Abstract
Organophosphorus compounds play an important role in the medicinal- or agricultural industry, and in the human body as well. Over the last years, heterocyclic phosphonates have received growing interest due to their potential biological activity. An efficient tool for the preparation of such derivatives is their synthesis via multicomponent reactions. These transformations possess several criteria of an “ideal synthesis”, such as high atom economy, fast and simple accomplishment, energy efficiency, and environmentally friendliness. A number of heterocyclic phosphonates were prepared by us utilizing multicomponent syntheses. In this proceeding, the synthesis of the diethyl (2-amino-3-cyano-4H-chromen-4-yl)phosphonate by the condensation of salicylaldehyde, malononitrile and diethyl phosphite is briefly introduced. The reaction was optimized in respect of the catalyst type, the catalyst amount, the reaction time, and the temperature.
1. Introduction
Heterocyclic phosphonates attract an intensively growing interest due to their importance in synthetic- and medicinal chemistry, and in agriculture as well [1,2,3,4]. One of the most convenient routes for the preparation of heterocyclic phosphonates is to apply multicomponent reactions [5]. From an environmentally-friendly aspect, these transformations have a number of benefits, such as the high atom economy, the fast and simple accomplishment, the utilization of simple starting materials and the ability to save time and energy [6,7]. Due to these advantages, they are suitable for the creation of molecular libraries.
In practical organic chemistry, the use of the MW technique has become common in the last few decades [8]. In most cases, MW-assisted reactions proceed faster, the selec-tivity is higher and the catalyst and the solvent are avoidable [9]. The efficiency of multicomponent reactions can be further increased applying MW irradiation [10]. However, a serious limitation of MW-assisted reactions is the fixed geometry of the magnetron, which prevent the use of traditional scale-up techniques [11]. To overcome this difficulty, the development of continuous flow MW systems came to the front [12]. Although various applications of the continuous flow MW technique have been reported over the last de-cade, the evolution of this field is still in progress [13]. In this proceeding, the synthesis of several types of heterocyclic phosphonates, such as isoindolin-1-one-3-phosphonates, (2-amino-4H-chromen-4-yl)phosphonates and 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one phosphonates carried out in a batch or a continuous flow MW reactor is briefly introduced.
As the first part of our project, a number of isoindolin-1-one-3-phosphonates (1) could be prepared by the catalyst- and solvent-free three-component condensation of 2-formylbenzoic acid, aliphatic primary amines, and various dialkyl phosphites under MW conditions (Figure 1) [14]. The reaction was optimized in detail on a selected model of 2-formylbenzoic acid, butyl amine, and diethyl phosphite. Then, the condensation was also performed with various aliphatic amines (butyl-, cyclohexyl-, or benzyl amine) and dialkyl phosphites (dimethyl-, diethyl-, di-i-propyl-, dibutyl or dibenzyl phosphite). Carrying out the reactions using 1.2 equiv. of the amine, complete conversions were obtained at 60 °C after 10–30 min. Altogether 15 isoindolin-1-one-3-phosphonates (1) were isolated in yields of 70–94%, from which 13 are new derivatives.
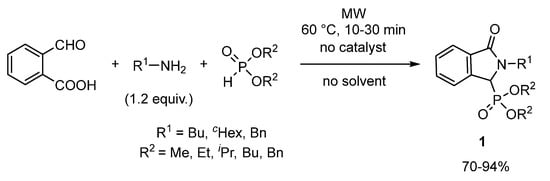
Figure 1.
MW-assisted reaction of 2-formylbenzoic acid, primary amines and dialkyl phosphites.
In order to further increase the productivity, the reaction of 2-formylbenzoic acid, butyl-, cyclohexyl-, or benzyl amine and diethyl phosphite was transferred into a con-tinuous flow MW reactor (Figure 2). The continuous flow system applied consisted of a dual HPLC pump, a CEM® MW reactor equipped with a commercially available CEM® continuous flow cell, a cooler and a back-pressure regulator operating at 17 bar. During the continuous flow reactions, ethanol was used as the solvent. Complete conversions were reached using 1.5 equivalents of the amines and of the phosphorus reagent at 60 °C for residence times of 30–45 min. The flow approach allowed the scaled-up synthesis of the target compounds in productivities of 0.6–1.8 g/h.
