Strength Retention of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Vitrimer Composite Material for Primary Structures: Towards Recyclable and Reusable Carbon Fiber Composites †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials
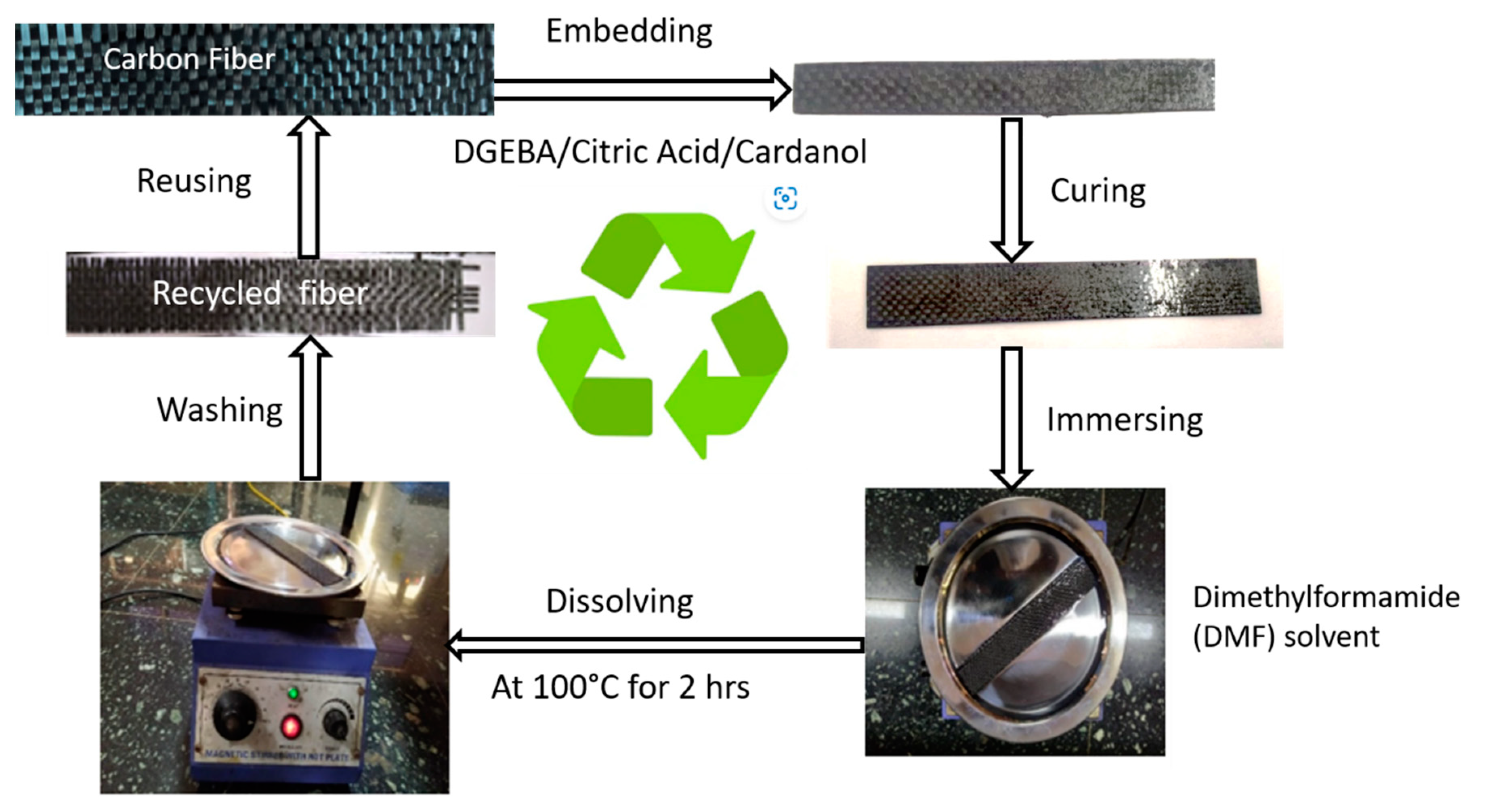
2.2. Specimen Fabrications
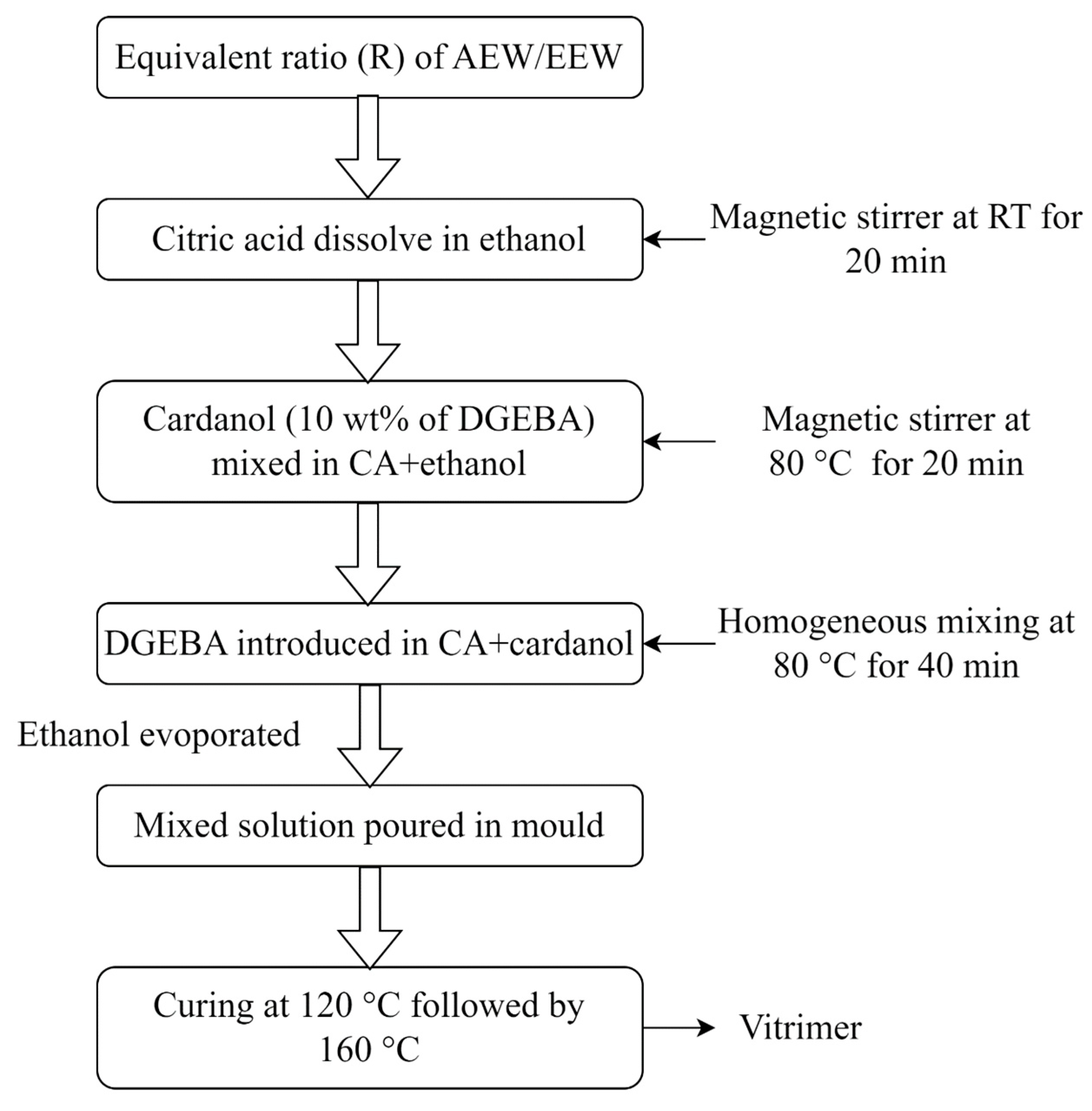
2.2.1. Vitrimer Preparation
2.2.2. Carbon Fiber–Vitrimer Composite
2.2.3. Recycling of Carbon Fiber
2.3. Functional Group Characterisation
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR)
2.4. Thermal Characterisation
2.4.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.5. Mechanical Testing
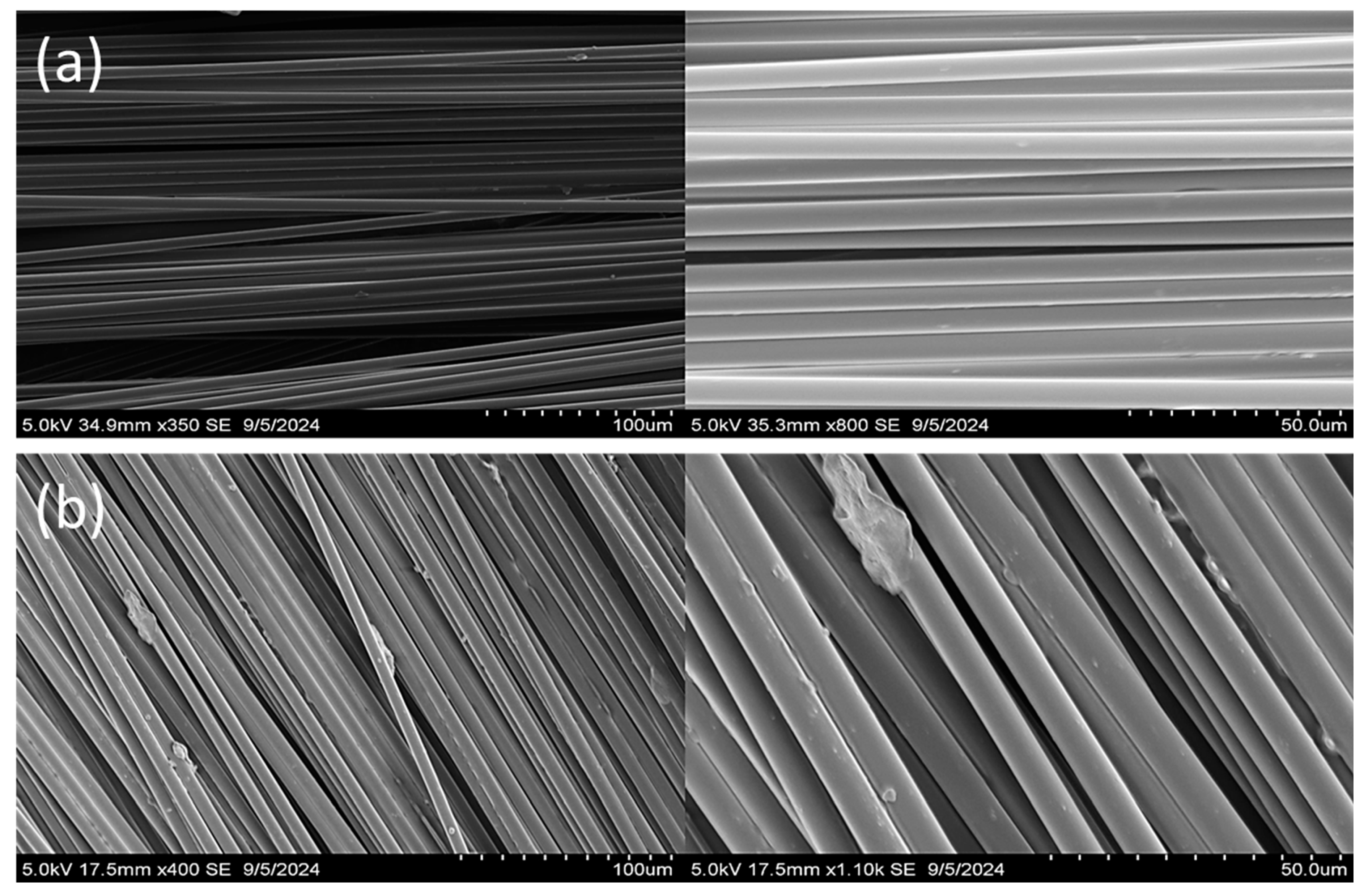
2.6. SEM Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectrometry
3.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
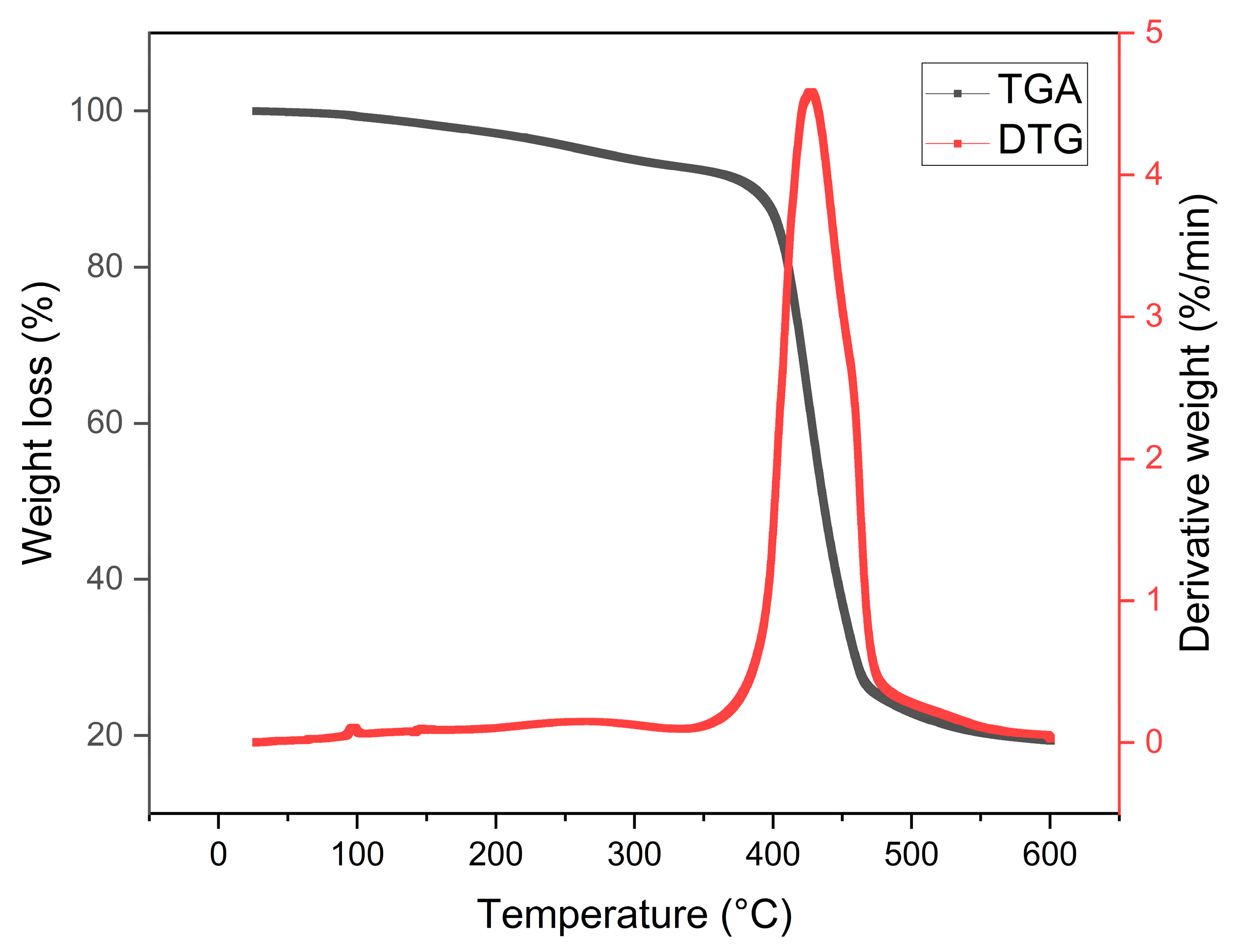
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.4. Mechanical Behavior
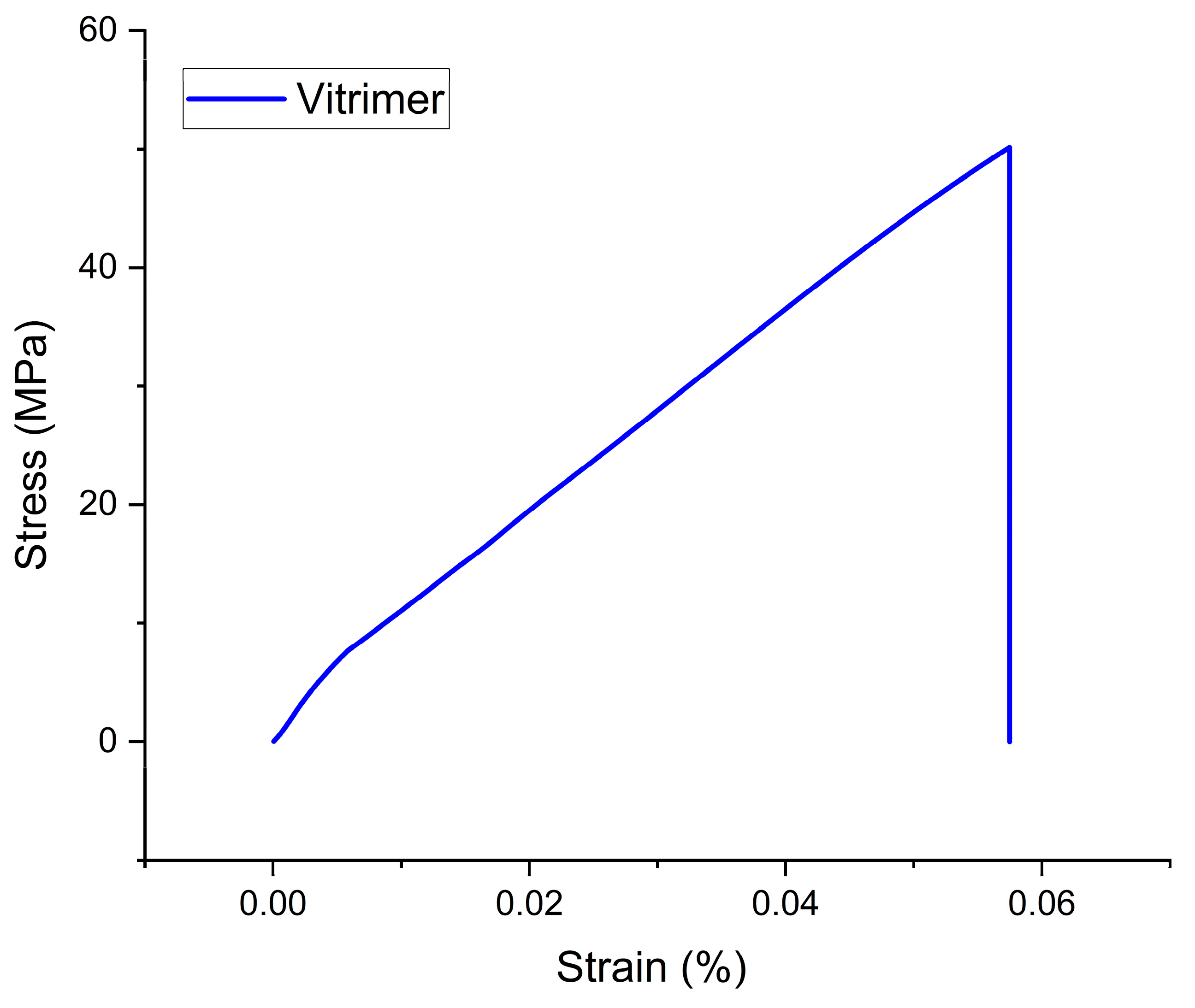
3.4.1. Vitrimer Polymer
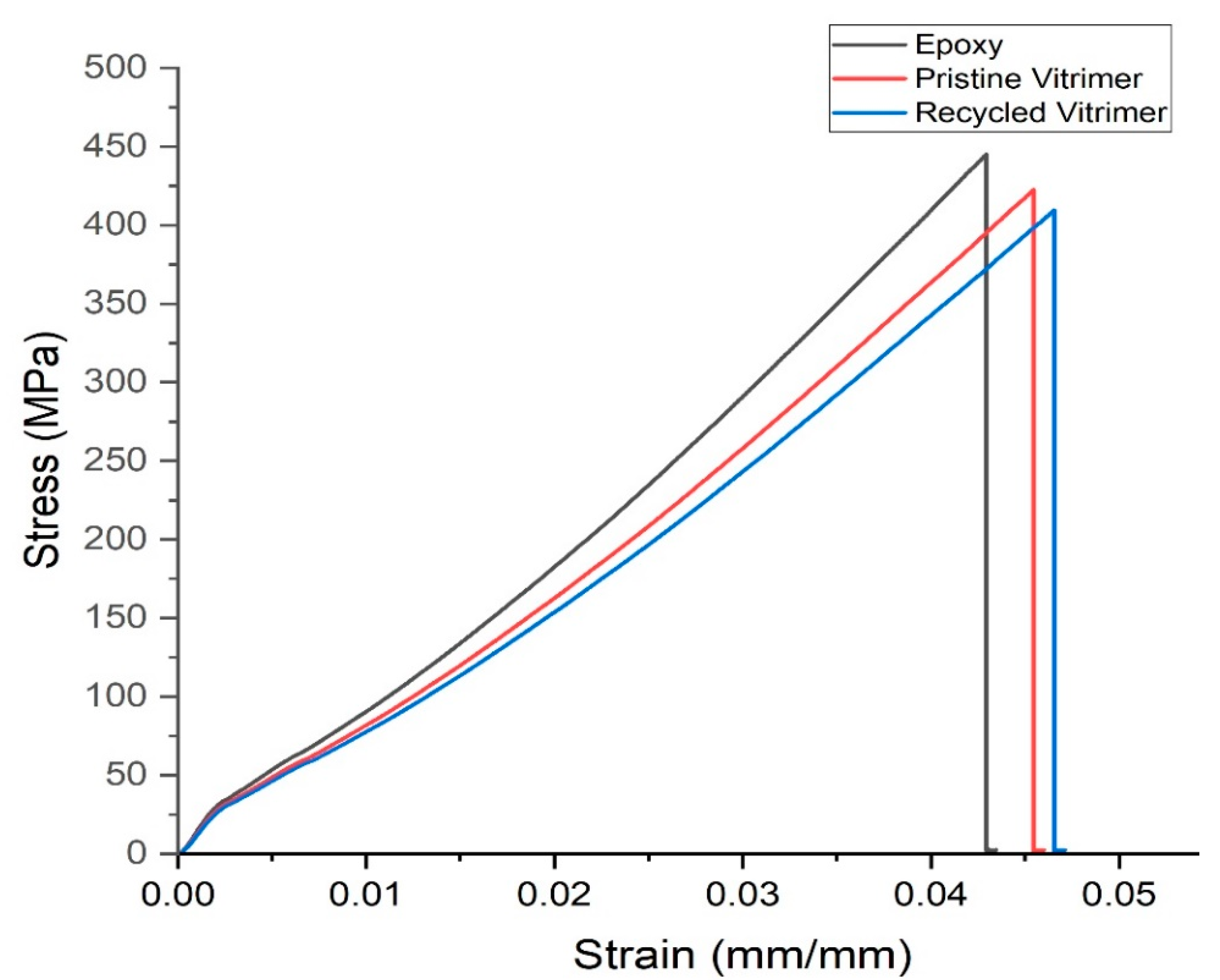
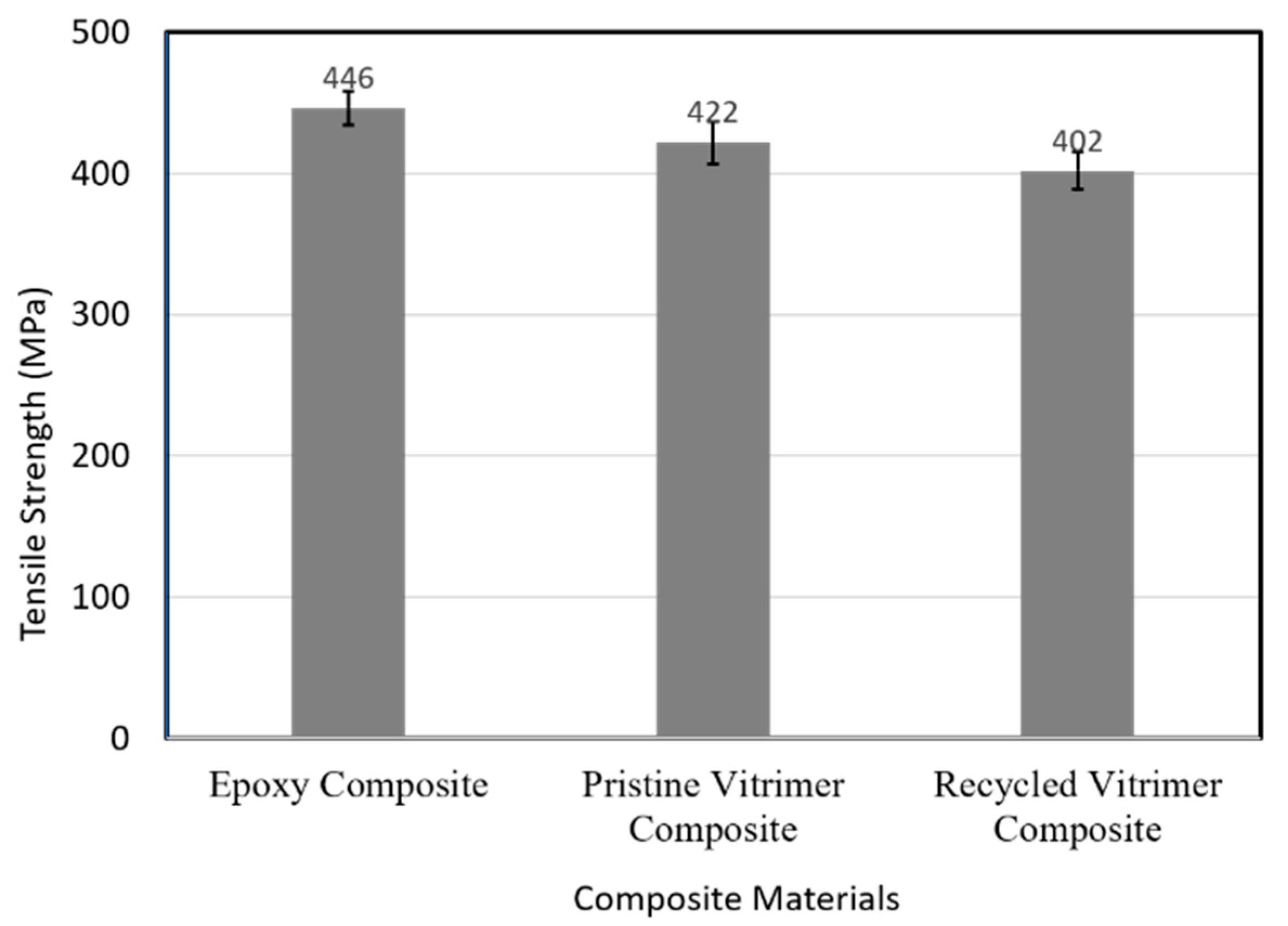
3.4.2. Composite Materials
3.5. Recycling of Vitrimer Composite
