Application of Reduced Graphene Oxide-Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite in the Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) Contaminated Wastewater
Abstract
1. Wastewater
1.1. Impact of Toxic Metal Presence in Wastewater and Challenges of Their Removal
1.1.1. Lead (Pb)
1.1.2. Cadmium (Cd)
1.2. Cadmium and Lead Wastewater Treatment
1.2.1. Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials
1.2.2. Reduced Graphene Oxide/Metal Oxide (rGO/MO) Nanocomposite
2. Review
2.1. Challenges with Various Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Toxic Metals
2.2. Nanocomposite
2.3. Adsorption Limitations
2.4. rGO/ZnONP Nanocomposite for Treatment of Pb and Cd in Wastewater
2.4.1. Cadmium (Cd) Wastewater Treatment
2.4.2. Lead (Pb) Wastewater Treatment
| Adsorbent | Adsorbent Nature | Equilibrium Time (min) | Toxic Metal Treated | Adsorption Efficiency (%) | Kinetic and Thermodynamic Model | Recycle Reaction | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnFe2O4/rGO | Crystalline, rough and wrinkled surface, and weak magnetism | 60 | Pb (II) | 98 | Langmuir and pseudo second order (chemisorption) | 5 | [76] |
| ZnO/GO | Weak crystallinity, hollow-shaped spaces, and flake-shaped morphology | 120 | Pb (II); Cd (II) | 97; 96 | Langmuir and pseudo second order (chemisorption) | - | [77] |
| ZnO/G | Well-surfaced spherical ZnO nanoparticles on graphene | 25 | Pb (II) | 92 | Endothermic, spontaneous, Langmuir, and pseudo second order | 3 | [75] |
| Fe3O4/rGO | Homogeneously dispersed nanoparticles on rGO sheet and magnetic and thermally stable composite | 45 | Pb (II) | 96 | Exothermic and spontaneous reaction, Temkin, chemisorption, and liquid film diffusion | - | [78] |
| CuO/rGO | Homogeneously dispersed nanoparticles on an rGO sheet with minimal sheet agglomeration | 175 | Cd (II) | 91 | Langmuir | - | [79] |
| TiO2/rGO | Irregular and mesoporous surface | 150 | Pb (II) | 89 | Langmuir and pseudo second order | - | [80] |
| ZnO/rGO | Good distribution of ZnO nanoparticles on rGO sheet and wrinkled surface | 90 | Cd (II) | 90 | Langmuir, pseudo second order, and chemisorption | - | [70] |
| PTP-SiO2/rGO | Sphere-shaped nanoparticles distributed moderately on rGO surface and amorphous nature | 60 | Cd (II), Pb (II) | 62, 66 | Jovanovic isotherm, spontaneous adsorption, and pseudo second order | 3 | [81] |
| WO3/rGO | Increased average crystallite size upon surfacing on rGO, strong bonding existing between WO3 and rGO, signaled by weakening and broadened WO3 Raman spectroscopy peak, and mesoporous surface | 200 | Pb (II), Cd (II) | 93.35, 89.95 | Electrostatic attraction | - | [82] |
| FA/GO | Well-covered graphene oxide surface by folic acid with uplifted roughness and irregularly shaped composite surface | 90 | Cd (II) | 82 | Freundlich isotherm, pseudo second order, endothermic, multilayered, and spontaneous adsorption | 2 | [83] |
| Mn–Fe3O4/G | Weak magnetism and well-dispersed particle on a graphene sheet | 58 | Cd (II) | 94 | Langmuir–Redlich–Peterson isotherm, spontaneous removal, chemisorption, and pseudo first and pseudo second order | 2 | [84] |
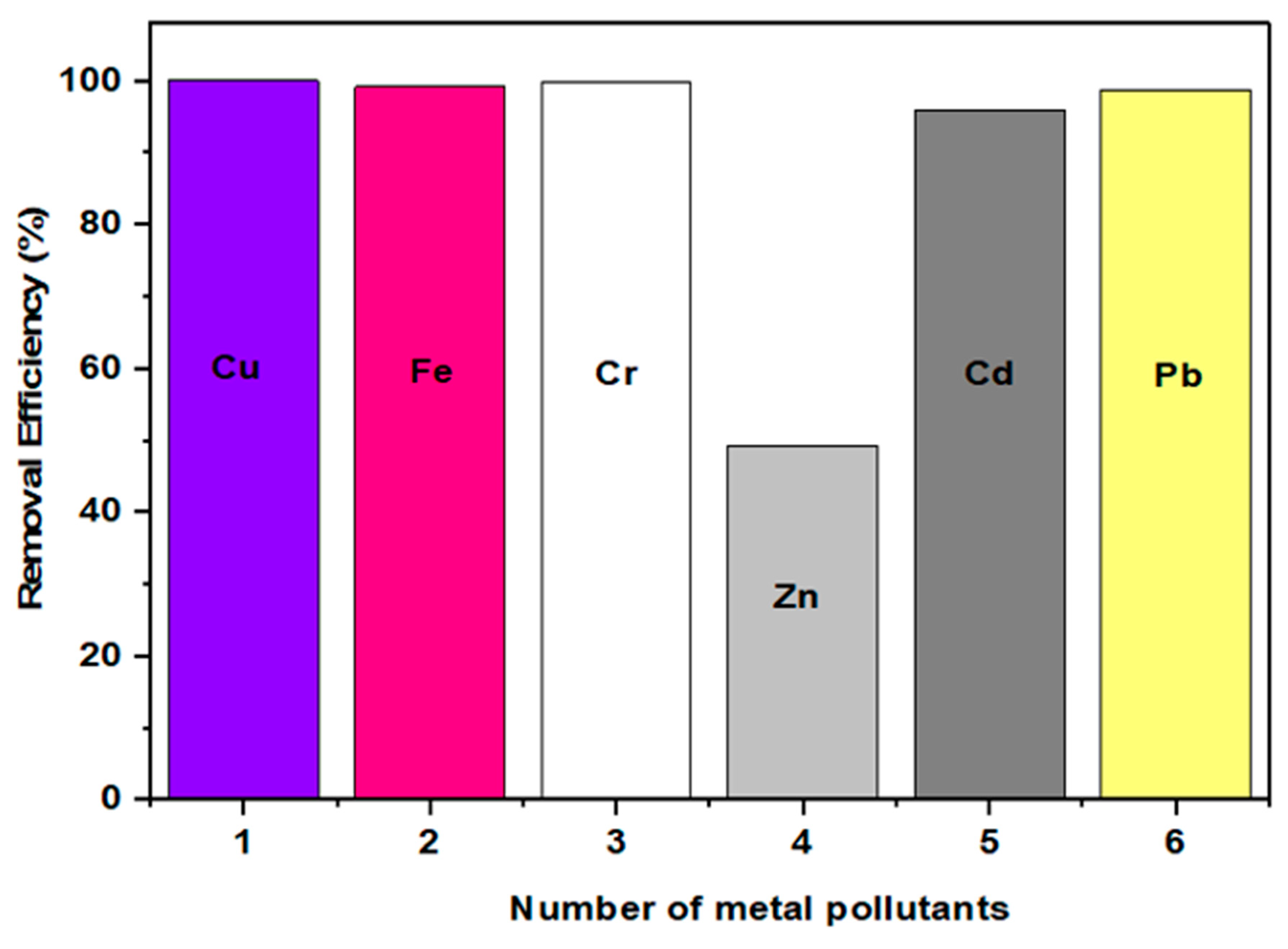
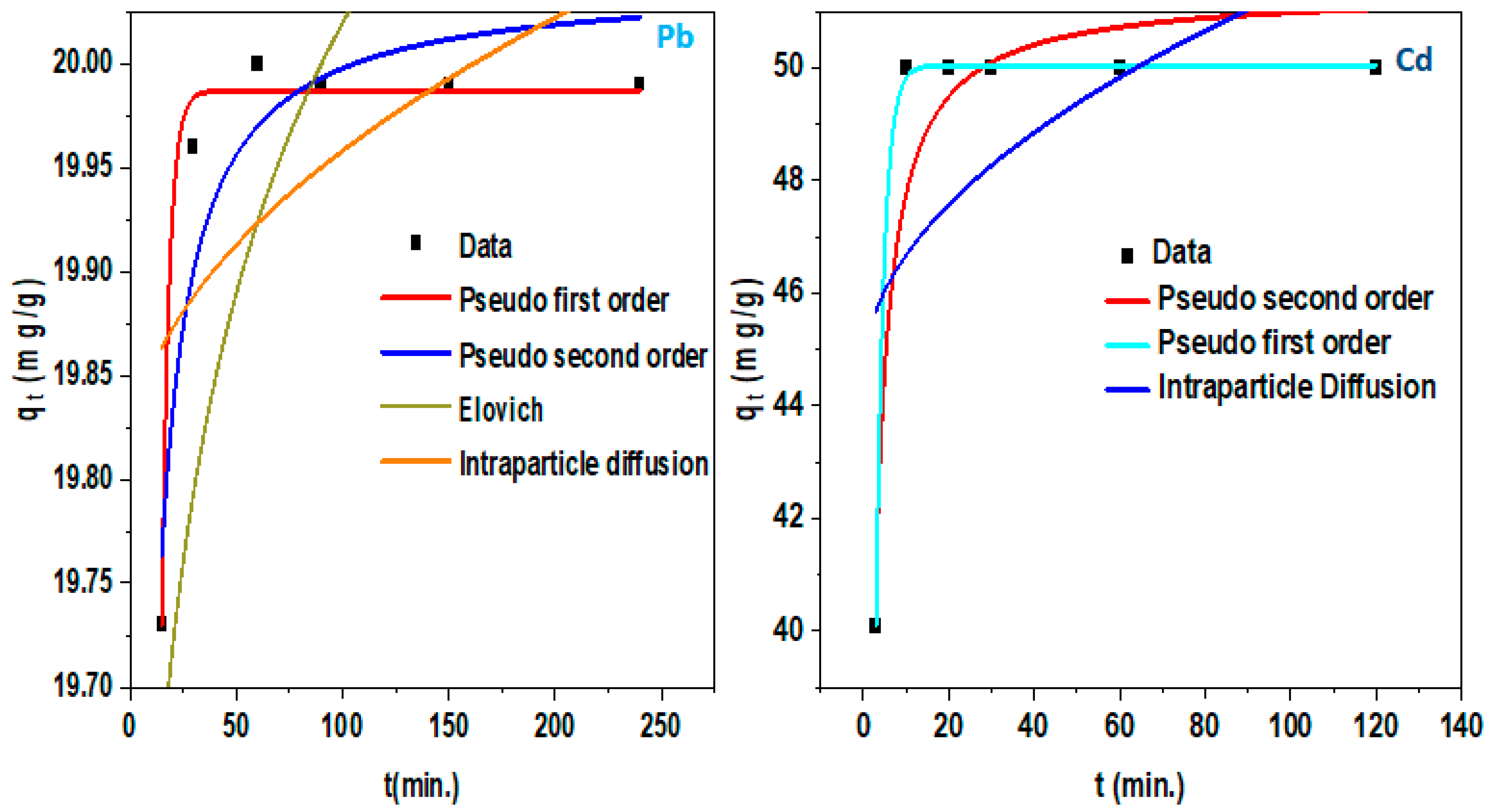
| ZnO/rGO | Slight agglomerated surface, sheet-like structure, and electronegative and photo-active surface | 10, 90 | Cd (II), Pb (II) | ~100 | Freundlich, Sips, and pseudo first order | 3, 7 | This study |
2.5. Experimental Procedure
2.5.1. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnONPs)
2.5.2. Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
2.5.3. rGO/ZnONP Nanocomposite
2.6. Characterization of Adsorbents
3. Adsorption Study
3.1. Adsorption Isotherms
3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Characterization
4.1.1. UV–Vis
4.1.2. FTIR
FTIR of ZnONPs, GO, rGO, and rGO/ZnONPs
4.1.3. Morphology of ZnONPs and rGO/ZnONPs
TEM
4.1.4. Defect Density Study
Raman Spectra of ZnONPs and rGO/ZnONPs
4.2. Removal Study
4.2.1. Adsorption Performance
4.2.2. Adsorption Mechanism
4.2.3. Kinetic Models
5. Conclusions