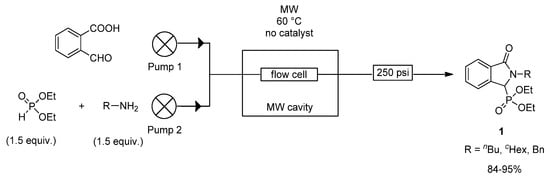
Figure 2.
Continuous flow MW reaction of 2-formylbenzoic acid, diethyl phosphite and primary amines.
In this paper, the MW-assisted synthesis of the diethyl (2-amino-3-cyano-4H-chromen-4-yl)phosphonate was studied by the condensation of salicylaldehyde, malononitrile and diethyl phosphite. The reaction was optimized in respect of the catalyst type, the catalyst amount, the reaction time, and the temperature.
2. Results and Discussion
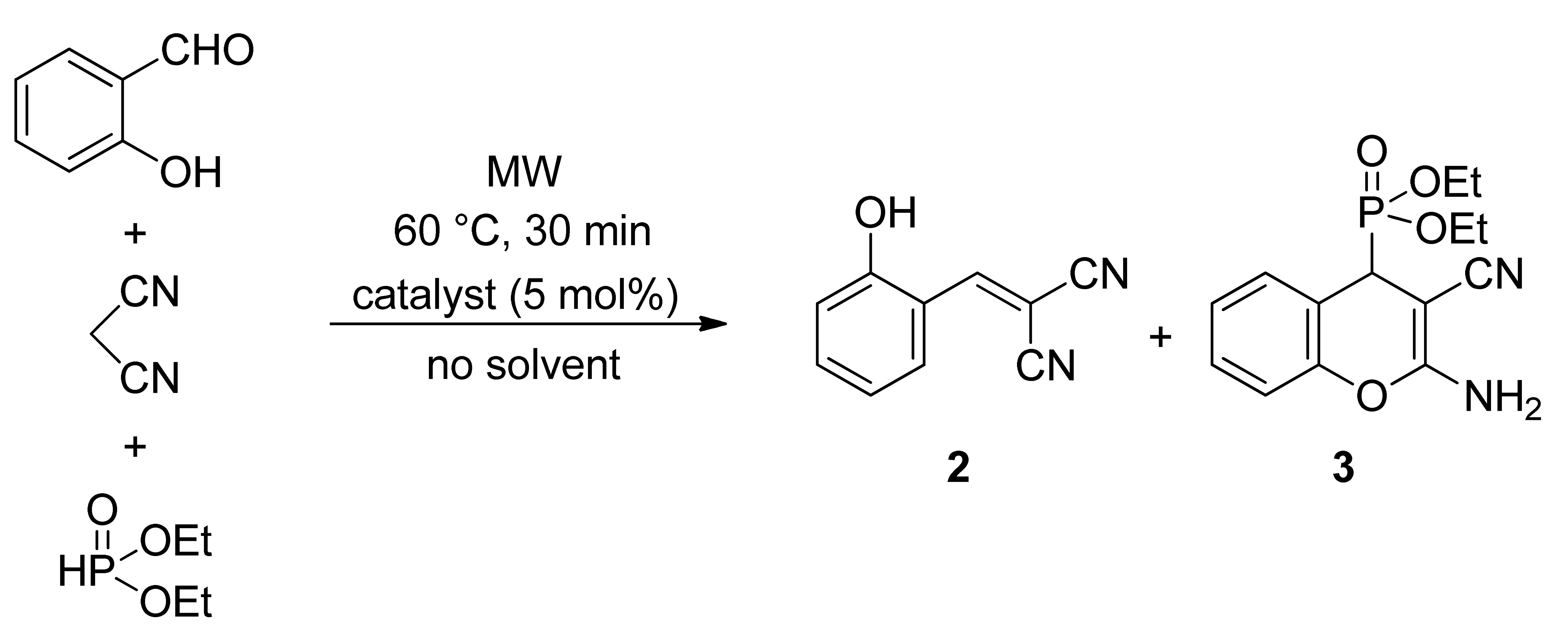
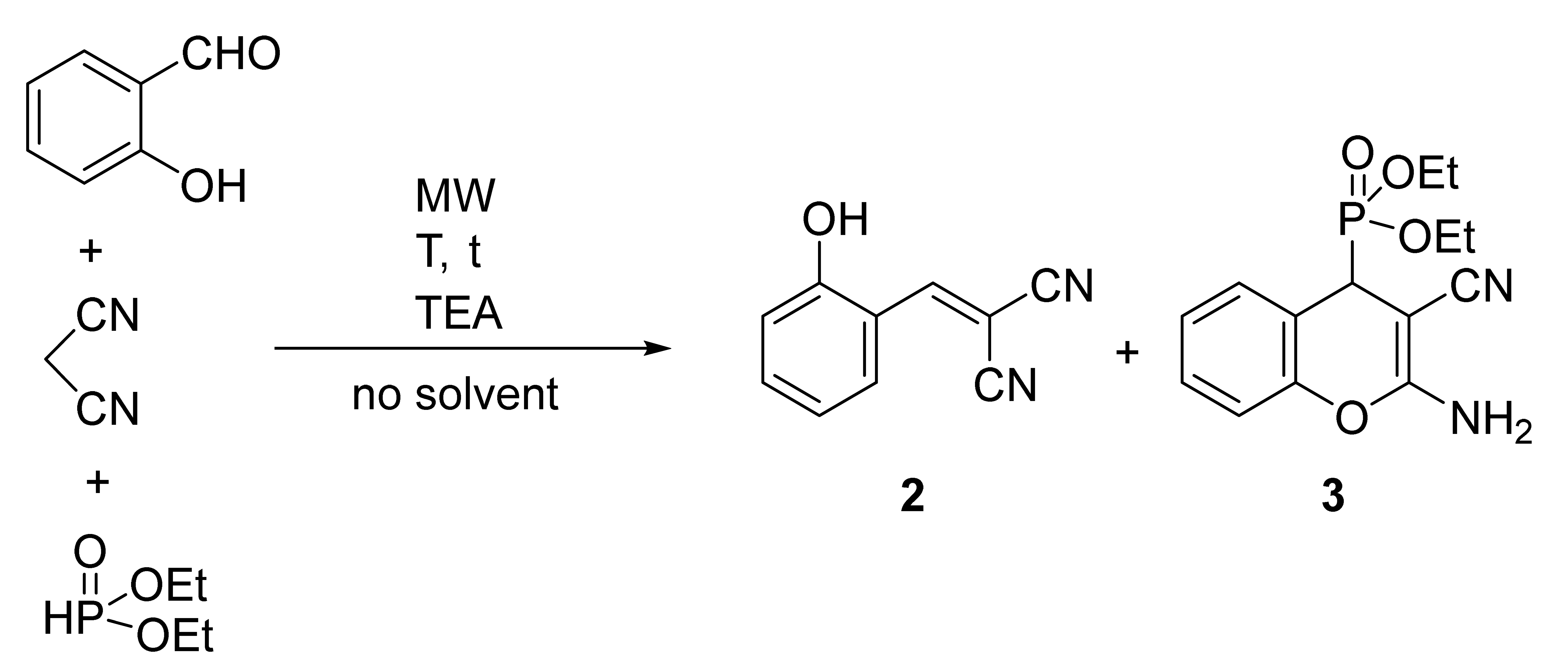
At first, we studied the solvent-free condensation of salicylaldehyde, malononitrile, and diethyl phosphite in the presence of 5 mol% of a catalyst at 60 °C for 30 min under MW conditions (Table 1). Without catalyst, no reaction was observed (Table 1, entry 1). Using p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA) as a Bronsted acid (Table 1, entry 2) or zinc trifluoromethanesulfonate (Zn(OTf)2) as a Lewis acid (Table 1, entry 3), there were only starting materials in the mixture, similarly to the uncatalyzed variation. In the presence of 18-crown-6, the reaction also did not reach any conversion (Table 1, entry 4). Then, an inorganic base, potassium carbonate (K2CO3) was tried out as a catalyst in the condensation (Table 1, entry 5). We obtained a conversion of 39%, and our desired product (3) was present in a proportion of 25% in the mixture, beside intermediate 2 ([M+H]+ = 171.1) formed in 75%. As using K2CO3, we have obtained a solid-liquid two-phase system, thus the experiment was also carried out using triethylbenzylammonium chloride (TEBAC) as a phase