Solvatochromic Behavior of Polarity Indicators in PILs and Their Mixtures with Molecular Solvents: Autoprotolysis and Its Relation to Acidity †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Ionic Liquids
2.2. Microsensors and Spectroscopic Behavior—UV-Vis Spectroscopy
2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solvatochromic Behavior of the Reichardt´s Dye (I)
3.1.1. Range of Mole Fractions (x)
3.1.2. Solvatochromic Behavior of Dye I in the Range of Mole Fractions
3.1.3. Range of Molar Concentration (C) vs. x
3.2. ∆pKa
3.3. TGA
3.4. Correlations
Td vs. ∆pKa and pKa
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Picquet, M.; Tkatchenko, I.; Tommasi, I.; Wasserscheid, P.; Zimmermann, J. Ionic liquids, 3. Synthesis and tilization of protic imidazolium salts in homogeneous catalysis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2003, 345, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Hou, Z.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.; Feng, B.; Wang, X.; Hua, L.; Huang, Q. Polyoxometalate-based protic alkylimidazolium salts as reaction-induced phase-separation catalysts for olefin epoxidation. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1955–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, C.G.; Fortunato, G.G.; Mancini, P.M.J. Nucleophilic and acid catalyst behavior of a protic ionic liquid in a molecular reaction media. Part 1. Phys. Org. Chem. 2009, 22, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Armstrong, D.W. Ionic liquids in separations. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Lu, X.; Sun, N.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution or extraction of crustacean shells using ionic liquids to obtain high molecular weight purified chitin and direct production of chitin films and fibers. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.S.Y.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Upfal, J.; Edye, L.A.; Doherty, W.O.S.; Patti, A.F.; Pringle, J.M.; Scott, J.L. Extraction of lignin from lignocellulose at atmospheric pressure using alkylbenzenesulfonate ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timperman, L.; Skowron, P.; Boisset, A.; Galiano, H.; Lemordant, D.; Frackowiak, E.; Beguin, F.; Anouti, M. Triethylammonium bis(tetrafluoromethylsulfonyl)amide protic ionic liquid as an electrolyte for electrical double-layer