Useful Predictor for Exacerbation of Esophagogastric Varices after Hepatitis C Virus Eradication by Direct-Acting Antivirals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Assessments
2.3. Measurement of Liver Stiffness
2.4. Endoscopic Examination for Assessing EGVs
2.5. CT Examination for Portal Hypertension
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Patients
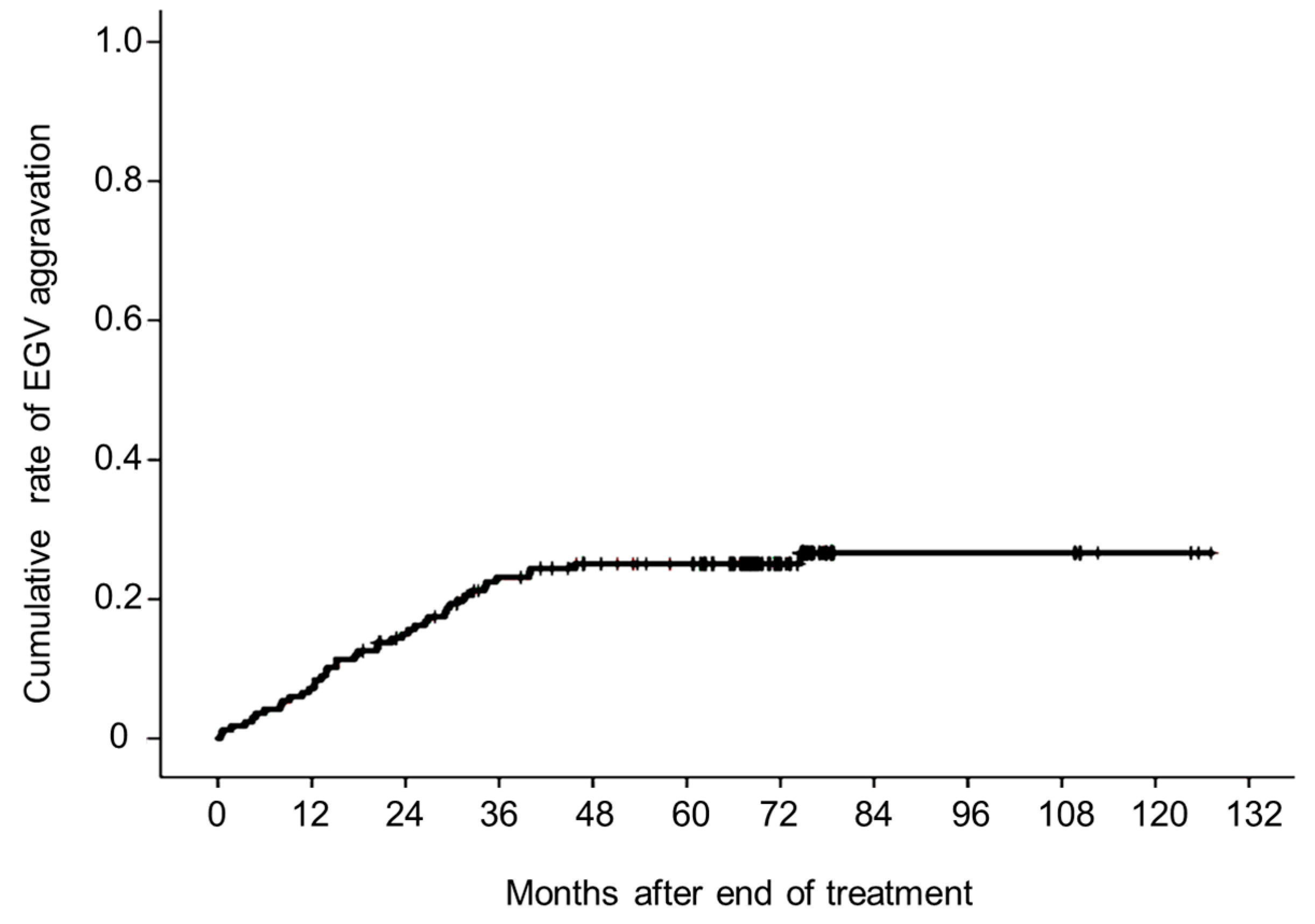
3.2. Aggravated EGVs after Eradicating HCV
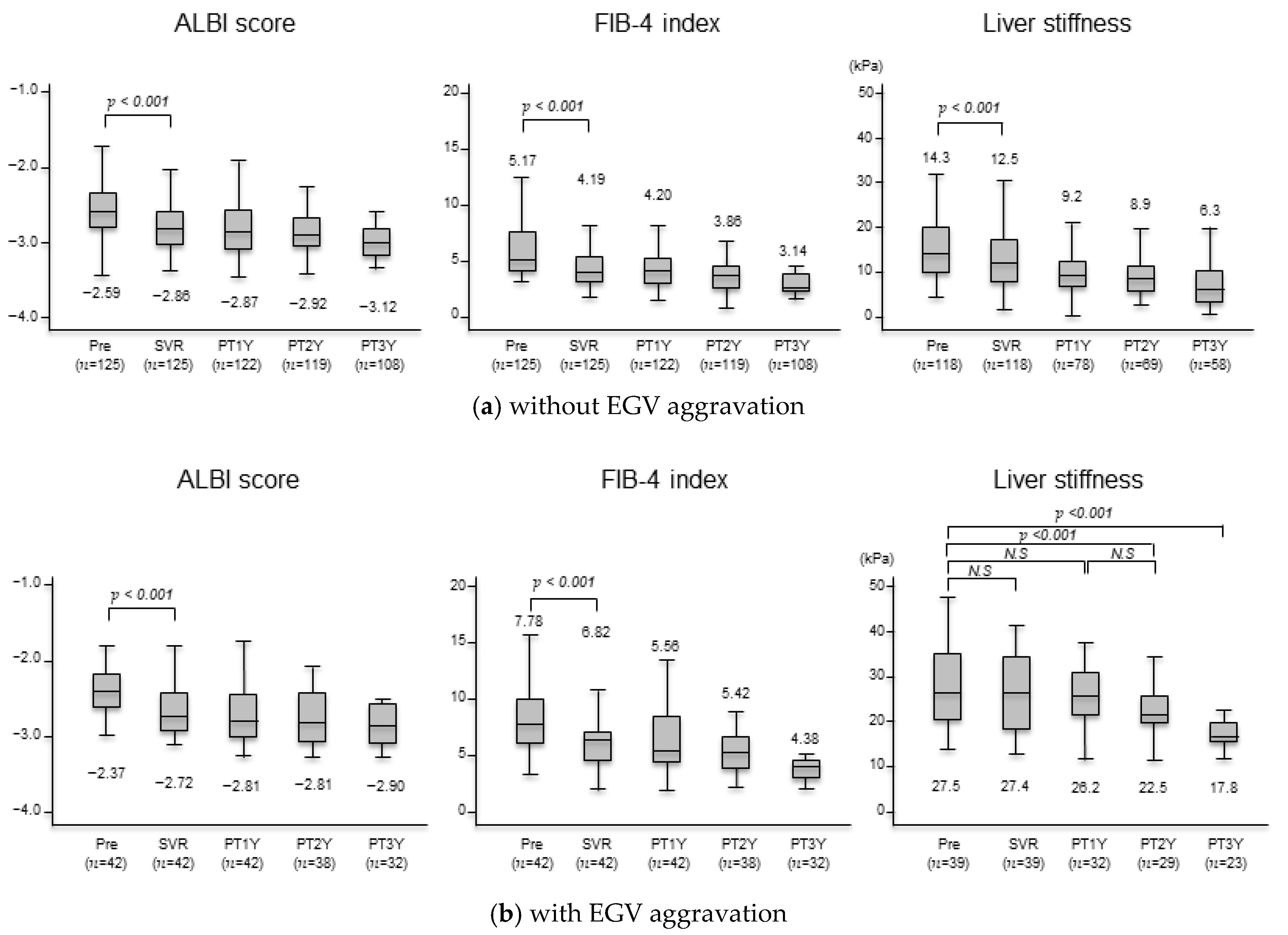
3.3. Changes in Liver Function Test, Serum Fibrosis Markers, and Liver Stiffness after Achieving SVR
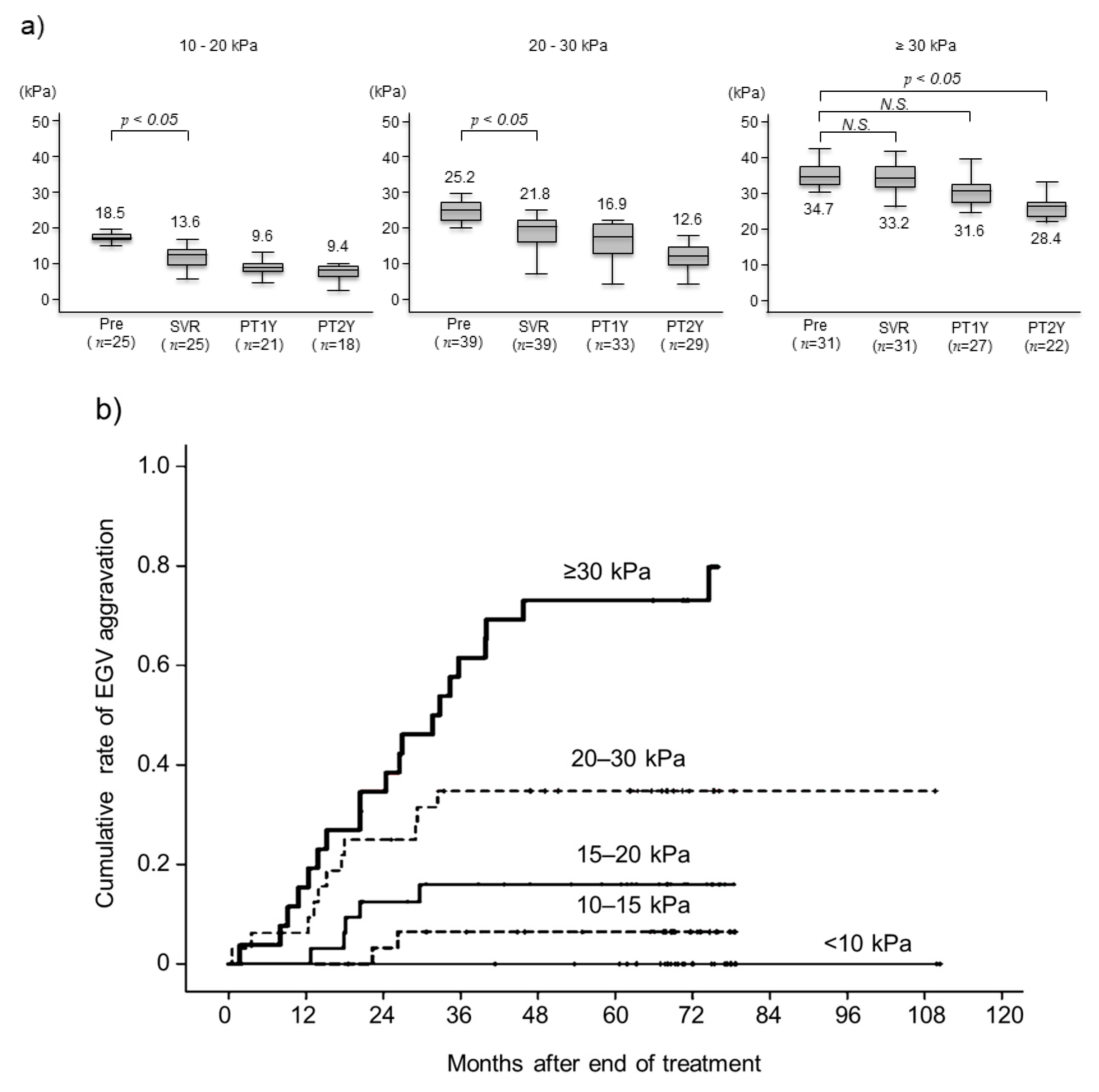
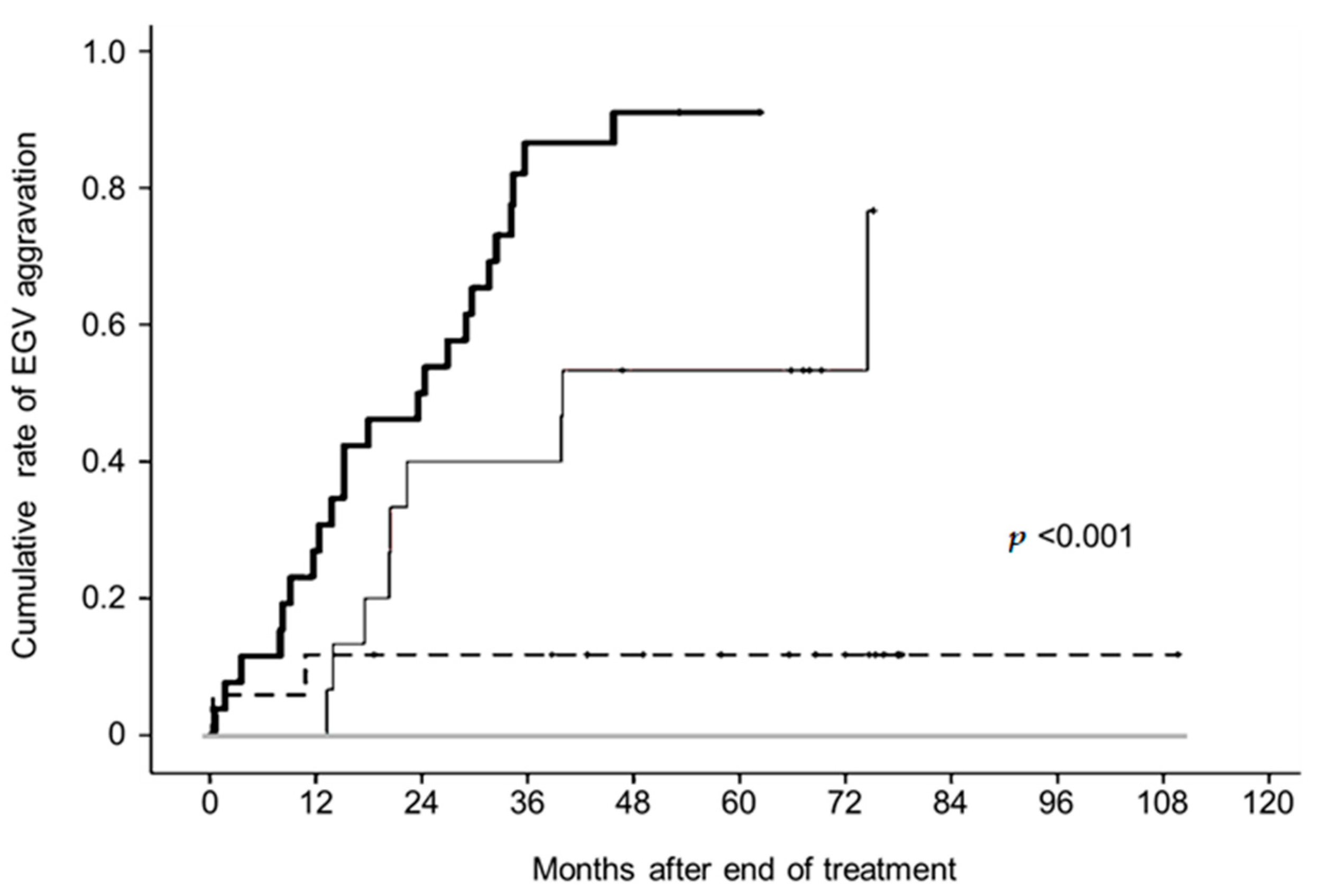
3.4. Changes in Liver Stiffness after Achieving SVR and Aggravated EGVs after Eradicating HCV by Pretreatment LSM
3.5. Serum Bile Acid and Predictive Factors Associated With Aggravated EGVs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carrat, F.; Fontaine, H.; Dorival, C.; Simony, M.; Diallo, A.; Hezode, C.; De Ledinghen, V.; Larrey, D.; Haour, G.; Bronowicki, J.; et al. Clinical outcomes in patients with chronic hepatitis C after direct-acting antiviral treatment: A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2019, 393, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, E.; Crespo, G.; Montironi, C.; Londoño, M.C.; Hernández-Gea, V.; Ruiz, P.; Lombardo, J.; Mariño, Z.; Díaz, A.; Colmenero, J.; et al. Portal pressure and liver stiffness measurements in the prediction of fibrosis regression after sustained virological response in recurrent hepatitis C. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandorfer, M.; Kozbial, K.; Schwabl, P.; Freissmuth, C.; Schwarzer, R.; Stern, R.; Chromy, D.; Stättermayer, A.F.; Reiberger, T.; Beinhardt, S.; et al. Sustained virologic response to interferon-free therapies ameliorates HCV-induced portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afdhal, N.; Everson, G.T.; Calleja, J.L.; McCaughan, G.W.; Bosch, J.; Brainard, D.M.; McHutchison, J.G.; De-Oertel, S.; An, D.; Charlton, M.; et al. Effect of viral suppression on hepatic venous pressure gradient in hepatitis C with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. J. Viral Hepatol. 