The Intelligent Connection Management Model to Enhance the Security of Cloud Computers in High-Density Fog Networks †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Improved data security: Secured server management ensures that all data transmitted across the fog network are encrypted and strongly protected, making them secure from unauthorized access, tampering, and malicious attacks.
- Data protection: Secured server management is designed to protect critical data to prevent unauthorized access, unauthorized changes, and malicious activities. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access and modify data stored in the system.
- Improved performance: Secured server management is designed to optimize network resources and maximize throughput, enabling high-density fog networks to run more efficiently.
2. Materials and Methods
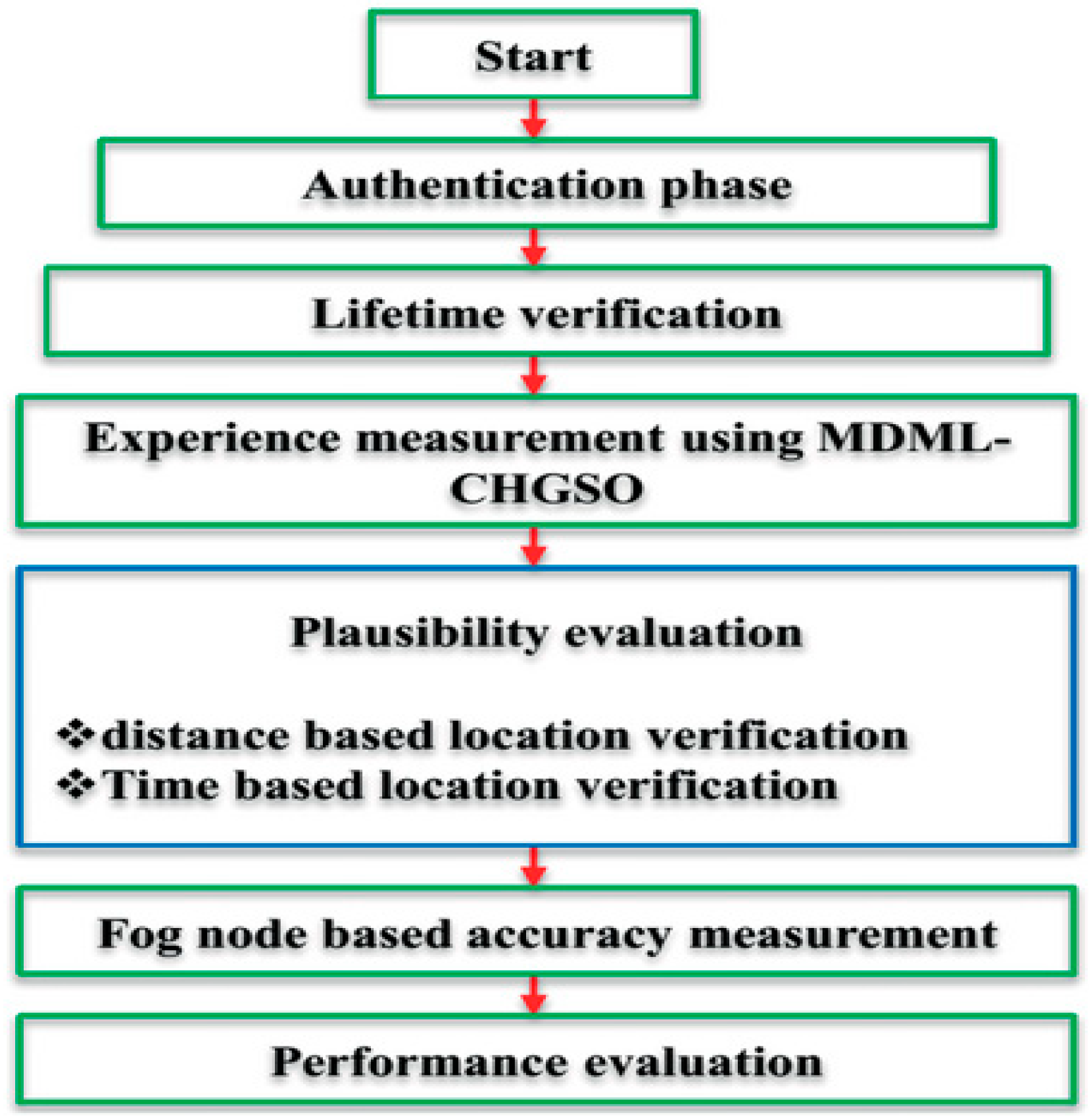
2.1. Proposed Model
2.2. Operating Principle
2.3. Functional Working
- Limited throughput: In scenarios of extreme congestion, throughput can be drastically reduced due to larger amounts of traffic competing for the same amount of available resources. This can lead to increased latency and slow data rates, resulting in poor performance for all users;
- Limited scalability: Extreme congestion can result in massive numbers of devices all vying for the same resources. This can overload some components of the system, leading to diminished scalability and slower speeds for devices that were not previously saturating the network;
- Limited Quality of Service (QoS): Device heterogeneity can lead to a variety of different device configurations and capabilities, making it difficult to guarantee uniform performance for all users. Device-to-device latencies can be unpredictable, and creating strategies to ensure QoS might be difficult;