capacitors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 8199–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anouti, M.; Timperman, L. A pyrrolidinium nitrate protic ionic liquid-based electrolyte for very low-temperature electrical doublelayer capacitors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 6539–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menne, S.; Pires, J.; Anouti, M.; Balducci, A. Protic ionic liquids as electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 31, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Banuelos, J.L.; Zhang, P.; Feng, G.; Dai, S.; Rother, G.; Cummings, P.T. Toward understanding the structural heterogeneity and ion pair stability in dicationic ionic liquids. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9193–9200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.; Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Ohno, H.; Scrosati, B. Ionic liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bideau, J.L.; Viau, L.; Vioux, A. Ionogels, ionic liquid based hybrid materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuthakki, B.; Greaves, T.L.; Krodkiewska, I.; Weerawardena, A.; Burgar, M.I.; Mulder, R.J.; Drummond, C.J. Protic ionic liquids and ionicity. Aust. J. Chem. 2007, 60, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic ionic liquids: Properties and applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 206–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumino, K.; Peppel, T.; Geppert-Rybczynska, M.; Zaitsau, D.H.; Lehmann, J.K.; Verevkin, S.P.; Kockerling, M.; Ludwig, R. The influence of hydrogen bonding on the physical properties of ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 14064–14075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Understanding the hydrogen bonds in ionic liquids and their roles in properties and reactions. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 6744–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Zhang, S. Hydrogen bonds: A structural insight into ionic liquids. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 2748–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, M.V.; Fernández, J.L.; Adam, C.G.; Della Rosa, C.D. Understanding the Role of Protic Ionic Liquids (PILs) in Reactive Systems: Rational Selection of PILs for the Design of Green Synthesis Strategies for Allylic Amines and β-Amino Esters. ChemPlusChem 2019, 84, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, G.G.; Mancini, P.M.; Bravo, M.V.; Adam, C. New Solvents Designed on the Basis of the Molecular-Microscopic Properties of Binary Mixtures of the Type (Protic Molecular Solvent + 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid). J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 11804–11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Li, H. Equilibrium in Protic Ionic Liquids: The Degree of Proton Transfer and Thermodynamic Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, C.G.; Bravo, M.V.; Mancini, P.M.E. Molecular solvent effect on the acidity constant of protic ionic liquids. Tethahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, P.M.; Adam, C.; Pérez, A.; Vottero, L.R. Solvatochromism in binary solvent mixtures. Response models to the chemical properties of reference probes. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2000, 13, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, C. Polarity of ionic liquids determined empirically by means of solvatochromic pyridinium N-phenolate betaine dyes. Royal Soc. Chem. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, S.M.; Hiroshi, K.; Tomohiro, Y.; Md Abu Bin Hasan, S.; Masayoshi, W. Physicochemical properties determined by ∆pKa for protic ionic liquids based on an organic super-strong base with various Brønsted acids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 5178–5186. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, Z.; Bustam, M.A.; Man, Z.; Khan, A.S. Thermal stability and kinetic study of benzimidazolium based ionic liquid. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zailani, N.H.Z.; Yunus, N.M.; Rahim, A.H.; Bustam, M.A. Thermophysical Properties of Newly Synthesized Ammonium-Based Protic Ionic Liquids: Effect of Temperature, Anion and Alkyl Chain Length. Processes 2020, 8, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshereksi, N.W.; Mohamed, S.M.; Arifin, A.; Ishak, Z.A.M. Thermal Characterisation of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Filled with Barium Titanate as Denture Base Material. J. Phys. Sci. 2014, 25, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek, P.G.J.K.H. Thermogravimetric analysis of thermal stability of poly(methylmethacrylate) films modified with photoinitiators. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivakumar, M.; Panduranga Rao, K. Synthesis and characterization of poly(methyl methacrylate) functional microspheres. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, M.; Xu, W.; Austen Angell, C. Ionic liquids by proton transfer: Vapor pressure, conductivity, and the relevance of ∆pKa from aqueous solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 15411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimenovski, J.; Izgorodina, E.I.; MacFarlane, D.R. Ionicity and proton transfer in protic ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 10341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, H.; Hayamizu, K.; Ishii, K.; Susan, M.A.B.H.; Watanabe, M. Physicochemical Properties and Structures of Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. 1. Variation of Anionic Species. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 16593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ligny, C.L. The dissociation constants of some aliphatic amines in water and methanol-water mixtures at 25. Recueil Travaux Chimiques Pays-Bas. Utrecht 1959, 79, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, E.L.M.; Silva, P.L.; Pliego, J.R. Theoretical Prediction of pKa in Methanol: Testing SM8 and SMD Models for Carboxylic Acids, Phenols, and Amines. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 5730–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rived, F.; Canals, I.; Bosch, E.; Rosés, M. Acidity in methanol–water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 439, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rived, F.; Canals, I.; Bosch, E.; Rosés, M. Dissociation constants of neutral and charged acids in methyl alcohol. The acid strength resolution. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 374, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshepelevitsh, S.; Kütt, A.; Lõkov, M.; Kaljurand, I.; Saame, J.; Heering, A.; Plieger, P.; Vianello, R.; Leito, I. On the Basicity of Organic Bases in Different Media. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Xiang, J.; Chen, R.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, S. Physicochemical properties determined by DpKa for protic ionic liquids based on an organic super-strong base with various Brønsted acids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 20007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Martinez, J.A.; Tang, L.; Belieres, J.