The Consequences of a Lack of Basic Sanitation in the Municipality of Maricá (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) Resulting in Low Concentrations of Metals but Dissemination of Endocrine Disruptors Through Local Environments: Subsidies for Local Environmental Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Site
3. Methodology
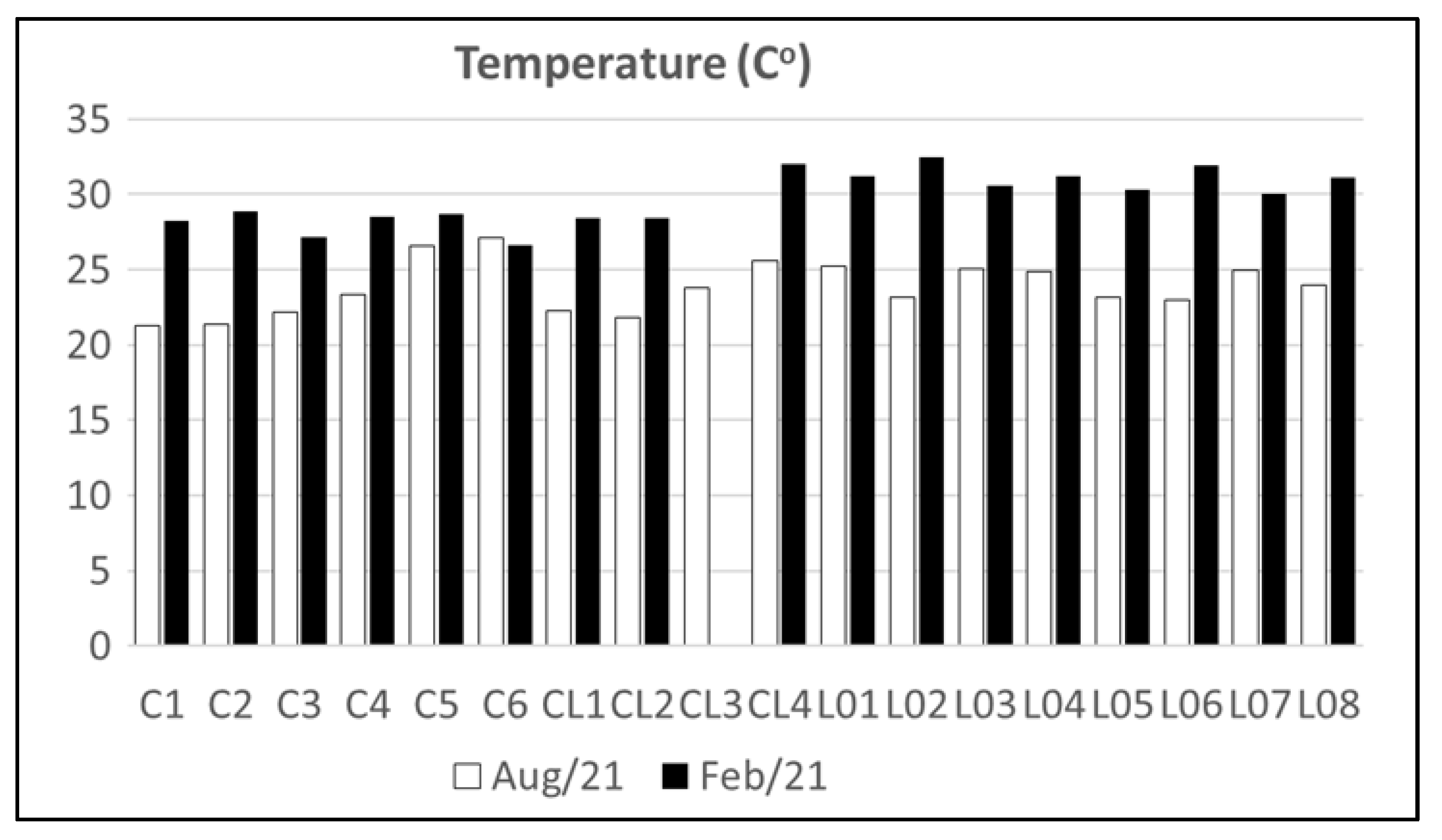
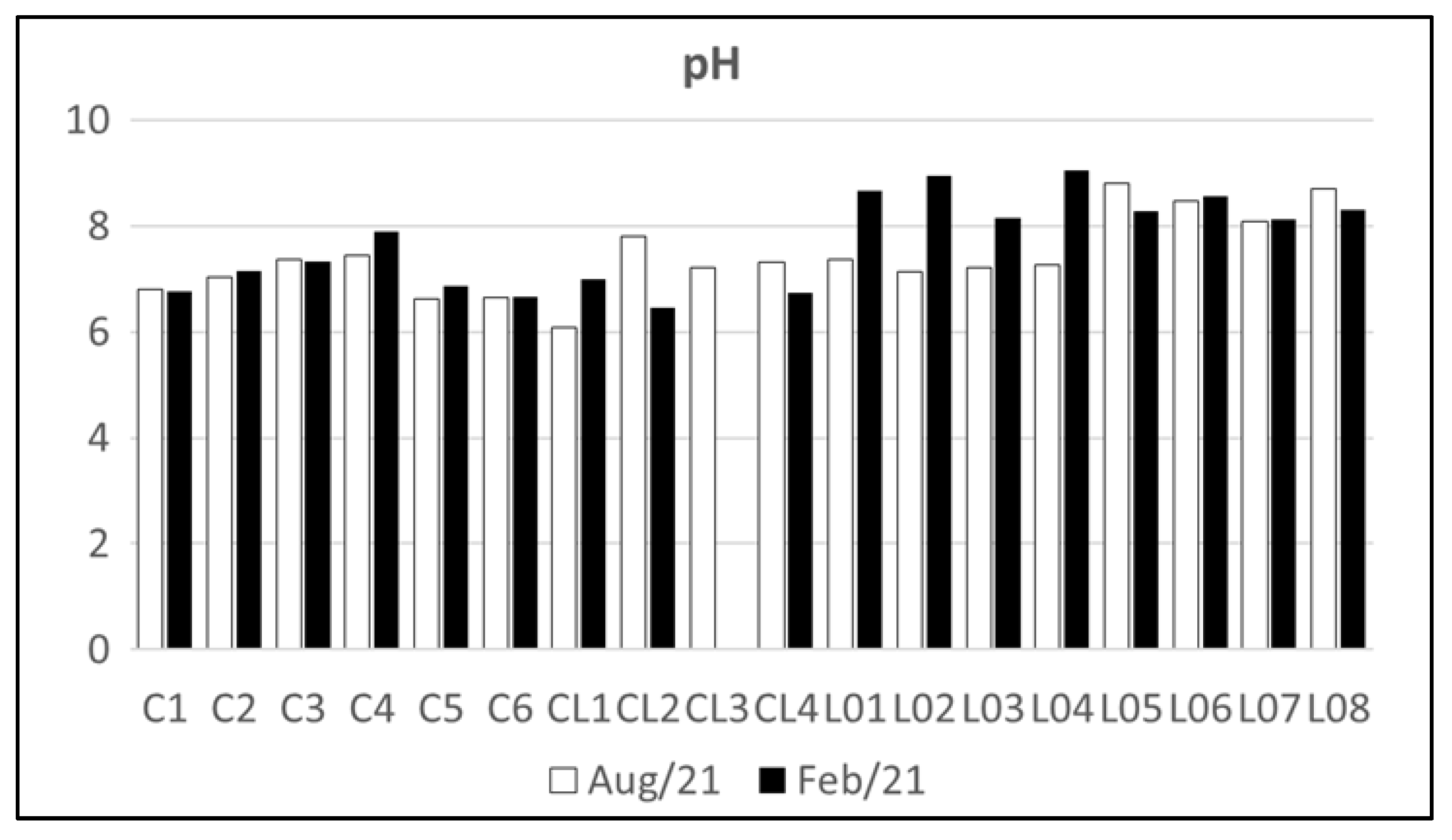
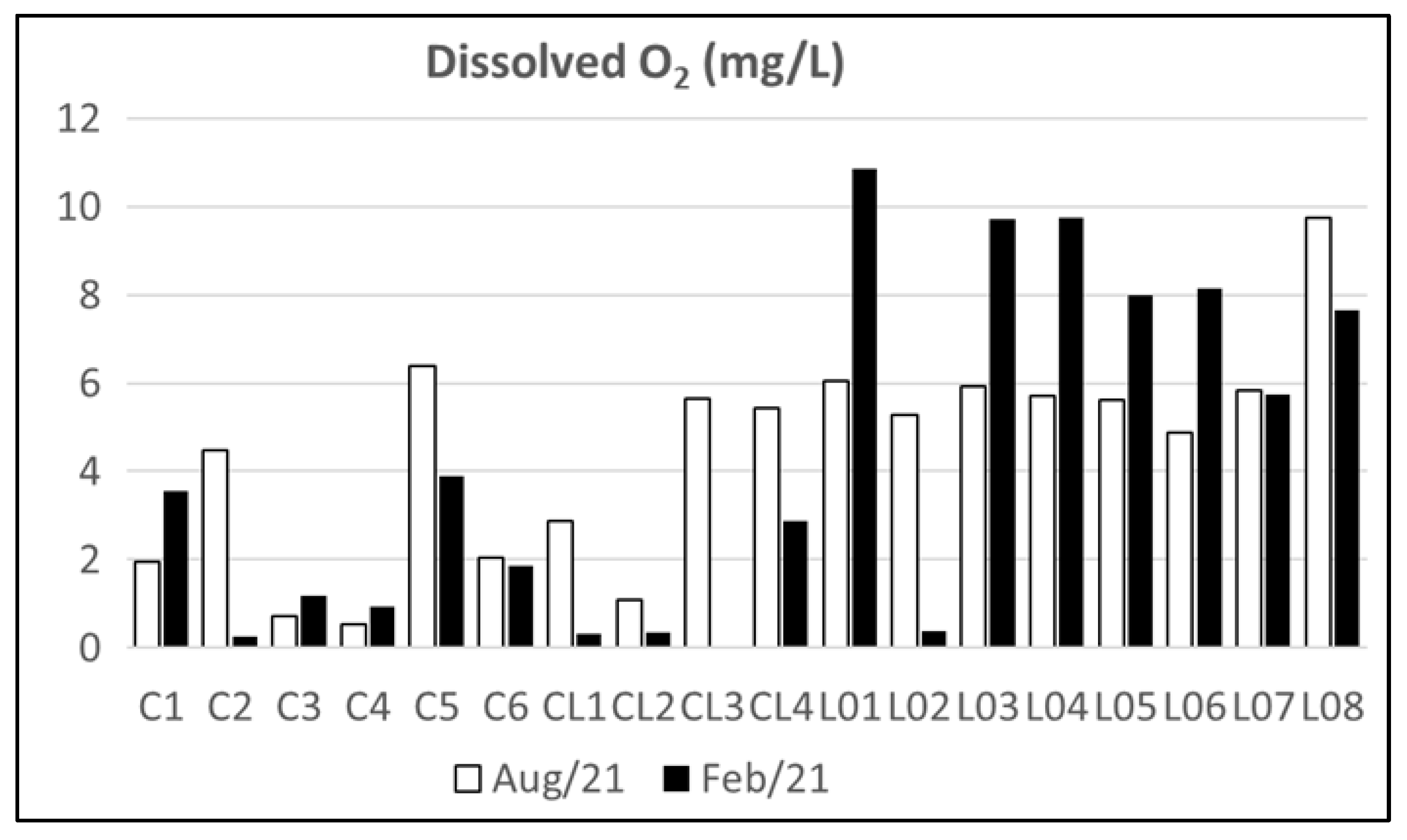
3.1. Water Column Parameters
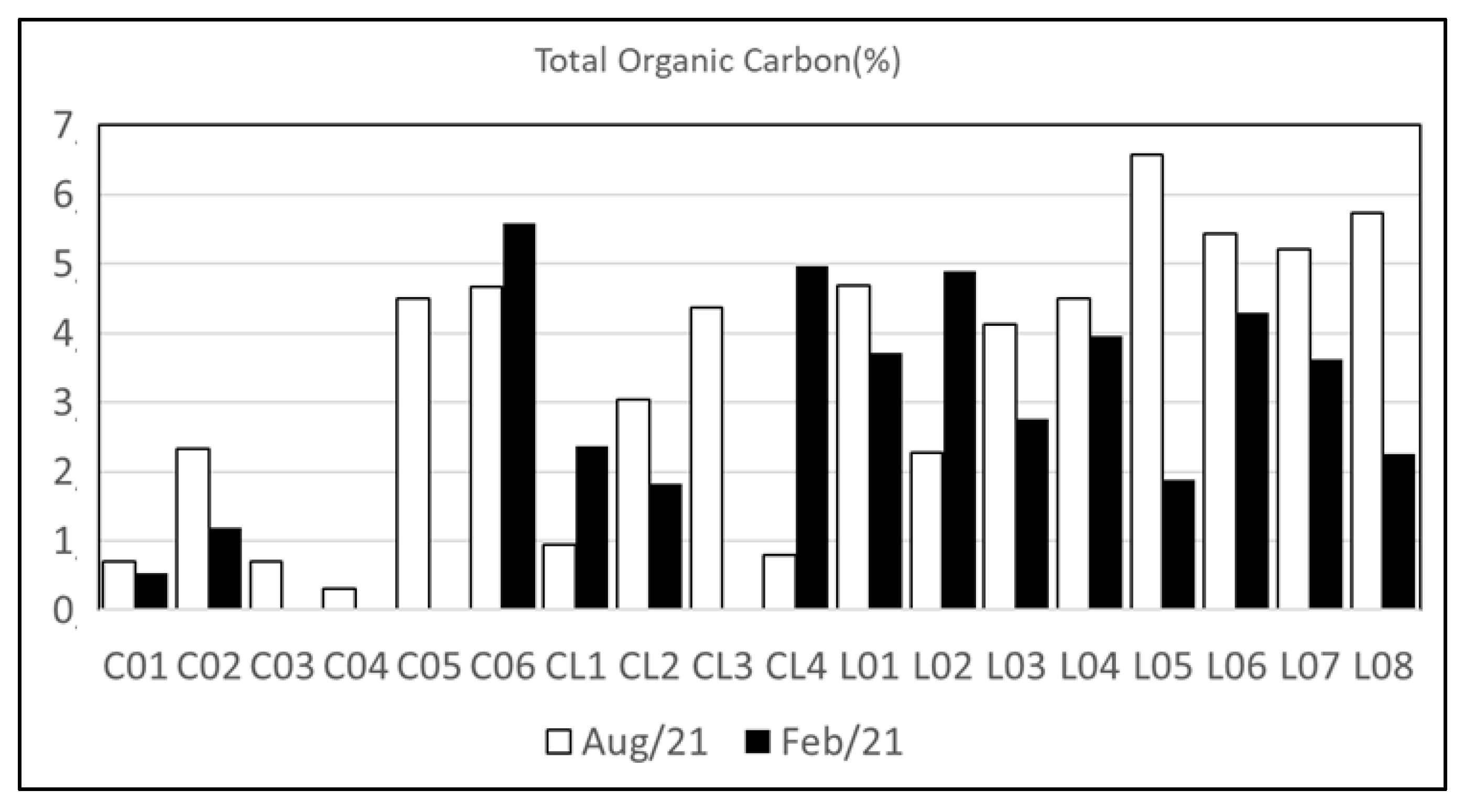
3.2. Sediment Parameters
3.3. Estrogenic Activity (YES Assay)
3.4. Statistical Analyzes
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Water
4.2. Sediment
4.3. Estrogenic Activity by the YES Assay
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jackson, J.; Sutton, R. Sources of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in urban wastewater, Oakland, C.A. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 405, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, S. Bisphenol A exposure, effects, and policy: A wildlife perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 104, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Céspedes, R.; Lacorte, S.; Raldúa, D.; Ginebreda, A.; Barceló, D.; Piña, B. Distribution of endocrine disruptors in the Llobregat River basin (Catalonia, NE Spain). Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojana, G.; Gomiero, A.; Jonkers, N.; Marcomini, A. Natural and synthetic endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in water, sediment and biota of a coastal lagoon. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoeller, R.T.; Brown, T.R.; Doan, L.L.; Gore, A.C.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Soto, A.M.; Woodruff, T.J.; Vom Saal, F.S. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Public Health Protection: A Statement of Principles from The Endocrine Society. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Mollier, J.; Brocklesby, R.W.K.; Caves, C.; Jayasena, C.N.; Minhas, S. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and male reproductive health. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2020, 19, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, K.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Mills, K.H.; Palace, V.P.; Evans, R.E.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Flick, R.W. Collapse of a Fish Population After Exposure to a Synthetic Estrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8897–8901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, E. Impacts of Xenobiotics on Crustacean Molting: The Invisible Endocrine Disruption. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2005, 45, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margiotta-Casaluci, L.; Owen, S.F.; Cumming, R.I.; de Polo, A.; Winter, M.J.; Panter, G.H.; Rand-Weaver, M.; Sumpter, J.P. Quantitative cross-species extrapolation between humans and fish: The case of the anti-depressant fluoxetine. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, H.; Karakuş, G.; Tamam, L.; Demirkol, M.E.; Namlı, Z.; Yeşiloğlu, C. Association of Orthorexic Tendencies with Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms, Eating Attitudes and Exercise. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 14, 3035–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encarnação, T.; Pais, A.A.; Campos, M.G.; Burrows, H.D. Endocrine disrupting chemicals: Impact on human health, wildlife and the environment. Sci. Prog. 2019, 102, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izah, S.C.; Srivastav, A.L. Level of arsenic in potable water sources in Nigeria and their potential health impacts: A review. J. Environ. Treat. Tech. 2015, 3, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Izah, S.C.; Chakrabarty, N.; Srivastav, A.L. A Review on Heavy Metal Concentration in Potable Water Sources in Nigeria: Human Health Effects and Mitigating Measures. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseenko, T.I. Surface Water Under Growing Anthropogenic Loads: From Global Perspectives to Regional Implications. Water 2022, 14, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironti, C.; Ricciardi, M.; Proto, A.; Bianco, P.M.; Montano, L.; Motta, O. Endocrine-Disrupting Compounds: An Overview on Their Occurrence in the Aquatic Environment and Human Exposure. Water 2021, 13, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; He, Y.; Jekel, M.; Reinhard, M.; Gin, K.Y. Emerging contaminants of public health significance as water quality indicator compounds in the urban water cycle. Environ. Int. 2014, 71, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, D.; Tang, H.; Yuan, S.; Luan, B. Rainfall Runoff and Dissolved Pollutant Transport Processes Over Idealized Urban Catchments. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taner, M.; Üstün, B.; Erdinçler, A. A simple tool for the assessment of water quality in polluted lagoon systems: A case study for Küçükçekmece Lagoon, Turkey. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.S.K. The Lagoons of Britain: An overview and conservation appraisal. Biol. Conserv. 1989, 49, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; Bartlett, J.; Nash, L.A. Coastal lagoon habitat re-creation potential in Hampshire, England. Mar. Policy 2007, 31, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specchiulli, A.; Pastorino, P.; De Rinaldis, G.; Scirocco, T.; Anselmi, S.; Cilenti, L.; Ungaro, N.; Renzi, M. Multiple approach for assessing lagoon environmental status based on water bodies quality indices and microplastics accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueira, J.M.; Pereira Júnior, A.O.; Barbosa de Araújo, R.S.; Silva, N.F.d. Economic and Social Impacts of the Oil Industry on the Brazilian Onshore. Energies 2020, 13, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, A.; Barbosa, G. Challenges to Environmental Sustainability: An analysis of the territorial transformation in the production of the urban space of Maricá/RJ. Mod. