Toll Automation System Using RFID and Web Portal †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
- A variety of techniques can use to accomplish automated toll collection. Some valuable suggestions and resources uncovered via the study are the toll square, controlled by a computer, which is frequently updated. The vehicle’s number plate is located using a camera while taking care of the photograph’s light, and the cost is kept low by grouping the number plate with the data set. This system makes use of infrared sensors right from the start.
- The client must obtain a transmitter from the workplace, which will have many customers focus points. When the consumer contacts the cost court, the transmitter should place an optical path with the beneficiary. It is grown, the switch crushed, the recipient searches the data set for a match, and the desired aggregate subtracted. The structure is considering RFID [3].
- Technology: The amount of the per-user-specified total is subtracting as soon as the RFID name appears, resulting in the planned information from the data set and the motor-constrained entry permitting the vehicle to pass through it. The remaining references are nearly identical to one another. Although our research uses RFID technology, the data set has limited. In addition, we remembered the GSM module, which beliefs to be the future degree in a substantial percentage of the papers, for our endeavor [4].
- The huge bottleneck generated before the scaffolds of inhabited metropolitan areas worldwide has much reduced because of a robotized toll-based collecting system. It is also the most straightforward approach to control the massive traffic flow. It precisely catches the radio recurrence using RFID innovation. In this technique, the RF follows a unique code associated with the vehicle that emits RF signals. Every automobile owner must have a record that includes an RFID tag. The indicators will be detected and communicated to the controlling device when the vehicle approaches the passage cost entry. The automobile owners will be permitted to pass if the judge has a sufficient balance on their record. A complex cost-based selection mechanism called the Canada 407 Express cost course had been discovered (ETR). This framework showed an optical camera with Optical Character Recognition (OCR) that collects pictures and detects missing tags. On the interstate in Gujrat, India, an automated cost collecting framework based on radio recurrence and tag operates financially, with Mitsubishi Heavy Industries providing the essential gear. On the Ahmadabad Mumbai National Highway, India has its first interoperable RFID-based electronic cost framework, allowing cars with electronic labels to communicate at a frequency of (850–950 MHz) with a range of up to 90 feet and a reaction time of 10 milliseconds. The motorist must acquire a receipt and pass through the entry, despite this approach is cost-effective [5].
3. Proposed System
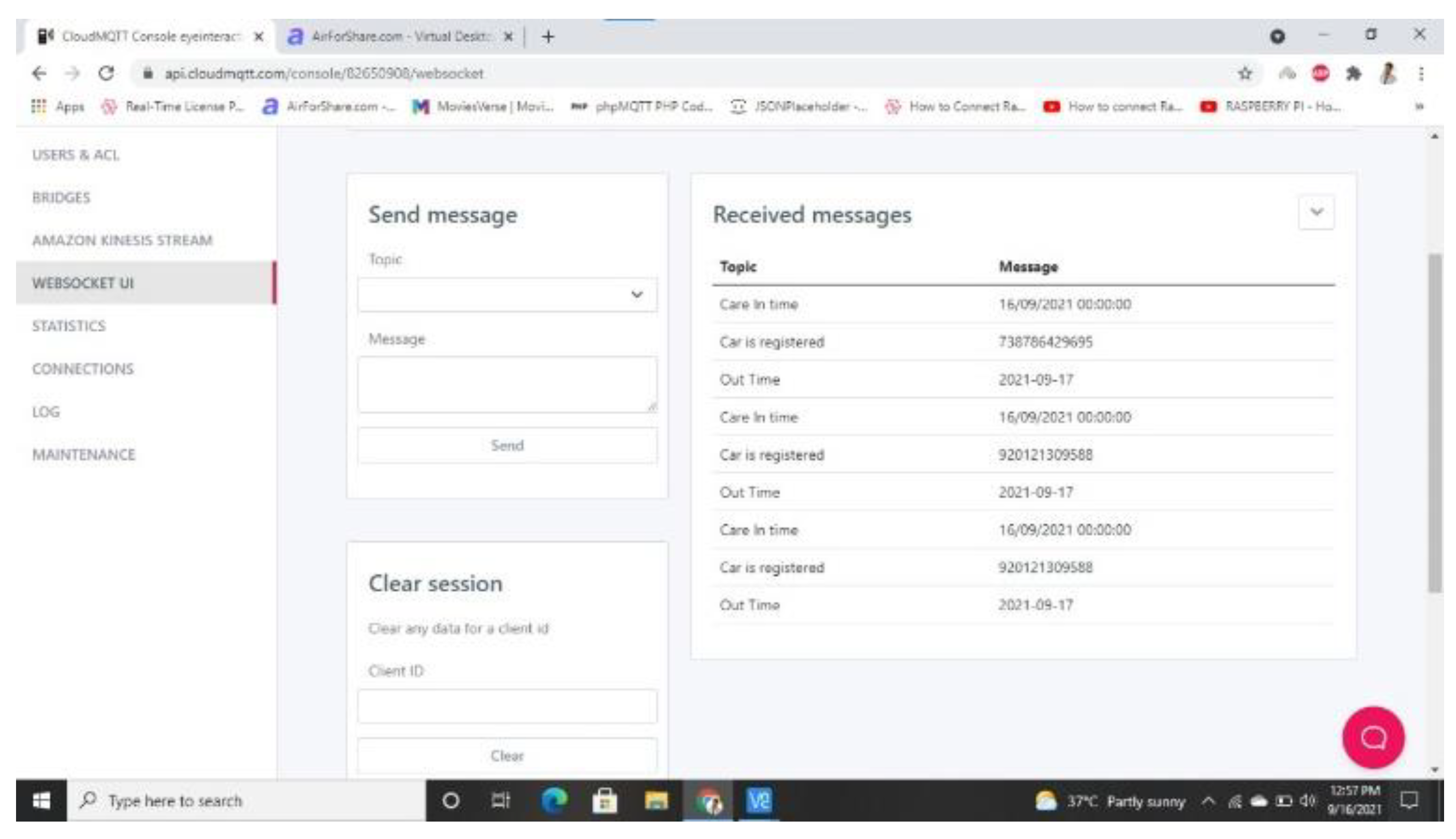
4. Results
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uke, N.J.; Thool, R.C. Moving Vehicle Detection for Measuring Traffic Count Using OpenCV. J. Autom. Control Eng. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andurkar, G.K.; Ramteke, V.R. Smart Highway Electronic Toll Collection. Int. J. Innov. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 2015, 3, 4087–4094. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, R.; Ahmed, M.; Alfasani, M.M.; Zaman, H.U. An advanced security system integrated with RFID based automated toll collection system. In Proceedings of the 2017 Third Asian Conference on Defence Technology (ACDT), Phuket, Thailand, 18–20 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulla, R.; Abdillahi, A.; Abbas, M.K. Electronic toll collection system based on radio frequency identification system. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2018, 8, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavke, A.; Pai, S. Advance automatic toll collection & vehicle detection during collision using RFID. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Nascent Technologies in the Engineering Field (ICNTE), Vashi, India, 27–28 January 2017. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, Z. Toll Automation System Using RFID and Web Portal. Eng. Proc. 2022, 20, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2022020044
Abbas Z. Toll Automation System Using RFID and Web Portal. Engineering Proceedings. 2022; 20(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2022020044
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Zeghum. 2022. "Toll Automation System Using RFID and Web Portal" Engineering Proceedings 20, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2022020044
APA StyleAbbas, Z. (2022). Toll Automation System Using RFID and Web Portal. Engineering Proceedings, 20(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2022020044




