Abstract
Background: Preterm inductions may be necessary for maternal comorbidities or fetal abnormalities. Previous studies have identified risk factors for undergoing a cesarean delivery (CD). Our study examined the insertion-to-expulsion time (IET) of cervical ripening balloons (CRB) in preterm inductions that achieved vaginal delivery (VD) compared to CD. Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study of preterm inductions with CRB between 2010 and 2021. Primary outcome was IET of CRB. IRB approval was obtained. Results: The study included 82 women. IET for cesarean patients was significantly greater, and required more removal of CRB at the allotted 12 h. Dilation before and after CRB was significantly greater in the vaginal cohort. There was no significant difference in maternal comorbidities, indication for induction or neonatal complications. Conclusions: Maternal comorbidities, induction indication and neonatal complications were similar between cohorts, making trial of induction with CRB in preterm women a reasonable option. Spontaneous expulsion of CRB and greater dilation may be predictors of vaginal delivery.
1. Introduction
There are many indications for women to undergo an induction of labor. In 2021, 32% of births were the result of an induction of labor [1]. Some of these indications lead to an induction of labor prior to 37 weeks [2]. Indications for preterm induction of labor include oligohydramnios, intrauterine growth restriction with maternal comorbidities or absent/reversed umbilical artery dopplers, pre-eclampsia with severe features, uncontrolled chronic hypertension, intrahepatic cholestasis, and pregestational diabetes with vascular complications [2]. Maternal and fetal wellbeing sometimes outweigh the risks of prematurity, leading to preterm inductions of labor.
In order to induce labor, induction agents are used to soften, thin, and dilate the cervix with the goal of achieving labor, and ultimately a vaginal delivery [3]. One commonly used agent is the cervical ripening balloon. Cervical ripening balloons (CRB) have been shown to be a safe and effective method of labor induction [3,4,5,6]. They are thought to work by mechanically dilating the cervix, as well as increasing prostaglandin release [6,7,8]. In multiple studies, the vaginal delivery rate after induction with a cervical ripening balloon has been as high as 83%, irrespective of gestational age [4,9].
However, vaginal delivery is not always achieved with induction of labor. Previous studies have found nulliparity, higher BMI, chronic hypertension or pre-eclampsia, lower gestational age, and lower modified Bishop score to be associated with cesarean delivery after attempt at induction of labor [10,11]. Despite these risk factors for unsuccessful vaginal delivery, cesarean sections are known to have increased morbidity and mortality for the mother, and thus trial of labor should be attempted if clinically appropriate and feasible [12,13]. In order to increase success rates of vaginal deliveries, multiple studies have shown that a combination of cervical ripening balloon and misoprostol can increase induction success and shorten induction to delivery time [14,15,16]. However, these studies only examined full-term inductions. Additionally, the duration for which a cervical ripening balloon may remain safely in place is unclear. Most studies have examined only term inductions of labor, with an average time of seven hours for which the balloon remained in place [17,18].
Our study examined the duration a cervical ripening balloon remains in place in preterm inductions that achieve vaginal delivery compared to those that result in cesarean section. We hypothesized that inductions that resulted in cesarean section had longer time to expulsion of the cervical ripening balloon. These patients would require more removal of the balloon at 12 h, per our institution’s protocol, compared to those that achieved vaginal delivery. We additionally hypothesized that more induction interventions are performed for those that ultimately undergo cesarean section, and that similar associations, found in prior literature for unsuccessful inductions of labor, exist in our patient population.
2. Materials and Methods
This was a single institution, retrospective chart review of a cohort of women between gestational age of 26 weeks and 0 days to 36 weeks and 6 days at time of induction between 1 January 2010, to 31 May 2021. All inductions of labor utilized a cervical ripening balloon, which was based on provider discretion. Data for all preterm inductions of labor resulting in either vaginal delivery or cesarean section were collected. Institutional Review Board Committee approval was obtained. Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective nature and minimal risk of this study.
