Journal Description
Chemistry Proceedings
Chemistry Proceedings
is an open access journal dedicated to publishing findings resulting from conferences, workshops, and similar events, in all areas of chemistry. The conference organizers and proceedings editors are responsible for managing the peer review process and selecting papers for conference proceedings.
Latest Articles
Determination of Pesticide Residues in Drinking Water Using the LC-MS/MS Method and Evaluation of the Results for 2023 and 2024
Chem. Proc. 2025, 19(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2025019003 - 20 Jan 2026
Abstract
This study focuses on the determination of pesticide residues in drinking water in Slovakia using the LC-MS/MS method, covering a target list of approximately 90 pesticides selected according to the national drinking water risk assessment. The aim of monitoring is to screen the
[...] Read more.
This study focuses on the determination of pesticide residues in drinking water in Slovakia using the LC-MS/MS method, covering a target list of approximately 90 pesticides selected according to the national drinking water risk assessment. The aim of monitoring is to screen the presence of pesticide substances in various water supply systems and to gain experience for setting higher-quality criteria for the control of drinking water. Drinking water samples were collected in 2023, 2024 and 2025 within the National Monitoring Project of the Presence of Pesticides in Public Water Supplies, including both Large-Supply Areas (>5000 inhabitants—2023) and Small-Supply Areas (500–5000 inhabitants—2024, 2025). A total of 211 samples were measured and evaluated in 2023, compared with 199 samples in 2024. This article presents the evaluation of results for 2023 and 2024, while data for 2025 will be assessed in 2026. The findings contribute to the improved surveillance and quality control of drinking water.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 1st International Online Conference on Separations)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Evaluation of Metal–Organic Framework-Based Adsorbents for Preconcentration of Pesticides from Water Samples
by
Yumi Tenawa, Mai Furukawa, Ikki Tateishi, Hideyuki Katsumata and Satoshi Kaneco
Chem. Proc. 2025, 19(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2025019002 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are porous crystalline materials composed of metal ions and organic ligands. By varying the combinations of metal centers and ligands, their structural properties, adsorption performance, and stability in aqueous environments can be tuned. Owing to these characteristics, MOFs have attracted
[...] Read more.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are porous crystalline materials composed of metal ions and organic ligands. By varying the combinations of metal centers and ligands, their structural properties, adsorption performance, and stability in aqueous environments can be tuned. Owing to these characteristics, MOFs have attracted attention as promising materials for environmental analysis and separation technologies. In this study, several MOFs with different metal ions and ligands were synthesized and evaluated for their adsorption performance for bensulfuron-methyl, a sulfonylurea herbicide. Among the tested MOFs, MIL-53(Al) exhibited the highest recovery. The results indicate that adsorption performance depends on the combination of metal ions and organic ligands.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 1st International Online Conference on Separations)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Synthesis and Structural Confirmation of a Novel 3,6-Dicarbonyl Derivative of 2-Chloropyrazine via Regioselective Dilithiation
by
Priyabrata Roy
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 87; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26696 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A novel 3,6-dicarbonyl-substituted derivative of 2-chloropyrazine has been synthesized for the first time via regioselective dilithiation using lithium 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidide (LiTMP) and subsequent trapping with methyl benzoate. The structure was unambiguously confirmed through Sonogashira coupling and diagnostic NMR analysis, establishing selective substitution at both
[...] Read more.
A novel 3,6-dicarbonyl-substituted derivative of 2-chloropyrazine has been synthesized for the first time via regioselective dilithiation using lithium 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidide (LiTMP) and subsequent trapping with methyl benzoate. The structure was unambiguously confirmed through Sonogashira coupling and diagnostic NMR analysis, establishing selective substitution at both the 3- and 6-positions. This result demonstrates that symmetrical 3,6-functionalization of 2-chloropyrazine is feasible under mild conditions, overcoming long-standing limitations of multiple metalations in electron-deficient heterocycles and opening new pathways for the synthesis of polyfunctional pyrazine frameworks.
