Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoclusters for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Toxic Metal Ions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Coffee Extraction
2.3. CSE-AgNCs Synthesis
2.4. Sensing Procedure
3. Results
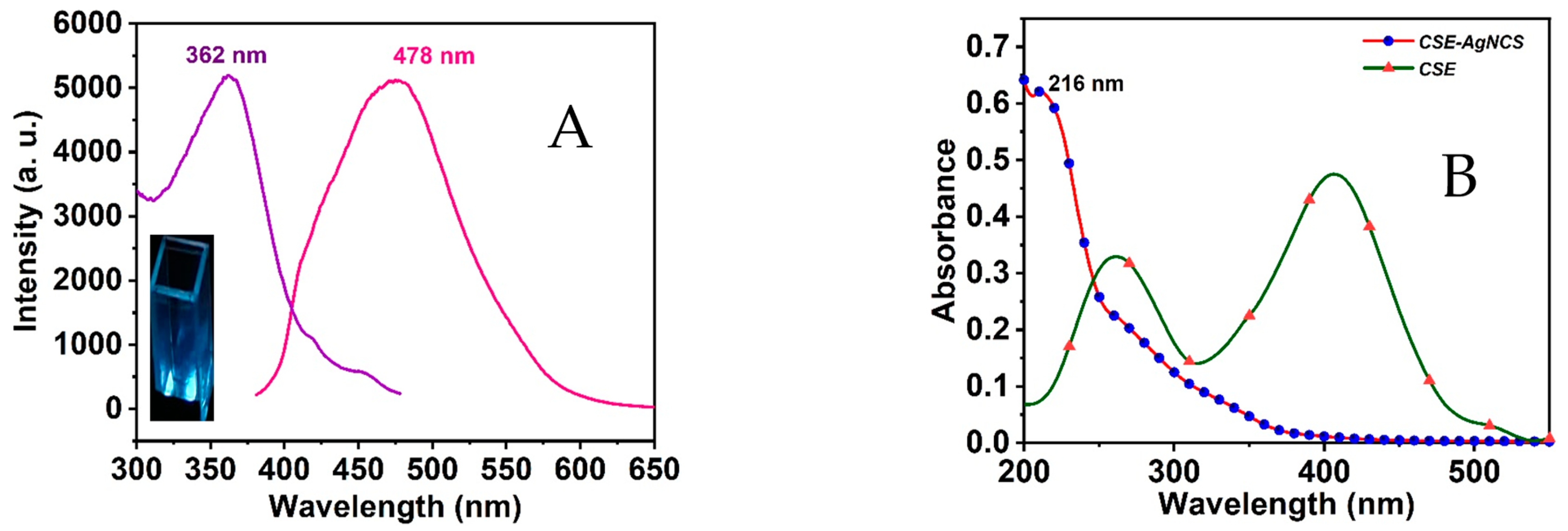
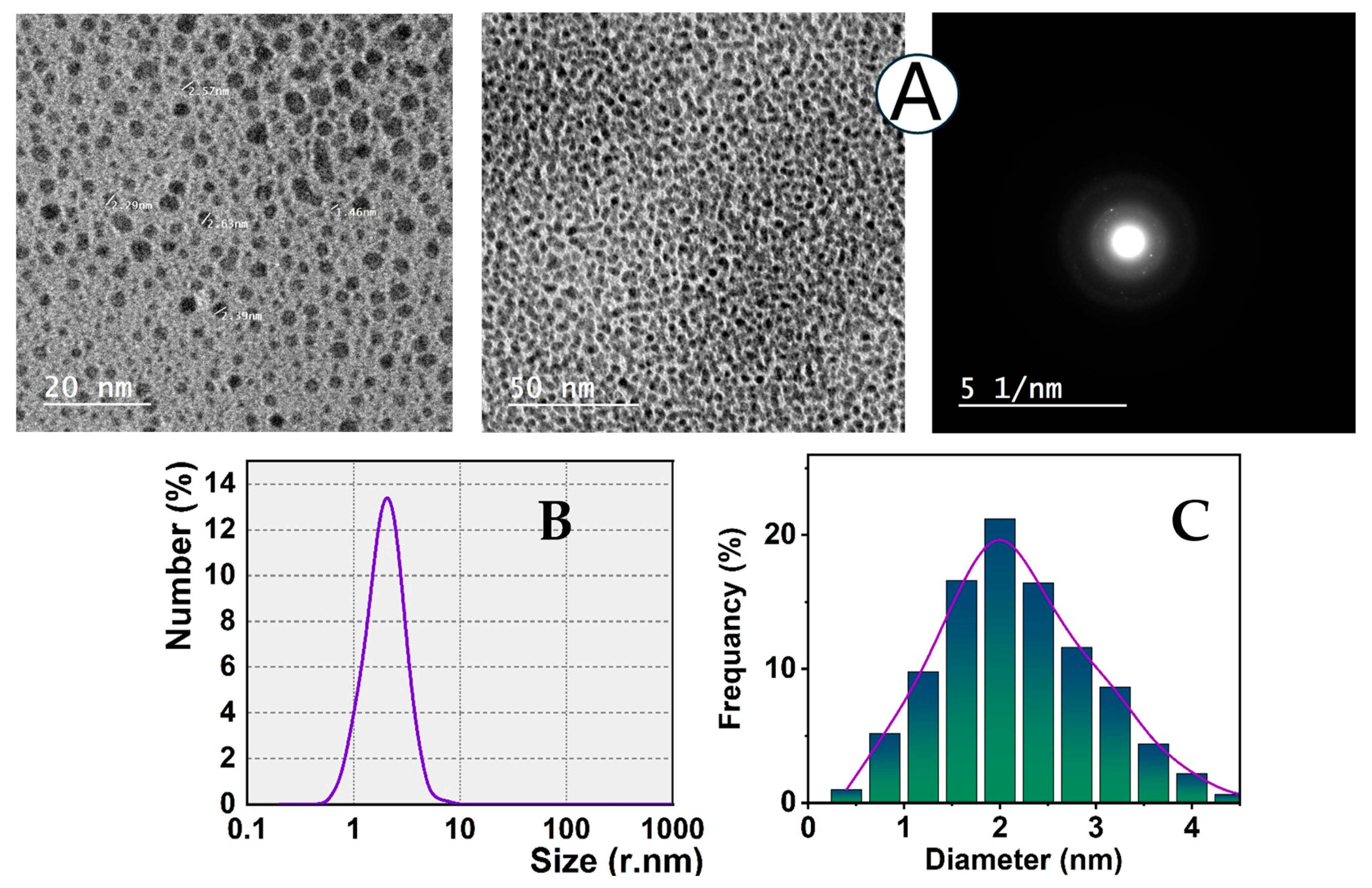
3.1. CSE-AgNCs Preparation
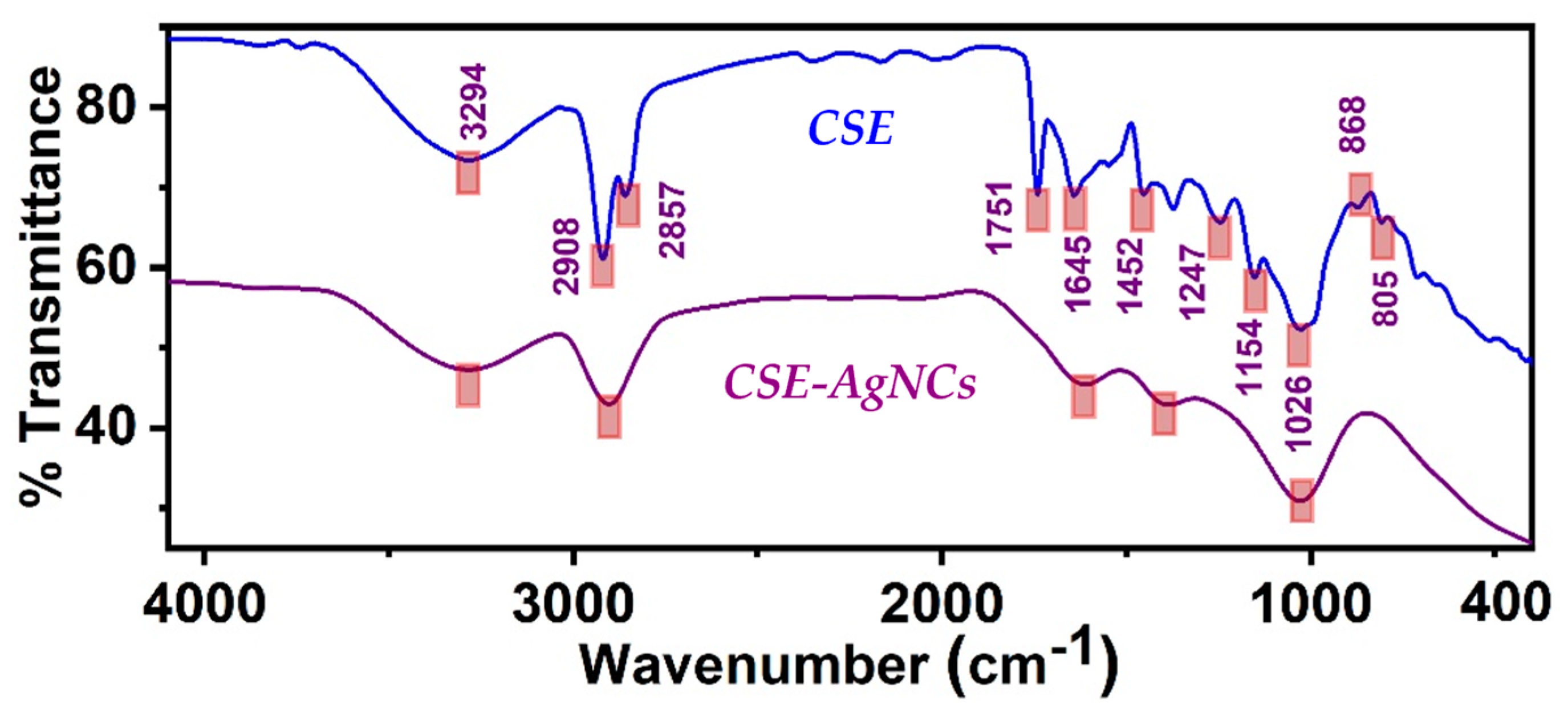
3.2. FT-IR Analyses
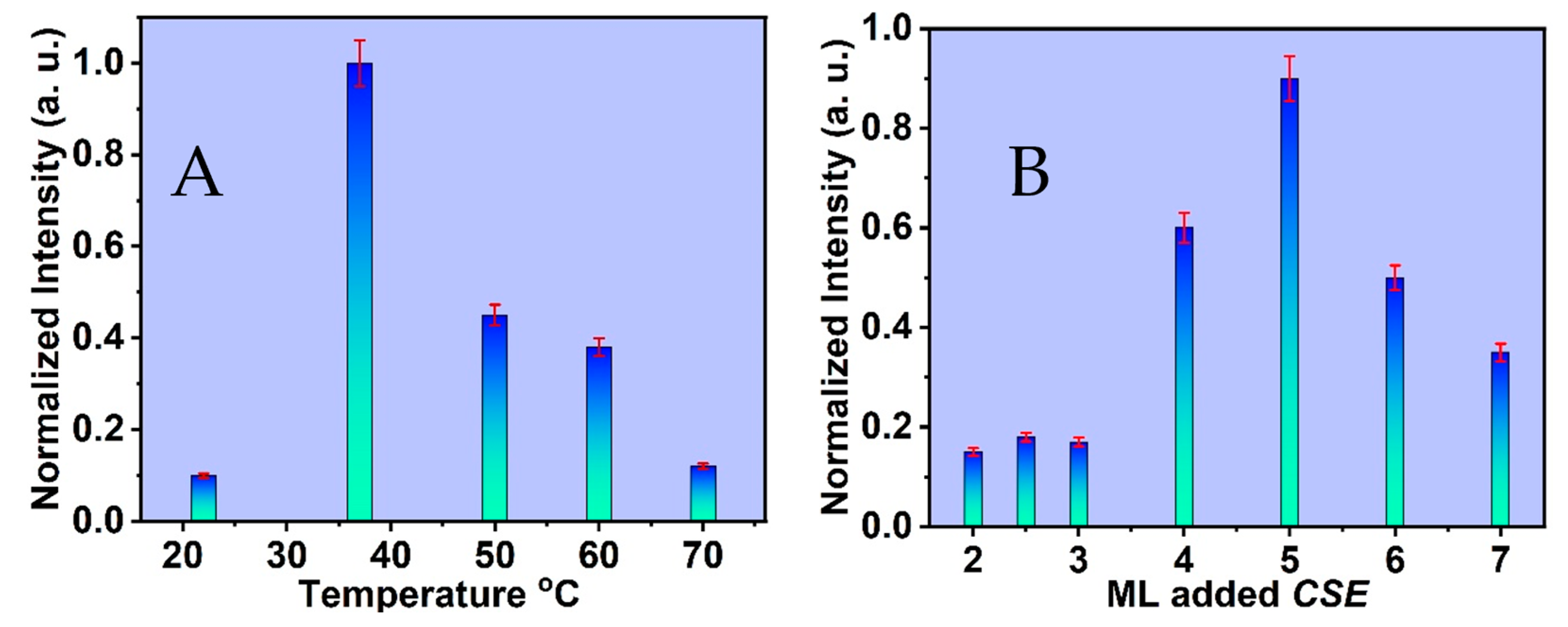
3.3. Optimum Conditions
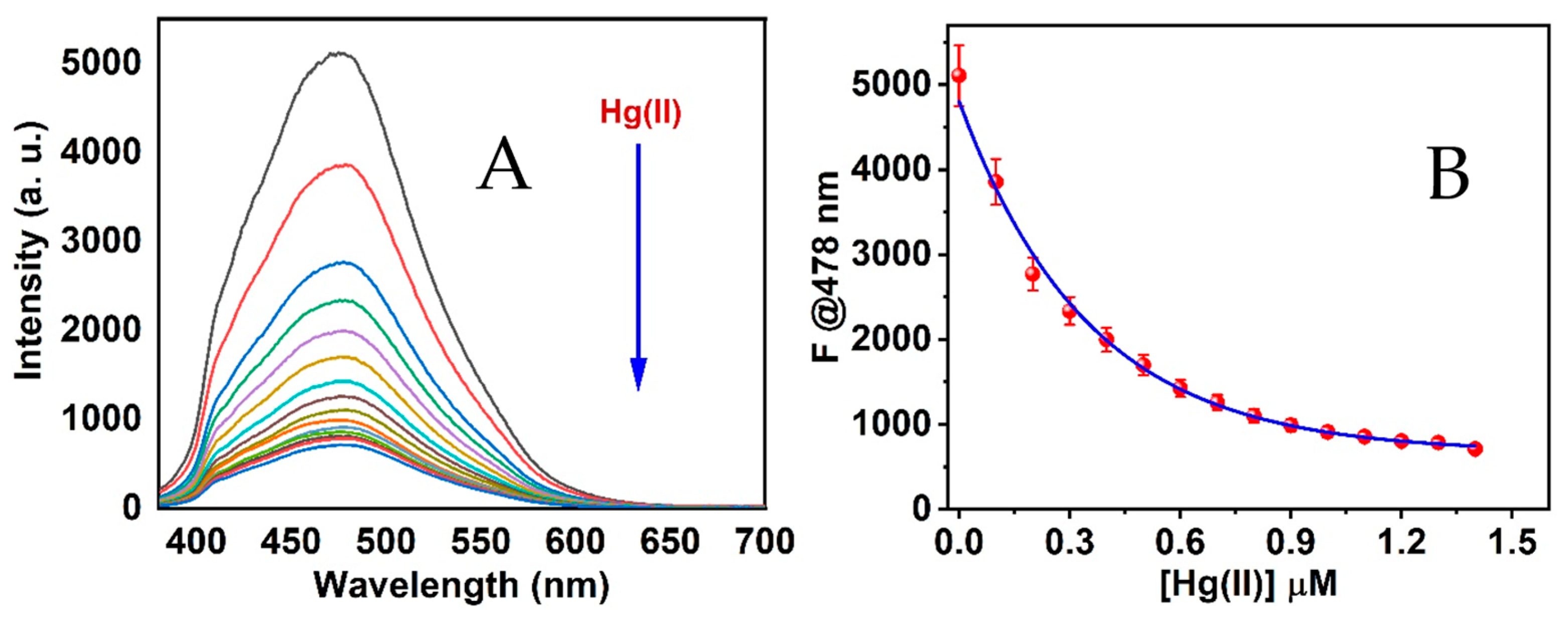
3.4. CSE-AgNCs Reactivity
3.5. Sensing Mechanism
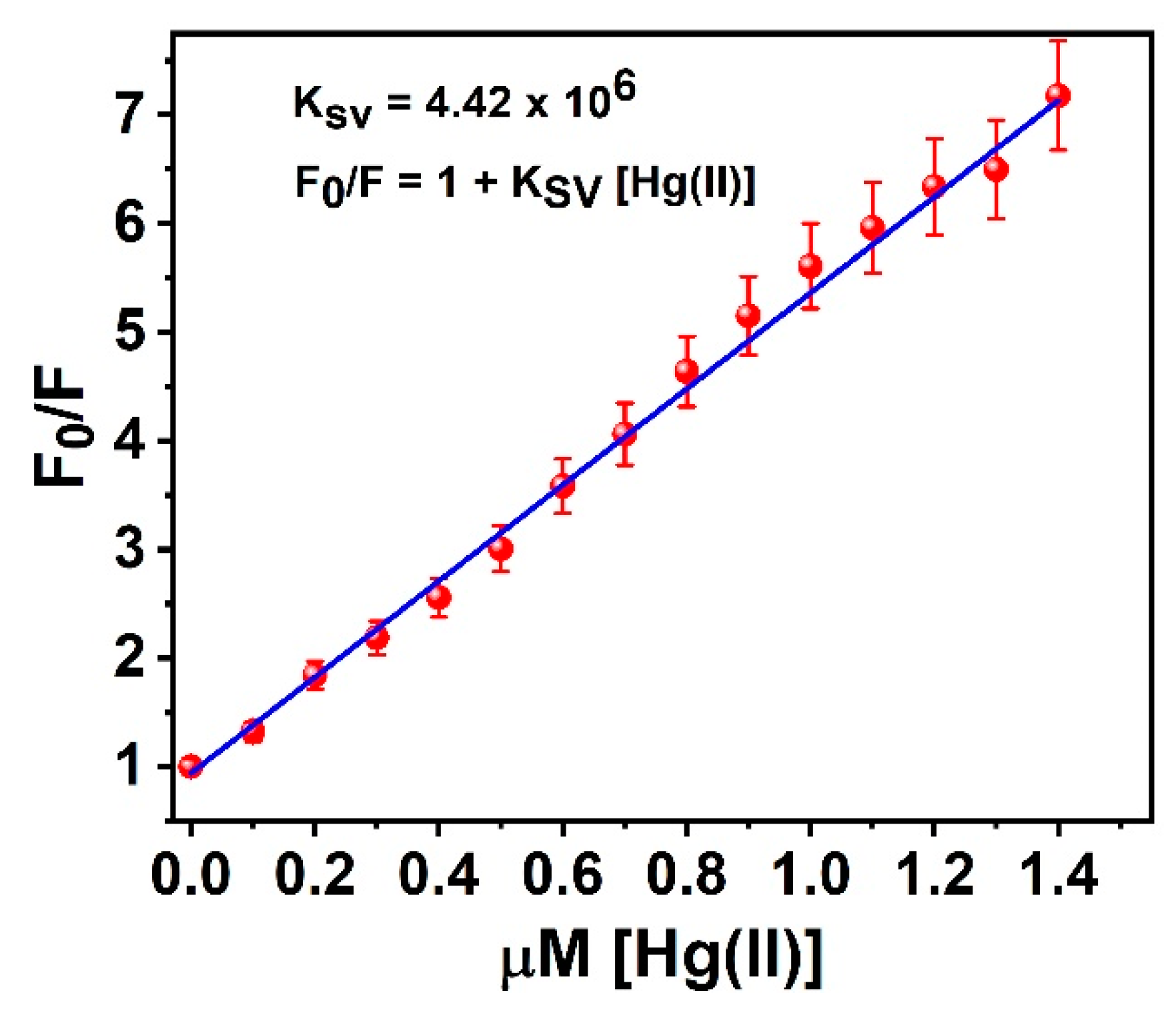
3.6. Binding Constant
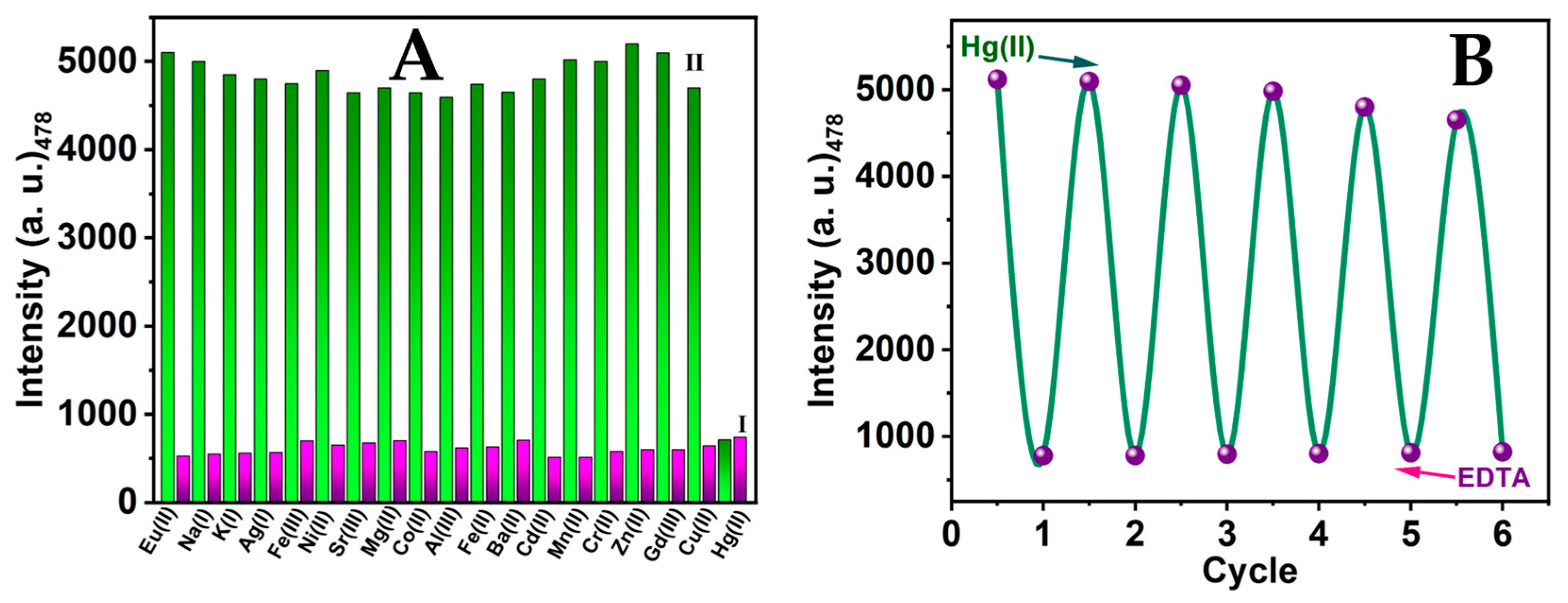
3.7. CSE-AgNCs Selectivity
3.8. Environmental Application
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baimenov, A.Z.; Berillo, D.A.; Moustakas, K.; Inglezakis, V.J. Efficient removal of mercury (II) from water using cryogels and comparison to commercial adsorbents under environmentally relevant conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gworek, B.; Dmuchowski, W.; Baczewska-Dąbrowska, A.H. Mercury in the terrestrial environment: A review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusset, F.; Reynolds, S.J.; Carravieri, A.; Amouroux, D.; Asensio, O.; Dickey, R.C.; Fort, J.; Hughes, B.J.; Paiva, V.H.; Ramos, J.A.; et al. A century of mercury: Ecosystem-wide changes drive increasing contamination of a tropical seabird species in the South Atlantic Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sulaiti, M.M.; Soubra, L.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. The causes and effects of mercury and methylmercury contamination in the marine environment: A review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2022, 8, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.N.; Tangpong, J.; Rahman, M.M. Toxicodynamics of lead, cadmium, mercury and arsenic-induced kidney toxicity and treatment strategy: A mini review. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulaikhah, S.T.; Wahyuwibowo, J.; Pratama, A.A. Mercury and its effect on human health: A review of the literature. Int. J. Public Health Sci. 2020, 9, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Alminderej, F.M.; Messaoudi, S.; Saleh, S.M. Ratiometric ultrasensitive optical chemisensor film based antibiotic drug for Al(III) and Cu(II) detection. Talanta 2021, 221, 121412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; Ali, R.; Hegazy, M.E.F.; Alminderej, F.M.; Mohamed, T.A. The natural compound chrysosplenol-D is a novel, ultrasensitive optical sensor for detection of Cu(II). J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 302, 112558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; Ali, R.; Alminderej, F.; Ali, I.A. Ultrasensitive optical chemosensor for Cu(II) detection. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 2019, 7381046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroua, L.M.; Ali, R.; Albadri, A.E.; Messaoudi, S.; Alminderej, F.M.; Saleh, S.M. A new, extremely sensitive, turn-off optical sensor utilizing Schiff base for fast detection of Cu(II). Biosensors 2023, 13, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazri, N.A.A.; Azeman, N.H.; Luo, Y.; Bakar, A.A.A. Carbon quantum dots for optical sensor applications: A review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 139, 106928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendler-Neumark, A.; Bisker, G. Fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotubes for protein detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.; Alminderej, F.M.; Saleh, S.M. A simple, quantitative method for spectroscopic detection of metformin using gold nanoclusters. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 241, 118744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.; Ali, I.A.; Messaoudi, S.; Alminderej, F.M.; Saleh, S.M. An effective optical chemosensor film for selective detection of mercury ions. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; El-Sayed, W.A.; El-Manawaty, M.A.; Gassoumi, M.; Ali, R. An eco-friendly synthetic approach for copper nanoclusters and their potential in lead ions sensing and biological applications. Biosensors 2022, 12, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; Ali, R.; Wolfbeis, O.S. New silica and polystyrene nanoparticles labeled with longwave absorbing and fluorescent chameleon dyes. Microchim. Acta 2011, 174, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; Elkady, E.M.; Ali, R.; Alminderej, F.; Mohamed, T.A. Novel chemical sensor for detection Ca(II) ions based on ferutinin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 205, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Ghannay, S.; Messaoudi, S.; Alminderej, F.M.; Aouadi, K.; Saleh, S.M. A reversible optical sensor film for mercury ions discrimination based on isoxazolidine derivative and exhibiting pH sensing. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, M.; Zhang, X.A.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Saleh, S.M.; Wang, X.D. Fluorescent proteins as efficient tools for evaluating the surface PEGylation of silica nanoparticles. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2017, 5, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; Ali, R.; Algreiby, A.; Alfeneekh, B.; Ali, I.A. A novel organic chromo-fluorogenic optical sensor for detecting chromium ions. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Saleh, S.M. Design a Friendly Nanoscale Chemical Sensor Based on Gold Nanoclusters for Detecting Thiocyanate Ions in Food Industry applications. Biosensors 2024, 14, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M.; Rafiq, M.; Hanif, M. Organic material based fluorescent sensor for Hg2+: A brief review on recent development. J. Fluoresc. 2017, 27, 31–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; Akkaya, E.U.; Yoon, J.; James, T.D. Fluorescent chemosensors: The past, present and future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7105–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Alfeneekh, B.; Chigurupati, S.; Saleh, S.M. Green synthesis of pregabalin-stabilized gold nanoclusters and their applications in sensing and drug release. Arch. Der Pharm. 