-P.; Zeller, R.; Angell, C.A.; Friesen, C. Hydrogen redox in protic ionic liquids and a direct measurement of proton thermodynamics. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 12586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anouti, M.; Caillon-Caravian, M.; Le Flock, C.; Lemordant, D. Alkylammonium-Based Protic Ionic Liquids. II. Ionic Transport and Heat-Transfer Properties: Fragility and Ionicity Rule. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 31–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Tokuda, H.; Watanabe, M. Ionicity in ionic liquids: Correlation with ionic structure and physicochemical properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, H.; Hayamizu, K.; Ishii, K.; Susan, M.A.B.H.; Watanabe, M. Physicochemical Properties and Structures of Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. 2. Variation of Alkyl Chain Length in Imidazolium Cation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, H.; Ishii, K.; Susan, M.A.B.H.; Tsuzuki, S.; Hayamizu, K.; Watanabe, M. Physicochemical Properties and Structures of Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. 3. Variation of Cationic Structures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, H.; Tsuzuki, S.; Susan, M.A.B.H.; Hayamizu, K.; Watanabe, M. How Ionic Are Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids? An Indicator of the Physicochemical Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 39–19593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miran, M.S.; Kinoshita, H.; Yasuda, T.; Susan, M.A.B.H.; Watanabe, M. Hydrogen bonds in protic ionic liquids and their correlation with physicochemical properties. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennuri, B.K.; Gardas, R.L. Measurement and correlation for the thermophysical properties of hydroxyethyl ammonium based protic ionic liquids: Effect of temperature and alkyl chain length on anion. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 427, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
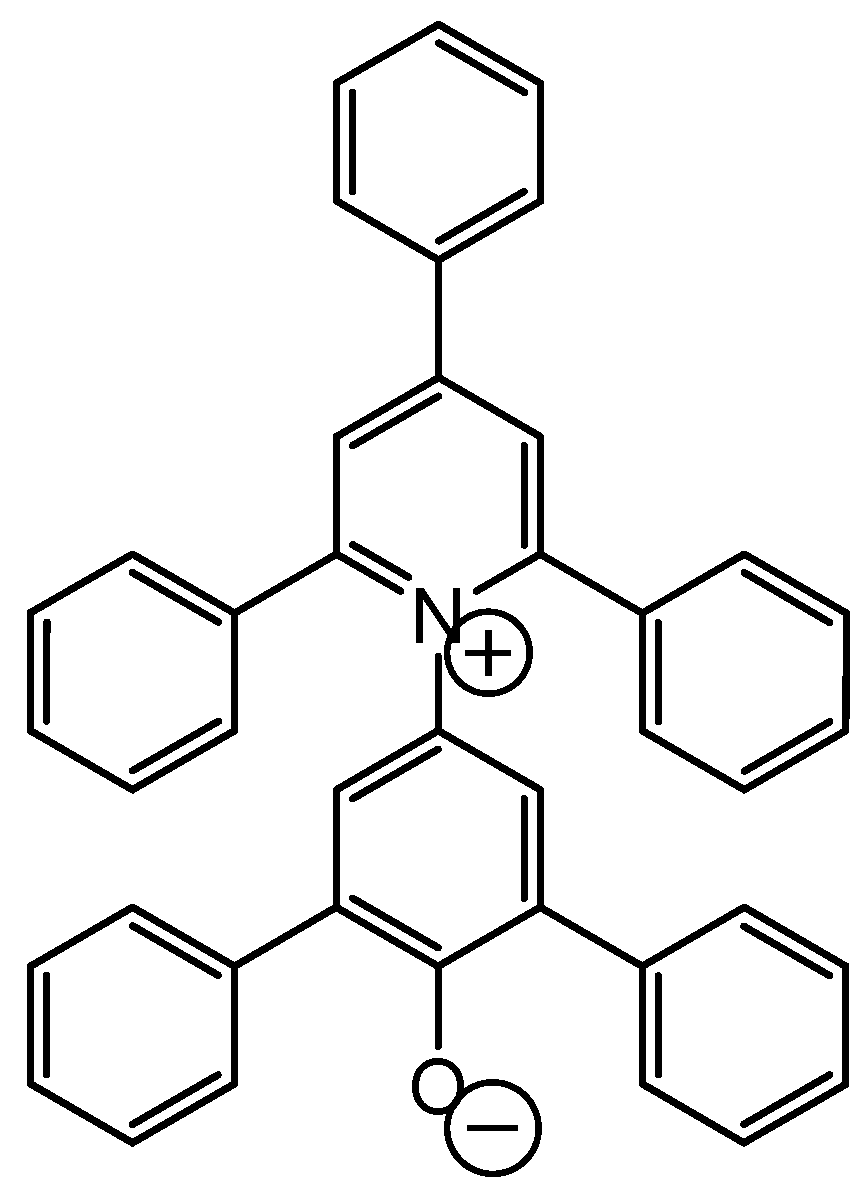
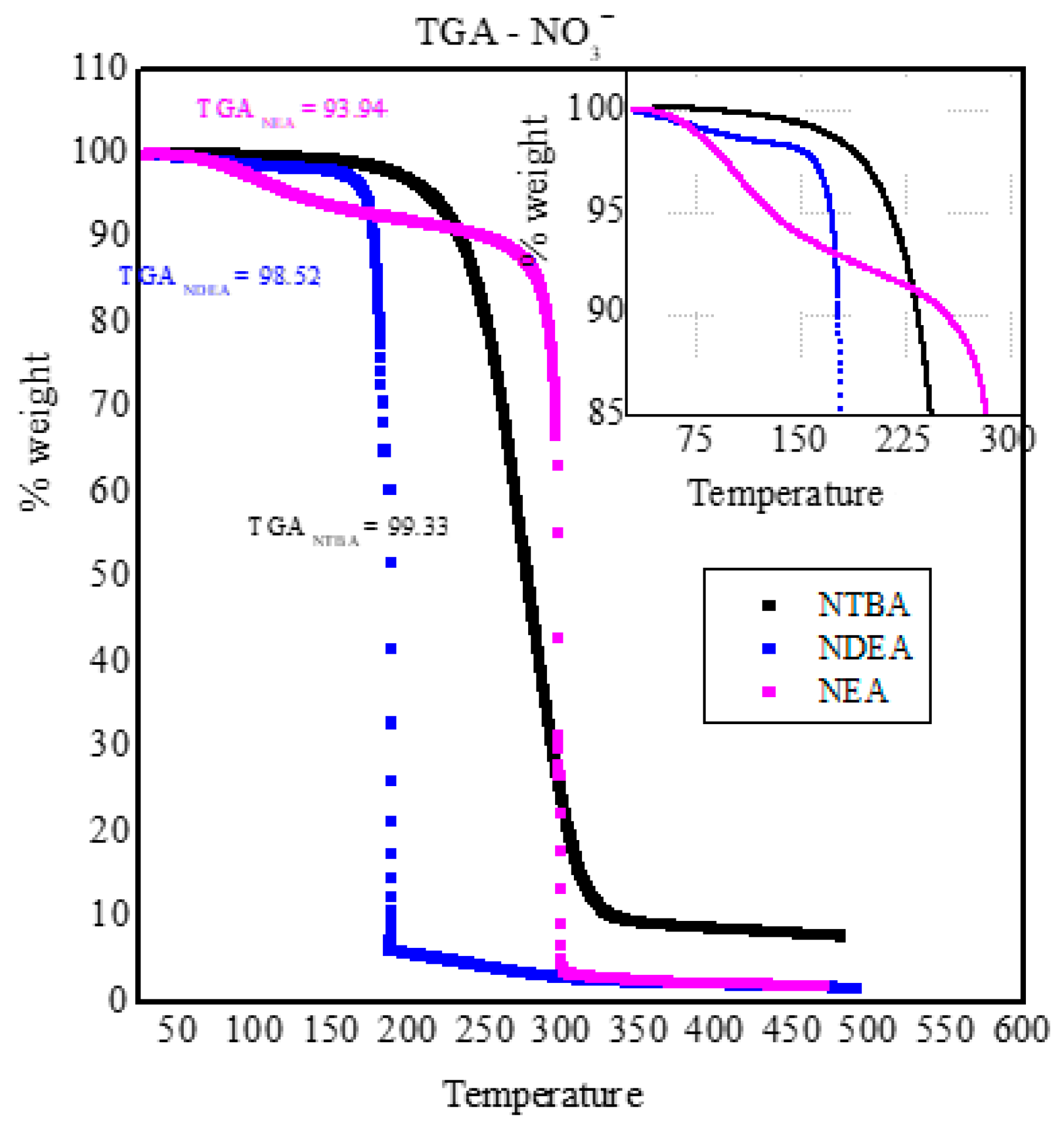
 NEA,
NEA,  NDEA,
NDEA,  NTBA).
NTBA).
 NEA,
NEA,  NDEA,
NDEA,  NTBA).
NTBA).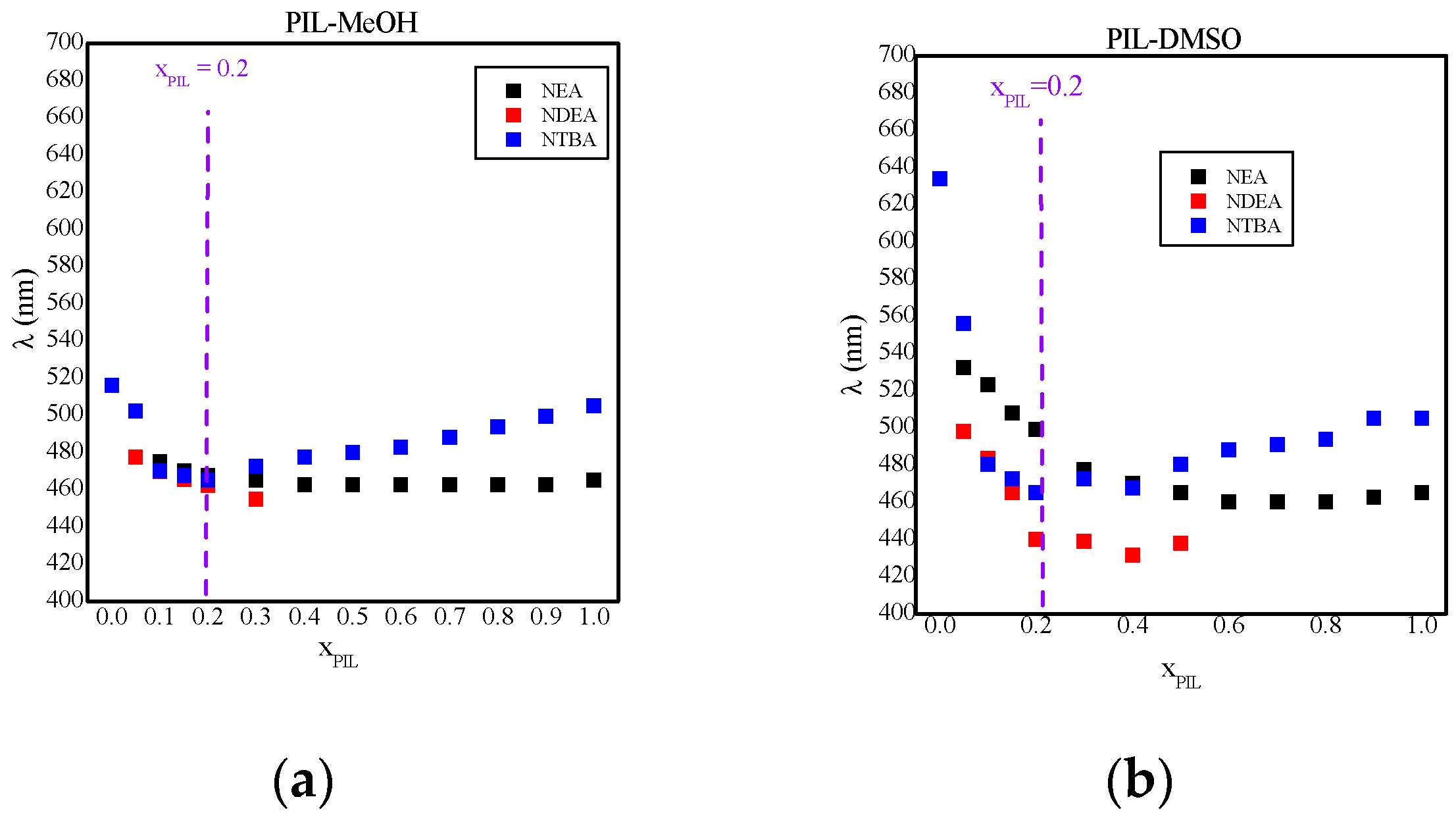
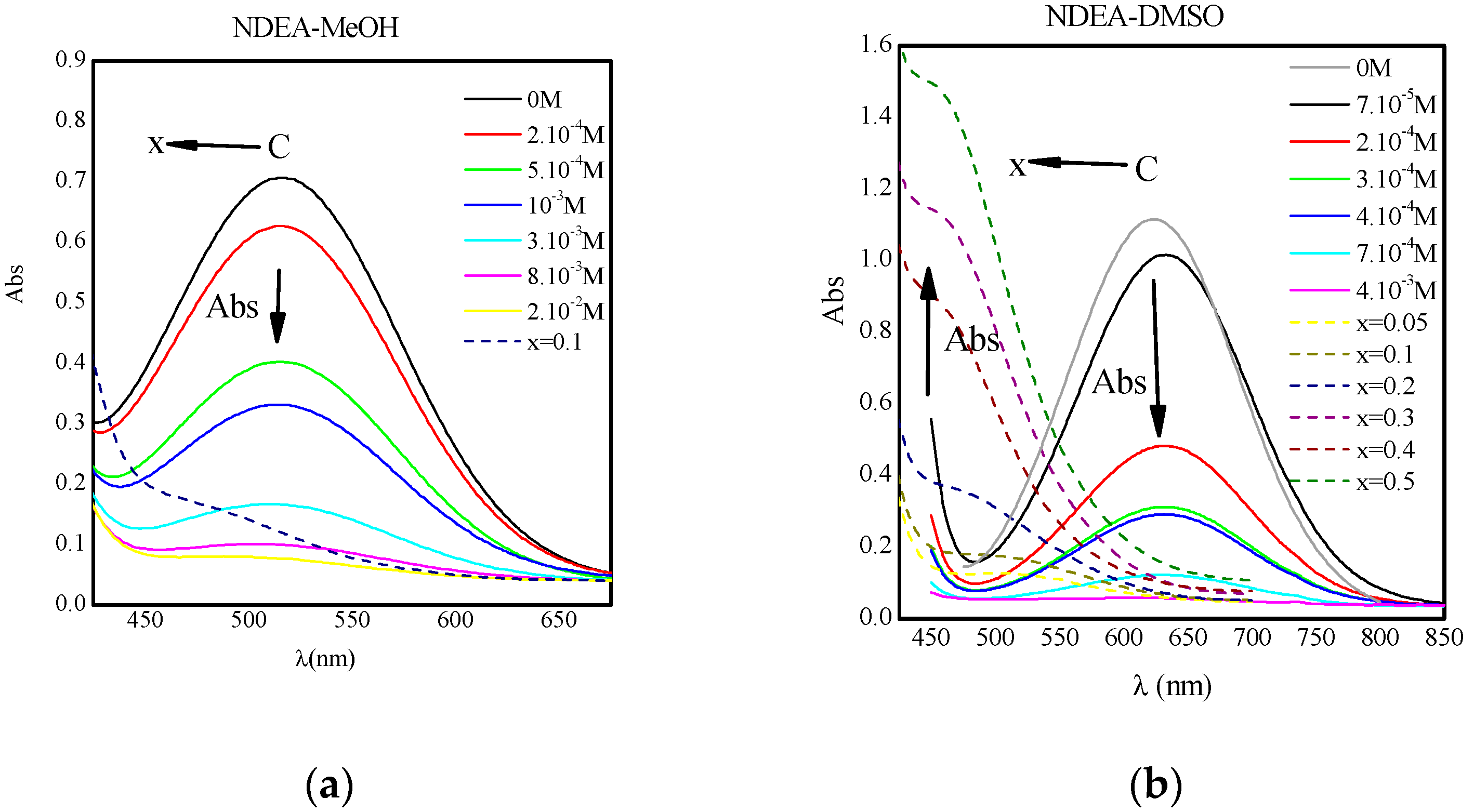
 MeOH y (b)
MeOH y (b)  DMSO.