2017, 24, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lens, S.; Alvarado-Tapias, E.; Mariño, Z.; Londoño, M.C.; LLop, E.; Martinez, J.; Fortea, J.I.; Ibañez, L.; Ariza, X.; Baiges, A.; et al. Effects of all-oral anti-viral therapy on HVPG and systemic hemodynamics in patients with hepatitis C virus-associated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandorfer, M.; Kozbial, K.; Schwabl, P.; Chromy, D.; Semmler, G.; Stättermayer, A.F.; Pinter, M.; Hernández-Gea, V.; Fritzer-Szekeres, M.; Steindl-Munda, P.; et al. Changes in hepatic venous pressure gradient predict hepatic decompensation in patients who achieved sustained virologic response to interferon-free therapy. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaoki, Y.; Aikata, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Fukuhara, T.; Masaki, K.; Tanaka, M.; Naeshiro, N.; Nakahara, T.; Honda, Y.; Miyaki, D.; et al. Risk factors for the exacerbation of esophageal varices or portosystemic encephalopathy after sustained virological response with IFN therapy for HCV-related compensated cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaoki, Y.; Imamura, M.; Teraoka, Y.; Morio, K.; Fujino, H.; Ono, A.; Nakahara, T.; Murakami, E.; Yamauchi, M.; Kawaoka, T.; et al. Impact of viral eradication by direct-acting antivirals on the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma development, prognosis, and portal hypertension in hepatitis C virus-related compensated cirrhosis patients. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, S.; Uchida, Y.; Uemura, H.; Kouyama, J.I.; Naiki, K.; Nakao, M.; Motoya, D.; Sugawara, K.; Nakayama, N.; Imai, Y.; et al. Involvement of portosystemic shunts in impaired improvement of liver function after direct-acting antiviral therapies in cirrhotic patients with hepatitis C virus. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Franchis, R. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Uojima, H.; Setsu, T.; Okubo, T.; Atsukawa, M.; Furuichi, Y.; Arase, Y.; Hidaka, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakazawa, T.; et al. Usefulness of autotaxin for the complications of liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrin, L.; Fourquet, B.; Hasquenoph, J.M.; Yon, S.; Fournier, C.; Mal, F.; Christidis, C.; Ziol, M.; Poulet, B.; Kazemi, F.; et al. Transient elastography: A new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2003, 29, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Japan Society for Portal Hypertension. The General Rules for Study of Portal Hypertension, 3rd ed.; Kanehara: Tokyo, Japan, 2013; pp. 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Puigvehí, M.; Londoño, M.C.; Torras, X.; Lorente, S.; Vergara, M.; Morillas, R.M.; Masnou, H.; Serrano, T.; Miquel, M.; Gallego, A.; et al. Impact of sustained virological response with DAAs on gastroesophageal varices and Baveno criteria in HCV-cirrhotic patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marco, V.; Calvaruso, V.; Ferraro, D.; Bavetta, M.G.; Cabibbo, G.; Conte, E.; Cammà, C.; Grimaudo, S.; Pipitone, R.M.; Simone, F.; et al. Effects of eradicating hepatitis C virus infection in patients with cirrhosis differ with stage of portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, M.W.; Kim, K.W.; Pyo, J.; Huh, J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Park, S.H. A Meta-analysis for the Diagnostic Performance of Transient Elastography for Clinically Significant Portal Hypertension. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzigotti, A. Non-invasive evaluation of portal hypertension using ultrasound elastography. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Franchis, R.; Bosch, J.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Reiberger, T.; Ripoll, C. Baveno VII—Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Jiang, W.; Shen, X.; Wu, S. Spleen and liver stiffness for noninvasive assessment of portal hypertension in cirrhotic patients with large esophageal varices. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2018, 46, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzutti, F.; Arena, U.; Romanelli, R.G.; Rega, L.; Foschi, M.; Colagrande, S.; Petrarca, A.; Moscarella, S.; Belli, G.; Zignego, A.L.; et al. Liver stiffness measurement predicts severe portal hypertension in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis. Hepatology 2007, 45, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, N.; Saitoh, S.; Akuta, N.; Sezaki, H.; Suzuki, F.; Fujiyama, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Hosaka, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Advantage of liver stiffness measurement before and after direct-acting antiviral therapy to predict hepatocellular carcinoma and exacerbation of esophageal varices in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y. An overview of bile acid synthesis and its physiological and pathological functions. Yi Chuan 2019, 41, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- LaRusso, N.F.; Hoffman, N.E.; Korman, M.G.; Hofmann, A.F.; Cowen, A.E. Determinants of fasting and postprandial serum bile acid levels in healthy man. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 1978, 23, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlberg, J.; Angelin, B.; Björkhem, I.; Einarsson, K. Individual bile acids in portal venous and systemic blood serum of fasting man. Gastroenterology 1977, 73, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, I.T.; Thompson, R.P.H. Kinetics of 14C-glycocholic acid clearance in normal man and in patients with liver disease. Gut 1978, 19, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblad, L.; Lundholm, K.; Schersten, T. Bile acid concentrations in systemic and portal serum in presumably normal man and in cholestatic and cirrhotic conditions. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1977, 12, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, G.; Cambri, S.; Ferrara, A.; Marzano, M.; Liberti, A.; Vellone, G.; Ciccarelli, A.F. Serum concentration of bile acids and portal hypertension in cirrhotic patients. Possible correlations. Riv. Eur. Sci. Med. Farmacol. 1989, 11, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano, M.; Milani, A.; Marra, L.; Rossi, L. Serum bile acids in cirrhosis: Correlation with liver function parameters and with the severity of the disease. Quad. Sclavo Diagn. Clin. Lab. 1986, 22, 355–361. [Google Scholar]
- Poupon, R.E.; Poupon, R.Y.; Grosdemouge, M.L.; Erlinger, S. Effect of portacaval shunt on serum bile acid concentration in patients with cirrhosis. Digestion 1977, 16, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, H.; Okuda, K.; Lida, S.; Ohnishi, K.; Ikawa, S.; Makino, I. Role of portal and splenic vein shunts and impaired hepatic extraction in the elevated serum bile acids in liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1984, 86, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Beppu, T.; Okabe, H.; Nitta, H.; Imai, K.; Doi, K.; Chikamoto, A.; Baba, H. Combined measurements of serum bile acid level and splenic volume may be useful to noninvasively assess portal venous pressure. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Category | |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 74 (48–90) |
| Sex, male/female | 82/85 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 22.3 (14.7–39.1) |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.3–3.6) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase, IU/L | 49 (12–351) |
| Alanine aminotransferase, IU/L | 37 (82–54) |