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huo, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, Q.; Song, P. A liquid phosphorus-containing imidazole derivative as flame-retardant curing agent for epoxy resin with enhanced thermal latency, mechanical, and flame-retardant performances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 386, 121984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Huo, S.; Shen, H.; Ran, S.; Wang, H.; Song, P.; Fang, Z. A bio-based ionic complex with different oxidation states of phosphorus for reducing flammability and smoke release of epoxy resins. Compos. Commun. 2020, 17, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Song, P.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Q.; Mai, Y. Epoxy nanocomposites simultaneously strengthened and toughened by hybridization with graphene oxide and block ionomer. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 168, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Ran, S.; Fang, Z.; Song, P.; Wang, H. Improved flame resistance and thermomechanical properties of epoxy resin nanocomposites from functionalized graphene oxide via self-assembly in water. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 165, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Guo, W.; Xu, Z.; Chen, S.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Miao, M.; Zhang, D. Synthesis of degradable hyperbranched epoxy resins with high tensile, elongation, modulus and low-temperature resistance. Compos. B Eng. 2020, 192, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, X.; Shi, K.; Yan, J.; Lin, S.; Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Yang, X. High performance epoxy composites prepared using recycled short carbon fiber with enhanced dispersibility and interfacial bonding through polydopamine surface-modification. Compos. B Eng. 2020, 193, 107987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wu, X.; Luo, C. Facile synthesis of Mn3O4 hollow polyhedron wrapped by multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a high-efficiency microwave absorber. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Shi, Q.; Dunn, M.L.; Wang, T.; Qi, H.J. Carbon fiber reinforced thermoset composite with near 100% recyclability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 6098–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Hui, D.; Singh, R.; Ahuja, I.P.S.; Feo, L.; Fraternali, F. Recycling of plastic solid waste: A state of art review and future applications. Compos. B Eng. 2017, 115, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ma, S.; Yan, S.; Zhu, J. Readily recyclable carbon fiber reinforced composites based on degradable thermosets: A review. Green. Chem. 2019, 21, 5781–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wei, J.; Jia, Z.; Yu, T.; Yuan, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; You, S.; Liu, R.; Zhu, J. Readily recyclable, high-performance thermosetting materials based on a lignin-derived spirodiacetal trigger. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montarnal, D.; Capelot, M.; Tournilhac, F.; Leibler, L. Silica-like malleable materials from permanent organic networks. Science 2011, 334, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, C.N.; Kloxin, C.J. Covalent adaptable networks: Reversible bond structures incorporated in polymer networks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4272–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloxin, C.J.; Bowman, C.N. Covalent adaptable networks: Smart, reconfigurable and responsive network systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7161–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Dong, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, T. Dynamic covalent polymer networks: From old chemistry to modern day innovations. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, B.; Sanka, R.V.S.P.; Binder, W.H.; Parthasarthy, V.; Rana, S.; Karak, N. Vitrimers: Associative dynamic covalent adaptive networks in thermoset polymers. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Sánchez, J.; Sánchez-Romate, X.F.; Espadas, F.J.; Prolongo, S.G.; Jiménez-Suárez, A. Electromechanical Properties of Smart Vitrimers Reinforced with Carbon Nanotubes for SHM Applications. Sensors 2024, 24, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Kuang, W.; Fifield, L.S. Carbon Fiber-Based Vitrimer Composites: A Path toward Current Research That Is High-Performing, Useful, and Sustainable. Materials 2024, 17, 3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.T.; Guo, Z.J.; Wang, W.Y.; Lei, X.F.; Zhang, B.L.; Zhang, H.P.; Zhang, Q.Y. Preparation of self-healing, recyclable epoxy resins and low-electrical resistance composites based on double-disulfide bond exchange. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 167, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorwanishpaisarn, N.; Kasemsiri, P.; Srikhao, N.; Son, C.; Kim, S.; Theerakulpisut, S.; Chindaprasirt, P. Carbon fiber/epoxy vitrimer composite patch cured with bio-based curing agents for one-step repair metallic sheet and its recyclability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiao, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Nie, X.; Chen, J. Bio-based epoxy vitrimer for recyclable and carbon fiber reinforced materials: Synthesis and structure-property relationship. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 227, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Li, S.; Gao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Ye, Y.; Cao, C.; Xue, H. Bio-Based Epoxy Vitrimers with Excellent Properties of Self-Healing, Recyclability, and Welding. Polymers 2024, 16, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM E1868-10(2021); Standard Test Methods for Loss-On-Drying by Thermogravimetry. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.astm.org/e1868-10r21.html (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- ASTM D638-22; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d0638-22.html (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Ruiz De Luzuriaga, A.; Martin, R.; Markaide, N.; Rekondo, A.; Cabanero, G.; Rodriguez, J.; Odriozola, I. Epoxy resin with exchangeable disulfide crosslinks to obtain reprocessable, repairable and recyclable fiber-reinforced thermoset composites. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, B.S.; Jamal, G.M.; Abdullah, O.G. Improving the tensile, toughness, and flexural properties of epoxy resin-based nanocomposites filled with ZrO2 and Y2O3 nanoparticles. Results Phys. 2022, 38, 105662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Y.; Song, L.; Kang, M.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M. Rapidly reprocessable, degradable epoxy vitrimer and recyclable carbon fiber reinforced thermoset composites relied on high contents of exchangeable aromatic disulfide crosslinks. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 199, 108278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; An, L.; Hu, Z.; Kuang, X. Fast and sustainable recycling of epoxy and composites using mixed solvents. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 199, 109895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartam, S.; Budhe, S.; Paul, J. Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Vitrimer Composite Material for Pressure Vessels: Towards Development of Sustainable Materials. Mater. Sci. Forum 2024, 1123, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Name | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|
| Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (DGEBA) | 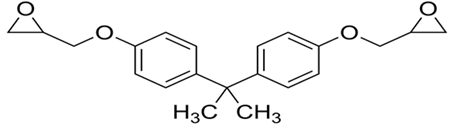 |
| Citric Acid |  |
| Cardanol |  |
| Dimethylformamide |  |
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (MPa) | % Elongation at Break |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitrimer Polymer | 50.01 ± 1.25 | 860 ± 80 | 0.058 ± 0.005 |
| Epoxy Composite | 446 ± 16.91 | 10,878 ± 93 | 0.042 ± 0.04 |
| Pristine Vitrimer Composite | 422.31 ± 18.5 | 9380 ± 82 | 0.045 ± 0.03 |