6. Recommendations/Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.; Prasad, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Shrivastava, M.; Gupta, N.; Nagar, S.; Bach, Q.V.; Kamyab, H.; Khan, S.A.; Yadav, S.; et al. Hazardous heavy metals contamination of vegetables and food chain: Role of sustainable remediation approaches—A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Natasha; Shah, A.H.; Saeed, F.; Ali, M.; Qaisrani, S.A.; Dumat, C. Heavy metal contamination and exposure risk assessment via drinking groundwater in Vehari, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 10, 39852–39864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, A.; Mandeep; Malik, J.; Kakkar, R. Mesoporous rGO@ZnO composite: Facile synthesis and excellent water treatment performance by pesticide adsorption and catalytic oxidative dye degradation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 160, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, X.J.; Hiew, B.Y.Z.; Lai, K.C.; Lee, L.Y.; Gan, S.; Thangalazhy-Gopakumar, S.; Rigby, S. Review on graphene and its derivatives: Synthesis methods and potential industrial implementation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 98, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.Z.N.; Wan Salleh, W.N.; Ismail, A.F.; Yusof, N.; Mohd Yusop, M.Z.; Aziz, F. Adsorptive removal of heavy metal ions using graphene-based nanomaterials: Toxicity, roles of functional groups and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Luch, A., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 101, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, D.; Bakhshpour, M.; Akgönüllü, S.; Aşır, S.; Denizli, A. Heavy Metal Ions Removal From Wastewater Using Cryogels: A Review. Front. Sustain. 2022, 3, 765592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, M.A.; Hezmee, M.N.M.; Haron, A.W.; Sabri, M.Y.M.; Rajion, M.A. The detrimental effects of lead on human and animal health. Vet. World 2016, 9, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, S.; Baskar, A.; Geevarghese, D.M.; Ali, M.N.V.S.; Bahubali, P.; Choudhary, R.; Lvov, V.; Tovar, G.I.; Senatov, F.; Koppala, S.; et al. Bioaccumulation of lead (Pb) and its effects in plants: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2022, 3, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Uddin, M.F.; Hossain, M.S.; Jubair, A.; Islam, M.N.; Rahman, M. Heavy metals contamination in shrimp and crab from southwest regions in Bangladesh: Possible health risk assessment. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, J.; Lunn, R.M.; Waalkes, M.P.; Tomatis, L.; Infante, P.F. Cadmium-induced cancers in animals and in humans. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2007, 13, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.U.; Liqun, C.; Coulter, J.A.; Cheema, S.A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Wenjun, M.; Farooq, M. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burakov, A.E.; Galunin, E.V.; Burakova, I.V.; Kucherova, A.E.; Agarwal, S.; Tkachev, A.G.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankole, M.T.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Mohammed, I.A.; Ochigbo, S.S.; Tijani, J.O.; Abubakre, O.K.; Roos, W.D. Selected Heavy Metals Removal from Electroplating Wastewater by Purified and Polyhydroxylbutyrate Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes Adsorbents. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topare, N.S.; Wadgaonkar, V.S. A review on application of low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals removal from wastewater. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 77, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.; Younesi, H.; Mehraban, Z.; Heikkinen, H. Selective adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Ni(II) ions from aqueous solution using chitosan-MAA nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 61, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alalwan, H.A.; Kadhom, M.A.; Alminshid, A.H. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using agricultural byproducts. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2020, 69, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, A.; Zhang, Y. Efficient removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater and fixation of heavy metals in soil by manganese dioxide nanosorbents with tailored hollow mesoporous structure. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albqmi, M.; Frontistis, Z.; Raji, Z.; Karim, A.; Karam, A.; Khalloufi, S. Adsorption of Heavy Metals: Mechanisms, Kinetics, and Applications of Various Adsorbents in Wastewater Remediation—A Review. Waste 2023, 1, 775–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreyling, W.G.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Chaudhry, Q. A complementary definition of nanomaterial. Nano Today 2010, 5, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, M.N.; Goh, P.S.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F. The roles of nanomaterials in conventional and emerging technologies for heavy metal removal: A state-of-the-art review. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehlivan, E.; Cetin, S.; Yanik, B.H. Equilibrium studies for the sorption of zinc and copper from aqueous solutions using sugar beet pulp and fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, D.L.; Airoldi, C.; de Sousa, K.S. Adsorption and thermodynamic studies of Cu(II) and Zn(II) on organofunctionalized-kaolinite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 5157–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannajad, M.; Kamran Haghighi, H. Removal of Heavy Metals from Polluted Solutions by Zeolitic Adsorbents: A Review. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda-Mbanga, B.G.; Prabakaran, E.; Pillay, K. Carbohydrate biopolymers, lignin based adsorbents for removal of heavy metals (Cd2+, Pb2+, Zn2+) from wastewater, regeneration and reuse for spent adsorbents including latent fingerprint detection: A review. Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 30, e00609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.T.; LaChance, A.M.; Zeng, S.; Liu, B.; Sun, L. Synthesis, properties, and applications of graphene oxide/reduced graphene oxide and their nanocomposites. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoso, W.A.; Haleem, N.; Baig, M.A.; Jamal, Y. Synthesis, characterization and heavy metal removal efficiency of nickel ferrite nanoparticles (NFN’s). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, R.; Khan, S.U.; Azam, A.; Farooqi, I.H. A study on effective adsorption of lead from an aqueous solution using Copper Oxide nanoparticles. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1058, 012074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prado-Audelo, M.L.; García Kerdan, I.; Escutia-Guadarrama, L.; Reyna-González, J.M.; Magaña, J.J.; Leyva-Gómez, G. Nanoremediation: Nanomaterials and Nanotechnologies for Environmental Cleanup. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 793765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.W.; Mudunkotuwa, I.A.; Rupasinghe, T.; Grassian, V.H. Aggregation and dissolution of 4 nm ZnO nanoparticles in aqueous environments: Influence of pH, ionic strength, size, and adsorption of humic acid. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6059–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.T.; Haes, A.J. What Does Nanoparticle Stability Mean? J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 16495–16507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velempini, T.; Ahamed, M.E.H.; Pillay, K. Heavy-metal spent adsorbents reuse in catalytic, energy and forensic applications- a new approach in reducing secondary pollution associated with adsorption. Results Chem. 2023, 5, 100901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, K.; Seo, B.K.; Hyun, J.H. Effective removal of radioactive cesium from contaminated water by synthesized composite adsorbent and its thermal treatment for enhanced storage stability. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, A.R.; Casals, E.; Puntes, V.; Komilis, D.; Sánchez, A.; Font, X. Use of cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles for the adsorption of dissolved cadmium (II), lead (II) and chromium (VI) at two different pHs in single and multi-component systems. Glob. Nest J. 2015, 17, 536–543. [Google Scholar]
- Dave, P.N.; Chopda, L.V. Application of iron oxide nanomaterials for the removal of heavy metals. J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 2014, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, V.; Kondal, N. ZnO Nanoadsorbents: A potent material for removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 41, 100380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosun; Ali, A.; Mannan, A.; Ali Shah, U.; Zia, M. Removal of of toxic metal ions (Ni2+ and Cd2+) from wastewater by using TOPO decorated iron oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mur, B.A. Green Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticle Synthesis Using Mangrove Leaf Extract from Avicenna marina: Properties and Application for the Removal of Toxic Metal Ions (Cd2+ and Pb2+). Water 2023, 15, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaba, E.Y.; Jacob, J.O.; Tijani, J.O.; Suleiman, M.A.T. A critical review of synthesis parameters affecting the properties of zinc oxide nanoparticle and its application in wastewater treatment. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Le, A.; Pung, S.