Fabrication of Electronic Silk Fabrics via RGO Adhesion Incorporating Oxygen Plasma Treatment †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
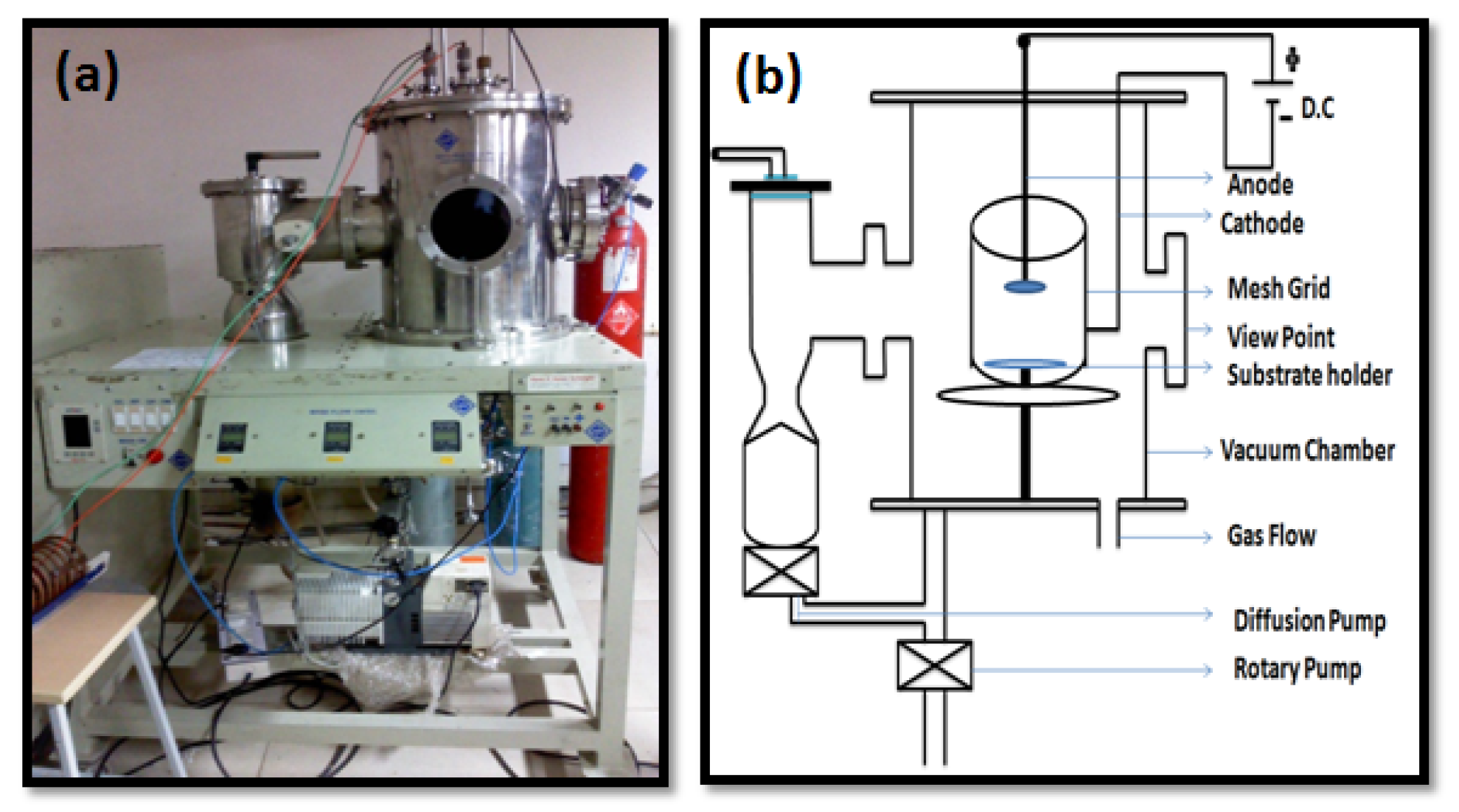
2.2.1. Silk Fabric Plasma Treatment
2.2.2. Fabrication of RGO on Silk Fabrics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results of Plasma Treated Silk Fabrics
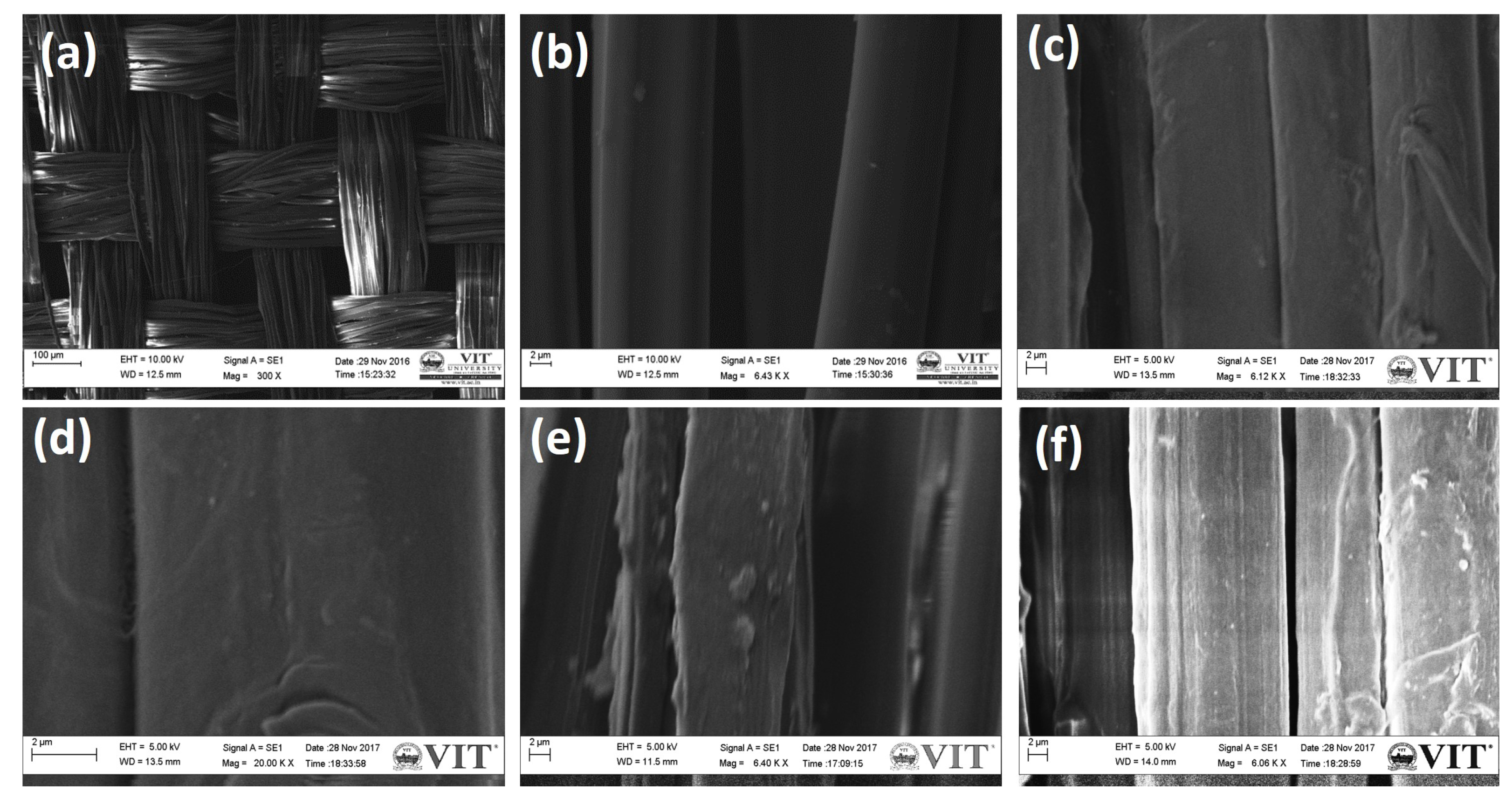
3.1.1. SEM Studies
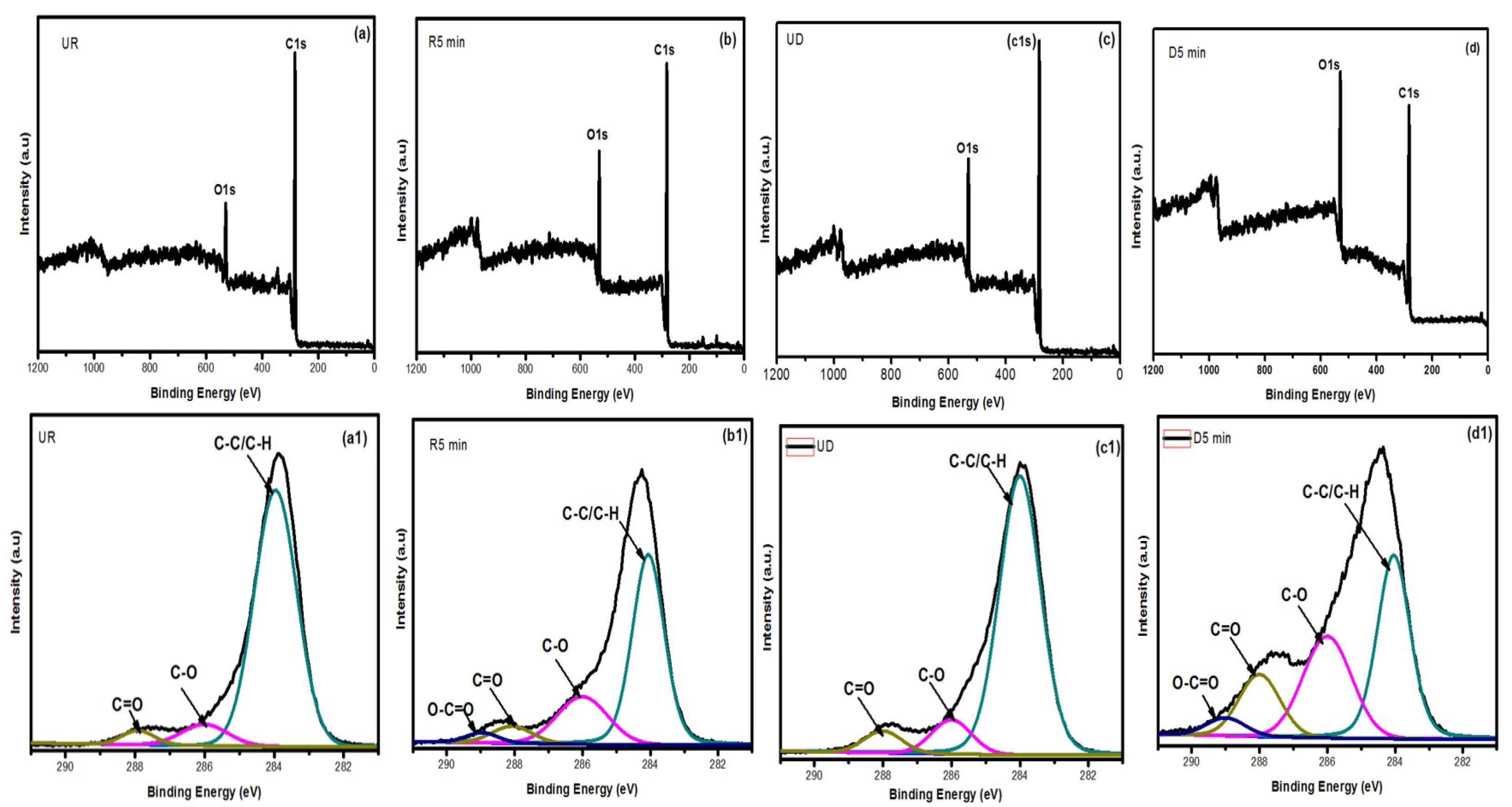
3.1.2. XPS
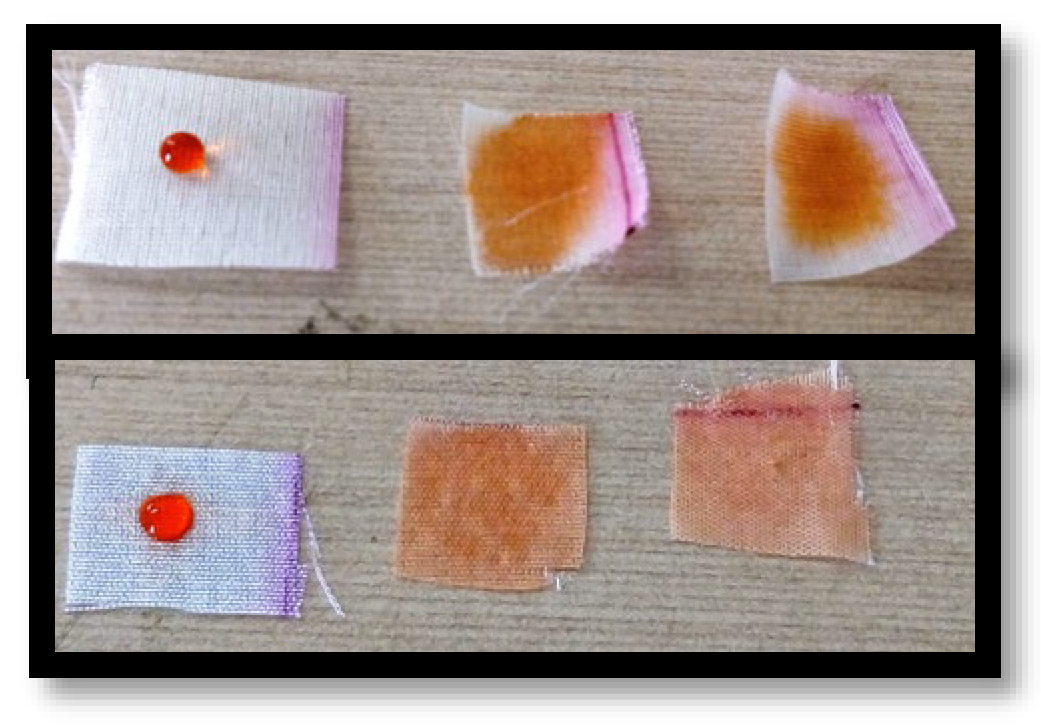
