Cyclopalladated Compounds with Bulky Phosphine (dppm): Synthesis, Characterization, and X-ray Diffraction †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
3. Experimental Part
Preparation of [Pd{R-C6H3C(H)=NCy]{PPh2CH2PPh2}[PF6] {R= 3-CHO, 4-CHO}. (1a, 1b)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albrecht, M. Cyclometalation using d-block transition metals: Fundamental aspects and recent trends. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 576–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiman, J.P.; Dubeck, M. The preparation of cyclopentadienyl [o-(phenylazo) phenyl] nickel. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 1544–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnis, S.S.; Burford, N. Phosphine complexes of lone pair bearing Lewis acceptors. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wei, X.J.; Handelmann, J.; Seitz, A.K.; Rodstein, I.; Gessner, V.H.; Gooßen, L.J. Coupling of Reformatsky Reagents with Aryl Chlorides Enabled by Ylide-Functionalized Phosphine Ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 6778–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horky, F.; Cisarova, I.; Stepnicka, P. Synthesis, Reactivity, and Coordination of Semihomologous dppf Congeners Bearing Primary Phosphine and Primary Phosphine Oxide Groups. Organometallics 2021, 40, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudret, B.; Delavaux, B.; Poilblanc, R. Bisdiphenylphosphinomethane in dinuclear complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1988, 86, 191–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, V.T.; Icsel, C.; Aygun, M.; Erkisa, M.; Ulukaya, E. Pd(II) and Pt(II) saccharinate complexes of bis (diphenylphosphino) propane/butane: Synthesis, structure, antiproliferative activity and mechanism of action. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odachowski, M.; Marschner, C.; Blom, B. A review on 1, 1-bis (diphenylphosphino) methane bridged homo-and heterobimetallic complexes for anticancer applications: Synthesis, structure, and cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 204, 112613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghipour, A.; Sayadi, M.; Sedghi, A.; Sabounchei, S.J.; Babaee, H.; Notash, B. A comparative study of palladium-based coordination compounds with bidentate (N, N, P, P and P, O) ligands; Design, synthesis, X-ray structural, catalytic activity and DFT studies. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2021, 515, 120039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansell, S.M. Catalytic applications of small bite-angle diphosphorus ligands with single-atom linkers. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 15157–15174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowson, G.R.; Haddow, M.F.; Lee, J.; Wingad, R.L.; Wass, D.F. Catalytic conversion of ethanol into an advanced biofuel: Unprecedented selectivity for n-butanol. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9005–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prades, A.; Fernández, M.; Pike, S.D.; Willis, M.C.; Weller, A.S. Well-Defined and Robust Rhodium Catalysts for the Hydroacylation of Terminal and Internal Alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8520–8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Willis, M.C. Enantioselective Three-Component Assembly of β′-Aryl Enones Using a Rhodium-Catalyzed Alkyne Hydroacylation/Aryl Boronic Acid Conjugate Addition Sequence. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 2734–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabounchei, S.J.; Ahmadi, M. An efficient protocol for copper-and amine-free Sonogashira reactions catalyzed by mononuclear palladacycle complexes containing bidentate phosphine ligands. Catal. Commun. 