Our primary objective was to compare the time interval from insertion to expulsion of cervical ripening balloon (IET) in preterm pregnancies that resulted in vaginal delivery compared to those that resulted in cesarean section at our institution. Our secondary objectives included comparison of cervical dilation before and after expulsion, induction indication, oxytocin use, and maternal and neonatal complications. We also evaluated indications for cesarean section. We additionally evaluated number of misoprostol doses. At our institution, the protocol for misoprostol use includes administration of 25 mcg vaginally or buccally every four hours if contracting less than two contractions in ten minutes. The misoprostol can be placed prior to or simultaneously with the CRB. All cervical ripening balloons were 18 French Cook balloons with 80 cc of saline instilled in the intrauterine balloon. Timing of misoprostol, CRB placement, and oxytocin administration were at the discretion of the practitioner. Data collected from medical records included patient demographics, medical comorbidities, social history, obstetrical history, labor induction indication, induction method and frequency of use, maternal complications, and neonatal complications. Labor course data collected included time from cervical ripening balloon placement to expulsion, initial cervical dilation, cervical dilation after expulsion, and indication for cesarean section if applicable. For our institution, in accordance with the manufacturer instructions for the cervical ripening balloon, any cervical ripening balloon that is not expelled by 12 h is deflated, and a second balloon can be replaced based on provider discretion. The number of cervical ripening balloons placed was also counted.
Previous studies of cervical ripening balloons in term inductions have demonstrated cervical ripening balloons are in place for an average of 7 +/− 3 h before being expelled [17,18]. We hypothesized that the number of hours for preterm induction will be 10 +/− 3 h for those that achieve vaginal delivery. We hypothesized that preterm inductions that result in cesarean section will require additional time with the cervical ripening balloon in place and require more removal of balloons after the allotted 12 h, thus predicting that the time to expulsion for preterm inductions undergoing cesarean section will be >12 h. In order to demonstrate a difference of at least 2 h in balloon expulsion time, with a power of 90% and type I error of 5%, the study required twenty-one women in each arm, for a total of forty-two subjects. Given the defined age for fertility rate as 15–50 years of age, we included all patients aged fifteen or older to include a complete age spectrum seen in pregnancy. Inclusion criteria were cephalic presentation and singleton pregnancy. Complete Bishop scores were not consistently documented in patient charts; therefore we used cervical exam less than 3 cm on admission. Exclusion criteria included inability to obtain sufficient information by chart review, multiple gestation, low-lying placenta, prior hysterotomy, and intrauterine fetal demise prior to induction. Women who initially presented to the hospital in spontaneous labor, defined as presentation with regular, painful contractions or with ruptured membranes were also excluded. All inductions resulted in a live birth.
A single-group analysis was performed on the cesarean delivery cohort. The cohort was separated into those who underwent cesarean section due to fetal status (non-reassuring fetal heart tracing, NRFHT) and those who underwent cesarean section for other indications, including arrest disorders of labor, failed induction of labor, and change in fetal presentation including all non-vertex fetuses.
All categorical variables were analyzed using a chi-square test of association. The continuous variables were analyzed with Student’s t-test. p-values less than or equal to 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
The study included 82 patients: 41 achieving vaginal delivery (VD) and 41 undergoing cesarean delivery (CD). All women who were induced with a cervical ripening balloon between 1 January 2010 and 31 May 2021 at a gestational age of 26 weeks and 0 days to 36 weeks and 6 days were deemed eligible. After exclusion of women based on our exclusion criteria, a total of 73 women underwent cesarean section following a preterm induction of labor with a cervical ripening balloon. Further, exclusion of those with missing data resulted in a total of 41 women in the CD cohort. This cohort was then matched 1:1 on baseline characteristics to those who achieved vaginal delivery after a preterm induction of labor with a cervical ripening balloon (Figure 1). Baseline characteristics included age, BMI, race, and parity (Table 1). There were no significant differences in gestational age, medical and obstetric comorbidities, or indication for induction between the groups (Table 2). A majority of indication for induction was due to maternal comorbidities; however, 17% of inductions were secondary to fetal indications, including oligohydramnios or fetal growth restriction with abnormal dopplers or concomitant maternal comorbidity (Table 2).