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S. Towards sustainable urban system through the development of small towns in India. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2021, 13, 777–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldatto, F.C.; Bortoluzzi, S.C.; Pinheiro de Lima, E.; Gouvea da Costa, S.E. Urban Sustainability Performance Measurement of a Small Brazilian City. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Vanacôr, L.; Perrin, P.; Carmouze, J.-P. Le système lagunaire de Maricá Guarapina (Brésil) et ses modifications écologiques récentes d’origine antropique. Rev. d’Hydrobiologie Trop. 1994, 27, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- INMET (All Weather Data). Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia (INMET). 2020. Available online: https://tempo.inmet.gov.br/TabelaEstacoes/# (accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Cruz, C.B.M.; Carvalho Júnior, W.; Barros, R.S.; Argento, M.S.F.; Mayr, L.M. Impactos Ambientais no Sistema Lagunar de Maricá Guarapina. In Proceedings of the Anais VIII Simpósio Brasileiro de Sensoriamento Remoto, Salvador, Brazil, 14–19 April 1996; pp. 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira Folharini, S.; de Oliveira, R.C.; dos Santos Furtado, A.L. Unidades geoambientais do Parque Nacional da Restinga de Jurubatiba, litoral norte fluminense. Rev. Dep. Geogr. 2020, 39, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho da Silva, A.L.; da Silva, M.A.M.; Gralato, J.C.A.; Silvestre, C.P.S. Geomorphological and sedimentary characterization of the Maricá coastal plain (Rio de Janeiro state). Rev. Bras. Geomorfol. 2014, 15, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoppers, B.; Kjerfve, B.; Carmouze, J.P. Trophic state and water turn-over time in 6 choked coastal lagoons in Brazil. Biogeochemistry 1991, 14, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, L.; Savergnini, F.; Silva, F.; Bernardes, M.; Crapez, M. Biochemical and microbiological tools for the evaluation of environmental quality of a coastal lagoon system in Southern Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2011, 71, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lins de Barros, F.M. Risco, Vulnerabilidade Física à Erosão Costeira e Impactos Sócio-Econômicos na Orla Urbanizada do Município de Maricá, Rio de Janeiro. Rev. Bras. Geomorfol. 2005, 6, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, L.G.R.; de Miranda, A.C.; de Medeiros, H.B. O sistema lagunar de Maricá: Um estudo de impacto ambiental. IX Fórum Ambient. Alta Paul. 2013, 9, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- EMBRAPA. Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solos; EMBRAPA: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Environmental Protection Agency—U.S. Method 3050B: Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, and Soils, Revision 2; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Method 7471B. Mercury in Solid or Semisolid Waste (Manual Cold-Vapor Technique); United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/7471b.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Routledge, E.J.; Sumpter, J.P. Estrogenic Activity of Surfactants and Some of Their Degradation Products Assessed Using a Recombinant Yeast Screen. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, G.; dos Santos Argolo, A.; da Cruz Felix, L.; Bila, D.M. Interferences in the yeast estrogen screen (YES) assay for evaluation of estrogenicity in environmental samples, chemical mixtures, and individual substances. Toxicol. Vitr. 2023, 88, 105551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, D.L.; Muylaert, S.; Nascimento, M.T.L.; Felix, L.C.; Gomes, G.; Bila, D.M.; Fonseca, E.M. Occurrence of emerging contaminants and analysis of oestrogenic activity in the water and sediments from two coastal lagoons in south-eastern Brazil. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 72, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frische, T.; Faust, M.; Meyer, W.; Backhaus, T. Toxic masking and synergistic modulation of the estrogenic activity of chemical mixtures in a yeast estrogen screen (YES). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dancey, C.P.; Reidy, J. Statistics Without Maths for Psychology: Using SPSS for Windows (Estatística Sem Matemática Para Psicologia: Usando SPSS Para Windows), 3rd ed.; Artmed Bookman: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2006; Available online: https://books.google.com.br/books/about/Estat%C3%ADstica_sem_Matem%C3%A1tica_para_Psicol.html?id=8ItYt2_fwV4C&redir_esc=y (accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Moore, W.S. The subterranean estuary: A reaction zone of ground water and sea water. Mar. Chem. 1999, 65, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrocicco, M.; Colombani, N. The Issue of Groundwater Salinization in Coastal Areas of the Mediterranean Region: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A. 9.09—Salinization and Saline Environments. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Nosrati, A.; Jafari, H.; Eggenkamp, H.G.M.; Mozafari, M. Overexploitation hazards and salinization risks in crucial declining aquifers, chemo-isotopic approaches. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 5, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpataku, K.V.; Gnazou, M.D.T.; Djanéyé-Boundjou, G.; Bawa, L.M.; Faye, S. Role of Natural and Anthropogenic Influence on the Salinization of Groundwater from Basement Aquifers in the Middle Part of Mono River Basin, Togo. J. Environ. Prot. 2020, 11, 1030–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Q.; Carter, B.R.; Feely, R.A.; Lauvset, S.K.; Olsen, A. Surface ocean pH and buffer capacity: Past, present and future. Sci. Rep. 2020, 9, 18624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli, G.; Papa, S.; Sagnella, E.; Fioretto, A. Heavy metal content in sediments along the Calore river: Relationships with physical–chemical characteristics. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Ayala, E.; Arguello-Pérez, M.; Adrián, T.; Mendoza, P.; Jorge, A.; Díaz-Gómez, J.; Pérez-Rodríguez, R.Y.; Núñez-Nogueira, G.; Sepúlveda-Quiroz, C.; Zepeda-González, F.; et al. Heavy metals in sediment and fish from two coastal lagoons of the Mexican Central Pacific. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2021, 49, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedepohl, K.H. Distribution of the Elements in Some Major Units of the Earth’s Crust. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaa, A.A.; Khan, A.A.; Haredy, R.; Al-Zubieri, A.G. Contamination Evaluation of Heavy Metals in a Sediment Core from the Al-Salam Lagoon, Jeddah Coast, Saudi Arabia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, H.; Yang, C.; Huang, Y. Contamination of Heavy Metals in Sediments from an Estuarine Bay, South China: Comparison with Previous Data and Ecological Risk Assessment. Processes 2022, 10, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R. Calculation and uses of mean sediment quality guideline quotients: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perin, G.; Bonardi, M.; Fabris, R.; Simoncini, B.; Manente, S.; Tosi, L.; Scotto, S. Heavy metal pollution in central Venice Lagoon bottom sediments: Evaluation of the metal bioavailability by geochemical speciation procedure. Environ. Technol. 1997, 18, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, F.H.; Sugauara, L.E.; de Marchi, M.R.; Choueri, R.B.; Castro, Í.B. Estrogen levels in surface sediments from a multi-impacted Brazilian estuarine system. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, M.F.B.; Fernandes, G.M.; Oliveira, A.H.B.; Morais, P.C.V.; Marques, E.V.; Santos, F.R.; Nascimento, R.F.; Swarthout, R.F.; Nelson, R.K.; Reddy, C.M.; et al. Emerging and traditional organic markers: Baseline study showing the influence of untraditional anthropogenic activities on coastal zones with multiple activities (Ceará coast, Northeast Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 139, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, M.F.; Pimentel, M.F.; Damasceno, É.P.; Jimenez, P.C.; Araújo, P.F.R.; Bezerra, M.F.; de Morais, P.C.V.; Cavalcante, R.M.; Loureiro, S.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. Endocrine disruption in Sphoeroides testudineus tissues and sediments highlights contamination in a northeastern Brazilian estuary. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, P.C.V.; Lima, M.F.B.; Martins, D.A.; Fontenele, L.G.; Lima, J.L.R.; da Silva, Í.B.; Pinheiro, L.S.; Nascimento, R.F.; Cavalcante, R.M.; Marques, E.V. Use of an environmental diagnostic study on a coastal lagoon as a decision support tool for environmental management policies in a coastal zone. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2020, 31, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffero, L.; Gomes, G.; Berazategui, M.; Fosalba, C.; Teixeira de Mello, F.; Rezende, C.; Bila, D.; Gacía-Alonso, J. Estrogenicity and cytotoxicity of sediments and water from the drinkwater source basin of Montevideo city, Uruguay. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Contam. 2018, 13, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, D.; Muylaert, S.; Nascimento, M.; Felix, L.; Andrade, J.J.D.D.; Silva, R.; Bila, D. Concentration and toxicity assessment of contaminants in sediments of the Itaipu–Piratininga lagoonal system, Southeastern Brazil. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 46, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorga, M.; Insa, S.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Occurrence and spatial distribution of EDCs and related compounds in waters and sediments of Iberian rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 503–504, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorde, S.P.; Jadhav, M.V. Assessment of Water Quality Parameters: A Review. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2013, 3, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, H.; Chen, X.; Gong, N.; Ahmad, S.; Lee, T.; Ismail, S.; Ni, S.-Q. Insight into impact of sewage discharge on microbial dynamics and pathogenicity in river ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denga, Z.; Zhao, Y. Impact of tidal mixing on water mass properties and circulation in the Bohai Sea: A typhoon case. J. Mar. Syst. 2020, 206, 103338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.G.; Zeng, G.M.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, M.Y.; Shen, L.Q.; Hu, L. Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






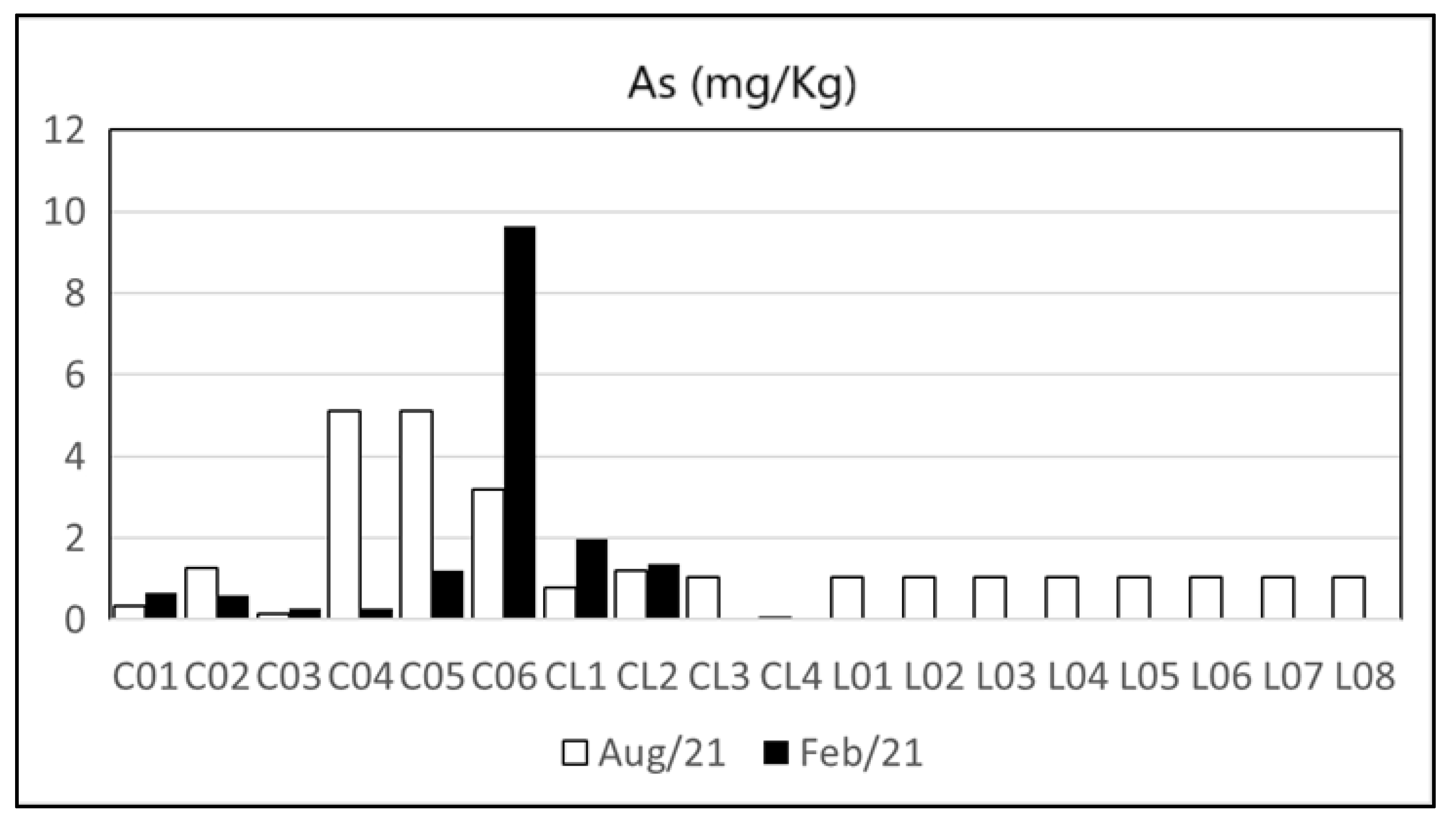

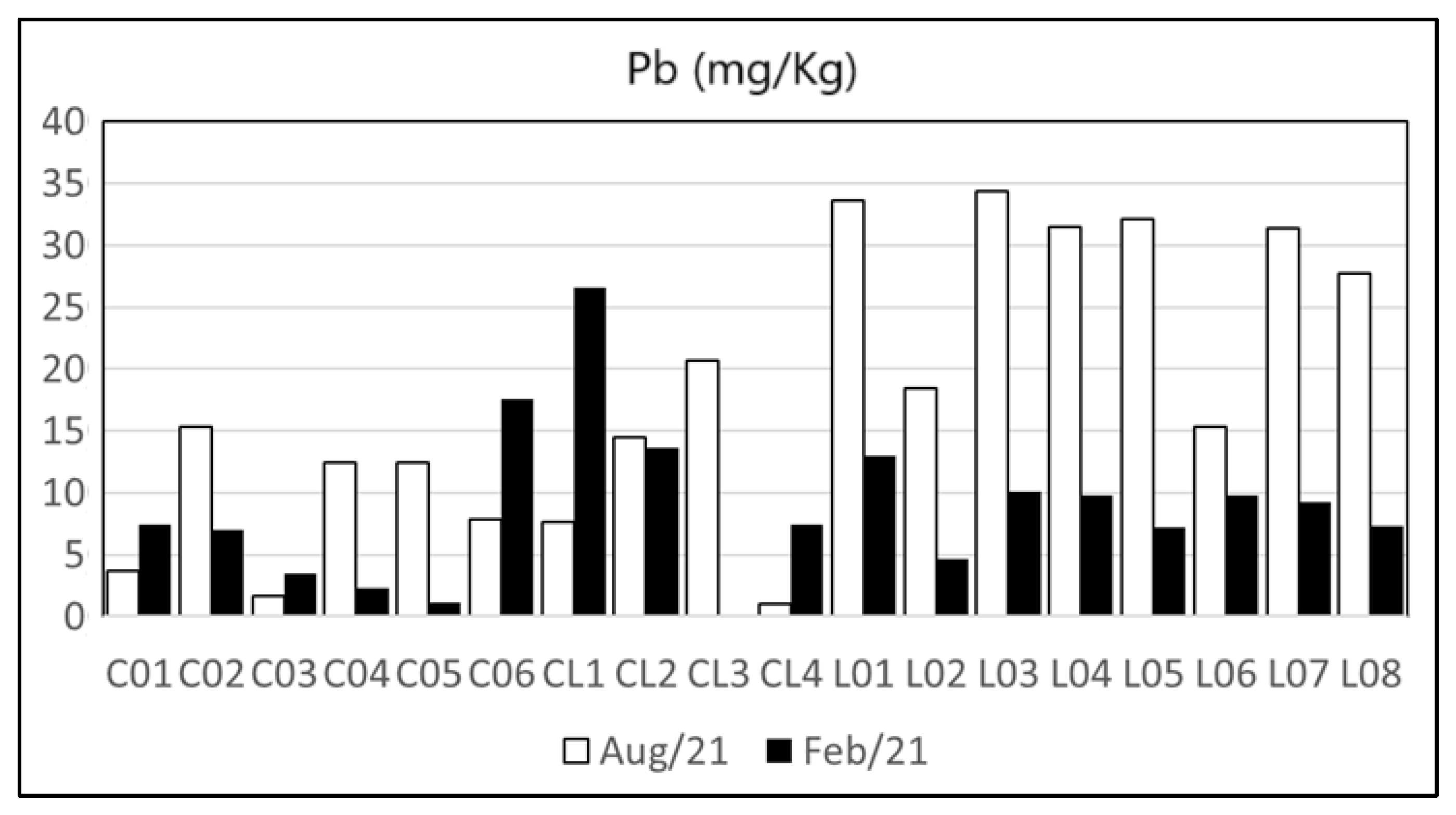
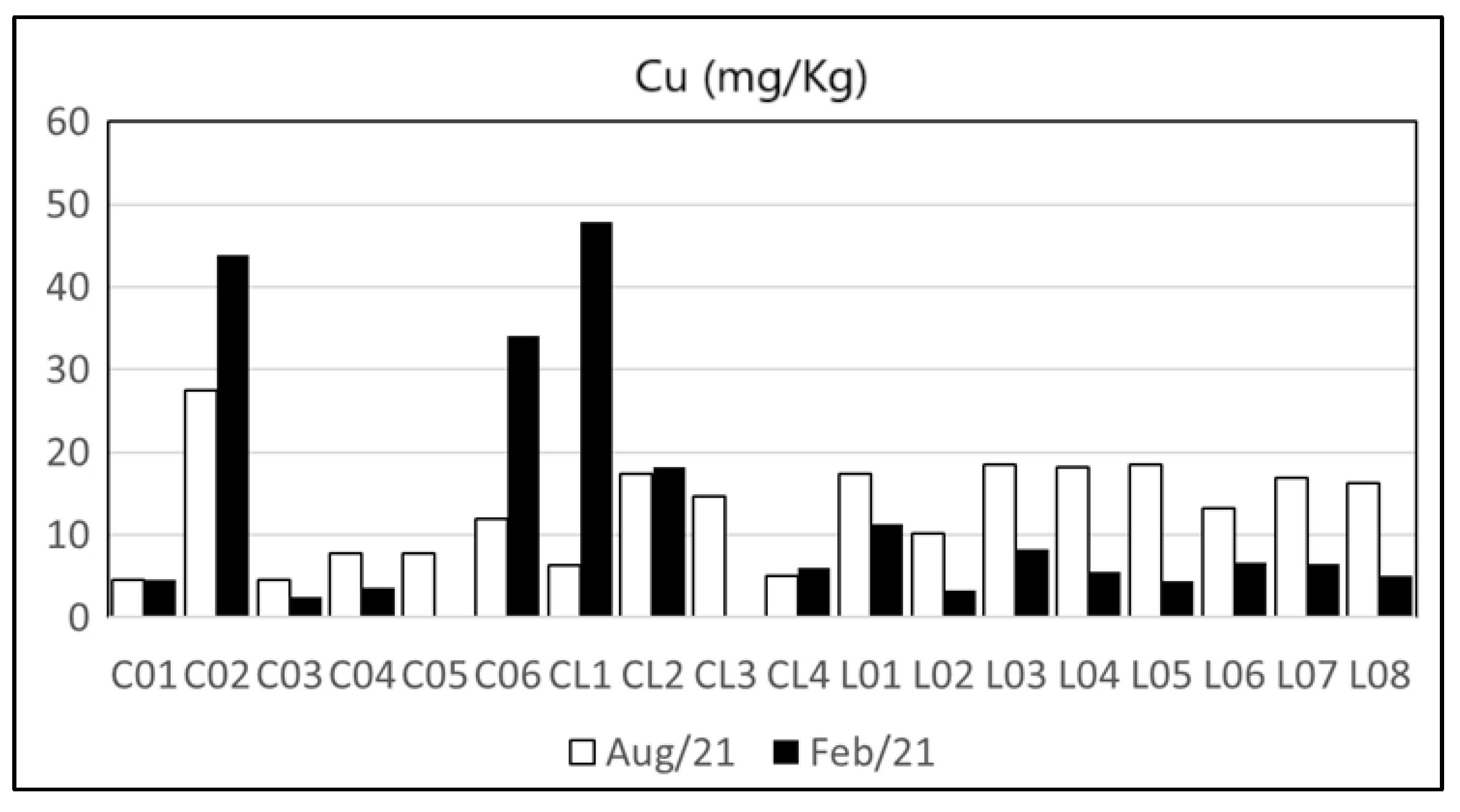

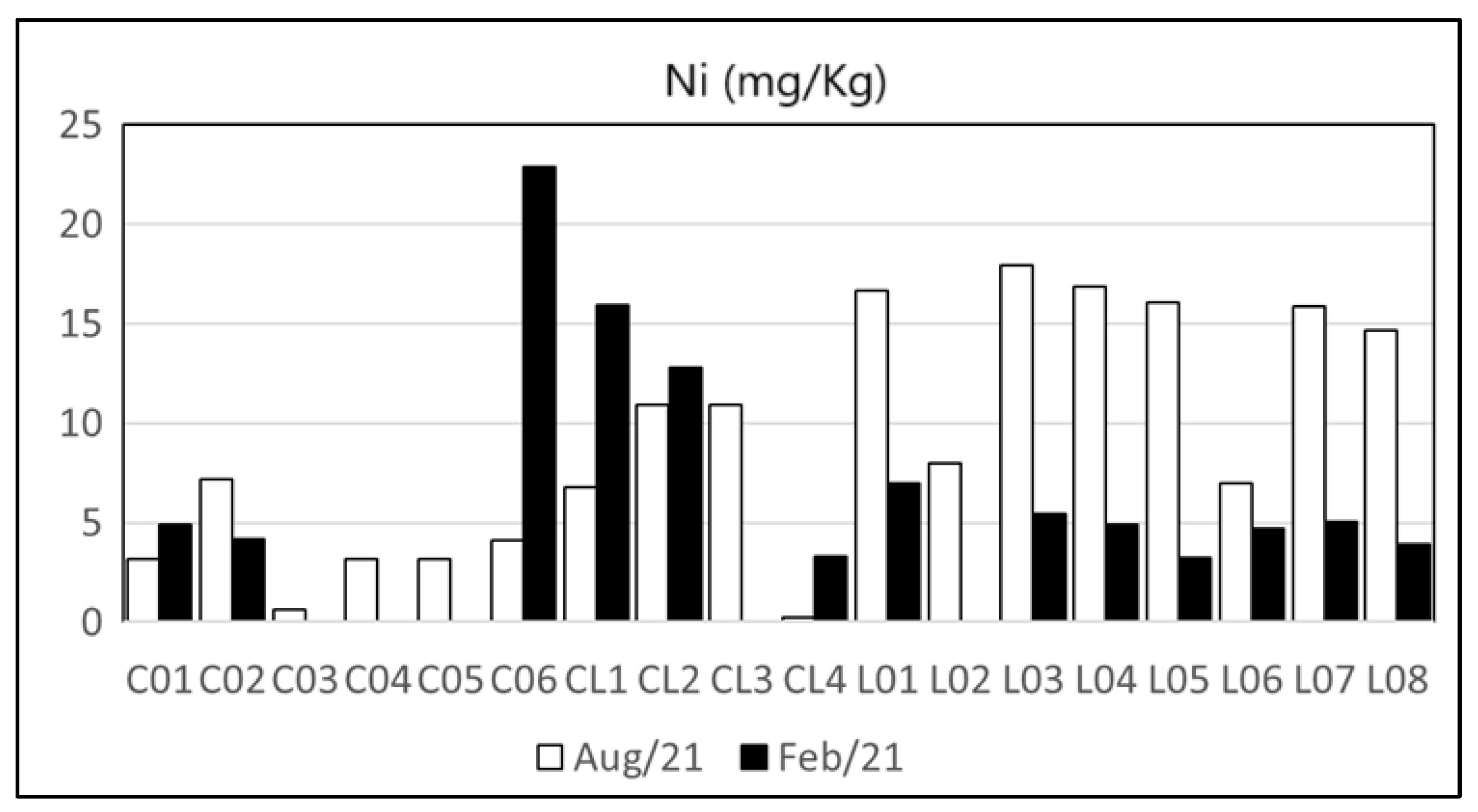

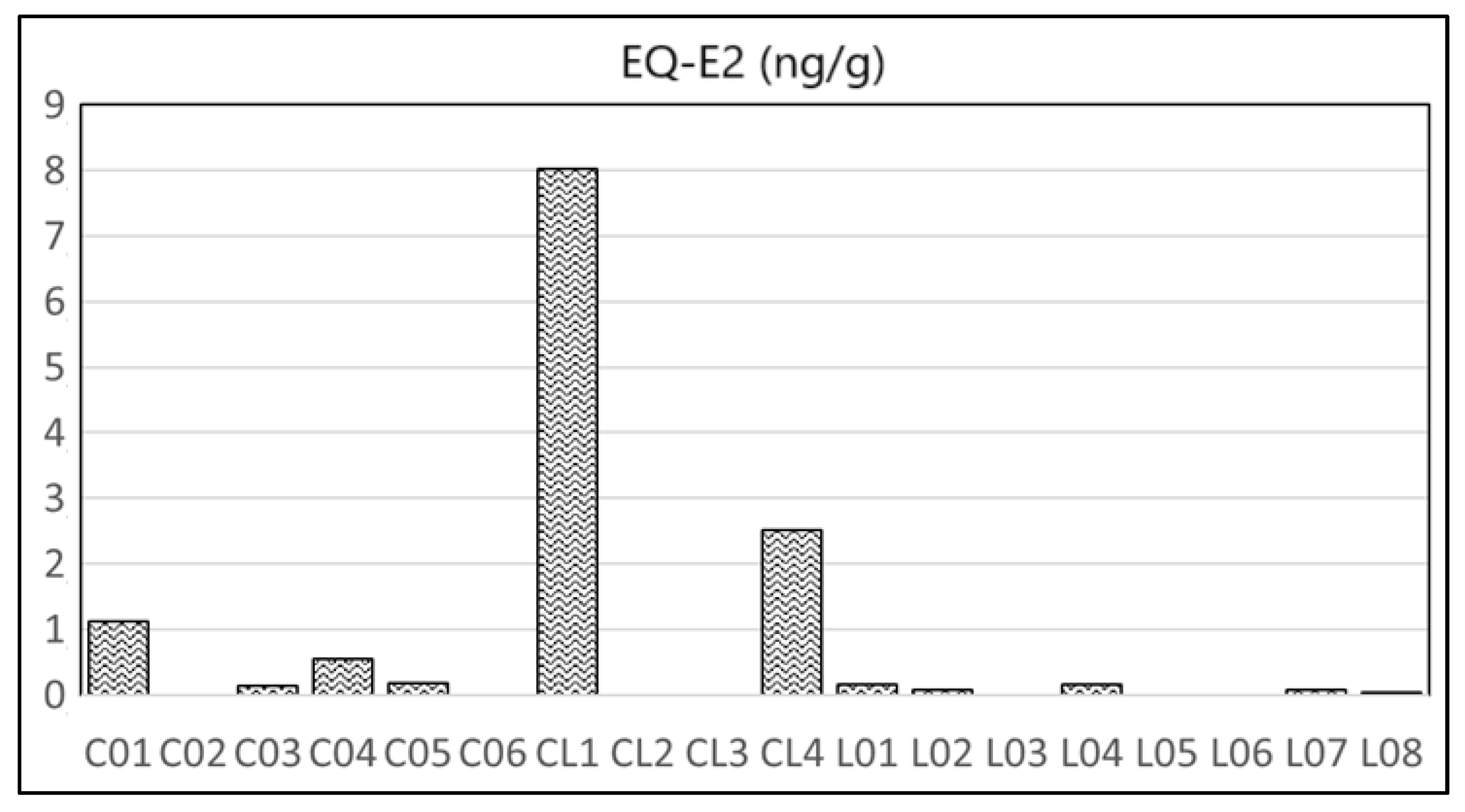
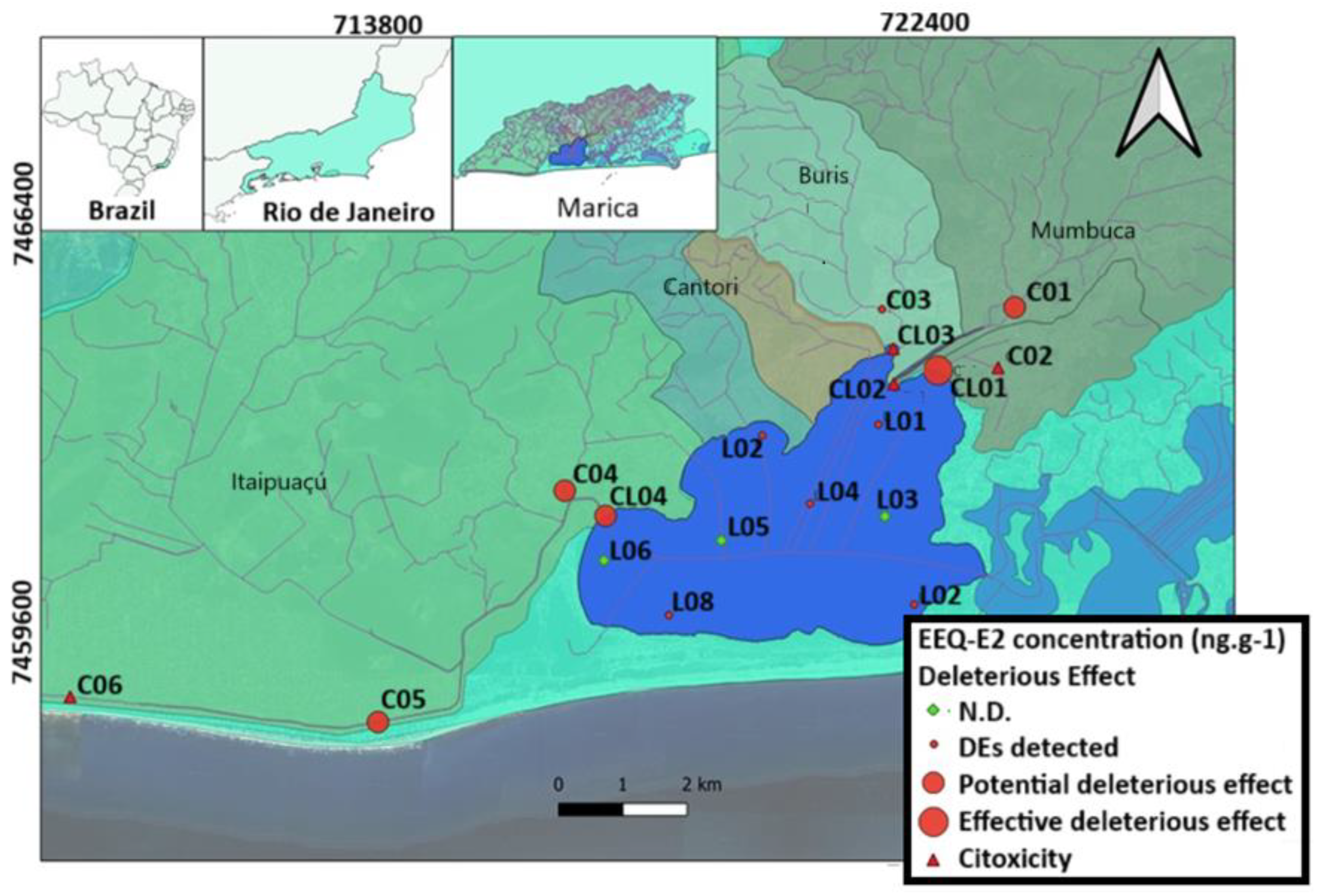
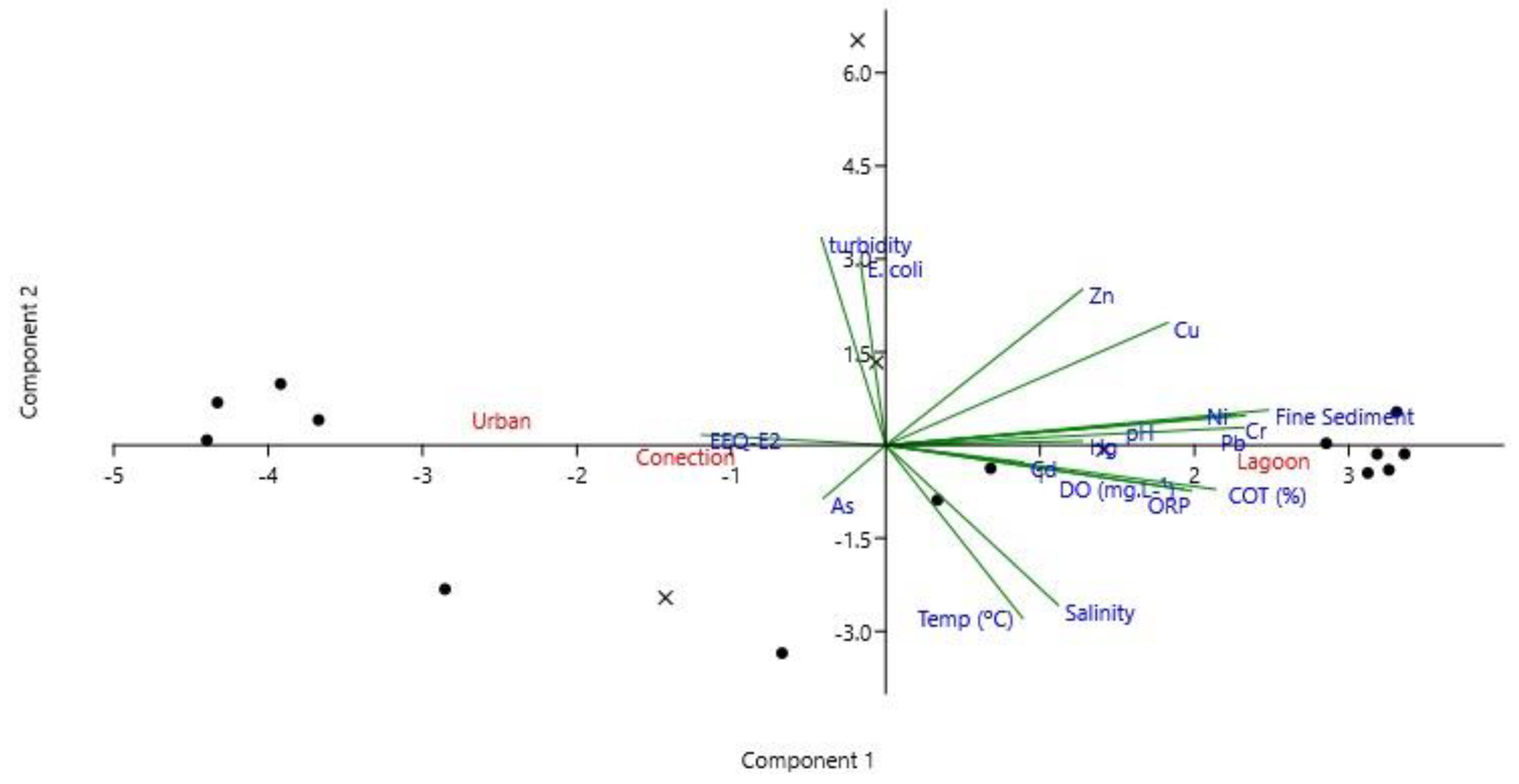
| Heavy Metal | Cu | Zn | Pb | Cd | Ni | As | Cr | Hg | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | ||||||||||
| Maricá’s watershed and lagoon | n.d.–47.9 | 5–232 | 1.07–34.41 | n.d.–2.89 | n.d.–22.9 | n.d.–9.62 | 0.42–77.42 | n.d. | Present Study | |
| Barra de Navidad and Colima Lagoon (Mexico) | 42.7–123.9 | 0.02–0.42 | 10.7–25.4 | n.d. | [52] | |||||
| Global average shale | 45 | 95 | 20 | 0.30 | 68 | 4.70 | 90 | 0.18 | [53] | |
| Red Sea | 92 | 227 | 64 | - | 51 | - | 60 | [54] | ||
| Shantou Bay (China) | 19.0–48.0 | 44.4–962.6 | 21.9–102.9 | 0.2–3.6 | 8.2–48.0 | - | 23.7–80.0 | - | [55] | |
| ERL | 34 | 150 | 47 | 1.2 | 8.2 | 81 | 0.15 | [56] | ||
| ERM | 270 | 410 | 218 | 9.6 | 70 | 370 | 0.71 | |||
| Non-polluted | <25 | <90 | <40 | - | - | <3 | <25 | ≤1.0 | [57] | |
