Accuracy and Fit of Ceramic Filled 3D-Printed Resin for Permanent Crown Fabrication: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Die Preparation
2.2. Sample Nesting and Printing
2.3. Fit Assessment
2.4. Trueness Assessment
2.5. Precision Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hull, C.W. Apparatus for Production of Three-Dimensional Objects by Stereolithography. U.S. Patent 638905, 8 August 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Abduo, J.; Lyons, K.; Bennamoun, M. Trends in computer-aided manufacturing in prosthodontics: A review of the available streams. Int. J. Dent. 2014, 2014, 783948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainjot, A.K.; Dupont, N.M.; Oudkerk, J.C.; Dewael, T.Y.; Sadoun, M.J. From Artisanal to CAD-CAM Blocks: State of the Art of Indirect Composites. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, A.; Marti Marti, B.; Sauret-Jackson, V.; Darwood, A. 3D printing in dentistry. Br. Dent. J. 2015, 219, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stansbury, J.W.; Idacavage, M.J. 3D printing with polymers: Challenges among expanding options and opportunities. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsolakis, I.A.; Papaioannou, W.; Papadopoulou, E.; Dalampira, M.; Tsolakis, A.I. Comparison in Terms of Accuracy between DLP and LCD Printing Technology for Dental Model Printing. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Luo, S.; Nie, J.; Zhu, X. Photo-curing 3D printing technique and its challenges. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhao, L.; Jian, M.; Mao, Y.; Yu, M.; Guo, X. EHMP-DLP: Multi-projector DLP with energy homogenization for large-size 3D printing. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, N.; Osman, R.B.; Wismeijer, D. Factors Influencing the Dimensional Accuracy of 3D-Printed Full-Coverage Dental Restorations Using Stereolithography Technology. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 29, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, N.; Osman, R.; Wismeijer, D. Effects of build direction on the mechanical properties of 3D-printed complete coverage interim dental restorations. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, J.; Edelhoff, D.; Guth, J.F. 3D Printing in Digital Prosthetic Dentistry: An Overview of Recent Developments in Additive Manufacturing. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Noort, R. The future of dental devices is digital. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, T.D. The clinical significance of marginal fit. Northwest Dent. 2012, 91, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, J.R.; Bayne, S.C.; Holland, G.A.; Sulik, W.D. Considerations in measurement of marginal fit. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1989, 62, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laumbacher, H.; Strasser, T.; Knüttel, H.; Rosentritt, M. Long-term clinical performance and complications of zirconia-based tooth- and implant-supported fixed prosthodontic restorations: A summary of systematic reviews. J. Dent. 2021, 111, 103723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hamad, K.Q.; Al-Rashdan, R.B.; Al-Rashdan, B.A.; Baba, N.Z. Effect of Milling Protocols on Trueness and Precision of Ceramic Crowns. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzade, M.; Aminikhah, M.; Afrashtehfar, K.I.; Alikhasi, M. Marginal and internal adaptation of single crowns and fixed dental prostheses by using digital and conventional workflows: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 126, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-León, M.; Methani, M.M.; Morton, D.; Zandinejad, A. Internal and marginal discrepancies associated with stereolithography (SLA) additively manufactured zirconia crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, H.; Nagy, K.; Pranno, N.; Zarone, F.; Admakin, O.; Mangano, F. Trueness and precision of 3D-printed versus milled monolithic zirconia crowns: An in vitro study. J. Dent. 2021, 113, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruse, N.D.; Sadoun, M.J. Resin-composite Blocks for Dental CAD/CAM Applications. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 1232–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Mehl, A.; Reich, S. New CAD/CAM materials and blocks for chairside procedures. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2013, 16, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Goujat, A.; Abouelleil, H.; Colon, P.; Jeannin, C.; Pradelle, N.; Seux, D.; Grosgogeat, B. Mechanical properties and internal fit of 4 CAD-CAM block materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.-I.; You, S.-G.; You, S.-M.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, J.-H. Evaluating the accuracy (trueness and precision) of interim crowns manufactured using digital light processing according to post-curing time: An in vitro study. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2021, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, R.B.; Alharbi, N.; Wismeijer, D. Build Angle: Does It Influence the Accuracy of 3D-Printed Dental Restorations Using Digital Light-Processing Technology? Int. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 30, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahayeri, A.; Morgan, M.; Fugolin, A.P.; Bompolaki, D.; Athirasala, A.; Pfeifer, C.S.; Ferracane, J.L.; Bertassoni, L.E. 3D printed versus conventionally cured provisional crown and bridge dental materials. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhom, M.; Zaghloul, H.; Mosleh, I.E.-S.; Eldwakhly, E. Effect of Different CAD/CAM Milling and 3D Printing Digital Fabrication Techniques on the Accuracy of PMMA Working Models and Vertical Marginal Fit of PMMA Provisional Dental Prosthesis: An In Vitro Study. Polymers 2022, 14, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitznagel, F.A.; Boldt, J.; Gierthmuehlen, P.C. CAD/CAM Ceramic Restorative Materials for Natural Teeth. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, R.B.; van der Veen, A.J.; Huiberts, D.; Wismeijer, D.; Alharbi, N. 3D-printing zirconia implants; a dream or a reality? An in-vitro study evaluating the dimensional accuracy, surface topography and mechanical properties of printed zirconia implant and discs. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 75, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methani, M.M.; Revilla-León, M.; Zandinejad, A. The potential of additive manufacturing technologies and their processing parameters for the fabrication of all-ceramic crowns: A review. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2020, 32, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.S.; Windeler, A.S. An investigation of dental luting cement solubility as a function of the marginal gap. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1991, 65, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualsaud, R.; Alalawi, H. Fit, Precision, and Trueness of 3D-Printed Zirconia Crowns Compared to Milled Counterparts. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Jeong, i.-D.; Lee, J.-J.; Bae, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, W.-C. In vitro assessment of the marginal and internal fits of interim implant restorations fabricated with different methods. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-S.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, K.-B. Evaluation of internal fit of interim crown fabricated with CAD/CAM milling and 3D printing system. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2017, 9, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, W.C. Trueness of milled prostheses according to number of ball-end mill burs. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igreţ, A.; Rotar, R.N.; Ille, C.; Topală, F.; Jivănescu, A. Marginal fit of milled versus different 3D-printed materials for provisional fixed dental prostheses: An in vitro comparative study. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2023, 96, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jivanescu, A.; Birkenheier, N.; Rotar, R.N.; Topala, F.; Goguta, L. Marginal fit of ceramic crowns fabricated with CAD-CAM technology using a direct and indirect digital workflow. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2019, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.C.; Chung, K.H.; Ramos, V., Jr. Assessment of the Adaptation of Interim Crowns using Different Measurement Techniques. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 29, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeb, L.A.; Ahdal, K.A.; Alotaibi, G.N.; Alshehri, A.; Alotaibi, B.M.; Alabdulwahab, F.; Deeb, M.A.; AlFawaz, Y.F.; Vohra, F.; Abduljabbar, T. Marginal Integrity, Internal Adaptation and Compressive Strength of 3D Printed, Computer Aided Design and Computer Aided Manufacture and Conventional Interim Fixed Partial Dentures. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2019, 9, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, C.S.; Niemann, K.D.; Schweitzer, D.D.; Hirata, R.; Atria, P.J. Microcomputed tomography evaluation of cement film thickness of veneers and crowns made with conventional and 3D printed provisional materials. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2021, 33, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earar, K.; Iliescu, A.A.; Popa, G.; Iliescu, A.; Rudnic, I.; Feier, R.; Voinea-Georgescu, R.N. Additive vs. subtractive CAD/CAM procedures in manufacturing of the PMMA interim dental crowns. A Comparative in vitro Study of Internal Fit. Rev. Chim. 2020, 71, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aali, K.A.; Alhamdan, R.S.; Maawadh, A.M.; Vohra, F.; Abduljabbar, T. Influence of contemporary CAD-CAM milling systems on the fit and adaptation of partially stabilized Zirconia fixed partial dentures. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaokutan, I.; Sayin, G.; Kara, O. In vitro study of fracture strength of provisional crown materials. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2015, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molin, M.; Karlsson, S. The fit of gold inlays and three ceramic inlay systems: A clinical and in vitro study. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1993, 51, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawafleh, N.A.; Mack, F.; Evans, J.; Mackay, J.; Hatamleh, M.M. Accuracy and reliability of methods to measure marginal adaptation of crowns and FDPs: A literature review. J. Prosthodont. 2013, 22, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H. Digital approach to assessing the 3-dimensional misfit of fixed dental prostheses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, G.; Ender, A.; Mehl, A. A 3-dimensional accuracy analysis of chairside CAD/CAM milling processes. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