DMSO.
 MeOH y (b)
MeOH y (b)  DMSO.
DMSO.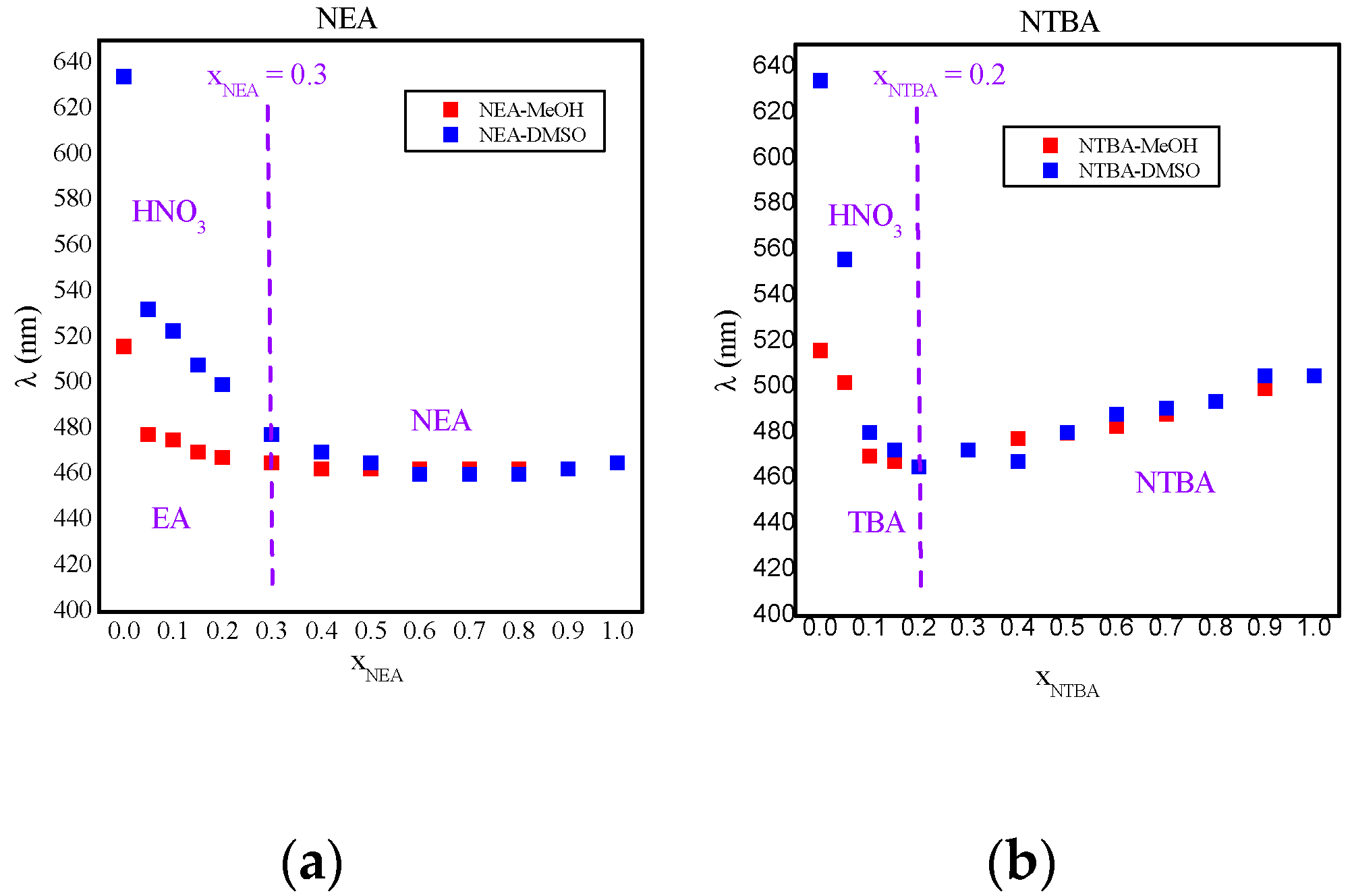