2013, 37, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabounchei, S.J.; Hosseinzadeh, M. C(sp2)–C(sp2) cross-coupling reaction catalyzed by a palladacycle phosphine complex: A simple and sustainable protocol in aqueous media. J. Chem. Sci. 2015, 127, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A.; Naghipour, A.; Babaee, H.; Notash, B. Synthesis, crystal structure study and high efficient catalytic activity of di-μbromo-trans–dibromobis [(benzyl)(4-methylphenyl)(phenyl) phosphine] dipalladium (II) in Suzuki–Miyaura and Heck–Mizoroki C–C coupling reactions. Polyhedron 2016, 119, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B. Chelating diphosphine–palladium (II) dihalides; outstandingly good catalysts for Heck reactions of aryl halides. Chem. Commun. 1998, 17, 1863–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, J.; Pfeffer, M. Palladacycles: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, G.C. The development of versatile methods for palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions of aryl electrophiles through the use of P (t-Bu)3 and PCy3 as ligands. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A. New synthetic transformations via organoboron compounds. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Song, M.; Mak, T.C.; Wu, Y. Highly efficient cyclopalladated ferrocenylimine catalyst for Suzuki cross-coupling reaction of 3-pyridylboronic pinacol ester with aryl halides. J. Organomet. Chem. 2006, 691, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregosin, P.S.; Kunz, R.W. Chemical Shifts. In 31P and 13C NMR of Transition Metal Phosphine Complexes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1979; pp. 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Vila, J.M.; Gayoso, M.; Pereira, M.T.; López, M.; Alonso, G.; Fernández, J.J. Cyclometallated complexes of PdII and MnI with N, N-terephthalylidenebis (cyclohexylamine). J. Organomet. Chem. 1993, 445, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