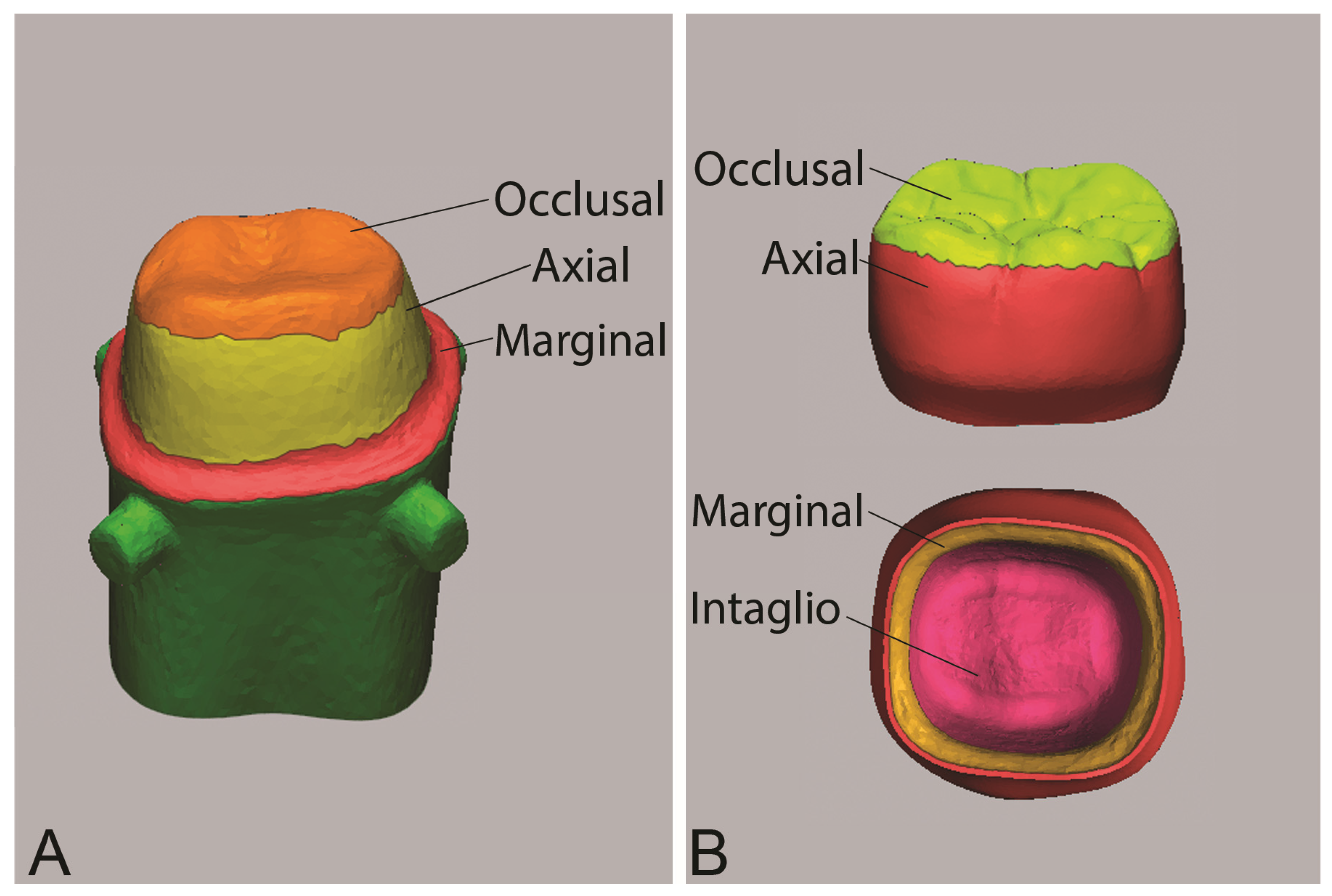
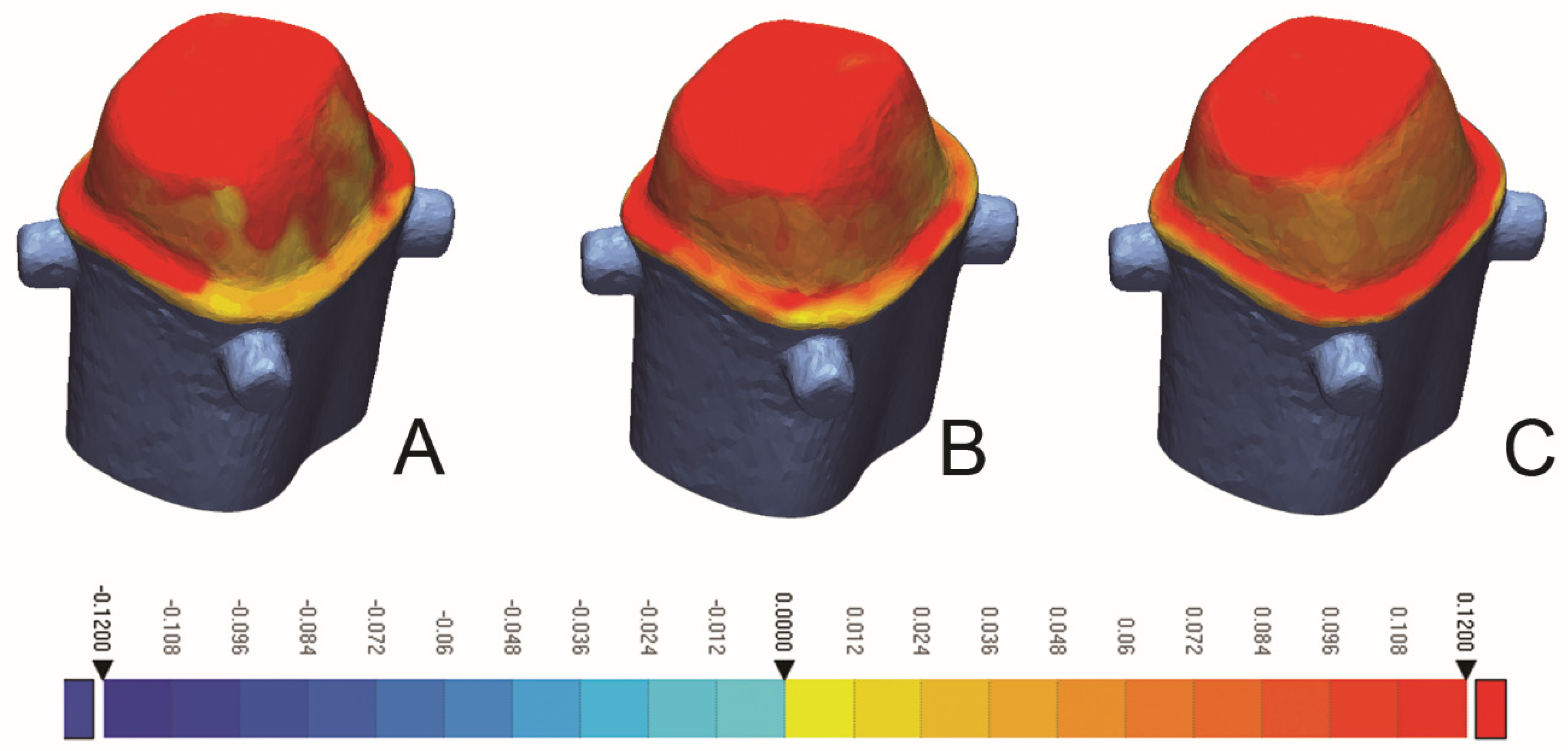
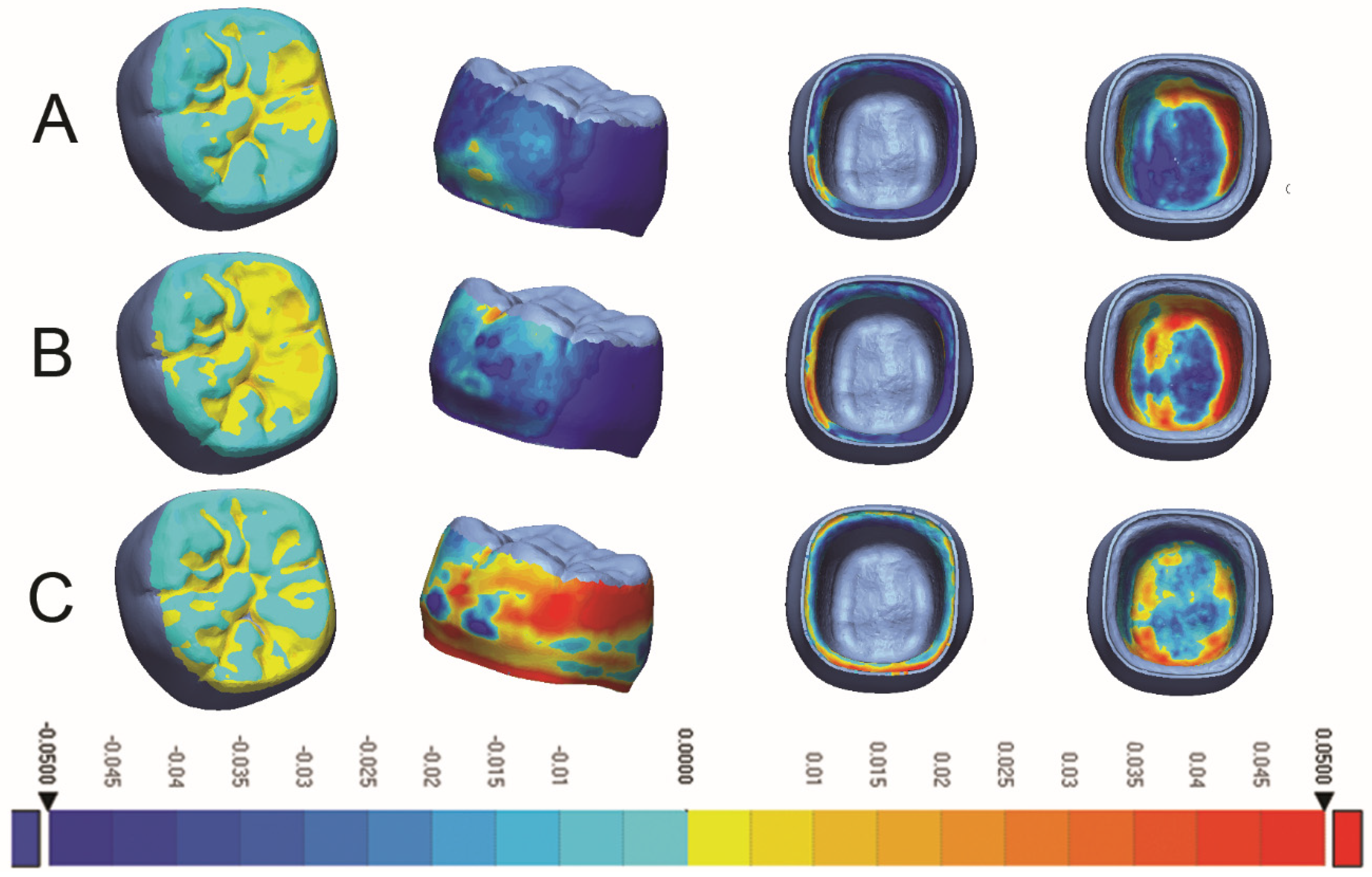
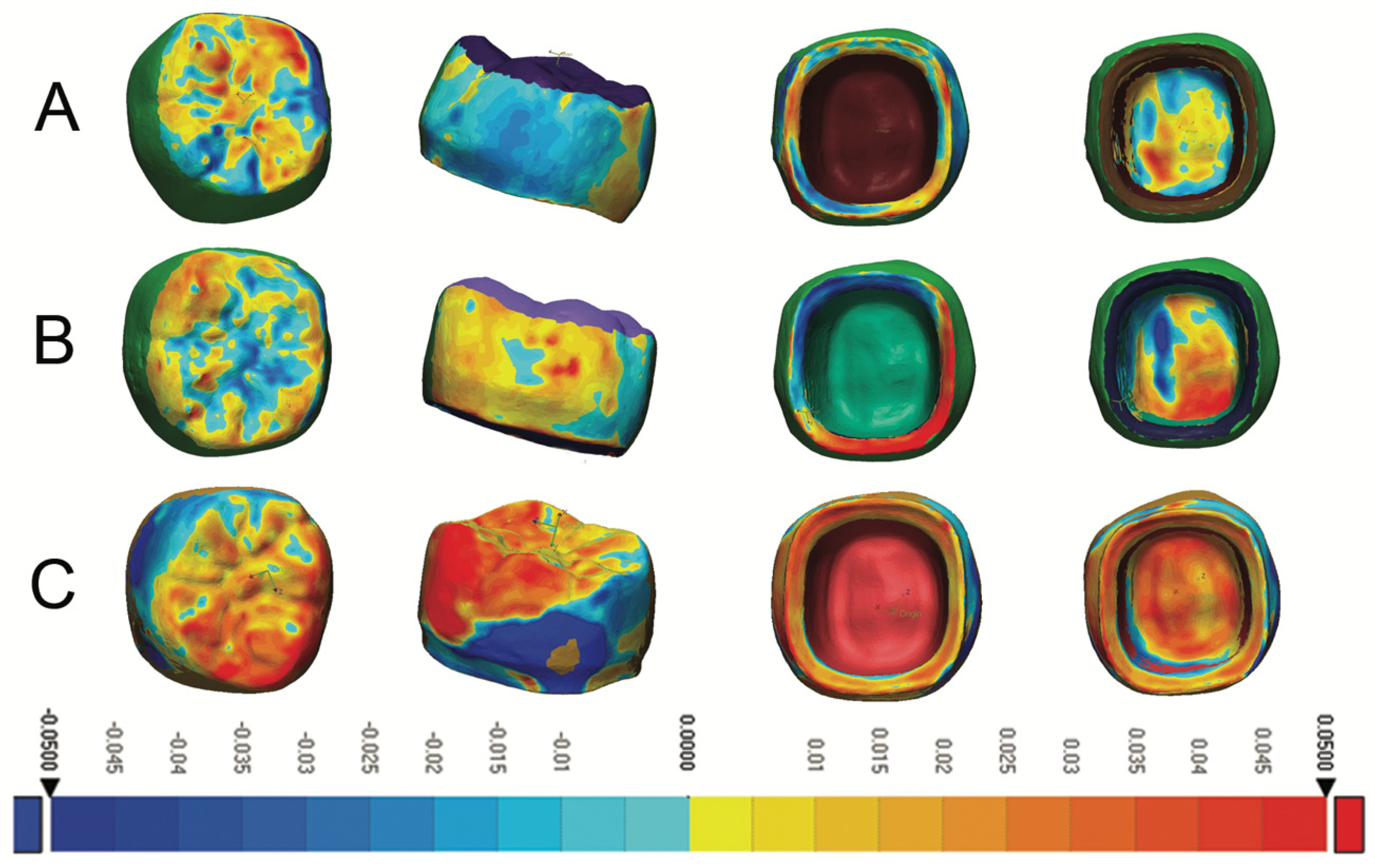
| Material | Manufacturer | Description and Composition | Production Parameters | Post-Production Processing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VarseoSmile Crown Plus (VSCP) | Bego Bremen, Germany | Resin matrix ceramic (RMC) [27] is a ceramic-infiltrated hybrid composite methacrylic ester matrix with ceramic fillers. Photopolymer: 4.4′-isopropylidiphenol, ethoxylated, and 2-methylprop-2enoic acid. | NextDent 5100 printing orientation: 45 Layer thickness: 50 | Cleaning in 96% ethanol NextDent light curing unit for 10 min |
| CROWNTEC (C) | Saremco, Dental AG, Rebstein, Switzerland | Esterification products of 4,4′-isopropylidiphenol, ethoxylated and 2-methylprop-2enoic acid, | NextDent 5100 printing orientation: 45 Layer thickness: 50 | Cleaning in 96% ethanol NextDent light curing unit for 5 min |
| Enamic (E) | (Vita Zhanfabric, Bad Säckingen, Germany) | Hybrid ceramic with a dual interpenetrating network structure Ceramic network (~86% by weight) Acrylate polymer network (~14% by weight) | Wet milled using prograMill PM7 5-axis dental milling machine (Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein) | Pre-polymerized No post-processing was needed |
| Area Measured | Varseo Smile Crown Plus Printed Mean ± SD | CROWNTEC Printed Mean ± SD | Enamic Milled Mean ± SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occlusal | 183.100 35.8462 | 186.30866.8505 | 156.93825.6208 | 0.220 |
| Axial | 86.285 17.3755 | 111.123 88.6660 | 82.91511.2574 | 0.339 |
| Marginal | 125.046 32.1901 | 138.67758.0090 | 112.58514.5458 | 0.250 |
| Overall | 131.869 21.2528 | 147.67769.8194 | 118.53113.9868 | 0.236 |
| Area Measured | Varseo Smile Crown Plus Printed Mean ± SD | CROWNTEC Printed Mean ± SD | Enamic Milled Mean ± SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occlusal | 44.6 6.45 a | 38.2 3.25 a | 28.6 6.58 a | p ≤ 0.05 * |
