- Proceeding Paper
Computational Screening and Synthesis of Some Isatin-Thiadiazole Hybrids Potentially Targeting Diabetes
- Monika,
- Nishtha Shalmali and
- Priyanshu
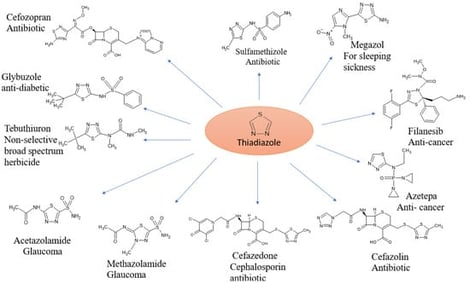
This study explores the design, synthesis and preliminary in silico screening of novel thiadiazole-isatin hybrid derivatives targeting diabetes mellitus. Building on thiadiazole and isatin compounds’ demonstrated antidiabetic potential, the research objectives were to design and synthesize thiadiazole-isatin hybrids and evaluate their antidiabetic potential. The methodology encompassed a literature review, computational screening using “molecular docking, ADME prediction, Lipinski’s rule”, and the synthesis of thiadiazole intermediates from thiosemicarbazide combined with isatin derivatives. The key findings revealed that compounds 2a and 2b exhibit favorable binding affinity with “human aldose reductase, monoglyceride lipase, GLP-1, and alpha-amylase”, satisfying Lipinski’s rule for optimal drug likeness. Docking scores ranged from −10.6 to −7.0 for 2a and −10.2 to −7.0 for 2b. Thiadiazole-isatin derivatives, particularly 2a and 2b, demonstrate promise as antidiabetic agents through multi-enzyme inhibition, warranting pre-clinical and in vitro validation. This research offers a novel therapeutic strategy for diabetes management and potential pharmaceutical lead compounds. Future directions include experimental validation, in vitro and in vivo efficacy studies, and structure–activity relationship exploration, contributing to innovative antidiabetic therapies.
11 November 2025