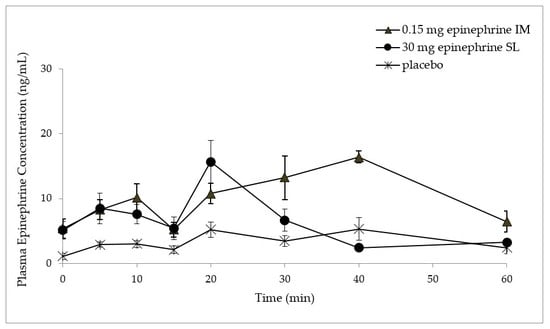
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simons, F.E.R.; Ardusso, L.R.F.; Bilo, M.B.; El-Gamal, Y.M.; Ledford, D.K.; Ring, J.; Sanchez-Borges, M.; Senna, G.E.; Sheikh, A.; Thong, B.Y.; et al. World Allergy Organization guidelines for the assessment and management of anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 587–593.e1–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, K.J.; Simons, F.E.R. Epinephrine and its use in anaphylaxis: Current issues. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 10, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, F.E.R.; Clark, S.; Camargo, C.A. Anaphylaxis in the community: Learning from the survivors. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noimark, L.; Wales, J.; Du Toit, G.; Pastacaldi, C.; Haddad, D.; Gardner, J.; Hyer, W.; Vance, G.; Townshend, C.; Alfaham, M.; et al. The use of adrenaline autoinjectors by children and teenagers. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chad, L.; Ben-Shoshan, M.; Asai, Y.; Cherkaoui, S.; Alizadehfar, R.; St-Pierre, Y.; Harada, L.; Allen, M.; Clarke, A. A majority of parents of children with peanut allergy fear using the epinephrine auto-injector. Allergy 2013, 68, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.C.; Tuuri, R.E.; Akhter, S.; Guerra, L.D.; Goodman, I.S.; Myers, S.R.; Nozicka, C.; Manzi, S.; Long, K.; Turner, T.; et al. Lacerations and embedded needles caused by epinephrine autoinjector use in children. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2016, 67, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.E.; Lareau, S.A. Novel technique for epinephrine removal in new generation autoinjectors. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2016, 27, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, S.C.; Weil, C.; Baty, F.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Powell, B. Retrieval of additional epinephrine from auto-injectors. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2013, 24, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawas-Qalaji, M.; Simons, F.E.; Collins, D.; Simons, K.J. Long-term stability of epinephrine dispensed in unsealed syringes for the first-aid treatment of anaphylaxis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009, 102, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, F.E.; Chan, E.S.; Gu, X.; Simons, K.J. Epinephrine for the out-of-hospital (first-aid) treatment of anaphylaxis in infants: Is the ampule/syringe/needle method practical? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawas-Qalaji, M.M.; Simons, F.E.R.; Simons, K.J. Sublingual epinephrine tablets versus intramuscular injection of epinephrine: Dose-equivalence for potential treatment of anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawas-Qalaji, M.; Rachid, O.; Simons, F.E.R.; Simons, K.J. Long-term stability of epinephrine sublingual tablets for the potential first-aid treatment of anaphylaxis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 111, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachid, O.; Rawas-Qalaji, M.M.; Simons, F.E.R.; Simons, K.J. Dissolution testing of sublingual tablets: A novel in vitro method. AAPS PhamSciTech 2011, 12, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachid, O.; Rawas-Qalaji, M.; Simons, F.E.R.; Simons, K.J. Rapidly-disintegrating sublingual tablets of epinephrine: Role of non-medicinal ingredients in formulation development. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawas-Qalaji, M.M.; Simons, F.E.; Simons, K.J. Fast-disintegrating sublingual tablets: Effect of epinephrine load on tablet characteristics. AAPS PharmSciTech 2006, 7, E72–E78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawas-Qalaji, M.M.; Simons, F.E.; Simons, K.J. Fast-disintegrating sublingual epinephrine tablets: Effect of tablet dimensions on tablet characteristics. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm 2007, 33, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachid, O.; Simons, F.E.R.; Rawas-Qalaji, M.; Simons, K.J. An electronic tongue: Evaluation of the masking efficacy of sweetening and/or flavouring agents on the bitter taste of epinephrine. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachid, O.; Rawas-Qalaji, M.M.; Simons, F.E.; Simons, K.J. Epinephrine (adrenaline) absorption from new-generation, taste-masked sublingual tablets: A preclinical study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. Pediatric Research Equity Act. 2003. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/DevelopmentResources/UCM077853.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2017).