Full article

Scheme 1
Open AccessConference Report
Abstracts of the 3rd International Electronic Conference on Catalysis Sciences
by
Evangelos Topakas and Keith Hohn
Chem. Proc. 2025, 17(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2025017013 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
The 3rd International Electronic Conference on Catalysis Sciences (ECCS 2025) was held online from 23–25 May 2025 and was chaired by Prof [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 3rd International Electronic Conference on Catalysis Sciences)
Open AccessConference Report
Abstracts of the 1st International Online Conference on Separations
by
Grzegorz Boczkaj
Chem. Proc. 2025, 19(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2025019001 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
The 1st International Online Conference on Separations (IOCS 2025), organized by MDPI during 15–17 October 2025, brings together researchers, professionals, and industry experts from around the world to explore the latest advancements in the dynamic field of separation science [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 1st International Online Conference on Separations)
Open AccessEditorial
Statement of Peer Review
by
Evangelos Topakas and Keith Hohn
Chem. Proc. 2025, 17(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2025017012 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
In submitting conference proceedings to Chemistry Proceedings, the volume editors of the proceedings certify to the publisher that all papers published in this volume have been subjected to peer review administered by the volume editors [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 3rd International Electronic Conference on Catalysis Sciences)
Open AccessProceeding Paper
LIFE.PTML Model Development Targeting Calmodulin Pathway Proteins
by
Maider Baltasar-Marchueta, Naia López, Sonia Arrasate, Matthew M. Montemore and Humberto González-Díaz
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26890 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Developing predictive models for drug efficacy is challenged by the complexity and heterogeneity of bioassay data. Here, we present LIFE.PTML, which is a methodology integrating drug Lifecycle (L), Information Fusion (IF), Encoding (E), Perturbation Theory (PT), and Machine Learning (ML) to predict compound
[...] Read more.
Developing predictive models for drug efficacy is challenged by the complexity and heterogeneity of bioassay data. Here, we present LIFE.PTML, which is a methodology integrating drug Lifecycle (L), Information Fusion (IF), Encoding (E), Perturbation Theory (PT), and Machine Learning (ML) to predict compound activity across diverse experimental conditions. Using a dataset of 3748 molecule–assay combinations targeting calmodulin (CaM) and related proteins, LIFE.PTML combines chemical and protein descriptors, quantifies experimental variability via perturbation operators, and trains non-linear classifiers, including XGBoost and Gradient Boosting. XGBoost achieved the best performance, with 88.9% test accuracy and an ROC AUC of 0.959, while feature importance analysis highlighted contributions from both drug- and protein-level descriptors. The results demonstrate that LIFE.PTML provides a robust, flexible, and interpretable framework for predictive chemoinformatics, facilitating the integration of multi-source data for drug discovery applications.
Full article
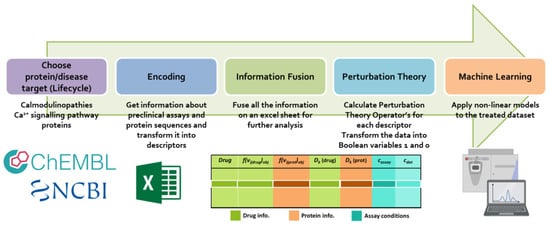
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Therapeutic Potential of 1-Deazapurines as Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors: Molecular Docking and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation
by
Faiza Boukli-Hacene, Hocine Allali, Sabri Ahmed Cherrak, Wassila Soufi and Said Ghalem
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26911 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Type 2 diabetes mellitus remains a critical metabolic disorder requiring novel therapeutic approaches. In this work, a library of 1-deazapurine derivatives was evaluated as α-glucosidase inhibitors through molecular docking with MOE software. The three top-ranked ligands—Methyl 6-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)-3-(2-phenylethyl)imidazo[4,5-b] pyridine-5-carboxylate (–6.1247 kcal/mol), 5-(furan-2-yl)-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-2-phenyl-7- (trifluoromethyl)imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (–5.7030
[...] Read more.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus remains a critical metabolic disorder requiring novel therapeutic approaches. In this work, a library of 1-deazapurine derivatives was evaluated as α-glucosidase inhibitors through molecular docking with MOE software. The three top-ranked ligands—Methyl 6-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)-3-(2-phenylethyl)imidazo[4,5-b] pyridine-5-carboxylate (–6.1247 kcal/mol), 5-(furan-2-yl)-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-2-phenyl-7- (trifluoromethyl)imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (–5.7030 kcal/mol), and 3-[2-phenylethyl]-5-thio phen-2-yl-7-(trifluoromethyl)imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (–5.5403 kcal/mol)—were further validated by molecular dynamics simulations. ADMET and drug-likeness predictions confirmed favourable pharmacokinetic behaviour, gastrointestinal absorption, and oral bioavailability. These findings highlight 1-deazapurines as promising scaffolds for developing new α-glucosidase inhibitors targeting type 2 diabetes.