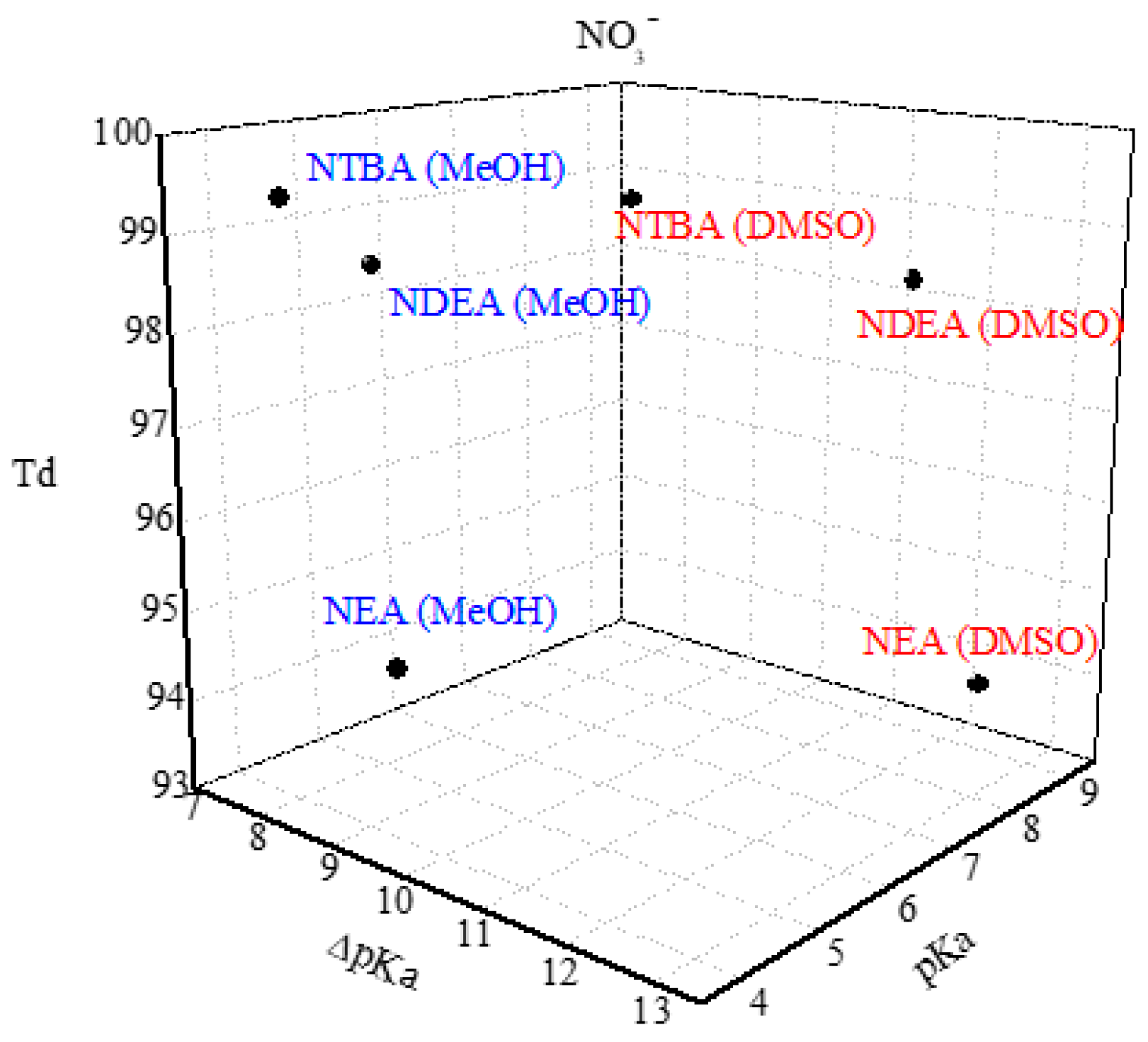
 NEA,
NEA,  NDEA,
NDEA,  NTBA).
NTBA).
 NEA,
NEA,  NDEA,
NDEA,  NTBA).
