Precipitation of Iron Oxide in Hydrogel with Superparamagnetic and Stimuli-Responsive Properties †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Iron Oxide in Hydrogels
2.1.1. Sensor Hydrogels
2.1.2. Actuator Hydrogels
2.1.3. Coprecipitation of Iron Oxide in Hydrogels
2.2. Characterization Methods
2.2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.2. Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM)
2.2.3. Swelling Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
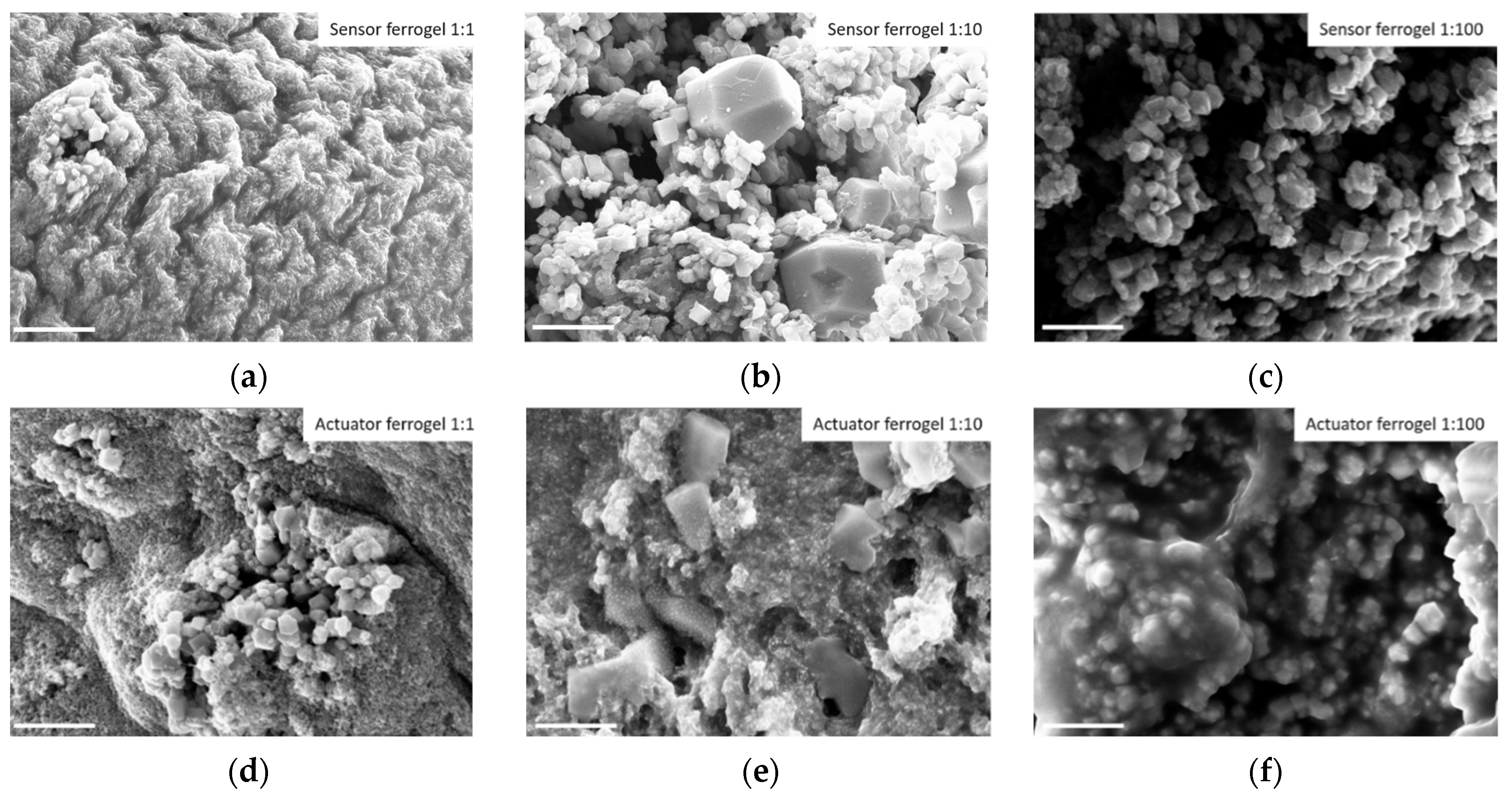
3.1. Morphological Properties
3.2. Magnetic Properties
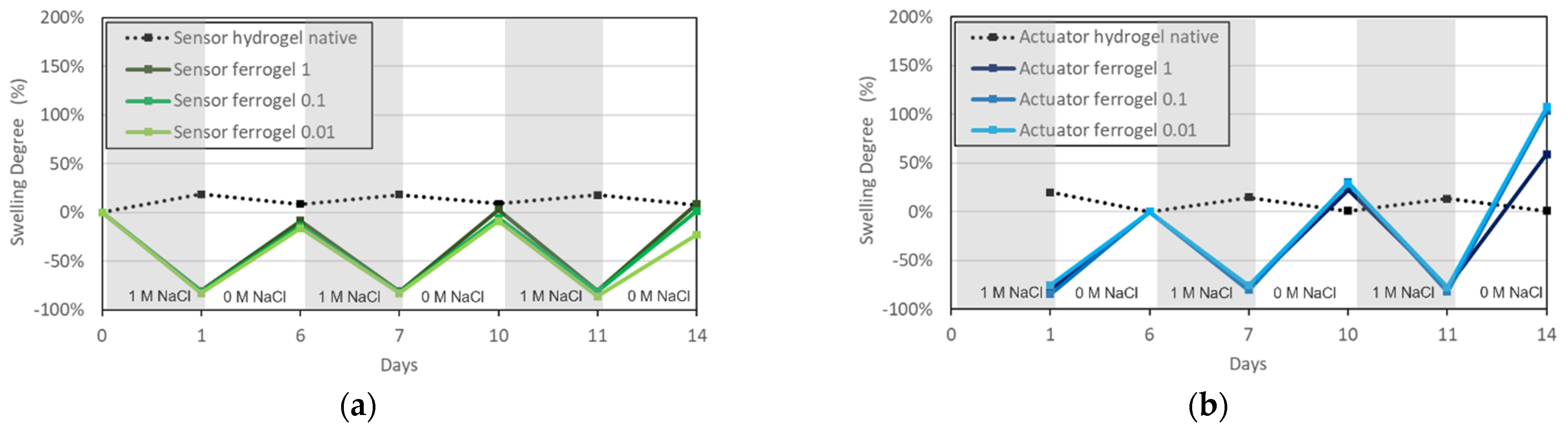
3.3. Reversibility of Ferrogel Swelling
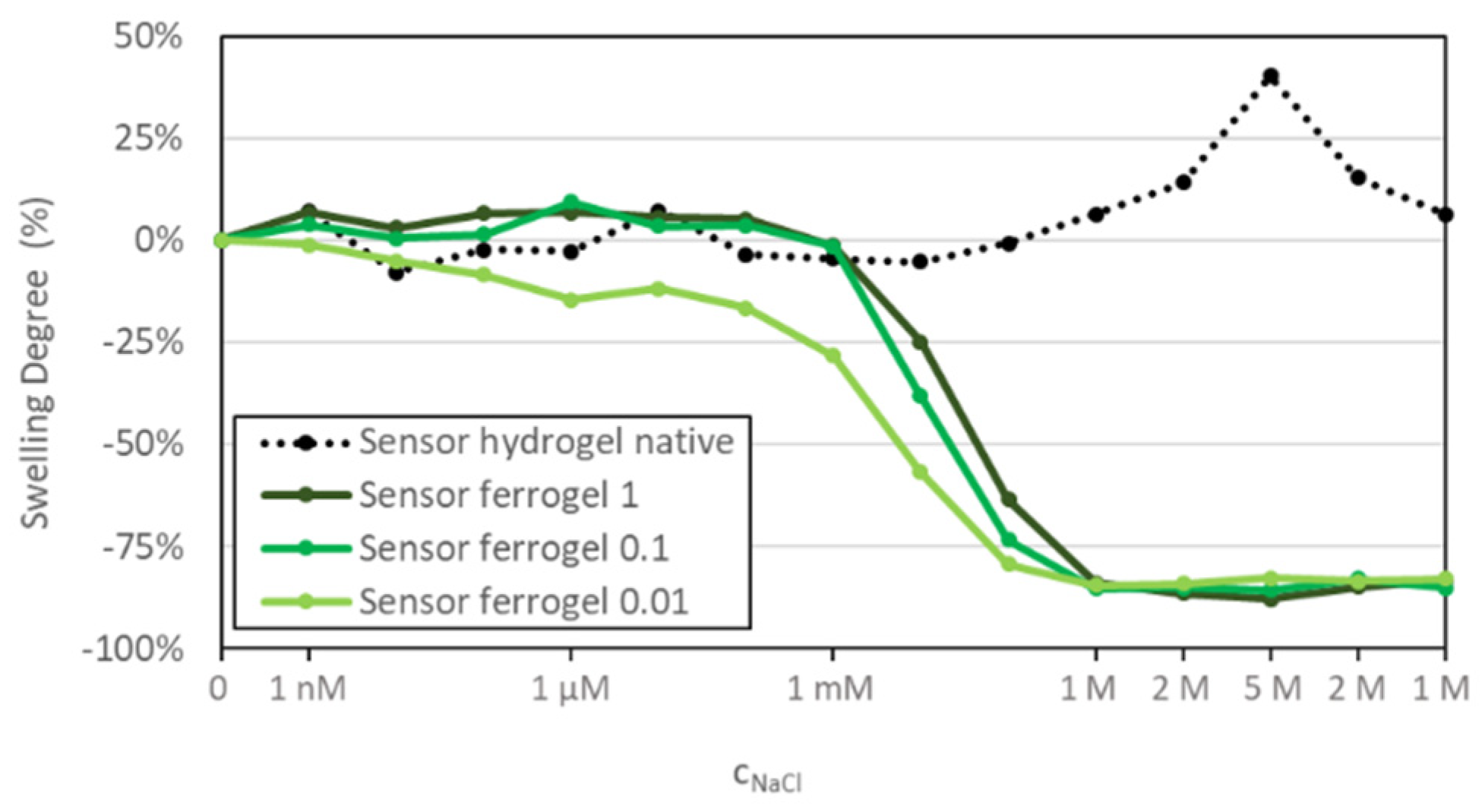
3.4. Sensitivity of the Sensor Ferrogel to Ionic Strength
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guenther, M.; Gerlach, G. Hydrogels for Chemical Sensors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, L.; Petersen, K.; Lum, G.Z.; Sitti, M. Soft Actuators for Small-Scale Robotics. In Advanced Materials; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; p. 1603483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobik, M.; Korus, I.; Dudek, L. The Effect of Magnetite Nanoparticles Synthesis Conditions on Their Ability to Separate Heavy Metal Ions. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2017, 43, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darezereshki, E.; Khodadadi Darban, A.; Abdollahy, M.; Jamshidi-Zanjani, A. Influence of Heavy Metals on the Adsorption of Arsenate by Magnetite Nanoparticles: Kinetics and Thermodynamic. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 10, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Matsuyama, T.; Ida, J. A Simple Magnetite Nanoparticle Immobilized Thermoresponsive Polymer Synthesis for Heavy Metal Ion Recovery. Powder Technol. 