2022, 355, 2100426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Saleh, S.M.; Aly, S.M. Fluorescent gold nanoclusters as pH sensors for the pH 5 to 9 range and for imaging of blood cell pH values. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3309–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, L.; Ma, C.; Gu, J.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G. Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Ag Nanoclusters for Detecting Cu2+ Ions and Its “Switch-On” Sensing Application for GSH. J. Spectrosc. 2021, 2021, 8829654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yourston, L.E.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A.V. Micro RNA sensing with green emitting silver nanoclusters. Molecules 2020, 25, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Shen, W.; Cui, H. Highly chemiluminescent silver nanoclusters with a dual catalytic center. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 6549–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bi, Y.; Zhao, H.; Shi, L.; Zhang, N.; Xin, X. In situ synthesis of well-dispersed silver nanoparticles from silver nanoclusters hydrogel for catalytic reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 683, 161759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, M.; Gao, P.; Zhang, G.; Shi, L.; Yuan, M.; Shuang, S. The synthesis of high bright silver nanoclusters with aggregation-induced emission for detection of tetracycline. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 129009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Wang, W.; Li, D.; Xu, S.; Sun, Y.; Lin, L.; Ma, L.; Li, J.; Li, L. Green preparation of silver nanocluster composite AgNCs@CF-g-PAA and its application: 4-NP catalytic reduction and hydrogen production. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 11807–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatoon, U.T.; Velidandi, A.; Rao, G.N. Sodium borohydride mediated synthesis of nano-sized silver particles: Their characterization, anti-microbial and cytotoxicity studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 294, 126997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhao, R.; Li, H.; Long, W.; Xu, W.; Guo, M.; Zhang, X. Atomically precise silver clusterzymes protect mice from radiation damages. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Aparicio, T.; Li, M.; Leong, K.W.; Zha, S.; Gautier, J. Inhibition of DNA replication initiation by silver nanoclusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 5074–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yan, Q.; Cao, S.; Wang, L.; Luo, S.H.; Lv, M. Inhibition of bacteria in vitro and in vivo by self-assembled DNA-silver nanocluster structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 41809–41818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediani, A.; Kamal, N.; Lee, S.Y.; Abas, F.; Farag, M.A. Green extraction methods for isolation of bioactive substances from coffee seed and spent. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2023, 52, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, M.N. Chlorogenic acids. In Coffee, 1 (Chemistry); Clarke, R.J., Macrae, R., Eds.; Elsevier Applied Science Publ.: London, UK, 1985; pp. 153–202. [Google Scholar]
- Schrader, K.; Kiehne, A.; Engelhardt, U.H.; Maier, H.G. Determination of chlorogenic acids with lactones in roasted coffee. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1996, 71, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paulis, T.; Schmidt, D.E.; Bruchey, A.K.; Kirby, M.T.; McDonald, M.P.; Commers, P.; Lovinger, D.M.; Martin, P.R. Dicinnamoylquinides in roasted coffee inhibit the human adenosine transporter. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 442, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Ding, Y.; Li, P.; Song, Q.; Wang, G.; Cheng, D. Effects of chlorogenic acid on the binding process of cadmium with bovine serum albumin: Amulti-spectroscopic docking study. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1204, 127531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska, M.; Sienkiewicz-Gromiuk, J.; Świderski, G.; Pietryczuk, A.; Cudowski, A.; Lewandowski, W. Zn(II) complex of plant phenolic chlorogenic acid: Antioxidant, antimicrobial and structural studies. Materials 2020, 13, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.; Matei, M.F.; Subedi, P.; Kuhnert, N. Does roasted coffee contain chlorogenic acid lactones or/and cinnamoylshikimate esters? Food Res. Int. 2014, 61, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, A.; Gholap, A.V. Characterization and determination of chlorogenic acids (CGA) in coffee beans by UV-Vis spectroscopy. Afr. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 3, 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- Moores, R.G.; McDermott, D.L.; Wood, T.R. Determination of chlorogenic acid in coffee. Anal. Chem. 1948, 20, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; Ali, R.; nd Elshaarawy, R.F. A ratiometric and selective fluorescent chemosensor for Ca(II) ions based on a novel water-soluble ionic Schiff-base. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 68709–68718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, J.; Cai, H.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Zong, H.; Yin, Y. Carbon dots/Ag nanoclusters-based fluorescent probe for ratiometric and visual detection of Cu2+. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 945, 169227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Y.; Deng, F.; Zhao, J.J.; He, J.; Ma, M.G.; Xu, F.; Sun, R.C. Environmentally friendly ultrosound synthesis and antibacterial activity of cellulose/Ag/AgCl hybrids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capek, P.; Paulovičová, E.; Matulová, M.; Mislovičová, D.; Navarini, L.; Liverani, F.S. Coffea arabica instant coffee-chemical view and immunomodulating properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, N.M.M.; Pastrana, J.M.; Lagos, Y.; Lozada, J.J. Evaluation of mercury (Hg2+) adsorption capacity using exhausted coffee waste. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 10, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Pujol, D.; Olivella, M.À.; De la Torre, F.; Fiol, N.; Poch, J.; Villaescusa, I. The role of exhausted coffee compounds on metal ions sorption. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, D.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Glutathione capped silver nanoclusters-based fluorescent probe for highly sensitive detection of Fe3+. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandalakshmi, K.; Venugobal, J.; Ramasamy, V.J.A.N. Characterization of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis method using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Jiang, Z. Fabrication of antimicrobial bacterial cellulose–Ag/AgCl nanocomposite using bacteria as versatile biofactory. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; Ali, R.; Hirsch, T.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Detection of biotin-avidin affinity binding by exploiting a self-referenced system composed of upconverting luminescent nanoparticles gold nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 4603–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, A. Coffee constituents. In Coffee: Emerging Health Effects and Disease Prevention; Chu, Y.-F., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar]
- Pujol, D.; Liu, C.; Gominho, J.; Fiol, N.; Villaescusa, I.; Pereira, H. The chemical composition of exhausted coffee waste. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 50, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthi, G.; Park, M. Synthesis of metal nanoclusters and their application in Hg2+ ions detection: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; Almotiri, M.K.; Ali, R. Green synthesis of highly luminescent gold nanoclusters and their application in sensing Cu(II) and Hg(II). J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2022, 426, 113719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Lang, T.; Saleh, S.M.; Meier, R.J.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Optical sensing scheme for carbon dioxide using a solvatochromic probe. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2846–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, D.; Banerjee, A.; Sahana, A.; Guha, S.; Lohar, S.; Adhikari, S.S.; Das, D. 9-Acridone-4-carboxylic acid as an efficient Cr(III) fluorescent sensor: Trace level detection, estimation and speciation studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaarawy, R.F.; Ali, R.; Saleh, S.M.; Janiak, C. A novel water-soluble highly selective “switch-on” ionic liquid-based fluorescent chemi-sensor for Ca(II). J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, N.; Tajik, M.; Mack, I.; Enck, P. The potential effects of chlorogenic acid the main phenolic components in coffee on health: Acomprehensive review of the literature. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 2215–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Added Hg(II) µM | ICP-MS µM | Found µM | RSD * (%) | Recovery (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral water | 0.10 | 0.103 | 0.0987 | 1.11 | 98.70 |
| 0.70 | 0.705 | 0.692 | 0.89 | 98.85 | |
| 1.40 | 1.429 | 1.386 | 0.79 | 99.00 | |
| Tap water | 0.10 | 0.116 | 0.098 | 0.097 | 97.00 |
| 0.70 | 0.707 | 0.683 | 0.88 | 97.57 | |
| 1.40 | 1.418 | 1.387 | 0.85 | 99.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleh, S.M.; Altaiyah, S.; Ali, R. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoclusters for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Toxic Metal Ions. Analytica 2025, 6, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6020015
Saleh SM, Altaiyah S, Ali R. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoclusters for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Toxic Metal Ions. Analytica. 2025; 6(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleh, Sayed M., Shahad Altaiyah, and Reham Ali. 2025. "Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoclusters for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Toxic Metal Ions" Analytica 6, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6020015
APA StyleSaleh, S. M., Altaiyah, S., & Ali, R. (2025). Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoclusters for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Toxic Metal Ions. Analytica, 6(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6020015