- Physical tests: Uniformity of dosage Units h905i. In USP/NF, 26th/21st ed.; United States Pharmacopeial Convention Inc.: Rockville, MD, USA, 2003.
- Physical tests: Tablet friability h1216i. In USP/NF, 26th/21st ed.; United States Pharmacopeial Convention Inc.: Rockville, MD, USA, 2003.
- Official monograph: Epinephrine injection. In USP/NF, 32nd/27th ed.; United States Pharmacopeial Convention Inc.: Rockville, MD, USA, 2009; p. 2261.
- Zahrah, F.; Shosha’a, K.; Alzahabi, K.; Khalil, A.; Rawas-Qalaji, M.; Rachid, O. A simple solid phase extraction method for optimizing the recovery of catecholamines and their metabolites from biological sample. In Proceedings of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Motosue, M.S.; Bellolio, M.F.; Van Houten, H.K.; Shah, N.D.; Campbell, R.L. Increasing emergency department visits for anaphylaxis, 2005–2014. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016, 5, 171–175.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frechen, S.; Suleiman, A.A.; Mohammad Nejad Sigaroudi, A.; Wachall, B.; Fuhr, U. Population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of epinephrine administered using a mobile inhaler. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 30, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Simons, F.E.; Simons, K.J. Epinephrine absorption after different routes of administration in an animal model. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1999, 20, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonds, R.S.; Asawa, A.; Ghazi, AI. Misuse of medical devices: A persistent problem in self-management of asthma and allergic disease. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015, 114, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawas-Qalaji, M.M.; Werdy, S.; Rachid, O.; Simons, F.E.; Simons, K.J. Sublingual diffusion of epinephrine microcrystals from rapidly disintegrating tablets for the potential first-aid treatment of anaphylaxis: In vitro and ex vivo study. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawas-Qalaji, M.; Rachid, O.; Mendez, B.A.; Losada, A.; Simons, F.E.; Simons, K.J. Adrenaline (epinephrine) microcrystal sublingual tablet formulation: Enhanced absorption in a preclinical model. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaartama, R.; Turunen, E.; Toljamo, K.; Kokki, H.; Lehtonen, M.; Ranta, V.P.; Savolainen, J.; Järvinen, K.; Jarho, P. The effect of hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin and sucrose on the sublingual absorption of midazolam in rabbits. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, M.T.; Hsieh, C.M.; Chen, R.N.; Chou, P.Y.; Ho, H.O. Rapid-onset sildenafil sublingual drug delivery systems: In vitro evaluation and in vivo pharmacokinetic studies in rabbits. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2774–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turunen, E.; Mannila, J.; Laitinen, R.; Riikonen, J.; Lehto, V.P.; Järvinen, T.; Ketolainen, J.; Järvinen, K.; Jarho, P. Fast-dissolving sublingual solid dispersion and cyclodextrin complex increase the absorption of perphenazine in rabbits. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedaya, M.A.; Thomas, T.; Abdel-Hamid, M.E.; Kehinde, E.O.; Phillips, O.A. Comparative pharmacokinetic study for linezolid and two novel antibacterial oxazolidinone derivatives in rabbits: Can differences in the pharmacokinetic properties explain the discrepancies between their in vivo and in vitro antibacterial activities? Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of European Medicines Agency. Reflection Paper: Formulations of Choice for the Paediatric Population. EMEA/CHMP/PEG/194810/2005. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2009/09/WC500003782.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2017).
- Committee for Human Medicinal Products of European Medicines Agency. ICH E11(R1) Guideline on Clinical Investigation of Medicinal Products in the Pediatric Population Step 5. EMA/CPMP/ICH/2711/1999. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2017/10/WC500236218.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2017).
