Journal Description
Reproductive Medicine
Reproductive Medicine
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on obstetrics and gynecology published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, FSTA, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 27.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 13.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
1.3 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
Telemedicine in Obstetrics: Building Bridges in Reproductive Healthcare—A Literature Review
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(4), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6040030 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
Telemedicine has emerged as a promising tool in obstetric and reproductive healthcare, offering new possibilities for patient-centered care delivery. This literature review explores its impact across key areas, including abortion, assisted reproduction, childbirth, contraception, gestational diabetes, mental health, opioid and smoking cessation, and
[...] Read more.
Telemedicine has emerged as a promising tool in obstetric and reproductive healthcare, offering new possibilities for patient-centered care delivery. This literature review explores its impact across key areas, including abortion, assisted reproduction, childbirth, contraception, gestational diabetes, mental health, opioid and smoking cessation, and perinatal care during the COVID-19 pandemic. A structured narrative approach was applied, with studies identified through PubMed and Scopus databases for screening, with selection based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, and synthesized narratively with attention to clinical outcomes, access, satisfaction, and barriers to implementation. Perspectives on the acceptance of telemedicine among healthcare providers, technological advancements enhancing reproductive outcomes, and telemedicine’s pivotal role in maintaining continuity of care during crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, are examined. The review also addresses challenges and barriers, including technological proficiency and patient acceptance, while emphasizing telemedicine’s potential to improve accessibility, patient satisfaction, and healthcare outcomes across diverse reproductive health services.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
Adiponectin as a Biomarker of Preeclampsia: A Systematic Review
by
Inês Carrilho, Melissa Mariana and Elisa Cairrao
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(4), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6040029 - 7 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Classified as a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy, preeclampsia is one of the leading causes of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. The abnormal trophoblast invasion that leads to a failed transformation of the uterine spiral arteries during placentation remains the most probable
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Classified as a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy, preeclampsia is one of the leading causes of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. The abnormal trophoblast invasion that leads to a failed transformation of the uterine spiral arteries during placentation remains the most probable cause for preeclampsia. It is known that adiponectin acts on the placenta, playing a regulatory role in placentation processes. Therefore, the aim of this systematic review is to compile scientific evidence to evaluate the role of adiponectin as a biomarker for preeclampsia. Methods: The protocol for this systematic review was registered on the PROSPERO database (ID CRD42024542403) and follows the PRISMA 2020 guidelines. Overall, twenty-nine studies were selected from the PubMed and Scopus databases, including case–control, prospective and retrospective cohort, cross-sectional, and bidirectional Mendelian randomization studies. Results: From the articles analyzed, nine studies indicated an increase in adiponectin levels in preeclampsia, eleven reported a decrease, eight detected no significant changes, and in two studies, it was not possible to determine the glycoprotein levels. Analysis of the evidence quality revealed that moderate and low evidence levels predominate, with stronger evidence for decreased adiponectin levels. Conclusions: Promoting the advancement of scientific research is crucial, particularly exploring the association between adiponectin and other biomarkers. This approach could facilitate the development of screening and diagnostic methods, enabling the implementation of specific preventive and therapeutic strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Addressing Common Oral Contraceptive Pill Concerns for the Primary Care Provider
by
Amelia C. Inclan, Danielle Snyder, Sophie G. Tillotson, Katelyn E. Flaherty, Angelica Byrd, Alyssa Pasvantis and Charlotte Chaiklin
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(4), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6040028 - 4 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Primary care providers are increasingly tasked with providing basic gynecologic care, including contraceptive therapy, to their patients. In the United States, oral contraceptive pills are the most frequently prescribed form of contraception; thus, it is critical that primary care providers are well versed
[...] Read more.
Primary care providers are increasingly tasked with providing basic gynecologic care, including contraceptive therapy, to their patients. In the United States, oral contraceptive pills are the most frequently prescribed form of contraception; thus, it is critical that primary care providers are well versed in addressing common patient questions. Well-documented concerns relating to oral contraception initiation include changes in weight, mood, cancer risk, libido, acne, and infertility. Herein, we provide a clinical case example of a patient with these common concerns, review the related evidence, and suggest appropriate counseling with the goal of helping primary care clinicians provide the highest level of evidence-based oral contraceptive care.
Full article
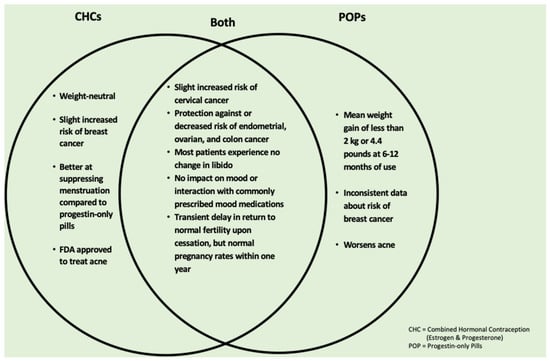
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Laparoscopic Management of Hemoperitoneum Due to a Cornual Pregnancy After an Ipsilateral Tubal Pregnancy: A Case Report
by
Raffaele Tinelli, Federica Savasta, Stefano Angioni, Giorgio Bogani, Livio Leo, Alessandro Messina and Alessandro Libretti
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(4), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6040027 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Cornual pregnancy (CP) is a rare but life-threatening form of ectopic pregnancy. Severe complications include uterine rupture and massive hemorrhage, often requiring complex surgical management despite prompt intervention. We report a case of a ruptured left CP at 12 weeks, occurring three
[...] Read more.