- Security vulnerabilities: Congestion of the network can allow malicious actors to create spoofed traffic and launch attacks on other devices, leading to potential security vulnerabilities. Moreover, users of different device types might be vulnerable to different tailored attacks, making it difficult to ensure comprehensive security.
3. Results and Discussion
- Data privacy concerns: As self-organizing algorithms and adaptive techniques are used to gather and filter data, there is a risk of the data being misused or sold to third parties, which could result in potential privacy concerns;
- Accuracy: Self-organizing algorithms and adaptive techniques are not 100% accurate, leading to errors in the data being collected and filtered. This may lead to incorrect decisions being made based on the data, and might negatively impact the product or service;
- Trust and liability: With AI models, it is not always clear who is accountable if the model produces an incorrect result. This can lead to users feeling less comfortable trusting the results, and can potentially create liability issues if something goes wrong.
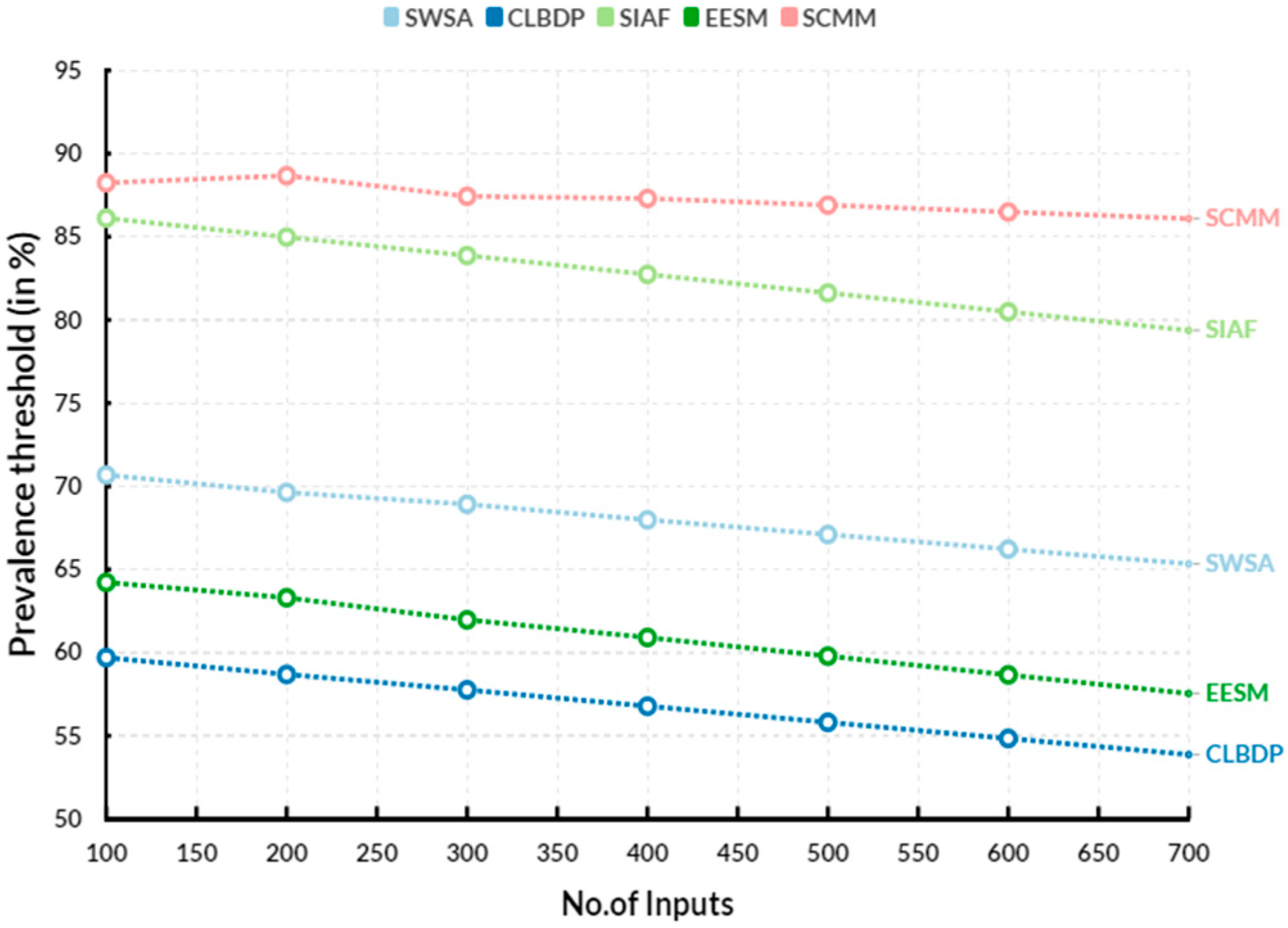
3.1. Prevalence Threshold
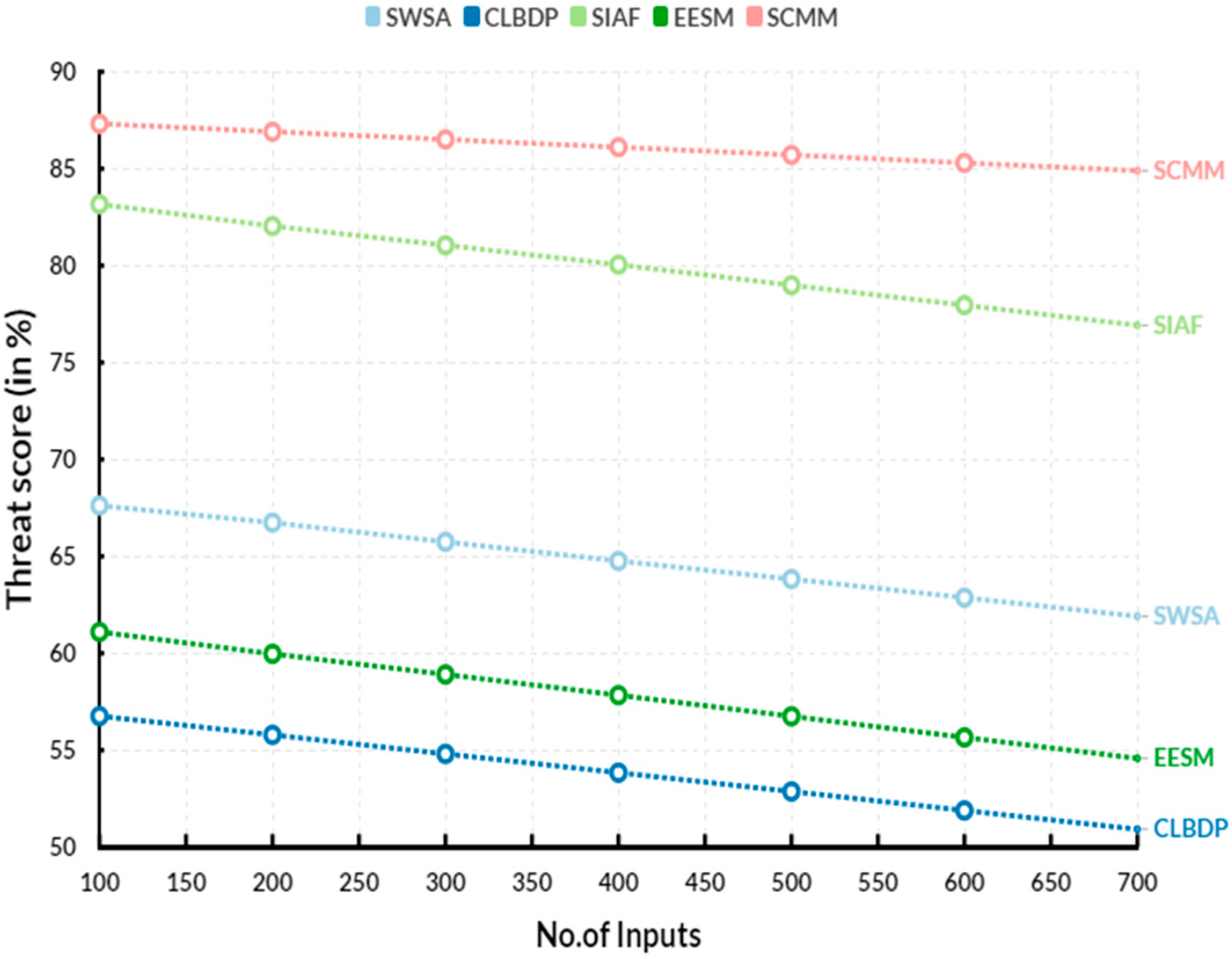
3.2. Threat Score
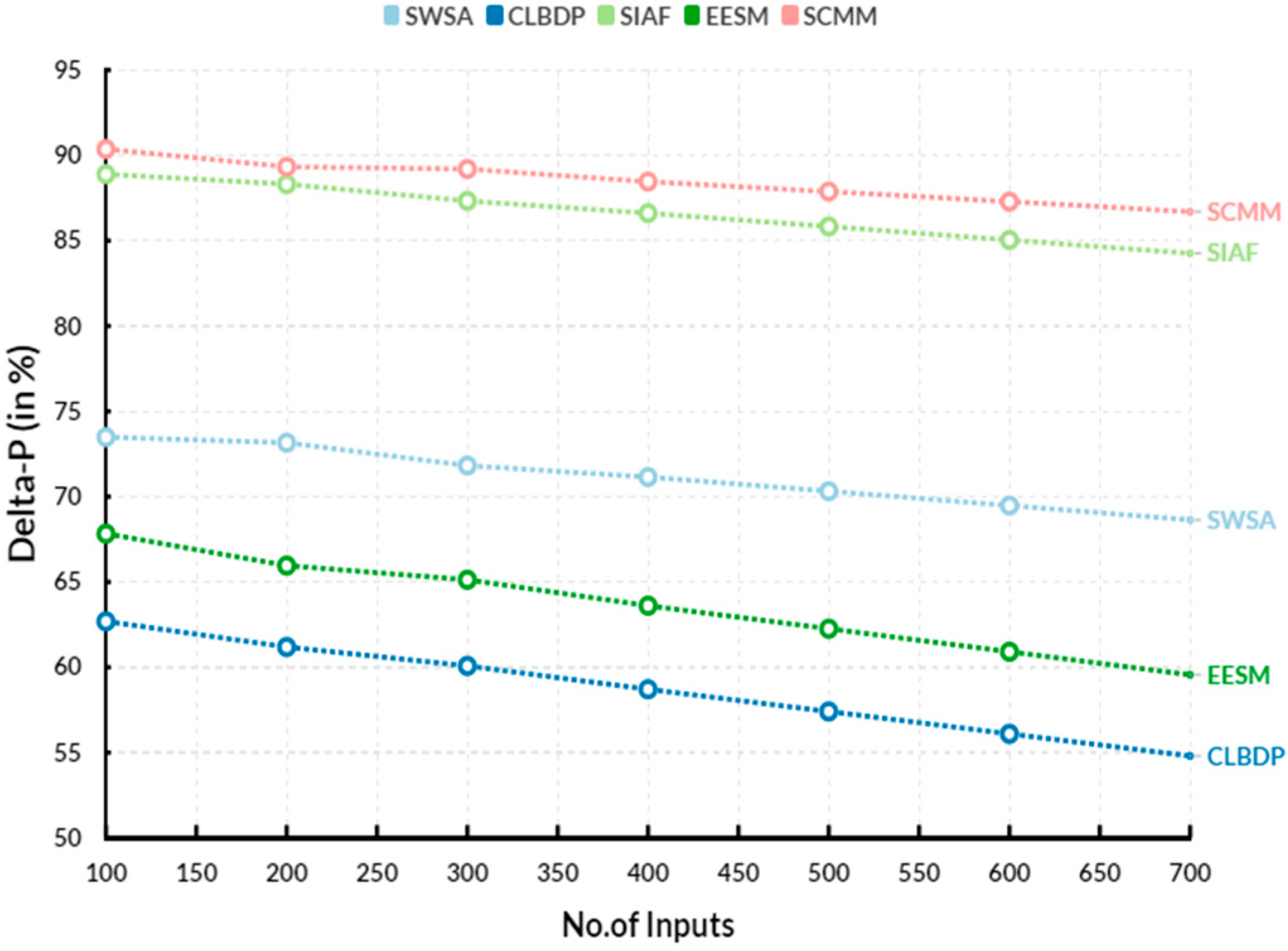
3.3. Delta-P
- Security: CS-CMM helps to ensure a secure environment for access to network resources, authentication of users, and a secure gateway between networks;
- Scalability: CS-CMM helps to efficiently scale with increasing volumes of network traffic and data, while at the same time maintaining acceptable levels of performance;