2019, 355, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivudu, K.S.; Rhee, K.Y. Preparation and Characterization of PH-Responsive Hydrogel Magnetite Nanocomposite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 349, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Odelius, K.; Edlund, U.; Zhao, C.; Albertsson, A.C. In Situ Synthesis of Magnetic Field-Responsive Hemicellulose Hydrogels for Drug Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2522–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.Y.; Hu, S.H.; Liu, K.H.; Liu, D.M.; Chen, S.Y. Preparation and Characterization of Smart Magnetic Hydrogels and Its Use for Drug Release. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 304, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jang, J.W.; Jo, Y.H.; Abdi, F.F.; Lee, Y.H.; Van De Krol, R.; Lee, J.S. Hetero-Type Dual Photoanodes for Unbiased Solar Water Splitting with Extended Light Harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tilley, S.D.; Cornuz, M.; Sivula, K.; Grätzel, M. Light-Inducedwater Splitting with Hematite: Improved Nanostructure and Iridium Oxide Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6405–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, S.; Zhao, X. Hydrogel Machines. Mater. Today 2020, 36, 102–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.M. Biomedical Nanomagnetics: A Spin through Possibilities in Imaging, Diagnostics, and Therapy. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2523–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muya, F.N.; Sunday, C.E.; Baker, P.; Iwuoha, E. Environmental Remediation of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution through Hydrogel Adsorption: A Critical Review. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erfkamp, J.; Guenther, M.; Gerlach, G. Hydrogel-Based Sensors for Ethanol Detection in Alcoholic Beverages. Sensors 2019, 19, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keplinger, C.; Sun, J.Y.; Foo, C.C.; Rothemund, P.; Whitesides, G.M.; Suo, Z. Stretchable, Transparent, Ionic Conductors. Science 2013, 341, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unni, M.; Rinaldi, C. Chapter 4: Magnetic characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. In Biomedical Nanotechnology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja, A.; Koh, P.Y. Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2009, 55, 22–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Teasdale, P.R.; John, R.; Zhang, S. Synthesis and Characterisation of a Polyacrylamide-Polyacrylic Acid Copolymer Hydrogel for Environmental Analysis of Cu and Cd. React. Funct. Polym. 2002, 52, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mieting, A.; Wang, S.; Schliephake, M.; Franke, D.; Guenther, M.; Odenbach, S.; Gerlach, G. Precipitation of Iron Oxide in Hydrogel with Superparamagnetic and Stimuli-Responsive Properties. Chem. Proc. 2021, 5, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2021005049
Mieting A, Wang S, Schliephake M, Franke D, Guenther M, Odenbach S, Gerlach G. Precipitation of Iron Oxide in Hydrogel with Superparamagnetic and Stimuli-Responsive Properties. Chemistry Proceedings. 2021; 5(1):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2021005049
Chicago/Turabian StyleMieting, Alice, Sitao Wang, Mia Schliephake, Daniela Franke, Margarita Guenther, Stefan Odenbach, and Gerald Gerlach. 2021. "Precipitation of Iron Oxide in Hydrogel with Superparamagnetic and Stimuli-Responsive Properties" Chemistry Proceedings 5, no. 1: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2021005049
APA StyleMieting, A., Wang, S., Schliephake, M., Franke, D., Guenther, M., Odenbach, S., & Gerlach, G. (2021). Precipitation of Iron Oxide in Hydrogel with Superparamagnetic and Stimuli-Responsive Properties. Chemistry Proceedings, 5(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2021005049