Full article
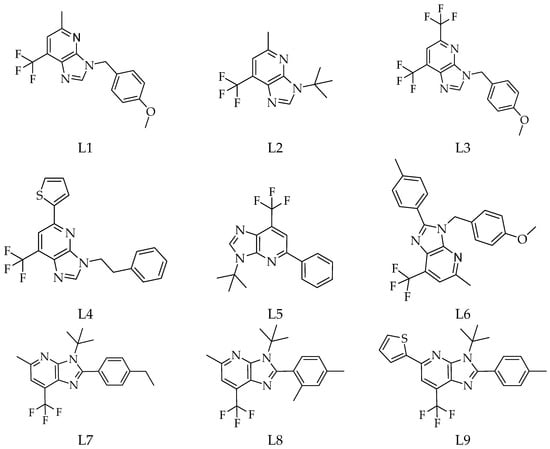
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Chitosan-Based Biosorption: A Sustainable Approach for Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater
by
Imane Lansari, Khadidja Tizaoui and Belkacem Benguella
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26919 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study investigates the application of natural chitosan as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Experimental results showed that Mn(II), Co(II), and Ni(II) ions were effectively retained on the chitosan surface. Kinetic analysis revealed a preferential adsorption
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the application of natural chitosan as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Experimental results showed that Mn(II), Co(II), and Ni(II) ions were effectively retained on the chitosan surface. Kinetic analysis revealed a preferential adsorption order of Co(II) > Mn(II) > Ni(II), following a pseudo-second-order model with rapid kinetics. Equilibrium adsorption capacities were influenced by initial concentration, temperature, and pH. Thermodynamic analysis indicated that the adsorption process was exothermic and physical in nature. Overall, chitosan proved to be a promising and cost-effective adsorbent for water decontamination.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Supramolecular Assemblies Driven by N-H…O and O-H…O Hydrogen Bonding Interactions: Experimental and Theoretical Investigation into the Supramolecular Architectures of Dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones
by
Sunshine Dominic Kurbah
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26921 - 27 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this paper, quantum chemical calculations at the DFT/6-311G (d,p) level of theory have been carried out to study the supramolecular structure of dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones. Theoretical studies such as Hirshfeld surface analysis, MEPS (molecular electrostatic potential surface), and HOMO–LUMO calculation were also carried out
[...] Read more.
In this paper, quantum chemical calculations at the DFT/6-311G (d,p) level of theory have been carried out to study the supramolecular structure of dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones. Theoretical studies such as Hirshfeld surface analysis, MEPS (molecular electrostatic potential surface), and HOMO–LUMO calculation were also carried out to obtain the energy gap and to determine the kinetic stability and chemical reactivity. The crystal structure of dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones shows the present of N-H…O and O-H…O hydrogen bonding interactions. The N-H…O bond lengths are 2.102 Å and 2.037 Å, respectively. The theoretical hydrogen bonding interactions were also compared with the available experimental data and found to be closely related.
