Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative chronic disorder in older people, caused by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the brain, which leads to dopamine depletion. Among its symptoms are resting tremor, rigidity, and dementia. Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) is a key enzyme in PD. The inhibition of it increases the level of dopamine in the brain by preventing its degradation, especially in the early stages of the disease. In the present work, we combined molecular docking with an ADME analysis of a new class of ten derivatives of indanone in order to reduce the metabolic depletion of dopamine through inhibiting the MAO-B. A molecular docking study was performed to clarify the bonding modes and affinities between the active site residues of MAO-B with the new class derivatives of indanone, followed by the ADME prediction to check the drug-likeness properties of the best ligands obtained using the method above. Molecular docking results show that the ligands L3 and L5 presented a high negative score energy (−8.809 kcal/mol, −9.276 kcal/mol), respectively, with good RMSD values (1.419 Å, 1.560 Å), respectively. Moreover, the ADME prediction gave promising results that those ligands have an oral bioavailability and a high level of gastrointestinal absorption, which means they can be good inhibitors against Parkinson’s disease.
1. Introduction
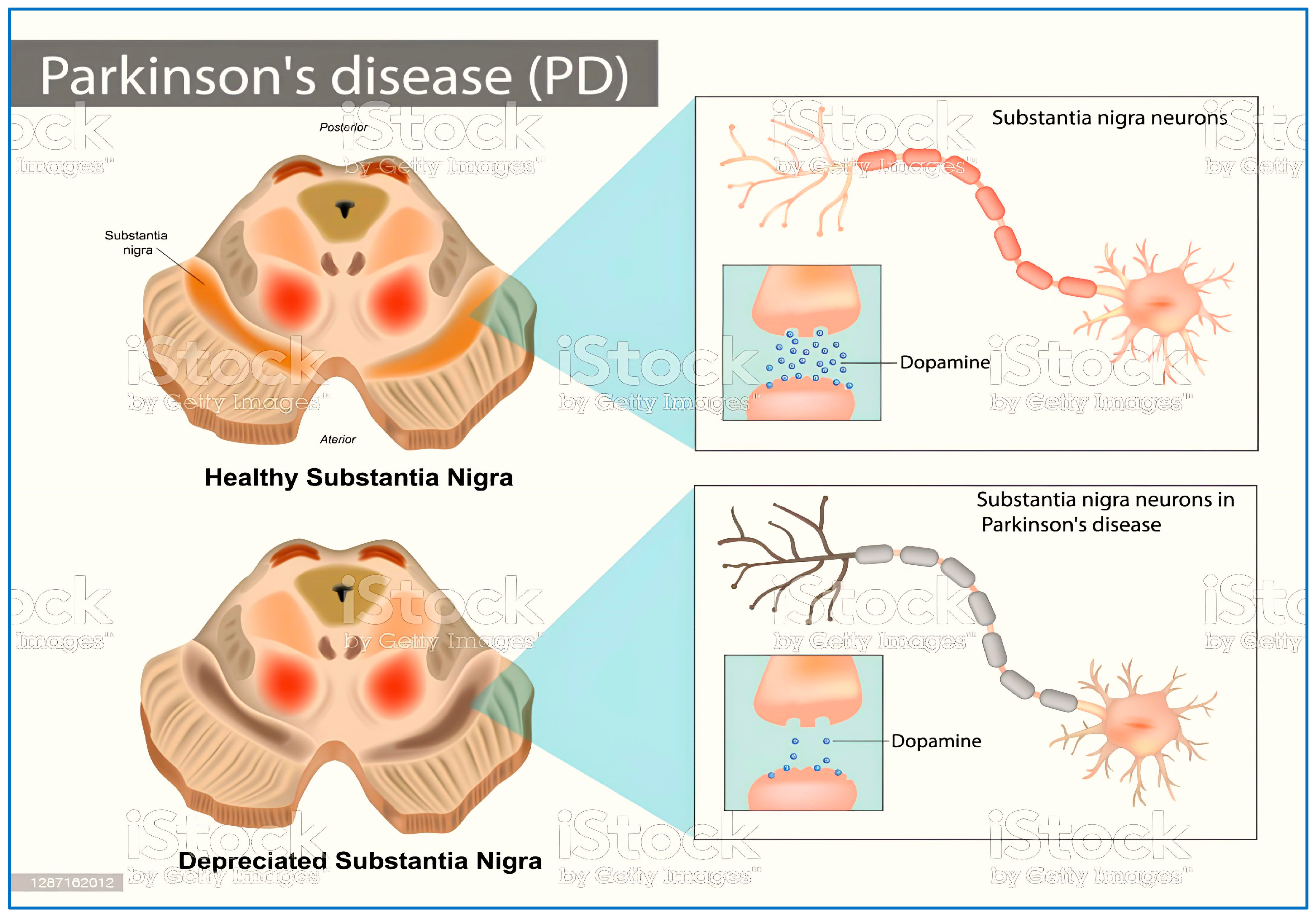
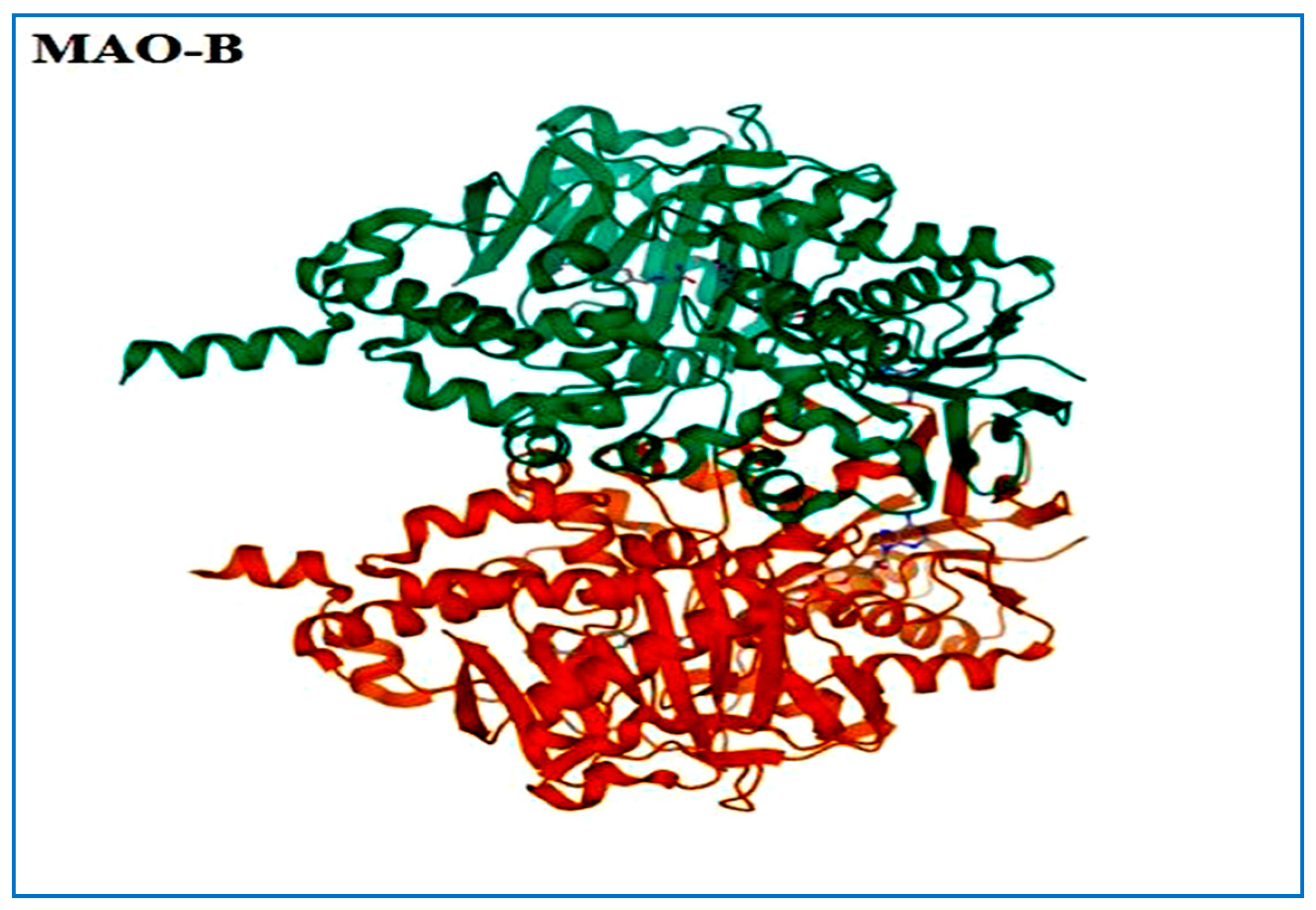
The prevalence of neurodegenerative disorders (NDs) is increasing, making them a global health concern of significant proportions. The aging population, especially in wealthy countries, has seen an elevation in the rate at which chronic diseases are spreading in recent years [1]. Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most commonneurodegenerative disease [2], caused by the death of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, which depletes dopamine (Figure 1). Motor symptoms include resting tremor, and rigidity, while non-motor symptoms include disorganization and coherence distortion [3]. MAO-B (monoamine oxidase B) (Figure 2) is a major target in PD. Inhibition of this enzyme boosts dopamine levels in the brain by preventing its breakdown, particularly in the early stages of illness [2].