- Availability: CS-CMM helps to provide a high level of reliability for FoNet services and resources, including backup and disaster recovery;
- Trust: CS-CMM helps to establish trust through the use of secure certificates, encryption, and authentication methods;
- Compliance: CS-CMM helps to ensure compliance with best practices and industry standards.
- For Security: Implementing two-factor authentication, and using digital certificates and robust encryption algorithms;
- For Scalability: utilizing distributed architectures, virtualization, and cloud computing;
- For Availability: establishing backup and disaster recovery systems, geographically distributed primary and secondary network components, and replication of data;
- For Trust: establishing a secure trust environment through authorization, authentication, and identity management;
- For Compliance: adopting industry-standard security frameworks.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Javanmardi, S.; Shojafar, M.; Mohammadi, R.; Persico, V.; Pescapè, A. S-FoS: A secure workflow scheduling approach for performance optimization in SDN-based IoT-Fog networks. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2023, 72, 103404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, V.; Golightly, L.; Modesti, P.; Xu, Q.A.; Doan, L.M.T.; Hall, K.; Kobusińska, A. A survey on intrusion detection systems for fog and cloud computing. Future Internet 2022, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, Y.I.; Gill, A.; Mishra, A. A systematic review of the purposes of Blockchain and fog computing integration: Classification and open issues. J. Cloud Comput. 