Background: Cornual pregnancy (CP) is a rare but life-threatening form of ectopic pregnancy. Severe complications include uterine rupture and massive hemorrhage, often requiring complex surgical management despite prompt intervention. We report a case of a ruptured left CP at 12 weeks, occurring three months after ipsilateral salpingectomy for a tubal pregnancy. Case Presentation: A 27-year-old woman, gravida 2, with a history of left salpingectomy, presented at 12 weeks of amenorrhea with severe pelvic pain and irregular uterine bleeding. Clinical examination, serum β-hCG testing, and transvaginal ultrasound confirmed hemoperitoneum due to rupture of a cornual pregnancy. Emergency laparoscopy was performed, with drainage of massive hemoperitoneum, excision of the ectopic gestation, and uterine wall repair. Uterine integrity was preserved, and the patient was discharged without complications. Discussion: Cornual ectopic pregnancy remains diagnostically and surgically challenging, with high risk of catastrophic hemorrhage. Transvaginal ultrasonography, supported by 3D ultrasound or MRI in equivocal cases, facilitates early diagnosis. Laparoscopy is increasingly recognized as the gold standard, offering reduced morbidity, faster recovery, and preservation of fertility compared with laparotomy, though it requires advanced surgical expertise. Long-term follow-up is essential due to the risk of uterine rupture in subsequent pregnancies, and elective cesarean delivery is often advised. Conclusion: This case demonstrates that minimally invasive laparoscopic management of ruptured CP with massive hemoperitoneum is feasible and safe when performed by experienced surgeons, but further studies are needed to optimize standardized protocols and assess reproductive outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pathology and Diagnosis of Gynecologic Diseases, 3rd Edition)
Open AccessReview
Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus During Pregnancy Using an Insulin Pump with an Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop System: A Narrative Review
by
Ingrid Dravecká
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(4), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6040026 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pregnancy in women with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is associated with a high risk of maternal and perinatal complications, and achieving optimal glycaemic control remains a clinical challenge. This article presents a narrative review of the evidence on advanced hybrid closed loop
[...] Read more.
Pregnancy in women with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is associated with a high risk of maternal and perinatal complications, and achieving optimal glycaemic control remains a clinical challenge. This article presents a narrative review of the evidence on advanced hybrid closed loop (AHCL) insulin delivery systems in pregnancy, with a focus on maternal glycaemic outcomes, neonatal outcomes, and psychosocial aspects. The relevant literature was identified through a structured search of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science (2010–2025), supplemented by guideline documents and reference screening. Eligible studies included randomised controlled trials, observational studies, and qualitative investigations. Data were synthesised thematically. Findings from key trials, including CONCEPTT, AiDAPT, and CRISTAL, demonstrate that AHCL systems improve time in range, lower mean glucose, and reduce hyperglycaemia without increasing hypoglycaemia. Some evidence also suggests improved neonatal outcomes, though statistical significance varies. Qualitative studies highlight reduced anxiety, improved sleep, and enhanced quality of life for women using AHCL during pregnancy. In conclusion, AHCL systems show strong promise in optimising maternal glycaemic control and potentially improving perinatal outcomes. However, larger, unbiased studies and real-world evaluations are needed to confirm their benefits and support broader clinical implementation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Role of the Setting in Controlling Anxiety and Pain During Outpatient Operative Hysteroscopy: The Experience of a Hysteroscopy Unit in North Italy
by
Alessandro Messina, Alessio Massaro, Eleonora Dalmasso, Ilaria Giovannini, Giovanni Lipari, Paolo Alessi, Tiziana Bruno, Sofia Vegro, Daniela Caronia, Federica Savasta, Valentino Remorgida, Alessandro Libretti and Bianca Masturzo
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(3), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6030025 - 12 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Outpatient operative hysteroscopy is a cornerstone in the management of intrauterine pathologies within reproductive medicine. However, procedural pain and anxiety remain key barriers leading to failed procedures and referrals for surgery under general anesthesia. This study aimed to assess whether a comfort-enhanced
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Outpatient operative hysteroscopy is a cornerstone in the management of intrauterine pathologies within reproductive medicine. However, procedural pain and anxiety remain key barriers leading to failed procedures and referrals for surgery under general anesthesia. This study aimed to assess whether a comfort-enhanced procedural environment could reduce perceived pain and increase procedural success rates. Methods: Analysis of 970 consecutive patients who underwent outpatient operative hysteroscopy at the Hysteroscopy Unit of “Degli Infermi” Hospital (Biella, Italy): 470 in 2023 under standard conditions, 500 in 2024 with an enhanced setting. Surgical technique, analgesic/sedation policies and operators were unchanged. The primary outcome was referral to the OR for completion of the procedure. Secondary outcomes included patient-reported pain assessed by Visual Analog Scale (VAS) in a consecutive subsample. Differences between years were evaluated with appropriate parametric/non-parametric tests. Results: Implementation of the enhanced environment was associated with a lower OR referral rate in 2023 versus 2024. Post hoc power for this comparison was approximately 60%. Mean VAS scores also decreased in 2024, with post hoc power >99%. No adverse events were recorded. Conclusions: Environmental and interpersonal modifications were associated with meaningful decline in reported pain and OR referrals. Prospective studies incorporating systematic case-mix and validated anxiety measures are warranted to confirm these results.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pathology and Diagnosis of Gynecologic Diseases, 3rd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Possibilities of Titanium Nickelide Implant Application in Radical Trachelectomy in Patients of Reproductive Age with Invasive Cervical Cancer