transfer catalyst (Table 1, entry 6). Although the conversion increased to 53%, the composition of the products remained almost the same. Using triethylamine (TEA) as a catalyst, the formation of the (chromenyl)phosphonate (3) in higher proportion (38%) was observed (Table 1, entry 7). Among the several types of catalysts tried out, TEA as an organic base was found to be the most effective, therefore we investigated the reaction further using this catalyst. In order to compare the MW and conventional heating, we carried out a reaction in an oil bath (Table 1, entry 8). Although the condensation reached 100% conversion, the proportion of the desired phosphonate (3) was only 29%; by 9% lower than in the MW-assisted experiment (Table 1, entries 7 vs. 8). The condensation was also performed in EtOH, where a conversion of 88% was obtained, and the ratio of product 3 was only 25% (Table 1, entry 9). The solvent-free reaction enabled a higher conversion and a better selectivity towards the desired product (3) (Table 1, entries 7 vs. 9).

Table 1.
Study of the reaction of salicylaldehyde, malononitrile and diethyl phosphite.
The model reaction was further optimized in respect of the catalyst load, the reaction time, and the temperature (Table 2). Applying 5 mol% of catalyst at 60 °C for 30 min, the condensation afforded the desired product (3) in a ratio of 38% (Table 2, entry 1). Then, the reaction was performed at 80 °C for 30 min, when the proportion of product 3 was 57%, which is by 19% higher than the reaction carried out at 60 °C (Table 2, entry 2). Next, the amount of TEA was changed to 10 mol% (Table 2, entries 3 and 4). At 