Full article
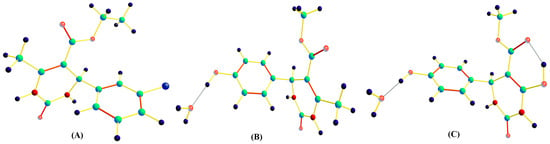
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Structure-Based Design and Synthesis of Novel Hybrid Molecules Derived from Anthranilic Acid as Drug Candidates
by
Miglena Milusheva, Vera Gledacheva, Mihaela Stoyanova, Mina Todorova, Iliyana Stefanova and Stoyanka Atanasova Nikolova
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26686 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hybrid molecules, integrating multiple pharmacophores within a single scaffold, represent a modern strategy in drug discovery, offering improved selectivity and safety. Anthranilic acid is a versatile building block with diverse biological activities. In this work, we designed and synthesized novel anthranilic acid-based hybrids
[...] Read more.
Hybrid molecules, integrating multiple pharmacophores within a single scaffold, represent a modern strategy in drug discovery, offering improved selectivity and safety. Anthranilic acid is a versatile building block with diverse biological activities. In this work, we designed and synthesized novel anthranilic acid-based hybrids with enhanced pharmacokinetic potential. The methods used include cheminformatics- guided library design, followed by amide bond formation between anthranilic acid derivatives and substituted 2-phenylethylamines. Purification and structural characterization were achieved via NMR, IR, and HRMS. The compounds exhibited favorable, predicted ADME/Tox profiles and synthetic accessibility. These results provide a foundation for further biological evaluation toward therapies for smooth muscle dysfunction and inflammation.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
In Silico Study of Obeticholic Acid Analogs as FXR Agonists
by
Julio A. Seijas, Silvia Vázquez-Gómez, Francisco Meijide and M. Pilar Vázquez-Tato
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 137; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-27271 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Nuclear receptors are ligand-activated transcription factors that, in response to lipophilic hormones, vitamins, and dietary lipids, regulate numerous aspects of mammalian physiology. Bile acid receptors represent well-defined targets for the development of novel therapeutic approaches for metabolic and inflammatory diseases. The farnesoid X
[...] Read more.
Nuclear receptors are ligand-activated transcription factors that, in response to lipophilic hormones, vitamins, and dietary lipids, regulate numerous aspects of mammalian physiology. Bile acid receptors represent well-defined targets for the development of novel therapeutic approaches for metabolic and inflammatory diseases. The farnesoid X receptor (FXR) was identified as an orphan steroid receptor-like nuclear receptor, and its activation is crucial in many physiological functions of the liver. A vital function of FXR is to influence the amount of bile acids in hepatocytes by reducing bile acid synthesis, stimulating the bile salt export pump, and inhibiting enterohepatic circulation, thereby protecting hepatocytes from toxic bile acid accumulation. FXR activation induces distinctive changes in circulating cholesterol in animal models and humans. We present an evaluation of the interaction of various obeticholic acid analogs and other bile salts by studying their binding energies and receptor-ligand interactions using AutoDock 4.2.6 software. The results open the possibility of using new alternatives by deriving structures at position 3 of the steroid nucleus.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Structural Insights into Plasmepsin Inhibition by Phenolic Compounds from African Mistletoe (Tapinanthus globiferus) Parasitizing Vitex Doniana
by
Momoh Hassanah, Jimoh Yusuf, Dauda Garba, Yau Jamilu, Mohammed Ibrahim Sule and Yahaya Mohammed Sani
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 114; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-27270 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The parasitic disease malaria necessitates novel drug targets due to increasing Plasmodium falciparum resistance. The purpose of this work was to investigate the antimalarial properties of four metabolites, namely catechin (Y10), catechin-3-gallate (Y11), 4-methoxyphenyl acryl aldehyde (Y12), and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy acryl aldehyde (Y13), derived
[...] Read more.