by
Alyona Chernyshova, Michael Krylyshkin, Alexander Chernyakov, Julia Truschuk, Ekaterina S. Marchenko, Sergey Fursov, Olga Tkachuk and Svetlana Tamkovich
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(3), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6030024 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objectives: The aim of this study is to demonstrate the efficacy of the modified technique of radical organ-preserving surgery of invasive cervical cancer (CC) in patients of reproductive age. Methods: This study included 118 patients of reproductive age (34.9 ± 4.8
[...] Read more.
Objectives: The aim of this study is to demonstrate the efficacy of the modified technique of radical organ-preserving surgery of invasive cervical cancer (CC) in patients of reproductive age. Methods: This study included 118 patients of reproductive age (34.9 ± 4.8 years) with a morphologically verified diagnosis of invasive CC (T1a-1bNxM0). All patients underwent organ-preserving surgery in the scope of radical trachelectomy. A shape memory mesh implant woven in the form of a stocking from superelastic nickelide titanium thread with subsequent fixation with separate sutures around the perimeter was used to form the uterine closure apparatus and to strengthen the utero-vaginal anastomosis. The mesh implant was made of superelastic thin nickelide titanium threads with a diameter of 60–40 microns on a metal knitting machine. All patients were prospectively followed up for a mean of 120 months. Results: No intraoperative or postoperative complications were revealed when using a shape memory implant made of titanium nickelide during radical trachelectomy to form a locking apparatus and strengthen the anastomosis zone. No cervical stenoses or mesh failures were noted in any case. The 5-year overall and recurrence-free survival rates were 100% and 98%, respectively. Two patients indicated recurrence; it occurred in 3 and 36 months. There were 42 spontaneous pregnancies, and 29 resulted in full-term delivery, whereas 2 and 11 ended in miscarriage and early abortion, respectively. Currently, 18 patients are at different stages of the use of assisted reproductive technologies. Conclusions: The shape memory implant made of titanium nickelide integrates well into the surrounding tissues and successfully imitates the effect of the cervix. The use of this sparing-surgery technique has shown reasonably good results in carrying the pregnancy to term and good reproductive outcomes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Self-Reported Use and Effectiveness of Marijuana for Pelvic Pain Among Women with Endometriosis
by
Anna E. Reinert, Maria Bolshakova, Alexander S. Wong and Victoria K. Cortessis
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(3), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6030023 - 8 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Legal access to cannabinoids is increasing, and patients with chronic pelvic pain from endometriosis were hypothesized to explore and find benefit from the use of marijuana for symptom management. A survey of women with endometriosis was conducted with the objective of characterizing
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Legal access to cannabinoids is increasing, and patients with chronic pelvic pain from endometriosis were hypothesized to explore and find benefit from the use of marijuana for symptom management. A survey of women with endometriosis was conducted with the objective of characterizing their experience with marijuana for management of pelvic pain: exploring symptom benefit, characteristics of use, and factors contributing to use and discontinuation. Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional survey was undertaken using an anonymous online questionnaire. Participants were recruited from an outpatient gynecology clinic using endometriosis ICD-10 diagnostic codes, and from the Endometriosis Association mailing list. Results: Marijuana use for symptom relief was reported by 78 (32.2%) Endometriosis Association participants, and 58 (46.8%) clinic participants. Within both populations, marijuana was considered very or moderately effective by most users (68.0 to 75.9%). Legality of recreational and medicinal marijuana in the state of residence was strongly associated with use (OR 7.13 [95% CI: 2.57–19.8]). Among users specifying current or past use, discontinuation was reported by 45% (54 of 121), and most frequently attributed to non-clinical factors of legal/employment risk and obstacles to marijuana access; 64.8% of former users attributed discontinuation to non-clinical factors only. Lack of symptom relief from other clinical management was the most cited motivation for initiation (55.1% clinic, 39.7% EA users). Conclusions: Marijuana use is common among women with endometriosis and chronic, refractory pelvic pain. Legality and access appear to impact use and discontinuation. While legal access to marijuana is associated with increased use, marijuana obtained outside of legal routes is also commonly being used for symptom relief.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Exploring the Role of Anti-Adhesion Gel in Outpatient Operative Hysteroscopy
by
Alessandro Messina, Safae El Motarajji, Ilaria Giovannini, Alessandro Libretti, Federica Savasta, Valentino Remorgida, Livio Leo and Bianca Masturzo
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(3), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6030022 - 28 Aug 2025
Abstract
Background: Outpatient operative hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure widely used for the diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine pathologies, including intrauterine adhesions (IUAs), which significantly affect fertility. Despite its therapeutic potential, the procedure itself may predispose patients to de novo adhesion formation. This
[...] Read more.