2022, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Abdullah, S.; Iftikhar, S.; Ahmad, I.; Ajmal, S.; Hussain, Q. A novel blockchain based secured and QoS aware IoT vehicular network in edge cloud computing. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 77707–77722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Inuwa, M.M. A review on fog computing: Issues, characteristics, challenges, and potential applications. Telemat. Inform. Rep. 2023, 10, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, T.; Rehman, A.; Haseeb, K.; Alam, T.; Jeon, G. Cloud-edge load balancing distributed protocol for IoE services using swarm intelligence. Clust. Comput. 2023, 26, 2921–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahanger, T.A.; Tariq, U.; Ibrahim, A.; Ullah, I.; Bouteraa, Y.; Gebali, F. Securing iot-empowered fog computing systems: Machine learning perspective. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Gupta, S.K. Flying through the secure fog: A complete study on UAV—Fog in heterogeneous networks. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2022, 35, e5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQahtani, S.A. An Evaluation of e-Health Service Performance through the Integration of 5G IoT, Fog, and Cloud Computing. Sensors 2023, 23, 5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kandpal, M. A comprehensive survey on trust management in Fog computing. In ICT Analysis and Applications; Fong, S., Dey, N., Joshi, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 314, pp. 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, K.; Sharma, S.C.; Kumar, M. A secure IoT applications allocation framework for integrated fog-cloud environment. J. Grid Comput. 2022, 20, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, V.