NTBA).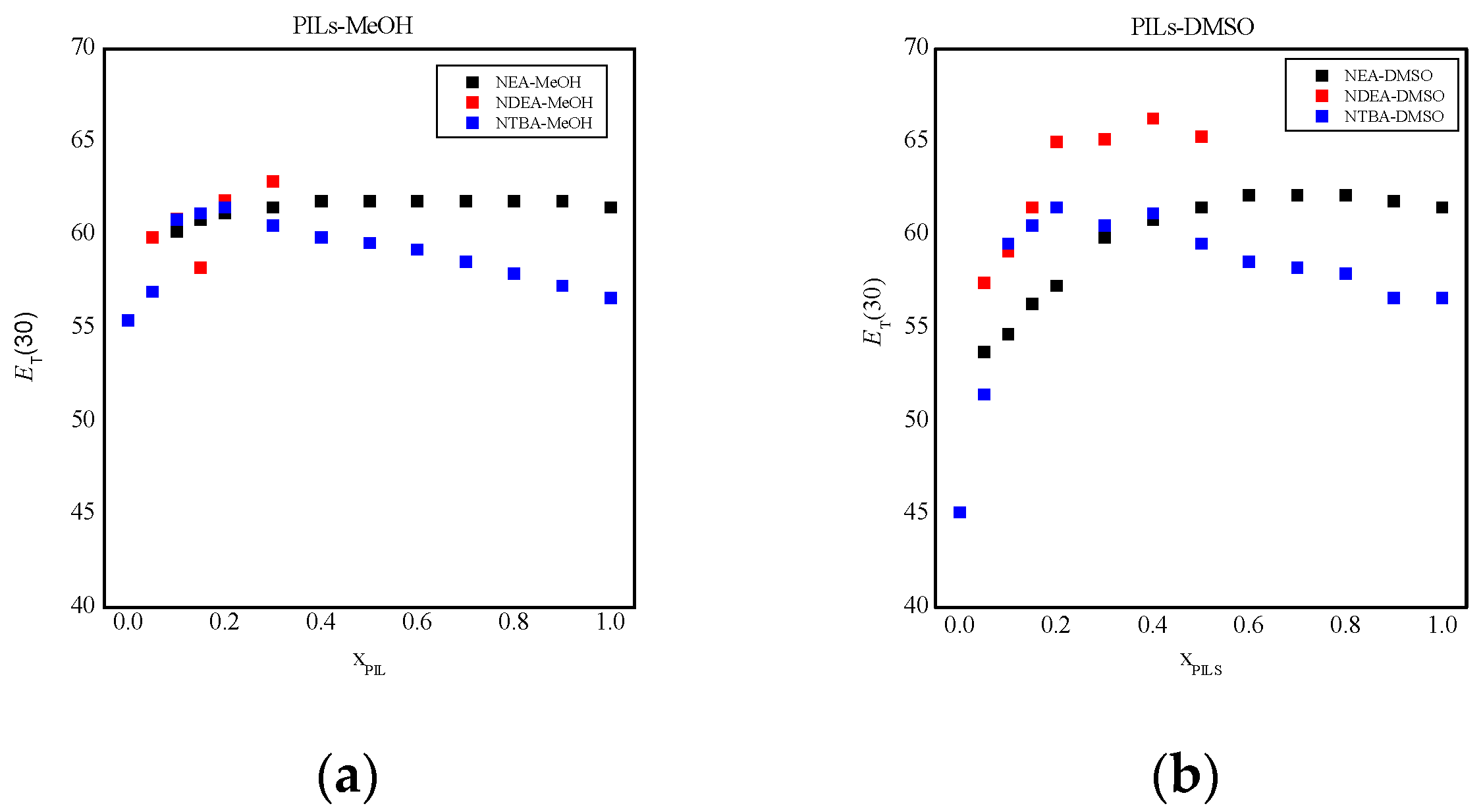
| Species | pKaw | pKaMeOH | pKaDMSO | ΔpKaW | ΔpKaMeOH | ΔpKaDMSO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNO3 | −1.3 | 3.18 | −1.72 | Am/HNO3 | ||
| EA | 10.63 | 11.00 | 10.90 | 11.93 | 7.82 | 12.62 |
| DEA | 10.98 | 11.00 | 10.50 | 12.28 | 7.82 | 12.22 |
| TBA | 10.89 | 10.78 | 8.4 | 12.19 | 7.60 | 10.12 |
| PILs | pKaPIL | |
|---|---|---|
| MeOH | DMSO | |
| NEA | 5.38 | 8.67 |
| NDEA | 5.21 | 7.87 |
| NTBA | 4.34 | 6.33 |
| pKadye | 5.10 | 8.90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adam, C.G.; Gamba, L.; Bravo, M.V. Solvatochromic Behavior of Polarity Indicators in PILs and Their Mixtures with Molecular Solvents: Autoprotolysis and Its Relation to Acidity. Chem. Proc. 2022, 8, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-25-11746
Adam CG, Gamba L, Bravo MV. Solvatochromic Behavior of Polarity Indicators in PILs and Their Mixtures with Molecular Solvents: Autoprotolysis and Its Relation to Acidity. Chemistry Proceedings. 2022; 8(1):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-25-11746
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdam, Claudia Guadalupe, Lucía Gamba, and Maria Virginia Bravo. 2022. "Solvatochromic Behavior of Polarity Indicators in PILs and Their Mixtures with Molecular Solvents: Autoprotolysis and Its Relation to Acidity" Chemistry Proceedings 8, no. 1: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-25-11746
APA StyleAdam, C. G., Gamba, L., & Bravo, M. V. (2022). Solvatochromic Behavior of Polarity Indicators in PILs and Their Mixtures with Molecular Solvents: Autoprotolysis and Its Relation to Acidity. Chemistry Proceedings, 8(1), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-25-11746