Background: Outpatient operative hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure widely used for the diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine pathologies, including intrauterine adhesions (IUAs), which significantly affect fertility. Despite its therapeutic potential, the procedure itself may predispose patients to de novo adhesion formation. This review evaluates the effectiveness of anti-adhesion gels, particularly hyaluronic-acid-based formulations, in preventing IUAs and improving reproductive outcomes after outpatient operative hysteroscopy. Materials and Methods: A systematic search was performed in PubMed, CINAHL, Embase, and Web of Science for studies published between January 2020 and May 2025. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were defined using PICO guidelines. Relevant studies were screened and selected by two independent reviewers. Results: Anti-adhesion gels, especially hyaluronic acid and its derivatives, were associated with a lower recurrence of IUAs and improved reproductive outcomes. Combination therapies, such as hyaluronic acid gel with intrauterine devices (IUDs), showed better efficacy than monotherapy. Several studies also reported increased endometrial thickness, higher implantation rates, and improved pregnancy outcomes, although live birth rates remained inconsistent. Conclusions: Hyaluronic-acid-based anti-adhesion gels appear effective in reducing postoperative adhesion formation and enhancing reproductive outcomes in outpatient hysteroscopy. The best results are seen with multimodal preventive strategies. However, heterogeneity across studies highlights the need for standardized, prospective, randomized controlled trials to establish optimal clinical use.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pathology and Diagnosis of Gynecologic Diseases, 3rd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessCase Report
Outpatient Hysteroscopic Treatment of Cervical Ectopic Pregnancy in a Primigravida Using the Ho:YAG Laser: A Case Report and Operative Protocol Evaluation
by
Dimitar Cvetkov, David Lukanovic and Angel Yordanov
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(3), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6030021 - 27 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and Clinical Significance: Cervical ectopic pregnancy (CEP) is a rare and potentially serious condition, in which the embryo implants within the cervical canal rather than the uterine cavity and is present in less than 1% of all ectopic pregnancies. There are
[...] Read more.
Background and Clinical Significance: Cervical ectopic pregnancy (CEP) is a rare and potentially serious condition, in which the embryo implants within the cervical canal rather than the uterine cavity and is present in less than 1% of all ectopic pregnancies. There are different treatment options depending on the particular situation and the woman’s reproductive desire but conservative approaches as the first line of treatment is preferred in all cases and hysteroscopic resection of the fetus is one of these options. Several types of laser systems are available for use in hysteroscopic surgery, including neodymium:YAG (Nd:YAG) lasers, KTP and Argon lasers, as well as diode lasers. The holmium:YAG (Ho:YAG) laser, although more commonly used in urology due to its ability to cut, coagulate, and vaporize tissue, has gained interest in gynecologic procedures because of its precision and favorable safety profile. Case Presentation: We present the case of a 32-year-old woman, pregnant for the first time, who was diagnosed with CEP and successfully treated using a Ho:YAG laser during an outpatient hysteroscopic procedure. As far as we know, this is the first published case using this approach. Conclusions: The Ho:YAG laser is a proven tool for outpatient hysteroscopic procedures like septum and adhesion removal. Its ability to both cut and coagulate offers a minimally invasive, fertility-sparing option for managing cervical ectopic pregnancy. With the right patient and proper backup plans in place, this approach could be a promising alternative to more aggressive treatments.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Pregnancy-Related Acute Kidney Injury: Risk Factors and Maternal Outcomes in High-Risk Women in Mwanza, Tanzania
by
Kahibi Bernard, Fridolin Mujuni, Dismas Matovelo, Edgar Ndaboine, Richard Kiritta and Ladius Rudovick
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(3), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6030020 - 19 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objective: Pregnancy-related acute kidney injury (PRAKI) remains a serious complication, with high rates of maternal morbidity and mortality, particularly in developing countries where delayed diagnosis and treatment are common. This study aimed to determine the proportion, associated risk factors, and maternal outcomes
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Pregnancy-related acute kidney injury (PRAKI) remains a serious complication, with high rates of maternal morbidity and mortality, particularly in developing countries where delayed diagnosis and treatment are common. This study aimed to determine the proportion, associated risk factors, and maternal outcomes among pregnant and postpartum women at high risk of developing AKI. Methods: This cross-sectional analytical study was conducted at Bugando Medical Centre in Mwanza, Tanzania, from May 2023 to February 2024, targeting high-risk obstetric patients. Results: Out of 4588 admissions, 420 patients were identified as being at risk of developing PRAKI. Among them, 101 (24.22%) were diagnosed with PRAKI, while 316 (75.78%) did not develop the condition. The leading associated risk factors were pre-eclampsia (40.59%) and postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) (40.24%), followed by sepsis (11.8%) and abortion-related complications (5.94%). Multivariate analysis revealed that living in rural areas and having a lower level of education were significantly associated with PRAKI. Patients from rural areas had an adjusted odds ratio (AOR) of 5.37 (p < 0.001), while those with informal or primary education had an AOR of 4.21 (p = 0.048). Conclusions: The study also found that maternal mortality was significantly higher among patients with PRAKI, particularly those affected by PPH. These findings highlight the urgent need for improved management of obstetric emergencies to reduce PRAKI incidence and improve maternal outcomes in high-risk populations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Polygenic Embryo Risk Scores: A Survey of Public Perception