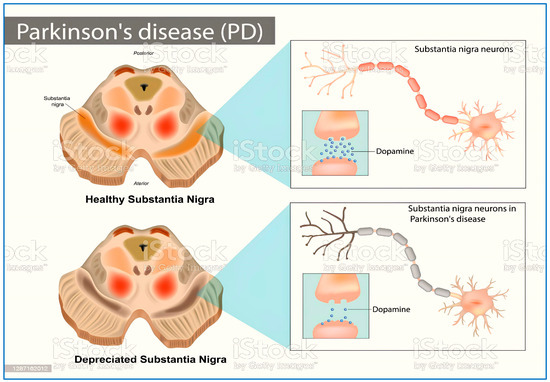
Figure 1.
Healthy and depreciated substantianigra because of Parkinson’s disease.
Figure 2.
3D structure of MAO-B.
This research is a structure-based drug design investigation of a new family of indanone derivatives to diminish the metabolic depletion of dopamine by inhibiting the Parkinson’s disease-related enzyme MAO-B.
2. Material and Methods
In order to understand the interactions and affinities between this new class of derivatives and the active site residues of the MAO-B target, we conducted a molecular docking analysis using the following parameters: the scoring energy, the RSMD value of the generated complexes, and the interaction kinds and distances. A computation of ADME-T characteristics was performed to investigate the drug-likeness proprieties of the best compounds generated using molecular modeling simulation.
MAO-B (PDB ID: 2C65) crystal structure were retrieved from the RCSB Database (www.rcsb.org/pdb, accessed on.14 October 2023). Compound structures were designed using the ChemDraw professional 16.0 program; they were then optimized using the Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) software (Version 2014.09) and the semi-empirical energy function AM1.
To facilitate the molecular docking process, cofactors, ions, and glycols have been removed from the chosen enzyme. The compounds were designed to be flexible, whereas the target was inflexible. All complexes’ molecular docking data were acquired using the same software. The ADME calculations were performed using the SWISSADME web-based program.
3. Results and Discussion
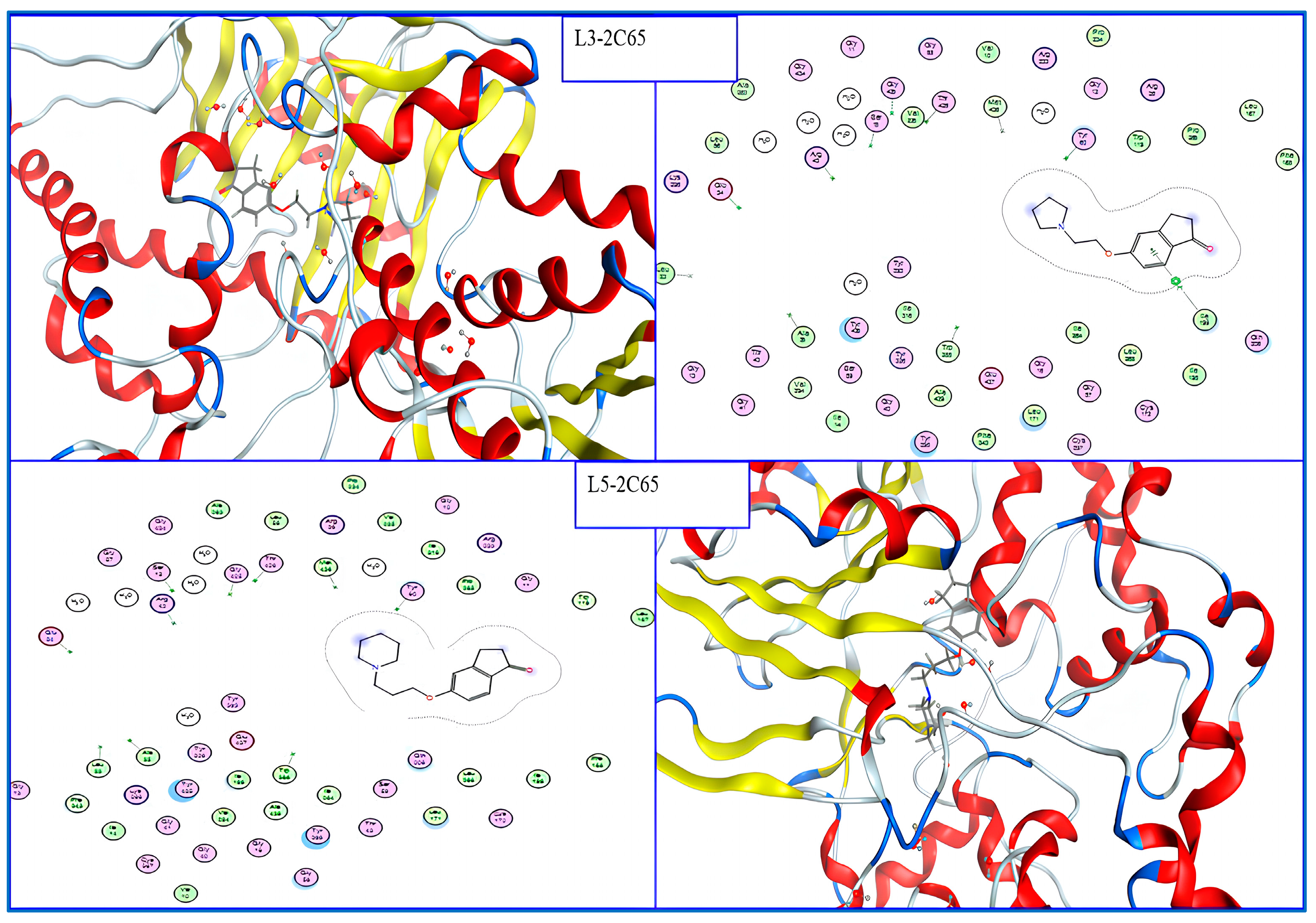
According to the results of the molecular docking studies (Figure 3), the formation of the complexes that are the most stable occurs when molecules L3: 5-(2-(Pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one and L5: 5-(3-(Piperidin-1-yl)propoxy)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one are incorporated into MAO-B (PDB: 2C65). From Table 1, both L3 and L5 have negative energy scores of −8.809 and −9.276 (kcal/mol) and good RMSD values of 1.419 (Å), 1.560 (Å), respectively; have passed all drug-likeness rules (Table 2) without any violations; and have a bioavailability score of 0.55 (Table 3), which indicates that they have excellent pharmacokinetic characteristics and good oral and gastrointestinal absorption; this means they are also considered excellent candidates for further study. The low values of the synthetic accessibility score (SA score) for these ligands (SA2) provide additional evidence for the ease with which they can be synthesized.