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Hu, Y.C. A systematic survey on fog and iot driven healthcare: Open challenges and research issues. Electronics 2022, 11, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowri, V.; Baranidharan, B. An Energy Efficient and Secure Model using Chaotic Levy Flight Deep Q-Learning in Healthcare System. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2023, 39, 100894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.R.; Saxena, D.; Kumar, J.; Singh, A.K.; Lee, C.N. An AI-driven intelligent traffic management model for 6g cloud radio access networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 12, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veni, T. Quantum-Based Resource Management Approaches in Fog Computing Environments: A Comprehensive Review. In Mobile Computing and Sustainable Informatics; Shakya, S., Ntalianis, K., Kamel, K.A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 126, pp. 743–752. [Google Scholar]
- Ometov, A.; Molua, O.L.; Komarov, M.; Nurmi, J. A survey of security in cloud, edge, and fog computing. Sensors 2022, 22, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, S.A. Fog Computing Architecture in higher education institutions. Eurasian Res. Bull. 2023, 17, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.Z.; Shahjalal, M.; Ahmed, S.; Jang, Y.M. 6G wireless communication systems: Applications, requirements, technologies, challenges, and research directions. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2020, 1, 957–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitturi, S.; Zunino, C.; Sauter, T. Industrial communication systems and their future challenges: Next-generation Ethernet, IIoT, and 5G. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 944–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehos, C.; González, J.L.; De Domenico, A.; Ktenas, D.; Dussopt, L. Millimeter-wave access and backhauling: The solution to the exponential data traffic increase in 5G mobile communications systems? IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marianthony Renjitham, A.J.; Subburaj, S.; Dhinnesh, A.D.C.N.; Jasmine, J.J.; Ambethkar Matta, R. The Intelligent Connection Management Model to Enhance the Security of Cloud Computers in High-Density Fog Networks. Eng. Proc. 2023, 59, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059105
Marianthony Renjitham AJ, Subburaj S, Dhinnesh ADCN, Jasmine JJ, Ambethkar Matta R. The Intelligent Connection Management Model to Enhance the Security of Cloud Computers in High-Density Fog Networks. Engineering Proceedings. 2023; 59(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059105
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarianthony Renjitham, Archana Jenis, Suganthi Subburaj, Ariputhran Durasamy Chandramohan Navin Dhinnesh, Jeyasekaran Jeno Jasmine, and Raja Ambethkar Matta. 2023. "The Intelligent Connection Management Model to Enhance the Security of Cloud Computers in High-Density Fog Networks" Engineering Proceedings 59, no. 1: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059105
APA StyleMarianthony Renjitham, A. J., Subburaj, S., Dhinnesh, A. D. C. N., Jasmine, J. J., & Ambethkar Matta, R. (2023). The Intelligent Connection Management Model to Enhance the Security of Cloud Computers in High-Density Fog Networks. Engineering Proceedings, 59(1), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059105