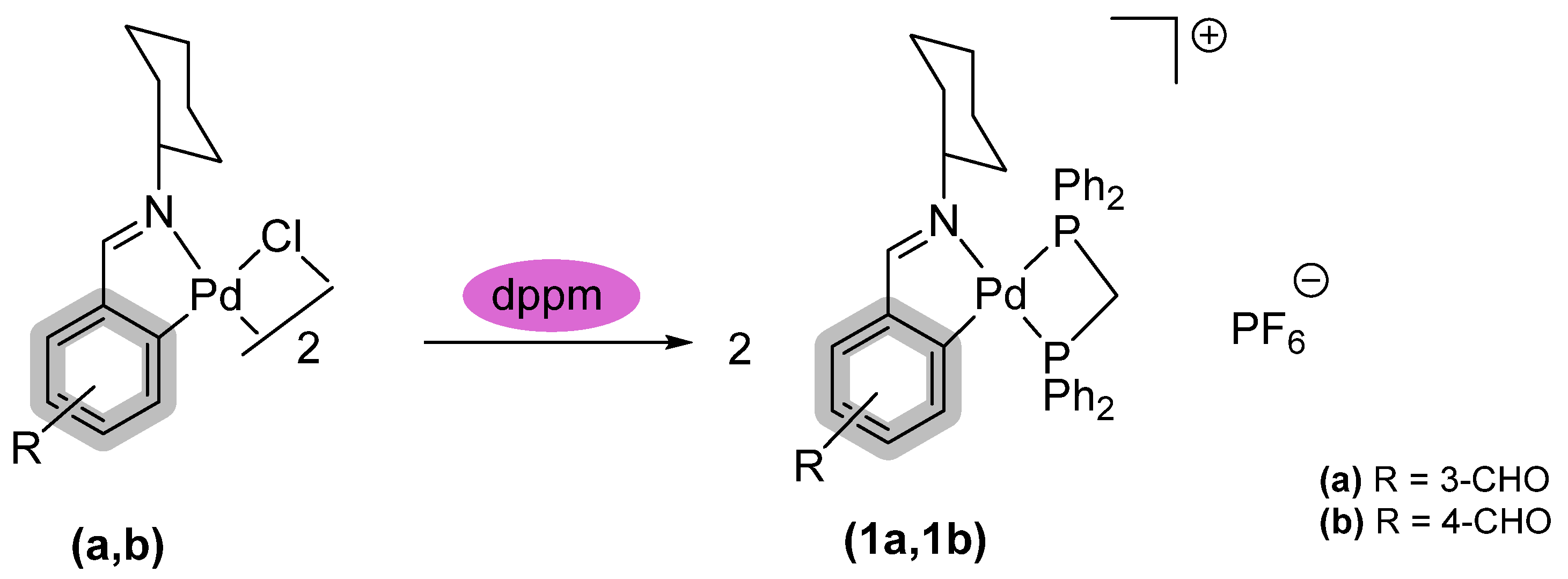
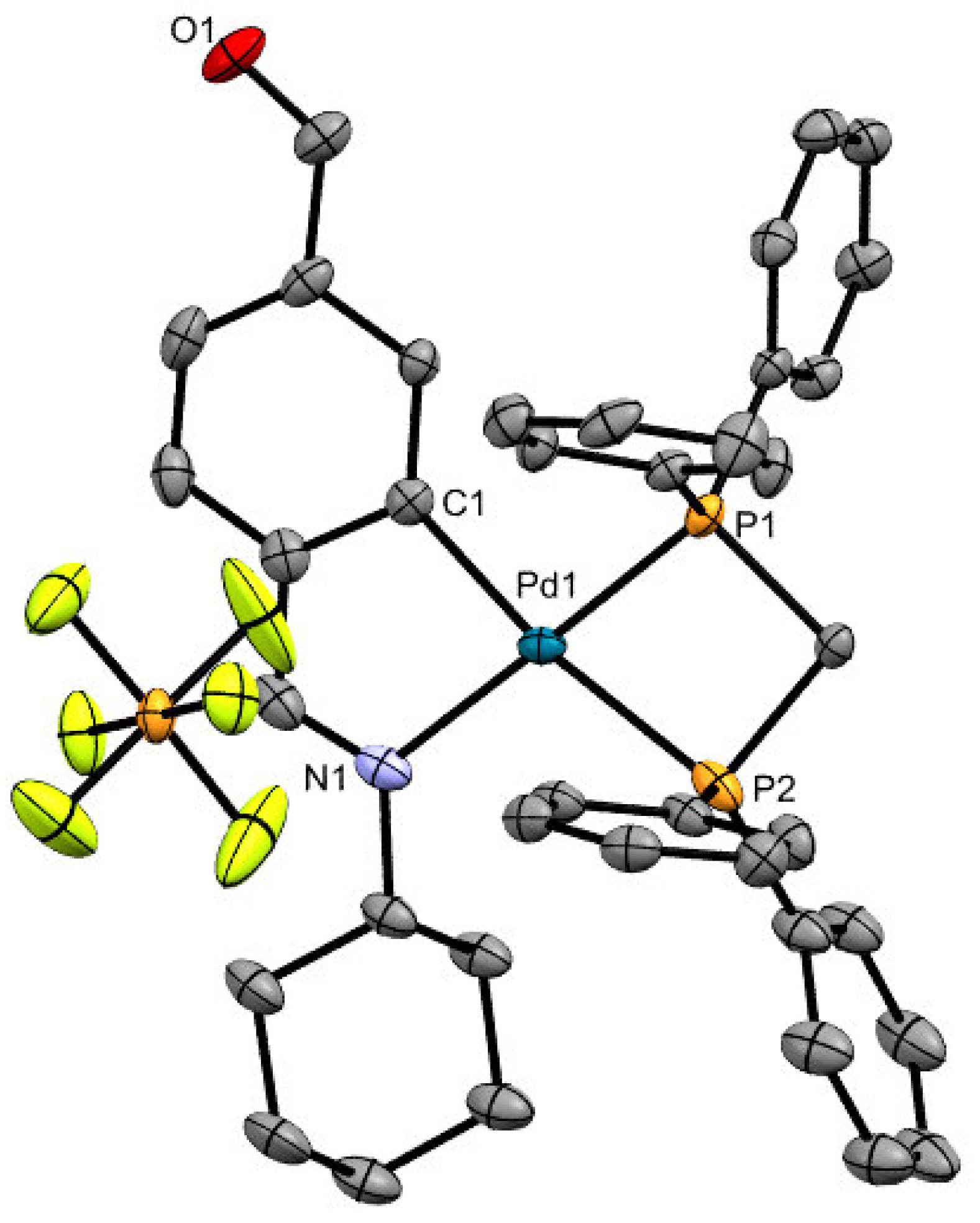
| Pd(1)-N(1) | 2.097(4) | C(1)-Pd(1)-N(1) | 81.02(16) |
| Pd(1)-C(1) | 2.025(4) | P(1)-Pd(1)-N(1) | 175.10(10) |
| Pd(1)-P(1) | 2.248(11) | N(1)-Pd(1)-P(2) | 109.25(11) |
| Pd(1)-P(2) | 2.463(13) | P(1)-Pd(1)-C(1) | 98.97(12) |
| P(1)-Pd(1)-P(2) | 70.15(4) | C(1)-Pd(1)-P(2) | 167.36(12) |
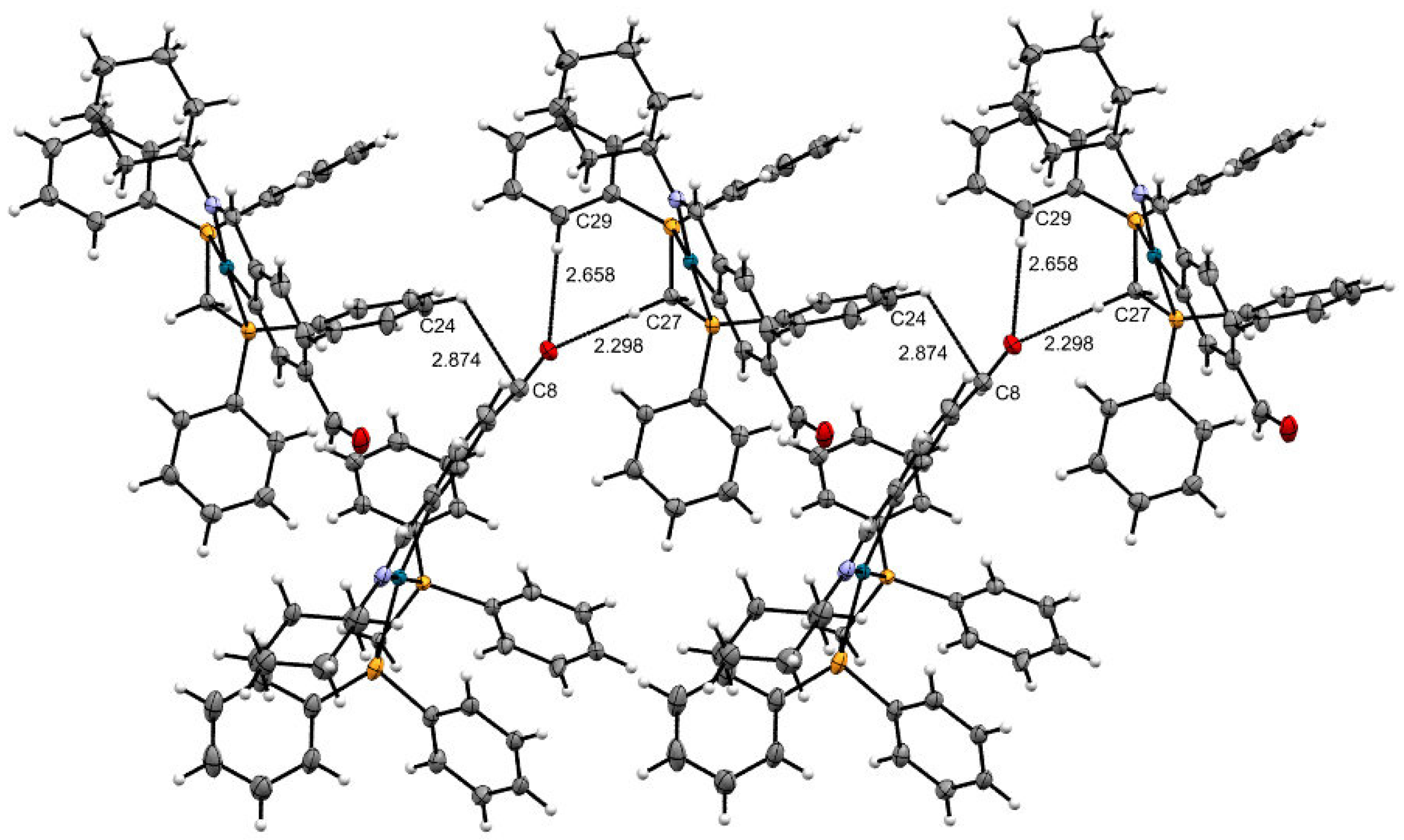
| C−H···Caryl | C−H | H···Caryl | C−Caryl | <(C−H···Caryl)º |
| C8−H24−C24 | 2.874 | 0.95 | 3.191 | 100.78 |
| C−H···O1 | C–H | H···O | C–O | <(C−H···O)º |
| C27−H27a−O1 | 0.99 | 2.298 | 3.337 | 128.91 |
| C29−H29−O1 | 0.95 | 2.658 | 3.288 | 178.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janabi, B.A.; Ortigueira, J.M.; Vila, J.M. Cyclopalladated Compounds with Bulky Phosphine (dppm): Synthesis, Characterization, and X-ray Diffraction. Chem. Proc. 2022, 12, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-26-13563
Janabi BA, Ortigueira JM, Vila JM. Cyclopalladated Compounds with Bulky Phosphine (dppm): Synthesis, Characterization, and X-ray Diffraction. Chemistry Proceedings. 2022; 12(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-26-13563
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanabi, Basma Al, Juan M. Ortigueira, and Jose Manuel Vila. 2022. "Cyclopalladated Compounds with Bulky Phosphine (dppm): Synthesis, Characterization, and X-ray Diffraction" Chemistry Proceedings 12, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-26-13563
APA StyleJanabi, B. A., Ortigueira, J. M., & Vila, J. M. (2022). Cyclopalladated Compounds with Bulky Phosphine (dppm): Synthesis, Characterization, and X-ray Diffraction. Chemistry Proceedings, 12(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-26-13563