80 °C under 30 min, compound 3 was already obtained in 72% (Table 2, entry 3). Prolonging the experiment for 45 min, 88% of the (chromenyl)phosphonate (3) was present in the mixture (Table 2, entry 4). When we increased the catalyst amount to 15 mol%, 86% of product 3 could be obtained after 30 min, while an irradiation of 45 min afforded the desired product (3) quantitatively (100%) (Table 2, entries 5 and 6). After column chromatography, the diethyl (2-amino-4H-chromen-4-yl)phosphonate (3) could be isolated in a yield of 93%.

Table 2.
Optimization of the TEA-catalyzed reaction of salicylaldehyde, malononitrile and diethyl phosphite under solvent-free MW conditions.
3. Experimental Part
Procedure for the Synthesis of the Diethyl (2-Amino-3-cyano-4H-chromen-4-yl)phosphonate (3)
The mixture of 1.0 mmol salicylaldehyde (0.11 mL), 1.0 mmol malononitrile (0.07 g), and 1.0 mmol diethyl phosphite (0.13 mL) and catalysts (0.05 mmol [0.010 g of PTSA, 0.018 g of Zn(OTf)2, 0.013 g of 18-crown-6, 0.07 g of K2CO3, 0.011 g of TEBAC or 0.007 mL of TEA], 0.10 mmol [0.014 mL of TEA] or 0.15 mmol [0.021 mL of TEA]) was irradiated in a sealed tube at 60–80 °C for 30–45 min in a CEM Discover® MW reactor equipped with a pressure controller. In the experiment marked by Table 1, entry 9, 1 mL of ethanol was used as the solvent. The product was purified by column chromatography using silica gel as the solid phase and dichloromethane:methanol 97:3 as the eluent. Yield: 93% (0.29 g), pale yellow crystal; Mp: 138–140 °C; Mp [15]: 138–140 °C; 31P NMR (CDCl3) δ: 21.8; δ [16] (CDCl3) 21.2; [M+H]+found = 309.1005, C14H18N2O4P requires 309.1004.