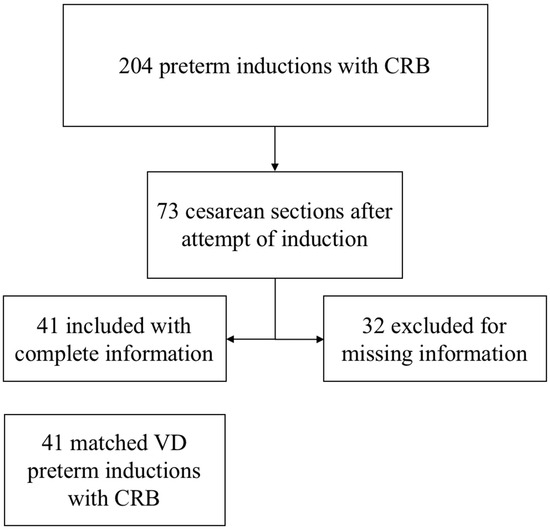
Figure 1.
Flowchart of patient selection.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics.

Table 2.
Medical and obstetric history.
IET for patients undergoing cesarean delivery was significantly greater and required more removal of CRB by balloon deflation (p = 0.02, Table 3). Of those who underwent vaginal delivery, 80.5% had CRB expulsion prior to 12 h, whereas only 51.3% of those who underwent cesarean delivery had CRB expulsion prior to 12 h (p = 0.02, Table 3). No women in the vaginal delivery cohort required removal of the CRB prior to spontaneous expulsion or the allotted 12 h; however, 5 women in the cesarean cohort required early removal for non-reassuring fetal heart tracing (NRFHT) (Table 3). At the start of the induction, 59% of vaginal delivery patients and 39% of cesarean delivery patients had CRB placed at initiation of induction, while 41% of vaginal delivery patients and 61% of cesarean delivery patients required ripening with misoprostol prior to balloon insertion (p > 0.05, Table 3). There was no significant difference in the number of misoprostol doses or use of second CRB between the vaginal and cesarean delivery cohorts (Table 3). Oxytocin use was universal among patients achieving vaginal delivery but only utilized in 87.5% of those patients who had a cesarean delivery (p = 0.03, Table 3). Dilation before and after CRB was significantly greater in the vaginal delivery cohort (p < 0.01, p = 0.01, Table 3).

Table 3.
Induction agents.
When performing a single-group analysis of the cesarean delivery cohort, comparing indication for cesarean section, there was no difference in time to balloon expulsion or dilation pre- and post-CRB between those with NRFHT indication and all other cesarean indications (Table 4). Additionally, there was no difference in number of misoprostol doses, oxytocin use, maternal comorbidities, or indication for induction (Table 4). The only significant difference between those who underwent cesarean delivery for NRFHT versus other indication was BMI, which was significantly higher in the other indication cohort (p = 0.01, Table 4). All other baseline characteristics were not significantly different (Table 4).

Table 4.
Indication for cesarean delivery.
Neonatal outcomes including respiratory distress, meconium aspiration, NICU admission, infection, and neonatal demise were not significantly different between the vaginal and cesarean delivery cohorts (Table 5). When compared in the single-group analysis of the cesarean delivery cohort, there remained no difference between those with NRFHT indication and those with other indication for cesarean delivery (Table 4).

Table 5.
Neonatal complications.
4. Discussion
Although lower gestational age is a risk factor for cesarean section, induction of labor with a cervical ripening balloon remains a safe and effective method for preterm induction of labor [3,4,5,6,10,11]. Prior studies have shown a high vaginal delivery success rate with induction using a cervical ripening balloon, with even greater success with the use of two cervical ripening agents simultaneously, such as the addition of a prostaglandin [4,5,6,7,8,9,14,16]. Among term inductions, one study found an average insertion-to-expulsion time of seven hours [17]. However, the timing for which a cervical ripening balloon safely remains in place in preterm inductions has not previously been described.