| Moderately polluted | 25–50 | 90–200 | 40–60 | - | - | 3–8 | 25–75 | - | ||
| Heavely polluted | >50 | >200 | >60 | >6 | - | >8 | >75 | >1.0 | ||
| Temp (°C) | pH | ORP | Turbidity | DO (mg·L−1) | Salinity | E. coli | COT (%) | Fine Sediment | EEQ-E2 | As | Cd | Pb | Cu | Cr | Hg | Ni | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp (°C) | 0.78168 | 0.071271 | 0.014823 | 0.00824 | 2.85 × 10−6 | 3.65 × 10−2 | 0.11622 | 0.49648 | 0.99101 | 0.37143 | 0.49311 | 0.3296 | 0.82113 | 0.491 | 0.056701 | 0.52227 | 0.83226 | |
| pH | −0.07028 | 0.93997 | 0.98377 | 0.59932 | 0.63212 | 0.11802 | 0.060061 | 0.12407 | 0.021983 | 0.81756 | 0.28844 | 0.098122 | 0.19539 | 0.12498 | 0.16024 | 0.18078 | 0.46851 | |
| ORP | 0.43492 | 0.019121 | 0.23589 | 0.000122 | 0.007643 | 1.42 × 10−4 | 0.095315 | 0.003466 | 0.29345 | 0.63756 | 0.39162 | 0.004436 | 0.18149 | 0.005251 | 0.1141 | 0.011922 | 0.32828 | |
| turbidity | −0.56376 | −0.00517 | −0.29427 | 0.29905 | 0.009718 | 0.37673 | 0.52023 | 0.86121 | 6.56 × 10−1 | 0.93767 | 0.40091 | 0.75073 | 0.50951 | 0.7322 | 0.44772 | 0.65609 | 0.44745 | |
| DO (mg·L−1) | 0.60176 | 0.13282 | 0.78306 | −0.25916 | 0.004925 | 0.000179 | 0.002411 | 0.001648 | 0.19935 | 0.92036 | 0.48976 | 0.002533 | 0.083402 | 4.44 × 10−3 | 0.046943 | 0.009357 | 0.23711 | |
| Salinity | 0.86912 | −0.12112 | 0.60631 | −0.59152 | 0.63166 | 0.039879 | 0.024156 | 0.093291 | 0.57995 | 0.27499 | 0.059901 | 0.080153 | 0.3862 | 0.13494 | 0.18203 | 0.11204 | 0.56472 | |
| E. coli | −0.51007 | −0.3936 | −0.79392 | 0.22896 | −0.78672 | −0.50235 | 0.056077 | 0.031332 | 0.087656 | 0.51824 | 0.79498 | 1.97 × 10−2 | 0.71656 | 0.045332 | 4.19 × 10−5 | 0.08778 | 0.65954 | |
| COT (%) | 0.38346 | 0.4514 | 0.40517 | −0.16219 | 0.66873 | 0.52847 | −0.47146 | 0.001425 | 0.007105 | 0.35801 | 0.010139 | 0.002489 | 1.23 × 10−2 | 0.006094 | 0.32052 | 0.006157 | 0.053431 | |
| Fine Sediment | 0.1714 | 0.37603 | 0.65049 | 0.044376 | 0.68663 | 0.40745 | −0.52272 | 0.69318 | 0.012163 | 0.81098 | 0.017428 | 1.17 × 10−7 | 0.00038 | 6.44 × 10−9 | 0.36719 | 3.99 × 10−9 | 0.000923 | |
| EEQ-E2 | −0.00332 | −0.60466 | −0.30233 | 0.13053 | −0.36505 | −0.16204 | 0.49202 | −0.68293 | −0.64824 | 0.27026 | 0.001132 | 0.012233 | 0.011342 | 0.015243 | 0.56386 | 0.03375 | 0.042629 | |
| As | 0.22406 | −0.05853 | −0.1192 | 0.019857 | 0.025386 | 0.27194 | 0.16839 | 0.23025 | 0.060674 | −0.31649 | 0.090331 | 0.40869 | 0.10441 | 0.57003 | 0.11507 | 0.64648 | 0.13202 | |
| Cd | 0.17848 | 0.27334 | 0.22208 | −0.21786 | 0.17984 | 0.46517 | 0.07061 | 0.60462 | 0.56779 | −0.77495 | 0.42344 | 0.020883 | 0.000953 | 0.028166 | 0.40923 | 0.007972 | 0.000633 | |
| Pb | 0.2438 | 0.40207 | 0.6374 | 0.080537 | 0.66632 | 0.42318 | −0.55872 | 0.66718 | 0.91378 | −0.64785 | 0.2075 | 0.55452 | 4.20 × 10−5 | 3.33 × 10−12 | 0.085608 | 7.35 × 10−10 | 0.000689 | |