by
Alexandra Peyser, Cailey Brogan, Lilli Zimmerman and Randi H. Goldman
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(3), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6030019 - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Preimplantation genetic testing for polygenic diseases (PGT-P) is a reproductive technology that has made it possible to assign risk scores to embryos for various complex polygenic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, breast cancer, and schizophrenia. Whether there is public interest in utilizing
[...] Read more.
Background: Preimplantation genetic testing for polygenic diseases (PGT-P) is a reproductive technology that has made it possible to assign risk scores to embryos for various complex polygenic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, breast cancer, and schizophrenia. Whether there is public interest in utilizing PGT-P and what public opinions are regarding this technology is unknown. Therefore, the objective of our study was to evaluate the opinion of the general United States (US) public regarding PGT-P. Methods: A web-based questionnaire consisting of 25 questions was administered to a nationally representative sample of adult US residents according to age and sex. The survey contained a description of PGT-P, followed by questions with Likert-scale responses ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree. Results: Of the 715 respondents recruited, 673 (94%) completed the survey. Most respondents agreed that use of PGT-P is ethical (54%), and another 37% were neutral; however, approximately 9% of respondents disagreed and were opposed to the use of PGT-P. Those that opposed PGT-P cited that it was “unethical” (46%) or “not natural” (39%), believed children could be negatively affected (31%), or stated that it went against their religion (15%). The majority of respondents did not know whether PGT-P was safe for embryos (68%) or children (67%) and felt that anyone should be able to utilize it (53%). Conclusions: Participants who were younger, were Atheist, or were Democrats were more likely to agree that “PGT-P is ethical”. This study identified that more than half of respondents supported the use of PGT-P. However, concerns regarding its safety and ethical implications persist.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Cervical Cancer During Pregnancy: A Multidisciplinary Approach to a Complex Oncological Case
by
Balázs Vida, Richárd Tóth, Petra Merkely, Nándor Ács, Zoltán Novák, Boglárka Balázs, Lilla Madaras, Ferenc Bánhidy, Ádám Tabányi, Márton Keszthelyi and Balázs Lintner
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(3), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6030018 - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Cervical cancer is the fourth most common malignancy among women, posing significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenges during pregnancy. Case presentation: This case report presents the treatment of a 32-year-old pregnant woman diagnosed with cervical cancer. Following the diagnosis at 7 weeks of
[...] Read more.
Background: Cervical cancer is the fourth most common malignancy among women, posing significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenges during pregnancy. Case presentation: This case report presents the treatment of a 32-year-old pregnant woman diagnosed with cervical cancer. Following the diagnosis at 7 weeks of gestation, histological and imaging examinations were performed, leading to the initiation of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Due to the tumor progression noticed under therapy, cesarean section was performed at 29 weeks, immediately followed by radical hysterectomy. Conclusions: The management of cervical cancer during pregnancy necessitates a multidisciplinary approach, based on the patient’s condition, tumor stage, and fetal maturity. This case highlights the limitations and complexities of treating cervical cancer during pregnancy and emphasizes the importance of individualized oncological and surgical planning.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Improvement in Sperm Recovery Rate and Total Motile Sperm Count Using α-Chymotrypsin in Highly Viscous Semen Sample Without Adversely Affecting Assisted Reproductive Technology Outcomes
by
Archana Ayyar, Marian Khalil, Maggie Wong, Rebecca Chung, Kathryn Coyne, Joseph Findley, Rachel Weinerman, Rebecca Flyckt, Katelyn Perroz Sofaly and Sung Tae Kim
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(3), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6030017 - 2 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objectives: To investigate the impact of α-chymotrypsin treatment on sperm recovery rate and total motile sperm count (TMC) in highly viscous semen for intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilization (IVF), particularly in cases of severely low sperm count. Methods: High
[...] Read more.
