- Review
Three-Dimensional Behaviors of Protein Molecules and Bacteria near Model Organic Surfaces in Real Crowding Conditions
- Tomohiro Hayashi,
- Glenn Villena Latag and
- Evan Angelo Quimada Mondarte
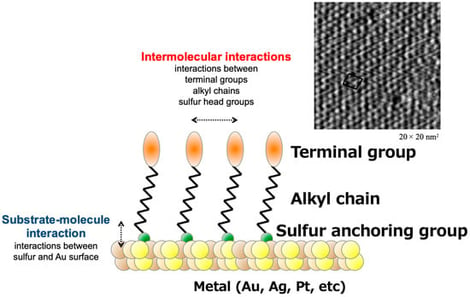
The interface between synthetic materials and biological systems is a critical determinant of performance in medical devices and biosensors. This review examines the evolution of biointerface science through the lens of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) of thiols on gold, a model system that offers atomic-level control over surface chemistry. We trace the field from the foundational structural characterization to the establishment of empirical design rules for bio-inertness. While early theoretical models attributed protein resistance to steric repulsion forces in polymer brushes, contemporary understanding has shifted toward the “water barrier” hypothesis, which posits that tightly bound interfacial water prevents direct biomolecular contact. We highlight recent studies that extend these concepts into “realistic” crowded biological environments. Their work reveals that fouling surfaces in crowded media generate a “viscous interphase layer” (VIL) that extends tens of nanometers into solution, whereas zwitterionic surfaces maintain a robust hydration shell that prevents this accumulation. Furthermore, this hydration barrier is shown to fundamentally alter bacterial mechanics, forcing microorganisms into a reversible, tethered “hovering” state at a significant biological interaction distance (>100 nm) from the surface, effectively precluding biofilm nucleation. These insights underscore that the future of antifouling material design lies in the precise engineering of interfacial hydration structures.
29 January 2026



![The optical transmission spectrum of a thin film highlights the elements to consider when determining thickness [47].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/applnano/applnano-07-00002/article_deploy/html/images/applnano-07-00002-g001-550.jpg)