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.9 (2.3–5.1) |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 140 (75–256) |
| Ammonia, μg/dL | 40 (10–128) |
| Platelet count, ×104/μL | 9.8 (3.0–29.5) |
| Prothrombin activity, % | 83 (31–112) |
| Alfa-fetoprotein, ng/mL | 7.3 (1.1–482.9) |
| FIB-4 index | 5.98 (3.27–26.09) |
| ALBI score | −2.56 (−3.43–−1.28) |
| Liver stiffness measurement, kPa | 18.9 (5.6–44.2) |
| Total bile acid, µmol/L | 32.3 (1.73–17.7) |
| Autotaxin, mg/L | 1.89 (0.76–43.29) |
| Past history of HCC treatment *, yes/no | 89/78 |
| Diameter of left gastric vein, mm | 4.9 (2.8–13.9) |
| Diameter of splenorenal shunt, mm | 8.1 (6.7–23.1) |
| Esophagogastric varices, F1/ F2 | 41/7 |
| Gastric varices, F1/F2 | 1/2 |
| DAA regimen, n | |
| Daclatasvir/asunaprevir | 81 |
| Sofosbuvir /ledipasvir | 31 |
| Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir | 16 |
| Elbasvir/grazoprevir | 6 |
| Daclatasvir/asunaprevir/beclabuvir | 1 |
| Sofosbuvir + ribavirin | 19 |
| Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir | 16 |
| Category | Univariate Analysis p-Value | Multivariate Analysis HR (95% CI) p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, <70/70≤ years | 0.559 | – | – |
| Sex, male/female | 0.649 | – | – |
| Body mass index, <23/23≤ kg/m2 | 0.562 | – | – |
| Total bilirubin, <1.0/1.0≤ mg/dL | 0.656 | – | – |
| Aspartate aminotransferase, <30/30≤ IU/L | 0.317 | – | – |
| Alanine aminotransferase, <20/20≤ IU/L | 0.258 | – | – |
| Albumin, <4.2/4.2≤ g/dL | 0.086 | – | – |
| Total cholesterol, <170/170≤ mg/dL | 0.382 | – | – |
| Ammonia, <40/40≤ μg/dL | 0.426 | – | – |
| Platelet count, <11.0/11.0≤ ×104/μL | <0.001 | 3.769 (1.424–9.977) | 0.008 |
| Prothrombin activity, <80/80≤ % | 0.351 | – | – |
| Alfa-fetoprotein, <5.0/5.0≤ ng/mL | 0.763 | – | – |
| FIB-4 index, <4.39/4.39≤ | 0.482 | – | – |
| ALBI score, <–2.82/–2.82≤ | 0.095 | – | – |