The parasitic disease malaria necessitates novel drug targets due to increasing Plasmodium falciparum resistance. The purpose of this work was to investigate the antimalarial properties of four metabolites, namely catechin (Y10), catechin-3-gallate (Y11), 4-methoxyphenyl acryl aldehyde (Y12), and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy acryl aldehyde (Y13), derived from Tapinanthus globiferus, a traditional medicinal plant. Docking studies with important Plasmodium aspartic proteases, Plasmepsins I and II, showed good binding affinities, and Y11 showed the best binding affinity and a critical interaction with the catalytic dyad of Plm-II. The ADMET profile showed drug-likeness with low toxicity. These findings therefore position these metabolites, particularly Y11, as promising lead compounds for the development of antimalarial drugs.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Tolerance of Hydroxyl and Ortho-Substituted Groups in the Hayashi–Miyaura Reaction: A Study on Nitroolefin Substrates
by
Tomáš Hlavatý, Pavel Drabina, Jiří Váňa and Jan Bartáček
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 111; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-27268 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study researches the underexplored potential of the palladium-catalyzed Hayashi–Miyaura reaction in asymmetric synthesis, focusing on the preparation of novel derivatives of 2,2-diaryl-1-nitroethanes. These compounds are of interest as potential building blocks in medicinal and materials chemistry, yet they remain largely unexamined in
[...] Read more.
This study researches the underexplored potential of the palladium-catalyzed Hayashi–Miyaura reaction in asymmetric synthesis, focusing on the preparation of novel derivatives of 2,2-diaryl-1-nitroethanes. These compounds are of interest as potential building blocks in medicinal and materials chemistry, yet they remain largely unexamined in enantioselective transformations. The study specifically targets three challenging substrates: 1,3-dimethoxy-5-(2-nitro-1-(o-tolyl)ethyl)benzene, 2-(2-nitro-1-phenylethyl)phenol, and 4-(2-nitro-1-phenylethyl)phenol. These molecules were selected to probe the reaction’s tolerance toward ortho-substitution and free hydroxyl groups—features known to complicate catalytic processes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Design, Synthesis, Spectral Characterization, and Antidepressant Evaluation of 2,4-Diphenylquinoline Derivatives
by
Abubakar Sadiq Yakubu, Asmau Nasir Hamza, Idris Yunusa Abdullahi, Maryam Abdullahi, Idris Abdullahi, Rabiu Bako and Idris Umar
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 142; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-27236 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Depression is a debilitating neuropsychiatric disorder and a leading cause of disability worldwide, with current therapeutic options often limited by delayed onset of action, inadequate efficacy, and undesirable side effects. The quinoline scaffold, a privileged structure in medicinal chemistry, has been reported to
[...] Read more.
Depression is a debilitating neuropsychiatric disorder and a leading cause of disability worldwide, with current therapeutic options often limited by delayed onset of action, inadequate efficacy, and undesirable side effects. The quinoline scaffold, a privileged structure in medicinal chemistry, has been reported to possess a wide spectrum of pharmacological properties, including central nervous system (CNS) modulation. In this study, two novel 2,4-diphenylquinoline derivatives—CMPD1 [2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-phenylquinoline] and CMPD2 [2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-phenylquinoline]—were rationally designed based on structure–activity relationship (SAR) insights and synthesized via the Friedländer condensation of appropriately substituted anilines with carbonyl precursors. Purification was achieved through recrystallization, and structural confirmation was performed using Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, proton nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy, confirming the expected chemical shifts and diagnostic signals for quinoline derivatives. The pharmacological activity was evaluated using murine models for antidepressant screening: the Forced Swim Test (FST) and Tail Suspension Test (TST). Both compounds produced statistically significant reductions in immobility time compared to the control group (p < 0.05), with CMPD2 showing slightly enhanced activity. The results suggest that electron-donating and electron-withdrawing substituents influence antidepressant potency, potentially through modulation of CNS receptor binding. These findings validate 2,4-diphenylquinoline derivatives as promising antidepressant leads, meriting further optimization, in vivo pharmacokinetic studies, and mechanistic investigations to establish their clinical translation potential.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
The Influence of Cucurbit[7]uril on the Photophysical Properties of Encapsulated Styryl Dye
by
Olga P. Kolesnikova, Denis A. Ivanov, Igor V. Kryukov and Nikolai Kh. Petrov
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 120; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26963 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The interaction between the styryl dye 4-{(E)-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]vinyl}-1-methylpyridinium iodide (DASPI) and cucurbit[7]uril (CB[7]) in aqueous solution was studied by optical spectroscopy methods. Due to negatively charged portals, cucurbit[7]urils can form complexes with cationic styryl dye. This complexation alters the photophysical properties of the dye,
[...] Read more.
