Canned Beans Aquafaba as an Egg White Substitute in the Technology of Low-Fat Mayonnaise †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sampling
2.2. Methods
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Rheological and Microstructural Properties
3.2. Sensory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morley, W.G. Mayonnaise. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcicek, A.; Karasu, S.; Bozkurt, F.; Kayacan, S. Egg Yolk-Free Vegan Mayonnaise Preparation from Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Gum Nanoparticles with or without Loading Olive Pomace Extracts. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 26316–26327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Official Aquafaba Site. Available online: http://www.aquafaba.com/ (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- He, Y.; Meda, V.; Reaney, M.J.T.; Mustafa, R. Aquafaba, a New Plant-Based Rheological Additive for Food Applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, G.N.; Taspinar, T.; Ozer, M.S. Aquafaba: A Multifunctional Ingredient in Food Production. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2022, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Menezes, R.C.; de Carvalho Gomes, Q.C.; de Almeida, B.S.; de Matos, M.F.R.; Pinto, L.C. Plant-Based Mayonnaise: Trending Ingredients for Innovative Products. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 30, 100599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goralchuk, A.; Gubsky, S.; Omel’chenko, S.; Riabets, O.; Grinchenko, O.; Fedak, N.; Kotlyar, O.; Cheremska, T.; Skrynnik, V. Impact of Added Food Ingredients on Foaming and Texture of the Whipped Toppings: A Chemometric Analysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 1955–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goralchuk, A.; Gubsky, S.; Tereshkin, O.; Kotlyar, O.; Omel’chenko, S.; Tovma, L. Development of a Theoretical Model for Obtaining the Whipped Emulsions from a Dry Fat-Containing Mixture and Its Experimental Verification. East.-Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2017, 2, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, R.; Reaney, M.J.T. Aquafaba, from Food Waste to a Value-Added Product. In Food Wastes and By-Products; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 93–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, T.F.; Christensen, C.H.; Hammershøj, M. Aquafaba as an Egg White Substitute in Food Foams and Emulsions: Protein Composition and Functional Behavior. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyl, C.; Sadler, G.D. PH and Titratable Acidity. In Food Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksonova, O.; Gubsky, S.; Murlykina, N.; Otroshko, N. Development of Vitamin D3-Fortified Dairy Sour Cream Desert. J. Hyg. Eng. Des. 2022, 40, 119–131. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 13299:2016; Sensory Analysis. Methodology. General Guidance for Establishing a Sensory Profile. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 8586:2012; Sensory Analysis. General Guidelines for the Selection, Training and Monitoring of Selected Assessors and Expert Sensory Assessors. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Mangiapelo, L.; Ianni, F.; Pagano, C.; Grispoldi, L.; Blasi, F.; Cenci-Goga, B.; Perioli, L.; Cossignani, L. Role of Apple Pomace in the Formulation of a Novel Healthy Mayonnaise. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 2835–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumah, S.H.; Andoyo, R.; Rialita, T. Protein Isolation Techniques of Beans Using Different Methods: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 443, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudra, S.G.; Hanan, E.; Sagar, V.R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Basu, S.; Sharma, V. Manufacturing of Mayonnaise with Pea Pod Powder as a Functional Ingredient. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 2402–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
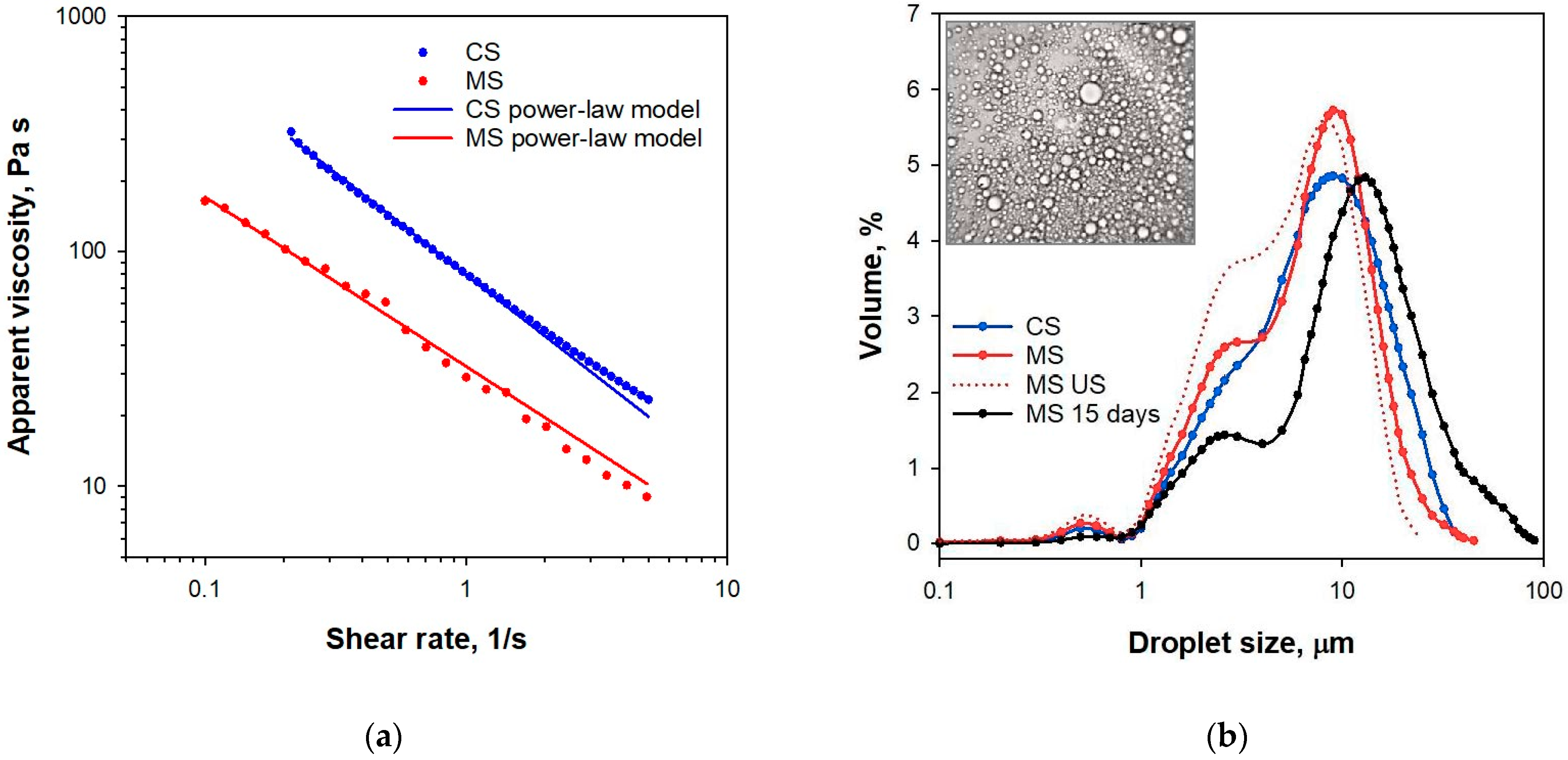

| Sample | Power-Law Equation | Static Yield Stress, Pa | Droplet Size Distribution | Acidity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consistency Index, Pa·sn | Flow Behavior Index | R2 | D43, µm | SPAN, µm | pH | TTA, % | ||
| CS | 79.6 ± 0.8 a | 0.135 ± 0.008 b | 0.9973 | 142 ± 7 a | 8.16 | 2.17 | 3.82 ± 0.01 a | 0.201 |
| MS * | 32.4 ± 0.8 b | 0.275 ± 0.014 a | 0.9957 | 132 ± 5 b | 8.40 | 1.74 | 3.66 ± 0.01 b | 0.691 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sachko, A.; Sema, O.; Grinchenko, O.; Gubsky, S. Canned Beans Aquafaba as an Egg White Substitute in the Technology of Low-Fat Mayonnaise. Eng. Proc. 2023, 56, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-16291
Sachko A, Sema O, Grinchenko O, Gubsky S. Canned Beans Aquafaba as an Egg White Substitute in the Technology of Low-Fat Mayonnaise. Engineering Proceedings. 2023; 56(1):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-16291
Chicago/Turabian StyleSachko, Anastasiia, Oksana Sema, Olga Grinchenko, and Sergey Gubsky. 2023. "Canned Beans Aquafaba as an Egg White Substitute in the Technology of Low-Fat Mayonnaise" Engineering Proceedings 56, no. 1: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-16291
APA StyleSachko, A., Sema, O., Grinchenko, O., & Gubsky, S. (2023). Canned Beans Aquafaba as an Egg White Substitute in the Technology of Low-Fat Mayonnaise. Engineering Proceedings, 56(1), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-16291