The specific time frame a CRB remains in place can assist practitioners in making clinical decisions regarding their patients undergoing preterm inductions of labor. When comparing preterm inductions resulting in vaginal delivery to those resulting in cesarean section, those who underwent cesarean section required more removal of the CRB at 12 h, whereas those who underwent vaginal delivery had more spontaneous expulsion prior to 12 h, with a majority of expulsions between 6 to 12 h. This time frame can help to guide practitioners in their expectations and counseling of patients regarding preterm inductions. Additionally, it has been previously shown that lower modified Bishop score is a risk factor for cesarean section [10,11]. Our findings supported the conclusion that a lower starting cervical dilation and lower post-balloon dilation are associated with cesarean delivery. It should be noted that neonatal complications were not significantly different between groups, strengthening the data to support the safety of the CRB and trial of induction of labor among preterm patients. Of note, there were no differences in maternal comorbidities or indication for induction between the groups, thus these factors should not contribute to a practitioner’s decision to trial an induction of labor in preterm patients using a CRB.
Our study has several strengths. The study was performed at a large, urban academic institution with a diverse population. This may increase the generalizability of our study results. In order to best exclude confounding bias, patients were matched on baseline characteristics (i.e., age, BMI, race, parity). There were no differences between comorbidities or gestational age that could also confound our results. Given that women presenting in spontaneous labor, defined as regular contractions, could confound our results, since regular contractions could lead to cervical change independently, these women were excluded. However, not all interventions to help achieve vaginal delivery (i.e., route of rupture of membranes) were compared and thus could be examined in future studies. Additionally, a single-group analysis of the cesarean cohort was performed in order to ensure the cesarean cohort data was not skewed by cesarean sections performed due to NRFHT. This analysis showed no difference in time to balloon expulsion or dilation pre- and post- CRB between those with NRFHT indication and all other cesarean indications, mostly including failure to progress and arrest disorders of labor. Therefore, the single-group analysis further supports the relationship between the cervical dilation, balloon expulsion time, and progression of labor with risk of cesarean section, without fetal status being a confounding variable.
Our study had several limitations. First, given the retrospective nature of the study, some data were missing and management decisions were based on individual provider practice. The variety in practice by practitioners, such as timing of misoprostol dosing or decision to place a second balloon, may introduce bias into our findings and could ideally be controlled for in future prospective studies. Missing data for complete Bishop scores were noted; thus, cervical dilation alone was used to assess for cervical change and labor progression. However, a complete Bishop score could influence overall labor progression and outcomes. In addition, labor patterns and outcomes might be different based on individual provider practice. Furthermore, the study was performed at a single institution, and thus may not be generalizable to other sites. It additionally included a small sample size, although the sample size was sufficient to power the study. Our study also included a large gestational age range. A majority of patients were of the late preterm gestation, consistent with the general population; however, IET based on gestational age was not analyzed. Future studies should further explore the relationship between IET and gestational age, as gestational age can influence labor patterns. Finally, when performing the single-group analysis of the cesarean cohort, the only significant difference between those who underwent cesarean delivery for NRFHT versus other indication was BMI, which was significantly higher in the “other indication” cohort. This is consistent with prior research associating high BMI with higher rates of cesarean section, and specifically with failure to progress or arrest disorders of labor [19,20]. The impact of BMI on the induction process for preterm inductions should be investigated further in future studies.
Practitioners need to manage expectations regarding preterm patients differently than those who are at term. Based on our findings, if a CRB is spontaneously expelled in a preterm induction, there is a higher chance of achieving vaginal delivery. Our findings additionally highlight the importance of a favorable starting exam, including more dilation, prior to induction, in the preterm population. Although those who underwent cesarean section more frequently required removal of the CRB, this does not imply removal of the CRB will result in cesarean section. Additionally, a less favorable starting exam also does not indicate that a cesarean section is inevitable. However, these findings can assist in patient counseling regarding their higher risk of cesarean section. Our study helps demonstrate a more specific time frame of balloon expulsion in the preterm population that may be associated with higher success rates of vaginal delivery versus cesarean section. These results can help practitioners to appropriately counsel their patients, so that patients are mentally, emotionally, and physically prepared for the possibility of a cesarean section, based on their cervical dilation and time to CRB expulsion.