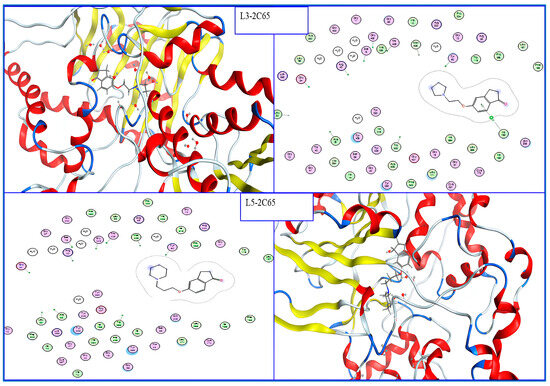
Figure 3.
2D and 3D interaction of the best compounds into MAO-B.

Table 1.
S-score (energy) and interactions between compounds and the active site residues of hMAO-B target.

Table 2.
ADME properties of the best ligands.

Table 3.
Drug-likeness, bioavailability score and synthetic accessibility of the best ligands.
4. Conclusions
In light of these findings and due to their low negative score energy, MAO-B-L3 and MAO-B-L5 complexes are the most stable.
Compounds L1: 6-(2-(Pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one and L2: 6-(3-(Piperidin-1-yl)propoxy)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one were also shown to be pharmacologically active, suggesting they could be useful as lead candidates for the cure or inhibition of Parkinson’s disease.
Author Contributions
Data collection, software, formal analysis, and first draft of the manuscript were prepared by M.M. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. I.D. contributed to the conceptualization and supervision of the study. N.M. and I.D. contributed to the interpretation of docking and ADME-T studies. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Mettai, M.; Daoud, I.; Mesli, F.; Kenouche, S.; Melkemi, N.; Kherachi, R.; Belkadi, A. Molecular docking/dynamics simulations, MEP analysis, bioisosteric replacement and ADME/T prediction for identification of dual targets inhibitors of Parkinson’s disease with novel scaffold. In Silico Pharmacol. 2023, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koszła, O.; Stępnicki, P.; Zięba, A.; Grudzińska, A.; Matosiuk, D.; Kaczor, A.A. Current approaches and tools used in drug development against parkinson’s disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, U.; Shabana, B.; Muhammad, A.S.; Bashir, A.; Ammara, S.; Zunera, C.; Fareeha, A.; Nimra, J.; Sundas, H.; Muhammad, F.A.; et al. Anti-Parkinson’s Evaluation of Brassica Juncea Leaf Extract and Underlying Mechanism of Its Phytochemicals. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2021, 26, 1031–1051. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).