- Zisowsky, J.; Krause, A.; Dingemanse, J. Drug development for pediatric populations: Regulatory aspects. Pharmaceutics 2010, 2, 364–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, F.E.; Gu, X.; Silver, N.A.; Simons, K.J. EpiPen Jr versus EpiPen in young children weighing 15 to 30 kg at risk for anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, B.; Chang, J.; Wu, S.J.; Wolfe, C.N.; Ternik, R.L.; Gunter, T.Z.; Victor, M.C. Feasibility of mini-tablets as a flexible drug delivery tool. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 525, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranmal, S.R.; Cram, A.; Tuleu, C. Age-appropriate and acceptable paediatric dosage forms: Insights into end user perceptions, preferences and practices from the Children’s Acceptability of Oral Formulations (CALF) Study. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 514, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.; Ranmal, S.R.; Ernest, T.B.; Liu, F. Patient acceptability, safety and access: A balancing act for selecting age-appropriate oral dosage forms for paediatric and geriatric populations. Int. J. Pharm. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ingredient (mg) 2 | Formulations | |
|---|---|---|
| Placebo | Epi 30 | |
| Epinephrine bitartrate | 0 | 54.58 |
| Microcrystalline cellulose (Ceolus® PH-301) | 123.00 | 80.86 |
| Microcrystalline cellulose (Ceolus® PH-M-06) | 20.50 | 13.48 |
| Mannitol (Ludiflash) | 34.10 | 34.10 |
| Citric acid | 2.50 | 2.50 |
| Low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose (LH11) | 15.90 | 10.48 |
| Magnesium stearate | 4.00 | 4.00 |
| Characteristics | Formulations | |
|---|---|---|
| Placebo | Epi 30 | |
| Diameter (mm) | 9.98 ± 0.01 | 9.98 ± 0.01 |
| WV (mg), (AV) a | 202 ± 2.58 (3.1) | 211 ± 2.85 (6.47) |
| CU (%), (AV) a | N/A | 102 ± 4.77 (10.94) |
| BF (kgf) | 2.53 ± 0.02 | 2.50 ± 0.01 |
| F (%) | 0.1 | 0.7 |
| DD (%) b | N/A | 102.97 ± 8.28 |
| Mean ± SEM * | Placebo Sublingual Tablets (Endogenous Epinephrine) | Epinephrine Sublingual Tablets (Epi 30) | EpiPens Jr® |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epinephrine dose (mg) | 0 | 30 | 0.15 |
| Cbaseline (ng/mL) | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 5.1 ± 1.4 | 5.4 ± 1.5 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 7.5 ± 1.7 † | 16.7 ± 1.9 | 18.8 ± 1.9 |
| Tmax (min) †† | 33.3 ± 7.2 | 21.0 ± 2.5 | 36.0 ± 2.5 |
| AUC0–1 h (ng/mL/min) | 220.1 ± 31.8 † | 372.3 ± 21.7 † | 654.2 ± 39.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rachid, O.; Rawas-Qalaji, M.; Simons, K.J. Epinephrine in Anaphylaxis: Preclinical Study of Pharmacokinetics after Sublingual Administration of Taste-Masked Tablets for Potential Pediatric Use. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010024
Rachid O, Rawas-Qalaji M, Simons KJ. Epinephrine in Anaphylaxis: Preclinical Study of Pharmacokinetics after Sublingual Administration of Taste-Masked Tablets for Potential Pediatric Use. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleRachid, Ousama, Mutasem Rawas-Qalaji, and Keith J. Simons. 2018. "Epinephrine in Anaphylaxis: Preclinical Study of Pharmacokinetics after Sublingual Administration of Taste-Masked Tablets for Potential Pediatric Use" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010024
APA StyleRachid, O., Rawas-Qalaji, M., & Simons, K. J. (2018). Epinephrine in Anaphylaxis: Preclinical Study of Pharmacokinetics after Sublingual Administration of Taste-Masked Tablets for Potential Pediatric Use. Pharmaceutics, 10(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010024