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.A.R., D.R.G. and L.S.; methodology, L.A.R., D.R.G. and L.S.; formal analysis, L.A.R., E.K.-B., S.F., D.R.G. and L.S.; investigation, L.A.R., D.R.G. and L.S.; data curation, L.A.R. and E.K.-B.; writing—original draft preparation, L.A.R.; writing—review and editing, E.K.-B., S.F., D.R.G. and L.S.; supervision, D.R.G. and L.S.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of New York University (s21-00706, Approved: 30 September 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective nature and minimal risk of this study.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Osterman, M.J.K.; Hamilton, B.E.; Martin, J.A.; Driscoll, A.K.; Valenzuela, C.P. National Vital Statistics Reports Births: Final Data for 2021. Natl. Vital. Stat. Rep. 2023, 72, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Medically indicated late-preterm and early-term deliveries. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 831. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 107, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Induction of labor. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 107. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 114, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, E.; Dilbaz, S.; Gelisen, O.; Dilbaz, B.; Ozturk, N.; Haberal, A. Unsuccessful labour induction in women with unfavourable cervical scores: Predictors and management. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2004, 44, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vaan, M.D.; Eikelder, M.L.T.; Jozwiak, M.; Palmer, K.R.; Davies-Tuck, M.; Bloemenkamp, K.W.; Mol, B.W.J.; Boulvain, M. Mechanical methods for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, CD001233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atad, J.; Hallak, M.; Ben-David, Y.; Auslender, R.; Abramovici, H. Ripening and dilatation of the unfavourable cervix for induction of labour by a double balloon device: Experience with 250 cases. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1997, 104, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, R.; Zafran, N.; Nachum, Z.; Garmi, G.; Kraiem, N.; Shalev, E. Single-balloon compared with double-balloon catheters for induction of labor: A randomized controlled trial. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 118, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manabe, Y.; Manabe, A.; Takahashi, A. F Prostaglandin levels in amniotic fluid during balloon-induced cervical softening and labor at term. Prostaglandins 1982, 23, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertholdt, C.; Morel, O.; Dap, M.; Choserot, M.; Minebois, H. Labor induction in indicated moderate to late preterm birth. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2020, 33, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievert, R.A.; Kuper, S.G.; Jauk, V.C.; Parrish, M.; Biggio, J.R.; Harper, L.M. Predictors of vaginal delivery in medically indicated early preterm induction of labor. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 217, 375.e1–375.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennen, C.S.; Bofill, A.; Magann, E.F.; Bass, D. Risk Factors for Cesarean Delivery in Preterm, Term and Post-Term Patients Undergoing Induction of Labor with an Unfavorable Cervix. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2009, 67, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, K.D.; Jackson, S.; Korst, L.; Fridman, M. Cesarean versus Vaginal Delivery: Whose Risks? Whose Benefits? Am. J. Perinatol. 2012, 29, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.H.; Bewley, S. Maternal mortality and mode of delivery. Lancet 1999, 354, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehl, S.; Ehard, A.; Berlit, S.; Spaich, S.; Su, M. Combination of misoprostol and mechanical dilation for induction of labour: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2011, 159, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ande, A.B.; Ezeanochie, C.M.; Olagbuji, N.B. Induction of labor in prolonged pregnancy with unfavorable cervix: Comparison of sequential intracervical Foley catheter-intravaginal misoprostol and intravaginal misoprostol alone. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2012, 285, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehl, S.; Weiss, C.; Dammer, U.; Heimrich, J.; Beckmann, M.W.; Faschingbauer, F.; Sütterlin, M. Double-balloon catheter and sequential oral misoprostol versus oral misoprostol alone for induction of labour at term: A retrospective cohort study. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 204, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoen, C.N.; Saccone, G.; Backley, S.; Sandberg, E.M.; Gu, N.; Delaney, S.; Berghella, V. Increased single-balloon Foley catheter volume for induction of labor and time to delivery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2018, 97, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei-Dan, E.; Walfisch, A.; Suarez-Easton, S.; Hallak, M. Comparison of two mechanical devices for cervical ripening: A prospective quasi-randomized trial. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2011, 25, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondwe, T.; Betha, K.; Kusneniwar, G.; Bunker, C.H.; Tang, G.; Simhan, H.; Reddy, P.; Haggerty, C.L. Maternal factors associated with mode of delivery in a population with a high cesarean section rate. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakita, T.; Reddy, U.M.; Landy, H.J.; Iqbal, S.N.; Huang, C.C.; Grantz, K.L. Indications for primary cesarean delivery relative to body mass index. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, 515.e1–515.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).