The interaction between the styryl dye 4-{(E)-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]vinyl}-1-methylpyridinium iodide (DASPI) and cucurbit[7]uril (CB[7]) in aqueous solution was studied by optical spectroscopy methods. Due to negatively charged portals, cucurbit[7]urils can form complexes with cationic styryl dye. This complexation alters the photophysical properties of the dye, such as absorption and fluorescence. It was previously found that the formation of 1:2 inclusion complexes leads to a shift in the absorption band. Such changes were previously attributed to protonation of the dye. To explain this effect, we hypothesize that it arises from the influence of the electrostatic field generated by the negatively charged portals of cucurbit[7]uril on the conjugated π-electron system of the dye.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Ligand-Based Identification of Naturally Occurring 1E3G Receptor Inhibitors for Treating Prostate Cancer
by
Abu Sayed, Ifteakhar Uddin, Sanjida Banu, Umme Ayman, Nabil Jonayeth Alvee, Mohammed Raihan Uddin and Joya Datta Ripa
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 143; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26893 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Prostate cancer is one of the most prevalent malignancies worldwide, with the androgen receptor (1E3G) playing a central role in disease progression. Methodology: This study applied computational approaches to identify natural 1E3G inhibitors. Potential ligands such as Cianidanol from Camellia sinensis and
[...] Read more.
Background: Prostate cancer is one of the most prevalent malignancies worldwide, with the androgen receptor (1E3G) playing a central role in disease progression. Methodology: This study applied computational approaches to identify natural 1E3G inhibitors. Potential ligands such as Cianidanol from Camellia sinensis and Gallocatechin from Phyllanthus amarus were optimized using Gaussian 16 with the DFT 6-31g(d,p) basis set. Molecular docking was performed using PyRx, while pharmacokinetics and toxicity were evaluated via admetSAR and ProTox-3.0. Network pharmacology (STRING, Cytoscape) and 100 ns molecular dynamics simulations (Desmond) ensured biological relevance and stability. Results: Cianidanol (−8.1 kcal/mol) and Gallocatechin (−8.4 kcal/mol) showed the strongest binding affinities and favorable ADMET profiles. Conclusions: These compounds represent promising natural 1E3G inhibitors for future prostate cancer therapy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Explainability of Diabetic Retinopathy Detection and Classification with Deep Learning Hybrid Architecture: AlterNet-K and ResNet-101
by
Lavkush Gupta, Richa Gupta, Parul Agarwal and Suraiya Praveen
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 141; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26888 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Diabetic retinopathy (DR), an eye disease that is a threatening cause of irreversible blindness, always challenging to detect and diagnose on time. There are many ophthalmic invasive procedures which exist in medical science for the diagnosis of oculi (eyes). These all require highly
[...] Read more.