| Liver stiffness measurement, <18.0/18.0≤ kPa | <0.001 | 4.834 (1.706–10.794) | 0.006 |
| Total bile acid, <33.0/33.0≤ µmol/L | <0.001 | 3.341 (1.350–8.173) | 0.009 |
| Autotaxin, <1.9/1.9≤ mg/L | 0.008 | 1.921 (0.685–5.832) | 0.286 |
| Past history of HCC treatment *, yes/no | 0.022 | 1.532 (0.523–4.386) | 0.485 |
| Diameter of left gastric vein, <5.0/5.0≤ mm | <0.001 | 5.891(2.596–14.228) | <0.001 |
| Diameter of splenorenal shunt, <8.0/8.0≤ mm | 0.051 | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagaoki, Y.; Yamaoka, K.; Fujii, Y.; Uchikawa, S.; Fujino, H.; Ono, A.; Murakami, E.; Kawaoka, T.; Miki, D.; Aikata, H.; et al. Useful Predictor for Exacerbation of Esophagogastric Varices after Hepatitis C Virus Eradication by Direct-Acting Antivirals. Livers 2024, 4, 352-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4030025
Nagaoki Y, Yamaoka K, Fujii Y, Uchikawa S, Fujino H, Ono A, Murakami E, Kawaoka T, Miki D, Aikata H, et al. Useful Predictor for Exacerbation of Esophagogastric Varices after Hepatitis C Virus Eradication by Direct-Acting Antivirals. Livers. 2024; 4(3):352-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4030025
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagaoki, Yuko, Kenji Yamaoka, Yasutoshi Fujii, Shinsuke Uchikawa, Hatsue Fujino, Atsushi Ono, Eisuke Murakami, Tomokazu Kawaoka, Daiki Miki, Hiroshi Aikata, and et al. 2024. "Useful Predictor for Exacerbation of Esophagogastric Varices after Hepatitis C Virus Eradication by Direct-Acting Antivirals" Livers 4, no. 3: 352-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4030025
APA StyleNagaoki, Y., Yamaoka, K., Fujii, Y., Uchikawa, S., Fujino, H., Ono, A., Murakami, E., Kawaoka, T., Miki, D., Aikata, H., Hayes, C. N., Tsuge, M., & Oka, S. (2024). Useful Predictor for Exacerbation of Esophagogastric Varices after Hepatitis C Virus Eradication by Direct-Acting Antivirals. Livers, 4(3), 352-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4030025