| Axial | 98.4 16.83 a | 65.5 23.86 a | 45.7 6.00 a | p ≤ 0.05 * |
| Marginal | 54.9 11.38 a | 36.7 16.17 a | 29.0 8.27 a | p ≤ 0.05 * |
| Intaglio | 31.9 13.19 a | 43.8 6.70 a | 25.8 4.56 a | p ≤ 0.05 * |
| Overall | 57.5 9.17 a | 46.1 6.48 a | 32.3 12.38 a | p ≤ 0.05 * |
| Area Measured | Varseo Smile Crown Plus Printed Mean ± SD | CROWNTEC Printed Mean ± SD | Enamic Milled Mean ± SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occlusal | 26.4 9.14 a | 17.8 2.45 a | 22.5 7.45 | 0.013 * |
| Axial | 37.1 19.02 | 32.1 3.76 | 35.9 2.88 | 0.611 |
| Marginal | 27.9 7.22 a | 31.0 7.20 | 20.5 5.33 a | 0.001 * |
| Intaglio | 22.3 10.52 | 20.9 4.54 | 19.7 6.85 | 0.695 |
| Overall | 28.4 9.58 | 25.5 3.19 | 24.7 7.09 | 0.377 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Ramadan, A.; Abualsaud, R.; Al-Dulaijan, Y.A.; Al-Thobity, A.M.; Alalawi, H. Accuracy and Fit of Ceramic Filled 3D-Printed Resin for Permanent Crown Fabrication: An In Vitro Comparative Study. Prosthesis 2024, 6, 1029-1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6050075
Al-Ramadan A, Abualsaud R, Al-Dulaijan YA, Al-Thobity AM, Alalawi H. Accuracy and Fit of Ceramic Filled 3D-Printed Resin for Permanent Crown Fabrication: An In Vitro Comparative Study. Prosthesis. 2024; 6(5):1029-1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6050075
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Ramadan, Anwar, Reem Abualsaud, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Ahmad M. Al-Thobity, and Haidar Alalawi. 2024. "Accuracy and Fit of Ceramic Filled 3D-Printed Resin for Permanent Crown Fabrication: An In Vitro Comparative Study" Prosthesis 6, no. 5: 1029-1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6050075
APA StyleAl-Ramadan, A., Abualsaud, R., Al-Dulaijan, Y. A., Al-Thobity, A. M., & Alalawi, H. (2024). Accuracy and Fit of Ceramic Filled 3D-Printed Resin for Permanent Crown Fabrication: An In Vitro Comparative Study. Prosthesis, 6(5), 1029-1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6050075