Diabetic retinopathy (DR), an eye disease that is a threatening cause of irreversible blindness, always challenging to detect and diagnose on time. There are many ophthalmic invasive procedures which exist in medical science for the diagnosis of oculi (eyes). These all require highly skilled medical practitioners with operational knowledge of diagnosing sensitive organs like the retina and its tiny vessels. Due to the dearth of retinal specialists, the eye’s organs’ sensitivity, and the complexity of retinal therapy, invasive procedures are time-consuming, costly, and have slow progress. The fundus images are the visual information of the rear part of the retina. The progression of lesions around the retinal tissue’s surface causes the electric signals to not able to reach at the visual cortex, thus causing blurry vision or vision loss experienced by patients. The older methods using retinal fundus images for diagnosing lesions and symptoms of DR take time, causing delays in treatment and hence reducing the chance of success. Therefore, for early diagnosis, using fundus or retinal images can save the required effort and time of both doctors and patients. Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques have the capability to learn the tissue structures of the eye’s anatomy and to provide an analysis of the disease through the retinal fundus images. This process consists of operations, first apply the image preprocessing techniques followed by segmentation and filtering, then classify the disease using the artificial intelligence-based model. The proposed model trained over a dataset of DR images, for the prediction of accurate results, followed by deciding if the diagnosis by the model is correctly classified or not using the Explainable AI (XAI) algorithm. The rapid growth and better outcome of machine learning and deep learning algorithms are reasons to adopt, enhance the early diagnosis and treatments of patients.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Exploration of New Inhibitors as Anti-Alzheimer Agents Through Molecular Modeling
by
Ferdaous Hasni, Ismail Daoud and Nadjib Melkemi
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 133; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26898 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that accounts for more than 80% of dementia cases worldwide. This a neurological disorder that encompasses various stages of development (mild, moderate, or severe cognitive impairment), including certain psychological and behavioral syndromes such as depression, psychosis,
[...] Read more.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that accounts for more than 80% of dementia cases worldwide. This a neurological disorder that encompasses various stages of development (mild, moderate, or severe cognitive impairment), including certain psychological and behavioral syndromes such as depression, psychosis, and aggression. The main drug classes currently used to treat AD are acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibitors. Advancements in bioinformatics and chemometrics have positioned the in silico approach as a pivotal tool in identifying novel therapeutic compounds.Therefore, we conducted a study to evaluate the effects of various newly developed N-substituted 5-chloro-2(3H)-benzoxazolone derivatives on AchE. The aim of this research paper was to utilize in silico ADMET profiling to investigate the potential of natural analogs as inhibitors of AchE, using computational techniques such as swissadme. Analysis of selected ligands with the highest affinity for the target was performed to evaluate ADME properties. The calculation of ADME properties proved that these ligands follow the rules of Lipinski, Veber, and Egan and confirmed the docking results, indicating that they are probably the best inhibitors. Furthermore, they could be utilized to create novel pharmaceutical medicines with which to treat individuals with AD.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Transforming Anionic Reverse Micelles: The Potential of Hydrophobic Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents—How the Mixture Between Camphor and Menthol Can Be an Excellent Choice for Reverse Micelle Preparation
by
Alejandra González Herrera, Néstor Mariano Correa, Fernando Moyano and Ruben Dario Falcone
Chem. Proc. 2025, 18(1), 131; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26920 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Reverse micelles (RMs) are versatile nanostructures traditionally formed in low-polarity organic solvents, but the need for greener alternatives has limited their broader applicability. Here, we demonstrate for the first time that a hydrophobic Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent (NADES), prepared from a simple 1:1
[...] Read more.
Reverse micelles (RMs) are versatile nanostructures traditionally formed in low-polarity organic solvents, but the need for greener alternatives has limited their broader applicability. Here, we demonstrate for the first time that a hydrophobic Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent (NADES), prepared from a simple 1:1 mixture of camphor and menthol (CM), can act as the continuous external phase for RM formation. Remarkably, CM dissolves the benchmark surfactant sodium dioctyl sulfosuccinate (AOT) at concentrations up to 0.5 M without co-surfactants and supports water solubilization up to W0 = [H2O]/[AOT] = 5, yielding thermodynamically stable systems. 1H and DOSY NMR analyses reveal clear structural rearrangements of the micellar interface, confirm the encapsulation of water in the polar core, and provide quantitative evidence of size modulation as a function of W0. The resulting CM/AOT/water assemblies represent the first example of NADES-based reverse micelles, offering an easily prepared, sustainable, and biocompatible platform. This breakthrough opens new perspectives for the development of green self-assembled systems with promising applications in areas such as food technology, pharmaceuticals, and nanomedicine.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

