-Y.; Sreekantan, S.; Matsuda, A.; Phu Huynh, D.; Phu Huynh Mechanisms, D. Mechanisms of removal of heavy metal ions by ZnO particles. Heliyon 2019, 5, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, T.; Durrani, T. The role of some important metal oxide nanoparticles for wastewater and antibacterial applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2021, 3, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaüque, E.F.C.; Zvimba, J.N.; Ngila, J.C.; Musee, N. Fate, behaviour, and implications of ZnO nanoparticles in a simulated wastewater treatment plant. Water SA 2016, 42, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khan, A.U.H.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R.; Fang, C.; Dharmarajan, R.; Shon, H. Interactions between zinc oxide nanoparticles and hexabromocyclododecane in simulated waters. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Inam, M.A.; Zam, S.Z.; Park, D.R.; Yeom, I.T. Assessment of Key Environmental Factors Influencing the Sedimentation and Aggregation Behavior of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Aquatic Environment. Water 2018, 10, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, M.; Shin, J.; Kim, K.; Yu, K.J. Electronic and Thermal Properties of Graphene and Recent Advances in Graphene Based Electronics Applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, F.; Kolahdouz, M.; Larimian, S.; Radfar, B.; Radamson, H.H. Graphene synthesis, characterization and its applications in nanophotonics, nanoelectronics, and nanosensing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 4347–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidu, R.; Matei, E.; Predescu, A.M.; Alhalaili, B.; Pantilimon, C.; Tarcea, C.; Predescu, C. Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewaters: A Challenge from Current Treatment Methods to Nanotechnology Applications. Toxics 2020, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Shi, X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, F.; Yu, T.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, D.; Wei, C. Strategies to improve the adsorption properties of graphene-based adsorbent towards heavy metal ions and their compound pollutants: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, C. A review on reduced Graphene oxide hybrid nano composites and their prominent applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedekar, V.V.; Zaeem, S.M.; Das, S. Graphene-metal oxide nanocomposites for supercapacitors: A perspective review. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2018, 9, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontakke, A.D.; Tiwari, S.; Purkait, M.K. A comprehensive review on graphene oxide-based nanocarriers: Synthesis, functionalization and biomedical applications. FlatChem 2023, 38, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, R.A.; Naikoo, G.A.; Srivastava, A.K.; Hassan, I.U.; Karna, S.P.; Giri, L.; Shaikh, A.M.H.; Rezakazemi, M.; Ahmed, W. Performance of graphene-zinc oxide nanocomposite coated-glassy carbon electrode in the sensitive determination of para-nitrophenol. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, M.; Ramachandran, R.; Wang, F. Graphene-zinc oxide (G-ZnO) nanocomposite for electrochemical supercapacitor applications. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2016, 1, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, B.S.; Jose, G.; Lu, Y.J.; Chen, J.P. Functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide as a Versatile Tool for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, H.; Ikram, M.; Ali, S.; Shahzadi, A.; Aqeel, M.; Haider, A.; Imran, M.; Ali, S. Enhanced drug efficiency of doped ZnO–GO (graphene oxide) nanocomposites, a new gateway in drug delivery systems (DDSs). Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, E.; Shanmugam, P.; Karuppannan, K.; Chinnasamy, T.; Venugopal, S. The biosynthesis of a graphene oxide-based zinc oxide nanocomposite using Dalbergia latifolia leaf extract and its biological applications. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 2166–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toporovska, L.; Turko, B.; Savchak, M.; Seyedi, M.; Luzinov, I.; Kostruba, A.; Kapustianyk, V.; Vaskiv, A. Zinc oxide: Reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite film for heterogeneous photocatalysis. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2020, 52, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Jiu, H.; Qi, G.; Huang, Y. ZnO-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites as efficient photocatalysts for photocatalytic reduction of CO2. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 6256–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi Avval, M.; Moghadam, P.N.; Baradarani, M.M. Synthesis of a new nanocomposite based-on graphene-oxide for selective removal of Pb2+ ions from aqueous solutions. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Hota, G. Functionalization of graphene oxide with metal oxide nanomaterials: Synthesis and applications for the removal of inorganic, toxic, environmental pollutants from water. In Handbook of Functionalized Nanomaterials for Industrial Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 299–326. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjith, K.S.; Manivel, P.; Rajendrakumar, R.T.; Uyar, T. Multifunctional ZnO nanorod-reduced graphene oxide hybrids nanocomposites for effective water remediation: Effective sunlight driven degradation of organic dyes and rapid heavy metal adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 325, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Peng, C.; Naz, I.; Amjed, M.A. Water Purification Using Magnetic Nanomaterials: An Overview. In Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 161–179. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elhamid, A.I.; Elgoud, E.M.A.; Aly, H.F. Alginate modified graphene oxide for rapid and effective sorption of some heavy metal ions from an aqueous solution. Cellulose 2022, 29, 6231–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, P.; Kiran, G.R.; Acharyya, S.G. Remarkable performance of GO/ZnO nanocomposites under optimized parameters for remediation of Cd (II) from water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 626, 157238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.C.; Gururani, P. Advances of graphene oxide based nanocomposite materials in the treatment of wastewater containing heavy metal ions and dyes. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, A.; Shahid, A.; Jahan, Z.; Bilal Khan Niazi, M.; Ali Inam, M.; Tawfeek, A.M.; M Kamel, E.; Saeed Akhtar, M. Development of ZnO-GO-NiO membrane for removal of lead and cadmium heavy metal ions from wastewater. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Maguana, Y.; Elhadiri, N.; Benchanaa, M.; Chikri, R. Activated Carbon for Dyes Removal: Modeling and Understanding the Adsorption Process. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, R.; Abdel-Aal, S.K. Facile synthesis of nanostructured ZnO–rGO based graphene and its application in wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 19667–19675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghozatloo, A.; Enayatollahi, A. Enhancing the effect of zinc oxide on the absorption of heavy metals from wastewater by using silica in graphene bed. Anal. Methods Environ. Chem. J. 2019, 2, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nik-Abdul-Ghani; Jami; Alam The role of nanoadsorbents and nanocomposite adsorbents in the removal of heavy metals from wastewater: A review and prospect. Pollution 2021, 7, 153–179. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.C.; Rawat, B.S.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, N.; Upadhyay, S.; Chetana, S.; Gururani, P.; Kimothi, S. Sustainable synthetic approach and applications of ZnO/r-GO in the adsorption of toxic Pb2+ and Cr6+ ions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 145, 110040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, T.; Zain-ul-Abdin; Waseem, M.; Hafeez, M.; Din, S.U.; Haq, S.; Mahfoz-ur-Rehman. Reduced Graphene Oxide/Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite: From Synthesis to its Application for Wastewater Purification and Antibacterial Activity. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3907–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, B.; Ye, J.; Jia, Q. Preparation, Characterization, and Application of Graphene–Zinc Oxide Composites (G–ZnO) for the Adsorption of Cu(II), Pb(II), and Cr(III). J. Chem. Eng. Data 2013, 58, 2395–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Mohamed, A.A. Facile adsorptive removal of dyes and heavy metals from wastewaters using magnetic nanocomposite of zinc ferrite@reduced graphene oxide. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 144, 109912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinkhani, O.; Hamzehlouy, A.; Dan, S.; Sanchouli, N.; Tavakkoli, M.; Hashemipour, H. Graphene oxide/ZnO nanocomposites for efficient removal of heavy metal and organic contaminants from water. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 105176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Bulin, C.; Li, B.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, H.; Sun, H.; Ge, X.; Xing, R.; Zhang, B. Efficient removal of aqueous Pb(II) using partially reduced graphene oxide-Fe3O4. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 1031–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.; Kaushal, S.; Singh, P.P. Green synthesis of a CuO/rGO nanocomposite using a Terminalia arjuna bark extract and its catalytic activity for the purification of water. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 2170–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, K.M.; Ali, M.H.H.; Al-Afify, A.G. Synthesis and use of TiO2@rGo nanocomposites in photocatalytic removal of chromium and lead ions from wastewater. J. Elem. 2020, 25, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.C.; Rawat, B.S.; Semwal, P.; Kumar, N. Effective removal of highly toxic Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions using reduced graphene oxide, polythiophene, and silica-based nanocomposite. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkoor, F.; Shoeb, M.; Mashkoor, R.; Anwer, A.H.; Zhu, S.; Jeong, H.; Baek, S.S.; Jung, J.; Jeong, C. Synergistic effects of tungstate trioxide hemihydrate decorated reduced graphene oxide for the adsorption of heavy metals and dyes and postliminary application in supercapacitor device. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, M.; Akrami, M.; Gheibi, M.; Azizi-Toupkanloo, H.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Tian, G. Cadmium and copper heavy metal treatment from water resources by high-performance folic acid-graphene oxide nanocomposite adsorbent and evaluation of adsorptive mechanism using computational intelligence, isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic analyses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 43999–44021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, D.; Basu, T.; Debnath, S.; Ghosh, A.K.; De, A.; Ghosh, U.C. Mechanistic insight for the sorption of Cd(II) and Cu(II) from aqueous solution on magnetic mn-doped Fe(III) oxide nanoparticle implanted graphene. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2013, 58, 2809–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Yarbrough, R.; Froeschle, M.; White, J.; Rathnayake, H. Band gap engineered zinc oxide nanostructures via a sol–gel synthesis of solvent driven shape-controlled crystal growth. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14638–14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tu, Q.; Francis, L.F.; Kortshagen, U.R. Band Gap Tuning of Films of Undoped ZnO Nanocrystals by Removal of Surface Groups. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabchinskii, M.K.; Shnitov, V.V.; Dideikin, A.T.; Aleksenskii, A.E.; Vul, S.P.; Baidakova, M.V.; Pronin, I.I.; Kirilenko, D.A.; Brunkov, P.N.; Weise, J.; et al. Nanoscale perforation of graphene oxide during photoreduction process in the argon atmosphere. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 28261–28269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faniyi, I.O.; Fasakin, O.; Olofinjana, B.; Adekunle, A.S.; Oluwasusi, T.V.; Eleruja, M.A.; Ajayi, E.O.B. The comparative analyses of reduced graphene oxide (RGO) prepared via green, mild and chemical approaches. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, S.; Ghamsari, M.S.; Lee, C.; Han, W.; Park, H.H.; Tafreshi, M.J.; Afarideh, H.; Ara, M.H.M. Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Sambucus ebulus. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, S.W.; James, O.O.; Sanusi, Y.K.; Olayinka, O.H. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using bashful (Mimosa pudica), leaf extract: A precursor for organic electronics applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, P.; Saravanan, K.; Manogar, P.; Johnson, J.; Vinoth, E.; Mayakannan, M. Green synthesis and characterization of biocompatible zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of its antibacterial potential. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2021, 31, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, A.S.; Yousef Mohamed, A.; Kim, D.H.; Luu Luyen Doan, T.; Chougule, S.S.; Jung, N.; Nam, S.; Lee, K. Design of zinc oxide nanoparticles and graphene hydrogel co-incorporated activated carbon for efficient capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, B.; Paul, B.; Purkayastha, D.D.; Dhar, S.S.; Behera, S. Facile synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles and studies of their catalytic activity towards ultrasound-assisted degradation of metronidazole. Mater. Lett. 2016, 168, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitiphattharabun, S.; Auewattanapun, K.; Htet, T.L.; Thu, M.M.; Panomsuwan, G.; Techapiesancharoenkij, R.; Ohta, J.; Jongprateep, O. Reduced graphene oxide/zinc oxide composite as an electrochemical sensor for acetylcholine detection. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandiran, J.; Yesuraj, J.; Arivanandhan, M.; Raja, A.; Suthanthiraraj, S.A.; Jayavel, R.; Nedumaran, D. Synthesis and Electrochemical Studies of rGO/ZnO Nanocomposite for Supercapacitor Application. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2018, 28, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitradevi, T.; Jestin Lenus, A.; Victor Jaya, N. Structure, morphology and luminescence properties of sol-gel method synthesized pure and Ag-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 7, 015011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drmosh, Q.A.; Yamani, Z.H.; Hendi, A.H.; Gondal, M.A.; Moqbel, R.A.; Saleh, T.A.; Khan, M.Y. A novel approach to fabricating a ternary rGO/ZnO/Pt system for high-performance hydrogen sensor at low operating temperatures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 464, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodwihok, C.; Wongratanaphisan, D.; Ngo, Y.L.T.; Khandelwal, M.; Hur, S.H.; Chung, J.S. Effect of GO Additive in ZnO/rGO Nanocomposites with Enhanced Photosensitivity and Photocatalytic Activity. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Jain, Y.; Kumari, M.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, S.K.; Sachdev, K. Synthesis and Characterization of Graphene Oxide (GO) and Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO) for Gas Sensing Application. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 376, 1700006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surekha, G.; Krishnaiah, K.V.; Ravi, N.; Padma Suvarna, R. FTIR, Raman and XRD analysis of graphene oxide films prepared by modified Hummers method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1495, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korepanov, V.I.; Chan, S.Y.; Hsu, H.C.; Hamaguchi, H.O. Phonon confinement and size effect in Raman spectra of ZnO nanoparticles. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Mandal, S.K. Precursor-and Time-Dependent Morphological Evolution of ZnO Nanostructures for Comparative Photocatalytic Activity and Adsorption Dynamics with Methylene Blue Dye. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16670–16680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, H.; Zhu, Y. Significantly enhanced photocatalytic performance of ZnO via graphene hybridization and the mechanism study. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 101, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobianu, C.; Cobianu, C.; Dumbravescu, N.; Serban, B.C.; Buiu, O.; Romanitan, C.; Comanescu, F.; Danila, M.; Marinescu, R.; Avramescu, V.; et al. Sonochemically synthetized ZnO-graphene nanohybrids and its characterization. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2020, 59, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sadanandhan, A.M.; Jain, S.L. Silver doped reduced graphene oxide as a promising plasmonic photocatalyst for oxidative coupling of benzylamines under visible light irradiation. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 9116–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpana, V.N.; Kataru, B.A.S.; Sravani, N.; Vigneshwari, T.; Panneerselvam, A.; Devi Rajeswari, V. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using culture filtrates of Aspergillus niger: Antimicrobial textiles and dye degradation studies. OpenNano 2018, 3, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; UllahKha, F.; Mahmood, S.; Mahmood, T.; Shamim, A. Different Approaches for the Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Open J. Chem. 2018, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiranakumar, H.V.; Naveen, C.S.; Thejas, R.; Prasanna, G.D.; Nagaraju, G.; Murugendrappa, M. V An impact of RGO on the ZnO nanoparticles: Structural, morphological, electrical, and gas sensing properties. Sens. Technol. 2024, 2, 2310479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaychuk, P.A. The revised potential—pH diagram for Pb—H2O system. Ovidius Univ. Ann. Chem. 2018, 29, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.A.; Al-Odayni, A.B.; Saeed, W.S.; Al-Kahtani, A.; Alharthi, F.A.; Aouak, T. Efficient Adsorption of Lead (II) from Aqueous Phase Solutions Using Polypyrrole-Based Activated Carbon. Materials 2019, 12, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaimee, M.Z.A.; Sarjadi, M.S.; Rahman, M.L. Heavy Metals Removal from Water by Efficient Adsorbents. Water 2021, 13, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpomie, K.G.; Conradie, J.; Adegoke, K.A.; Oyedotun, K.O.; Ighalo, J.O.; Amaku, J.F.; Olisah, C.; Adeola, A.O.; Iwuozor, K.O. Adsorption mechanism and modeling of radionuclides and heavy metals onto ZnO nanoparticles: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, S.; Lai, C.W.; Gan, S.; Zamiri, G.; Akbarzadeh Pivehzhani, O.; Johan, M.R. Application of efficient magnetic particles and activated carbon for dye removal from wastewater. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20684–20697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.M.; Rane, N.R.; Li, X.; Otari, S.V.; Girawale, S.D.; Palake, A.R.; Kodam, K.M.; Park, Y.-K.; Ha, Y.-H.; Yadav, K.K.; et al. Magnetic nanostructured adsorbents for water treatment: Structure-property relationships, chemistry of interactions, and lab-to-industry integration. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Zhou, X.; Cai, N.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H. Simultaneous removal of cadmium, lead, chromate by biochar modified with layered double hydroxide with sulfide intercalation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, K.; Kumar, V.; Choudhary, S.; Mankotia, P.; Kumar, B.; Mishra, H.; Moulick, A.; Ekielski, A.; et al. A Review of Adsorbents for Heavy Metal Decontamination: Growing Approach to Wastewater Treatment. Materials 2021, 14, 4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, M.; Lee, I.; Hong, Y.; Kumar, V.; Kim, H. Multifunctional β-Cyclodextrin-EDTA-Chitosan polymer adsorbent synthesis for simultaneous removal of heavy metals and organic dyes from wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.Z.N.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Yusof, N.; Mohd Yusop, M.Z.; Hamdan, R.; Awang, N.A.; Ismail, N.H.; Rosman, N.; Sazali, N.; Ismail, A.F. Pb(II) removal and its adsorption from aqueous solution using zinc oxide/graphene oxide composite. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2020, 208, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Z.; Li, X. Amino-functionalized graphene oxide for Cr(VI), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal from industrial wastewater. Open Chem. 2020, 18, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherono, F.; Mburu, N.; Kakoi, B. Adsorption of lead, copper and zinc in a multi-metal aqueous solution by waste rubber tires for the design of single batch adsorber. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

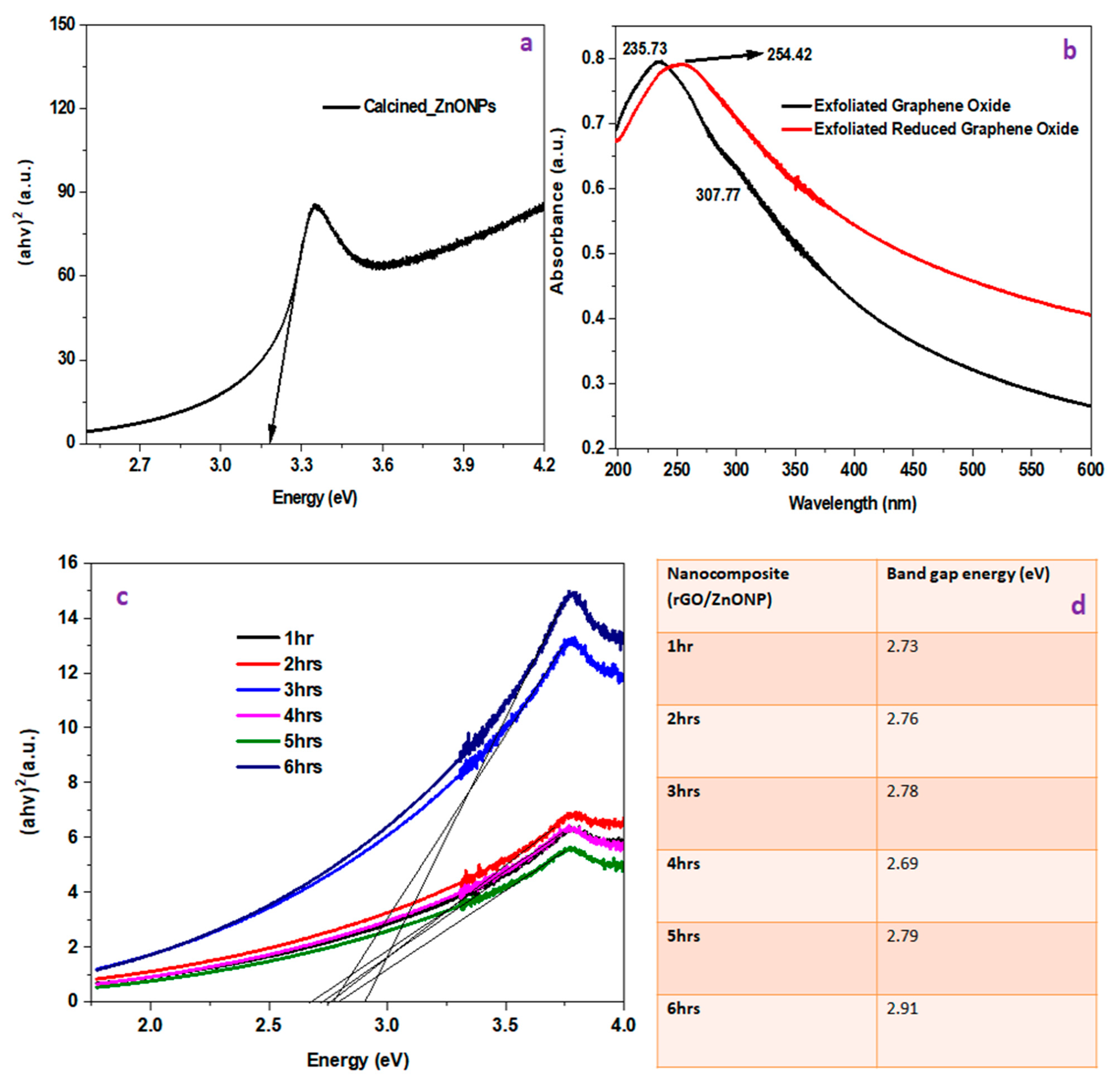
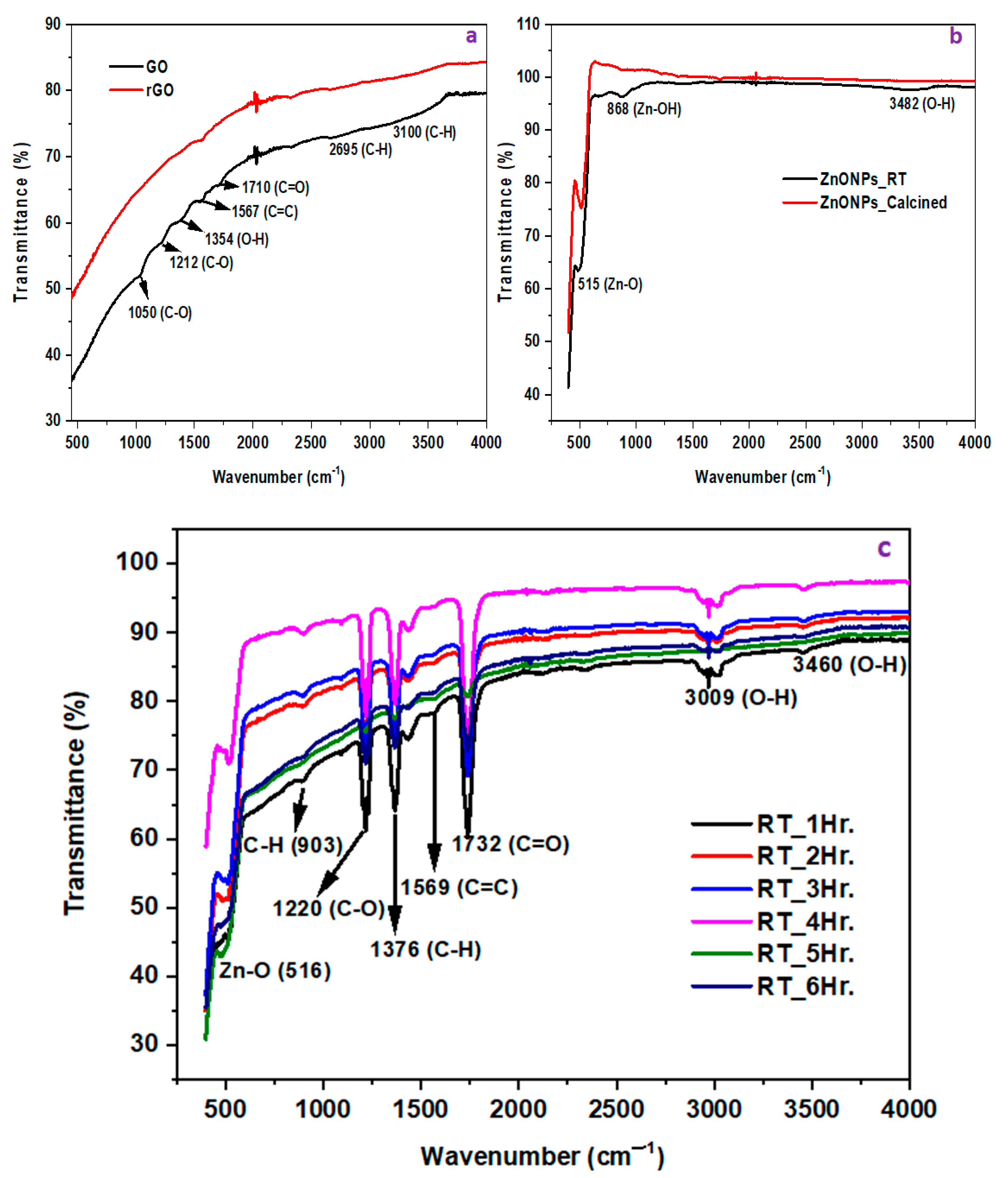
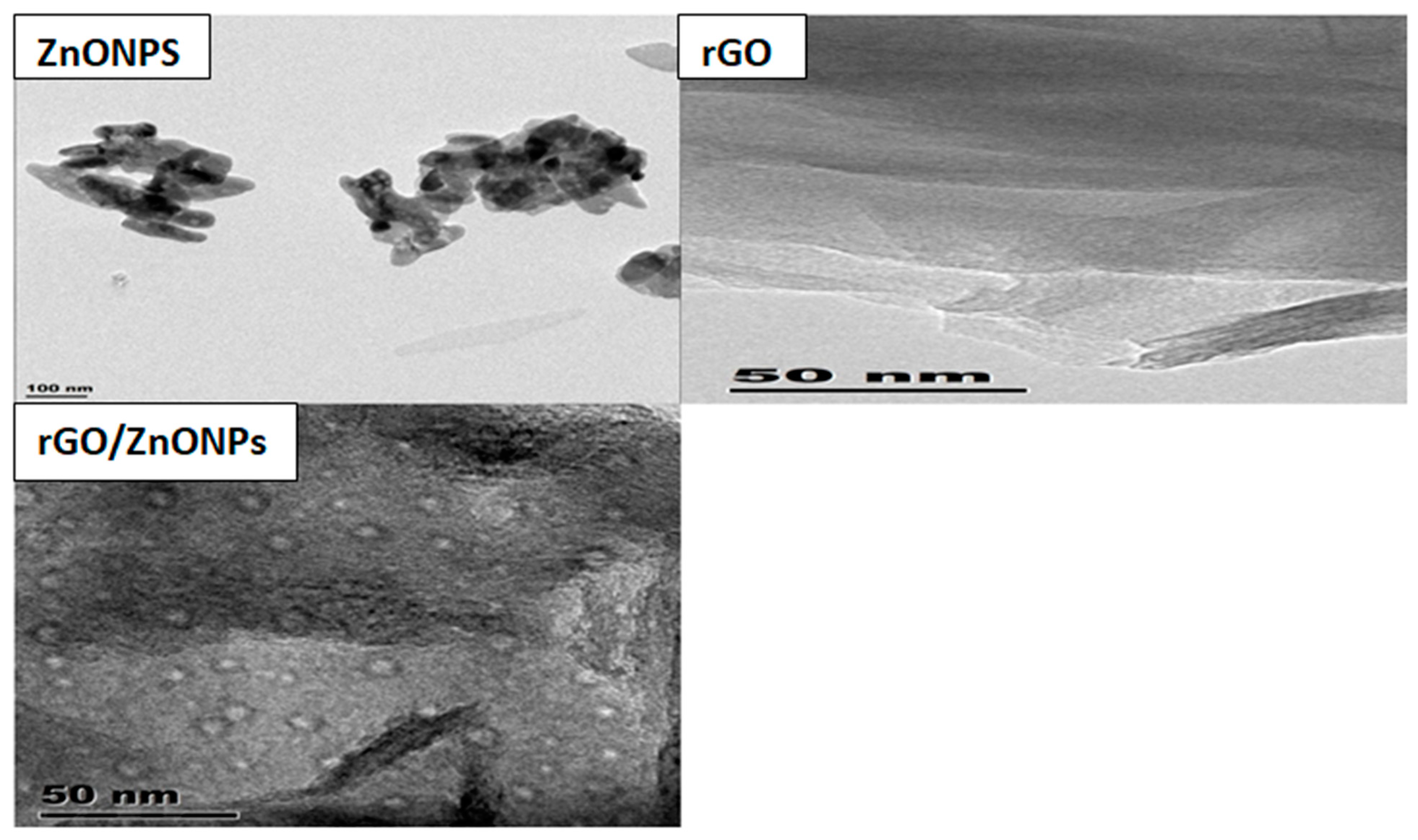

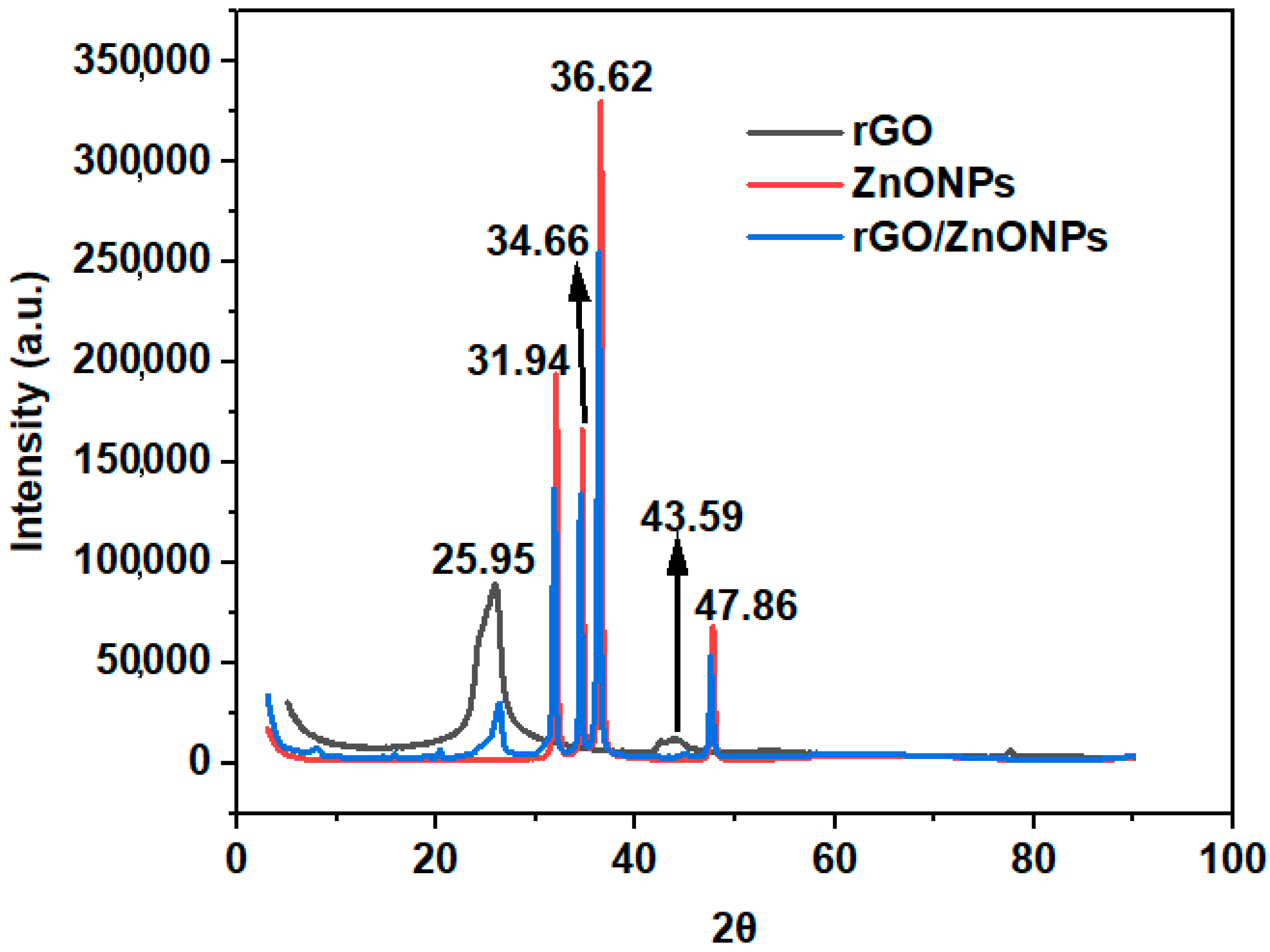

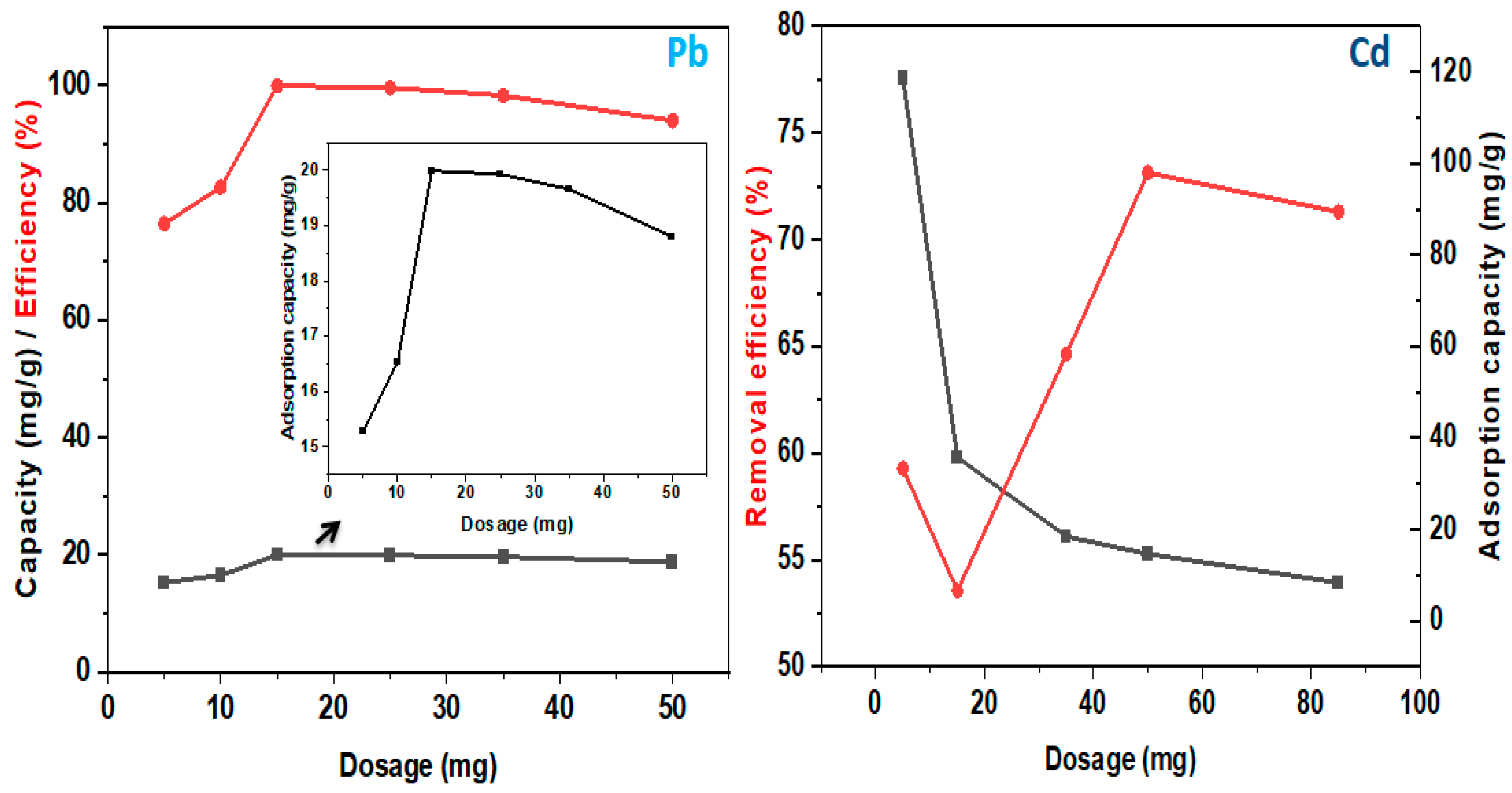
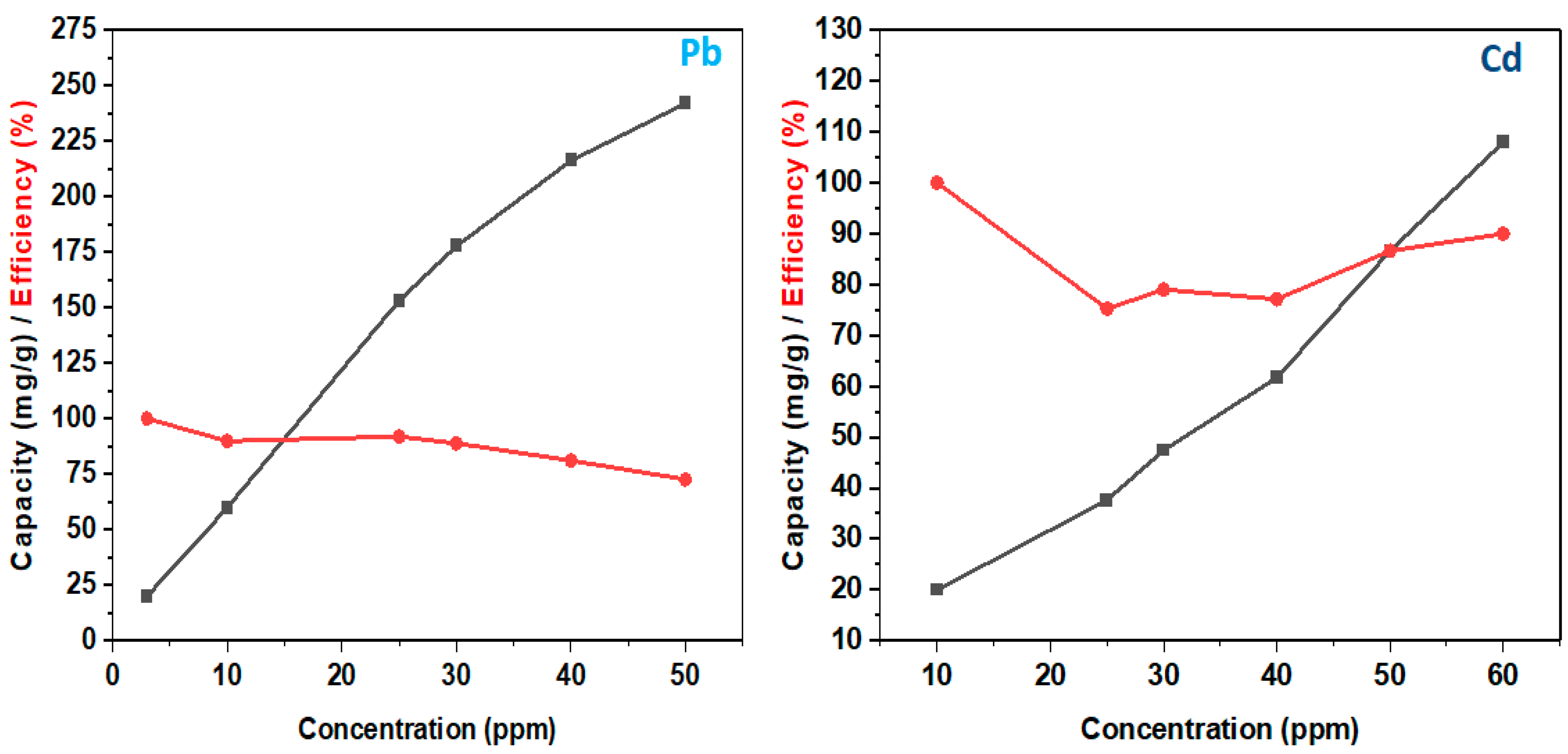

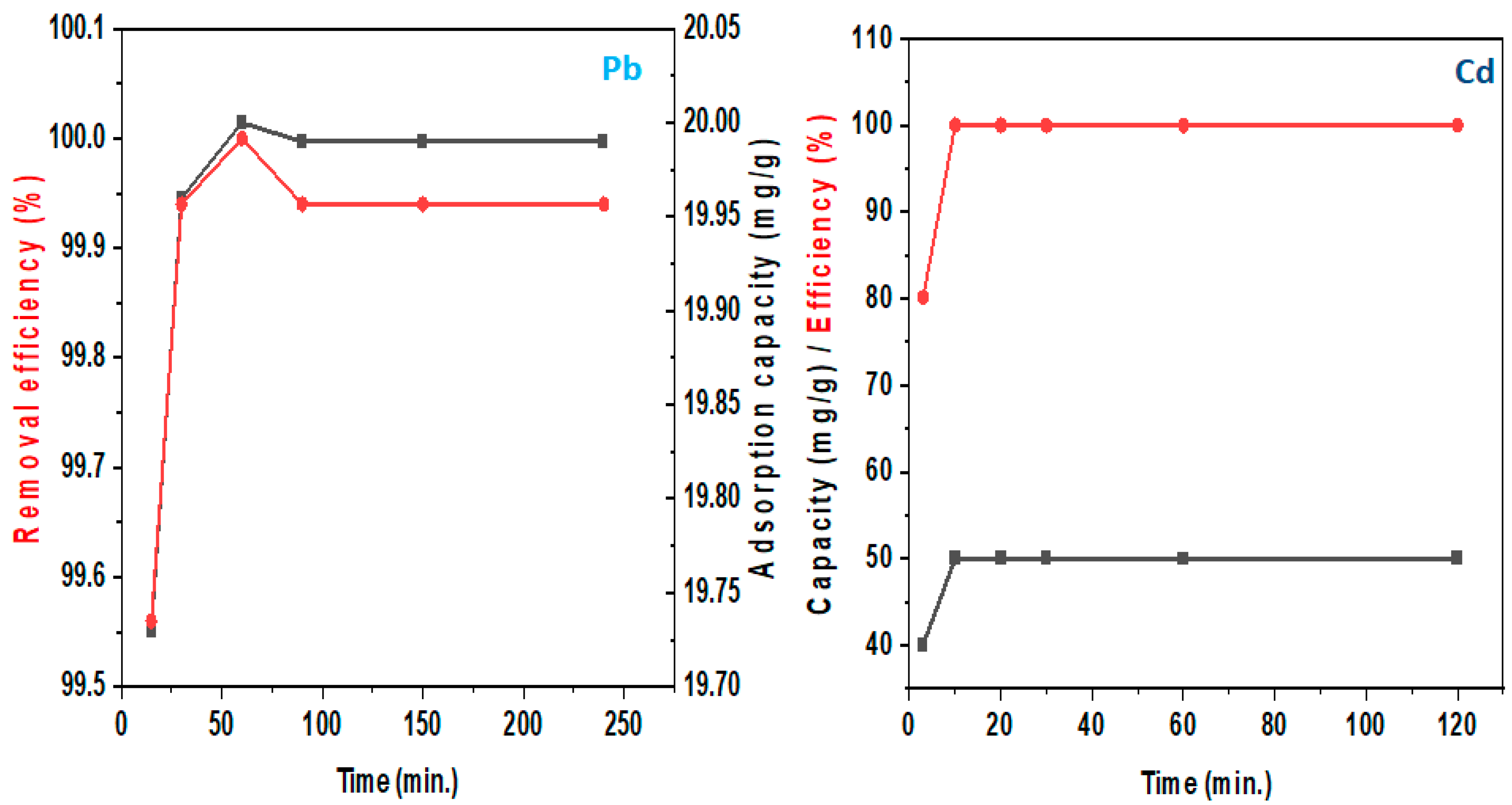
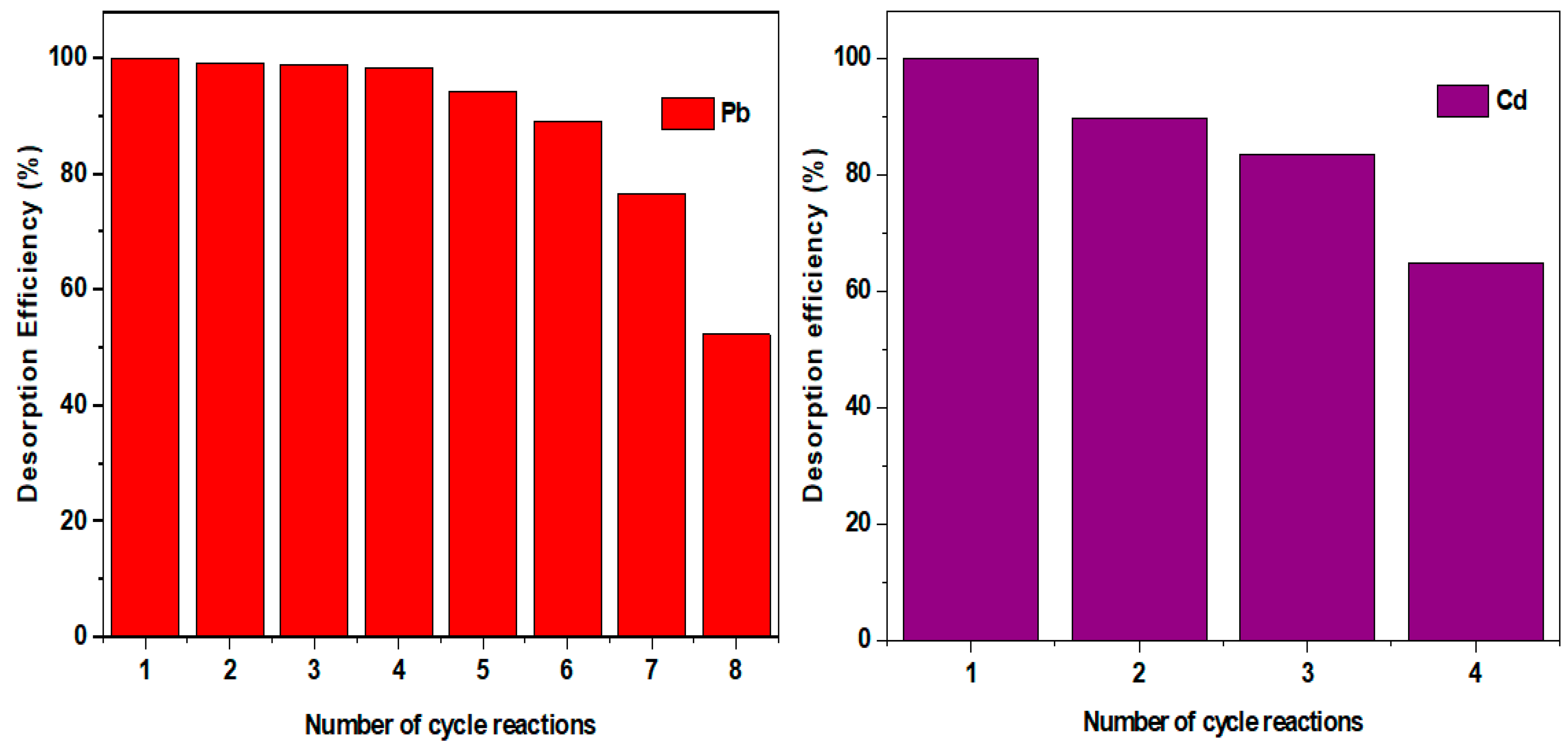
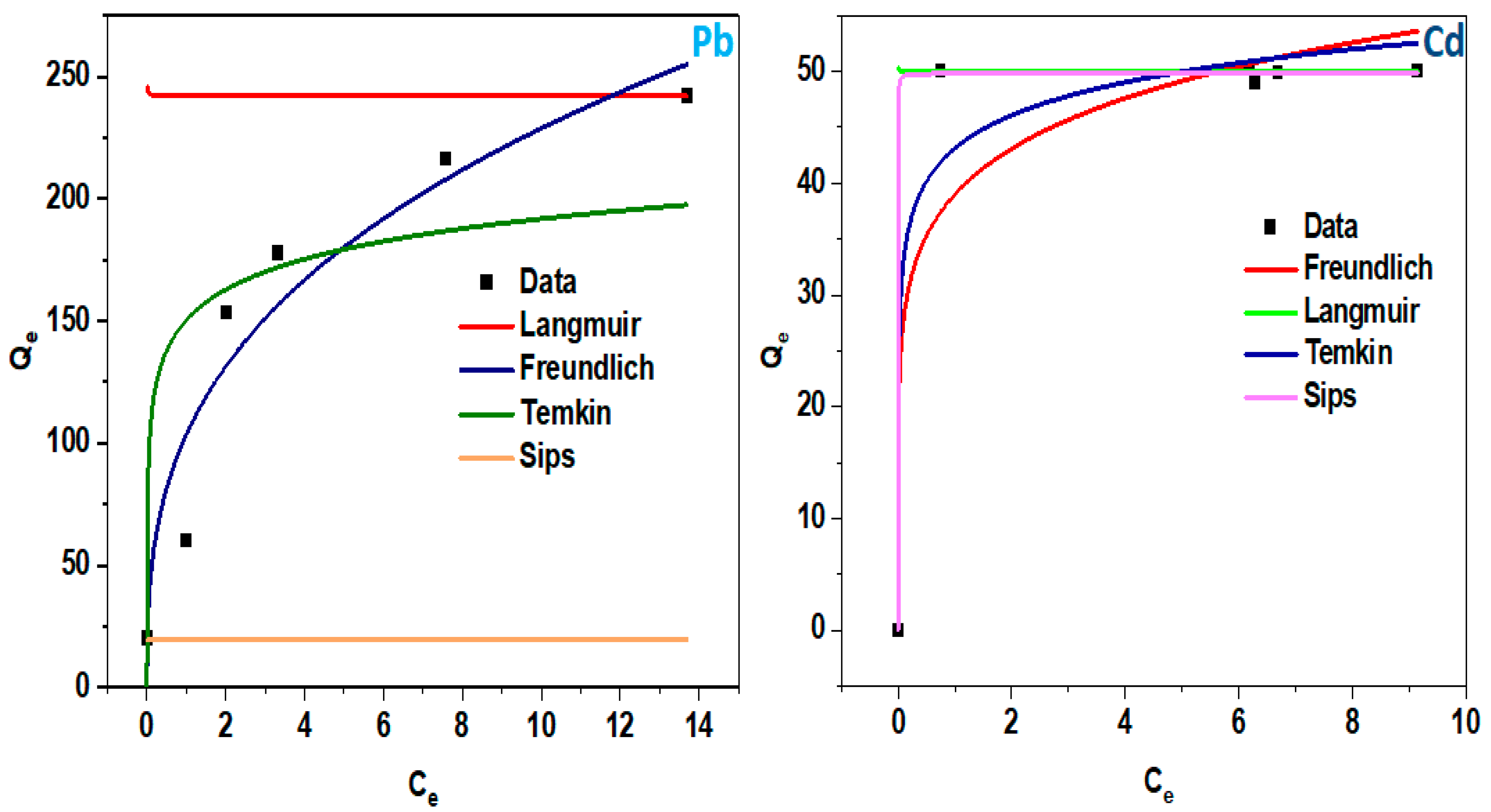
| Pollutant | Isotherm Model | Parameter | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pb (II) | Langmuir | qmax | 242.0133 |
| KL | −4424.779 | ||
| R2 | −1.319 | ||
| Freundlich | n | 0.345 | |
| Kf | 0.479 | ||
| R2 | 0.915 | ||
| Temkin | B | 18.00530 | |
| At | 427.121 | ||
| R2 | 0.698 | ||
| Sips | qm | 19.552 | |
| K | 1.368 | ||
| n | 0.687 | ||
| R2 | −2.447 | ||
| Cd (II) | Langmuir | qmax | 50.003 |
| KL | −2.510 | ||
| R2 | 0.350 | ||
| Freundlich | n | 0.143 | |
| Kf | 39.0222 | ||
| R2 | 0.838 | ||
| Temkin | B | 4.255 | |
| At | 20.357 | ||
| R2 | 0.952 | ||
| Sips | qm | 49.999 | |
| K | 0.7 | ||
| n | 50.734 | ||
| R2 | 0.999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motitswe, M.G.; Badmus, K.O.; Khotseng, L. Application of Reduced Graphene Oxide-Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite in the Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) Contaminated Wastewater. Appl. Nano 2024, 5, 162-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano5030012
Motitswe MG, Badmus KO, Khotseng L. Application of Reduced Graphene Oxide-Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite in the Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) Contaminated Wastewater. Applied Nano. 2024; 5(3):162-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano5030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotitswe, Moeng Geluk, Kassim Olasunkanmi Badmus, and Lindiwe Khotseng. 2024. "Application of Reduced Graphene Oxide-Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite in the Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) Contaminated Wastewater" Applied Nano 5, no. 3: 162-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano5030012
APA StyleMotitswe, M. G., Badmus, K. O., & Khotseng, L. (2024). Application of Reduced Graphene Oxide-Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite in the Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) Contaminated Wastewater. Applied Nano, 5(3), 162-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano5030012