Objectives: To investigate the impact of α-chymotrypsin treatment on sperm recovery rate and total motile sperm count (TMC) in highly viscous semen for intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilization (IVF), particularly in cases of severely low sperm count. Methods: High viscosity was defined by the inability to form a thread exceeding 2 cm from a semen drop after 30 min of incubation at 37 °C with repeated pipetting. Semen samples were treated with 5 mg of α-chymotrypsin for 5–10 min at 37 °C and washed using a 90% gradient solution. A total of 35 patients were included, with comparisons made to the same patients’ prior untreated samples using paired t-tests. Severely low sperm count was classified as TMC below 10 million. Results: Treatment with α-chymotrypsin significantly improved TMC (22.2 million vs. 11.6 million, p = 0.0004) and motile sperm recovery rate (38.9% vs. 16.2%, p = 0.00002). In cases of severely low sperm count, α-chymotrypsin treatment resulted in a marked increase in recovery rate (43.0% vs. 10.0%, p = 0.02) and TMC (5.89 million vs. 1.21 million, p = 0.004). Fertilization using treated samples achieved an 87.8% success rate, with a 56.4% usable blastocyst rate, comparable to standard IVF outcomes (n = 9, average age = 34.9 years). Conclusions: α-chymotrypsin treatment significantly enhances sperm recovery and TMC in highly viscous semen, demonstrating particular efficacy in patients with severely low sperm counts without affecting fertilization or blastocyst rate in IVF.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
HSP60 Reduction Causes an Abnormal Genotype and Sex Distribution and Impairs Mitochondrial Activity in Mouse Spermatozoa
by
Robert Hauffe, Michaela Rath, Simran Chopra, Karin Müller and André Kleinridders
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(3), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6030016 - 26 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objective: Fertility relies on efficient energy metabolism in gametes, which is largely determined by mitochondrial activity. The mitochondrial chaperone complex HSP60/HSP10 folds the majority of mitochondrial matrix proteins and thus enables proper function and metabolism. Although it is known that mitochondrial dysfunction
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Fertility relies on efficient energy metabolism in gametes, which is largely determined by mitochondrial activity. The mitochondrial chaperone complex HSP60/HSP10 folds the majority of mitochondrial matrix proteins and thus enables proper function and metabolism. Although it is known that mitochondrial dysfunction impacts male fertility through reduced spermatozoa activity, the importance of HSP60 expression for male fertility remains elusive. Methods: We bred male and female Hsp60+/− with wild-type C57BL/6N mice and analyzed alterations in offspring numbers and characteristics. We further determined testes size as well as spermatozoa quality. Results: We show that breeding Hsp60+/− mice shifted the expected genotype ratio in the pups towards wild-type offspring. Additionally, breeding with Hsp60+/− shifts the sex ratio towards male offspring, independent of parental genotype. In males, HSP60 reduction did not alter testis size or volume, but led to a lower proportion of spermatozoa with active mitochondria and a lower velocity of rapid spermatozoa compared to wild-type counterparts. Accordingly, spermatozoa of Hsp60+/− mice exhibited a further decrease in ATP synthase expression. Conclusions: This suggests that reduced mitochondrial function in Hsp60+/− spermatozoa is a selective disadvantage to sperm, motion performance and fertilization, and mitochondrial dysfunction might be a general selective disadvantage to female offspring.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Prenatal Screening for Chromosomal Defects
by
Veronika Frisova
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(2), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6020015 - 11 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Chromosomal defects are a significant cause of perinatal death and childhood disability, occurring in 3.6–6.0 per 1000 births in unscreened populations. Common chromosomal defects include trisomy 21, 18, and 13, triploidy, and sex chromosome abnormalities. Screening for these defects began in the mid-1960s
[...] Read more.
Chromosomal defects are a significant cause of perinatal death and childhood disability, occurring in 3.6–6.0 per 1000 births in unscreened populations. Common chromosomal defects include trisomy 21, 18, and 13, triploidy, and sex chromosome abnormalities. Screening for these defects began in the mid-1960s with the advent of amniocentesis, and various methods have since been developed to improve screening performance. Initial screening was based solely on maternal and gestational age, a method incorporated later into all subsequent screening methods giving an a priori background risk. This a priori background risk, which is further refined by maternal serum biochemistry, results of ultrasound examinations, and most recently, results of non-invasive prenatal testing by cell-free DNA in maternal blood. This paper will describe methods of screening for all chromosomal defects and their performance. Unlike most reviews, this paper covers not only screening tests for Down syndrome, but also screening methods for the other most common and less common chromosomal defects.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Chronic Endometritis: A Silent Contributor to Infertility and Reproductive Failure—A Comprehensive Review
by
Mihai Lucan, Mircea Sandor, Alin Bodog, Diana Mocuta, Cristina Daniela Aur, Liliana Sachelarie and Anca Huniadi
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(2), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6020014 - 3 Jun 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Chronic endometritis (CE) is a persistent, often asymptomatic inflammatory condition of the endometrium, increasingly recognized as a potential contributor to infertility and recurrent implantation failure. Despite its clinical significance, CE remains underdiagnosed due to a lack of standardized diagnostic criteria and its subtle
[...] Read more.