4. Conclusions
The above-mentioned example greatly proves the relevancy of MW-assisted multicomponent reactions in the synthesis of heterocyclic phosphonates. The optimized pre-paration of the diethyl (2-amino-3-cyano-4H-chromen-4-yl)phosphonate was elaborated, and the desired product could be isolated in a high yield. Extension of the reaction for the synthesis of various new (chromenyl)phosphonates is being investigated. Due to the potential biological activity of heterocyclic phosphonates obtained in similar reactions, these molecular libraries can be used for in-vitro screening at various indications, which may result in new promising lead compounds for drug development.
Funding
The above project was supported by the Hungarian Research Development and Innovation Office (FK123961), by the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary in the frame of FIEK_16-1-2016-0007 (Higher Education and Industrial Cooperation Center) project and by the bilateral Hungarian-Slovenian Science and Technology Cooperation project (2018-2.1.11-TÉT-SI-2018-00008). E.B. was supported by the János Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences (BO/00278/17/7), and by the ÚNKP-20-5-BME-288 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry of Human Capacities.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Moonen, K.; Laureyn, I.; Stevens, C.V. Synthetic methods for azaheterocyclic phosphonates and their biological activity. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6177–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, R.K. (Ed.) Phosphorus Heterocycles II. In Topics in Heterocyclic Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Tappe, F.M.J.; Trepohl, V.T.; Oestreich, M. Transition-metal-catalyzed CP cross-coupling reactions. Synthesis 2010, 18, 3037–3062. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, T.E.; Abdel-Kariem, S.M. Methods for the synthesis of α-heterocyclic/heteroaryl-α-aminophosphonic acids and their esters. Arkivoc 2015, 2015, 246–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji, M. Multicomponent Reactions: A simple and efficient route to heterocyclic phosphonates. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 1269–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dömling, A.; Wang, W.; Wang, K. Chemistry and biology of multicomponent reactions. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3083–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.J.J. (Ed.) Multicomponent Reactions 1. In Science of Synthesis; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, N.Z.; Bálint, E.; Keglevich, G. Microwave-Assisted Syntheses in Organic Chemistry. In Milestones in Microwave Chemistry; Keglevich, G., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 11–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kappe, C.O.; Stadler, A.; Dallinger, D. Microwaves in Organic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; Volume 52. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Shi, F.; Tu, S.J. Microwave-assisted multicomponent reactions in the heterocyclic chemistry. Curr. Org. Chem. 2010, 14, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, E.; Keglevich, G. The Spread of the Application of the Microwave Technique in Organic Synthesis. In Milestones in Microwave Chemistry; Keglevich, G., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- de la Hoz, A.; Loupy, A. (Eds.) Microwaves in Organic Synthesis, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Estela, L.; Pouxb, M.; Benamaraa, N.; Polaerta, I. Continuous flow-microwave reactor: Where are we? Chem. Eng. Process. 2016, 113, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajti, Á.; Tóth, N.; Rávai, B.; Csontos, I.; Szabó, P.; Bálint, E. Study on the microwave-assisted batch and continuous flow synthesis of N-alkyl-isoindolin-1-one-3-phosphonates by a special Kabachnik–Fields condensation. Molecules 2020, 25, 3307–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossaini-Sarvani, M.; Roosta, A. Synthesis of 2-amino-4H-chromen-4-yl phosphonats via C-P bond formation catalyzed by nano-rods ZnO under solvent-free condition. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2014, 17, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnammagari, S.; Cho, B.; Jeong, Y. Choline chloride based eutectic solvent for the efficient synthesis of 2-amino-4H-chromen-4-yl phosphonate derivatives via multicomponent reaction under mild conditions. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2018, 193, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).