| Recycled Vitrimer Composite | 402 ± 17.5 | 8995 ± 64 | 0.045 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nartam, S.; Rautela, V.; Budhe, S.; Paul, J.; de Barros, S. Strength Retention of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Vitrimer Composite Material for Primary Structures: Towards Recyclable and Reusable Carbon Fiber Composites. Appl. Mech. 2024, 5, 804-817. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech5040045
Nartam S, Rautela V, Budhe S, Paul J, de Barros S. Strength Retention of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Vitrimer Composite Material for Primary Structures: Towards Recyclable and Reusable Carbon Fiber Composites. Applied Mechanics. 2024; 5(4):804-817. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech5040045
Chicago/Turabian StyleNartam, Sudhanshu, Vishal Rautela, Sandip Budhe, Jinu Paul, and Silvio de Barros. 2024. "Strength Retention of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Vitrimer Composite Material for Primary Structures: Towards Recyclable and Reusable Carbon Fiber Composites" Applied Mechanics 5, no. 4: 804-817. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech5040045
APA StyleNartam, S., Rautela, V., Budhe, S., Paul, J., & de Barros, S. (2024). Strength Retention of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Vitrimer Composite Material for Primary Structures: Towards Recyclable and Reusable Carbon Fiber Composites. Applied Mechanics, 5(4), 804-817. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech5040045