Chronic endometritis (CE) is a persistent, often asymptomatic inflammatory condition of the endometrium, increasingly recognized as a potential contributor to infertility and recurrent implantation failure. Despite its clinical significance, CE remains underdiagnosed due to a lack of standardized diagnostic criteria and its subtle clinical presentation. Objective: This review aims to synthesize the current evidence on the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of CE, highlighting its impact on reproductive outcomes and the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions. A comprehensive literature review was conducted, analyzing 85 peer-reviewed studies published in the last decade, of which 65 were deemed relevant and retained for further analysis. These studies were selected based on their relevance to the pathophysiology, diagnostic methodologies, and treatment outcomes for CE, focusing on their implications for fertility and assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs). The findings suggest that CE is associated with impaired endometrial receptivity, increased inflammatory markers, and reduced implantation and pregnancy rates with ARTs. Histopathological assessment using CD138 immunostaining remains the gold standard for diagnosis, while hysteroscopy and molecular microbiological techniques provide complementary diagnostic value. Antibiotic treatment has been shown to significantly improve implantation rates and pregnancy outcomes, particularly in women with recurrent implantation failure. Emerging therapies, including probiotics and regenerative medicine approaches, are being explored as potential adjuncts to the conventional treatment. Early and accurate diagnosis of CE is essential for optimizing reproductive outcomes. Standardized diagnostic protocols and individualized treatment strategies are crucial for improving implantation success and pregnancy rates in affected women. Future research should focus on refining the diagnostic methods and exploring novel therapeutic options to enhance endometrial health and fertility outcomes.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Changes in Sperm Glutathione and Glutathione Redox States Correlate to Poor Sperm Qualitative Measures
by
Caroline G. Ploeger, Kate Hansen, Ammon Bayles, Adriana Burger, Jason Hansen and Timothy Jenkins
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(2), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6020013 - 19 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: In the past 50 years, human reproductive capacity has steadily declined with elusive and idiopathic origins. Amongst theorized causes, oxidative stress has been proposed to directly contribute to male infertility. The glutathione (GSH) and glutathione disulfide (GSSG) molecular couple reflect cellular
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: In the past 50 years, human reproductive capacity has steadily declined with elusive and idiopathic origins. Amongst theorized causes, oxidative stress has been proposed to directly contribute to male infertility. The glutathione (GSH) and glutathione disulfide (GSSG) molecular couple reflect cellular redox environments and are thus reflective of oxidative stress in most cells. Shifting GSH/GSSG redox states to abnormal, more oxidizing conditions can disrupt normal cellular activities. This study explores the correlation between the GSH/GSSG redox system and factors involved in male infertility, including sperm quality, specifically sperm motility and total count. Methods: Semen samples from 98 patients underwent high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for GSH/GSSG analysis. A protein assay determined the protein concentration for normalization, and GSH/GSSG redox potentials (Eh) were calculated using the Nernst equation. Results: A significant inverse correlation between GSH/GSSG Eh and sperm count was identified (p = 0.0046 and R2 = 0.071). Analysis also found that cellular GSH concentrations (p < 0.001 and R2 = 0.11) and total GSH (GSH + (GSSG × 2); p = 0.0039 and R2 = 0.074) were significantly and positively correlated with total sperm count, whereas GSSG concentrations were not. The correlation between redox potential and motility was not significantly different (p = 0.11 and R2 = 0.02). Conclusions: This study shows that total sperm count decreases with increasing redox potential, indicating that more oxidized systems, such as the GSH/GSSG system, are associated with lower sperm counts in ejaculated sperm samples. These findings support a potential link between oxidative stress and sperm parameters. As understanding of the relationship between GSH/GSSG Eh and sperm quality improves, this may inform future potential therapies and approaches aimed at supporting male reproductive health.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Beyond the Cure: Optimizing Follow-Up Care for Cervical Cancer Survivors
by
Retika Mohan, Mena Abdalla, Anna-Lucia Koerling and Sahathevan Sathiyathasan
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(2), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6020012 - 14 May 2025
Abstract
Cervical cancer is a significant global health challenge, ranking as the fourth most common malignancy in women worldwide (age-standardized incidence: 13.3/100,000). In the UK, prevalence is markedly lower (7.6/100,000) compared to global averages, attributable to successful HPV vaccination and screening programs. post-treatment follow-up
[...] Read more.