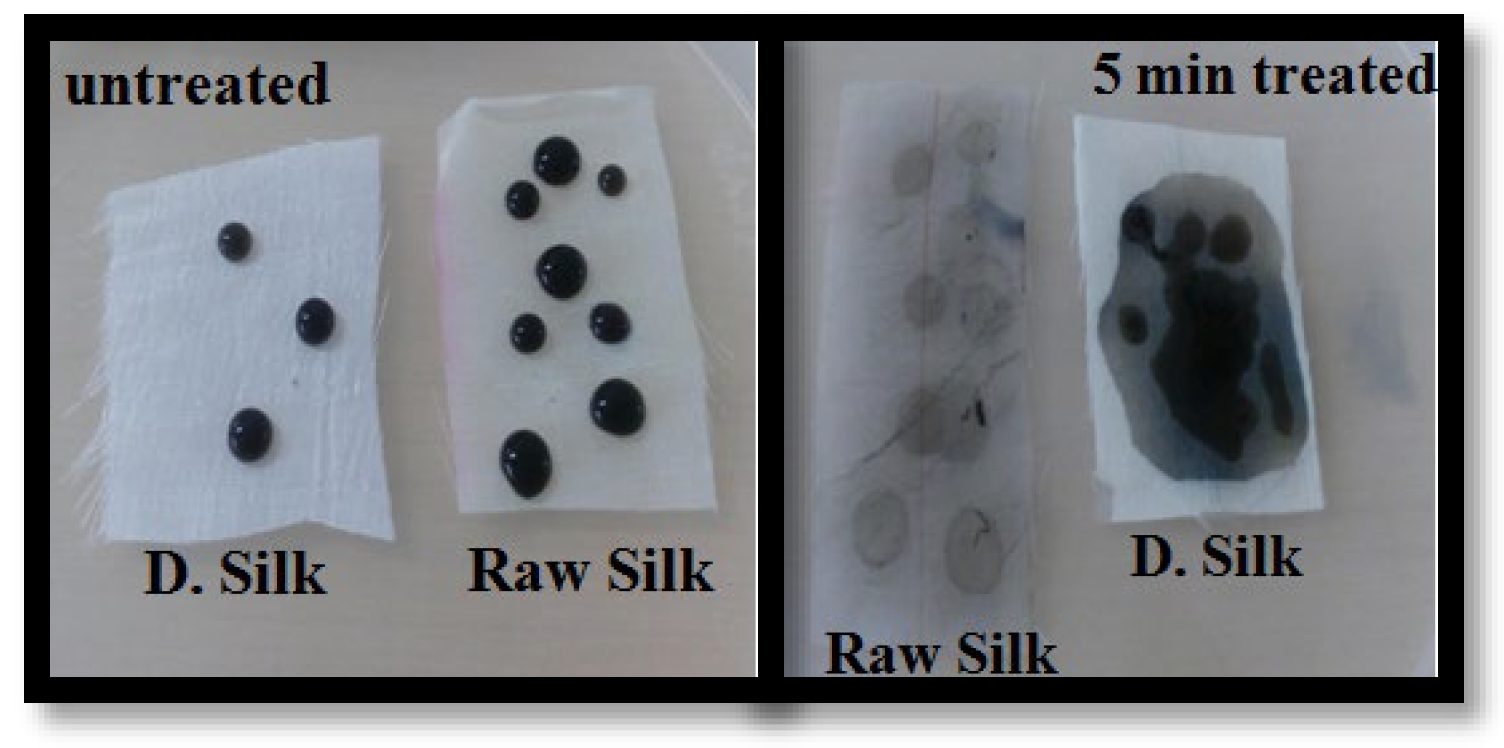
3.1.3. Wetting Property
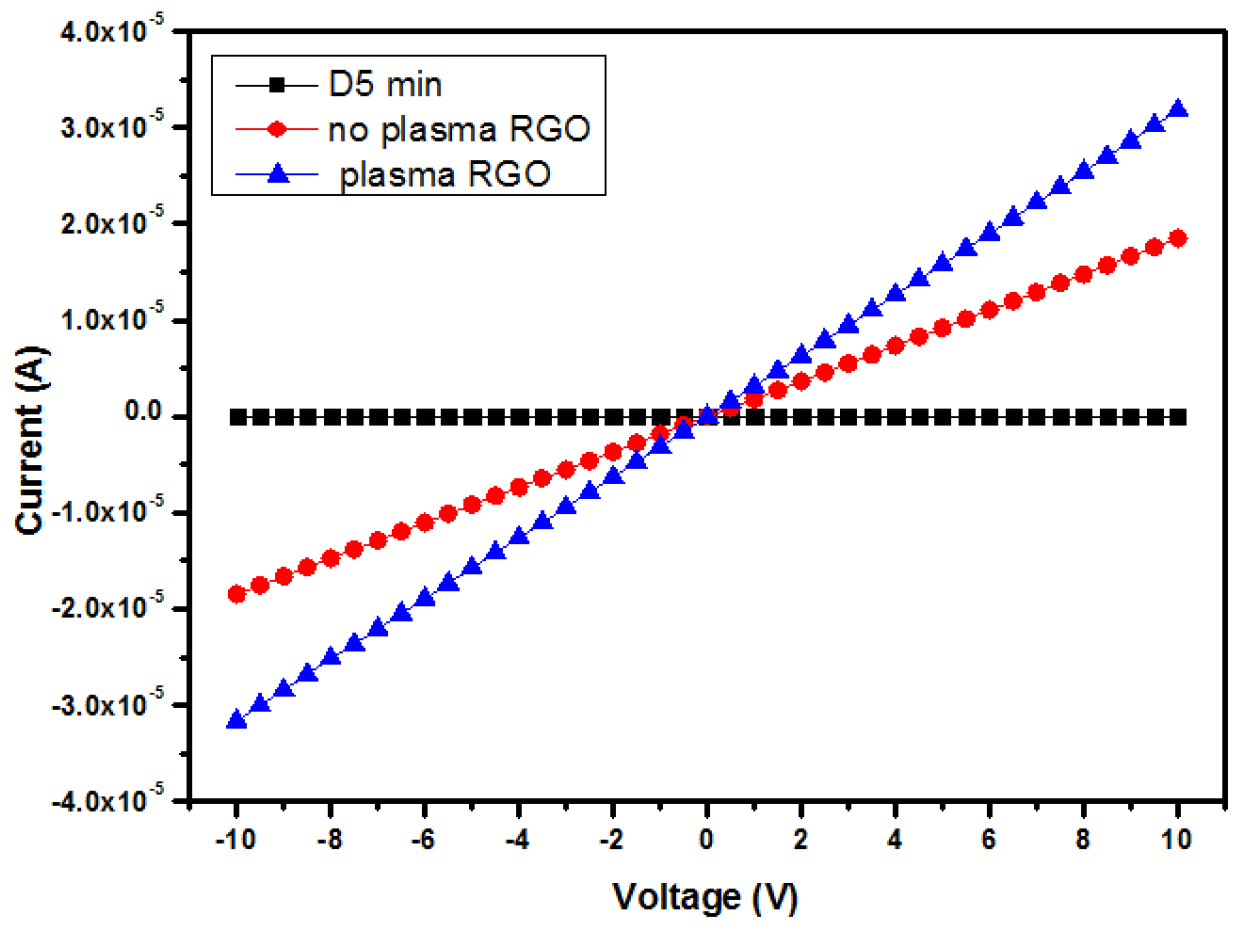
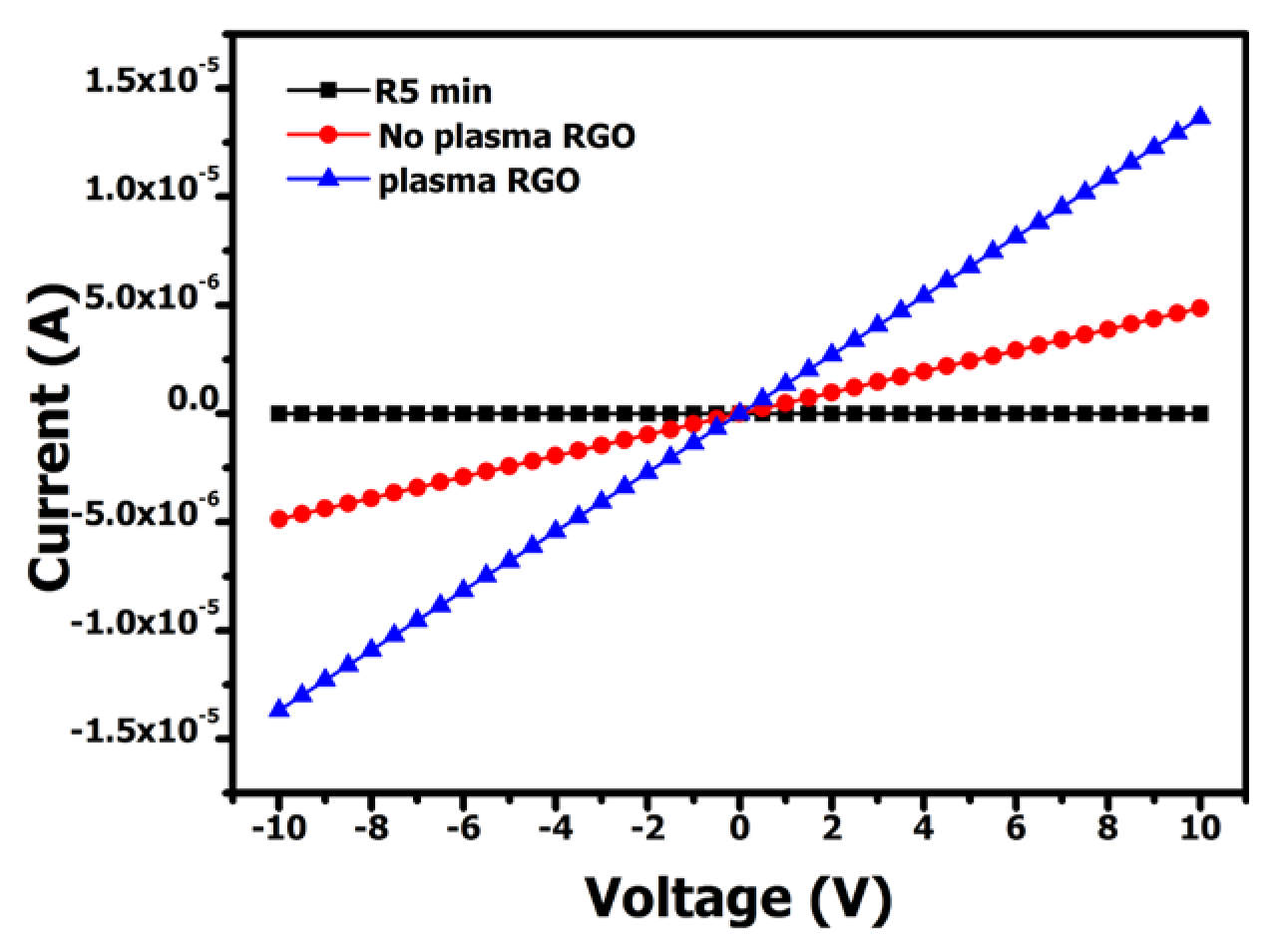
3.1.4. I-V Electrical Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asakura, T.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk production and processing. Encyclop. Agric. Sci. 1994, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Manna, J.; Goswami, S.; Shilpa, N.; Sahu, N.; Rana, R.K. Biomimetic Method To Assemble Nanostructured