| Cu | 0.057364 | 0.32006 | 0.32972 | 0.16632 | 0.41912 | 0.21739 | −0.0951 | 0.57653 | 0.74587 | −0.653 | 0.39534 | 0.72663 | 0.8124 | 4.20 × 10−5 | 0.7787 | 1.38 × 10−5 | 2.18 × 10−9 | |
| Cr | 0.17355 | 0.37519 | 0.6281 | 0.086732 | 0.6374 | 0.36627 | −0.49104 | 0.61964 | 0.94063 | −0.63235 | 0.14349 | 0.53136 | 0.97727 | 0.8124 | 0.23742 | 5.69 × 10−12 | 0.000142 | |
| Hg | 0.48532 | 0.36846 | 0.41066 | −0.20437 | 0.50318 | 0.35138 | −0.85851 | 0.26539 | 0.24167 | −0.18547 | 0.40966 | −0.23016 | 0.44312 | 0.076344 | 0.31327 | 0.53911 | 0.59322 | |
| Ni | 0.16141 | 0.33023 | 0.57838 | 0.11272 | 0.5939 | 0.38756 | −0.4265 | 0.61905 | 0.94416 | −0.56889 | 0.11607 | 0.61969 | 0.95499 | 0.83851 | 0.97569 | 0.16593 | 3.68 × 10−5 | |
| Zn | −0.05375 | 0.18252 | 0.24444 | 0.19112 | 0.29354 | 0.14545 | 0.11527 | 0.46225 | 0.71178 | −0.54768 | 0.36884 | 0.74299 | 0.72351 | 0.94829 | 0.77829 | −0.14457 | 0.81574 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gil, M.L.; da Fonseca, E.M.; Pierri, B.S.; Delgado, J.d.F.; Lima, L.d.S.; da Cunha, D.L.; Corrêa, T.R.; Neves, C.V.; Bila, D.M. The Consequences of a Lack of Basic Sanitation in the Municipality of Maricá (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) Resulting in Low Concentrations of Metals but Dissemination of Endocrine Disruptors Through Local Environments: Subsidies for Local Environmental Management. Eng 2024, 5, 3467-3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040181
Gil ML, da Fonseca EM, Pierri BS, Delgado JdF, Lima LdS, da Cunha DL, Corrêa TR, Neves CV, Bila DM. The Consequences of a Lack of Basic Sanitation in the Municipality of Maricá (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) Resulting in Low Concentrations of Metals but Dissemination of Endocrine Disruptors Through Local Environments: Subsidies for Local Environmental Management. Eng. 2024; 5(4):3467-3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040181
Chicago/Turabian StyleGil, Moisés L., Estefan M. da Fonseca, Bruno S. Pierri, Jéssica de F. Delgado, Leonardo da S. Lima, Danieli L. da Cunha, Thulio R. Corrêa, Charles V. Neves, and Daniele M. Bila. 2024. "The Consequences of a Lack of Basic Sanitation in the Municipality of Maricá (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) Resulting in Low Concentrations of Metals but Dissemination of Endocrine Disruptors Through Local Environments: Subsidies for Local Environmental Management" Eng 5, no. 4: 3467-3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040181
APA StyleGil, M. L., da Fonseca, E. M., Pierri, B. S., Delgado, J. d. F., Lima, L. d. S., da Cunha, D. L., Corrêa, T. R., Neves, C. V., & Bila, D. M. (2024). The Consequences of a Lack of Basic Sanitation in the Municipality of Maricá (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) Resulting in Low Concentrations of Metals but Dissemination of Endocrine Disruptors Through Local Environments: Subsidies for Local Environmental Management. Eng, 5(4), 3467-3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040181