Cervical cancer is a significant global health challenge, ranking as the fourth most common malignancy in women worldwide (age-standardized incidence: 13.3/100,000). In the UK, prevalence is markedly lower (7.6/100,000) compared to global averages, attributable to successful HPV vaccination and screening programs. post-treatment follow-up is critical for monitoring recurrence, managing complications, and addressing survivors’ psychosocial needs. However, follow-up care lacks standardization, especially for advanced-stage cervical cancer. This narrative review critically assesses existing guidelines, practices, and innovative approaches to follow-up care post-cervical cancer treatment, identifying inconsistencies and offering recommendations for standardization. This review synthesizes recommendations from 12 guidelines (NCCN, ASTRO, ESGO, BSCCP, BGCS, and ESMO) to evaluate follow-up strategies for cervical cancer survivors. Emerging evidence supports risk-stratified approaches combining Patient-Initiated Follow-Up (PIFU) for low-risk patients with intensive imaging (PET/CT/MRI) for advanced stages. Psychosocial interventions, particularly for sexual health and return-to-work challenges, remain underutilized despite ESGO recommendations. Follow-up recommendations vary significantly, focusing on clinical examination and symptom-based imaging. Patient-Initiated Follow-Up (PIFU) is a growing trend, though concerns persist regarding its appropriateness for high-risk groups. Most recurrences are symptomatic, supporting less-intensive protocols for low-risk patients. Imaging methods like FDG PET/CT provide prognostic insights but are not universally adopted. Psychosocial and psychosexual care needs remain under addressed. Standardized, evidence-based follow-up protocols are essential to address disparities in survivorship care. Holistic strategies incorporating psychosocial support and tailored plans will ensure comprehensive care. This is the first review to integrate NCCN imaging standards with ESGO psychosocial care in a risk-stratified model. Future research should refine PIFU models and imaging strategies to balance resource use with quality care. Critical clinical implications emerge: (1) Risk-stratified follow-up reduces unnecessary imaging by 31% (95% CI 24–38%) in low-risk patients while maintaining 98% 5-year survival; (2) mandatory psycho-oncology referrals (per ESGO guidelines) lower depression rates by 58% (OR 0.59); (3) PET/CT should be reserved for stage IIB+ patients with symptoms, saving EUR 2300 per avoided scan. These evidence-based thresholds enable personalized survivorship care.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
Small Bowel Obstructions Caused by Barbed Sutures in Robotic Surgery: A Systematic Review
by
Renata Pajtak and Krinal Mori
Reprod. Med. 2025, 6(2), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed6020011 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Barbed sutures have been recognised to offer numerous advantages compared to traditional sutures in minimally invasive procedures including holding tension. However, they are also associated with increased reports of small bowel obstructions (SBOs) in laparoscopic procedures. We are the first to conduct
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Barbed sutures have been recognised to offer numerous advantages compared to traditional sutures in minimally invasive procedures including holding tension. However, they are also associated with increased reports of small bowel obstructions (SBOs) in laparoscopic procedures. We are the first to conduct a review on the incidence of SBOs secondary to the use of barbed sutures in robotic surgery. Our aim is to raise awareness about this rare complication and promote early recognition and timely intervention, leading to a reduction in the incidence of severe complications and thereby improving patient outcomes. Methods: A systematic review of the literature was performed by searching the Ovoid Medline, PubMed and Cochrane Databases. After applying our exclusion criteria of articles unavailable in English, seven articles remained. We examined the literature and calculated the median and mean ranges for surgical procedures, time to presentation, symptoms of presentation, type of complications involving the bowel, the type of barbed suture and the additional length of hospital stay. Results: Our systematic review revealed eight cases of bowel obstruction secondary to the use of a barbed suture during robotic surgery. Robotic sacrocolpopexy had the highest complication rate: the median time to presentation was 14 days with vomiting being the most common presenting symptom. Most cases were resolved with a diagnostic laparoscopy and truncation of the barbed suture, and length of re-admission was a median of 4 days. Discussion: The introduction of new devices always carries advantages as well as unfortunate complications. Minimisation of complications through learnt surgical techniques including shortening thread tails and prompt recognition of the complication on re-presentation are key to optimising future patient care. Conclusions: Further prospective trials in this field will be useful to assess the appropriate use of the barbed suture as well as research dedicated to exploring alternate adhesive sutures.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Endocrines, IJMS, JCM, Women, Reprod. Med.
Gynecological Endocrinology Updates
Topic Editors: Alessandro Genazzani, Stefano LuisiDeadline: 30 November 2025
Topic in
CIMB, IJMS, Reprod. Med., Biology, Life
Recent Research in Germ Cells
Topic Editors: Malgorzata Kloc, Jacek KubiakDeadline: 31 May 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Reprod. Med.
Pathology and Diagnosis of Gynecologic Diseases, 3rd Edition
Guest Editors: Cinzia Giacometti, Mariateresa MirandolaDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Reprod. Med.
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Fetal Medicine
Guest Editors: Giorgio Pagani, Anna Fichera, Valentina StagnatiDeadline: 30 June 2026
Special Issue in
Reprod. Med.
Update in Reproductive Surgery
Guest Editor: Simone FerreroDeadline: 31 July 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Reprod. Med.
Recent Advances in Preeclampsia
Collection Editor: Berthold Huppertz
Topical Collection in
Reprod. Med.
Reproductive Medicine in Europe
Collection Editor: Simone Ferrero