Ag@ZnO on Cotton Fabrics: Application as Self-Cleaning Flexible Materials with Visible-Light Photocatalysis and Antibacterial Activities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8076–8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rigueiro, J.; Elices, M.; Llorca, J.; Viney, C. Effect of degumming on the tensile properties of silkworm (Bombyx mori) silk fiber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 84, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheila, S.; Ghoranneviss, M.; Moazzenchi, B. Application of plasma in different branches of industries. In Proceedings of the 4th RMUTP International Conference: Textiles & Fashion, Bangkok, Thailand, 3–4 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chi-Wai, K.; Lam, C.-F.; Chan, C.-K.; Ng, S.-P. Using atmospheric pressure plasma treatment for treating grey cotton fabric. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Guruvenket, S.; Rao, G.M.; Komath, M.; Raichur, A.M. Plasma surface modification of polystyrene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 236, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenton, G.C.S.M.J. Surface modification of polymer surfaces: Atmospheric plasma versus vacuum plasma treatments. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, K.V.; Sarma, B.; Sarma, A. Plasma treatment on cotton fabrics to enhance the adhesion of Reduced Graphene Oxide for electro-conductive properties. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 84, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarma, B.; Rani, K.V.; Gupta, D.N. Fabrication of Electronic Silk Fabrics via RGO Adhesion Incorporating Oxygen Plasma Treatment. Eng. Proc. 2023, 52, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023052005
Sarma B, Rani KV, Gupta DN. Fabrication of Electronic Silk Fabrics via RGO Adhesion Incorporating Oxygen Plasma Treatment. Engineering Proceedings. 2023; 52(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023052005
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarma, Bornali, K. Vinisha Rani, and D. N. Gupta. 2023. "Fabrication of Electronic Silk Fabrics via RGO Adhesion Incorporating Oxygen Plasma Treatment" Engineering Proceedings 52, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023052005
APA StyleSarma, B., Rani, K. V., & Gupta, D. N. (2023). Fabrication of Electronic Silk Fabrics via RGO Adhesion Incorporating Oxygen Plasma Treatment. Engineering Proceedings, 52(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023052005




